Neuroanatomy full set for anki
1/939
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
940 Terms
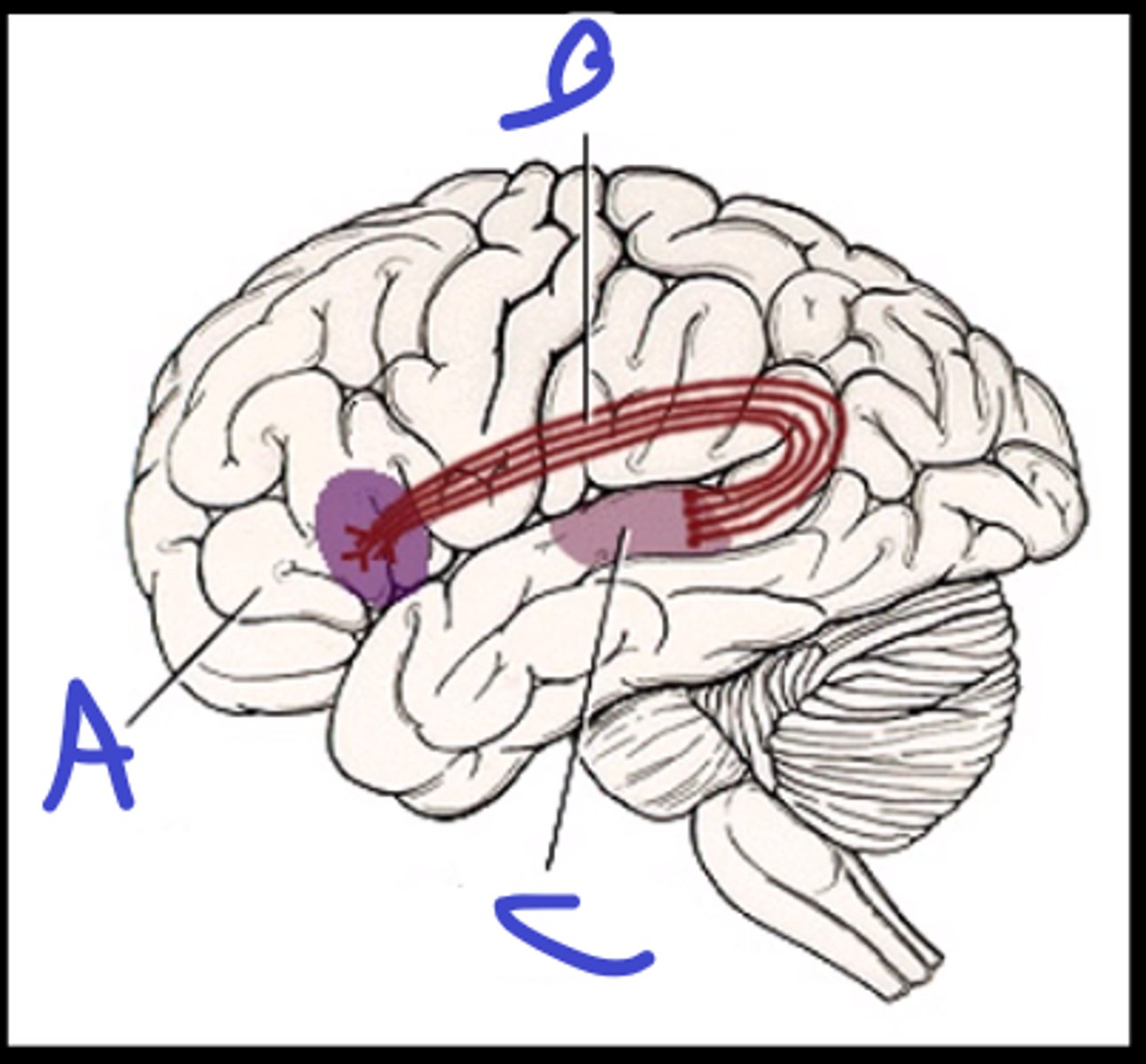
broca's area
a
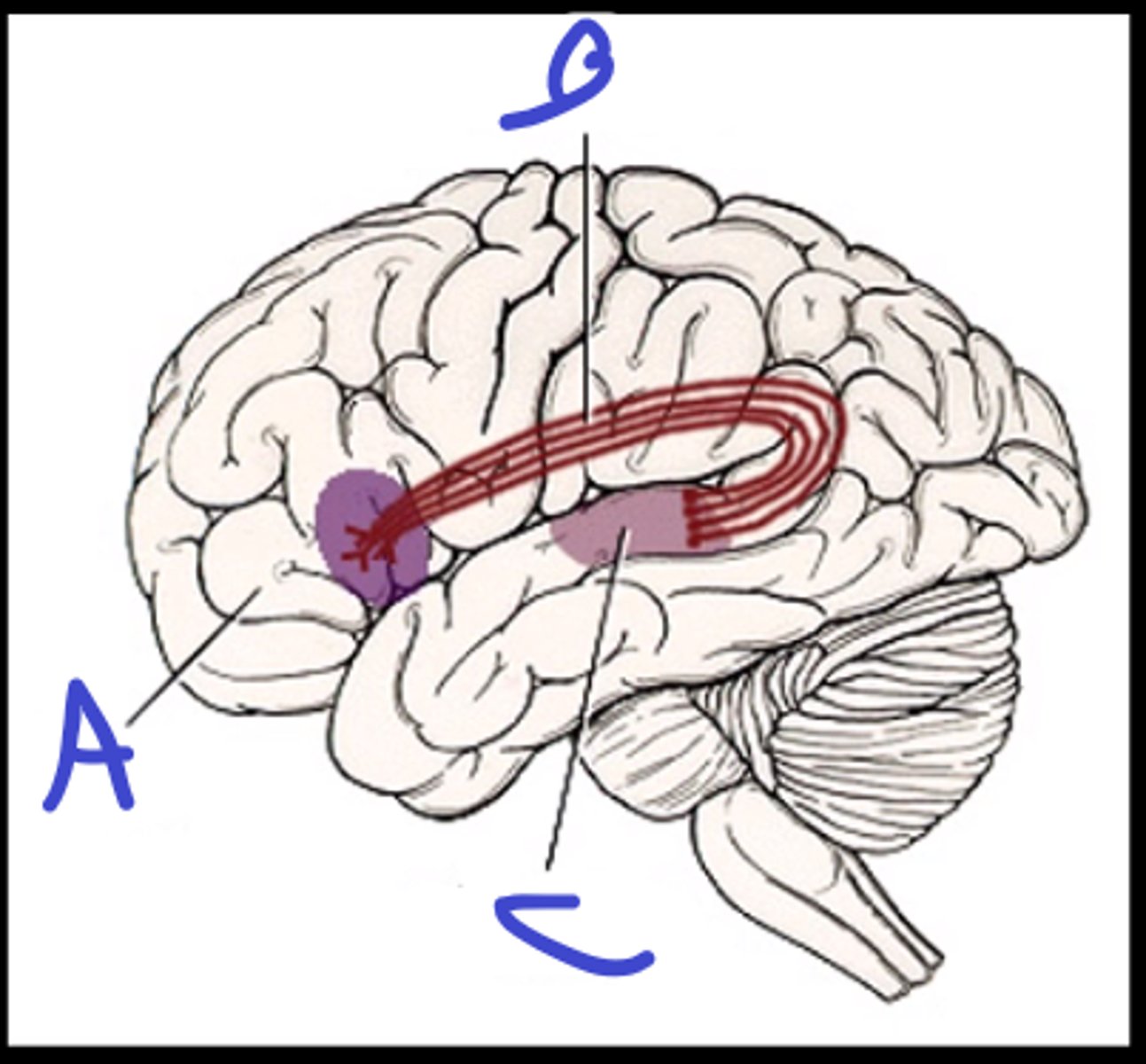
arcuate fasciculus
b
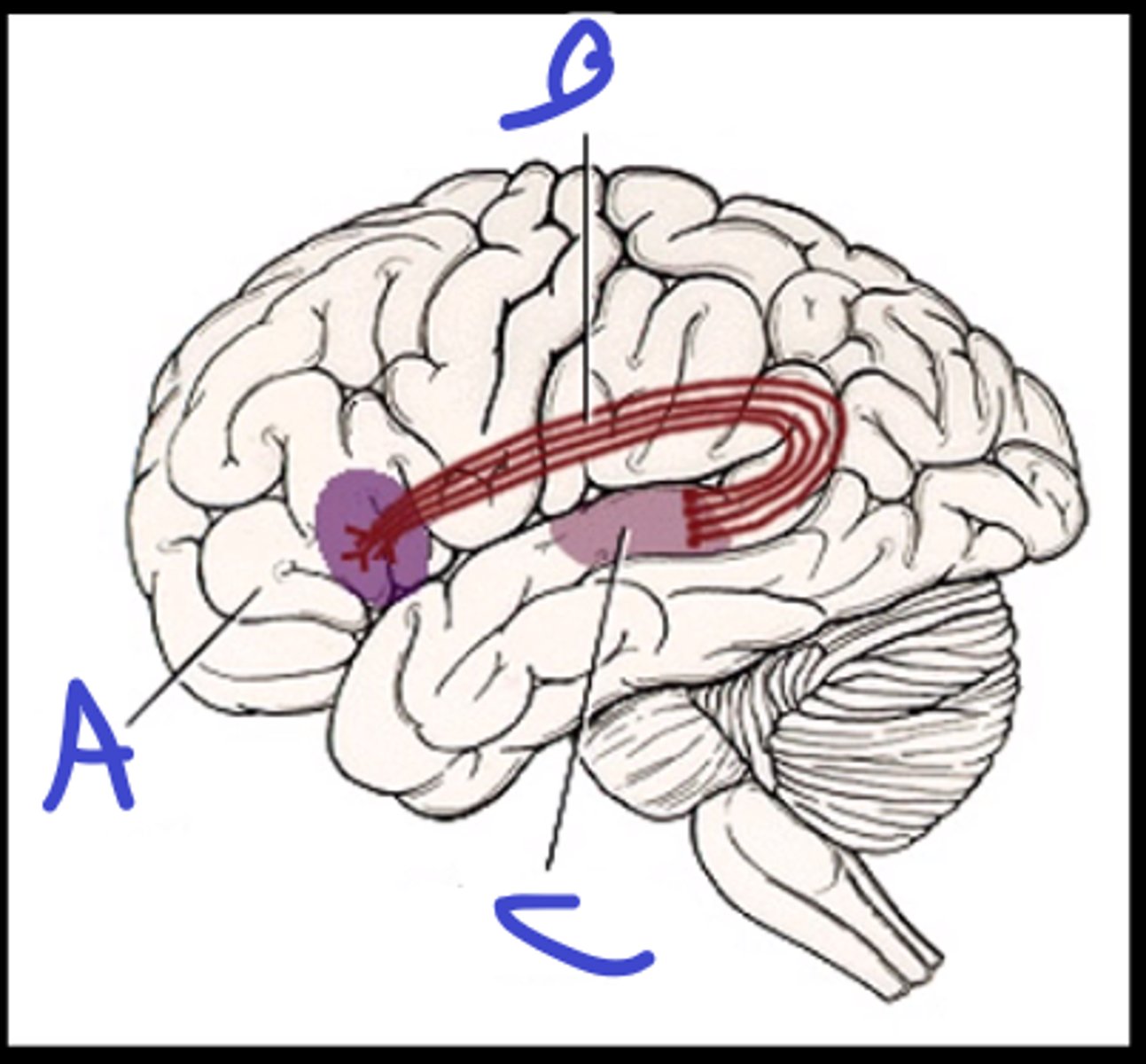
wernicke's area
c
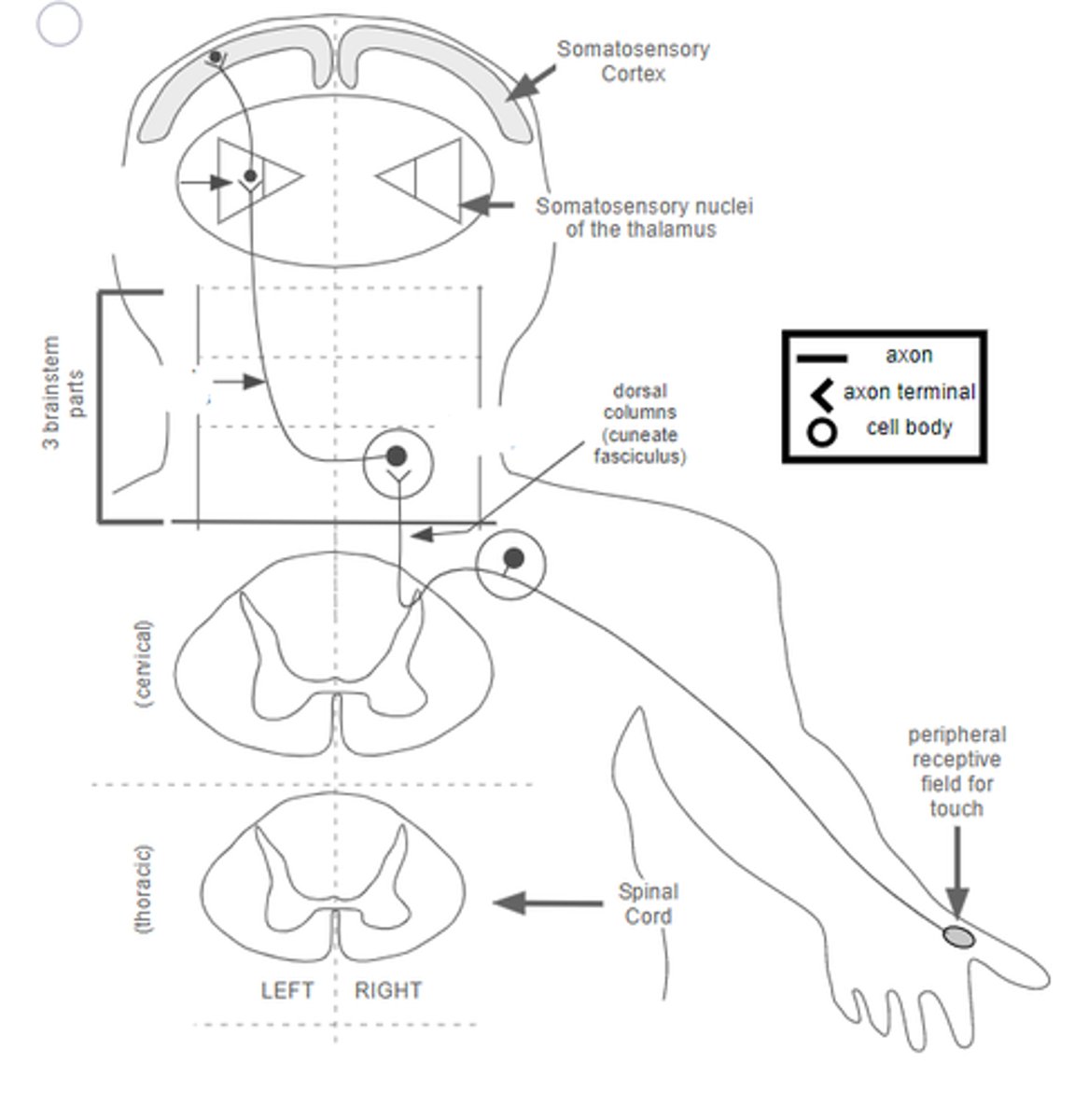
drg>cuneate n>cross mid>medial lemniscus>VPL>somatosensory cortex
describe pathway of touch/conscious proprioception
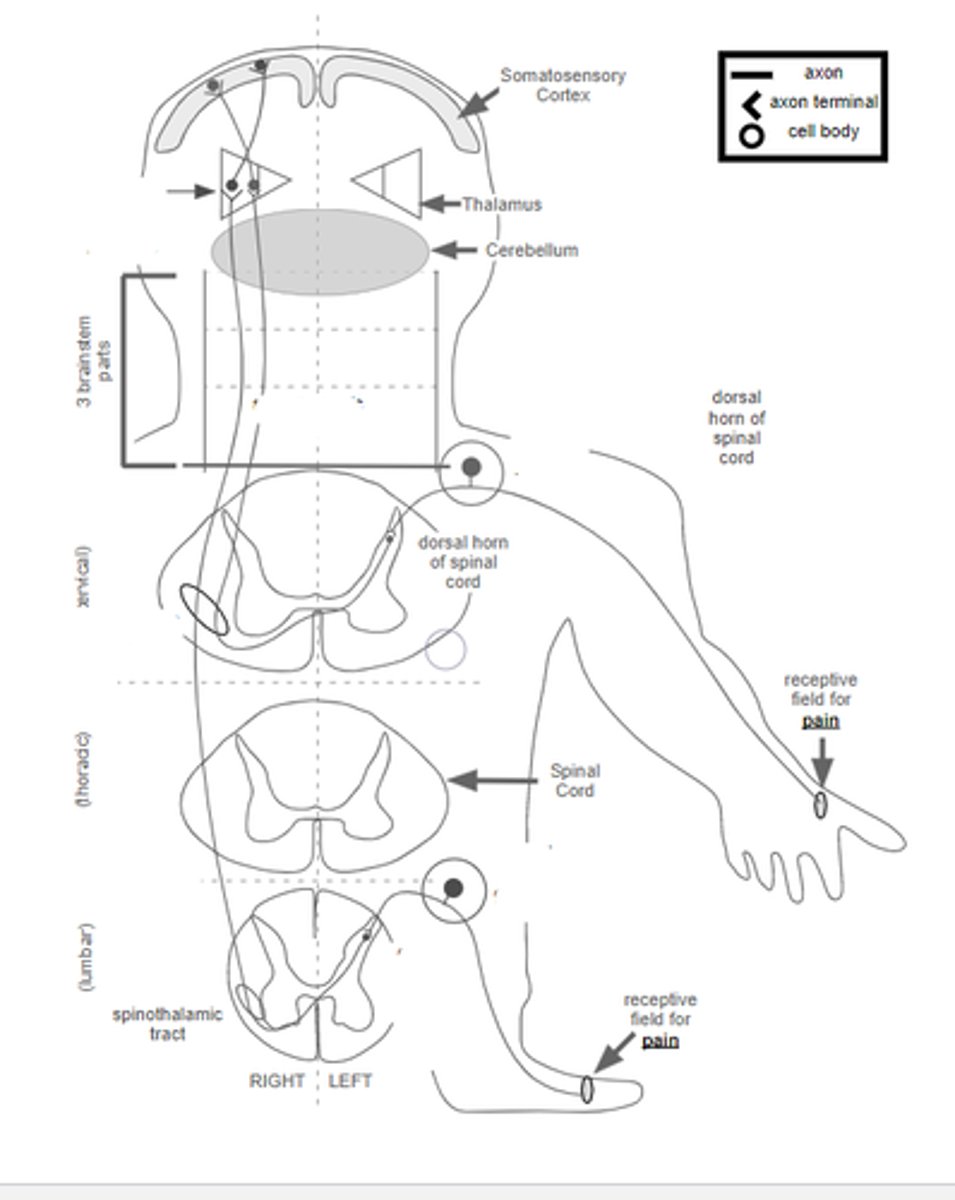
drg>dorsal horn n>cross mid>spinothalamic tract>VPL>somatosensory cortex
describe pathway of pain
trigem gang>spinal tri nuc>cross mid>spinothalamic
describe pathway of pain for head
drg>clarke's column>dorsal spinocerebellar tract>cerebellum
no crossing of mid
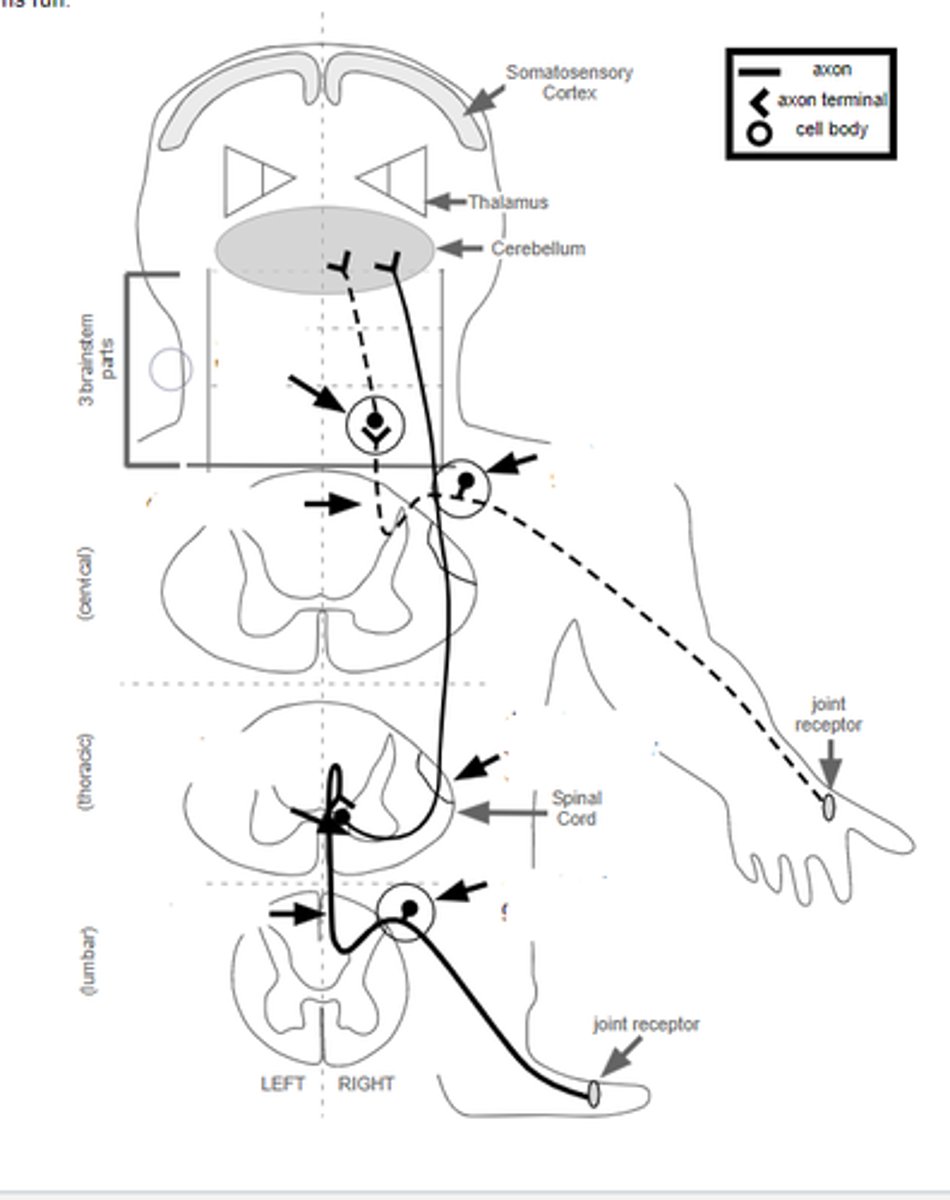
describe pathway of unconscious proprioception from foot
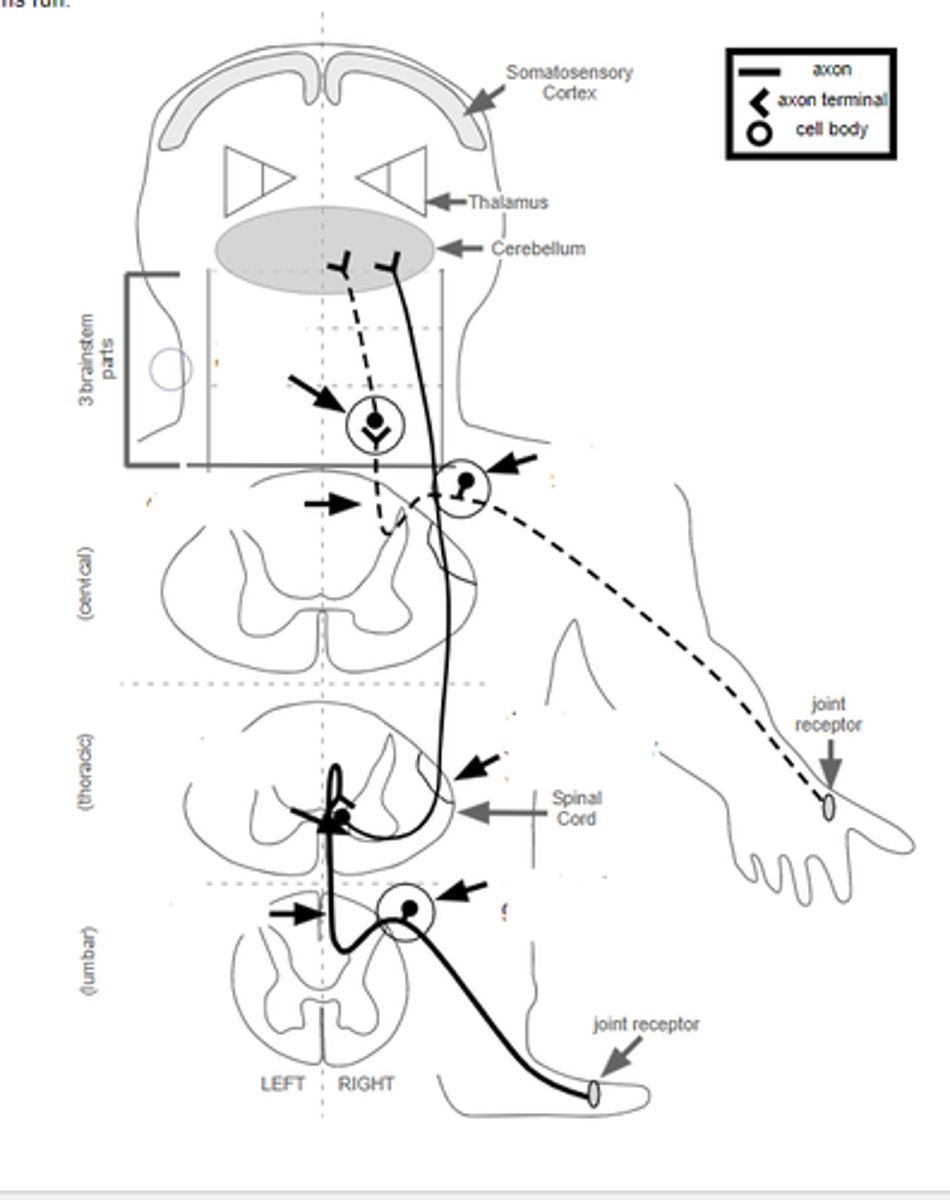
drg>ext cuneate nuc>dorsal spinocerebellar tract>cerebellum
no crossing of mid
describe pathway of unconscious proprioception from hand
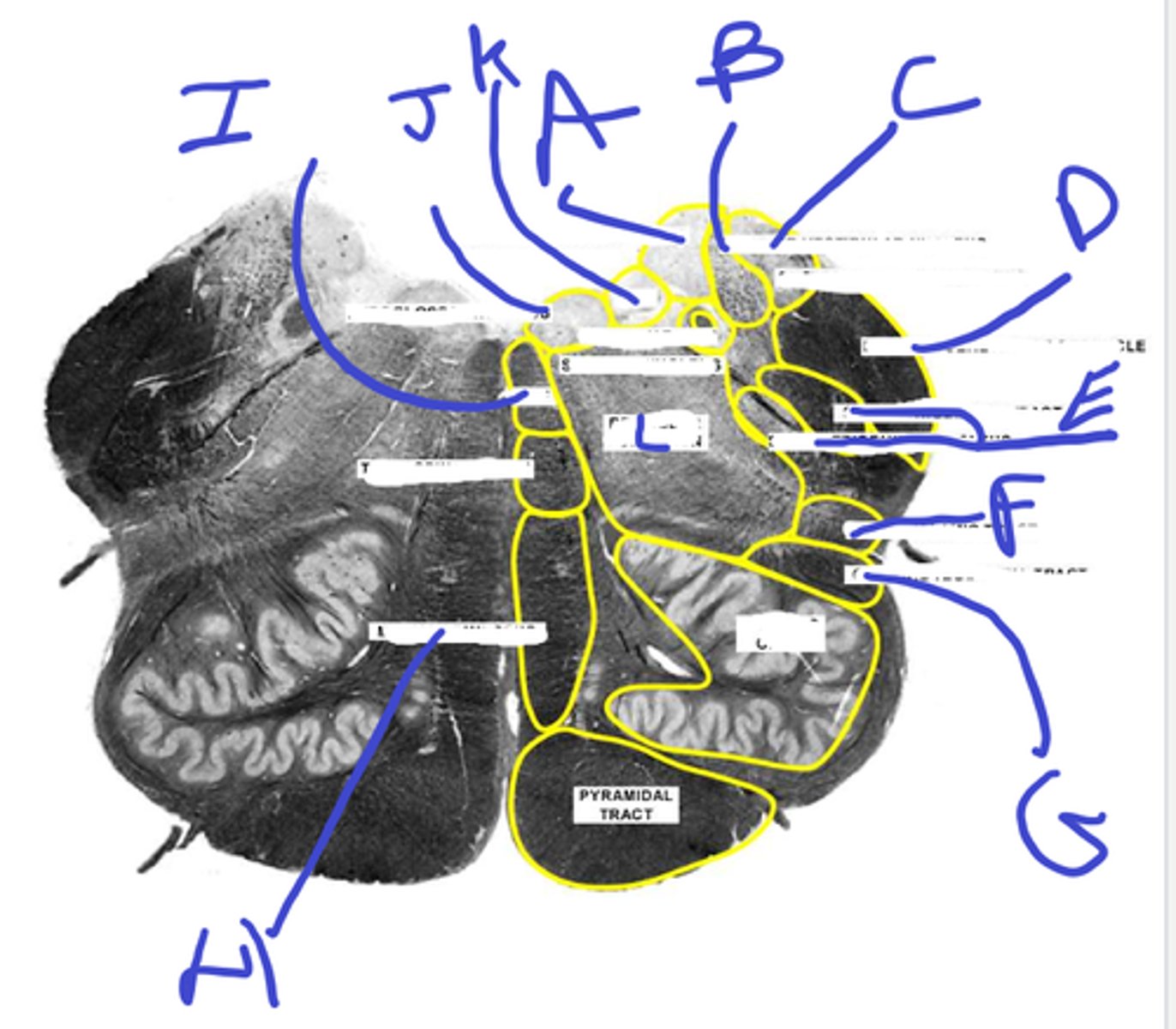
a-med vestibular nuc
b-dorsal cochlear nuc
c-inf vestibular nuc
d-ventral cochlear nuc
e-inf cerebellar peduncle
abcde
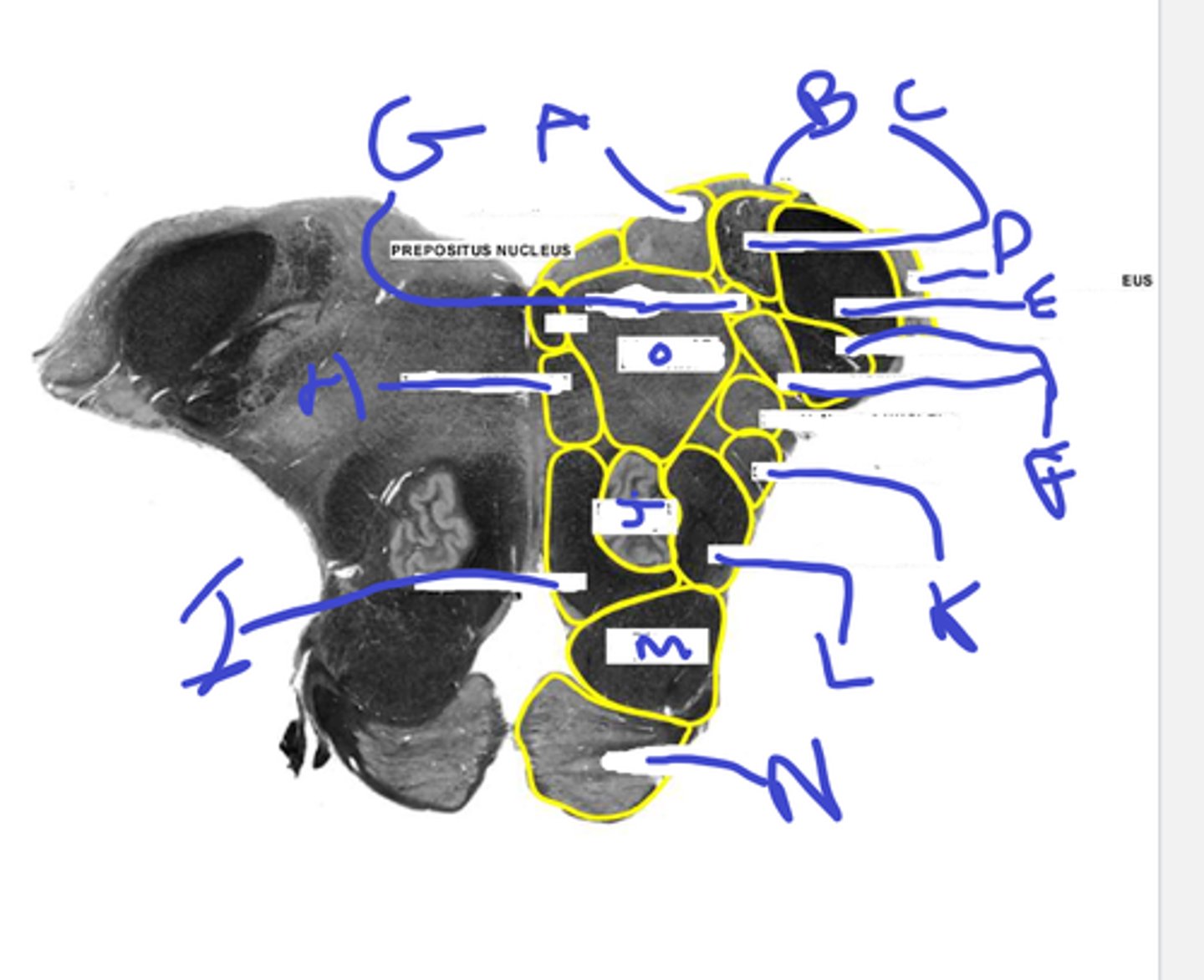
f-spinotrigeminal tract/nuc
g-solitary nuc
h- mlf is one circle dorsal
i-medial lemniscus
j-inf olive
fghij
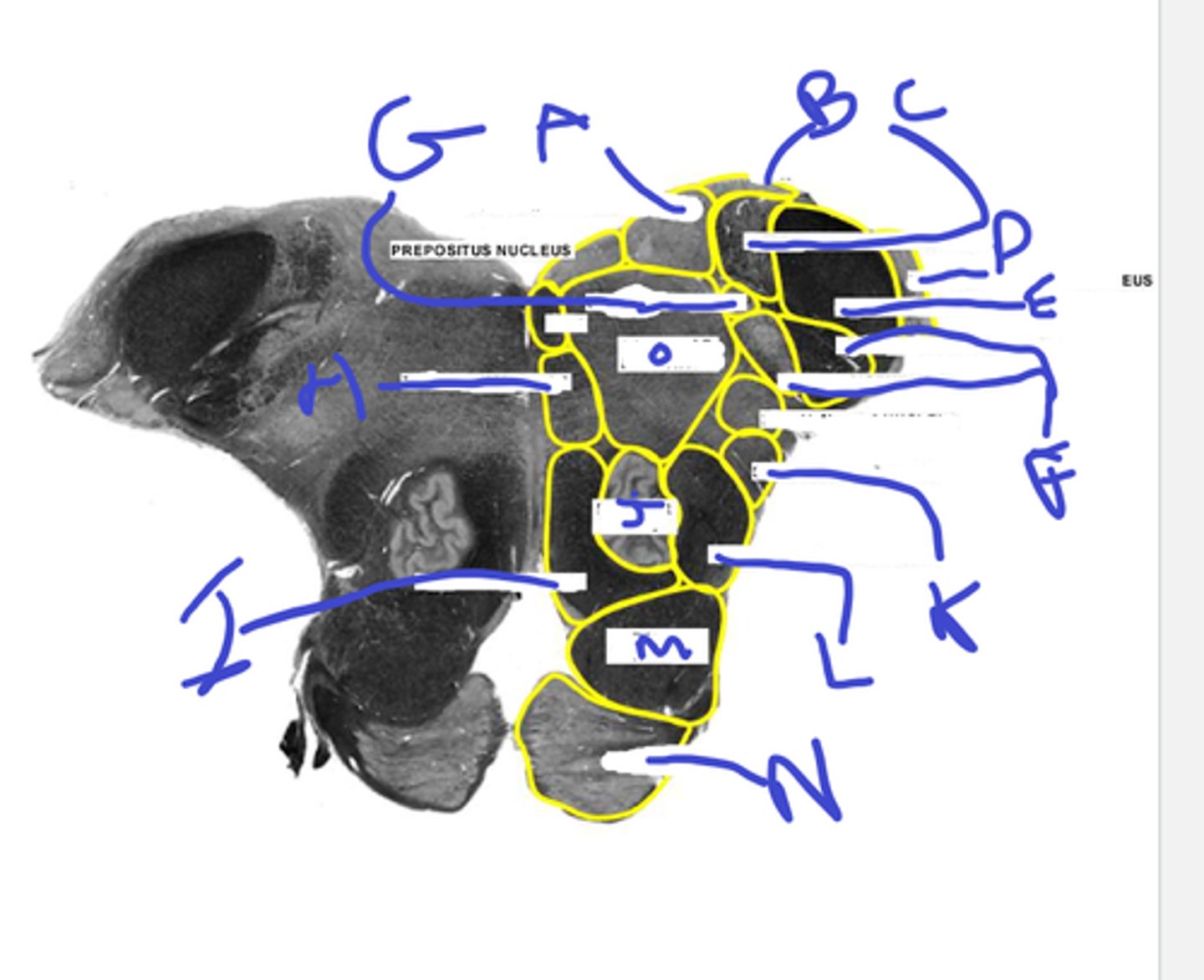
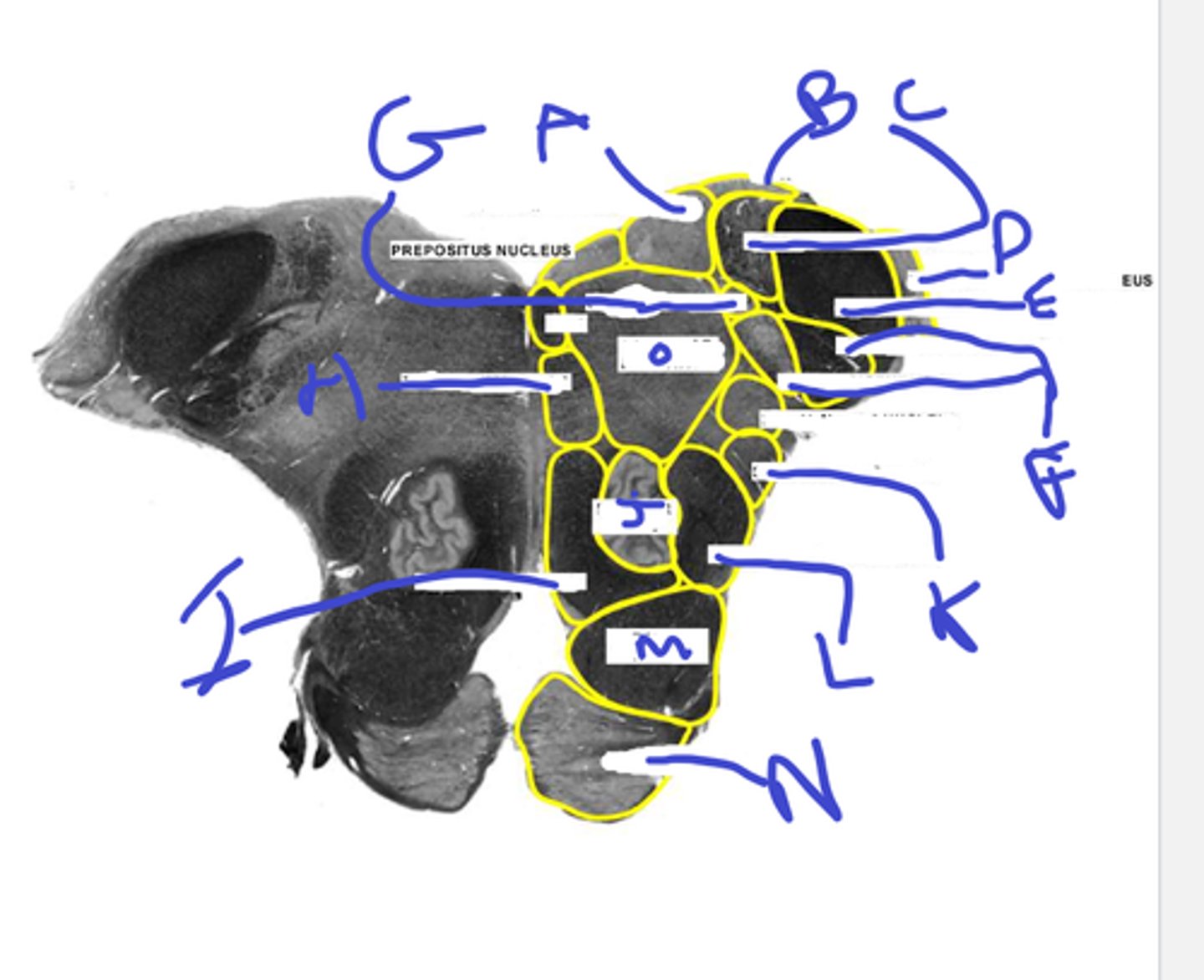
k- spinothalamic
l-central tegmental tract
m-pyr tract
n-pontine nuc
o-reticular formation
klmno
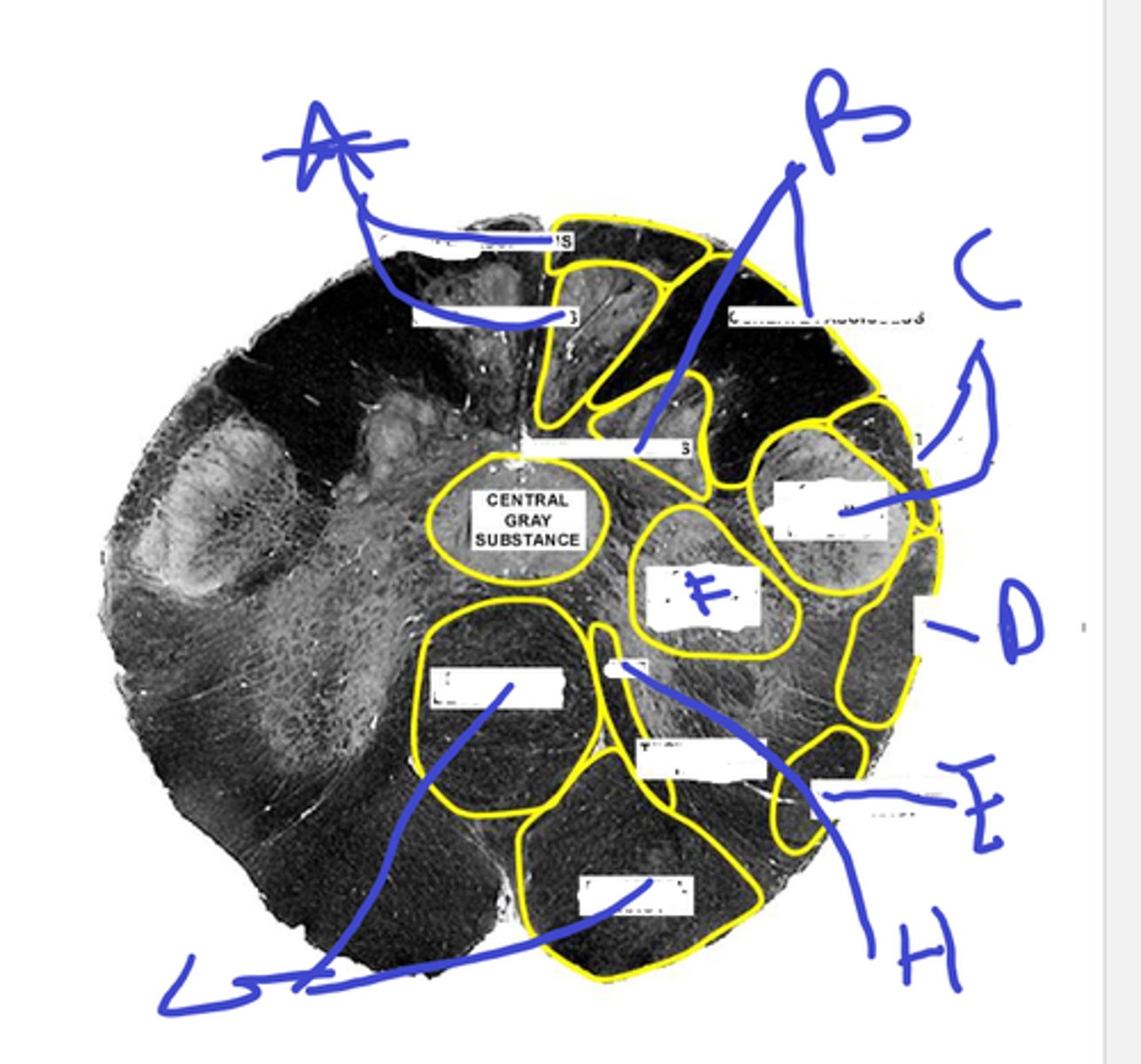
a-gracile
b-cuneate
c-spinal trigeminal
d-dorsal spinocerebellar tract
e-spinothalamic
f-spinal accessory nuc
g-pyramidal stuff
abcdefg
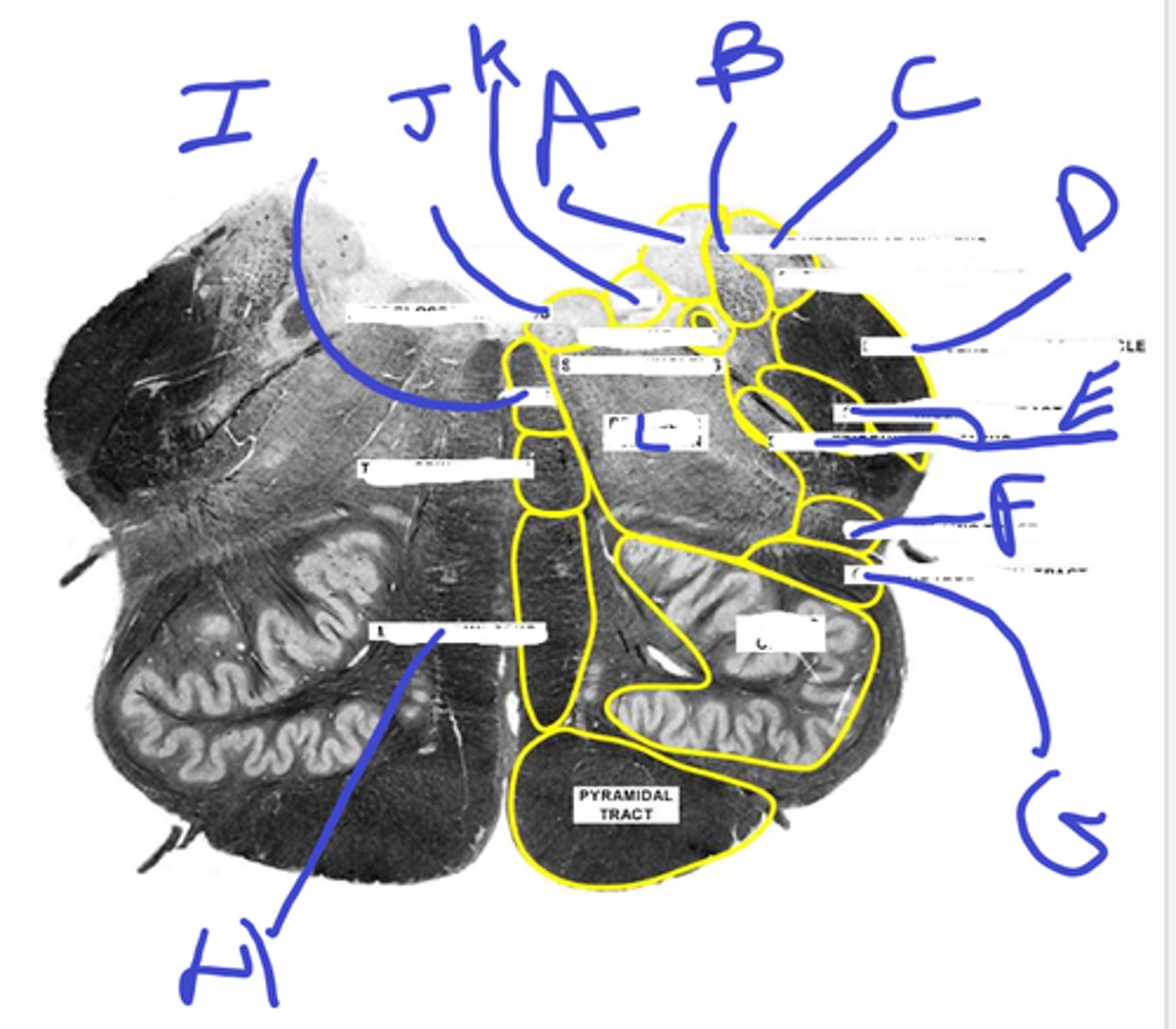
a-med vest nuc
b-inf vest nuc
c-ext cuneate nuc
d-inf cerebellar ped
e-spinal trigem tract/nuc
abcde
f-spinothalamic
g-central tegmental
h-medial lemniscus
i-mlf
j-hypoglossal
k-dmx
l-reticular formation
f-l
a- facial motor
b-spinothalamic
c-central tegmental tract
d-medial lemniscus
abcd
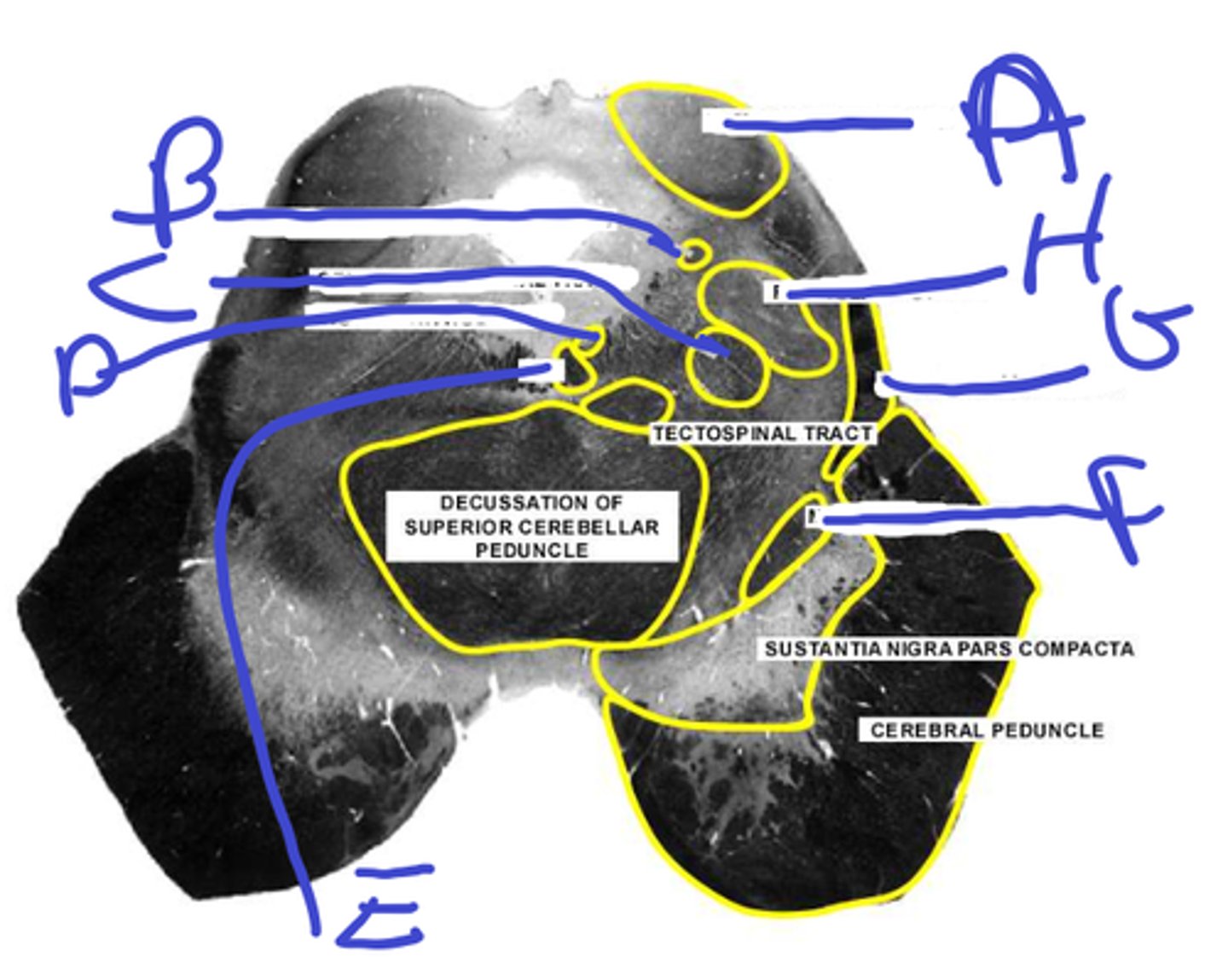
a- inf colliculus
b-mesencephalic trigem tract
c-central tegmental tract
d-trochlear nuc
abcd
e-mlf
f-medial lemniscus
g-spinothalamic
h-reticular formation
efgh
a-up
b-down
c-right
d-left
e-central vision
abcde
locus ceruleus
norepinephrine
attention
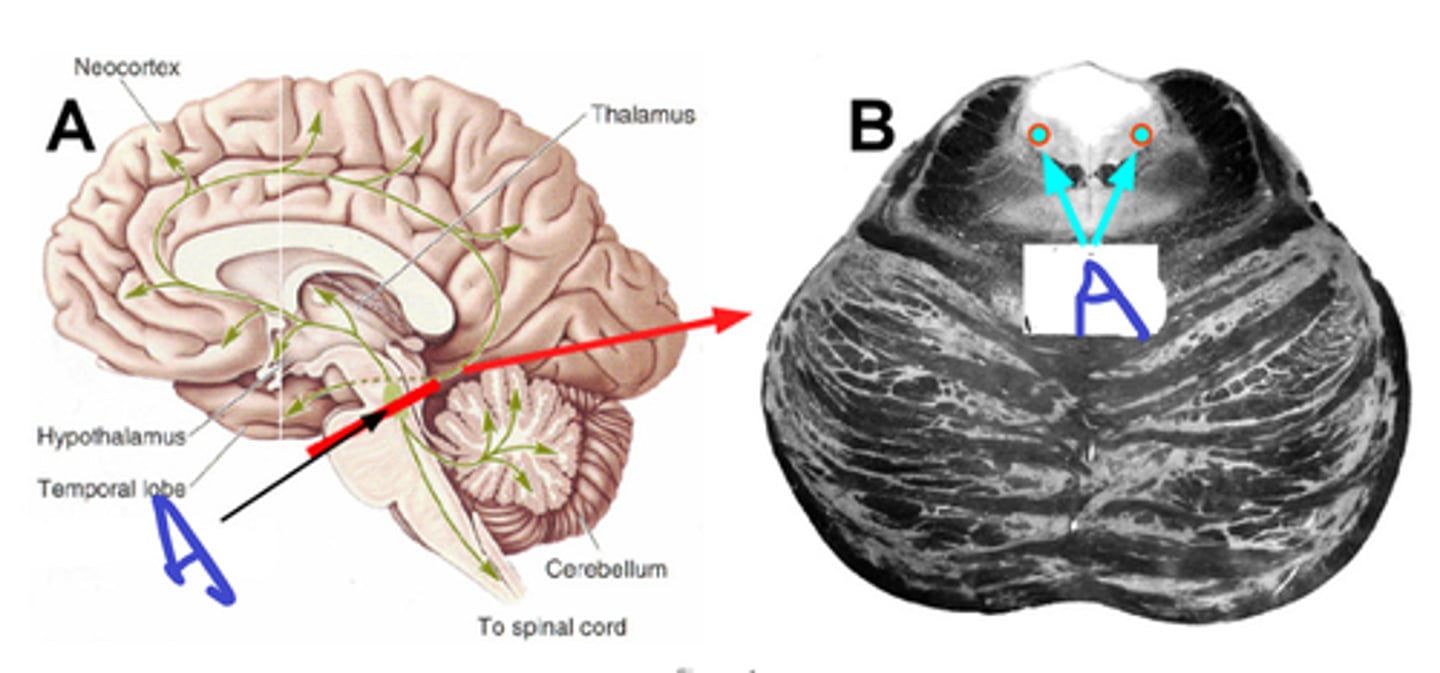
name A.
what origins from this.
function of this system.
notice where axons terminate.
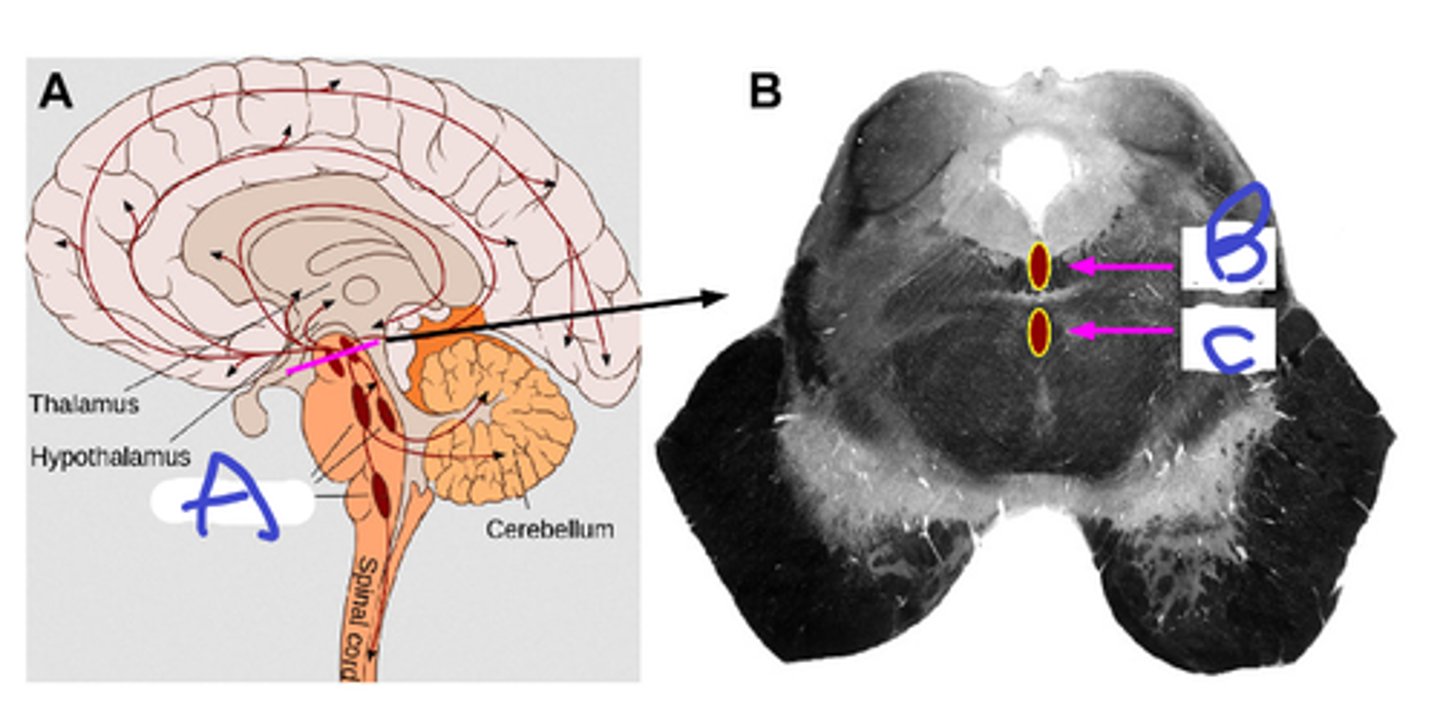
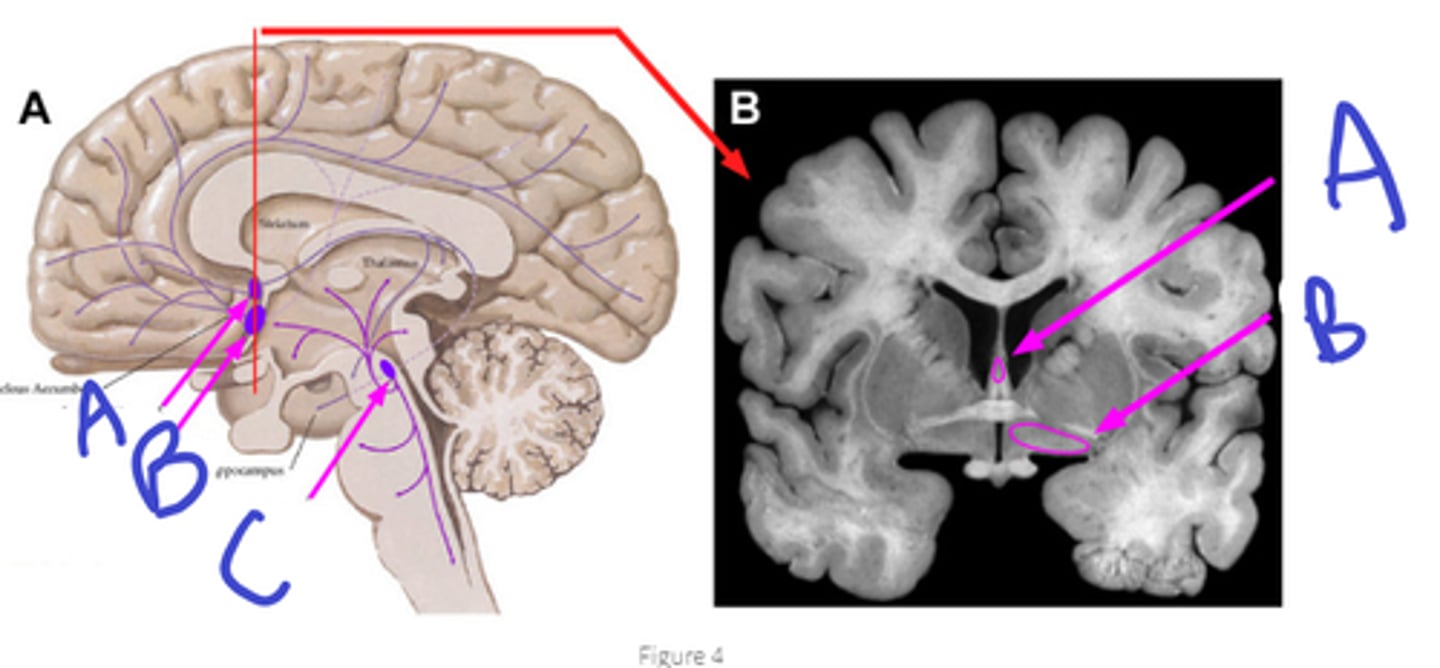
raphe nuclei,
b-dorsal r nuc,
c-medial r nuc
A
extra credit: B, C
notice where axons terminate
serotonin,
mood
what originates in raphe nuclei, purpose of that system
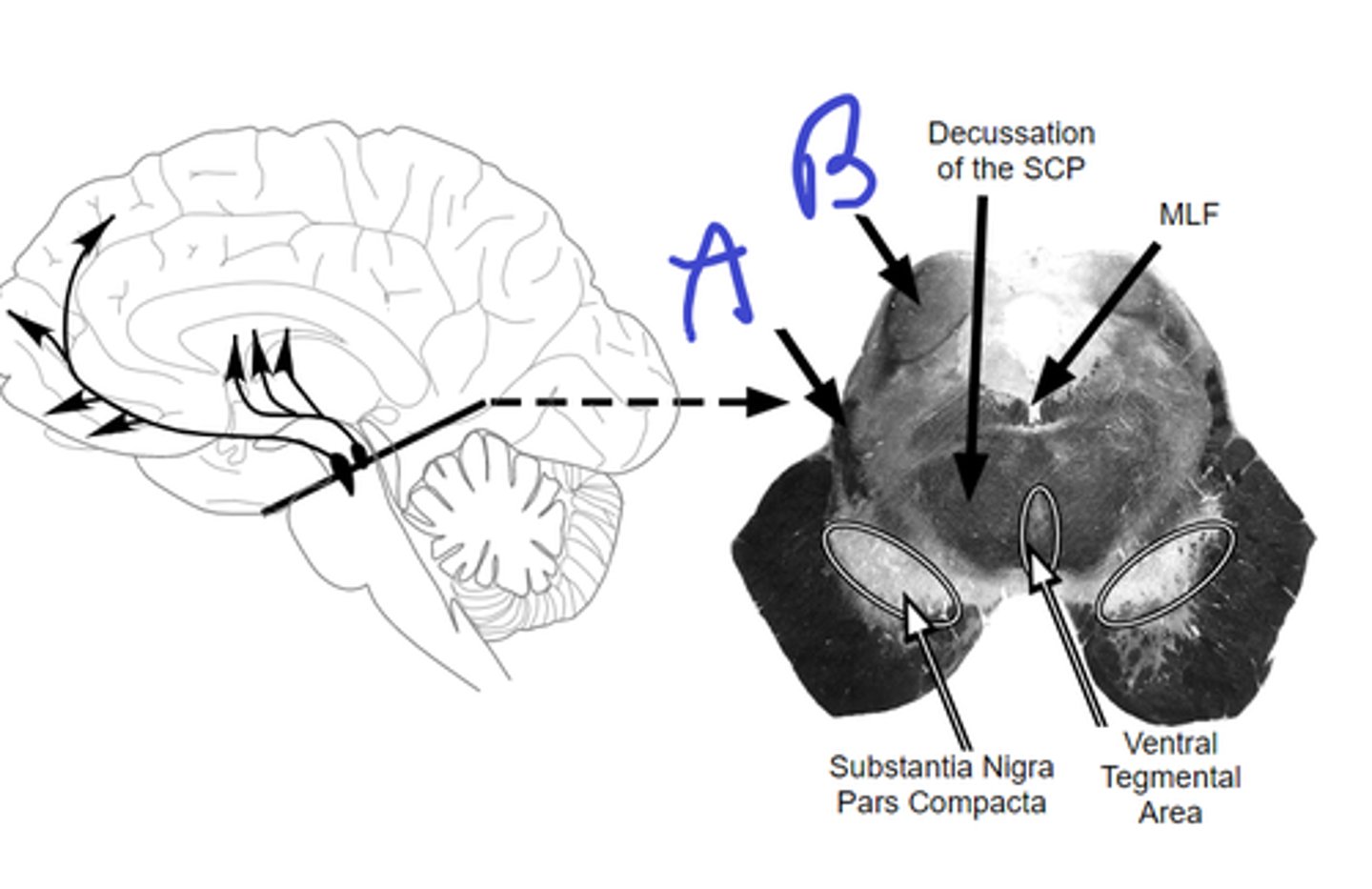
a-ventral tegmental area,
b-substantia nigra pars compacta
A
B
notice where axons terminate
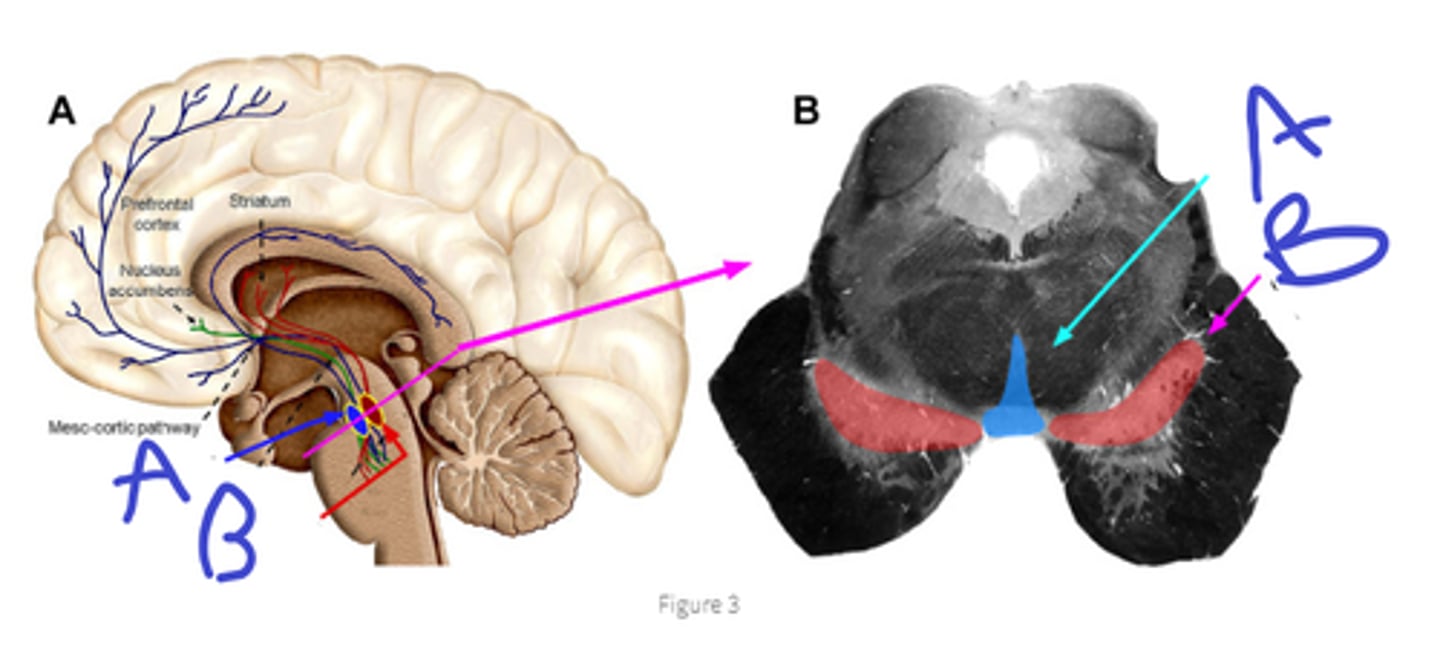
dopamine,
reward
what originates in SNc, VTA
what is the purpose of this system
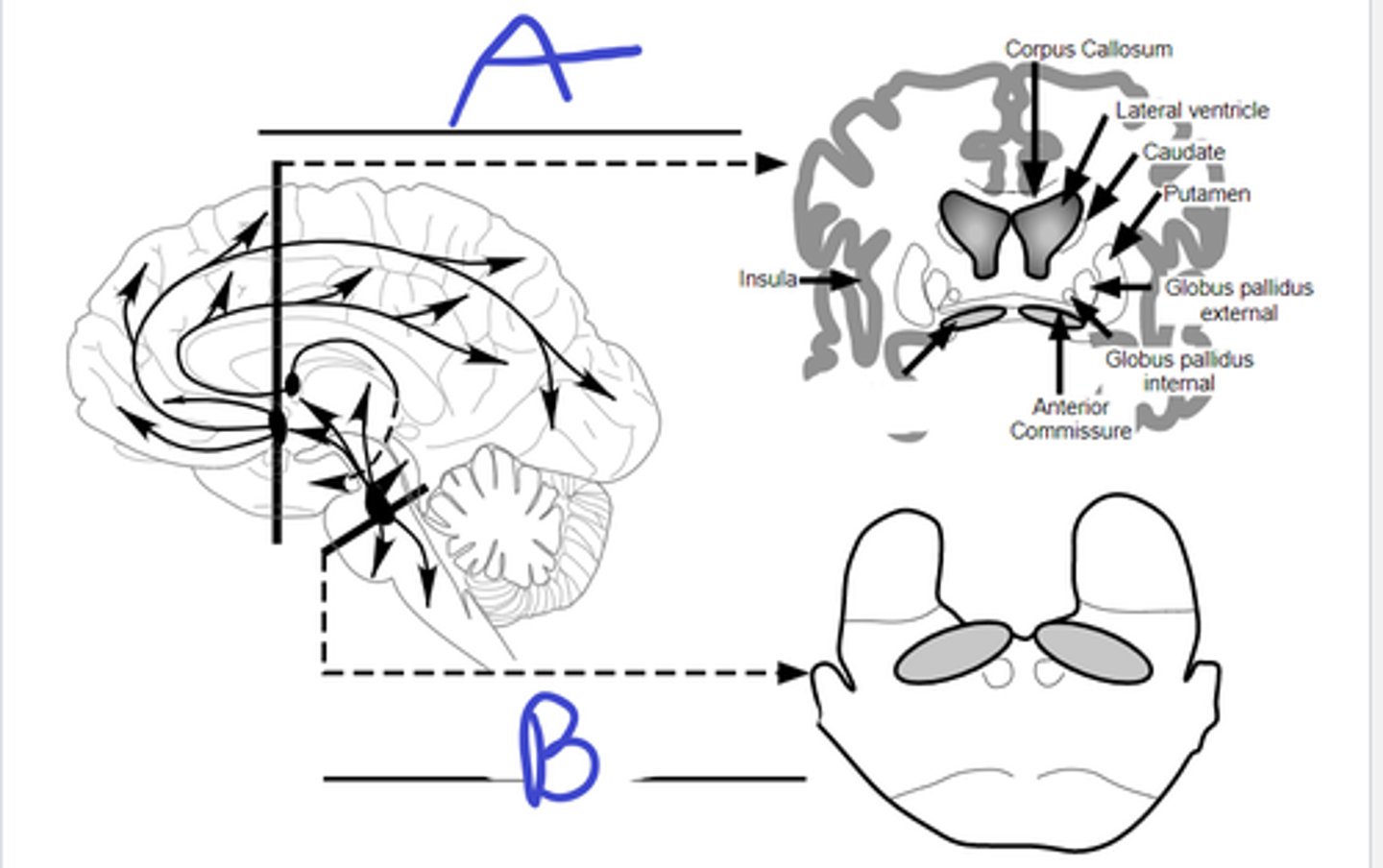
a-septal nuc,
b-basal nucleus of meynert,
c-pontomesencepahlic tegmental complex
acetylcholine
learning/arousal
A
B
C
what originates here
purpose of system
basal forebrain-meynert
first neurons to die in Alzheimer's
seam
raphe-- means what in greek
blue spot
locus ceruleus-- means what in latin
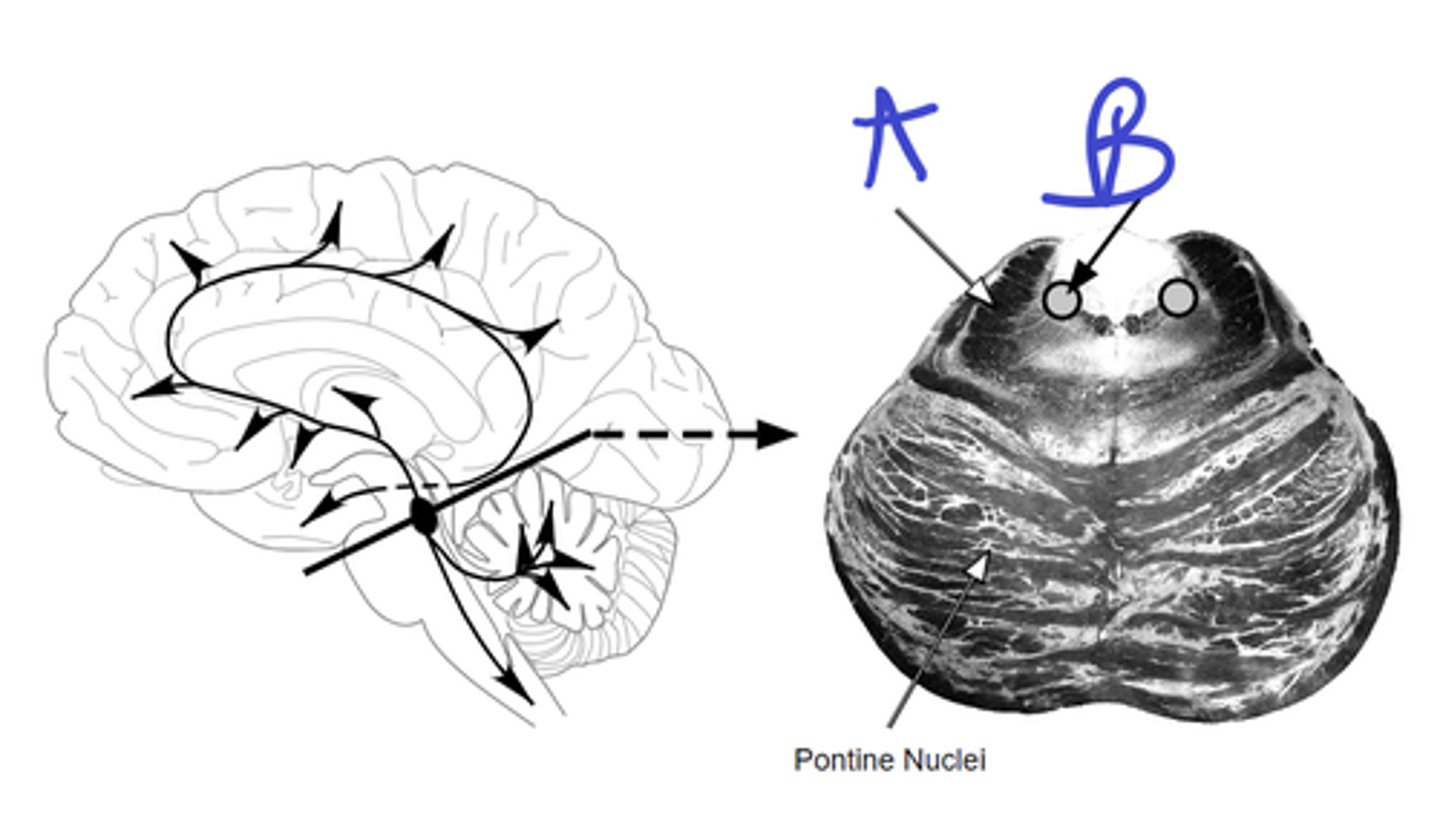
a-basal nucleus of meynert
b-pontomesencephalotegmental complex
A
B
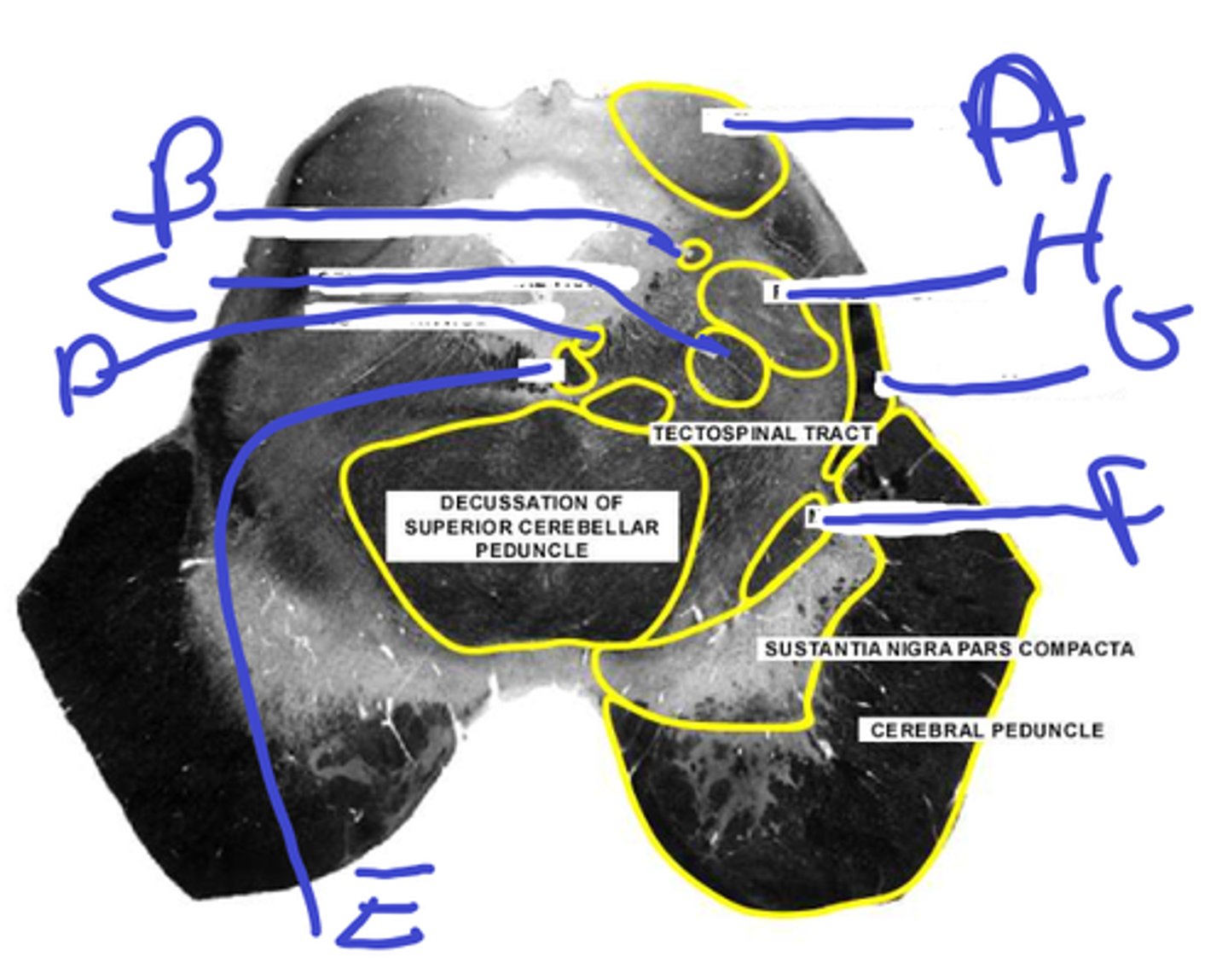
A-supeior cerebellar peduncle
B-locus ceruleus
A
B
a-spinothalamic tract
b-inf colliculus
A
B
sulcus cinguli
a
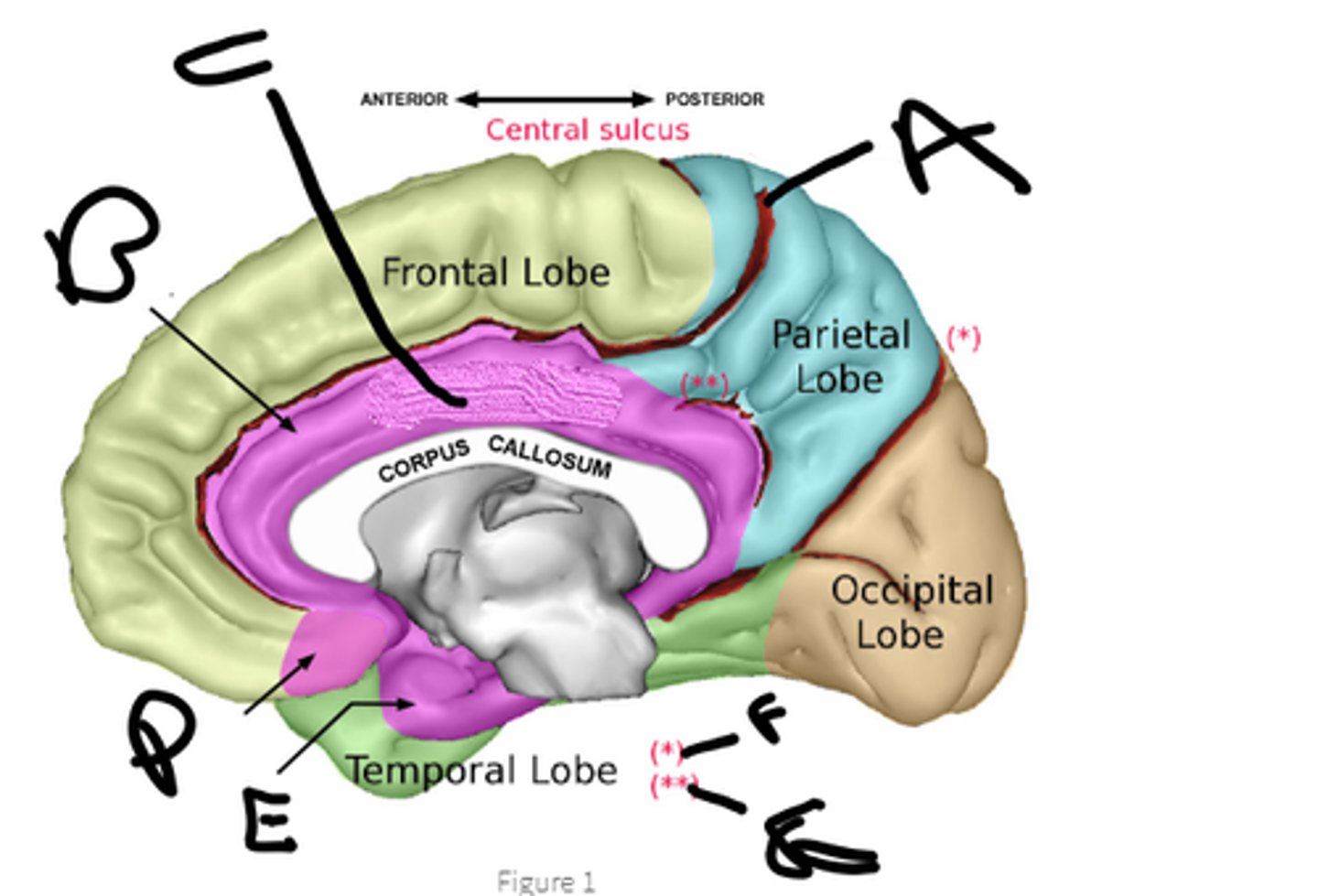
cingulate cortex
b
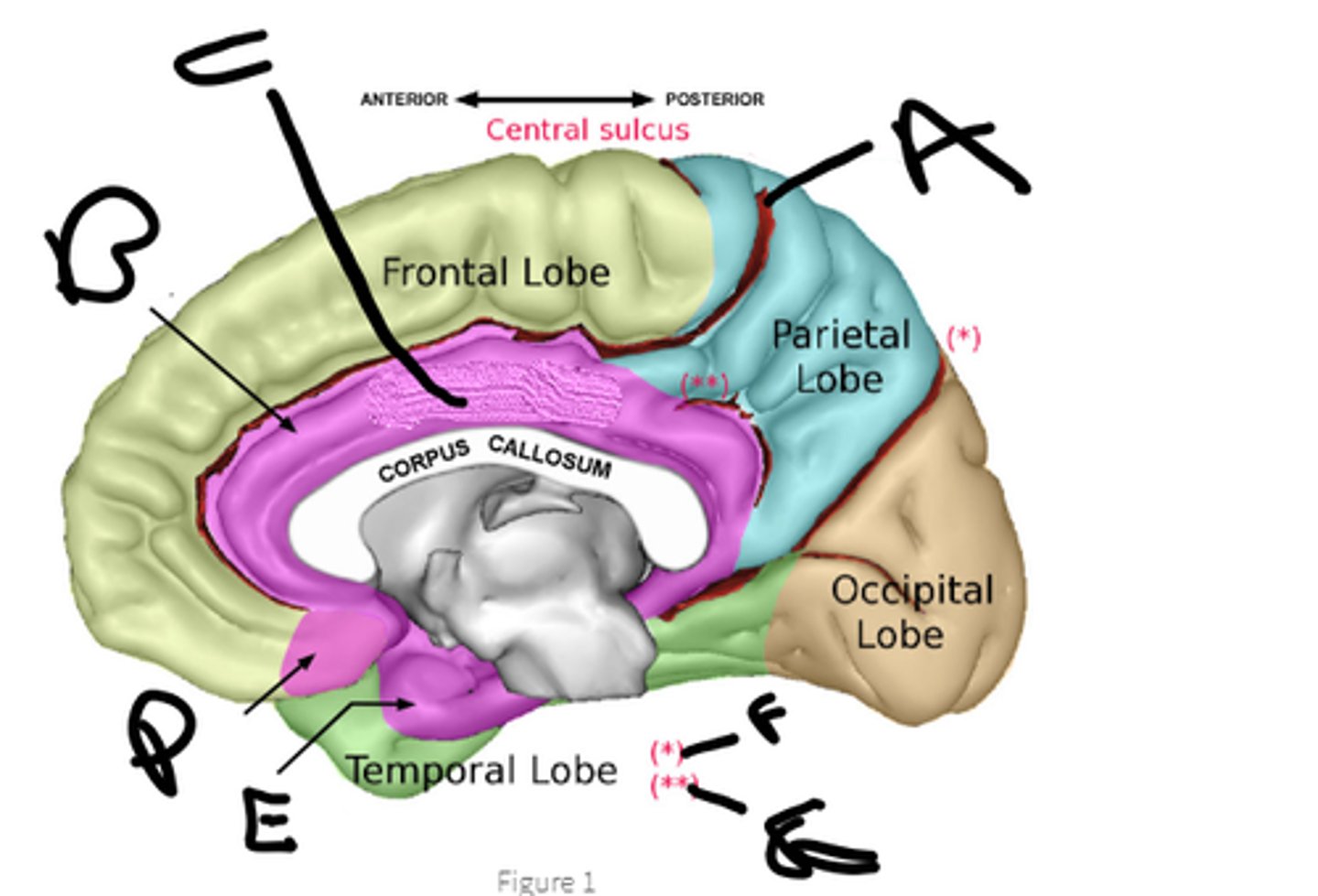
limbic lobe
c
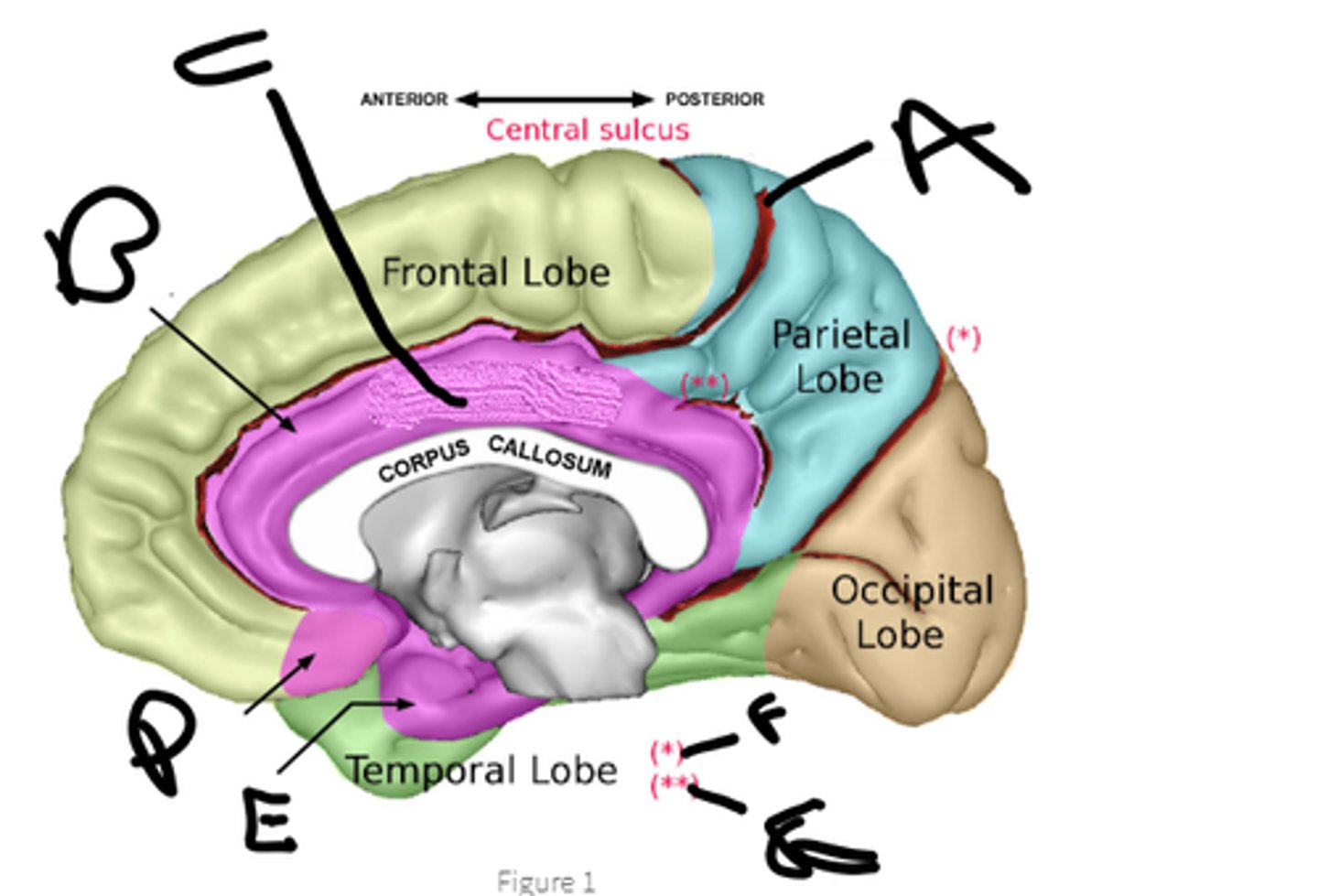
orbital cortex
d
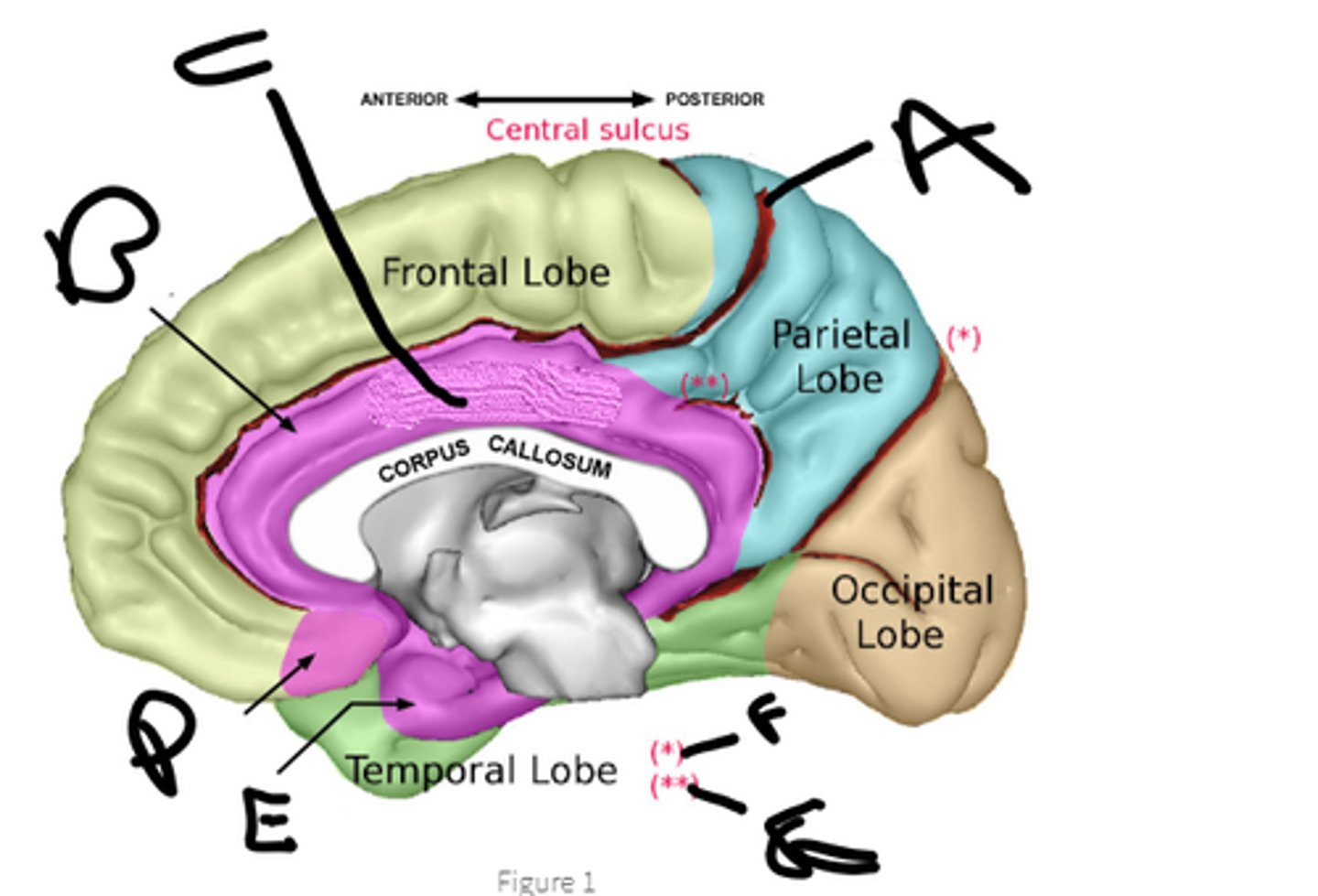
medial temporal cortex
e
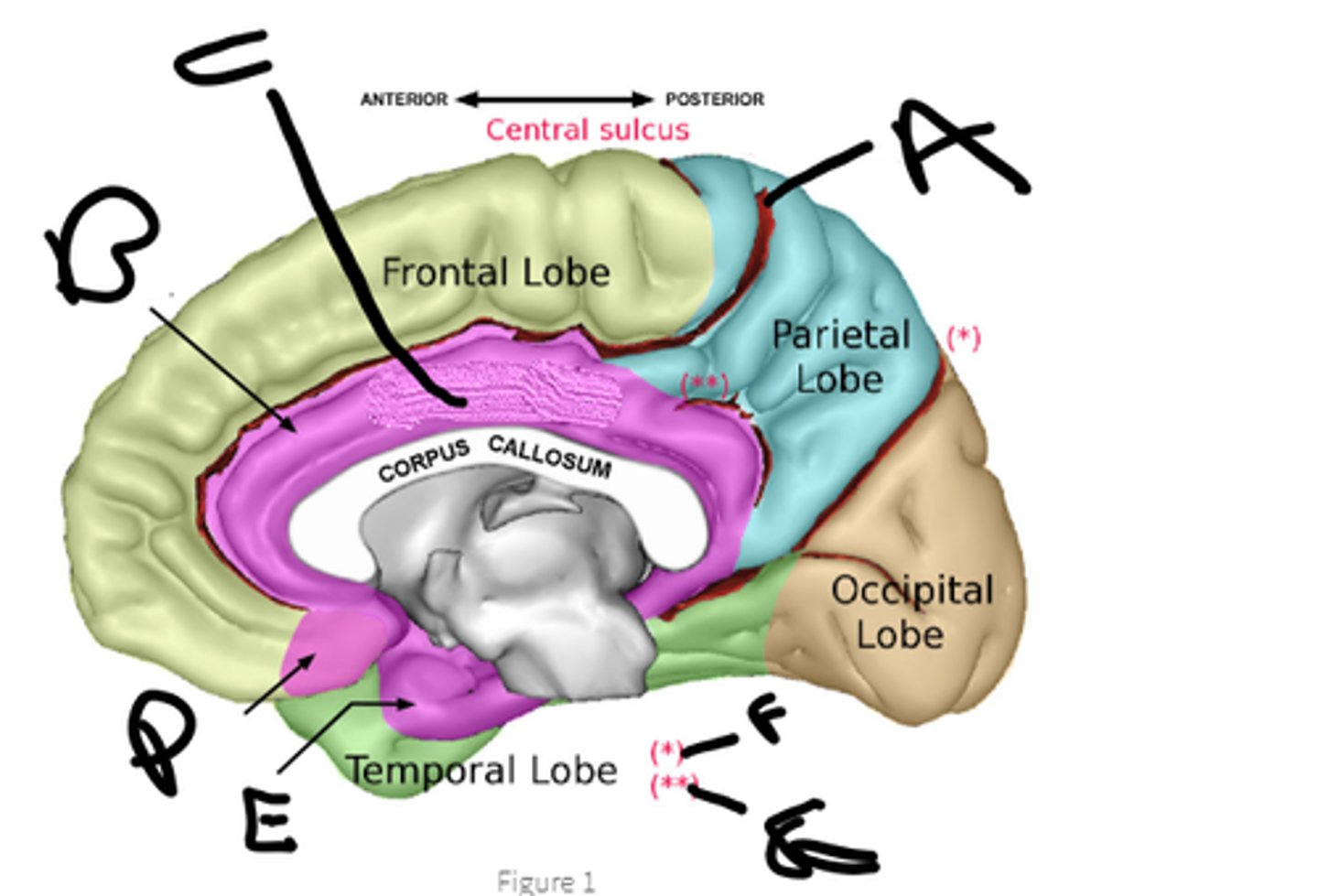
pariteo-occipital sulcus
f
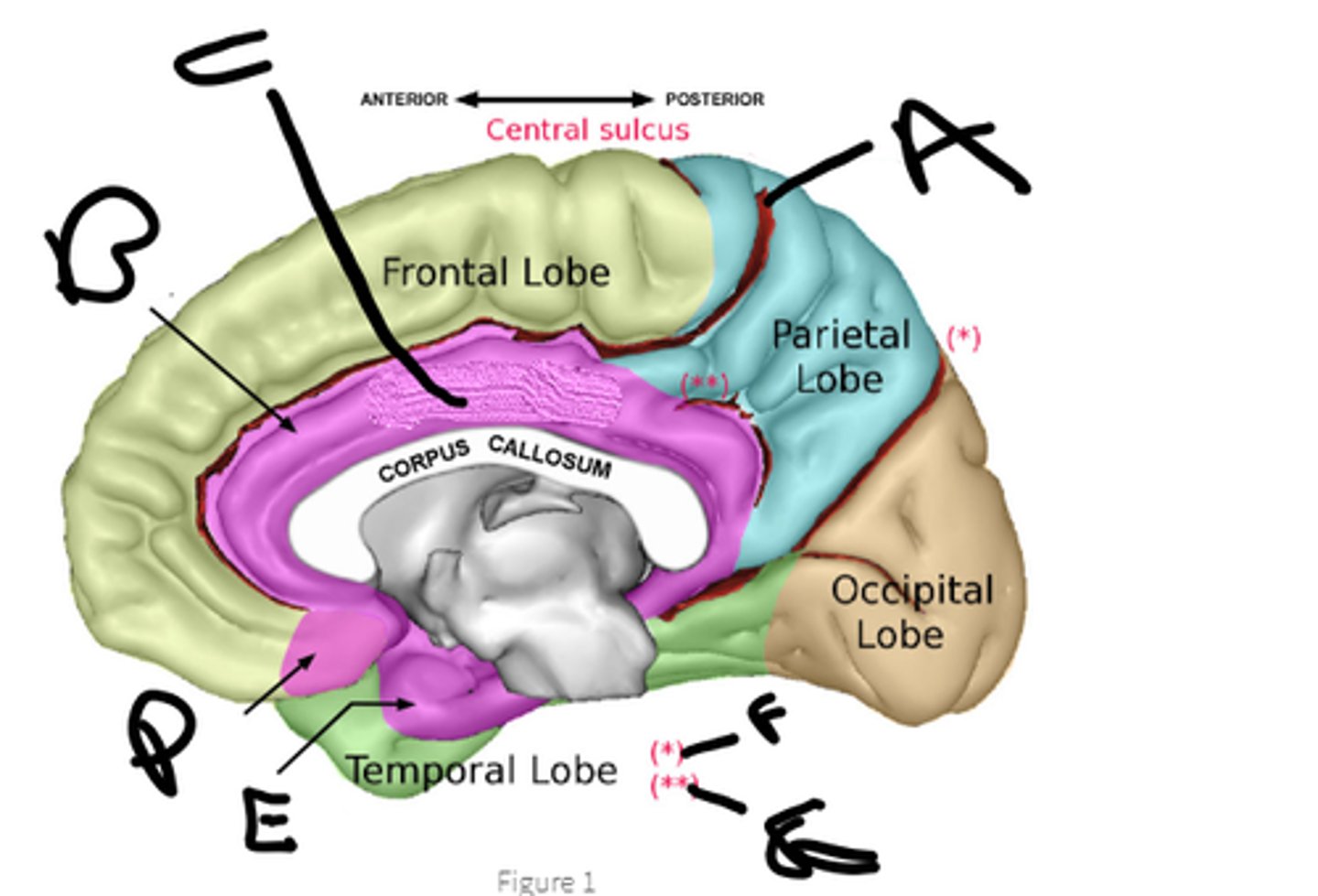
subparietal sulcus
g
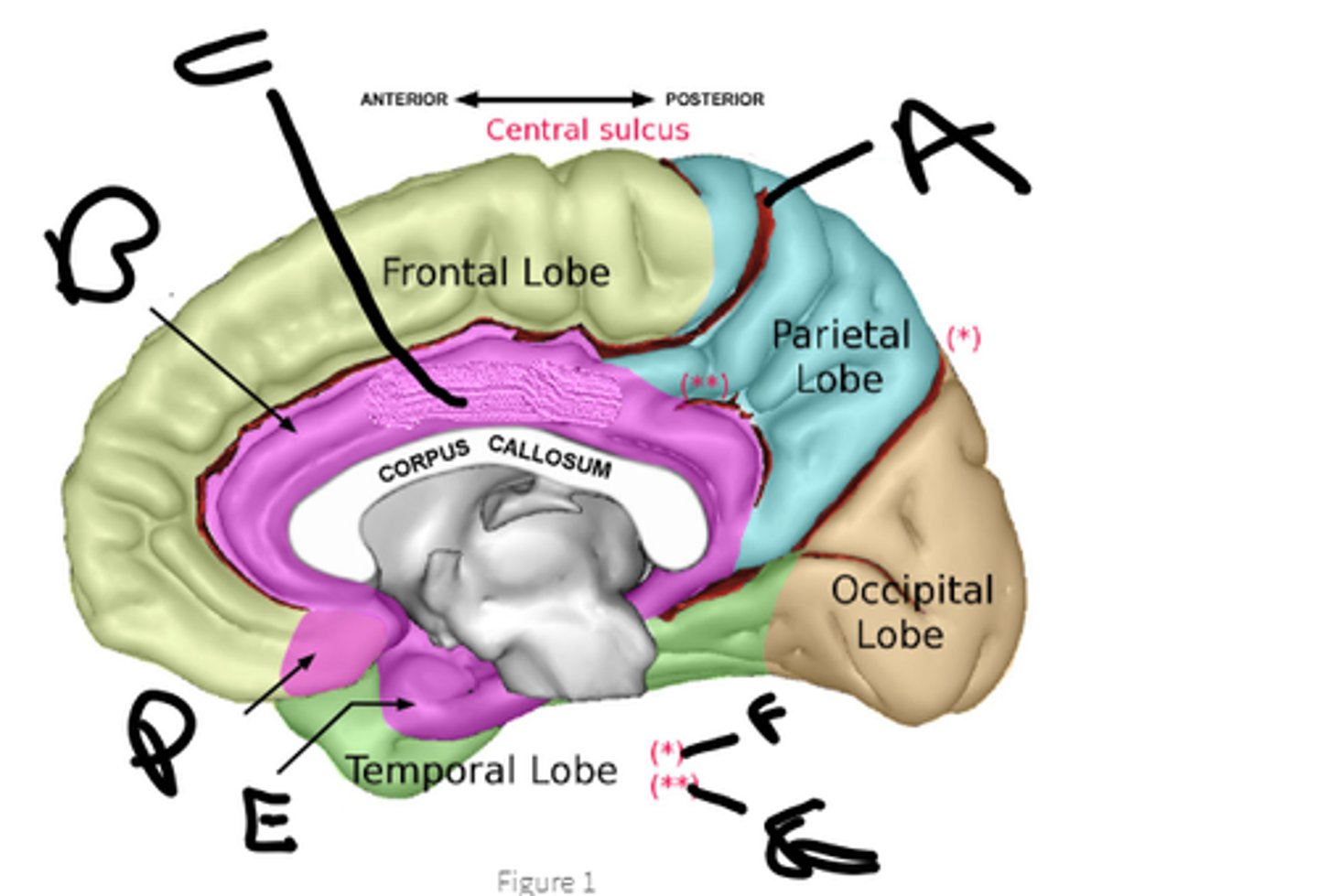
hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, cingulate cortex, nucleus accumbens, septal nuclei
name the 6 brain structures of the limbic system
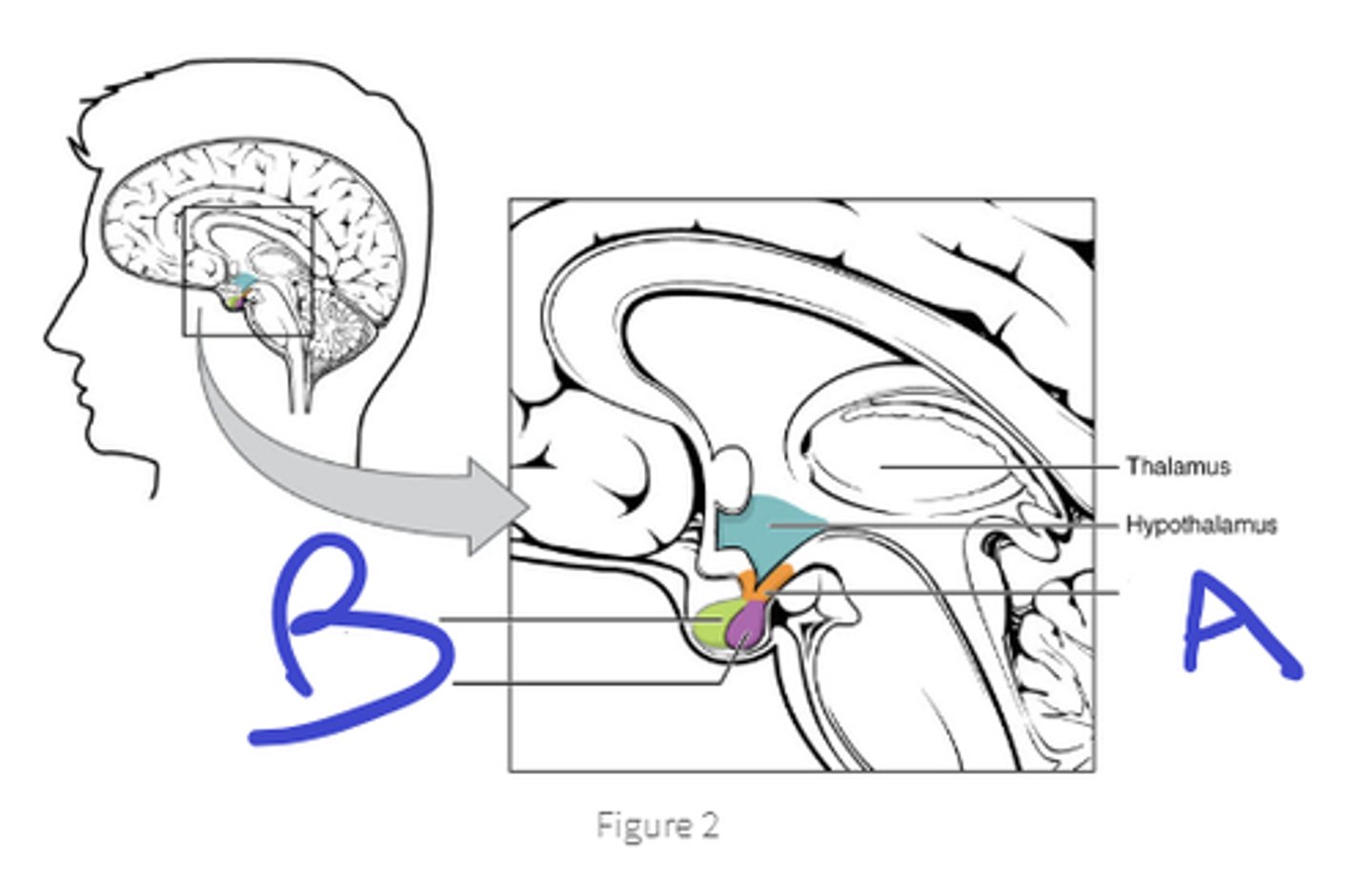
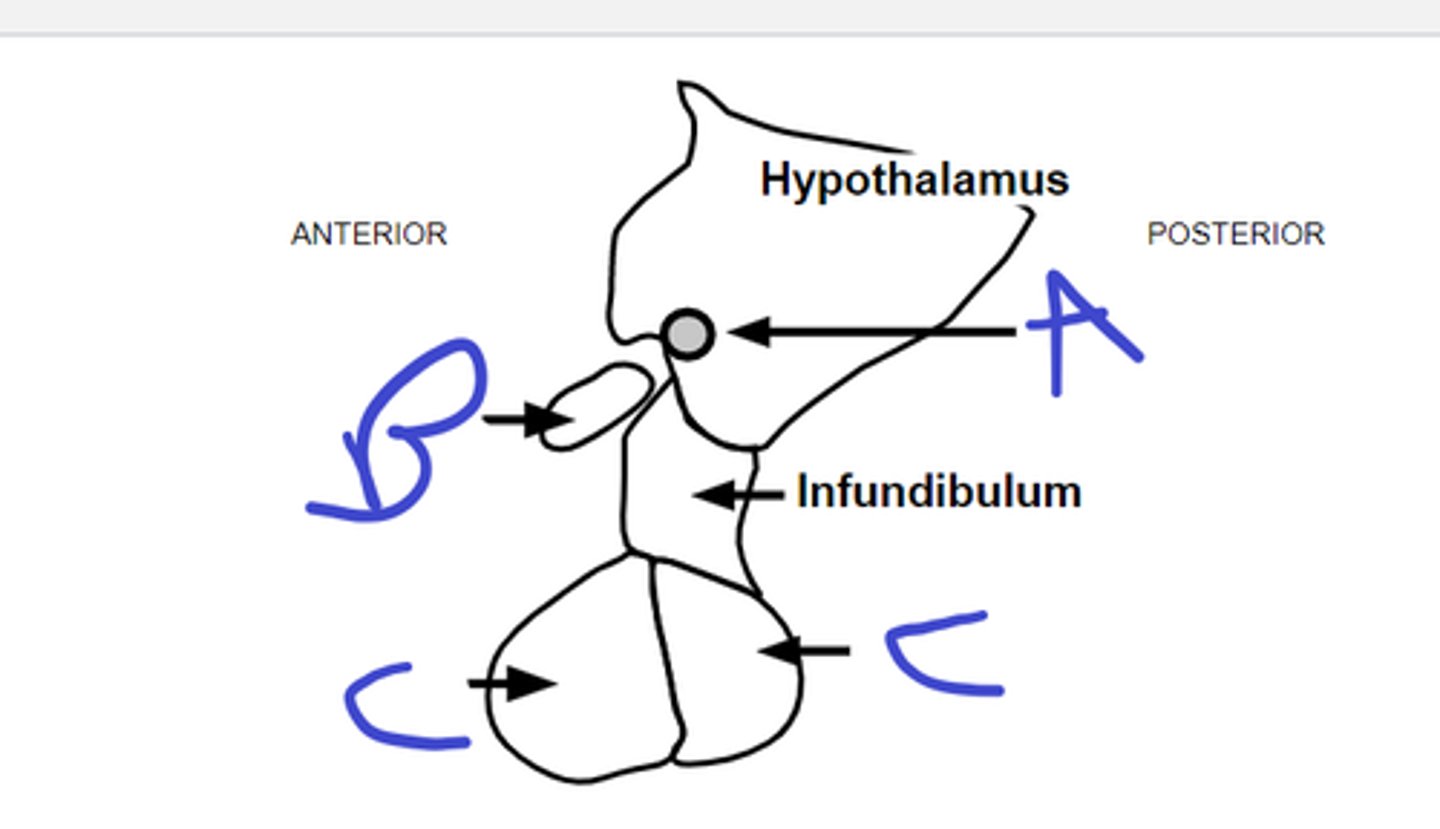
infundibulum
a
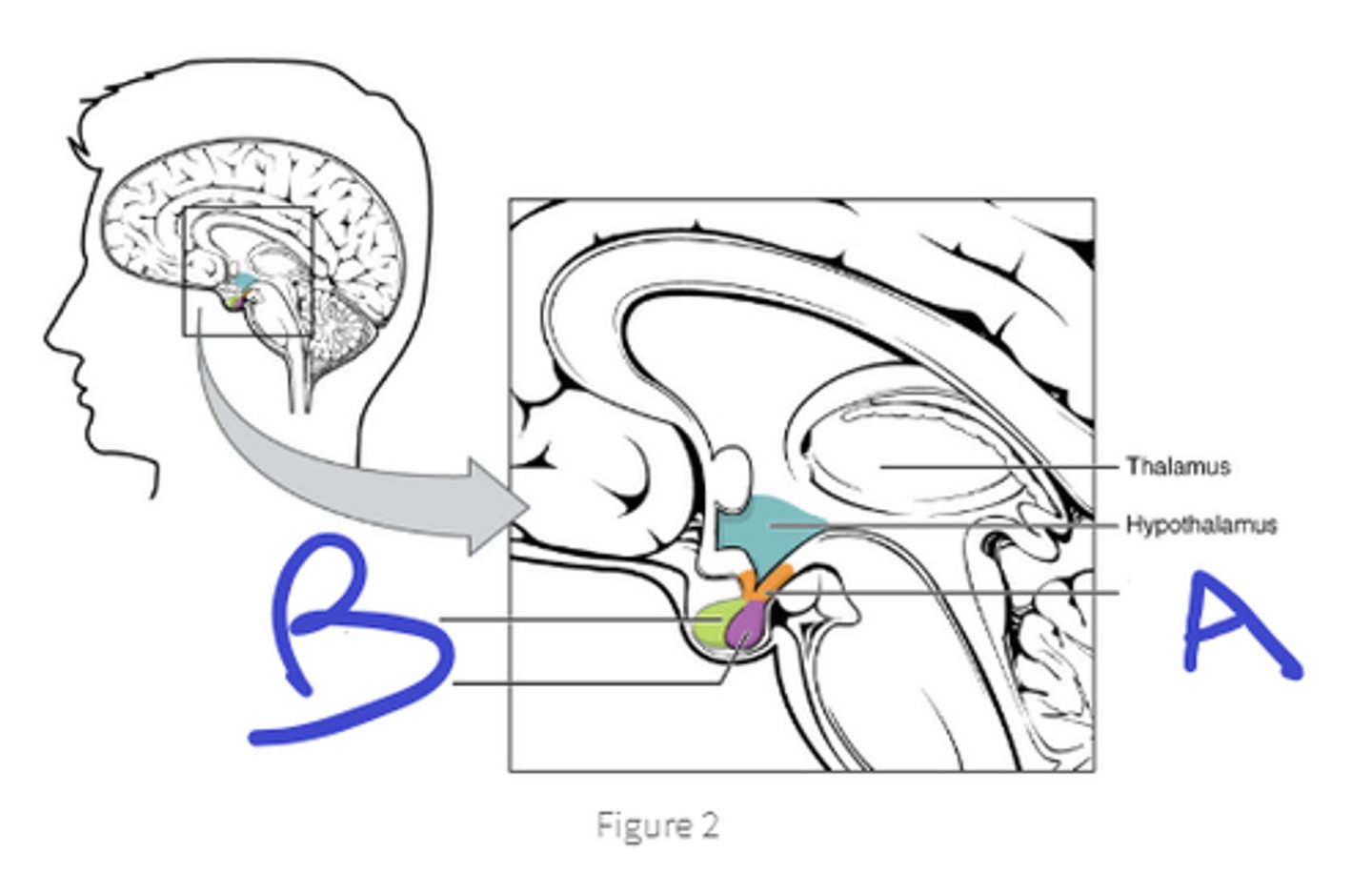
green- anterior pituitary
purple-posterior pituitary
b
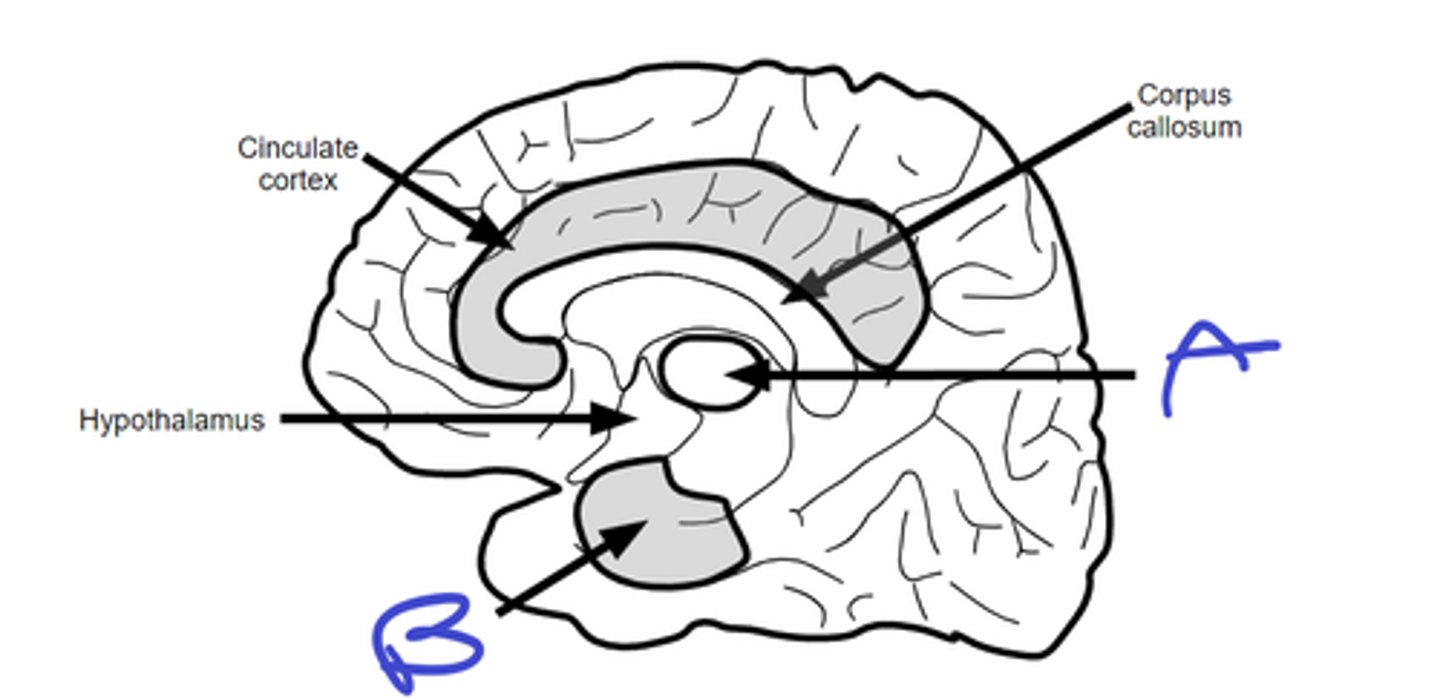
septal area, medial forebrain bundle
a, name area and tract
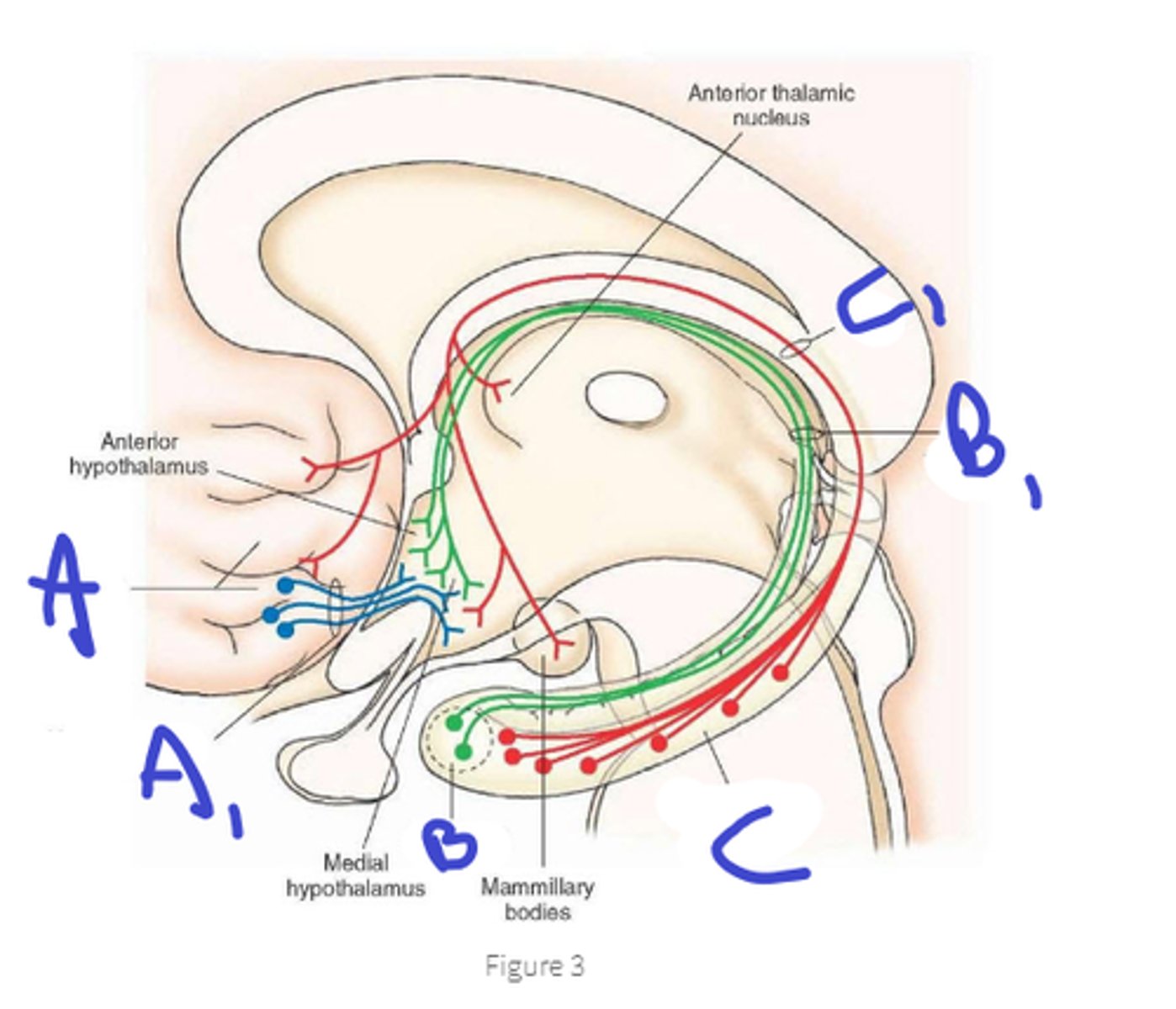
amygdala, stria terminalis
b, name area and tract
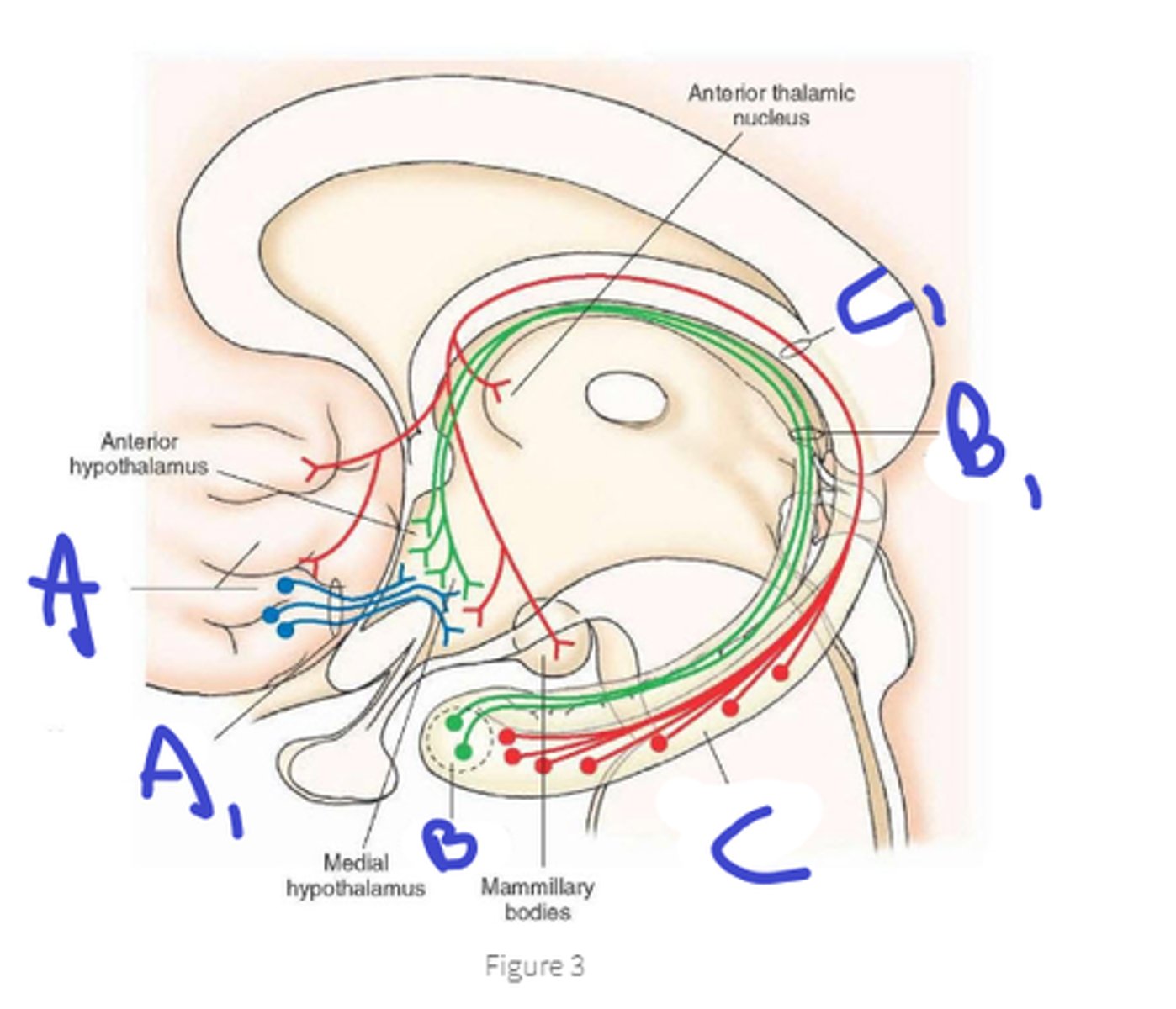
hippocampal formation, fornix
c, name area and tract
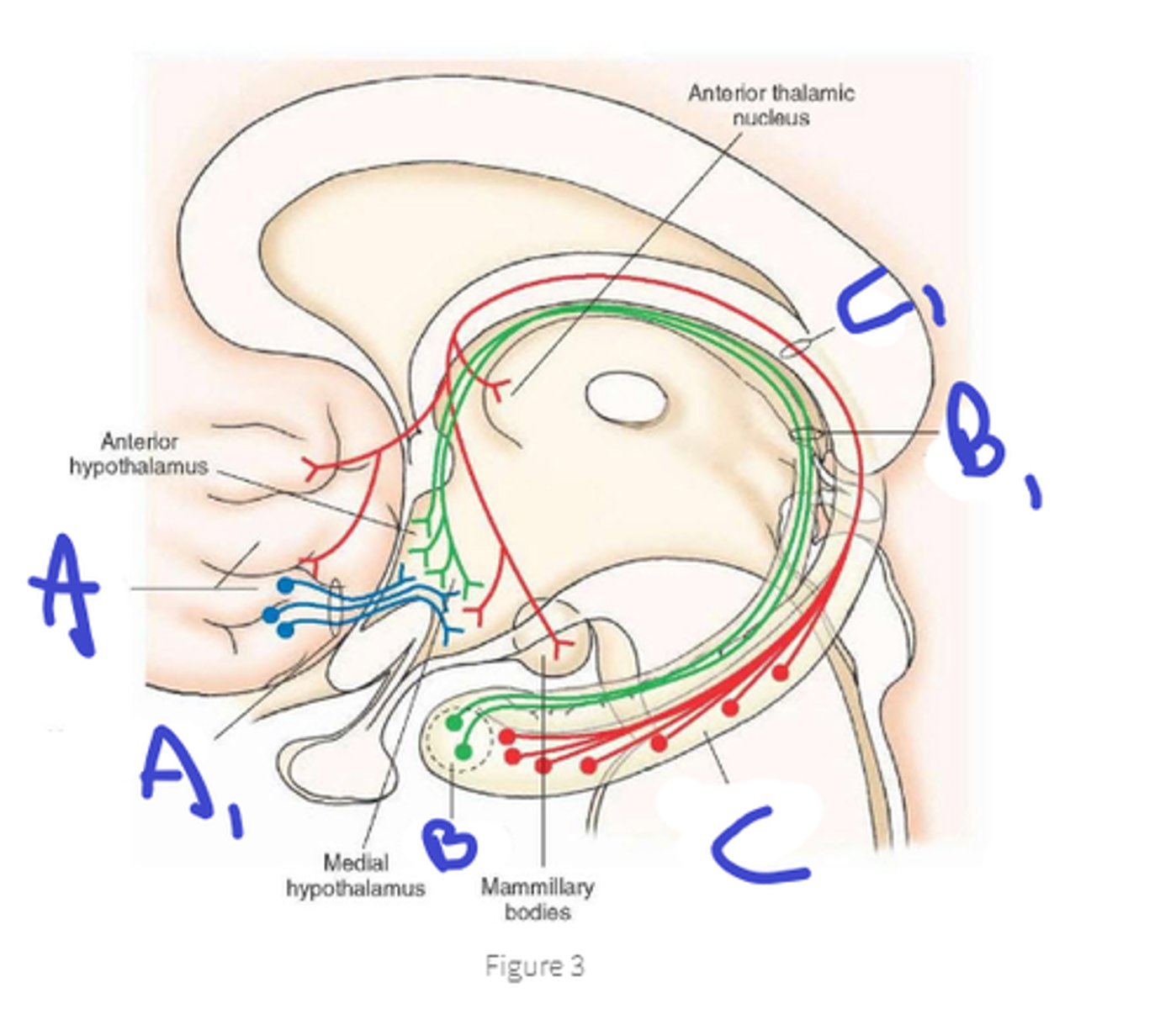
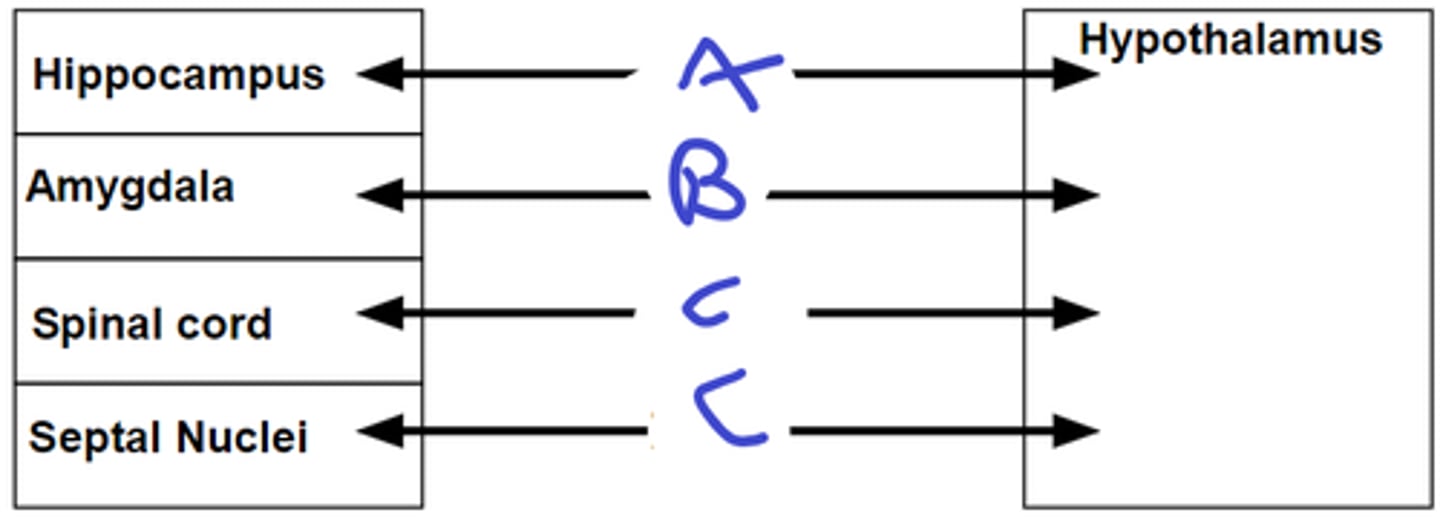
1. back to amygdala, hippocampus, septal nuclei
2. pregang autonomic neurons(brainstem and spinal cord)
3. anterior thalamus relays to prefrontal, orbital and cingulate regions
4. neural and humoral to pituitary gland
output of the hypothalamus
maintain homeostasis and prepare the body for emotional responses
hypothalamus 2 basic functions
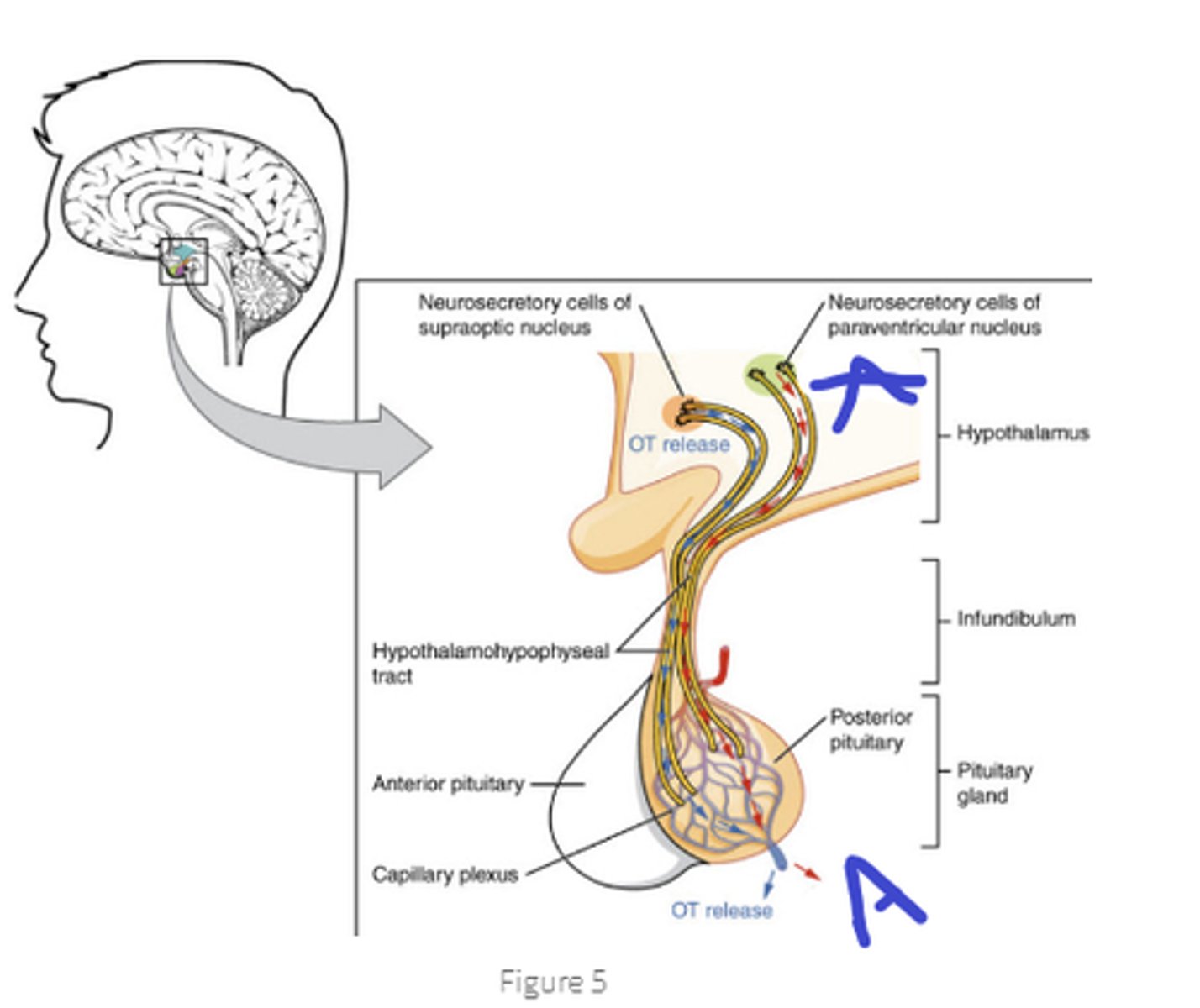
ADH release, neural signal
released into capillary bed so that they enter the blood
what is the hypothalamus releasing to the posterior pituitary, what kind of signal.
What does the pituitary do with this signal
amygdala
what is it
orbital, cingulate, entorhinal and temporal cortex
hypothalamus, hippocampus, brainsteam, septal and thalamus
amygdala inputs
feeling of emotions
mainly fear
rage, defensive postures and fleeing
function of amygdala?
when stimmed in human what is most commonly elicited
what about animals
hippocampus
a
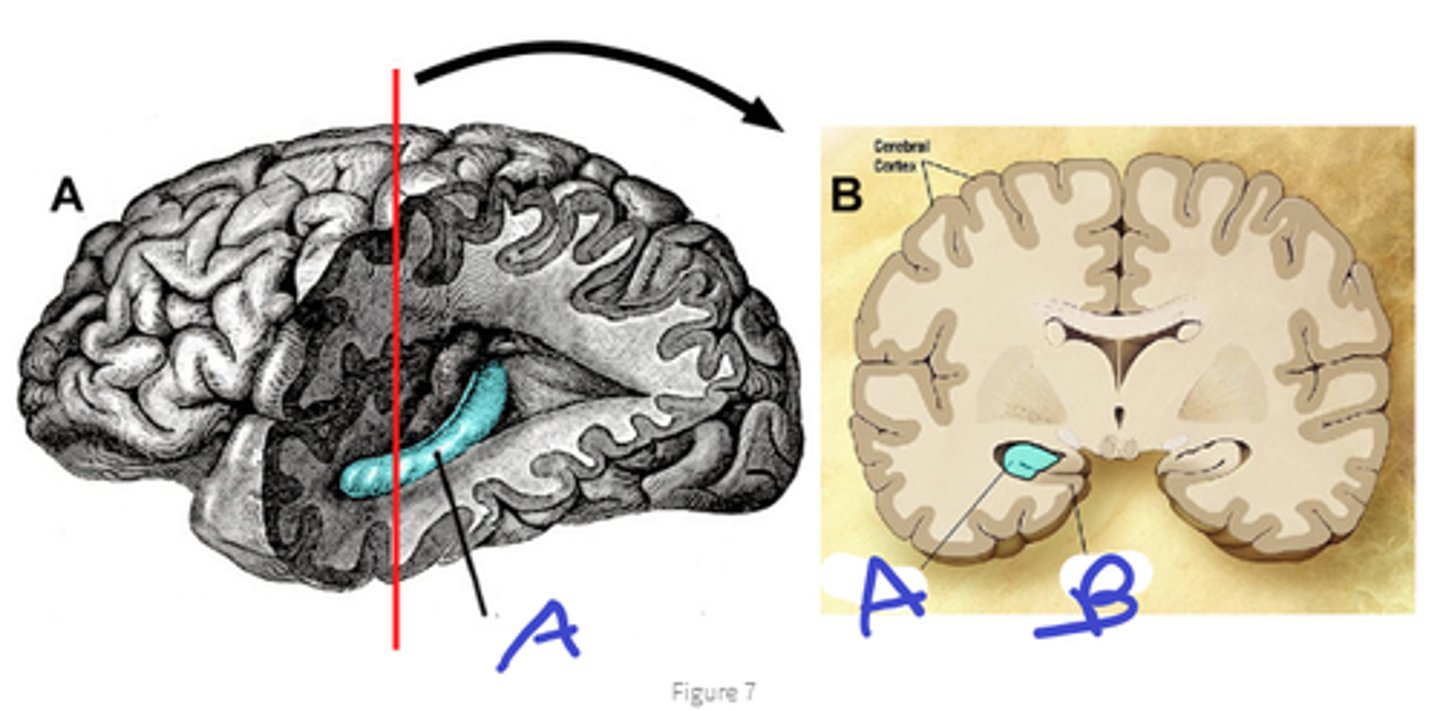
entorhinal cortex
b
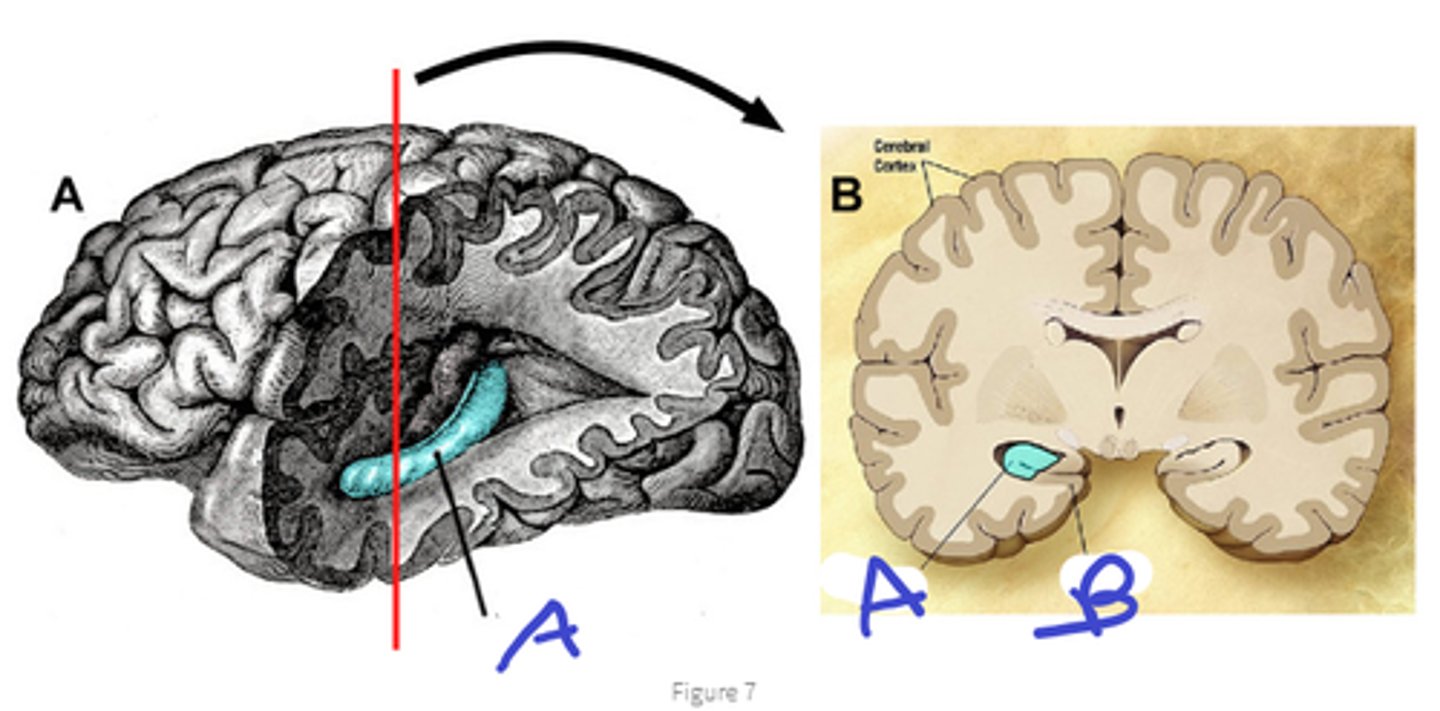
biggest input from entorhinal cortex(this has input from cingulate, orbital and prefrontal)
also input from amygdala and hypothalamus
input to hippocampus
consolidation, formation of new declarative memories
function of hippocampus
VP thamalus(somatosensory--pain) and anterior thalamus
input to cingulate cortex
a-cingulate cortex
b-VP thalamus
A
B
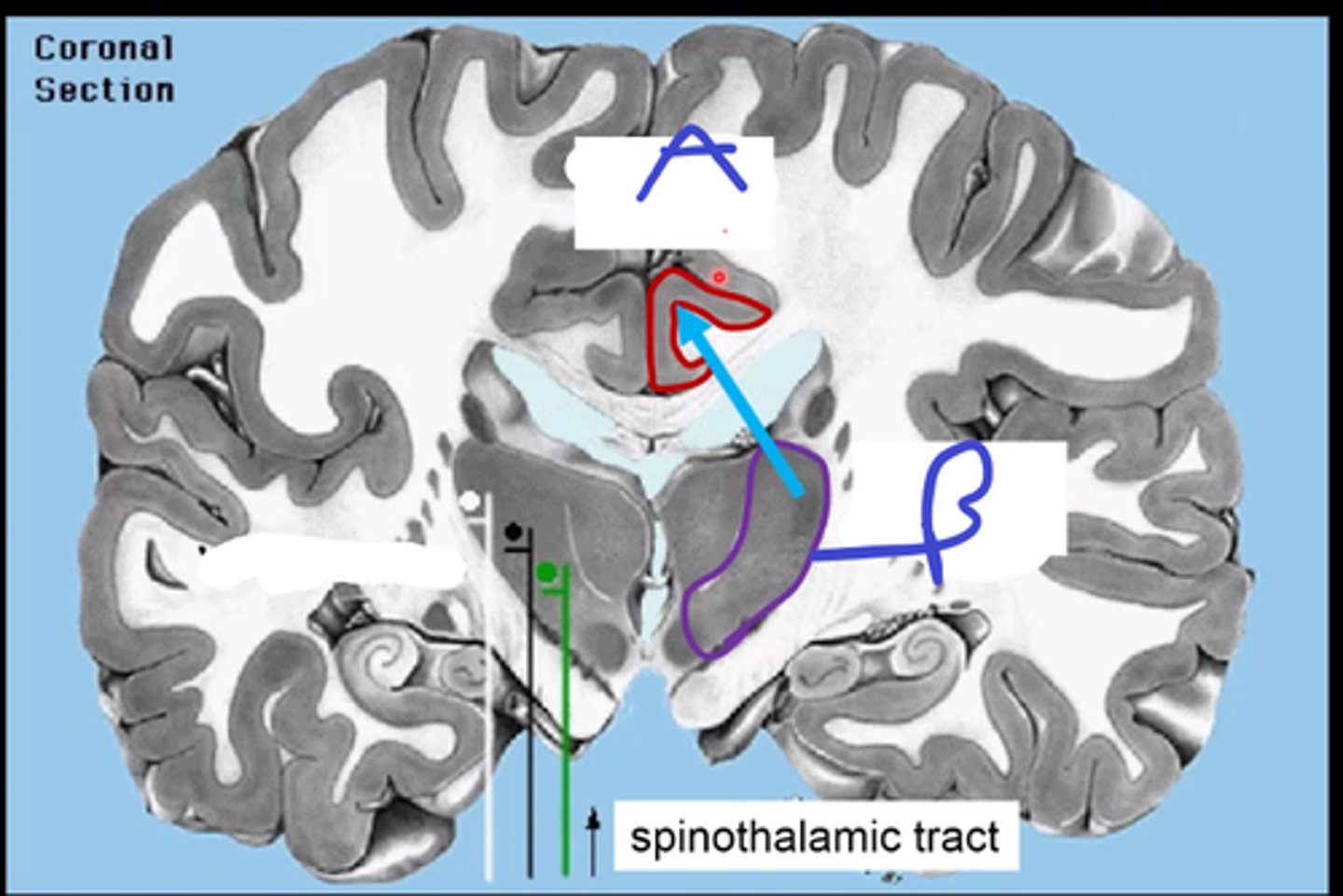
mediate emotional responses to pain
function of cingulate cortex
nucleus accumbens
a
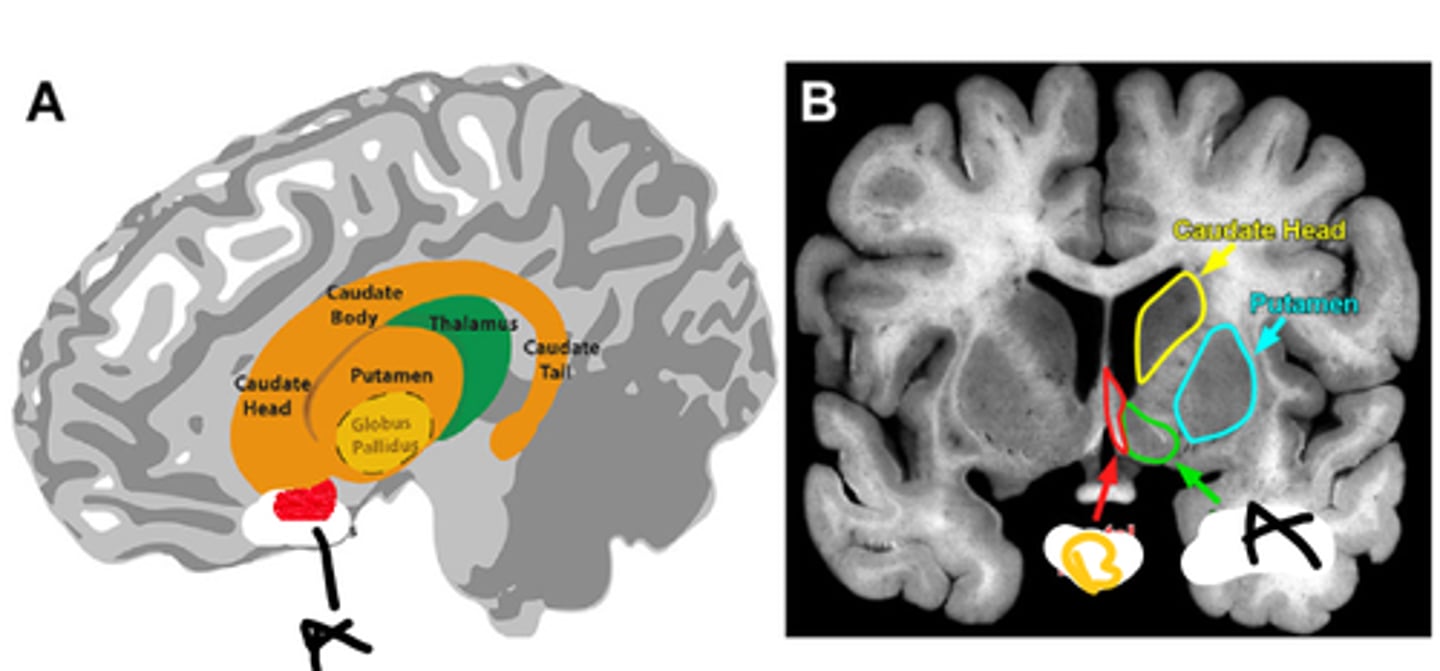
septal nuclei
b
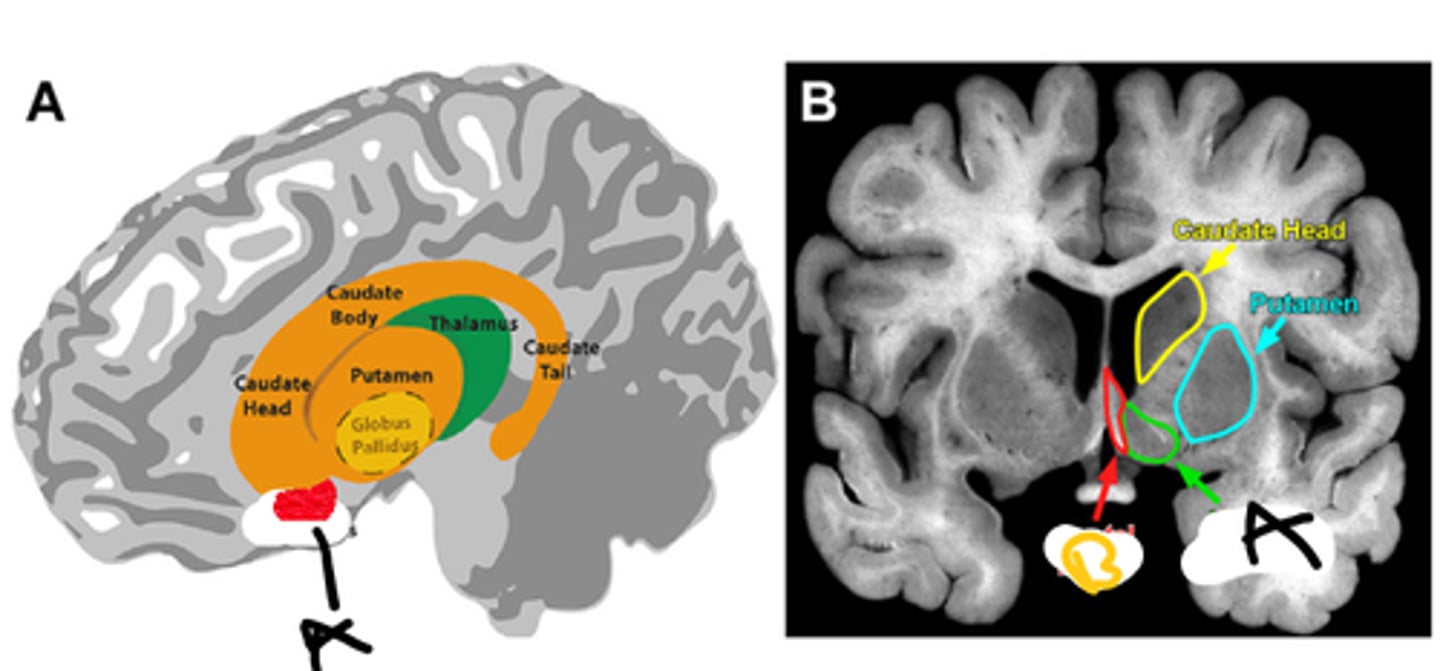
amygdala and ventral tegmental area(dopamine source)
accumbens inputs
modulating motivation and reinforcement, site of action for many addictive drugs
function of accumbens
hippocampus, amygdala
input of septal nuclei
extreme feeling of pleasure and joy
function of septal nuclei
sham-rage: animal become chronically angry and violent
damage to septal nuclei causes
recognize potential threats to homeostasis or well being and
restrain/modify behavior motivated by the limbic system
2 influences of the cerebral cortex tot he limbic system
Phineas Gage
destroyed frontal cortex bilaterally,
unrestrained in trying to satisfy his drives
who is this? what damage sustained?
how behavior changed?
nuc accumbens
a
a-fornix
b-stria terminalis
c-medial forebrain bundle
what connects these structures
a
b
c
a- interthalamic adhesion
b-entorhinal cortex
a
b
medial temporal cortex
limbic cortex
medial border(limbus) of the cerebral cortex
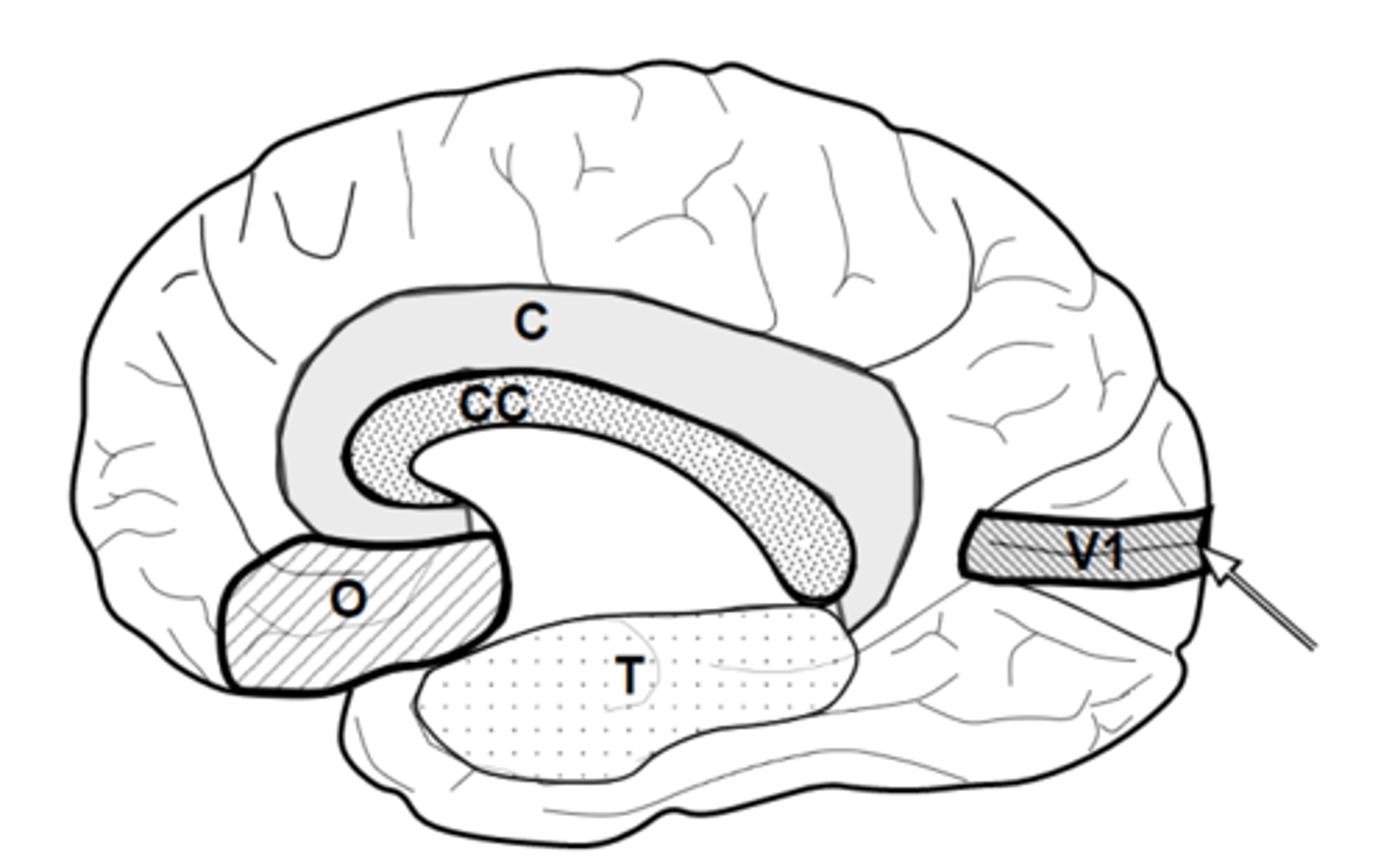
what is T
what does C, O and T make up
why is it called that
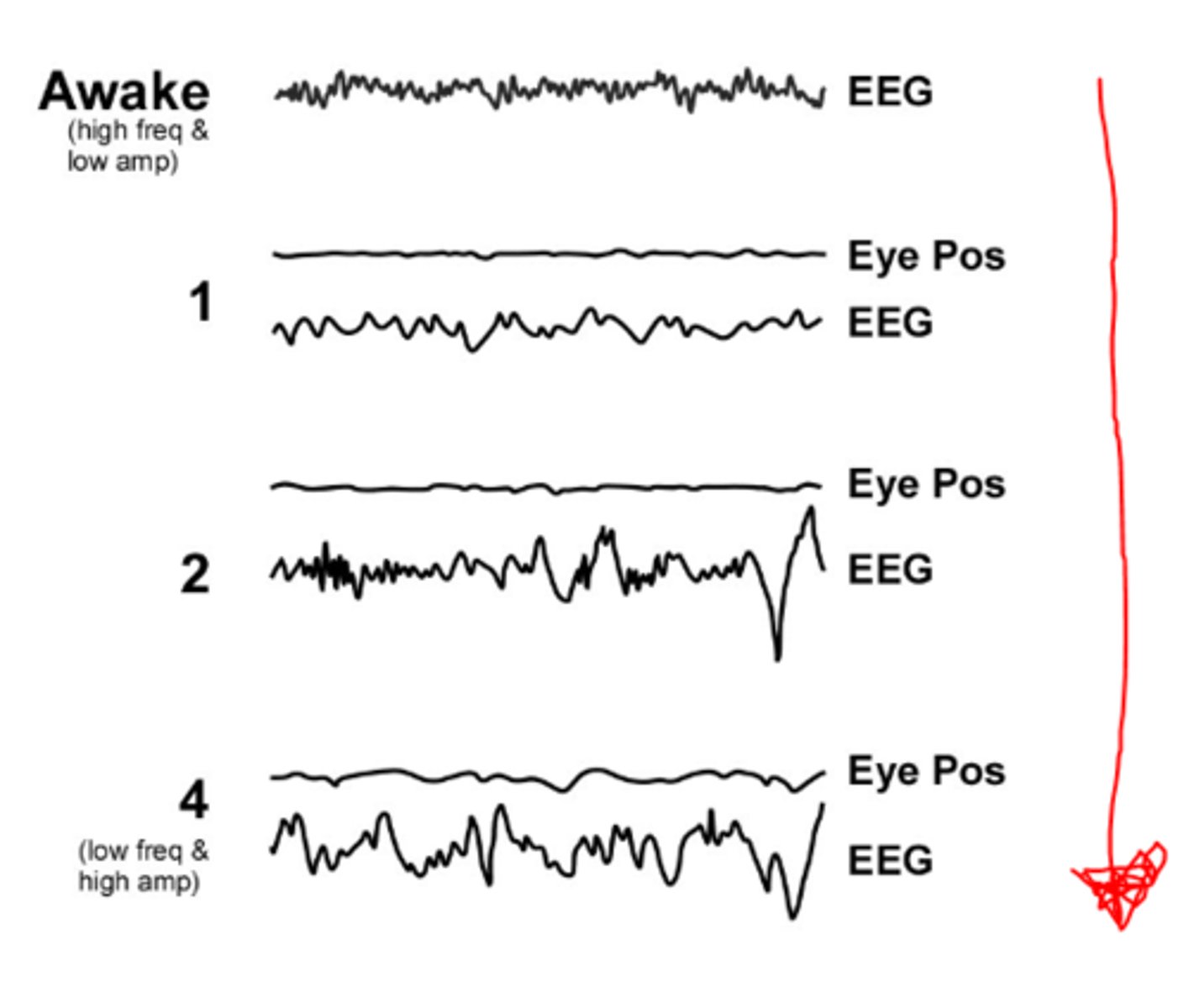
electroencephalogram
EEG acronym go
large changes in eeg amplitude and frequency during sleep unlike recording of an awake brain
why is EEG useful
because positive ions flow into neurons to depolarizing them and negative ion flow out
why do firing neurons provide negative voltage to the EEG
high freq and low amp
awake eeg characteristics
slow wave sleep
sleep stages 3/4
higher amp and lower freq
describe the trend as we move from awake to slow wave sleep
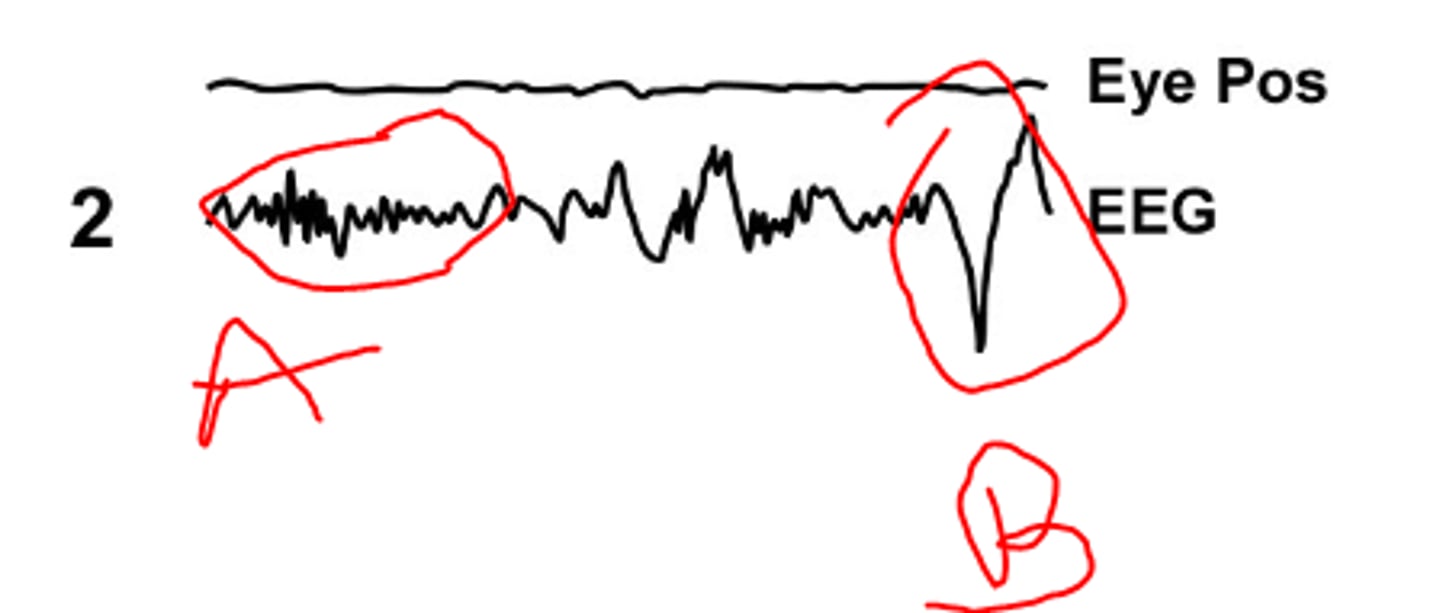
sleep spindle
a
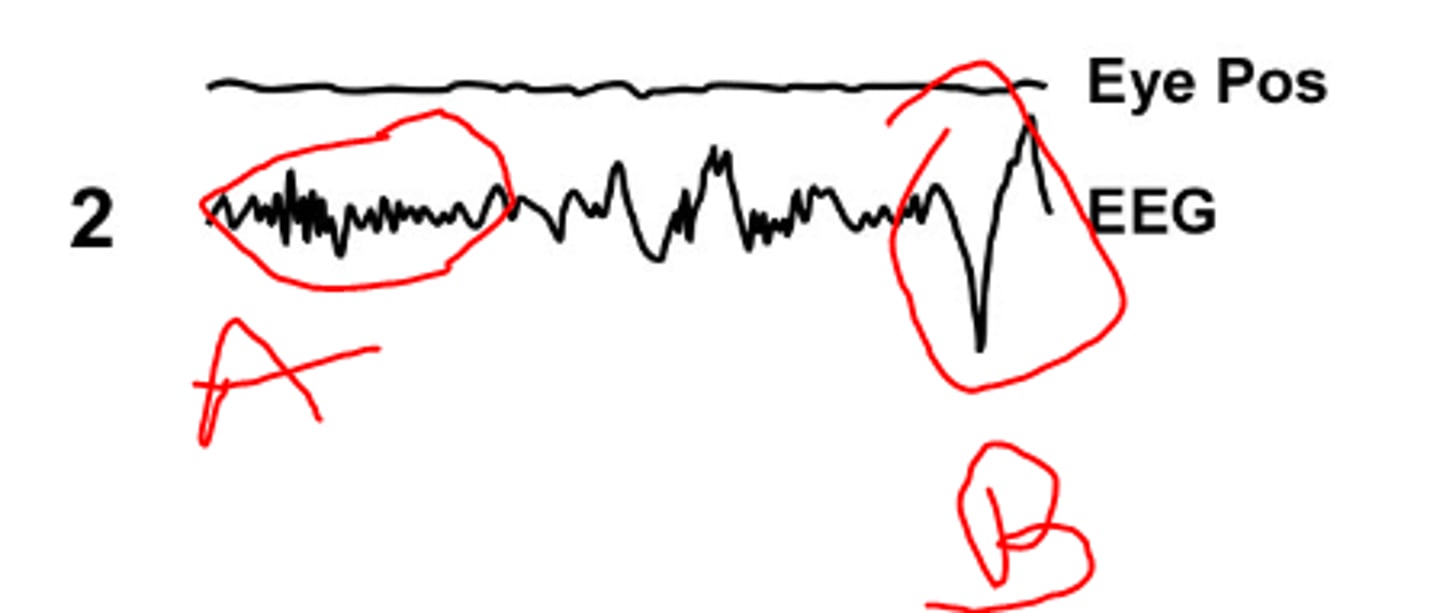
k complex
b
rapid eye movements, high freq and low amp very much like an awake EEG
describe REM sleep

normal muscle tone and regulate our body temperature nearly normally
NREM sleep body observations
inhibits muscle tone, do not regulate body temp>>drifts towards room temp due to no shiver muscles excited
also DREAMS!!
REM sleep body observations
inhibitory center in medulla
what inhibits during REM
eye muscles, diaphragm(for breathing mildly necessary) and muscles that control ossicles
what isn't inhibited during REM
1-4
NREM stages
2-cycle of 1-4-REM occurs on avg 4 times a night
3-REM last longer after cycles, 3/4 become shorter
4-dreams last longer,more vivid and more bizarre with chronological cycles
describe average sleep cycle
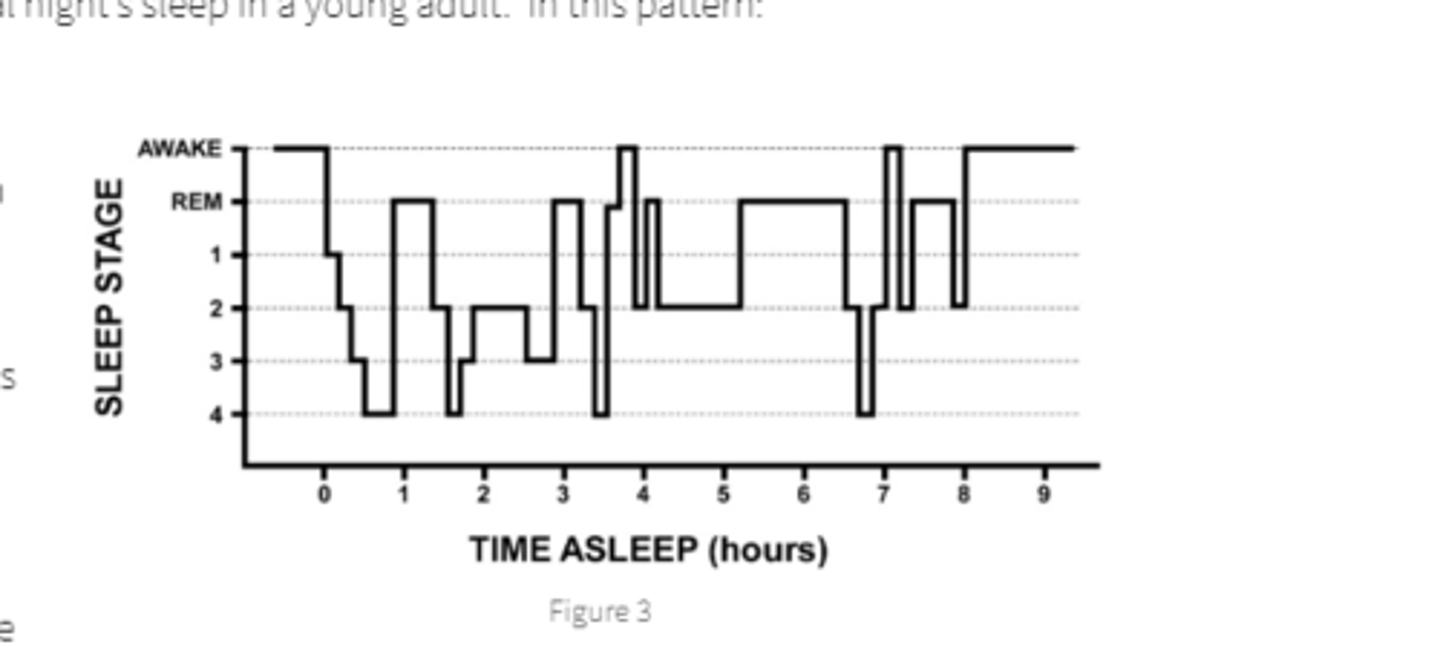
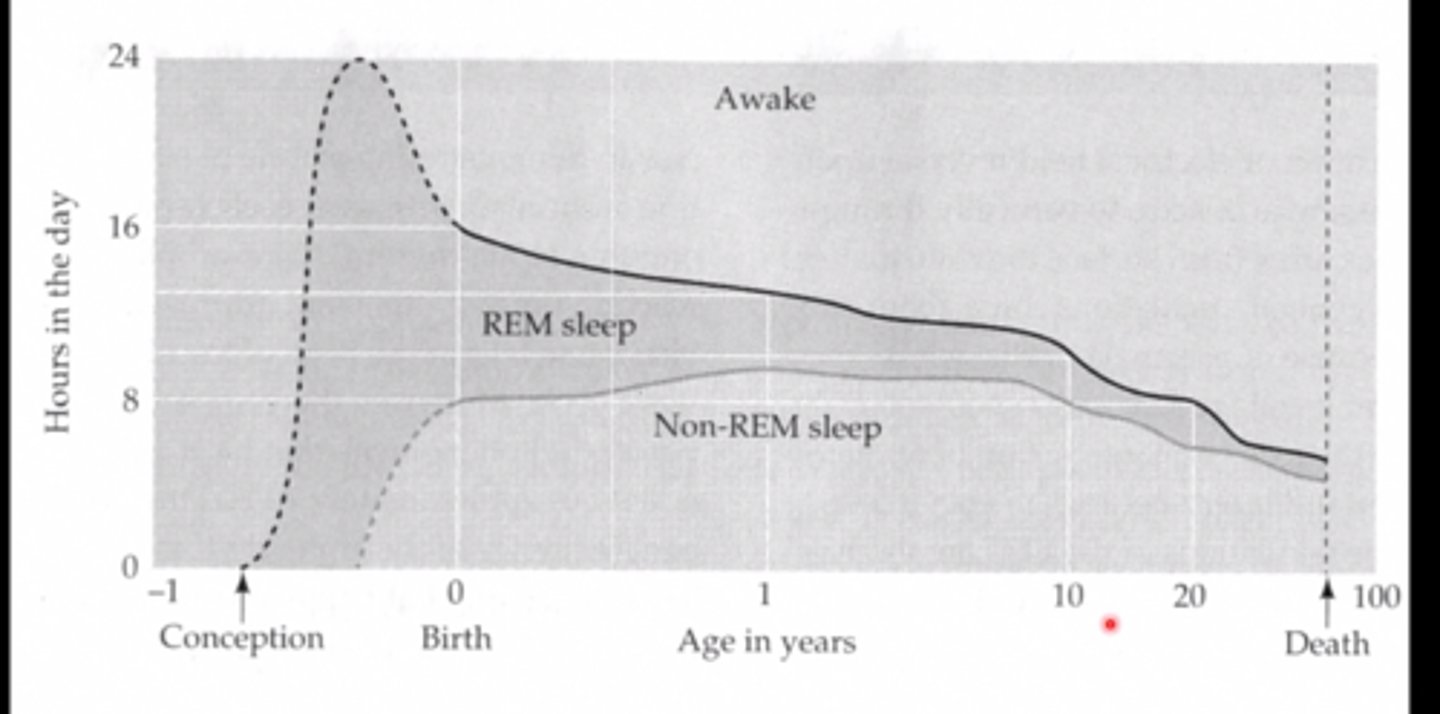
REM decreases with age as well as 3/4 sleep.
not good, mechanism for sleep is deteriorating
whats up with getting old and sleep
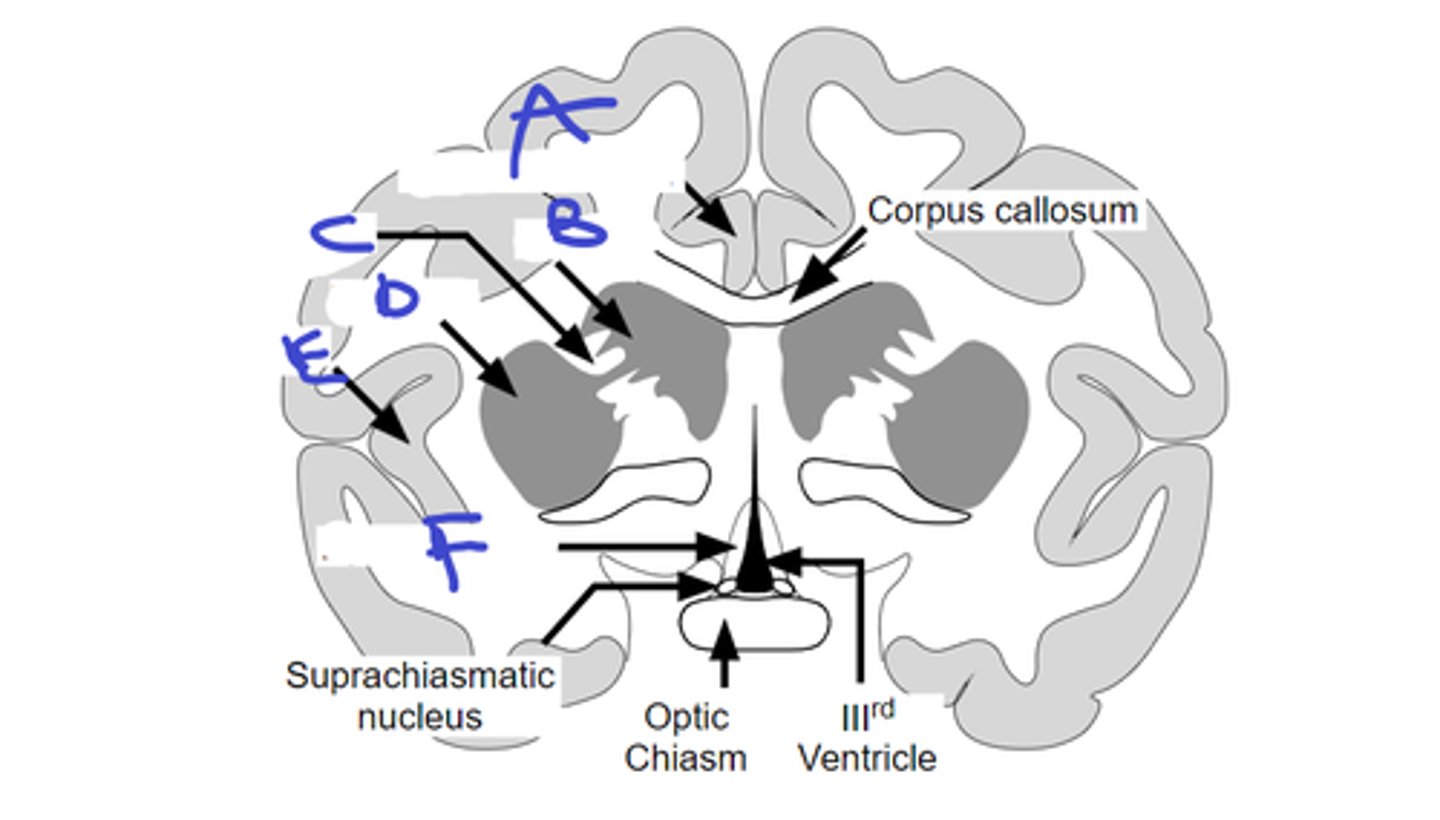
suprachiasmatic nucleus, SCN input from subset of retinal gang
name A and its input
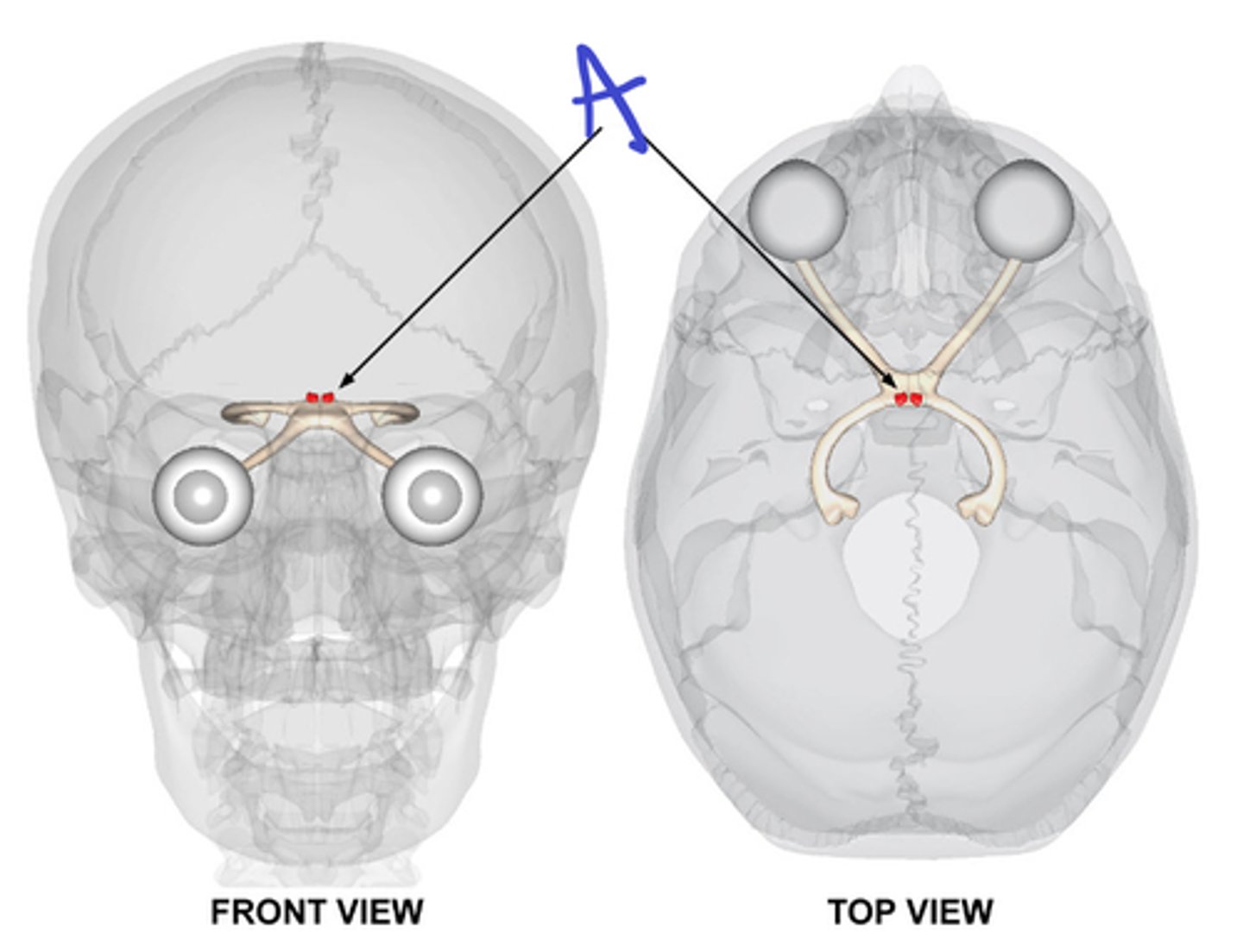
locking our activity/quiescence cycle to the light/dark cycle
The SCN is necessary for
to cortex to produce low amp, high freq
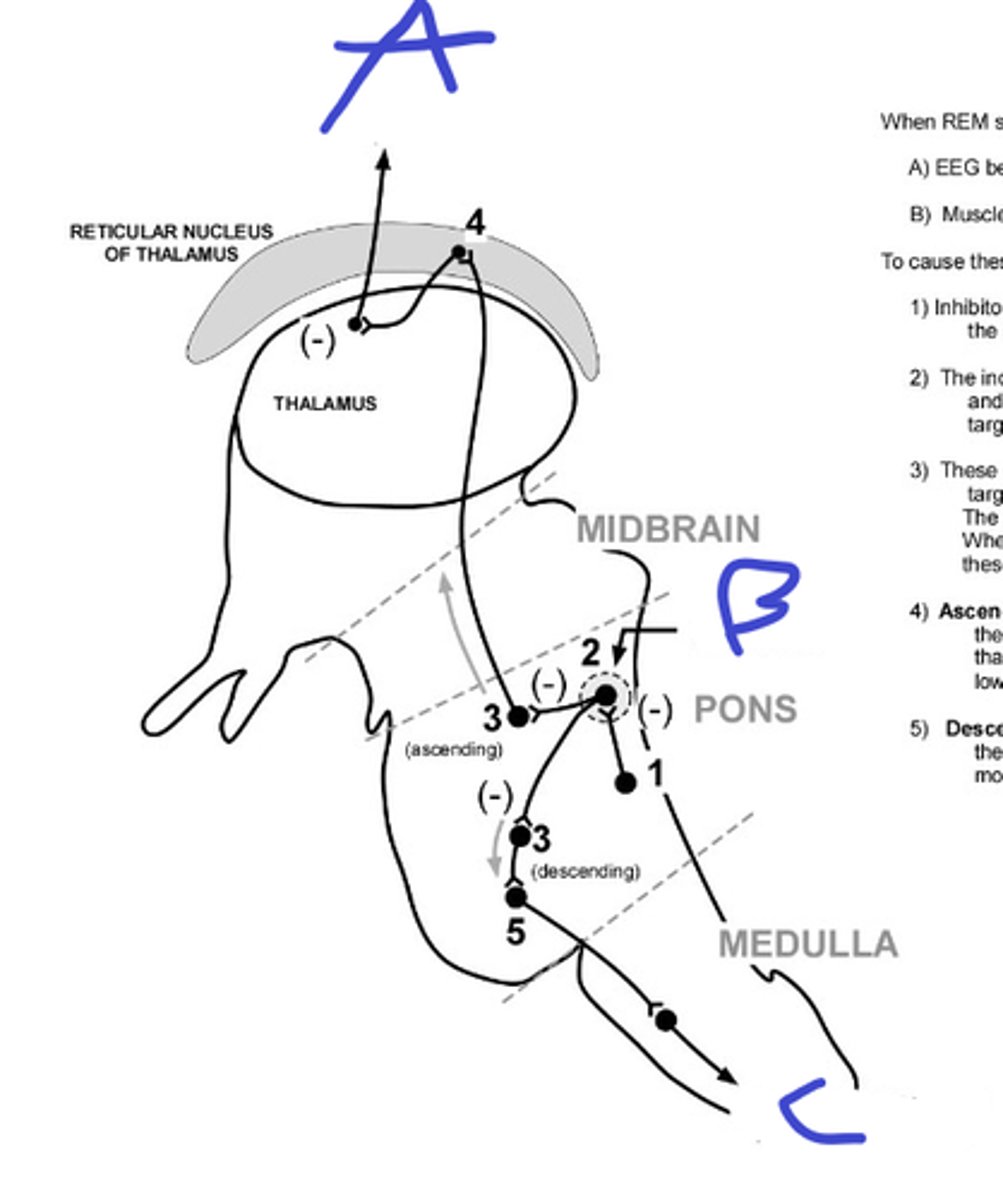
A
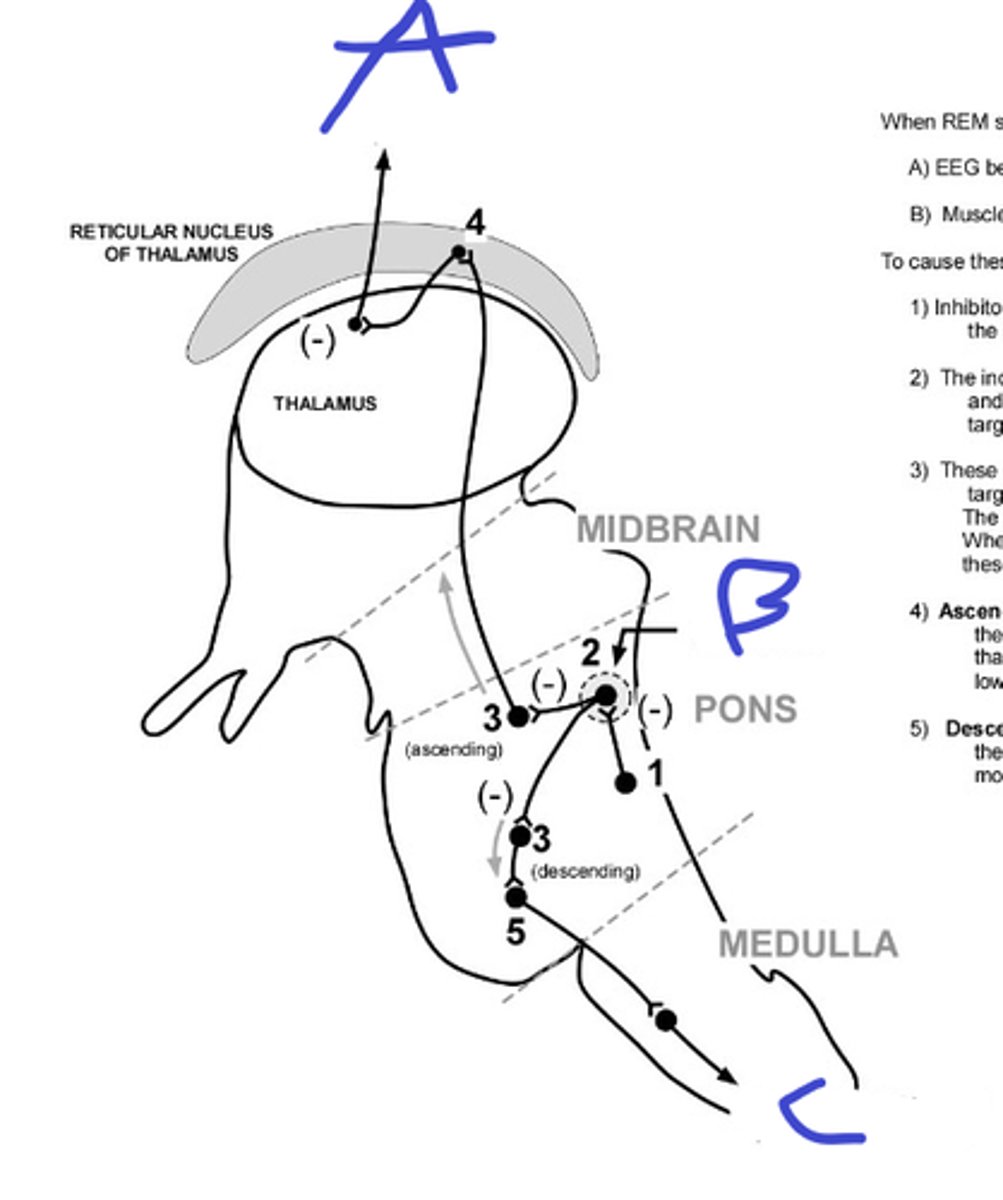
locus ceruleus and raphe nuclei, supporting REM sleep
b, name nuclei and circuit purpose
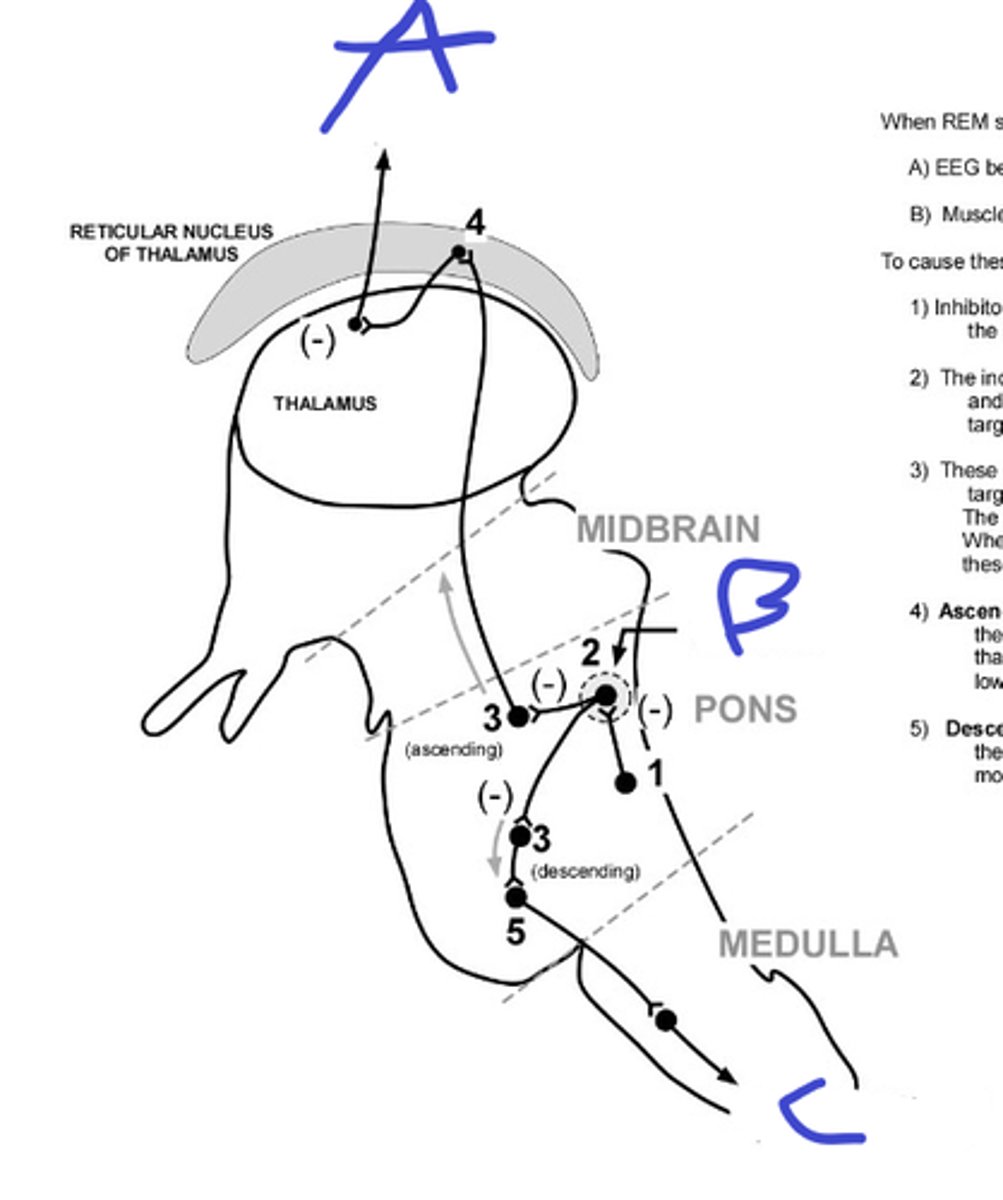
to spinal cord for inhibiting muscle
c
share environment, allow repair(repair oxidative stress and allow neuron proliferation), eating, memory
name sleep implications
more
sleep less eat----
GABAergic neurons fire at the start of REM
name type or neuron and when they fire
REM start
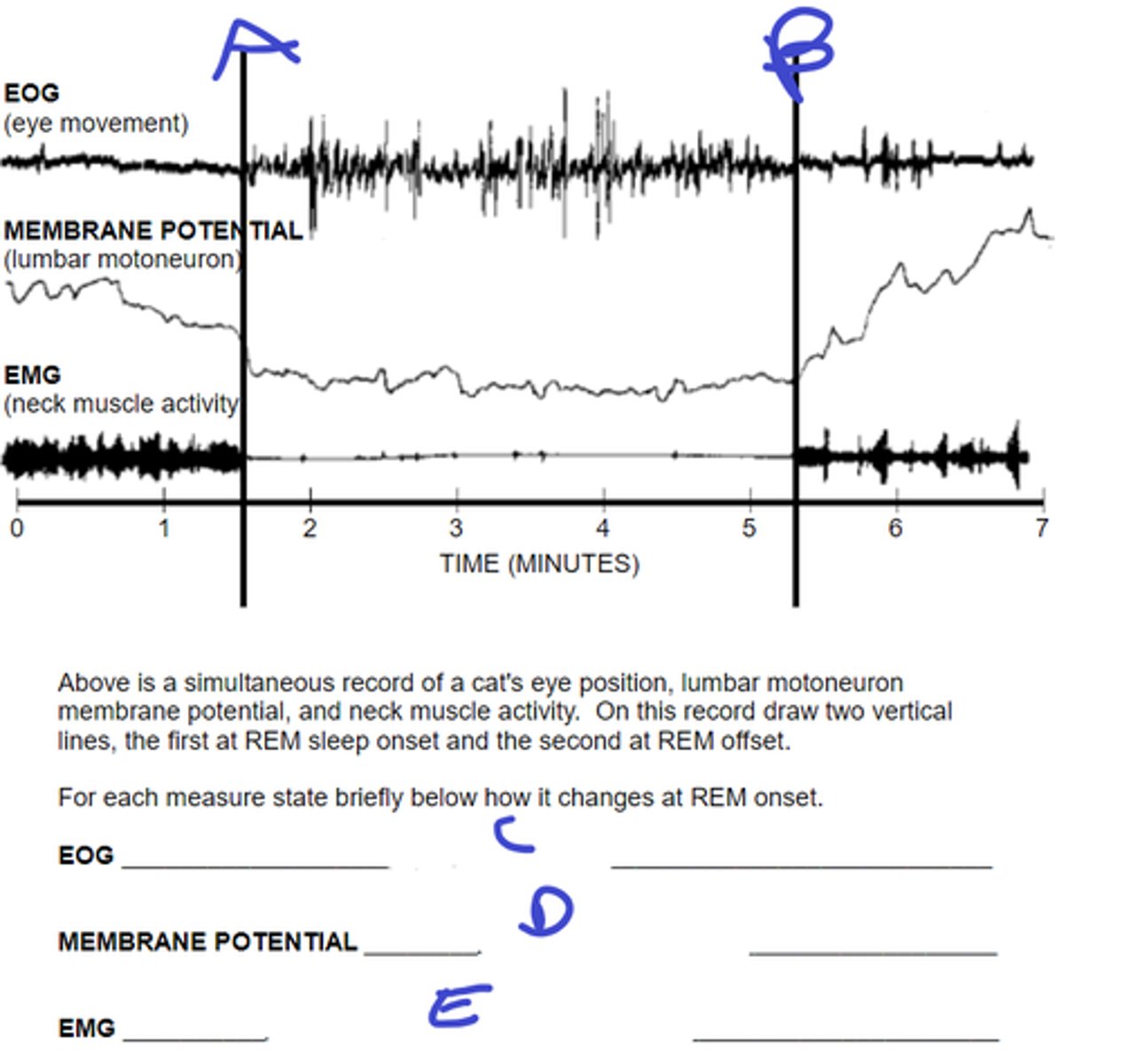
what does A signify
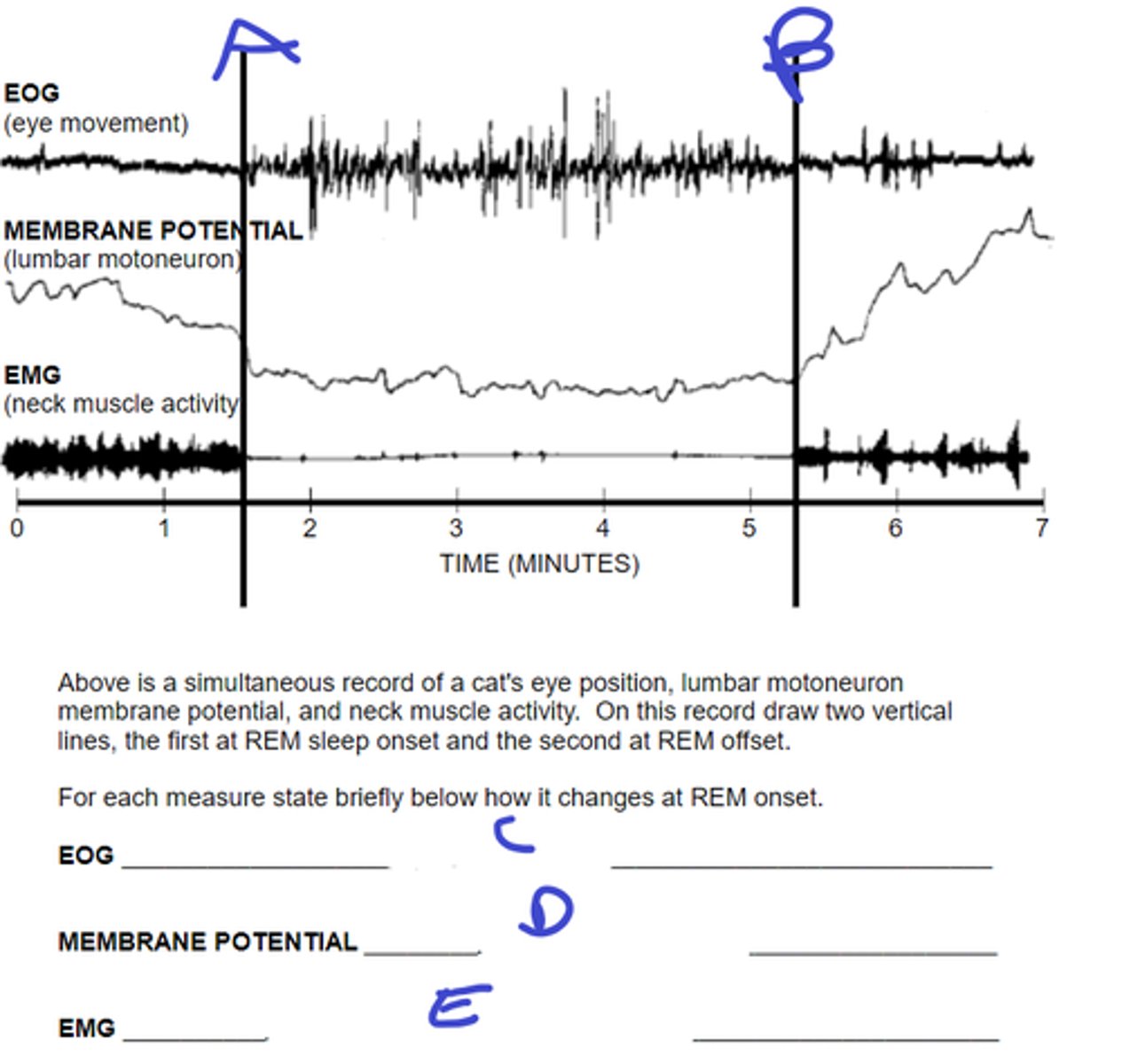
REM stop
what does B signify
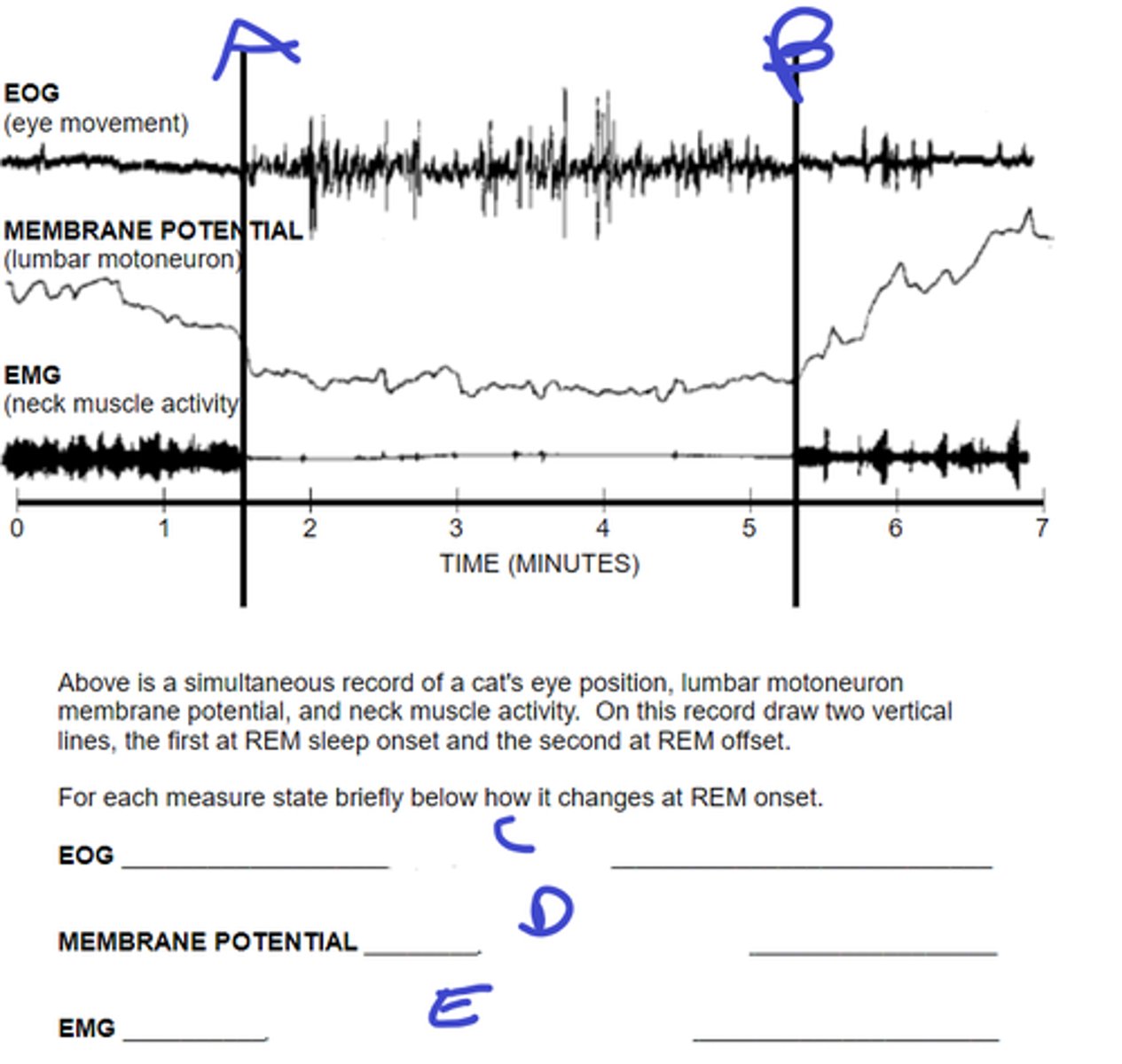
eyes start moving
C: describe movement during REM onset
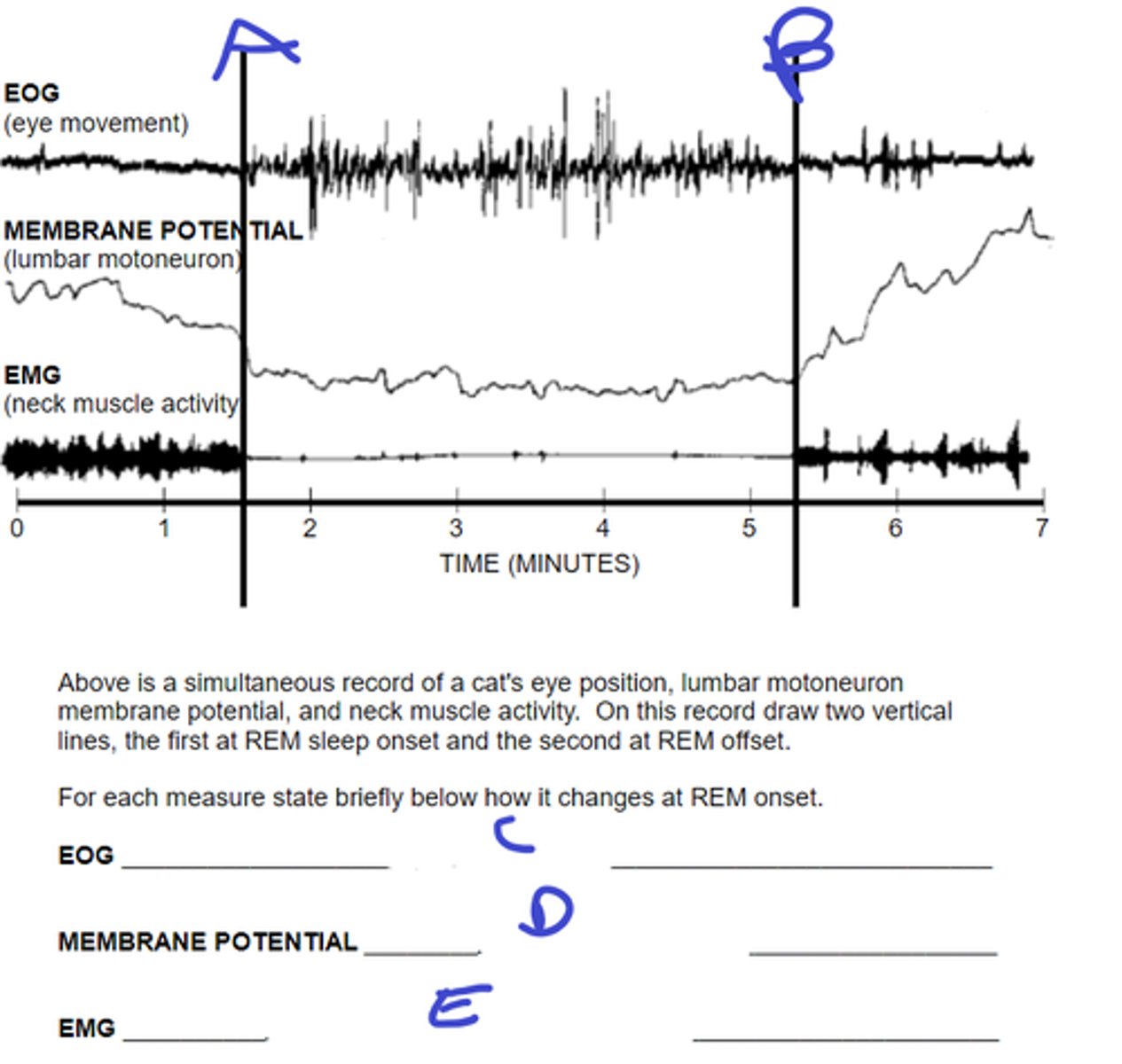
rapidly hyperpolarize, become silent at Vrest
D: describe motorneuron membrane potential during REM onset
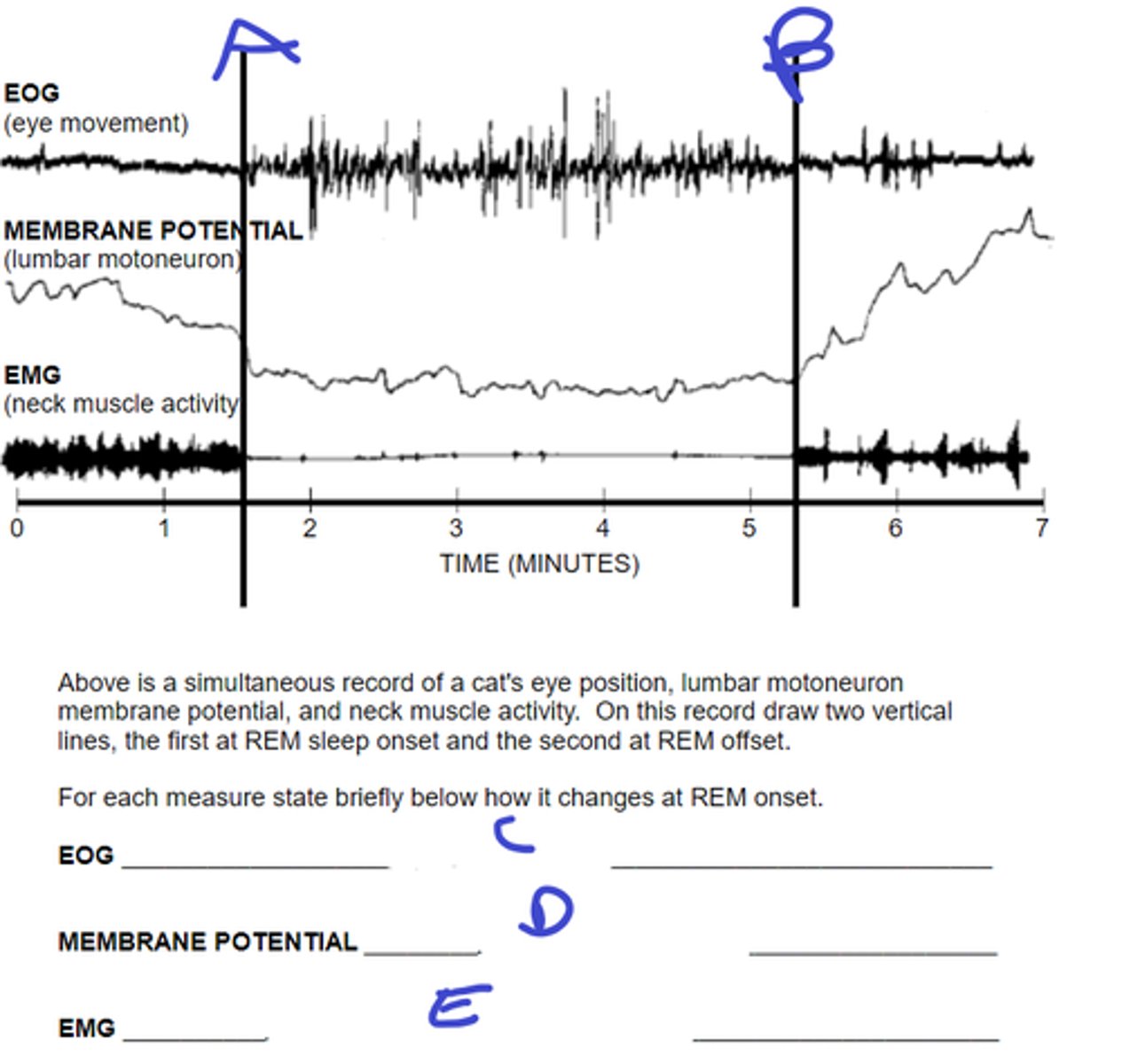
activity dec to nothing
E: describe muscle activity during REM onset
a-scn
b-optic chiasm
c-pituitary gland
A
B
C
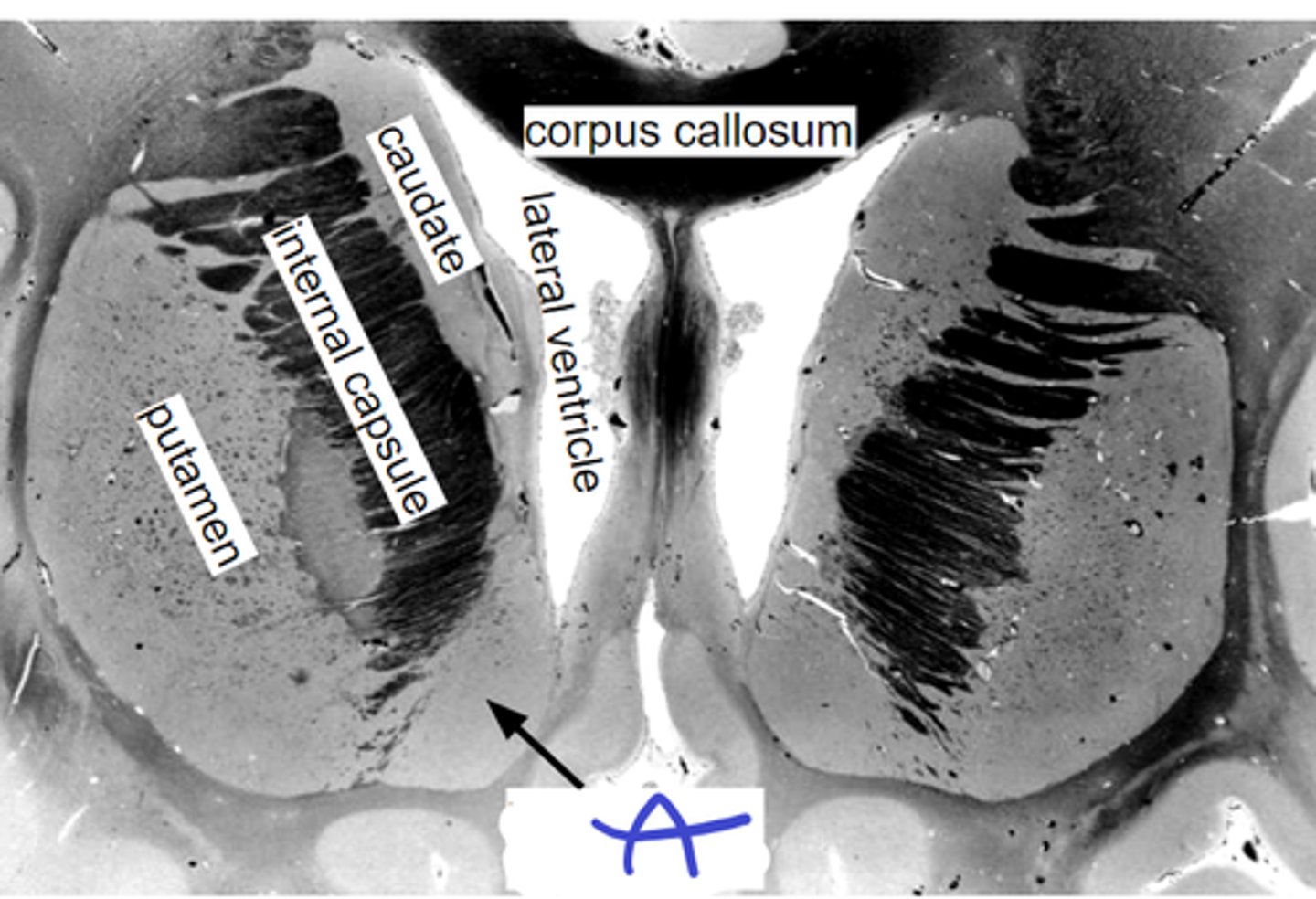
a-cingulate c
b-caudate n
c-internal capsule
d-putamen n
e-insula c
f-hypothalamus
abcdef