apes energy unit
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
how many coal fired coal plants are there, where is the biggest located, and what is the avg home usage in the US
589
largest = Indiana (25 tons/min - 24/7)
avg home usage = 10-15k kwh/yr (=10-15k lbs coal)
efficiency of coal fired plants (how much is used)
33% efficient (66% lost)
incandecent lightblub = 10% efficient
what is the 2nd law of thermodynamics
with each energy conversion, usable energy is lost —> less efficient
voltage vs current
voltage = potential for energy, how much can flow
current = actual amount of electricity flowing
what is petroleum/oil mostly used for, what place has the most of it
use = transportation (gasoline/diesel)
place = Saudi Arabia
3 types of petroleum/oil extratction
pump jacks (land based)
oil rig (off shore)
tar sands (ex. in canada)
pump jacks
old tech (more sustainable/environmentally friendly)
land based
roads to lead to it — concrete
lower habitat loss

oil rigs
new tech (less sustainable/not environmentally friendly)
off shore
has to go through thousands of ft of water and then it can dig
uses LOTS of electrcity
bad bc of potential oil spills

tar sands in canada
bad
surface mining
sand grains are covered in oil and they want to seperate the oil from the sand
uses fossil fuels to heat the sand and get the oil off
50x more polluting (bc ur using ff to get ff)
the deep water horizon spill
semi-submersable oil rig that exploded april 2020, oil exploded and the rig caught on fire, oil spilled in the gulf, 1st tried to set the oil in the water on fire and later used a chemical spray that made the oil solid (sinks)
effects: can’t eat the fish, air is polluted, poured over 1 million gallons of chemicals into the water to solidify the oil (but it’s still in the water)
how many passenger vehicles in the US, how much oil does US demand per day
256 million passenger vehicles
demand 19 million barrels/day
transportation of the petroleum/oil, how could it be bad
pipelines (1000s of miles of it)
bad bc of potential leaks and impedes migratory patterns
refining of petroleum/oil
crude oil —> furnice —> distiller column
uses of refined petroleum/oil (hightest —> lowest temp)
high temp = cars (emmisions/exhaust — CO2, SOx, NOx, PM - soot/ash, CO - colorless and oderless and can kill u) ~~ 8,887g CO2/gallon
second to high = airplane/jet
second to low = trucks (*transportation)
low temp = asphalt/road (it’s an ingredient in tar)
conservations of petroleum/oil
manufacture IN country (don’t need as much fuel for transport)
biofuels: ethonol (made of corn/”sugar based” — 10% in all gas) & biodiesel (made of fats, veg oil, and ALGAE)
end fossil fuel subsidies
raise CAFE (corp avg fuel efficiency) standards: required mpg - higher
bike, walk, carpool, public transport, HOV lanes (promotes ridesharing)
raise gas prices (ex. UK ~~ $10/gallon)
better city planning for walkable/bikeable cities
don’t idle ur car
hybrid (mpg) vs electric (embodied energy)
#1 place in natural gas
russia (#2 is US)
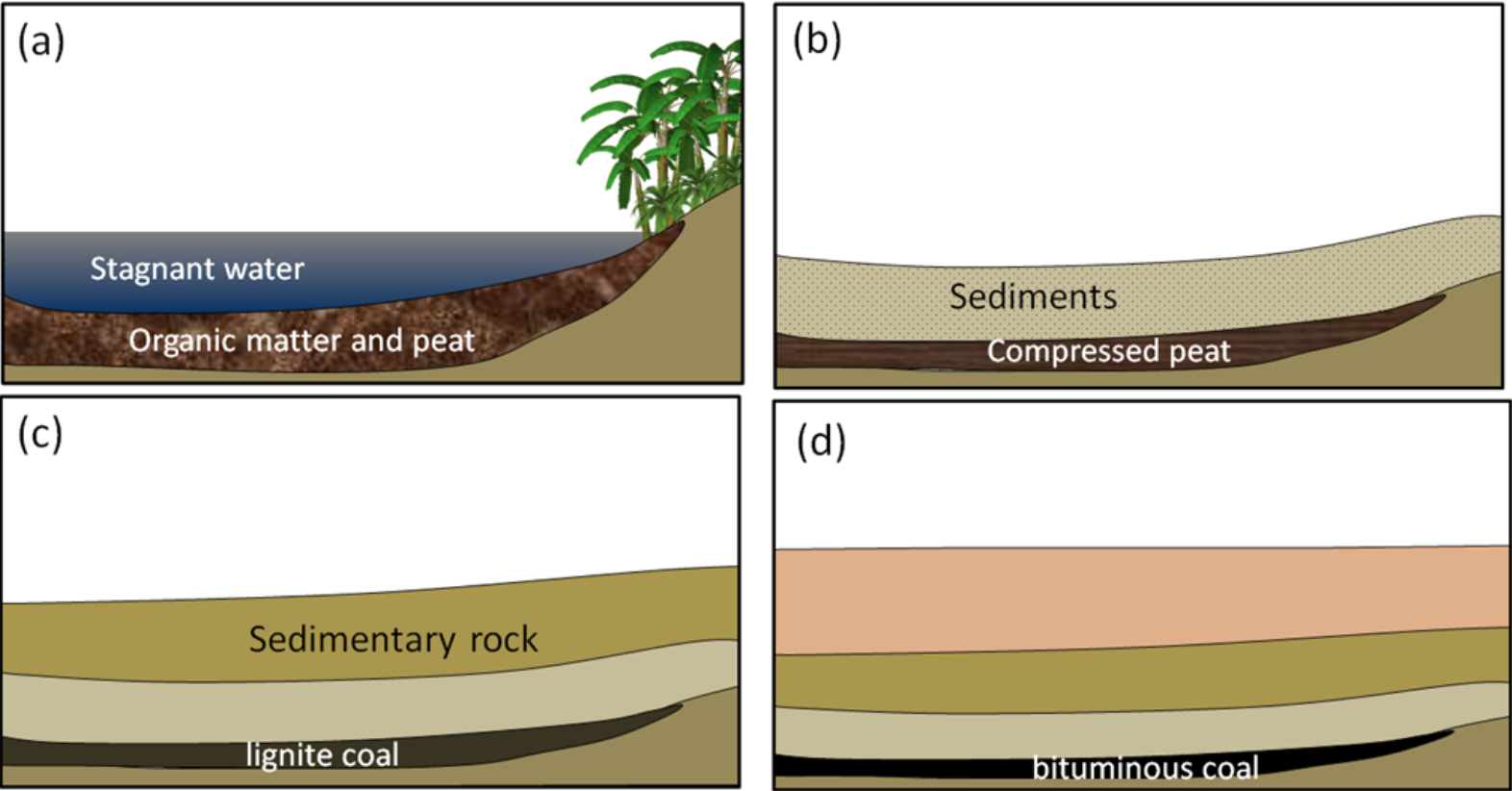
formation of natural gas (an all fossile fuels) — the 4 stages
peat: poo/dead stuff (organic matter) piles up @ bottom of lake, pond, river | wet
~ 1 million yrs later ~
lignite: after lots of yrs the organic matter is underground now —> water gets squeezed out, matter is packed together
~ 1 million yrs later ~
bituminous: u can now mine it, further underground, has high sulfur tho (lots of impurities) —> acid rain due to sulfur emissions
~ 1 million yrs later ~
anthracite: hardest, highest carbon, burn the best, cleaner
extraction of natural gas
hydrolic fractoring/fracking
force hydrochloric acid down
crack/shake/frack (causes earthquakes) — in the shale layer
shaking loosens the gass and the fluid takes it
pull gas and fluid out
seperate gas and fluid
bad stuff: liquid forced down finds its way into aquifer —> contaminates, & the fluid is made of over 560+ chemicals
what is natural gas used for
buses/transportation, heating, cooking, electricity
triple bottom line of natural gas extraction (enviromental)
extreme freshwater usage —> depleting aquifers
groundwater contamination w/ CH4 and fracking fluid
increased FF combustion bc of tractor trailers & diesel generators that pump fluid (800 gallons/day)
methan leaks during extraction
methane = strongest GG
burning CH4 emits ½ as much CO2 as burning coal
triple bottom line of natural gas extraction (money)
singing bonus for leasing land
costs of insurance/medical bills, loss of works/livlihood
low property values
triple bottom line of natural gas extraction (people)
health problems from injesting contaminiated water and inhaling fumes
loss of taste, smell, hair (ex. that cat in the vid), chronic headaches, neuropathy: dead nerves)
legislation: fracking is exempt from Clean Air/Water Acts
what other thing can we use as renewable energy
poo 💩
extraction of coal for electricity produciton
habitat loss
decreased biodiversity
increased FF for machinery and transport
unsafe for workers
processing of coal for electricity production
clean it —> crush it
creates waste products (coal slurry — liquid + coal dust)
power plant (coal) for electricity production
combustion
heat boils water —> steam
steam turns a turbine
excites electrons in generator (circular motion) —> electricity
power plant puts out CO2, SOx, NOx, PM, Hg (mercury)
mercury put out —> goes into ocean —> fish absorb it —> we eat it —> bad 👎
transmission (electricity production)
power grid - OLD (1950)
long distances ~ 2nd law of thermodynamics (the longer it is, the more energy/heat u lose)
33% efficient (33% of the coal is getting to ur house, the rest is lost as heat)
HEAT LOSS
heat, AC, lights (electricity production)
~10 cents kwh = 1lbs coal
SUBSIDIES make every step cheaper and cheaper
conservation of electricity
lessen use of ur thermostat
summer: 70°+, open windows
winter: 65°, heavy curtains help w heat retention
less light, turn off appliances/unplug when not in use
*support legislation to end FF subsidies
solutions for electricity use (heat)
biomass: burn firewood and trash
carbon neutral: no net increase of carbon, when u chop up/burn the tree, it releases the carbon it was storing — not making more
biogas: renewable, formation of methane
poo, waste, plant material
biodigester: capture methane (in a big bag the size of the classroom) —> use for cooking, heating, energy heat
on community lvl

solutions for electricity use (others)
multi-source (ex. solar panels)
localized-closer distance (increased efficieny)
what is uraniam and what is it mostly used for
uraniam = a metal we mine out of the ground —> used for nuclear fision
used mostly for electricity (rather than transportation)
leader in nuclear power
France (gets most of its power from nuclear power)
pros and cons of nuclear power
pros
normally (per every day) nothing goes into the air, water, or soil (no harmful emissions)
high yield energy***
reprocessing
cons
thermal pollution (from the warm water used to cool machinery)
spent fuel (nuclear fuel that has been used in a reactor)
terrorist attack target x NIMBY (fuel is sitting around and there’s fear of terrorist attacks, “not in my backyard” — put it somewhere else)
uranium is surface mined
describe the nuclear power process (include what is bad)
neutron collides w/ uranium atom —> splits the atom —> releases energy in the form of heat —> heat boils water —> steam turns a turbine —> generator is powered
^free neutrons used to continue the reaction
bad: fragments (waste) are radioactive (spontaneously releasing energy) —> health hazards (ex. cancer ~ thyroid, vomiting, diarrhea, development problems)
renewable resources: wind (causes, benefits)
caused by changes in atmospheric temp/pressure
convection cell (look at pic)
creates jobs (for maintanance/installation of wind turbines)
renewable resources: geothermal (how does it work, con)
taking advantage of the earth’s heat (heat comes interior comes from nuclear decay)
GHP (geothermal heat pump)
10-12 ft underground is a constant 55°F
you use that heat and bring it into buildings for heating/cooling (start at 55 instead of 0 and then go up)
uses LESS electricity
con: pricey bc of excavation ($20-25k)
renewable resources: tidal/wave (causes, how it’s used, con)
tides caused by gravitational pull of the sun/moon (2 high tides, 2 low tides)
wind causes waves
tidal barrage = most efficient, as tide goes in/out the turbine spins
can have a wind turbine at the top to make even more electricity
con: site specific bc you can only do it near coastlines
renewable resources: solar
PV (photovoltaic — production of electricity when exposed to sunlight)
nuclear fusion: helium joining, how the sun gets its power
very expensive — only stores electricity if it has a battery
net metering = $$
if you’re connected to the grid, you can sell your excess power to the power company (ex. in the summer, Tucker’s power goes to surrounding neighborhoods)
renewable resources: thermal
use sun’s heat to produce electricity
passive system: basic, no moving parts, just capture the sun’s rays (ex. greenhouse, solar oven)
active system: mechanical components (fans, pumps) to circulate heat-carrying fluids
aka concentrated solar energy/power: uses groups of mirrors to concentrate solar energy on a central collector (then makes steam —> turbine —> generator —> electricity)
con: takes up a lot of land/space, site specific (ex. desert area), steam turbines required for electricity —> water access/evaporation are concerns, also since they’re far away efficiency goes down (33% efficiency/2nd law of thermo concept)
most common source of energy in developed countries
coal
most common source of energy in developing countries
biomass (ex. they go outside and cut a tree)
most common renewable in developed countries
hydro
identify which country had the largest reserves for each resource: coal, petroluem, and natural gas
coal = US
petroluem = Saudi Arabia
natural gas = Russia
the following characterizes which renewable:
multi use of land
used offshore
rare earth magnets
fastest growing sector
wind
the following characterizes which renewable:
California obtains 60%
can be localized
low emissions
geothermal (on a divergent boundary)
which country is on a divergent boundary
iceland
US gets most of its oil from ____________ and ____________
canada and mexico