Fertilisers and Eutrophication
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is a fertiliser?
Anything that involves putting nutrients, such as nitrates and phosphates, into the soil for plant growth.
Why are fertilisers needed?
The nutrients the plants need are often lost from the sol when farmers harvest crops and remove livestock from fields. So they are replaced by farmers by artificial or natural fertilisation.
Name examples of natural fertiliser
Manure
Compost
Crop residue
Sewage
What are advantages and disadvantages of using natural fertiliser?
Advantages
Slow release of nutrients over time, so they are less likely to be washed away
They improve soil structure
Disadvantages
A lot is needed to have the same effect as the nutrient concentration is lower
The specific nutrients present varies and is difficult to control
Harder to apply to specific areas
Name examples of artificial fertiliser
Powders/pellets containing chemical compounds (e.g. ammonium nitrate)
What are advantages and disadvantages of using artificial fertiliser?
Advantages
The nutrients are in a high concentrated amount
Easy application to the soil
The nutrient content is known, so dosage can be controlled
Disadvantages
Nutrients are applied immediately and are highly soluble in water, so can leach out of the soil when it rains
It will not improve soil structure
What is leaching?
When water-soluble compounds in the soil are washed away often into nearby ponds and rivers which can lead to eutrophication.
Leaching is more likely to occur with chemical fertilisers as they’re relatively soluble and excess unused minerals are likely to leach into waterways especially if applied before heavy rainfall.
It is less likely to occur with natural fertilisers as they’re relatively soluble nitrogen and phosphorus are still contained in organic molecules that need to be decomposed before absorbed by plants. This means their release into soil is much more controlled.
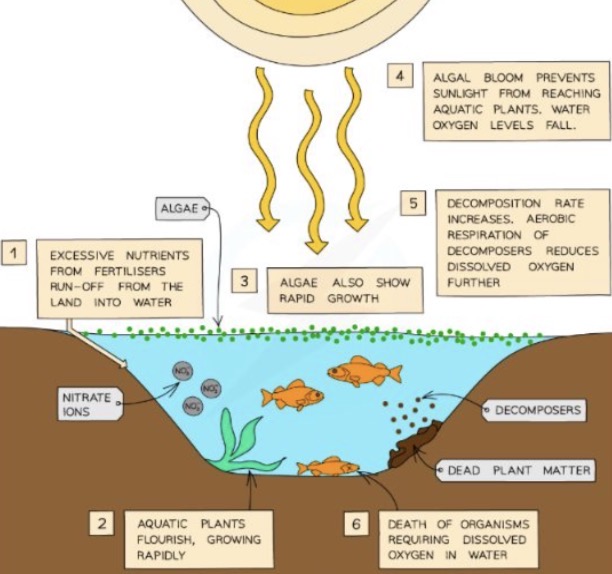
Describe the stages of eutrophication
Excessive nutrients in the soil from fertiliser use will runoff from the land and into the water of aquatic ecosystems, such as lakes (leaching).
Aquatic plants will grow rapidly due to the added nitrates in the water. Algae also sow rapidly due growth on the surface of the lake.
The algal bloom prevents sunlight from reaching the aquatic plants beneath.
Aquatic plants stop photosynthesising, and so dissolved oxygen levels in the lake decrease.
Aquatic plants die and the rate of decomposition increases.
As saprobiotic microorganisms respire aerobically, this causes the levels of dissolved oxygen in the lake to fall further.
This causes other aerobically respiring organisms, such as fish, to die from lack of dissolved oxygen in the water.