Bio-Molecules Terms
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Macromolecules
Large organic molecules made of monomer
Monomer
1 unit “building blocks”
Polymer
Multiple monomers chemically bonded.
Where is energy stored?
Chemical Bonds
Hydrolysis
Reaction that breaks apart a molecule and forms water. (Releases energy)
Dehydration Synthesis
Reaction that forms molecules with the removal of water. (Stores energy)
Organic Molecules
Must have both carbon and hydrogen atoms linked together. (Main Elements, C-H)
Inorganic Molecules
Doesn’t have carbon AND hydrogen atoms linked together. (O=C=O)
Carbohydrates - Nickname
Carbs or Sugars
Carbohydrates
Composed of elements arranged in 1 carbon, 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen (1:2:1 ratio)
Carbohydrates - Shape
Ring
Glucose
Main source of energy
Monosaccharide
One ring, Glucose (made in photosynthesis)
Disaccharide
2 monomers (Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose)
Polysaccharides
2 or more monosaccharides bonded together. (Ex. Starch, Cellulose, Chitin, Glycogen.
Building blocks of lipids
Glyceral & Fatty Acids
Lipids - Function
Long term energy source, makes up cell membranes, provide insulation.
What has twice as much energy and calories as carbs?
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
Codes for and produces proteins (DNA and RNA), the blueprint of life
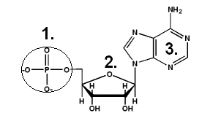
Nucleic Acid- Composition
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus (C, H, O, N, P)
Nucleic Acid- Structure
Phosphate group, 5-Carbon sugar, and a Nitrogenous base.
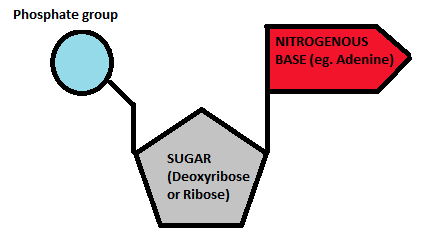
Which group is this building block for?
Nucleic Acids
What is used for long-term energy storage?
Lipids
What builds tissues like bone and muscle?
Proteins
What is a major part of cell membranes?
Lipids
What has a name that ends in "ose”?
Carbohydrates
What is are nucleic acids made of?
Nucleatide
What forms antibodies that help you fight disease?
Proteins
What has a ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, that is 1:2:1?
Carbohydrates
What includes enzymes that control reaction rates (is a catalyst)?
Proteins
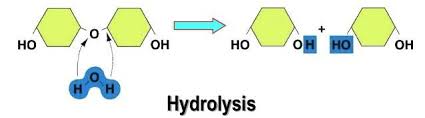
What process is this?
Hydrolysis

What process is this?
Dehydration Synthesis
What is made up of mostly of Carbon and Hydrogen, with some Oxygen?
Lipids
What has monosaccharides as its monomer?
Carbohydrates
What is Protein made up of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
What has the most energy per gram?
Lipids
What has an amino acid as its monomer?
Proteins
What stores genetic information?
Nucleic Acids
What is used as a source of quick and primary energy?
Carbohydrates
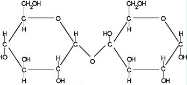
What type of organic compound is this?
Carbohydrate
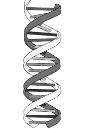
What would this be an example of?
Nucleic Acids
Which has starch, cellulose, and chitin as examples?
Nucleatide Which has starch, cellulose, and chitin as examples?
What has fatty acids as its monomer?
Lipids
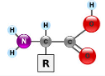
What has building blocks like this?
Proteins
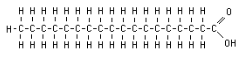
What organic compound is this?
Lipid
What has monomers made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base?
Nucleic Acids
What group do enzymes belong to?
Proteins
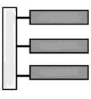
What building blocks like this?
Lipids
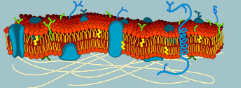
What macromolecules make up the majority of the cell membrane? (lollipop)
Lipids
A nucleotide consists of
Phosphate group, 5 carbon sugar group, and a nitrogen base
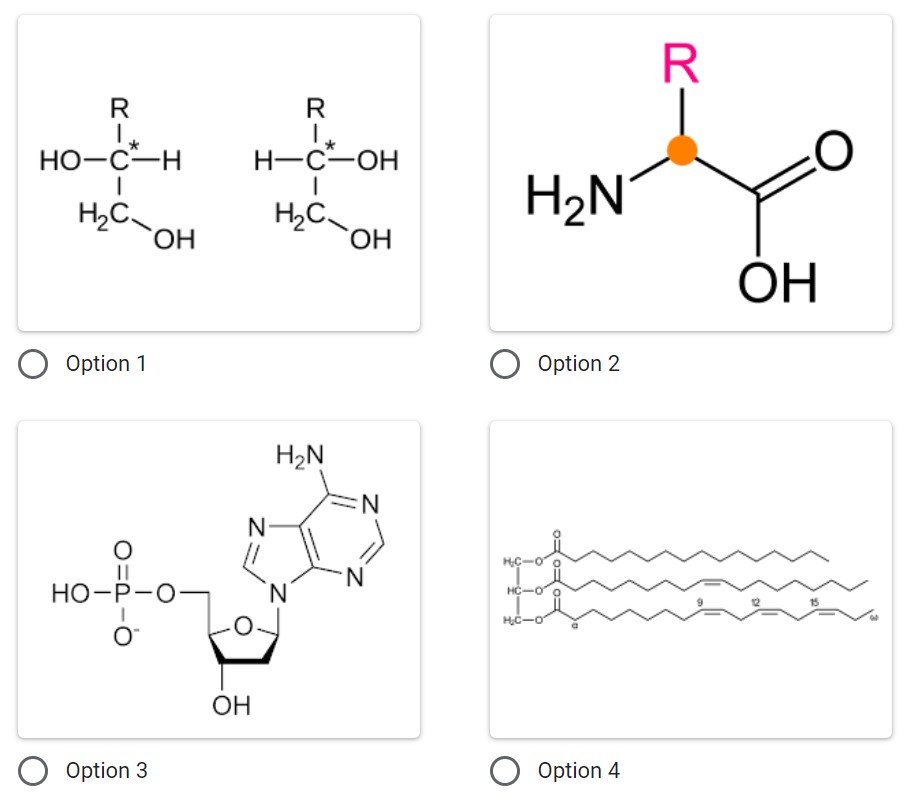
Which of the following represents a nucleotide which is the monomer for Nucleic Acids?
Option 3
How many amino acids exist for ALL living organisms? These are attached in different combinations to form proteins.
20
Protein monomers are linked together by what?
peptide bonds
All the functions of protein
Makes bone and muscle, transports things in/out cell, helps fight disease, and acts as a catalyst
Identify functions of carbohydrates
Quick source of energy for the cell
Structural compound making up cell parts like the cell wall.
How many simple sugar units in a monosaccharide?
1
Examples of Lipids
Waxes, Cholesterol, Oils, Steroids, Phospholipids, Triglycerides (Fats)
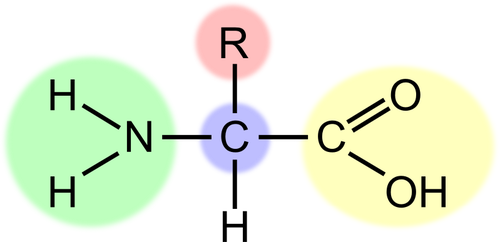
The part of an amino acid (protein) that varies from amino acid to acid is the
R group
Protein Structure
Amino Acid —> Poly Peptide Chain —> Protein
Changes in protein can cause
the protein to unfold and become non-functional
Catalyst
a substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction
Enzymes
Special proteins that are biological catalyst
Enzymes - Role
to lower the activation rate of biochemical reactions
Subtrates
the reactants that bind to the enzyme
Active Site
the specific location where a substrate binds to an enzyme
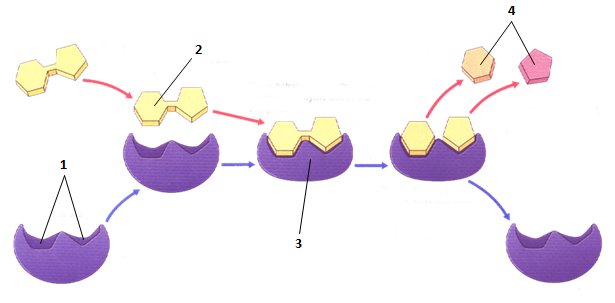
Label the diagram
1 - Active Site
2 - Substrate
3 - Enzyme Substrate Complex
4 - Product
Denature
changes shape of enzyme
What happens if an enzyme is denatured?
The enzyme cannot function, which could lead to organism death
What factors affect enzymes?
Temperature and pH
Changes in temperature and pH can cause
the denaturing of an enzyme
Enzymes are never
consumed or altered in a reaction
ends in “ase”
Enzyme
What is the enzyme for lactose
lactase
Enzymes can be
reused
Enzymes are very _________ and only bind with ___ _________
specific, 1 enzyme