Chapter 12 Conditioning, reinforcement, potentiation, and memory nd memory
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Engram
A neural pathway of what has been learned
Were Ashley’s cuts successful?
No, his failed attempts to sever the engram via lesions indicated that indicates conditioning and memory do not rely on a single cortical region
Lashley’s two principles about the nervous system
Equipotentiality: all parts of the cortex contribute equally to complex functioning behaviors (e.g., learning)
Mass action: the cortex works as a whole, and more cortex is better
Which brain area did Thompson discover learning occurs?
The lateral interpositus nucleus in the cerebellum, not the cortex as Lashley thought
What type of amnesia did patient HM have?
Mild retrograde amnesia and severe anterograde amnesia
Procedural memory, priming, and conditioning brain regions
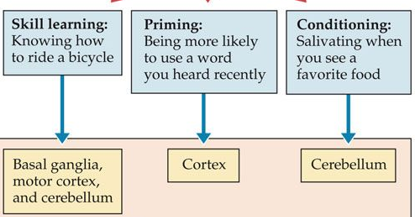
Did HM lose his implicit memory?
No, it was only his episodic memories that were largely lost, and semantic damaged, although less so
Did HM lose his STM?
No, his STM worked fine, but his LTM didn’t.
Radial maze

Place cells
hippocampal neurons that respond most strongly when an animal is in a particular place and headed in a particular direction

Time cells
hippocampal neurons that respond most strongly at a particular point within a sequence of times
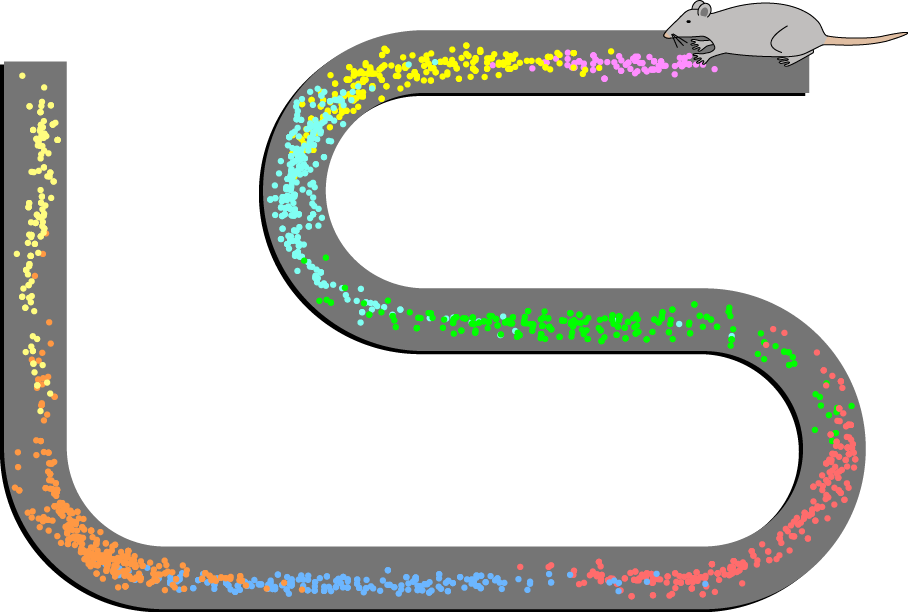
Where do place cells receive input?
Entorhinal cortex
Grid cells
entorhinal cortex cells that respond when an animal is in any of a number of places arranged in a hexagonal grid pattern
Place cells vs grid cells location
Place cells: hippocampus
Grid cells: entorhinal cortex
Hebbian Synapse
A synapse that increases in effectiveness because of simultaneous activity in the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
Three properties of long-term potentiation
Specificity
Cooperativity
Associativity