PLA OU Spring 2026 Exam Review
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of 105 vocabulary flashcards based on the lecture notes covering aviation regulations, required equipment, atmospheric conditions, and flight safety protocols.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Pilot Qualifications
Certificate, Medical, Government issued photo id, flight review, required endorsements, Recent flight experiences; 3 takeoffs and landings in the preceding 90 days. Night passengers → full-stop landings at night
Required Documents
Supplements, Placards, Airworthiness certificate, Registration, Radio operating license, Operating limitations, Weight and balance.
Airworthiness Certificate
Document verifying that an aircraft is safe to fly and must be visible to passengers and crew. Can be invalidated if aircraft is unworthy.
Registration Certificate
Document indicating the aircraft's owner and registration with the FAA. Expires every 7 years
Operating Limitations
Instructions found in the POH or placarded in the aircraft detailing performance constraints.
Weight and Balance
Serial number specific
Required Inspections
AV1ATES
ADs
Airworthiness Directives; mandatory maintenance actions required to address safety issues.
Emergency ADs
Airworthiness Directives requiring immediate action.
Non-Emergency ADs
Airworthiness Directives that should be addressed but can wait until the next scheduled maintenance.
Recurring ADs
Airworthiness Directives that need periodic checks.
Non-Recurring ADs
One-time fixes identified by an Airworthiness Directive.
Special Airworthiness Information Bulletin
Similar to an AD but not legally mandated for compliance. Posted by Piper. Precursor to AD
Instruments Required
91.205 ATOMATOFLAMES
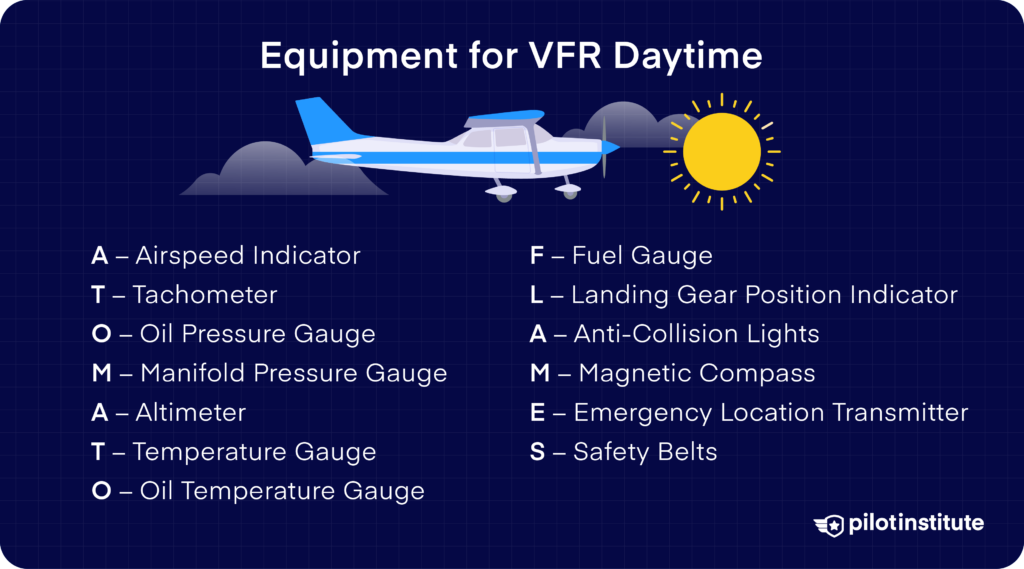
F.L.A.P.S. AT NIGHT
Fuses, Landing lights, Anti-collision lights, Position lights, Source of power.
Stable Atmosphere
Resists vertical motion. Stratus clouds
Unstable Atmosphere
Does not resist vertical motion. Characterized by cumulus clouds, showery precipitation, and turbulent conditions.
Cold Front
Triggers thunderstorms, high winds, and can also create good visibility.
Cumulus Phase
The initial stage of a thunderstorm marked by building clouds.
Mature Phase
The second stage of a thunderstorm when it reaches its highest intensity. Updrafts and downdrafts
Dissipating Phase
Final phase of a thunderstorm where the storm weakens. Microbursts
Types of Structural Ice
Rime, Clear, Mixed ice.
AIRMET
Advisories for GA pilots regarding weather conditions. Issued every 6 hours and valid for 6 hours.
Tango AIRMET
Indicates moderate turbulence and strong surface winds ≥ 30 kt, Low-level wind shear.
Zulu AIRMET
Indicates moderate icing and freezing levels.
Sierra AIRMET
Indicates mountain obstructions and IFR conditions.
Sigments
Hazardous weather to all aircraft. Issued any time conditions occur, valid for up to 4 (up to 6 for hurricanes). Issued for Severe or extreme turbulence, Severe icing, Widespread dust/sandstorms with visibility < 3 SM, Volcanic ash clouds
Convective Sigments
specifically address severe convective activity. issued hourly and valid for 2 hours. Severe thunderstorm due to:
Surface winds greater than or equal to 50 knots. Hail at the surface greater than or equal to ¾ inch in diameter. Tornadoes. Embedded or severe thunderstorms expected to persist for over 30 minutes. Lines of thunderstorms: At least 60 miles long, with storms affecting at least 40% of the Convective SIGMET area. Thunderstorms producing heavy or greater precipitation affecting 40 percent or more of an area at least 3,000 square miles.
Pressure Altitude
Altitude determined by setting the altimeter to 29.92 inches of mercury.
Indicated Airspeed
Speed shown by the aircraft's airspeed indicator.
True Airspeed
Indicated airspeed corrected for temperature and pressure.
Ground Speed
True airspeed adjusted for wind speed and direction.
True North
The direction along the earth's surface towards the North Pole.
Magnetic North
Direction that a magnetic compass points, slightly off-center from true north.
Density Altitude
Pressure altitude adjusted for nonstandard temperature.
Absolute Altitude
Height of an aircraft above the terrain.
True Altitude
Actual height above mean sea level (MSL).
Altitude Limitations
Limits defined for the performance and instrument readings in aviation.
Gyroscopic Instruments
Instruments that rely on gyroscopes including turn coordinators and attitude indicators.
Induced Drag
Drag resulting from the generation of lift.
Parasitic Drag
Drag due to the aircraft's shape and the airflow around it. Skin Friction drag, Interference drag, Form drag
V Speeds
Critical airspeeds for aircraft operations including Vso, Vs1, Vy, Vx, Vfe, Vo, Vno, Vne.
Maneuvering Speed (Vo)
Maximum speed for full deflection of controls without exceeding design load factors.
Spin Recovery Procedure
PARE: Power idle, Ailerons neutral, Rudder opposite, Elevator forward.
Load Factor Increase
Resulting in a higher stall speed due to increased wing loading.
Forward Center of Gravity Effects
Higher stall speed, slower cruise speed, and increased stability.
Rearward Center of Gravity Effects
Lower stall speed, higher cruise speed, and reduced stability.
Density Altitude Effects
Increased takeoff distance and reduced climb performance due to altitude changes.
Weather Cold Front Effects
Cumulus clouds, possible heavy rain and thunderstorms.
Weather Warm Front Effects
Stratus clouds, light showers.
TAF Publication Frequency
Terminal Aerodrome Forecasts published every 6 hours for 24-30 hour periods.
METAR Indicators
BR for mist, DZ for light drizzle, RA for rain, etc.
Flight Required Actions
NW KRAFT: NOTAMs, Weather, ATC delays, Runway lengths, Alternate routes, Fuel, Takeoff distances.
IM SAFE Checklist
Illness, Medication, Stress, Alcohol, Fatigue, Eating.
AV1ATE Inspection
Annual, VOR, 100 Hour, Altimeter, Transponder, ELT checks.
Performance Calculations
Required to ensure safe aircraft operations.
Altitude Rules for Cross-Country
Odd or even thousand feet based on the magnetic course. 360-179 is odd, 180-359 is even.
Magnetic Compass Errors
Variation- Difference between true north and magnetic north
Deviation- Compass error caused by magnetic fields in the aircraft
Magnetic Dip- Caused by the Earth’s magnetic field dipping toward the poles.
Oscillation- Erratic movement of the compass caused by turbulence or rough air.
Northerly Turning Errors (UNOS)- Undershoot North. Overshoot South
Acceleration Errors (ANDS)- On east or west headings, acceleration causes the compass to turn north, while deceleration causes it to turn south. Accelerate North, Decelerate South.
Angle of Attack
The angle between the wing's chord line and the direction of airflow (relative wind)
Risk management acronym
Pilot, Aircraft, Environment, External pressures.
Flight Stability Factors
Impact of center of gravity positioning on aircraft performance.
Turn Coordinator Operation
Uses precession to indicate direction of turn and rate.
High Pressure Systems Direction
Flow down and out, clockwise.
Low Pressure Systems Direction
Flow up and in, counterclockwise.
Squall Line Definition
Line of severe thunderstorms that can form along a cold front.
Im SAFE Definition
A self-check evaluating fitness to fly. Illness, medicine, stress, fatigue, alcohol, eating/emotions
VFR Visibility Requirements
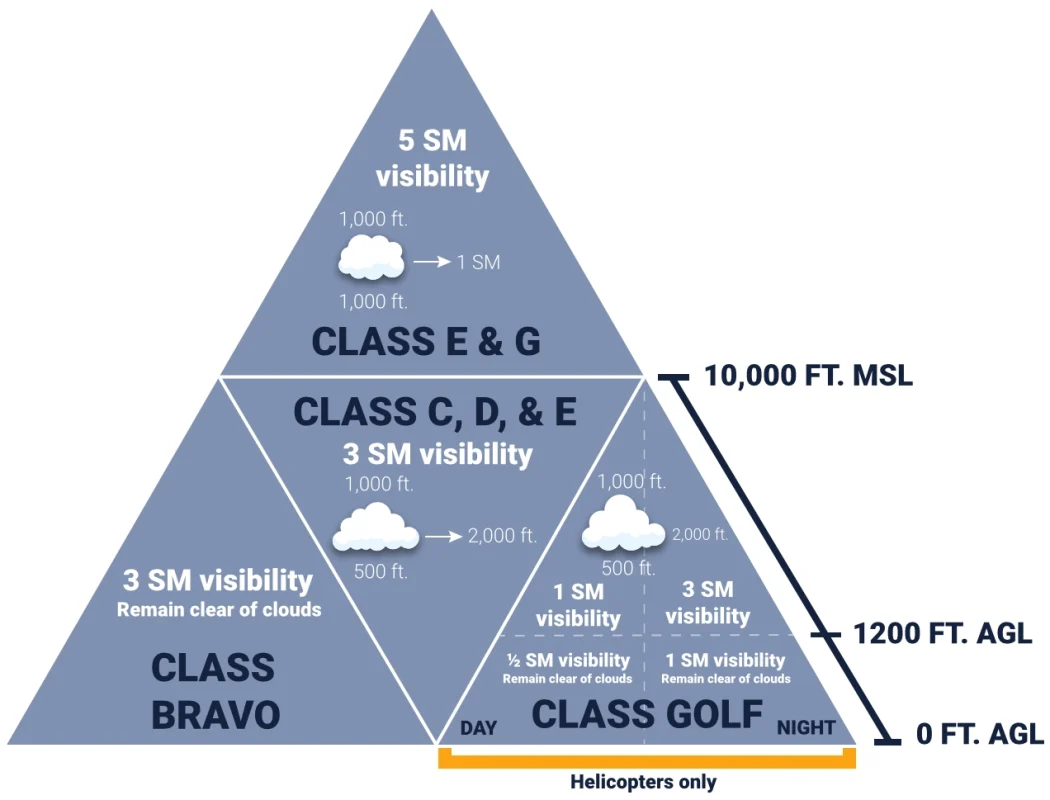
Class A Airspace
Only IFR flights; no VFR weather minimums.
Class B Airspace Requirements
ATC clearance and transponder with Mode C needed/ADSB- out, two way radio
Class C Airspace Requirements
Must establish two-way communications, mode C transponder and have ADSB-out
Class D Airspace requirements
two way radio
Takeoff and Landing Distance Calculations
Utilize charts in Pilot Operating Handbook.
Hypoxia Types
Hypoxic, Hypemic, Stagnant, Histotoxic.
Hypoxic Hypoxia
Not enough oxygen available to breathe
Cause: High altitude, inadequate cabin pressurization
Common scenario: Flying above ~10,000–12,000 ft without supplemental oxygen
Symptoms: Euphoria, headache, dizziness, poor judgment (dangerous combo in the cockpit)
Fix: Descend, use supplemental oxygen
Hypemic Hypoxia
Blood can’t carry enough oxygen
Cause: Carbon monoxide poisoning, anemia, blood loss
Aviation classic: CO from a cracked exhaust or heater
Symptoms: Headache, cherry-red lips (rare), fatigue, confusion
Fix: 100% oxygen, fresh air, land ASAP
Histotoxic Hypoxia
Cells can’t use the oxygen they have
Cause: Alcohol, drugs, cyanide poisoning
Big FAA tie-in: Alcohol consumption before flight
Symptoms: Impaired judgment, dizziness, poor coordination
Fix: Remove the toxin, oxygen (limited help), medical treatment
Stagnant Hypoxia
Oxygenated blood isn’t moving properly
Cause: Poor circulation, G-forces, shock
Aviation example: High-G maneuvers in aerobatics or fighters
Symptoms: Tunnel vision, grayout, blackout
Fix: Reduce Gs, proper anti-G straining, restore circulation
Types of Fog
Advection, Steam, Upslope, Radiation, Precipitation fog, Ice fog.
Advection fog
when a layer of warm, moist air moves over a cold surface (winds below 15kts and common in coastal areas with a sea breeze)
Steam Fog (Evaporation Fog)
occurs when cold, dry, air moves over warm water (common over bodies of water during the coldest times of year, resembles smoke, can produce icing)
Upslope Fog
occurs when moist, stable, air is forced up sloping land features like a mountain range (wind is required for formation and continued existence)
Radiation Fog
occurs when the ground cools rapidly due to terrestrial radiation and the surrounding air reaches its dewpoint (occurs on clear nights with relatively little to no wind and must be at least 20ft thick or it will be considered ground fog)
Ice Fog
when the ground cools rapidly and the surrounding air reaches its dewpoint when the temperature is much below freezing and the water vapor turns directly into ice crystals (usually 15°F or colder and mostly found in arctic regions)
Precipitation fog
As warm rain falls through cool air, the precipitation saturates the cool air. This fog is dense and long-lasting.
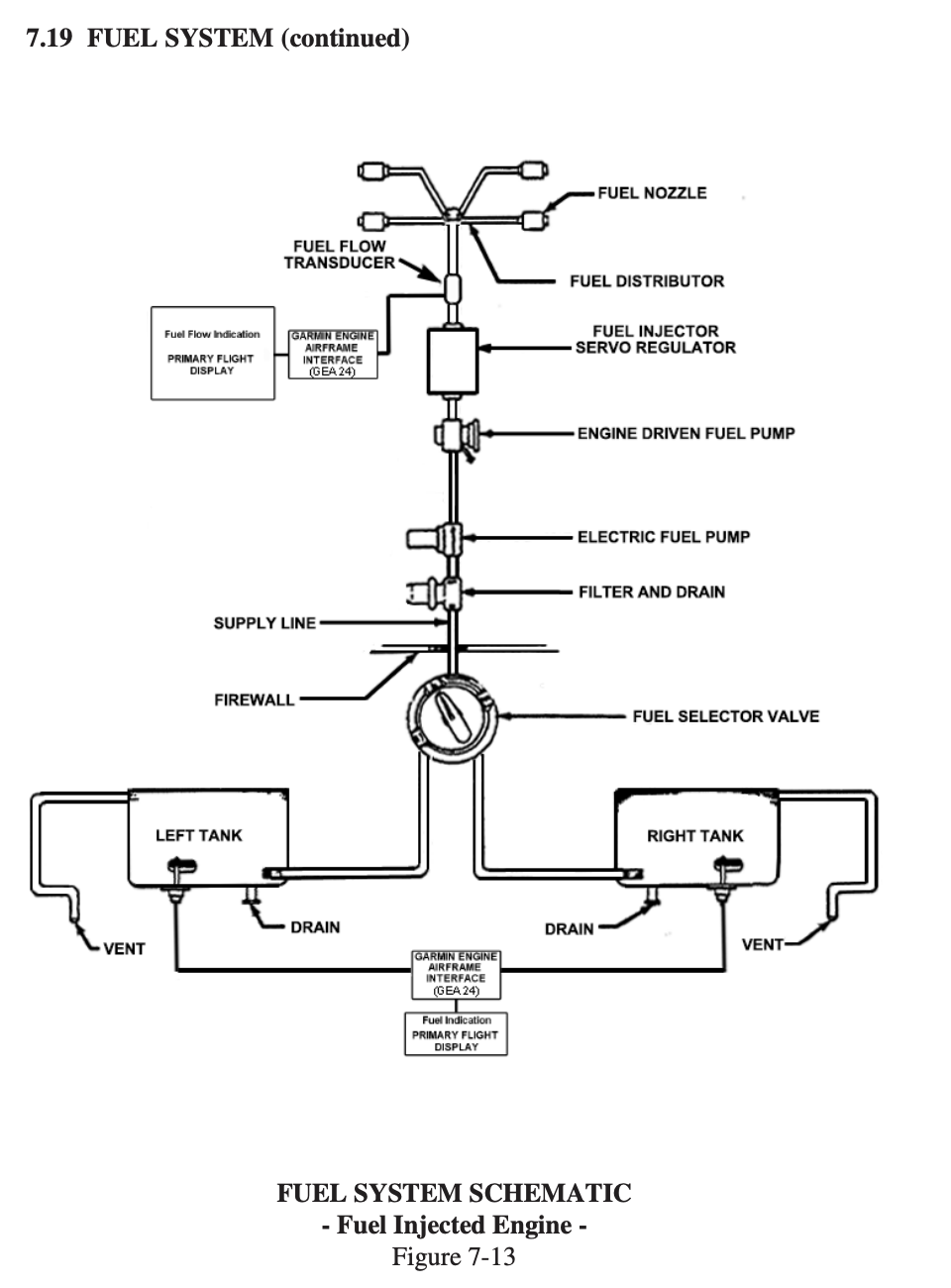
Fuel System
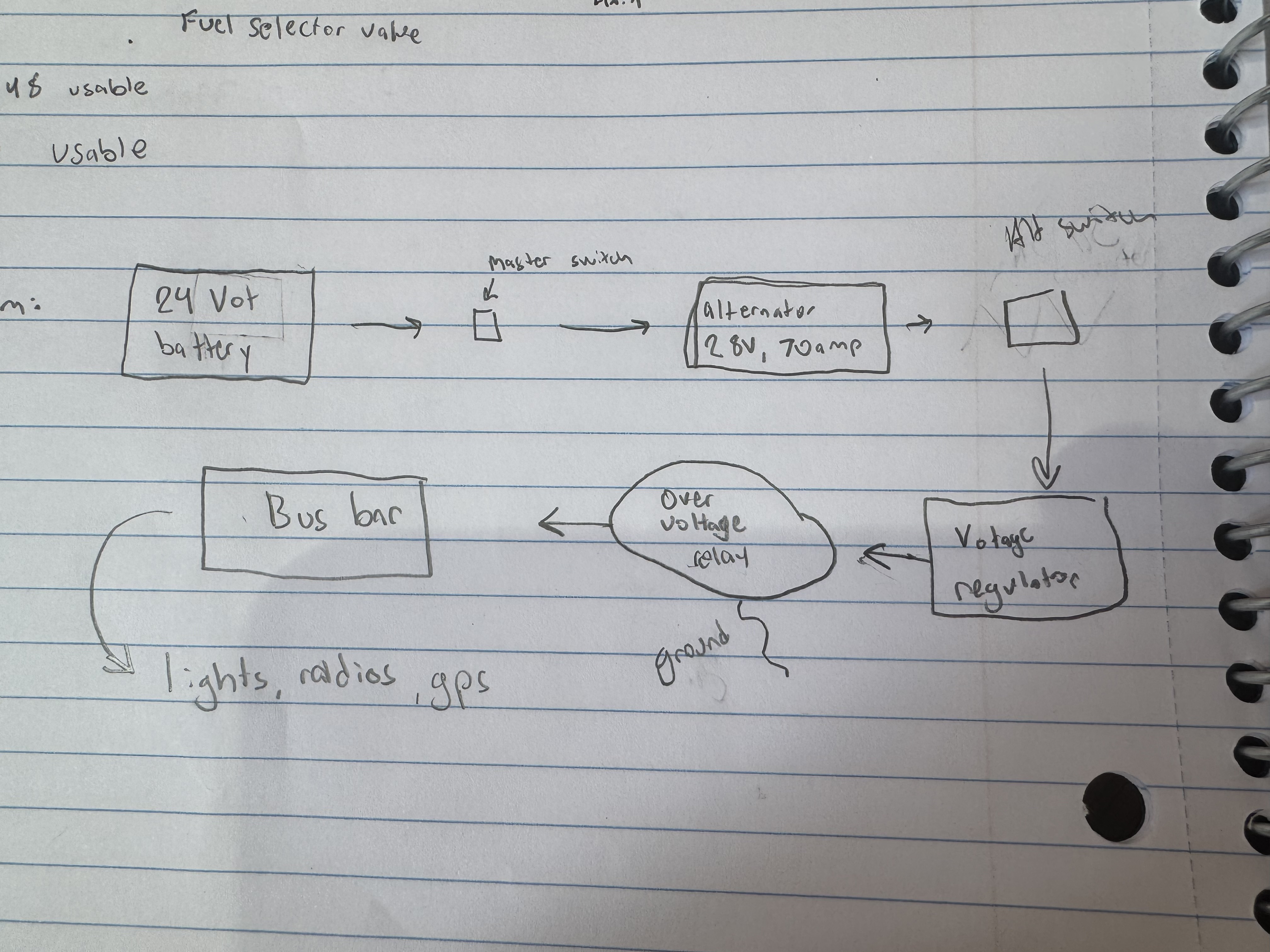
Electrical System
Special Use Airspace
MOA, Controlled firing, Prohibited, Restricted, Alert, Warning, National security
TFRs
Vip, Airshow, National disaster, Space launch, Sporting event
P-factor
The "bite" of the downward moving blade is greater than the "bite" of the upward moving blade. This moves the center of thrust to the right of the prop disc area, causing a yawing moment toward the left
Gyroscopic Precession
rigidity in space and precession. Precession causes a force applied to the propeller to only be felt 90 degrees from the location of where the force is being applied, in the direction of rotation. In other words, if a propeller experiences a force in the 12 o’clock position, and the propeller is spinning in a clockwise direction, the force will only be felt in the 3 o’clock position.
Torque
According to Newton’s third law that states “for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction,” the clockwise rotation of the aircraft’s propeller causes an opposite reaction in an anti-clockwise direction, which causes the aircraft to roll to the left during flight.
Spiraling Slipstream
The slipstream created behind the propeller of an aircraft is displaced into a corkscrew pattern, meaning the slipstream does not blow directly backward but “spirals”. This spiraling slipstream has the unintended consequence of striking (the technical term is “impinging”) the vertical stabilizer (i.e., rudder) on the left side, which creates subsequent yaw to the left.
Pitot Static System
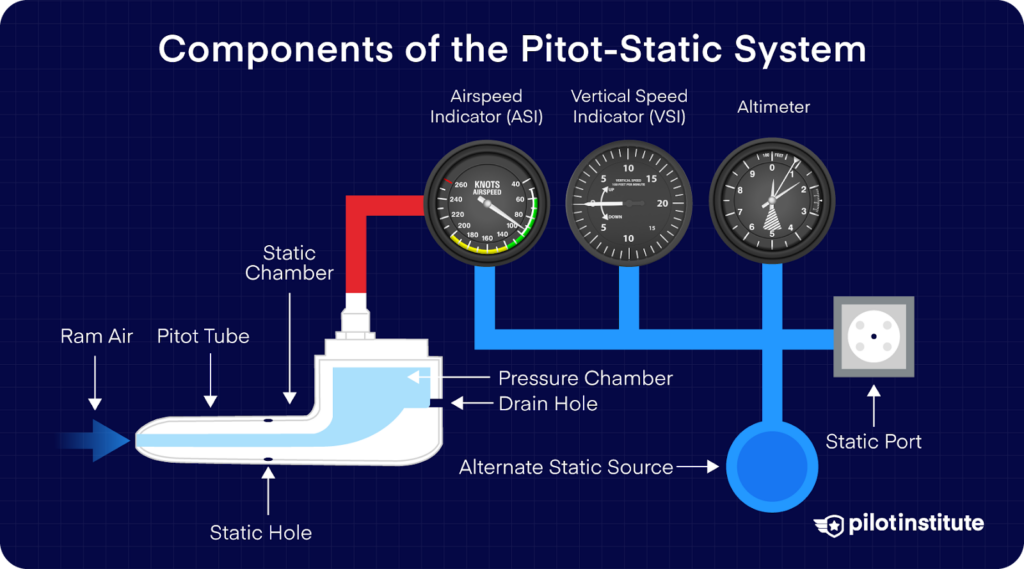
OU Weather Minimums
Solo Traffic Pattern: 1,500' ceiling 3 miles visibility
Solo Area Work: 2,500' ceiling 5 miles visibility
Solo X-C: 2,500' ceiling 10 miles visibility
Dual - All flights, except Instrument*: 1,000' ceiling 3 miles visibility
Wind - Solo: Maximum 25 knots (including gusts) Dual Maximum 35 knots (including gusts) Cross Wind no more than max demonstrated which is 17kts