nutrition + pain
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
There is no one definitive lab test to show malnutrition, BUT serum albumin levels are the….
Best indicators for overall nutrition status
an NPO order means…
nothing by mouth
Which diet order is this?
see-through liquids like water, pulp-free juices (apple, white grape), clear broths, gelatin, popsicles (no fruit bits), clear sodas (ginger ale, Sprite), tea/coffee (no milk/cream), and sports drinks, offering hydration and some energy before procedures or for digestive issues, while avoiding anything with pulp, milk, or red/purple coloring.
Clear liquids
which diet order is this?
foods that are liquid at room temperature or melt at body temperature, including dairy, strained soups, and smooth, blended items
Full liquid
Which diet order is this?
mashed potatoes with gravy, blended cream soups, scrambled eggs, yogurt, pureed meats, applesauce, and thickened liquids TYPICALLY FOR THOSE W/ DIFFICULTY SWALLOWING
dysphagia (pureed)
Which diet order is this? Who is this typically for?
(THOSE WHO have difficulty chewing or dental issues)
minced meat, scrambled eggs, mashed potatoes, ground meat with gravy, cooked soft vegetables, yogurt, and mashed bananas.
mechanical
Which diet order is this?
consuming 20-35 grams of fiber daily from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, and nuts to promote digestive health,
high fiber
Which diet order is this?
Fresh/frozen fruit and vegetables / grilled vegetables
Reasonable meat portions seasoned with no-salt seasoning.
Rice
Unsalted peanut butter
low-sodium
Which diet order is this?
high-fiber foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins to reduce LDL ("bad" fat) by limiting saturated/trans fats
low cholesterol
which diet order is this?
a healthy eating plan focused on controlling blood sugar by emphasizing nutrient-rich, low-fat foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting sugar, refined carbs, saturated/trans fats, and sodium
Diabetic
Which diet order is this?
a meal plan that strictly avoids gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and their derivatives,
Gluten free
Which diet order is this?
limits high-fiber foods and dairy to reduce the volume and frequency of stool, helping to rest the intestines
Low residue (low fiber)
A pt who is dysphagia what is a main concern for the nurse OTHER than aspiration?
aspiration pneumonia = getting food into lungs
A pt who has been NPO for more than 4-7 days what does the nurse give atp?
IV fluid nutrients
how are ENTERAL feedings done?
tubing straight into the GI system
what dies PARAENTERAL feedings consist of?
IV nutrients
What are the two types of nutrients given thru an IV? when both are combined, what is it called? *just the abbrev*
And how many times do you change this tubing?
parenteral nutrition and fat emulsions (TPN)
Every 24 hrs
if it’s a person’s fist time doing a tube feeding, WHAT are the appropiate steps for proper positions?
X-rays
What are three common responses to tube feeding?
What do you do if these two complications happen?
cramping, nasuea/vomiting
SLOW down the rate
If a patient starts aspiratiing during feeding what do you (as the nurse) do?
Stop the feeding
what is ONE very important thing we do NOT pt’s with dysphagia to NOT use?
a straw
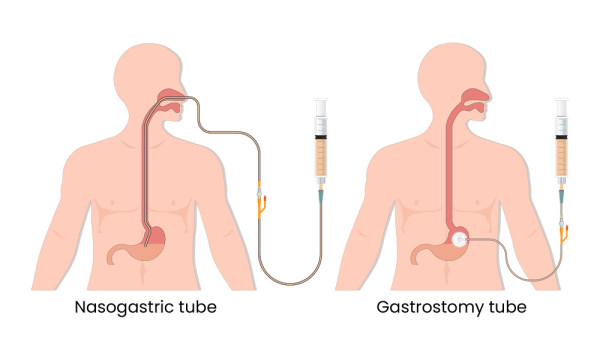
are nasogastric and nasojejunal tube feedings for permeant use or acute?
acute
Are gastric and jejunum tubings permanent use or acute?
permenant
in OLDCARTS, C stands for what? What does this mean? What is another term this can be called?
Character = describes HOW the pain FEELS (quality)
What is the Gate-Control Theroy?
THe gate which is the spinal cord is blocked by overstimulating/confusing nerve receptors
When a pt is physically depenedant on an opiod what does this mean?
the body built up a NEED the drug bc w/o = withdrawl symptoms
What does it mean when a pt is addicted?
psychologically the pt thinks they NEED the drugs
What happens when a patient has built up a tolerance?
typically need MORE of a dose for it to work
explain the statement: Over-sedation leads to respiratory depression?
TOO much pain meds decreases the function of the CNS, leading to shut down of lung function decreasing breathe rate
List all ENTERAL feeding methods?
nasogastric, Nasojejunal, Jejunum, & gastric
ONE complication from parenteral feedings can be manifested thru
increased urination
becoming lethargic
high blood sugar/glucose
increased thrist
What condition is this?
Hyperglycemia
Another complication from parenteral feedings manifest as Diaphoretic, shaky, Loss of Consciousness, confused… ALL mean what?
Hypoglycemia
How do nurses treat hyperglycemia & hypoglycemia of pt on paraenteral IV’s?
Give a dose of insulin AND slow down rate/ give dextrose