Chapter 24
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Digestive System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Digestive system contains
Alimentary canal
GI tract
Accessory organs
Alimentary canal
Tube from mouth to anus (technically inside of tube is “outside the body”!)
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract
stomach and intestines
Accessory organs include
Liver
Pancreas
Gallbladder
Alimentary Canal Tissue Layers (from deepest to most superficial)
Mucosa
Epithelial tissue layer
Lamina propria loose connective tissue
Muscularis mucosae – smooth muscle
Submucosa
Loose connective tissue with vessels and nerve
Muscularis externa
Smooth muscle for propulsion and mixing
Inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer
Serosa
Areolar tissue topped with simple squamous mesothelium
Nervous System of Alimentary Canal
Extensive nerves from the CNS
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
Is the nervous network to esophagus, stomach, intestines containing multiple parasympathetic nerve fibers
Two plexuses
What are the two plexus that the Enteric nervous system has?
Submucosal plexus
In submucosal layer
Myenteric plexus
Between muscles of muscularis externa
Circulation of the Alimentary Canal
Foregut
esophageal arteries
Celiac trunk
Midgut
superior mesenteric artery
Hindgut
inferior mesenteric artery
Hepatic portal system
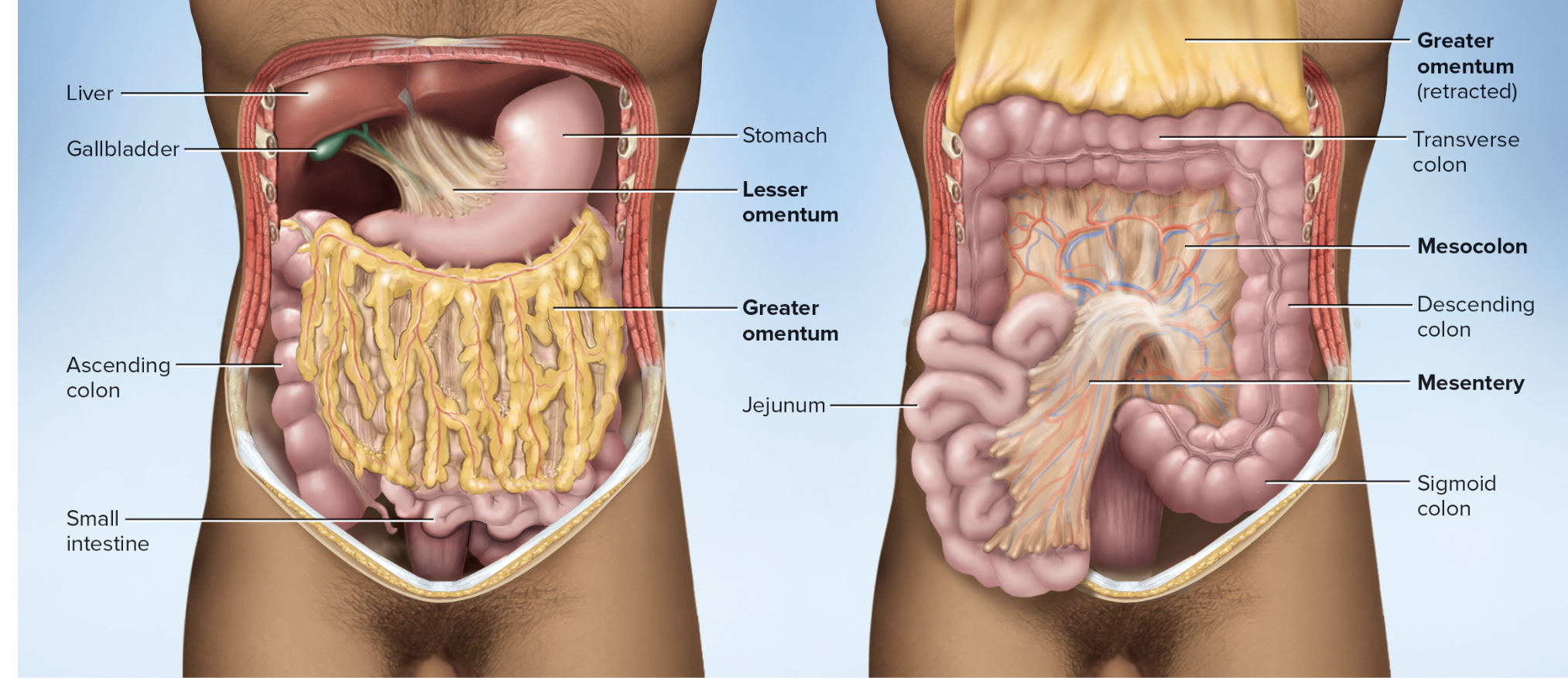
Peritoneum includes
Mesenteries
connective tissue sheets holding abdominal viscera in place
Posterior and anterior mesentery
Posterior and anterior mesentery
two-layered membranes that may hang freely or connect organs together or to abdominal wall
lesser omentum
greater omentum
Mesocolon
Lesser Omentum
Extends from lesser curvature of stomach to liver
Greater Omentum
Hangs down like an apron from stomach’s greater curvature
Mesocolon
Mesentery of the colon
Mesenteries locations
The mouth (Oral (buccal) cavity) includes
Cheeks and lips
Labial frenulum – median fold attaching lip to gum
Vestibule – space just inside lips and cheeks
Palate
Hard (bony)
Soft – includes uvula
The tongue includes
lingual papillae
body
anterior two-thirds
Root
posterior one-third
Lingual Frenulum
Lingual Frenulum
Attachment to floor of mouth
“Tongue-tied”
Contains both intrinsic and extrinsic muscles to mix food with saliva
Chemical and mechanical digestion
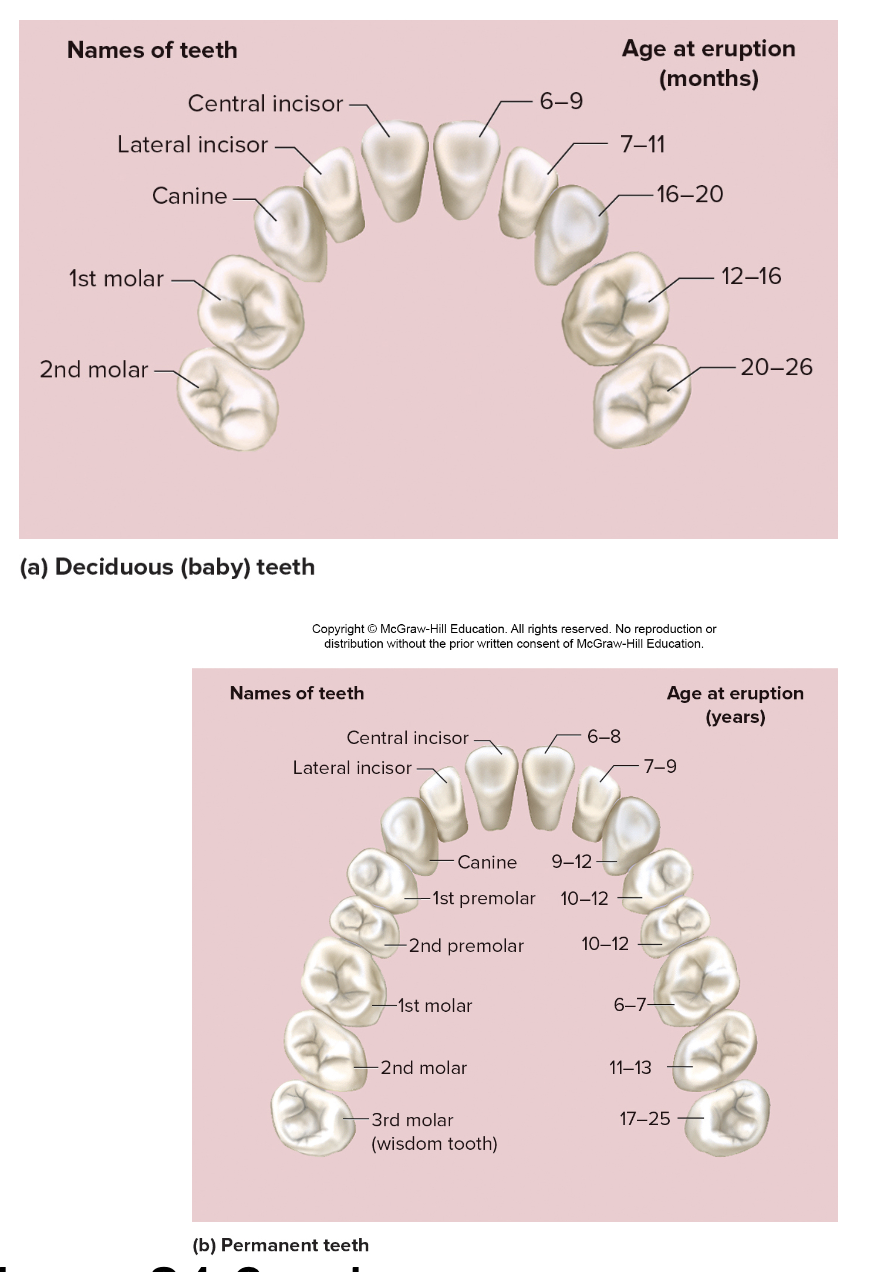
The teeth (dentition) includes
Mastication- chewing
Incisors- slicers (chisels)
Canines- Punctures and shred
Premolars and molars- crush and grind
20 deciduous vs 32 permanent teeth
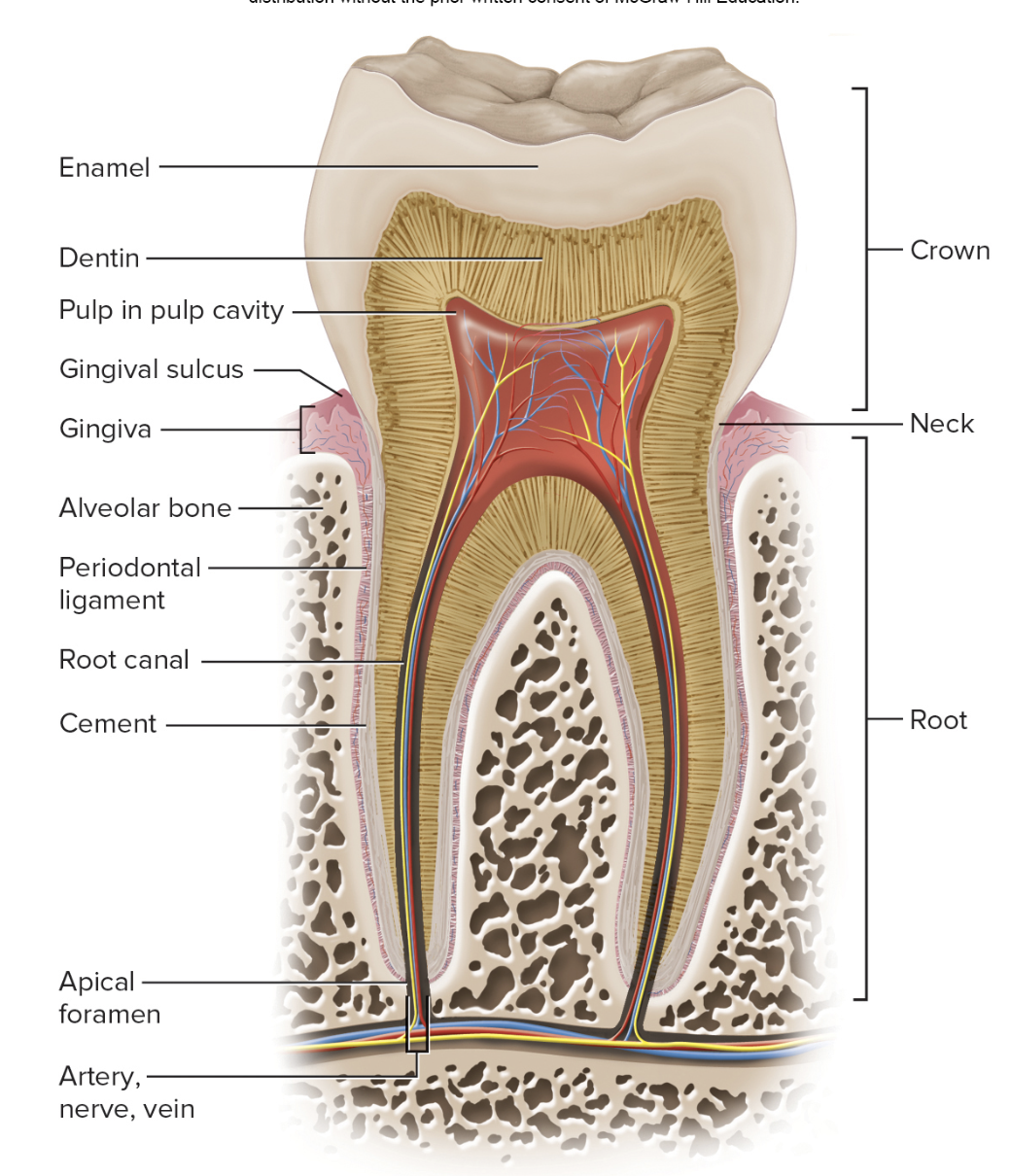
Tooth includes
crown, neck, root
Embedded in mandible or maxilla
Alveolus- socket
Periodontal ligament
cement of root
Gingiva- surrounds neck
Enamel covers crown
Internal structures
dentin
Pulp cavity, root canal
spaces for nerves and vessels
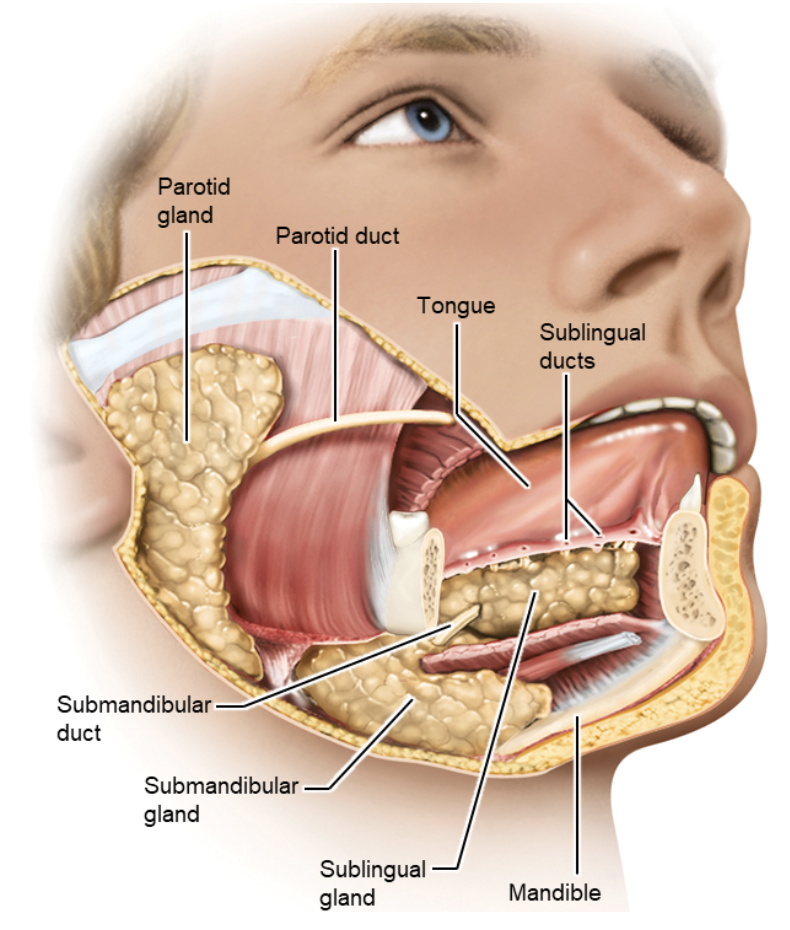
What are the main salivary glands, their locations, and opening?
Parotid – near ear
Duct opens at 2nd upper molar
Submandibular – under jaw
Duct opens at lower central incisors
Sublingual – under tongue
Several duct openings under tongue.
Pharynx
Oropharynx and Laryngopharynx pass food
Walls contain skeletal muscle that we control for swallowing
Esophagus
Esophagus is posterior to trachea
Starts behind larynx and ends at lower esophageal sphincter located at the cardiac orifice to stomach
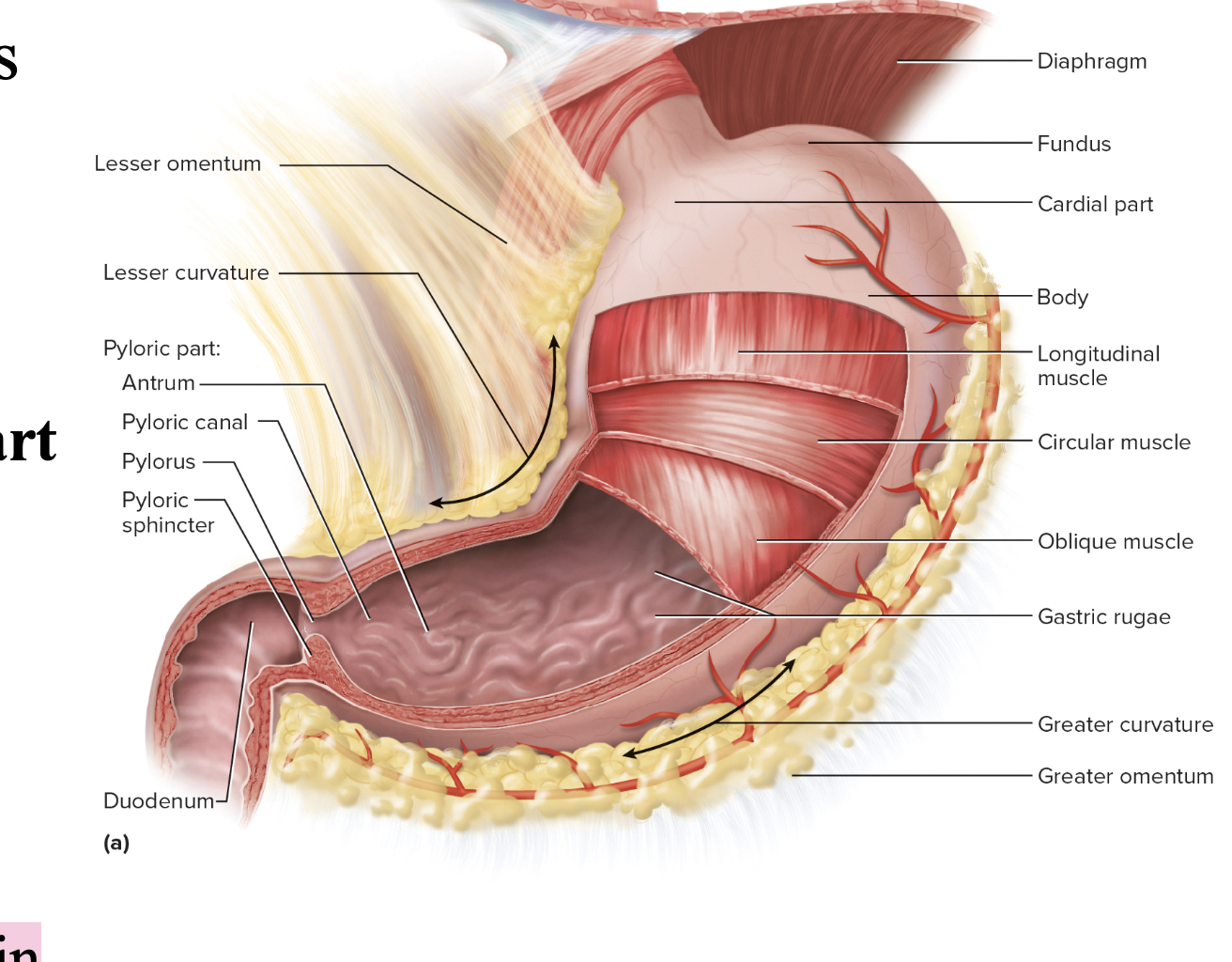
Stomachs anatomy External Anatomy “Gross Anatomy”
lesser curvature
greater curvature
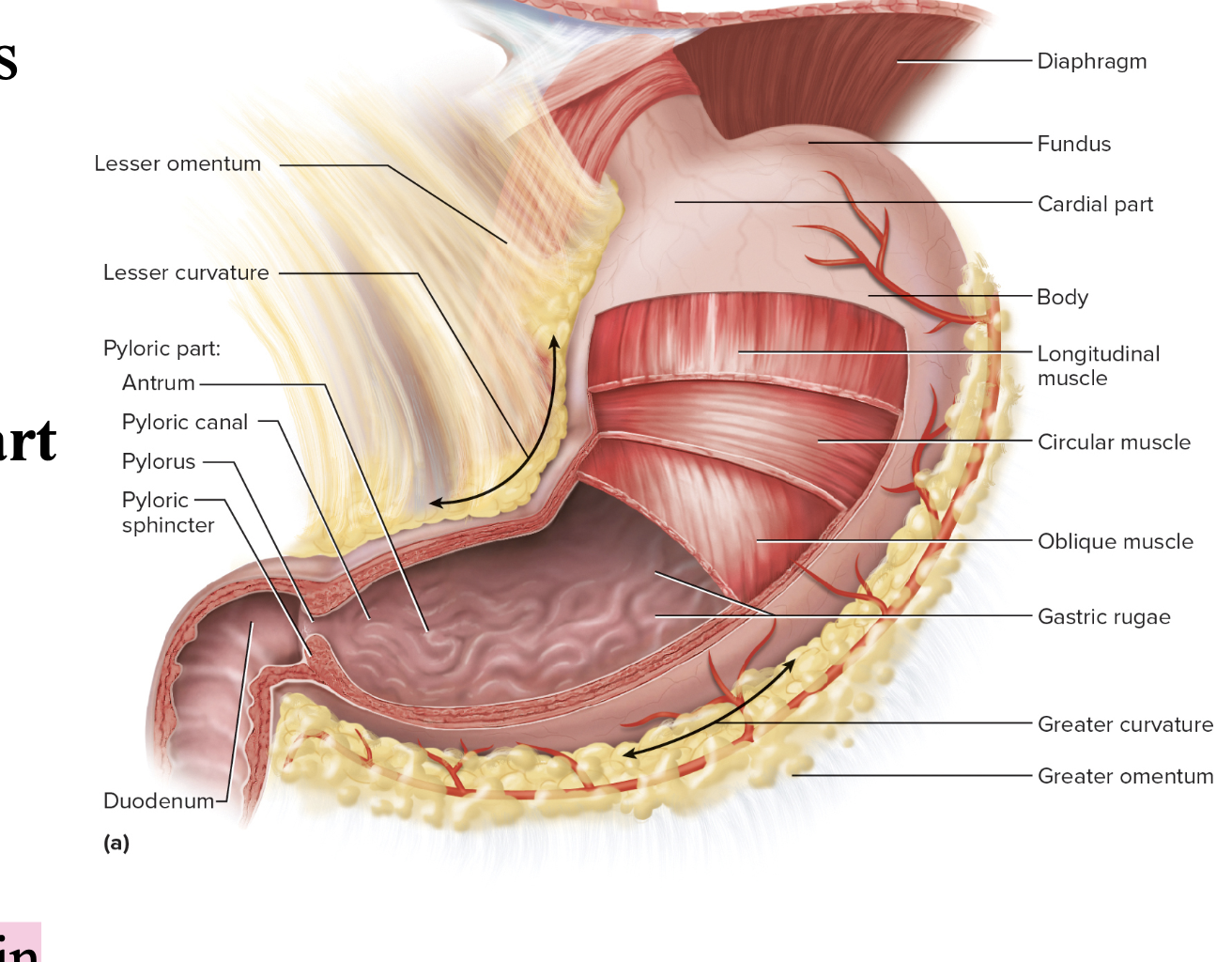
stomach “gross” anatomy divided into portions called
Cardiac/Cardial
Fundus
Body
Pylorus/Pyloric part contains the
Antrum
Pyloric canal
Pyloric sphincter

stomach “gross” anatomy of the gastric rugae
internally
Longitudinal folds in empty stomach
The Stomach: Microscopic Anatomy
Gastric pits of mucosa with glands/cells
Mucous cells
Regenerative (stem) cells
Parietal cells
Chief cells
Enteroendocrine cells
Mucous cells
secrete mucus that protects the stomach lining and aids in digestion.
Regenerative (stem) cells
make new cells for the gastric epithelium, replacing those lost through wear and tear.
Epithelial cells are frequently replaced (they
live only 3 to 6 days)
Chief cells
pepsinogen (enzyme that breaks down proteins)
Enteroendocrine cells
digestive hormones
Mucous coat
for protection
Is thick and highly alkaline (basic) to counteract the stomach acid
Tight junctions
between epithelial cells
Prevent seepage of acidic gastric juice
Small Intestine: Duodenum length and contains?
First 25 cm (10 in.) of SI
Contains circular folds (plicae circulares) to increase surface area for absorption
Small intestines: Duodenum function
Receives and mixes stomach contents, pancreatic juice, and bile
Major duodenal papilla for bile and pancreatic duct secretions
Minor duodenal papilla for accessory pancreatic duct secretions
Duodenojejunal flexure

Small Intestine: Jejunum location and function
Region of SI following the duodenum
Lies mostly within umbilical region
Most digestion and absorption occur here
Very prominent circular folds (plicae circulares)
Small Intestine: Ileum location, contains, an function
Location: Last portion of the SI, sparse circular folds
contains: lymphatic nodules called Peyer’s patches
Function: connects to the cecum of the large intestine
ileocecal junction
ileal papilla
small intestine microscopic anatomy includes
Intestinal Villi
Enterocytes
Goblet cells
Lacteals
Capillary bed
Intestinal crypts
goblet cells and enterocytes
paneth cells
Enterocytes
(absorptive cells) each have tiny microvilli projections to increase absorption
Goblet cells
secrete mucus
Lacteals
lymphatics for lipid absorption
Paneth cells
enteroendocrine cells in crypts
(Colon)-Cecum (pouch)
First part of the LI
Ileum attaches to cecum at the ileocecal valve
Contains the appendix – a blind tube that contains lymphatic tissue
The Large Intestine (Colon) CONTAINS
Ascending colon
transverse colon
left colic (Splenic) flexure
descending colon
sigmoid colon
Ascending colon location
On right side of body
The large intestines include the
colon, rectum, and anal canal.
Right colic (Hepatic) flexure location
Bend in LI between ascending and transverse colon
Transverse colon location
Runs right to left horizontally
Left colic (Splenic) flexure location
Bend in LI between transverse and descending colon
Descending colon location
On left side of body
Sigmoid colon location
Last portion
S-shaped
Other features of the large intestine (colon)
Taeniae Coli
(longitudinal m.)
Haustra/haustum (pouch/pouches)
Omental appendices (fat)
Diverticula/um
Rectum
Transverse rectal folds (valves) – holds and retains feces
Anal canal
~3 cm long
Anal columns – folds
Anal sinuses – depressions between folds
Internal (smooth m.) and external (skeletal m.) anal sphincters
Internal sphincter – involuntary
External sphincter - voluntary
Large Intestine: Microscopic Anatomy type of epithelium?
Epithelium is mostly simple columnar with many goblet cells
Exception: anal canal has stratified squamous
Large Intestine: Microscopic Anatomy contains
Has intestinal crypts but no villi or circular folds
Abundant lymphatic tissue
Mucosa specialized for fluid and electrolyte absorption
The Liver function
Body’s largest gland
Digestive function is bile production
Other functions:
Makes bilirubin – decomposition of hemoglobin
Urobilinogen
Metabolized bilirubin
Makes feces brown and urine yellow
The livers gross anatomy lobes?
right (largest), left, quadrate, and caudate
The livers gross anatomy ligament?
Falciform ligament – separates R. lobe from L. lobe
Round ligament- remnant of umbilical vein
The livers gross anatomy hepatis?
Porta hepatis – area between quadrate and caudate lobes
Contains hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, bile duct
The livers Hepatic lobules?
small cylinders with central vein with radiating plates of hepatocytes
hepatic sinusoids
stellate macrophages (Kupfer cells)
Bile canaliculi → bile ductules → right/left hepatic ducts
Hepatic sinusoids
leaky capillaries
Stellate macrophages (Kupfer cells)
clean blood running through sinusoids
Livers Circulation
Hepatic portal vein
hepatic artery
hepatic veins
Hepatic portal vein
Brings nutrient-rich blood from veins of GI tract to liver
Hepatic artery
Brings arterial blood
Aorta→ celiac trunk→ common hepatic a. → hepatic artery proper →hepatic a.
Hepatic veins
Exit from top of liver and empty into inferior vena cava
The Gallbladder location, function, and anatomy?
Location: Sac on underside of liver
Function: Stores and concentrates bile
Anatomy: Has fundus (head), cervix (neck)
Cystic duct – from gallbladder merges with common hepatic duct
Bile passages
Two hepatic ducts merge to form the common hepatic duct
Common hepatic duct merges with cystic duct to form bile duct
Bile duct merges with main pancreatic duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla at major duodenal papilla of the duodenum

The Pancreas location and function?
Function: Lies posterior to stomach
Head (near duodenum), body, and tail (near spleen)
Function:
Acinar cells (Exocrine) secrete pancreatic juice for digestion
Enzymes, zymogens (inactive precursors of enzymes), sodium bicarbonate (alkaline fluid), water, and electrolytes
Pancreas islets (Endocrine) secrete hormones
The pancreas Branching Ducts
Pancreatic duct merges with Bile duct to form hepatopancreatic ampulla at major duodenal papilla
Accessory pancreatic duct – opens at minor duodenal papilla
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix, with swelling, pain, and a threat of gangrene, perforation, and peritonitis.
Ascites
Accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity, often causing extreme distension of the abdomen. Most often caused by cirrhosis of the liver and frequently associated with alcoholism. The diseased liver "weeps" fluid into the abdomen.
Ulcerative colitis
Chronic inflammation resulting in ulceration of the large intestine, especially the sigmoid colon and rectum. Tends to be hereditary but exact causes are not well known.
Crohn’s disease
Inflammation of small and large intestines, similar to ulcerative colitis in symptoms and hereditary predisposition. Produces granular lesions and fibrosis of intestine; diarrhea; and lower abdominal pain.