brain and neuropsychology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the nervous system
a network of cells in the human body and is the main communication system
Name the 2 main jobs of the nervous system
To collect and respond to information in the environment
To control the working of different organs and cells in the body
What is the central nervous system (CNS) made up of and what does it do
Brain and spinal cord
Receiving, processing, and responding to sensory information
What does the peripheral nervous system (PNS) do
It supports the CNS, receiving messages from the CNS and sending messages to it using nerve cells
What does the autonomic nervous system (ANS) do
Co-ordinates involuntary actions like breathing, heart rate and digestion
What does the somatic nervous system (SNS) do
Controls the voluntary movement of our muscles, except reflex responses
What is the key function of the autonomic nervous system
Homeostasis, which is a process to make the body maintain a balanced state
What are the 2 divisions of the ANS and what do they do
Sympathetic division-represents a state of physiological arousal, preparing body for the fight or flight response
Parasympathetic division-counteracts the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by producing opposite effects, called the rest and digest response.
Name the 3 steps if the flight or flight response and what happens after
1. The brain detects threat
2. The release of adrenaline
3.The flight or flight response
After that, the parasympathetic division takes the body back to its regular state (rest and digest)
Outline the James- Lange theory of emotion (3 points)
1. An event activates the hypothalamus to instruct the sympathetic division of the ANS to release adrenaline
2. The brain then interprets these changes. The result of this is emotion
3. If there are no physiologic changes in the body, then no emotion is experienced
An advantage of the James-Lange theory of emotion
There are real life examples. Emotional states follow physiological arousal in cases like phobias or heart attacks.
A disadvantage of the James-Lange theory of emotion
Challenged by the Cannon-Bard theory. This theory argues that emotion and physiological arousal happen at the same time. For example, a person would blush at the same time that they feel embarrassed
What are neurones
They are nerve cells that send chemical and electrical signals to one another. They are the nervous system's main way of communicating.
What are the 3 types of neurones and what do they do
Sensory neurones- The carry messages from the PNS to the CNS
Relay neurones- They connect sensory neurones to motor neurones
Motor neurones- They carry messages from the CNS to effectors in our body
Structure of neurones
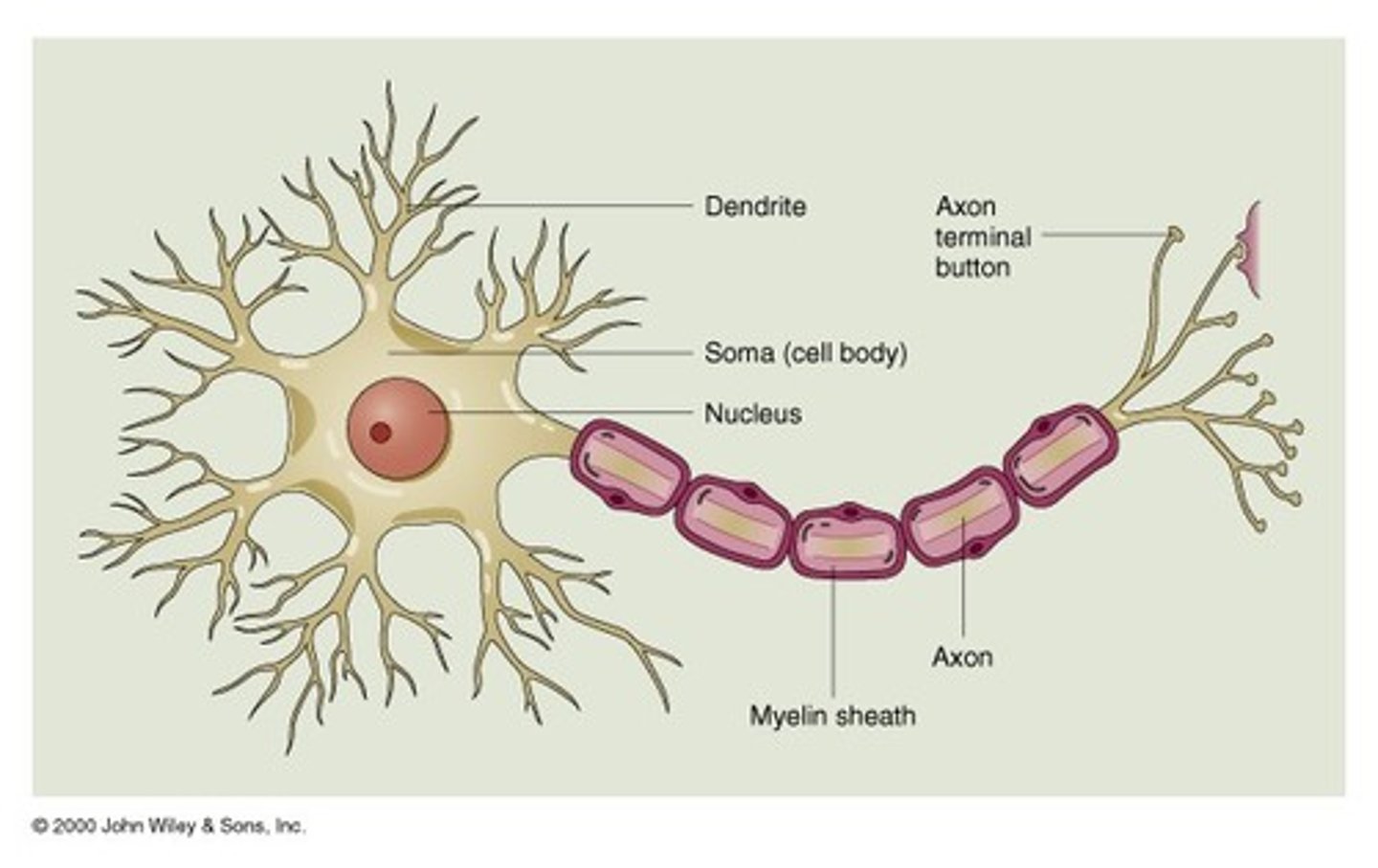
What does the cell body do
They include a nucleus and sticking out of them are dendrites which carry electrical signal away from neighboring neurons to the cell body
What does an axon do
Carry electrical signal away from the cell body and down the neuron. They are covered in a fatty layer called the myelin sheath
What does the myelin sheath do
Protects the axon and also speeds up the electrical signal. The sheath has gaps called nodes of Ranvier. These make the signal go even faster as it 'jumps' between each gap.
Explain how neurons communicate
They communicate via synaptic transmission. Each neurone is separated by a synapse. A synapse is made of space between neurones.
Signals within neurones are sent electronically, but signals between neurones are sent chemically
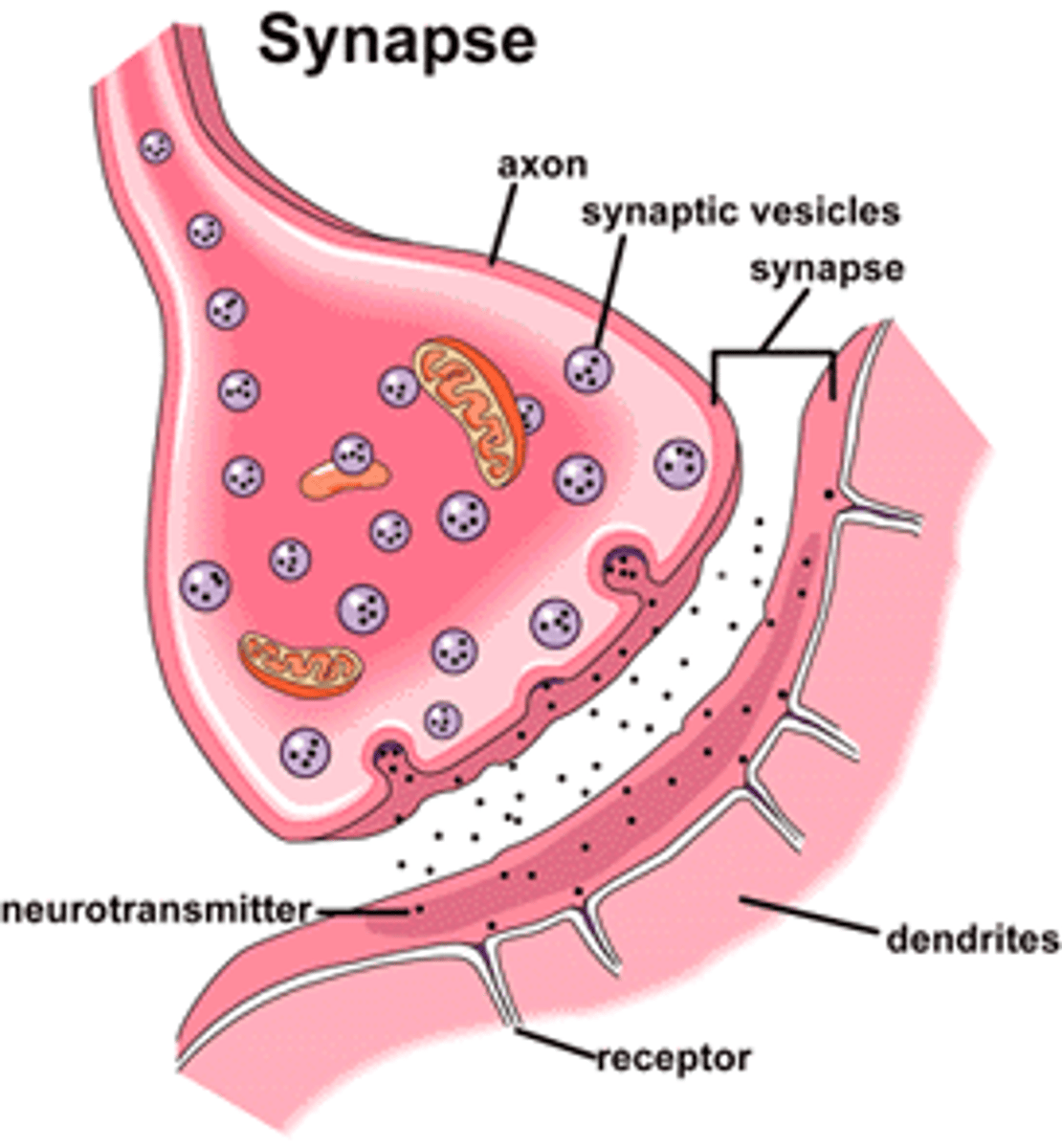
How are neurotransmitters released
When an electric signal reaches the end of a neuron ,it arrives at a terminal button where small sacs called vesicles which contain neurotransmitters release the neurotransmitter molecules. They then travel across the synaptic cleft
Reuptake of neurotransmitter
Once it crosses the synaptic cleft, it attaches to the next neuron at receptor sites which are located on the dendrites. Here the chemical message it turned back into an electrical signal
Excitation and Inhibition
Some neurotransmitters are excitatory, like adrenaline, increasing its likelihood to fire
Some are inhibitory, like serotonin, making it less likely to fire
Explain Hebb's theory (3 points)
1.The brain can adapt, change structure and make new connections as we learn at any time or age
2. Learning leaves a trace in the brain, known as an engram, which can be made permanent with practice
3. During learning, groups of neurones, known as cells assemblies fire together. The more this happens, the stronger the synaptic connections, making them more efficient
Advantage of Hebb's theory
It has a scientific basis. It explained the cognitive processes in terms of brain function, providing a scientific basis for understanding behaviour
Disadvantage of Hebb's theory
It is reductionist. It reduces learning to a neuronal level and learning is a complicated activity. A complete theory would have to include all factors of learning, including the biology
Brain diagram
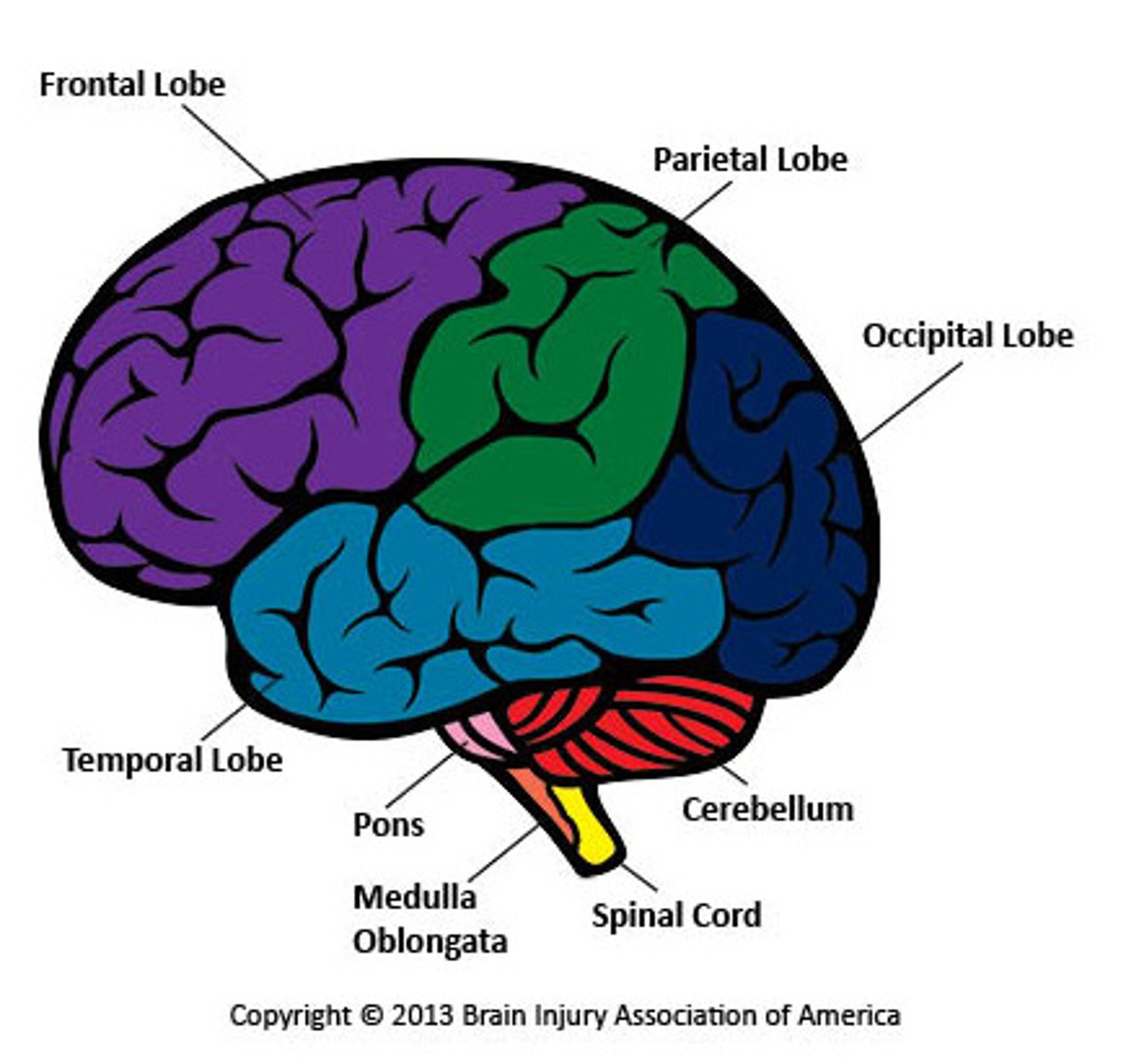
What does the motor area do and what would damage to it cause
Controls voluntary movement for opposite sides of the body. Damage to it would lead to problems on opposite sides of the body
What does the somatosensory area do and what would damage to it cause
Where sensory information from our skin is processed. Damage to it would make the person less able to feel things like pain and temperature
What is the function of the visual area and what would damage to it cause
Receives and processes visual information. Damage to it may cause blindness
What would damage to the auditory area cause
Partial or total hearing loss
What is the function of the Broca's area and what would damage to it cause
It controls speech production. Damage to it would cause difficulty to form and remember words. Known as aphasia
What is the function of the Wernicke's area and what would damage to it cause
Understanding language. Damage to it would cause difficulty understanding language and producing meaningful speech
What was the aim of Penfield's study?
To describe the responses patients gave when parts of their brain were electrically stimulated
What was the method used in Penfield's study?
Patients with epilepsy lay down on an operating table and were conscious. Penfield then stimulated different areas of the brain using the Montreal procedure and recorded their responses. Over 30 years, he studied over 1000 cases.
What were the results of Penfield's study?
If stimulation was applied to the visual area, then the patient reported seeing colours and shadows. When applied to the somatosensory area,it produced a tingling sensation or a false sense of movement.
What is the conclusion from Penfield's study
The area of the temporal lobe that he stimulated has a role in storing memories. They are stored in 2 ways: the facts of the experience and the meaning of the experience. This area is called the interpretive cortex
An advantage of Penfield's study
He used a precise method. The Montreal procedure not only treated epilepsy but also meant that Penfield could make investigations by stimulating parts of the brain
Disadvantage of Penfield's study
All of the people he studied were epileptic patients. The findings could have been different in people without epilepsy
What is cognitive psychology?
The study of the mental processes of the mind, like memory and perception
Where is the amygdala and what does it do
It is in the temporal lobe and plays a key role in processing emotions
The effects of a stroke
A stroke is when blood supply to a part of yuor brain is interrupted by blockage or bleed. Outcomes depend on what part of the brain is affected.
How does a CT scan work
It scans x-rays to produce 2D picture of "slice" through brain
An advantage of a CT scan
Can be useful for revealing abnormal structures within the brain.
Disadvantage of a CT scan
Require more radiation than regular X-rays. The more detailed the scan is, the more radiation is needed, meaning it cannot be used often
How does a PET scan work?
They work by measuring metabolic activity in the brain. A person is injected with a radiotracer, like glucose. When the substance is taken up by the brain, the areas with the most activity will absorb most of it
An advantage of a PET scan
They show localisation of function, for example if a person is solving a puzzle, the parts of the brain related can be identified.
Disadvantage of a PET scan
Sometimes the results are not easy to interpret, for example the same task may have different brain function for some people.
How do fMRI scans work
When a brain area is active, it uses more oxygen so blood oxygen is directed to the area. This is called the haemodynamic response. These can be picked up by radio signals which can produce 3D images on a computer screen
An advantage of an fMRI scan
It does not use radiation so it is very safe
Disadvantage of an fMRI scan (2 points)
It is very expensive
Only effective when the person is very still so difficult to use with children
What was the aim of Tulving's gold study
To see whether thinking about episodic memories produced different blood flow than thinking about semantic memories
What was the method of Tulving's study
6 volunteers (including Tulving & his wife) were injected with a gold radiotracer and placed into a PET machine. They then had to recall 4 episodic memories (about personal experiences), and 4 semantic memories (historical facts) in a randomised order. On a signal, the participant would think about the topic ands their brain's blood flow was monitored
What were the results of Tulving's study
There were clear differences for 3 of 6 participants
When the participants thought about semantic memories, there was more concentration of blood flow to the back of the brain whereas when it was episodic memory, there was more concentration of blood to the front of the brain
An advantage of Tulving's study
It produced scientific evidence. Sometimes in studies, participants will show demand characteristics but that it nearly impossible to show in this study, making it reliable.
Disadvantage of Tulving's study
The sample size was very small. There were only 6 participants, including Tulving and his wife and the pattern was only found in 3 participants, making the results inconclusive