Business
1/68
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Above the line promotion
This refers to the various forms of promotion, such as television and radio advertising, print advertising in newspapers and magazines, and so on, that are aimed at mass or large audiences. Above-the-line promotion is generally not targeted.
Below the line promotion
Below-the-line promotion refers to the various types of promotion that are focused on specific segments or groups and do not rely on mass promotion techniques, such as radio and television. Some below-the-line promotional techniques include fliers, banners, SMS, emails, pamphlets, sponsorships and in-store promotions.
Marketing
The management process of identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements in a profitable way. It is the art of determining the goods and services required to meet the needs and wants of customers in a sustainable way.
Needs and Wants and goods
Needs are essential to human survival (such as basic clothing, shelter, food, water, sanitation), whereas wants are not required but are desired to improve quality of life. Goods are tangible, physical items produced and sold to satisfy consumer needs and wants
Customer
Customer is somebody who always purchases the product,
Consumer
Consumer is the end user or someone who will actually use the product or service., almost like a target audience. However the consumer might not always purchase the product or service.
Product.
A product is an item offered for sale. Something that a company seeks to sell to satisfy customer needs and wants.
The product is the good or service being marketed to your target audience to fulfill their specific needs and desires.
Service
The action of helping or doing work for someone.
Profit
A financial gain, especially the difference between the amount earned and the amount spent in buying, operating, or producing something.Profit is the financial benefit after all expenses are deducted from revenue.
Market-orientation
Meaning that they ask questions and ask their the clients of the market because they focus
A business approach where companies focus on the market to form their products around.
Developing and promoting goods that meet the demands of its customers.
Product-orientation
A business approach where companies focus on their product and try to create the highest quality of product they can make.
Creativity
The ability to imagine and create a range of unique idea or concepts.
Sustainability.
Meeting the needs of the present without comprising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Business activity must ensure sustainabiltiy by balancing exological, social and exonmoic needs of people today and those of the future.
Deposit
A sum of money paid into a bank or building society account. A sum payable as a first instalment on the purchase of something
Deduction
Something that is or may e subtracted
Reduces the amount of a taxpayer's income that's subject to tax
Balance
Balance is the sum of all deposits minus the deductions or liabilities owed.
Total amount of money in a bank account.
Price
The amount of money required to purchase a good or service
Place
The location of where a product or service is sold
Promotion
Promotion is how you advertise your product or service and the distribution channels used to advertise to customers. Online advertising, posters, effective marketing campaign, tv commercials
Marketing Plan
A strategic guide that helps businesses map out their advertising and promotional strategies to attract prospective customers and connect with their intended audience
Marketing Strategy
A marketing strategy is a business's plan for reaching prospective consumers and turning them into customers.
A blueprint organizations create to get people interested in what they're selling.
Marketing Mix
A marketing mix includes multiple areas of focus as part of a marketing plan. It includes the and four Ps: product, price, placement, and promotion.
Marketing mix refers to a framework that uses the four Ps.
Each element is examined independently but often relies on each other. If one p changes it will often impact the other ps
Outlets
A point from which goods are sold or distributed
Advertising
Paid, non-personal communication aimed at promoting a product, service, or brand through mass media channels.
Promotion
A broader set of activities designed to stimulate immediate sales or interest in a product/service, often including discounts or incentives.
Social marketing
Social marketing is a well-planned, long-term strategy that uses marketing strategies to improve people's lives and the environment. Improves living quality. Marketing for the 'good'
Social media marketing
which is an advertisement that uses public networks such as youtube, facebook, instagram and othersuuuu that advertise there products. Although both are advertisements Social marketing is a non for profit advertisement that creates and influence or change in behaviour, while social medial marketing is used to promote a product.
Product life cycle
The product life cycle describes the different stages of a product
Extension strategy
Action of extending a life product when it is entering the maturity-declining stage of its product life cycle. Extension Strategies Price reductions Redesigning e.g. limited editions Repacking – new appearance New markets e.g overseas, new use Brand extension e.g. modified version of the product ‘Mini’ cars
Product life cycle
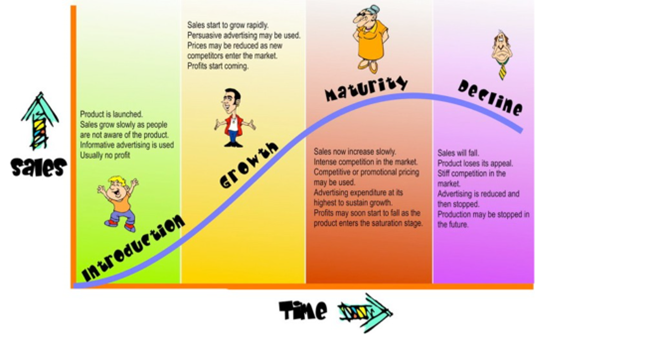
Introduction
- Low sales, high costs
- Little/no profit
- High promotional spending
Growth
- Rapid sales increase
- Competitors enter
- Profits rise
Maturity
- Sales peak
- Intense competition
- Price wars
Saturation
- Market fully covered
- Minimal growth
- High competition
Decline
- Sales drop
- Profit erosion
- Obsolescence
Focus Groups
A focus group is a qualitative research method where a small group of people (6–10 participants) discusses a product, service, or idea under the guidance of a moderator.
Boston Matrix
The Boston Matrix is a tool that can be used to calculate the relative market share of different products. It is typically used when a company wants to know how its products compare to those of its competitors.
Dog
Dying dogs Operating in an unattractive market with a low market share Come to the end of their useful phase, products that have failed in the market, or at the end of the decline phase. They don't go anywhere, and have no real potential. Not worth investing in because they use up more management time and resources than justified, so best strategy is to sell it or phase it out. 4. Question marks are in development, stars are in growth, cash cows are in maturity, dying dogs are in decline phase
Star
Stars High relative market share and high growth markets. These are the best in the market (market leader), but require high marketing spending to promote it and grow/maintain market growth so sometimes isn't as profitable as you would think. Often need to repel challenges from competitors, and create barriers to entry so it is harder for other competitors to enter and take more market share.
Cash-cow
Cash cows Have a high market share but are in a low growth Market. Not very exciting as they are in a low growth market (at maturity, and product/business is likely not going to grow as is also at maturity), however generates a great positive cashflow Defend the market share, reduce investment back into the business to maximize cash flow and profits, in order to invest these profits in high-potential questions markets and stars.
Question mark
Question marks Also operate in high growth markets but have a low market share. These have potential to be stars (or dogs) however are not as strong as other competitors Strategy is to be as successful as possible, using selective market segmentation and positioning to build a competitive advantage. Often have negative cash flows as they need high investments, most are not profitable
Product perception map

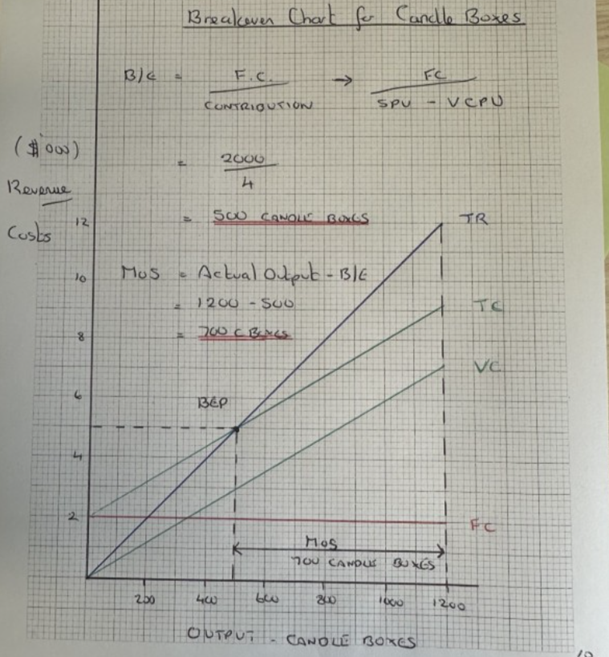
Costs
Total revenue = Selling price x units solds
Total costs = Fixed cost + Variable costs
Variable costs = cost per unit x units sold
Fixed costs = are costs such as rent
Profit = Total revenue - Total costs
Break even = Fixed cost/selling price per unit – variable costs
Margin of Safety = actual output – BeP
Competitor
A competitor is a business or brand that offers similar products or services in the same market, targeting the same customer base. Competitors vie for market share, customers, and profitability, often influencing pricing, innovation, and marketing strategies.
Competitor based pricing
Competitor-based pricing (or competitive pricing) is a strategy where a business sets its prices based on competitors' pricing rather than solely on costs or customer demand. The goal is to stay competitive in the market while maintaining profitability.
Cost plus
Cost-plus pricing (or markup pricing) is a straightforward pricing method where a business sets the selling price of a product by adding a fixed profit margin (%) to its total production cost. Key Formula: Selling Price = Total Cost + ( Markup % × Total Cost )
packaging
Protection, Imformation, Advertisement, convenient, unique
Creativity
The use of imagination and original ideas to develop unique and effective marketing strategies, products, or campaigns.
Producer, wholesaler,retailer,consumer
The creator or manufacturer of a product. Buys in bulk from producers and sells to retailers. Sells directly to consumers. The end user of the product.
Purpose of Packing
Protection against damage, spoilage, and pilferage. -Improves brand awareness/promotes brand - Attracts customers/stand out from other products - Showcase creativity
Location
The location needs to be convenient for customers to access the product/service
Primary market research
Involves gathering new data for a specific purpose, using methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups and observations.
Secondary Market Research
Involves the collection of second-hand data and information that already exists, previously gathered by others, such as media articles and government publications.
Sales forecasting
The process of predicting future sales based on historical data, market trends, and economic conditions. Helps businesses plan inventory, staffing, and budgets.
Methods: Qualitative (expert opinions) and quantitative (statistical models).
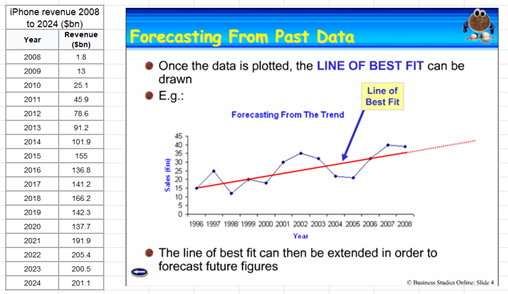
Extrapolation
A statistical method used to estimate future values by extending past trends. It assumes that historical patterns will continue.
Example: If a company’s sales grew by 5% annually for the past 5 years, extrapolation predicts a similar growth rate for the next year.
Sales forecasting
The process of predicting future sales based on historical data, market trends, and economic conditions. Helps businesses plan inventory, staffing, and budgets.
Methods: Qualitative (expert opinions) and quantitative (statistical models).
Internal source of finance
Internal sources of finance refer to funds generated from within a business, without relying on external parties. These include retained profits (reinvested earnings), sale of unused assets (equipment, property), owner’s savings, and reducing working capital (e.g., collecting receivables faster). Since these funds come from the business’s own operations or reserves, they do not create debt or dilute ownership. Internal financing is typically low-cost, flexible, and low-risk, making it ideal for small expansions or short-term needs. However, it may be limited by the company’s profitability or asset base.
External source of finance
External sources of finance involve obtaining funds from outside the business, such as bank loans, venture capital, issuing shares, or government grants. These funds are essential for large-scale growth, startups, or businesses lacking sufficient internal resources. Unlike internal financing, external sources often come with costs (interest, dividends) and conditions (collateral, loss of control). While they provide greater capital and faster access to funds, they also introduce risks like debt burdens or shareholder demands.
Hyper Market
A large retail store combining a supermarket (groceries) and department store (appliances, clothing) under one roof.
Example: Walmart, Carrefour.
Agent
A person/entity authorized to act on behalf of another (the principal) in business transactions.
Types: Real estate agents, sales agents, insurance agents.
Mass media
Communication channels that reach large audiences (TV, radio, newspapers, social media). Used for advertising, news, and public awareness.
Government Grants
Non-repayable funds provided by governments to support businesses, NGOs, or projects (e.g., renewable energy initiatives).
Government Incentives
Benefits (tax breaks, subsidies, low-interest loans) offered to encourage specific business activities (e.g., R&D, job creation).
Government Bonds
Debt securities issued by governments to raise funds. Investors lend money in exchange for periodic interest payments and return of principal at maturity.
Example: U.S. Treasury Bonds.
Comparison BTL and ATL
Above the Line (ATL) Promotion offers the advantage of mass reach, making it highly effective for building brand awareness and credibility quickly through channels like TV, radio, and billboards. However, its broad targeting often leads to high costs and inefficient spending, as it reaches many non-relevant audiences, and its impact on direct sales is difficult to measure.
Below the Line (BTL) Promotion excels in cost efficiency and precise audience targeting, using methods like social media ads and email campaigns to drive measurable, short-term results. Yet, its limited reach makes it less effective for large-scale brand awareness, and some tactics risk appearing intrusive if overused. Combining both strategies often yields the best balance of visibility and engagement.
Comparison Internal and External sources of finance
Advantages: Internal financing, such as retained profits or asset sales, offers significant benefits, including no repayment obligations (avoiding debt), no loss of ownership or control, and lower costs since no interest or dividends are required. It also provides greater flexibility as businesses aren’t bound by lender or investor conditions. Additionally, relying on internal funds can improve financial discipline by encouraging efficient resource management.
Disadvantages: However, internal financing has limitations, primarily its limited availability, as it depends on the company’s profitability or asset base. Large-scale expansions may be difficult without external support. Using retained profits can also reduce shareholder dividends, potentially disappointing investors. Selling assets might weaken operational capacity, and excessive cost-cutting (e.g., delaying payments to suppliers) could harm business relationships.
Advantages: External financing, such as bank loans, venture capital, or issuing shares, provides access to larger funds, enabling rapid growth, major investments, or market entry. It allows businesses to leverage others’ capital without depleting internal reserves. Some forms, like government grants, offer non-repayable funds, while equity financing (e.g., selling shares) avoids debt burdens. Venture capitalists may also provide valuable expertise and networking opportunities.
Disadvantages: The downsides include high costs (interest, fees, or profit-sharing), loss of control (if equity is sold), and strict eligibility requirements (collateral, credit checks). Debt financing increases financial risk, as missed payments can lead to bankruptcy, while equity financing dilutes ownership. External funding often comes with legal or contractual obligations, restricting business flexibility. Additionally, securing external capital can be time-consuming, with no guaranteed approval.
Capital
Refers to the financial resources or assets that a business or individual uses to generate income, fund operations, and invest in growth. It can come in different forms, including money, machinery, buildings, and even intellectual property.
Consumer Buying Process
Problem Recognition – The consumer identifies a need or problem.
Information Search – The consumer gathers information about potential solutions.
Evaluation of Alternatives – The consumer compares different options.
Purchase Decision – The consumer selects a product and makes the purchase.
Post-Purchase Evaluation – The consumer assesses whether they are satisfied with the purchase.
Advertisement vs promotion
Advertisement and promotion are both essential marketing strategies used to attract customers and increase sales. However, there are some key differences between the two. Advertisement is a paid form of communication that is typically used to reach a large audience through various channels such as television, radio, print, and online platforms. On the other hand, promotion refers to the activities and tactics used to promote a product or service, such as discounts, giveaways, contests, and special events. While advertisements focus on creating brand awareness and generating interest, promotions are more focused on driving immediate sales and creating a sense of urgency among consumers. Ultimately, both advertisement and promotion play a crucial role in the overall marketing mix of a business.