Schema (A3.2 Database design)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Schema
Architecture showing how data is organized and how relationship between data is managed = logical view of database
I. Types
Types of schema
Conceptual schema (I)
Describes structure w/o considering how physically implemented
High-level representation defining structure and organization
Defines: entities, attributes, relationships
Abstract model that hides details (implementation of data structures, physical storage)
Most vague
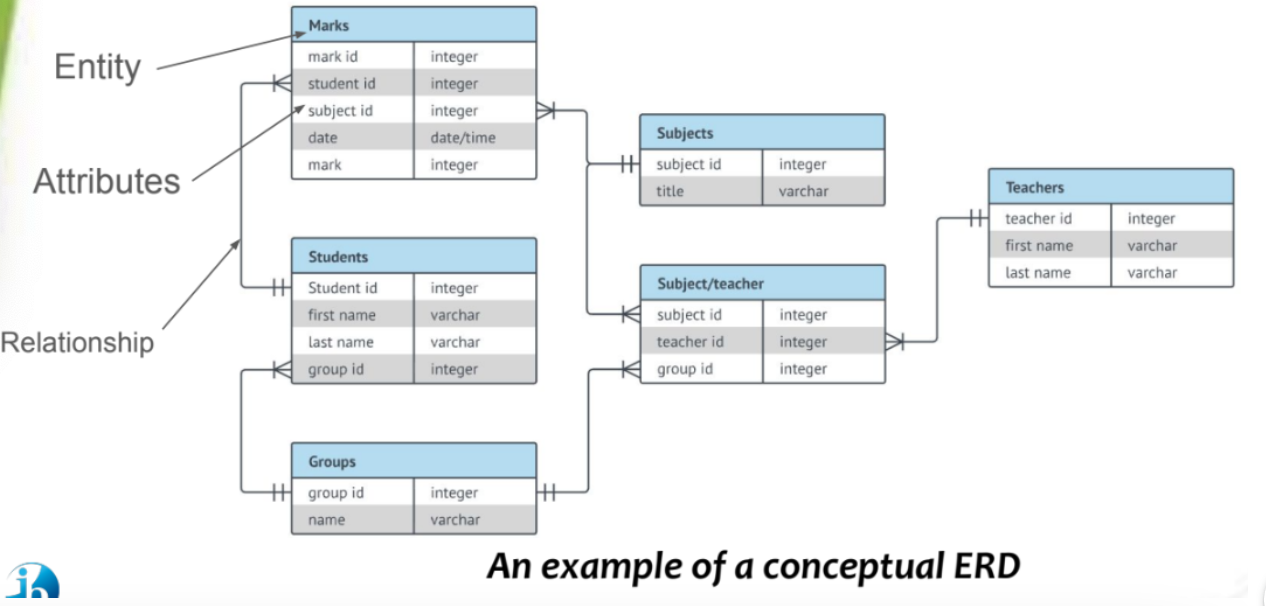
Logical schema (I)
Design of structures of table (field, datatypes) and relationships
Defines structure, attributes, fields, data types etc
Doesn’t consider requirement of specific DBMS

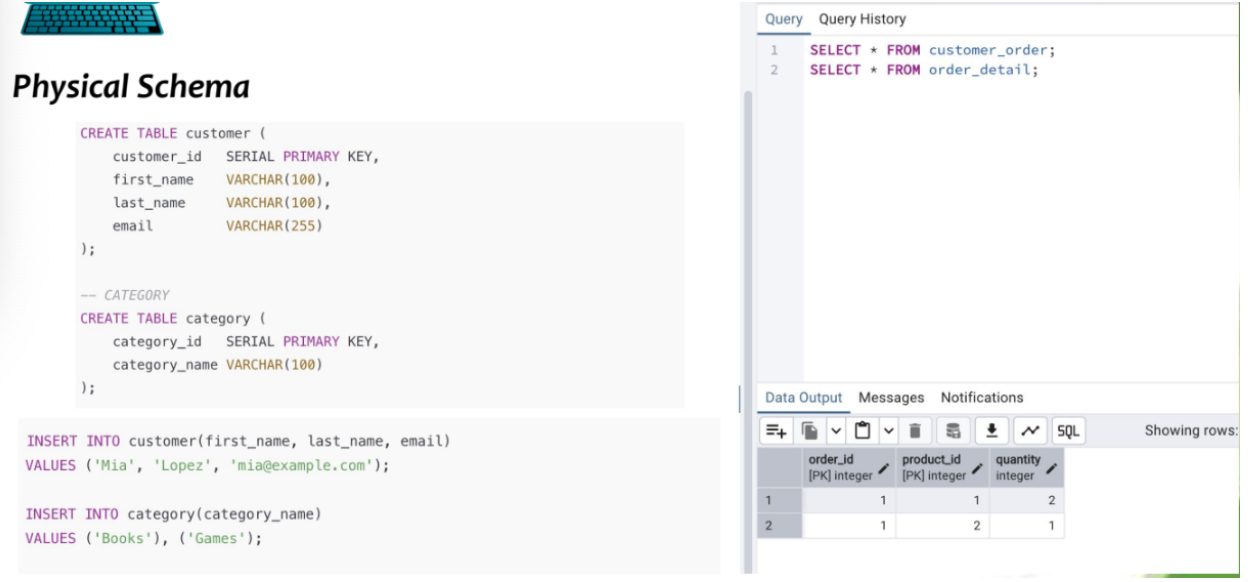
Physical schema
Implementation of logical schema in specific DBMS = show how data is stored, indexed, accessed
THE actual db
Includes: specifics of storage devices, access methods, indexing, partitioning, access methods, views, configuration of db on storage media
Translates logical schema → implementation fitting requirements of specific DBMS
When write queries to create physical DB
II. Uses of schemas
Data organization: clear structure
Data security: defines user permissions and views
Data integrity: rules and constraints to maintain data accuracy and consistency
Performance: through use of queries
Scalability: allows for changes to DB w/o disrupting current applications