sorted midterm 2
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
3 main meanings of the term “network”
1. network as a computer technology; 2. network as application of internet (e.g. telelearning, teleworking); 3. computer network as a „social concept“ (e.g. social networks on Facebook)
How internet works, video
internet is a wire buried in ground. It is useful because 2 computers connected directly to this wire can communicate. Server is special computer connected directly to internet and web pages are files on that server’s hard drive. Every server has its own IP address that help computers find each other (we give them names as google.com). so your computer isn’t server bcs its not connected directly to the internet, they are clients bcs they are connected indirectly to internet through internet service provider. Everything connected directly or indirectly has an IP address (computer, server, cell phones). Anywhere 2 or more pieces of internet intersect there’s a piece of equipment called a router that direct your packets (picture splitted inn parts, files) around the internet helping each packet get one step closer to its destination. That way it cannot miss you and get to your boss 😊
computer network
A computer network is a system that connects computers and other devices (e.g., printers) via communications media so that data and information can be transmitted among them.
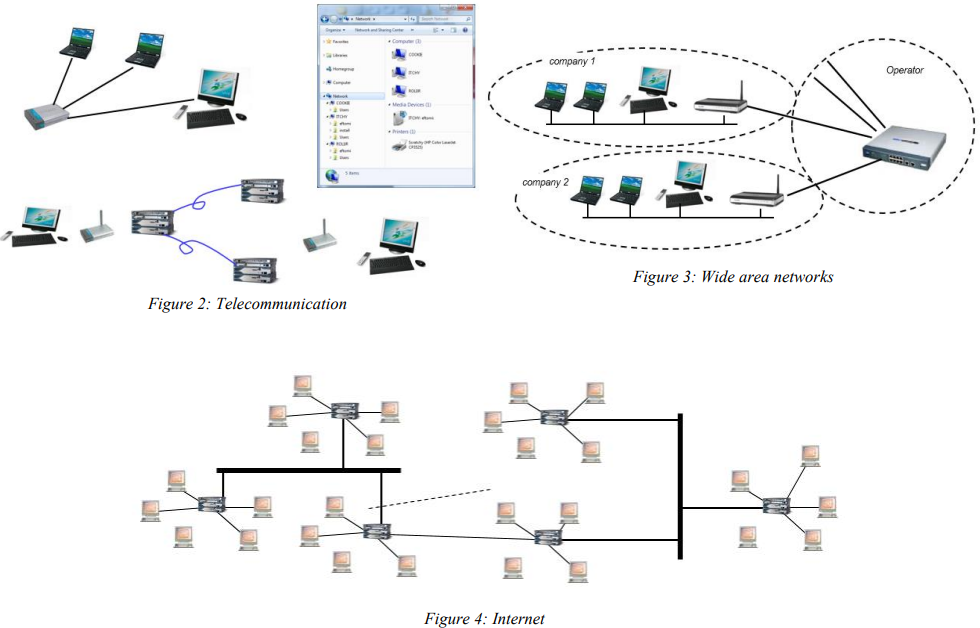
types of computer networks, local area network LAN:
A local area network (LAN) connects two or more devices in a limited geographical region, usually within the same building, so that every device on the network can communicate with every other device. A local area network LAN may extend within one company, within one building or on entire premises (of a company). The user is mostly the owner of the network. High transmission rates. Copper or fiber optic cables can be used in a wired network as transfer media: the network can be wireless (WLAN). Home area networks HAN as a recent trend to connect digital devices within one household.Although it is not required, many LANs have a file server or network server.
A wide area network (WAN):
A wide area network (WAN) is a network that covers a large geographic area. WANs typically connect multiple LANs. WANs have large capacity, and they typically combine multiple channels (e.g., fiber-optic cables, microwave, and satellite). The Internet is an example of a WAN.
Internet protocol (IP):
Each computer on the internet has an assigned address, called the Internet Protocol (IP) address that distinguishes it from all other computers. The IP address consists of sets of numbers, in four parts, separated by dots (135.62.128.91). You can access a Web site by typing this number in the address bar of your browser. The address must be unique so that computers on the internet know where to find one another. Because the numeric IP addresses are difficult to remember, most computers have names as well. ICANN accredits certain companies called registrars to register these names, which are derived from a system called the domain name system (DNS). Domain names consist of multiple parts, separated by dots that are read from right to left. For example, consider the domain name business.auburn.edu.
Domain names:
Each server has its own IP address, e.g. 193.2.82.196 Domain Name System „translates“ those numbers in more understandable form: miha.ef.uni-lj.si Domain names need to be registered.
Reference models in communication networks – uniform resource locator URL:
A character string that points to a specific resource anywhere on the web. It consists of:
the web protocol http://,
the domain name of the web server www.google.com,
the directory name or folder on that server,
the file within the directory, including optional extension /index.html
World wide web and client-server architecture:
client sends request, Server finds the file, server sends the file, client shows the file to the user
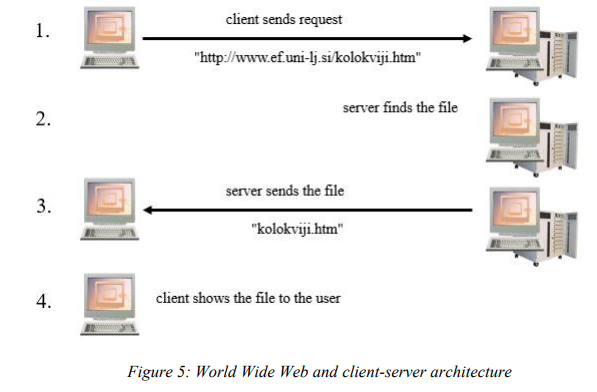
Network coordination types: client-server
Client-server architecture
Client-server architecture – one of the most common coordination principles used in computer network, the server computer offers one or more services to a client computer (file sharing etc). example is requesting a webpage, general idea of picture is video lesson
Note:
Very important: you will likely not be setting up computer networks in your company However: especially the wireless networks are often the problematic part in terms of security. You will need to set strict rules as to what can be done, especially in the era of BYOD
Telepresence systems:
Telepresence systems - a set of technologies which allow a person to feel as if they were present, to give the appearance or effect of being present via telerobotics, at a place other than their true location. (Zoom)
Teleworking:
the action or practice of working from home, making use of the internet, email, and the telephone for communication with colleagues. Disadvantages: feelings of isolation, communication barriers, challenges in maintaining a healthy work-life balance, increased stress levels…
Teleworking allows workers to work anytime and anyplace. In 6 years time about 50 per cent of the employees and 43 per cent of self-employed could work from home, through innovative arrangements made Rothwell (1989) possible by IT development an evolution toward increasing home telework—with the exception of a few categories of individuals—as new work patterns develop in response to technological change.....
Telelearning:
Tele-learning (alternatively written as telElearning or TelElearning) is also referred to as tele-education, and in contexts where technologies are used widely to support learning and teaching, it can be included as an element of distance learning, Elearning, e-learning, technology-based learning…
Telecommuting:
Unlike most other forms of virtual work, the telecommute definition implies that you’ll still be part of a traditional office setting. Requirements vary, but expect to be in person for things like meetings and training. Often, telecommuting is remote work that’s limited by distance from the main office or a satellite location. Telecommuting usually means working from home while staying connected to a physical office.
Collaboration:
Virtual collaboration (see e.g. Volvo innovation jam), Workflow technologies, Groupware, Teleconferencing, Videoconference, Web conferencing, Real-time collaboration tools.
e-learning:
learning conducted via electronic media, typically on the internet. E-learning does not usually replace the classroom setting, but it enhances it by taking advantage of new content and delivery technologies. E-learning and distance learning are not the same thing, but they do overlap. E-learning refers to learning supported by the Web. It can take place inside classrooms as a support to conventional teaching, such as when students work on the Web during class. It also can take place in virtual classrooms, in which all coursework is done online and classes do not meet face-to-face. In these cases, e-learning is a part of distance learning. Distance learning (DL) refers to any learning situation in which teachers and students do not meet face-to-face.
Internet from net
The internet, sometimes simply called the net, is a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks and electronic devices that communicate with each other using an established set of protocols.
Distance learning:
a method of studying in which lectures are broadcast or lessons are conducted by correspondence, without the student needing to attend a school or college.
Opening challenge (from 2019 slides ☺):
Should SEB LU close its buildings and move exclusively (or at least mainly) to e-learning? Why hasn‘t e-learning already replaced the „normal“ learning – you have top courses (Coursera) & top professors (e.g. lectures from MIT; https://ocw.mit.edu/index.htm) available online: Blended learning: online courses and in-class courses
Benefits of e-learning:
Lower health risks (COVID-19) Self-paced learning increases content retention. Online materials deliver high-quality, current content. Students have the flexibility of learning from any place at any time at their own pace. Learning time generally is shorter, and more people can be trained due to faster training time. Training costs can be reduced.Despite these benefits, e-learning has some drawbacks.
Drawbacks of e-learning:
Instructors may need training to be able to teach electronically. The purchase of additional multimedia equipment may be necessary. Students must be computer literate and may miss the face-to-face interaction with instructors. There are issues with assessing students’ work, as instructors really do not know who completed assignments.
Teleworking benefits for employees:
Reduced stress, improved family life (!?) Employment opportunities for single parents and persons with disabilities lower costs, - Increased employee productivity, performance, creativity and morale - Ability to retain skilled employees
Teleworking benefits for employers:
Increased productivity Ability to retain skilled employees Lower costs: Big British and American firms pay on average $5,000 per employee in annual rental costs.
Teleworking savings:
Numbers From Home $10,000 How much employers save on each remote worker — you read that right — when it comes to desk space and related expenses. Inc24 Media, 2020 54 Mn Working from home for just half the week can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 54 Mn tonnes every year, according to Global Workforce Analytics estimates.
Telecommuting Disadvantages For Employees:
There are also drawbacks. Working from home offers employees fewer opportunities to talk and network with their employees, relations with coworkers suffer and feelings of isolation can appear, and workers appear to be working more than, if they didn’t work from home. There is also potential for slower promotions, difficulty in supervising work, security problems, additional training costs and workplace culture suffers
Telecommuting Disadvantages For Employers:
Difficulties in supervising work - Potential information security problems - Additional training costs - Workplace culture, commitment… - Issue of technology (money, skills)Insights from practice –
Companies who Adopt Remote Work will Replace Every Company who Doesn’t:
- Talent: Remote work companies can hire anyone on the planet. Fixed offices limit your hiring range. Talented workers demand remote work. - Efficiency: Lower costs (no real estate). Traditional offices are full of distractions. Remote work also shifts value from time spent to productivity. - Workers having more flexibility to decide their work schedule, able to operate when they are most productive rather than a fixed day, enables a far better future of work than the one we currently experience.
IBM-international business machines:
IBM is giving thousands of its remote workers in the U.S. a choice this week: Abandon your home workspaces and relocate to a regional office—or leave the company. Corporate leaders argue that putting workers in the same physical space hastens the speed of work and sparks innovation The company has rebuilt design and digital marketing teams to quickly respond to real-time data and customer feedback, collaborations that happen more easily when teams work shoulder to shoulder. Recall of remote workers. Same with YAHOO, HP (critical turnaround period)
Insights from practice (2) – Yahoo:
Yahoo CEO Marissa Mayer has instituted a HR plan today to require Yahoo employees who work remotely to relocate to company facilities. The move will apparently impact several hundred employees, who must either comply without exception or presumably quit. It impacts workers such as customer service reps, who perhaps work from home or an office in another city where Yahoo does not have one.
Insight from practice (3) – HP:
„During this critical turnaround period, HP needs all hands on deck. We recognize that in the past, we may have asked certain employees to work from home for various reasons. We now need to build a stronger culture of engagement and collaboration and the more employees we get into the office the better company we will be.“ In an email sent to employees on February 5, 2015 the company has said that "everyone except for approved employees (teleworkers, etc) will be in office five days a week — no exceptions". The company, which has a workforce of more than 317,500 people globally, has informed the employees that it will be "tracking badge swipes to the office".
Insight from practice (4) – Google:
"The surprising question we get is: 'How many people telecommute at Google?' ” Mr Pichette said at a talk in Sydney on Monday. "And our answer is: 'As few as possible'. There is something magical about sharing meals. There is something magical about spending the time together, about noodling on ideas, about asking, “What do you think of this?” Google’s CFO, Patrick Pichette. GOOGLE also tries to minimize telework. (To not hurt company culture)
missing Insights from practice (5) – Twitter:
General guidelines:
Focus on goals Communication needs to be open and expectations need to be clear Figure out how to foster community. Final thought: will my kids still distinguish between „tele“ and „in person“ meetings?
Web 2.0/social media:
Web 2.0 sites enable users to interact and collaborate on social media, creating user-generated content in a virtual community, unlike traditional websites that limit content viewing. Examples include social networking sites, blogs, wikis, video sharing sites, hosted services, web applications, mashups, and folksonomies.
And an even newer term: Web 3.0:
Web3 refers to a potential new iteration of the internet that runs on public blockchains, the record-keeping technology best known for facilitating cryptocurrency transactions. The appeal of Web3 is that it is decentralized, so that instead of users accessing the internet through services mediated by the likes of Google, Apple, or Facebook, it’s the individuals themselves who own and control pieces of the internet. Web3 does not require “permission,” meaning that central authorities don’t dictate who uses what services, nor is there a need for “trust,” referring to the idea that an intermediary does not need to facilitate virtual transactions between two or more parties. Web3 theoretically protects user privacy better as well, because it’s these authorities and intermediaries that are doing most of the data collection.
When we talk about social networks‘ use in business there are at least 3 inter-connected things:
- what the company deliberately publishes on its profiles (see for example Poslovna informatika or Poslovna logistika on Facebook and the case here; case is non-exam material)
- what the customers publish on their profiles
- how the company uses the data/responds to posts/content by the customers
Opening case – United airlines:
Recent stat: July 2012: 187,850 passenger reports of mishandled baggage (only for various US airlines in one month!) The most famous movie in the history of United Airlines, one of the largest airlines in the world over 19 million views (last year it was 15 million views, two years ago 12 million)
Concluding remark:
»Yes, I think social media is a wonderful and powerful tool. But remember that great service is about how you treat people, not what tool you use. So before you dive into social media support, take a good look at your existing customer service channels. Are they performing well? Do you have good MPR (minutes per resolution), not just a good response time? Do the majority of surveyed customers say your team sufficiently assisted them? Are your support employees happy and empowered? If so, then congrats…and feel free to expand into social media!”
e-business:
E-business is a process that an organization conducts over a computer-mediated network: - Production – procurement, ordering, stock replenishment, payment processing, production control - Customer-focused – marketing, selling, customer order processing - Internal or management-focused – employee service, training, recruiting, information sharing
Electronic commerce (e-commerce):
describes the process of buying, selling, transferring, or exchanging products, services, or information via computer networks, including the Internet. E-commerce covers outward-facing processes that touch customers, suppliers and external partners, including sales, marketing, order taking, delivery, customer service, purchasing of raw materials and supplies for production and procurement of indirect operating-expense items.
Electronic business (e-business):
is a somewhat broader concept. In addition to the buying and selling of goods and services, e-business refers to servicing customers, collaborating with business partners, and performing electronic transactions within an organization. E-business includes e-commerce but also covers internal processes such as production, inventory management, product development, risk management, finance, knowledge management and human resources. E-business strategy is more complex, more focused on internal processes, and aimed at cost savings and improvements in efficiency, productivity and cost savings.
Pure versus Partial Electronic Commerce:
Pure versus Partial Electronic Commerce depends on the degree of digitization involved. - Brick-and-mortar organizations - Virtual organizations - Click-and-mortar organizations Important: cross-channel integration
can take several forms depending on the degree of digitization involved. The degree of digitization is the extent to which the commerce has been transformed from physical to digital. This concept can relate to both the product or service being sold and the delivery agent or intermediary. In other words, the product can be either physical or digital, and the delivery agent can be either physical or digital.
Types of E-Commerce:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) - Business-to-Business (B2B) - Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) - Business-to-Employee (B2E) - E-Government - Mobile Commerce (m-commerce)
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and B2B:
In B2C, the sellers are organizations, and the buyers are individuals - Business-to-Business (B2B): In B2B transactions, both the sellers and the buyers are business organizations. B2B comprises the vast majority of EC volume.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C);
In C2C (also called customer-to-customer), an individual sells products or services to other individuals. The major strategies for conducting C2C on the Internet are auctions and classified ads.
Business-to-Employee (B2E):
In B2E, an organization uses EC internally to provide information and services to its employees. For example, companies allow employees to manage their benefits and to take training classes electronically. In addition, employees can buy dis-counted insurance, travel packages, and tickets to events on the corporate intranet. They also can order supplies and materials electronically. Finally, many companies have electronic corporate stores that sell the company’s products to its employees, usually at a discount.
E-Government:
E-government is the use of Internet technology in general and e-commerce in particular to deliver information and public services to citizens (called government-to-citizen or G2C EC) and to business partners and suppliers (called government-to-business or G2B EC). G2B EC is much like B2B EC, usually with an overlay of government procurement regulations. That is, G2B EC and B2B EC are similar conceptually. However, the functions of G2C EC are conceptually different from anything that exists in the private sector (e.g., B2C EC).E-government is also an efficient way of conducting business transactions with citizens and businesses and within the governments themselves. E-government makes government more efficient and effective, especially in the delivery of public services. An example of G2C electronic commerce is electronic benefits transfer, in which governments transfer benefits, such as Social Security and pension payments, directly to recipients’ bank accounts.
Mobile Commerce (m-commerce):
The term m-commerce refers to e-commerce that is conducted entirely in a wireless environment. An example is using cell phones to shop over the Internet.
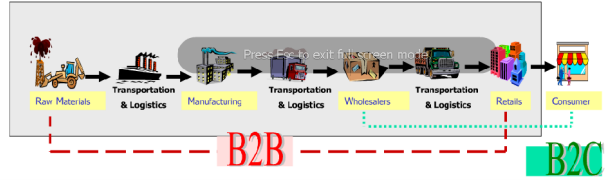
Traditional commerce:
In traditional commerce, both dimensions are physical. Purely physical organizations are referred to as brick-and-mortar organizations. In contrast, in pure EC all dimensions are digital. Companies engaged only in EC are considered virtual (or pure-play) organizations. All other combinations that include a mix of digital and physical dimensions are considered partial EC (but not pure EC). Clicks-and-mortar organizations conduct some e-commerce activities, yet their primary business is carried out in the physical world.
Clicks-and-mortar organizations:
cross-channel integration
are examples of partial EC. A common alternative to the term clicks-and-mortar is clicks-and-bricks. Cross-channel integration – customer-focused digital marketing technique used by marketers globally to provide their customers with a consistent experience when interacting with their brand across multiple digital channels
Why E-Business?
- Lower costs of doing business - Lower levels of inventory - Shorter business cycles - Higher quality of products & services - Lower costs of marketing and sales - New sales opportunities; New industries within e-business (e-business is changing many old industries and making new industries): - eBay, Alibaba, Google, Wikipedia, Cyworld / Facebook / Linked-In, Innocentive, sciQuest, ChemConnect, Uber, AirBnB, Bitstamp (Bitcoin), Blockhain
Business model:
Whenever a business enterprise is established, it employs a particular business model that describes the design of the value creation, delivery, and capture mechanisms it employs. The essence of a business model is in defining the manner by which the enterprise delivers value to customers, entices customers to pay for value, and converts those payments to profit. It thus reflects management's hypothesis about what customers want, how they want it, and how the enterprise can organize to best meet those needs, get paid for doing so, and make a profit. A business model defines what is the value you create, how will you deliver that value to the customer and how you will capture the value (revenue/profit).
1. Value creation (proposition value):
What value do customers get from your business? Netflix: customers want to watch movie Facebook: communication with friends/family, being in instant touch with friends, FB delivers reality/real info/real experience MySpace: have an alternative reality online, imaginary friends/different personality (different value from FB, bankrupt)
2. Value delivery
Ex. Uber and AirBnB: they don’t have their own cars/apartments, they just provide an online service
3. Value capture:
In e-business, there are multiple ways of creating revenues: Social media: advertising. selling products (CyWorld – selling virtual products: furniture, flowers, swimming pool…), donations (the Guardian), premium subscriptions (Linked-in)
Major E-Commerce Mechanisms:
Businesses and customers can buy and sell on the Internet through a number of mechanisms. The most widely used mechanisms are Electronic catalogs, Electronic auctions, E-storefronts, E-malls, and E-marketplaces. - Auctions: selling, bidding (online auctions) - Forward Auctions - Reverse Auctions: who offers the least gets the product (procurement; the suppliers compete for the bid – lower and lower prices)
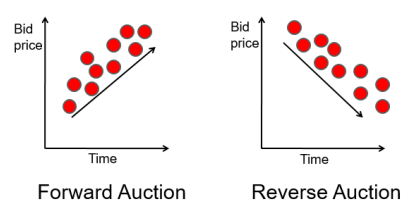
E-auctions:
An auction is a competitive buying and selling process in which prices are determined dynamically by competitive bidding. Electronic auctions (e-auctions) generally increase revenues for sellers by broadening the customer base and shortening the cycle time of the auction. Buyers generally benefit from e-auctions because they can bargain for lower prices. In addition, they do not have to travel to an auction at a physical location.
There are two major types of auctions:
forward and reverse. In forward auctions, sellers solicit bids from many potential buyers. Usually, sellers place items at sites for auction, and buyers bid continuously for them. The highest bidder wins the items. Both sellers and buyers can be either individuals or businesses. The popular auction site eBay.com is a forward auction. In reverse auctions, one buyer, usually an organization, wants to purchase a good or a service. The buyer posts a request or a quotation (RFQ) on its web site or on a third-party site. The RFQ provides detailed information on the desired purchase. Interested suppliers study the RFQ and then submit bids electronically. Everything else being equal, the lowest-price bidder winds the auction. The reverse auction is the most common auction model for large purchases (in terms of either quantities or price). Governments and large corporations frequently use this approach, which either may provide considerable savings for the buyer.
Online Service Industries:
In addition to purchasing products, customers can also access needed services via the Web. Selling books, toys, computers, and most other products on the Internet can reduce vendors’ selling costs by 20 to 40 percent. Further reduction is difficult to achieve because the products must be delivered physically. Only a few products, such as software and music, can be digitized and then delivered online for additional savings. In contrast, services, such as buying an airline ticket and purchasing stocks or insurance, can be delivered entirely through e-commerce, often with considerable cost reduction. Not surprisingly, then, online delivery of services is growing very rapidly, with millions of new customers being added each year. One of the most pressing EC issues relating to online services (as well as in marketing tangible products) is disintermediation.
Intermediaries, also known as middlemen, have two functions:
(1) They provide information, and (2) they perform value-added services such as consulting. The first function can be fully automated and most likely will be assumed by e-marketplaces and portals that provide information for free. When this occurs, the intermediaries who perform only (or primarily) this function are likely to be eliminated. The process whereby intermediaries are eliminated is called disintermediation.
Disintermediation:
removal or reduction of intermediaries between sellers and buyers (key issue in online service industries)
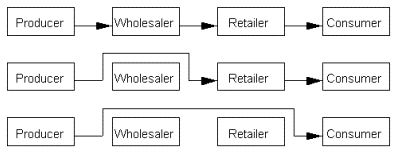
Re-intermediation:
reintroduction of an intermediary between consumers and a producer (for example wholesaler and retailer)
Why do we need intermediaries in e-business? (ex. Booking):
- Everything in one place - Information is truthful - Trust -> very low cost
How the change in one industry affects other industries? (Ex. Uber):
Driverless cars (car and transport industry/production of cars) change: - Logistics/distribution - Personal logistics - Media industry - Advertising industry - Architecture/city design - Tourism (hotels, motels…)
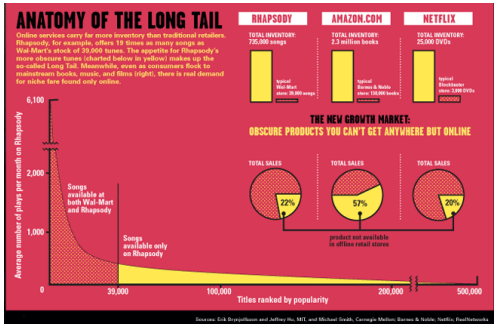
The Long Tail:
The long tail is a business strategy that allows companies to realize significant profits by selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers, instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The long tail concept considers less popular goods that are in lower demand. The strategy theorizes that consumers are shifting from mass-market buying to more niche or artisan buying. - The idea is that you can as a company generate quite a lot of money if your online - Large number of products in very low quantities and a high price à revenue from longtail companies
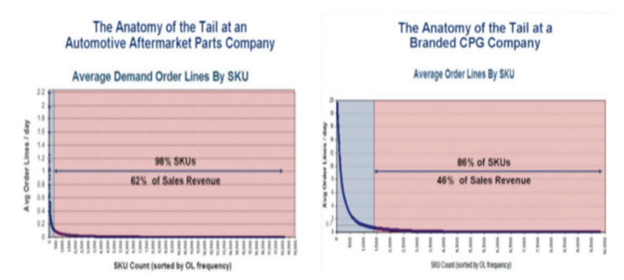
Issues in E-Tailing:
Channel conflict, Order fulfillment
Order fullfilment:
- Unless your product is digital you need to deliver it to the customer - Whenever you’re selling a physical product à the order fulfillment is very important
Issues in E-Tailing:
Despite e-tailing’s increasing popularity, many e-tailers continue to face serious issues that can restrict their growth. Perhaps the two most significant issues are channel conflict and order fulfillment. Clicks-and-mortar companies may face a conflict with their regular distributors when they sell directly to customers online. This situation, known as channel conflict, can alien-ate the distributors. Channel conflict has forced some companies to avoid direct online sales. Channel conflict can arise in areas such as pricing and resource allocation—for example, how much money to spend on advertising. Another potential source of conflict involves the logistics services provided by the offline activities to the online activities. This is the order fulfillment conflict. For example, how should a company handle returns of items purchased online? As a result, many companies are integrating their online and offline channels, a process known as multichanneling.
Online Advertising:
As more and more activity is moving online, so is advertising. Internet advertising is growing rapidly. Where to advertise depends on the statistics (for example if targeted audience is gen z, advertise on social media since they spend a lot of time there).
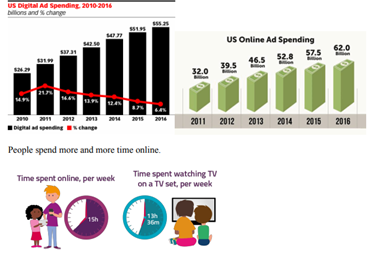
Advantages of online advertising:
- Efficiency = Targeting your customers is efficient - Relatively cheap and large audience for little money (online) - TV and newspaper ads are expensive; - Interactivity (data collection); - Flexibility (in real-time); - More information available= - Additional product information available by clicking on advertisement - More information available than with other media - Access to printable reductions - Easy access to the website to order the product - More time to see the product than with TV advertising; - Measurement made easier - You can measure an ad online -> how many people clicked on it etcOnline advertising is not the dominant .
Disadvantages of online advertising:
- Other target groups are excluded (less educated and old people à newspaper and TV) - Legal limitations - GDPR - You can block ads with different ad blockers - If you have a different purpose of advertising (respecting or knowing the brand) à better to use TV - Advertising/banner blindness. Seven in 10 Americans said they were more likely to remember the annoying or offensive ads. Nearly nine in 10 Americans said they were less likely to buy products that had annoying or offensive ads
Difference between internet and TV:
- “The web is an interactive medium, not a passive consumption medium. That is why search advertising has been so successful, because it works with the flow of users wanting to decide where they want to go and what they want to do. The display ad industry is still dominated by one-way communication.” - “You can’t fall asleep on the internet, can you?” - More than 60 percent of Americans, according to a 2013 Nielsen survey, admitted to binge[1]watching shows, and nearly eight in 10 Americans have used technology to watch their favourite shows on their own schedule.
Which activities are better done by humans and which by computers:
computers + humans = better decision making.
Not just for fun, watson in medicine:
One area IBM scientists are working to improve with Watson is its ability to process unstructured data - physicians' notes, research published in peer-reviewed medical and science journals, radiological images, biofeedback from wireless monitoring devices, and even comment threads from online patient communities. All of that information can be used in the melting pot of data analytics. “Ninety percent of the world's information has been created over the past 10 years, and 80% of that 90% is unstructured data,” said Manoj Saxena, general manager of Watson solutions in IBM's Software Group. “That data needs to be digestible.” - “Health care pros make accurate treatment decisions in lung cancer cases only 50% of the time. Watson has shown the capability (on the utilization management side) of being accurate in its decisions 90% of the time.”
Why did it take 14 more years for a computer to play jeopardy than to play chess?
chess is just calculating the moves, jeopardy is data gathering and only one specific answer
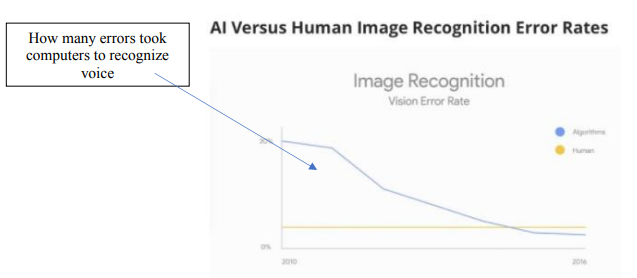
Computers like IBM’s Watson:
Computers like IBM’s Watson are improving in processing unorganized data (Physician’s notes, images) and starting to become better than humans. They are getting smaller and being used in medical fields.
Not the first human-machine fight:
On May 11, 1997, Deep Blue, an IBM-built computer beat Gari Karsparov, arguably the best (human) chess player in the history.
ALPHAGO:
ALPHAGO, the artificial intelligence system built by the Google subsidiary DeepMind defeated the human champion, Lee Se-dol, 4:1 in the tournament of the strategy game of Go (March, 2016)
Cicero:
We introduce Cicero, the first AI agent to achieve human-level performance in Diplomacy, a strategy game involving both cooperation and competition that emphasizes natural language negotiation and tactical coordination between seven players. Cicero integrates a language model with planning and reinforcement learning algorithms by concluding players’ beliefs and intentions from its conversations and generating dialogue in pursuit of its plan: Meta fundamental ai research diplomacy team et al., Human-level play in the game of Diplomacy by combining language models with strategic reasoning, 2022
Important question:
Deep blue: 1997 Watson: 2011 Alphago: 2016 ChatGPT/Cicero and many others: 2022/2023 Why did it take 14 more years for a computer to play jeopardy than to play chess? chess is very structured game, can explain rules in one minute. And what will happen in 2026? doing any work humans can do. “Machines will be capable, within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do”
Turing test:
Turing test – Series of questions to decide whether you’re talking to a human or computer.
Computers vs humans:
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang has predicted that artificial general intelligence (AI) could arrive as early as five years. Huang, who leads the world's leading maker of AI chips, said that if AI could pass every test and submit it to the computing industry, it would do well on every single test within five years. This prediction is part of Silicon Valley's long-term goal to create computers that can think like humans.
Management:
Management is a process by which organizational goals are achieved through the use of resources (people, money, energy, materials, space, time).
3 basic roles of a manager:
Managers have three basic roles: - Interpersonal roles (figure head, leader, liaison) - Informational roles (monitor, disseminator, spokesperson, analyzer) - Decisional roles (entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator)
Early information systems:
Early information systems primarily supported the informational roles. In recent years, information systems have been developed that support all three roles.
Decision:
Decision refers to a choice that individuals and group make among two or more alternatives.
Decision making:
Decision making is a systematic process composed of three major phases: intelligence, design and choice. (Implementation base was added later.) Once the choice is made, the decision is implemented.
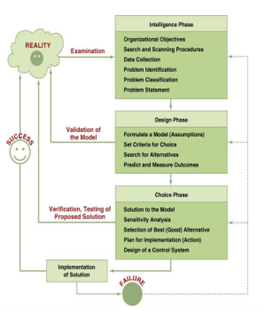
The decision-making process:
The decision-making process starts with the intelligence phase, in which managers examine a situation and identify and define the problem or opportunity. In the design phase, decision makers construct a model for the situation. They do this by making assumptions that simplify reality and by expressing the relationships among all the relevant variables. Managers then validate the model by using test data. Finally, decision makers set criteria for evaluating all of the potential solutions that are proposed. The choice phase involves selecting a solution or course of action that seems best suited to resolve the problem. This solution (the decision) is then implemented. Implementation is successful if the proposed solution solves the problem or seizes the opportunity. If the solution fails, then the process returns to the previous phases. Computer based decision support assists managers in the decision-making process.
Why managers need IT support:
- The number of alternatives to be considered constantly increases. (A key to good decision making is to explore and compare many relevant alternatives. The greater the number of alternatives, the more a decision maker needs computer-assisted searches and comparisons.) - Decisions must be made under time pressure. (It often is not possible to manually process information fast enough to be effective.) - Decisions are more complex. (It is usually necessary to conduct a sophisticated analysis in order to make a good decision.) - Decision makers, as well as the information, can be situated in different locations. Bringing everything together quickly and inexpensively can be a major challenge.
A Framework for Computerized Decision Analysis,
bi:
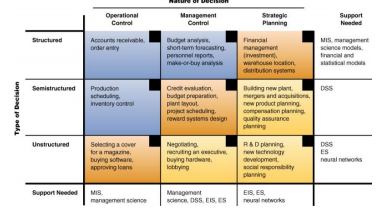
To better understand BI, you will note that various types of decisions can be placed along two major dimensions: problem structure and the nature of the decision.
problem structure:
The first dimension is problem structure, where decision-making processes fall along a continuum ranging from highly structured to highly unstructured (see the left column in Figure 12.2). Structured decisions deal with routine and repetitive problems for which standard solutions exist, such as inventory control. In a structured decision, the first three phases of the decision process - intelligence, design, and choice - are laid out in a particular sequence and the procedures for obtaining the best (or at least a good enough) solution are known. Two basic criteria used to evaluate proposed solutions are minimizing costs and maximizing profits. These types of decisions are candidates for decision automation. At the other extreme of complexity are unstructured decisions. These decisions are intended to deal with “fuzzy,” complex problems for which there are no cut-and-dried solutions. An unstructured decision is one in which there is no standardized procedure for carrying out any of the three phases. In making such a decision, human intuition and judgment often play an important role. Typical unstructured decisions include planning new service offerings, hiring an executive, and choosing a set of research and development (R&D) projects for the coming year. Although BI cannot make unstructured decisions, it can provide information that assists decision makers. Located between structured and unstructured decisions are semi-structured decisions, in which only some of the decision process phases are structured. Semi-structured decisions require a combination of standard solution procedures and individual judgment. Examples of semi-structured decisions are evaluating employees, setting marketing budgets for consumer products, performing capital acquisition analysis, and trading bonds.
the nature of decisions:
The second dimension of decision support deals with the nature of decisions. All managerial decisions fall into one of three broad categories: 1. Operational control – executing specific tasks efficiently and effectively. 2. Management control – acquiring and using resources efficiently in accomplishing organizational goals. 3. Strategic planning – the long-range goals and policies for growth and resource allocation. Note that strategic decisions define the context in which management control decisions are made. In turn, management control decisions define the context in which operational control decisions are made.
decision-support matrix:
The three primary classes of problem structure and the three broad categories of the nature of decisions can be combined in a decision-support matrix.
Structured and some semi-structured decisions:
Structured and some semi-structured decisions, especially of the operational and management control type, have been supported by computers since the 1950s. Decisions of this type are made in all functional areas, but particularly in finance and operations management. Problems that lower-level managers encounter on a regular basis typically have a high level of structure. Examples are capital budgeting (e.g., replacement of equipment), allocating resources, distributing merchandise, and controlling inventory. For each type of structured decision, prescribed solutions have been developed, which often include mathematical formulas. This approach is called management science or operations research, and it is executed with the aid of computers.
Business Intelligence:
To provide users with access to corporate data, many organizations are implementing data warehouses and data marts. Users analyze the data in warehouses and marts using a wide variety of BI tools. Many sellers offer integrated packages of these tools under the overall label of business intelligence (BI) software.
There are two types of BI systems:
- Those that provide information in structures format, Those that provide data analysis tools.
Those that provide information in structures format:
Dashboards - They provide rapid access to timely information, provide direct access to management reports, are very user friendly and supported by graphics.
Those that provide data analysis tools
3 types of analysis:
● Multidimensional data analysis (online analytical processing – OLAP) - Provides users with a look at what is happening or what has happened. Allows users to analyze data in such a way that they can quickly answer business questions. ● Data mining - It means searching for valuable business information in a large database or data warehouse. Data mining performs two basic operations: predicting trends and behaviors, and identifying previously unknown patterns and relationships. ● Decision support systems (DSSs) - They combine models and data in an attempt to analyze semi-structured problems and some unstructured problems that involve extensive user involvement. Models are simplified representations, or abstractions, of reality. DSSs enable business managers and analysts to access data interactively, to manipulate these data, and to conduct appropriate analyses. Decision support systems can enhance learning and contribute to all levels of decision-making. DSSs also employ mathematical models. Finally, they have the related capabilities of three types of analysis: sensitivity analysis, what-if analysis, and goal seeking analysis.
Sensitivity analysis:
Sensitivity analysis is the study of the impact that changes in one or more parts of a decision-making model have on other parts. Most sensitivity analyses examine the impact that changes in input variables have on output variables. Most models include two types of input variables: decision variables and environmental variables. “What is our reorder point for these raw materials?” is a decision variable (internal to the organization). “What will the rate of inflation be?” is an environmental variable (external to the organization). The output in this example is the total cost of raw materials. Companies generally perform a sensitivity analysis to determine the impact of environmental variables on the result of the analysis. Sensitivity analysis enables the system to adapt to changing conditions and to the varying requirements of different decision-making situations. It provides a better understanding of the model as well as of the problem that the model purports to describe.
What-if analysis:
What-if analysis attempts to predict the impact of a change in the assumptions (input data) on the proposed solution. For example, what will happen to the total inventory cost if the originally assumed cost of carrying inventories is 12 percent rather than 10 percent? In a well-designed BI system, managers themselves can interactively ask the computer these types of questions as often as they need to.