Intergration of Physiology 1-5
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
How does the endocrine system control aspects of physiology?
Via the secretion of hormones
What are the 2 major control systems?
Endocrine and neuronal (nervous) system
What other systems does the endocrine system interact with?
Cardiovascular, digestive and immune system
What is a hormone?
Signalling molecule secreted into the blood to act on another part of the body
What hormones have slow/prolonged actions?
Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones (T3, T4)
What hormones have a rapid/short action?
Peptides and adrenal amines
What does lipophilic mean?
Fat soluble molecules that do not dissolve readily in an aqueous environment e.g blood plasma
What are the properties of a lipophilic molecule? (3)
Diffuse out of cells that synthesis them
Bound to carrier proteins in the blood
Can diffuse into target cells and act on intercellular receptors
What is an intracellular receptors?
Protein found inside a cell which ligand binds to steroids/ thyroid hormones to regulate gene hormones
What does an intracellular receptor do?
Regulate (increase/decrease) expression of hundreds of target genes
What effect does intracellular receptors have?
Effects have slow onset and prolonged duration - the change in gene expression takes time to occur
Are peptides and adrenal amines hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic
What are peptides and adrenal amines stored in and how are they secreted?
Stored in vesicles and secreted by exocytosis
Why do peptides and adrenal amines need no carrier proteins?
They dissolve readily in blood plasma - soluble in watery aqueous environment
How does peptides and adrenal amines get inside their target cells?
They act on plasma membrane receptors - when they get to the target cells they have to bind to receptors expressed on the outside of the cell
What are the two effects of plasma membrane receptors?
Have rapid onset of action
Are often short lived
Membrane bound receptors are mechanism of action for?
Hydrophilic peptides and amine hormones
What is the 3 basic domain of membrane bound receptor?
Extracellular (binds hormones)
Transmembrane
Intracellular (necessary for effects in target cells - change in enzyme activity)
What are the major endocrine organs? (8)
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal glands - cortex and medulla
Pancreas
Testes
Ovaries
Hypothalamus
Releasing hormone - CRH, TRH, GnRH
Dopamine, somatostatin
Pituitary gland
Growth hormone, oxytocin, LH, ACTH
Thyroid gland
Thyroid hormones (T3,T4)
Calcitonin
Parathyroid glands
Parathyroid hormone
Adrenal cortex
Cortisol, aldosterone
Adrenal medulla
Epinephrine, norepinephrine
Pancreas
Insulin, glucagon
Testes
Testosteron
Ovaries
Oestrogens, progesterone
Pineal glands
Secrets melatonin - important for biological rhythms
Adipose tissue (fat) and gastrointestinal tract
Secret many hormones involved in energy balance and metabolism
Placenta
Secrets hormones involved in foetal and maternal development
Negative feed back loops
Regulates homeostasis - imposes a brake on the system
Positive feed back system
Amplifies the original signal
Requires additional control mechanism
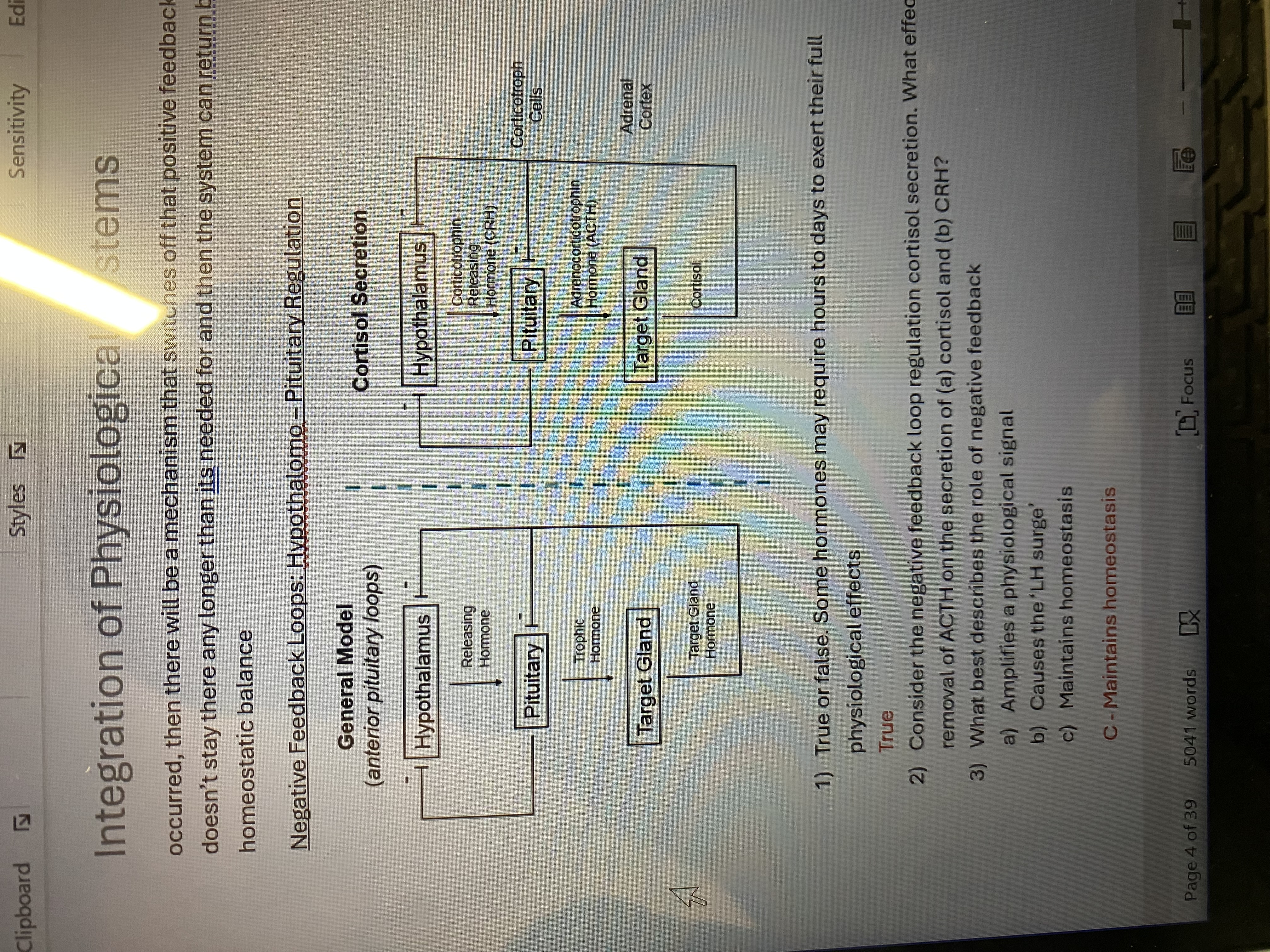
Hypothalamo- pituitary regulation
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Adheres to the trachea, just below the larynx
What does the thryroid gland do?
Secrete T4, T3 and calcitonin
What are T3 and T4?
Iodine containing hormones acting throughout the body - important for terms of development, growth and development
What does calcitonin do?
Regulates plasma calcium
What does follicular cells do?
Secrete T4 and T3
What does the colloid do? (Lumen of the thyroid epithelial cell)
Consist of thyroglobulin (glycoprotein) this is where T3 and T4 are made
Where are c cells located?
Present in the basement membrane and between follicles
What do c cells do?
Secrete calcitonin
Why does the thyroid gland have a rich blood supply?
Lots of capillary so hormones can directly be released into the blood
Thyroid feedback pathway (4)
What two components are needed for the synthesis of T4 and T3?
Thyroglobulin and iodine
How is T3 and T4 synthesised and secreted?
Synthesised in follicular cell rough endoplasmic reticulum. Packaged into vesicles and released into linen by exocytosis
How is T4 and T3 stored as?
Colloid
Iodine trapping
Where is the adrenal gland located
Above the kidney
What are the 2 major functional regions of the adrenal cortex?
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
What does the adrenal cortex (outside) produce?
Steroid hormones
What does the adrenal medulla (inside) produce?
Small polar amine molecules
What is characterised by intracellular lipid droplets?
Adrenal cortex
What is synthesised in the adrenal cortex?
Steroid hormones
What are the three subregions of the adrenal cortex?
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
What does the Zona glomerulosa secrete?
Mineralocorticoids
What does the Zona fasciculata secrete?
Glucocorticoid
What does Zona reticularis secrete?
Sex steroids
from what are steroid hormones synthesised from?
Cholesterol
How are steroid hormones transported from?
Transported bound to plasma proteins