Lecture 4 - coverings
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
wip
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
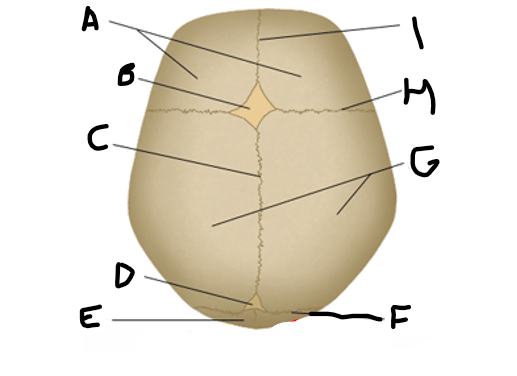
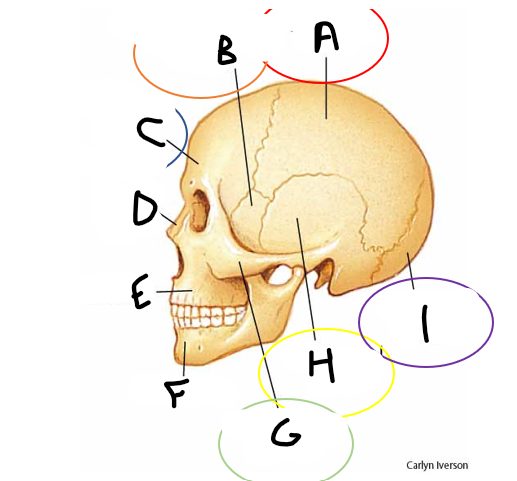
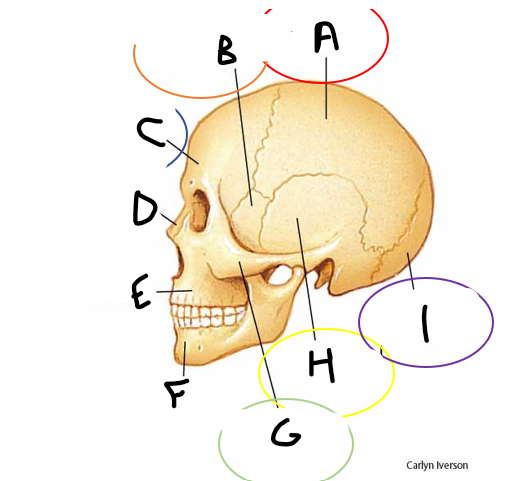
anterior fontanelle
B
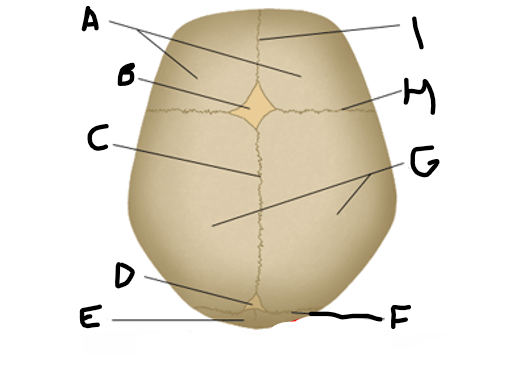
sagittal suture
C
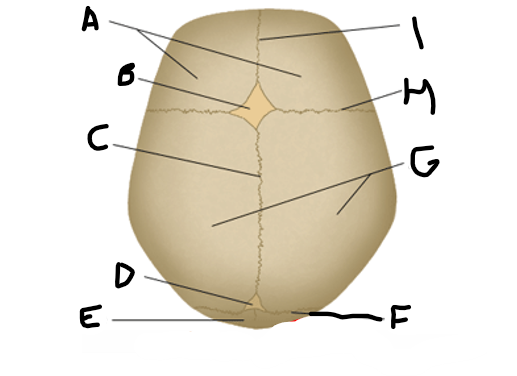
posterior fontanelle
D
lambdoid suture
F
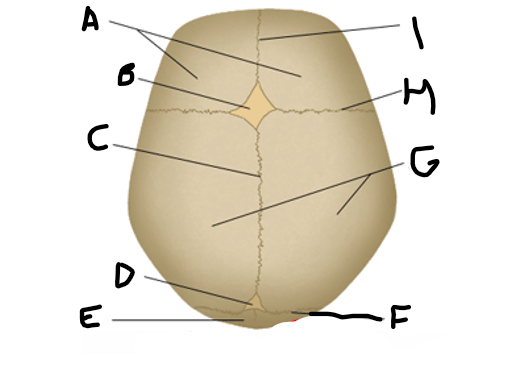
coronal suture
H
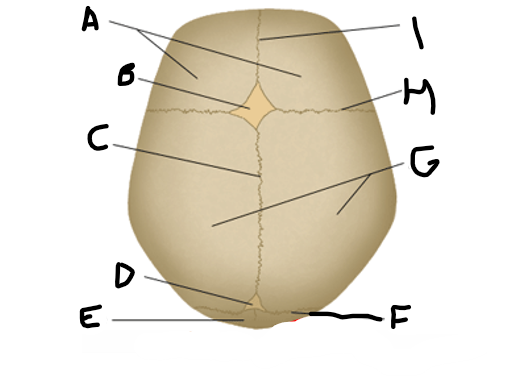
metopic suture
I
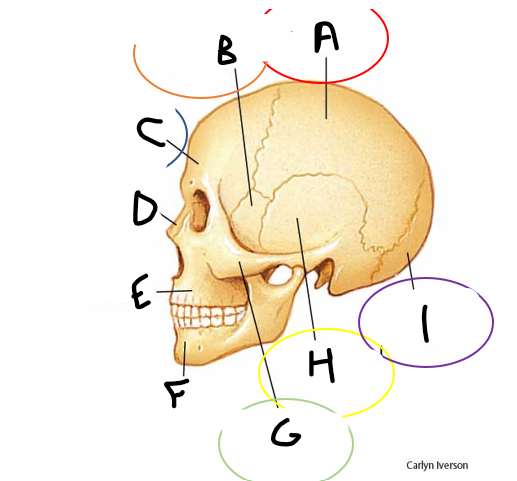
A
parietal bone
B
sphenoid bone
C
frontal bone
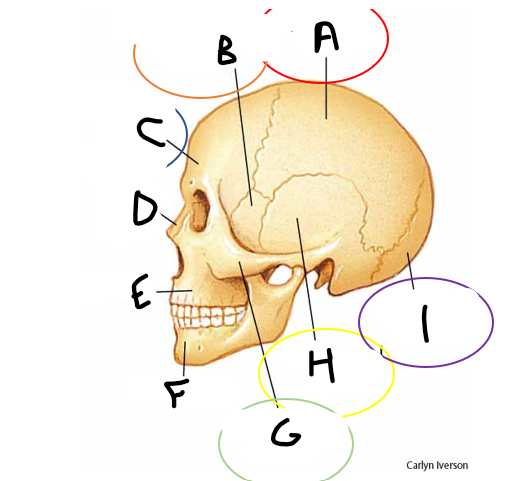
D
nasal bone
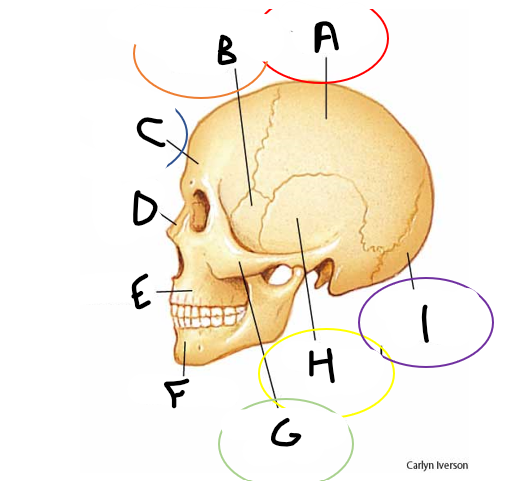
E
maxilla
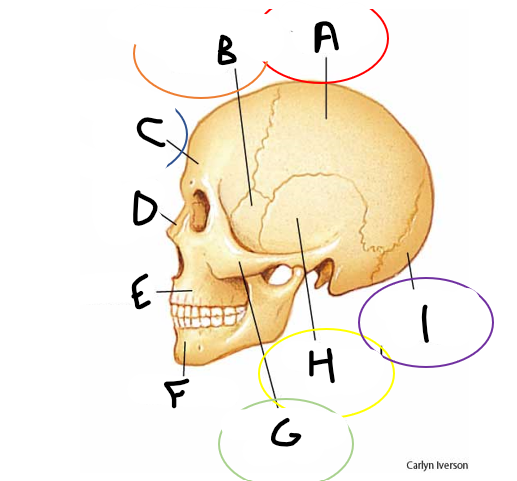
F
mandible
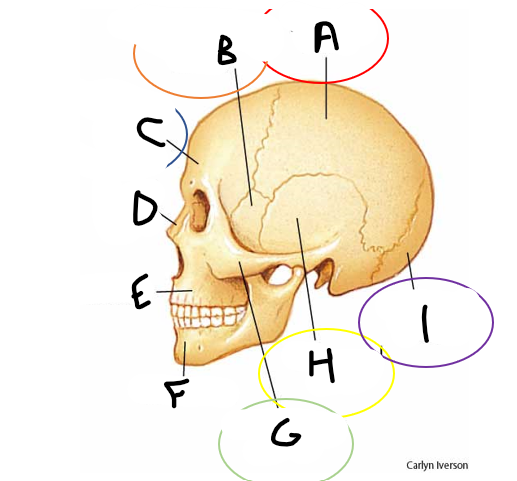
G
zygomatic bone
H
temporal bone
I
occipital bone
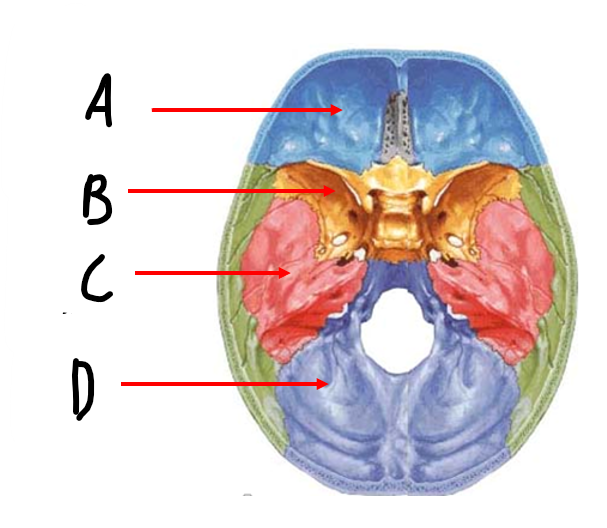
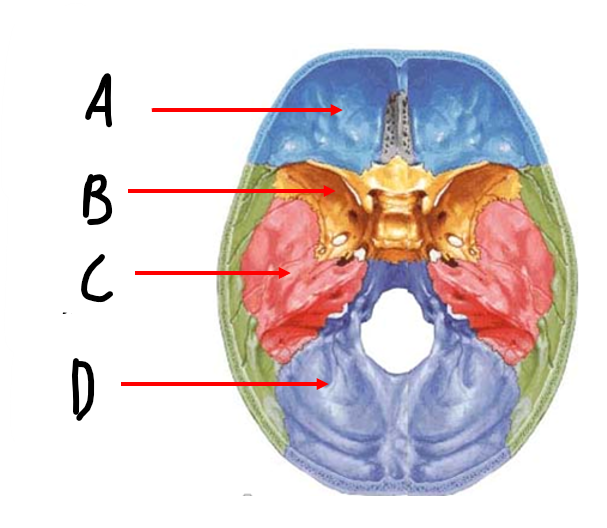
contains the frontal lobes and forms roof of the orbit
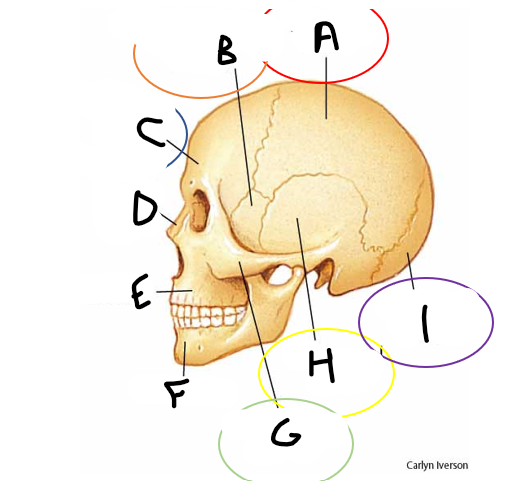
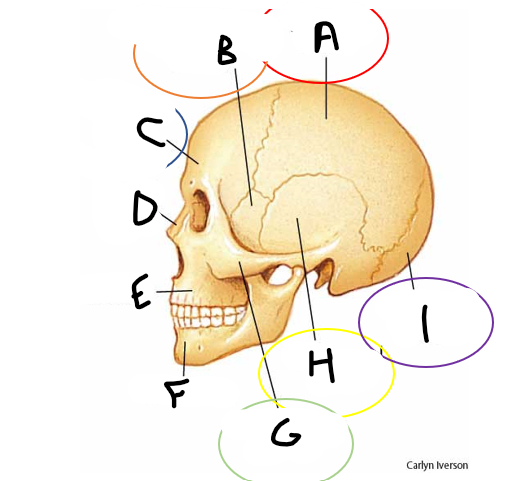
anterior cranial fossa
contains the temporal lobe
middle cranial fossa
accommodates brainstem and cerebellum
posterior cranial fossa
A
anterior cranial fossa
B
sphenoid bone
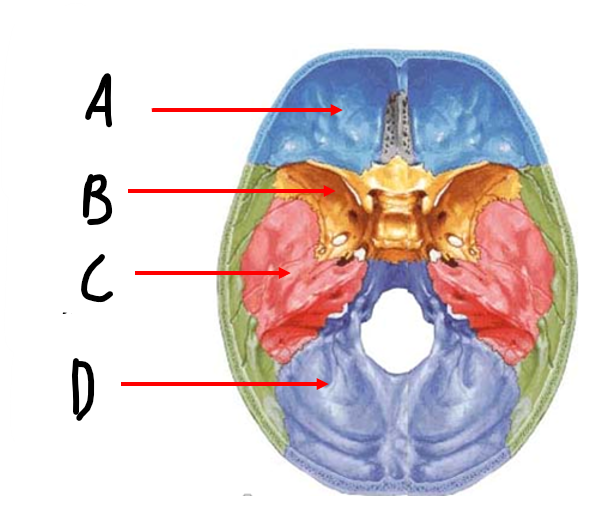
C
middle cranial fossa
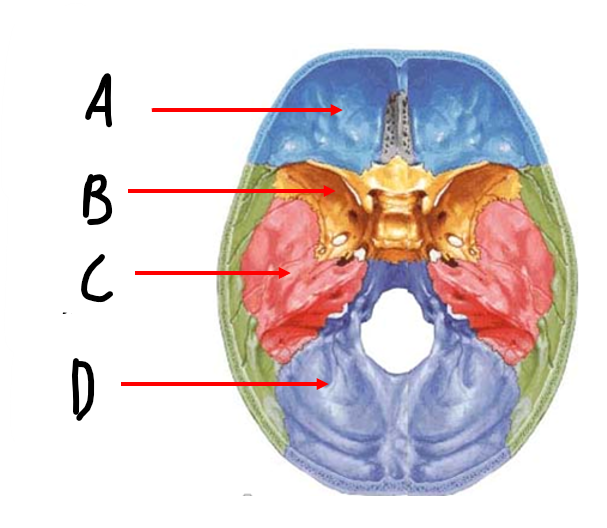
D
posterior cranial fossa
what is the hole at the bottom of the skull for the brainstem and spinal cord
foramen magnum
list the meninges from outside in
dura, arachnoid, pia
what are the arachnoid trabeculae
the “spiderwebs” in the subarachnoid space
falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli made of
dura
the leptomeninges include
pia and arachnoid
projections of the arachnoid membrane into the dura mater layer. where CSF is drained into the venous sinus system
arachnoid granulation
is the epidural space a potential or actual space
in the brain: potential
in the spinal cord: actual
tearing of middle meningeal artery → bleeding into extradural space
epidural hematoma
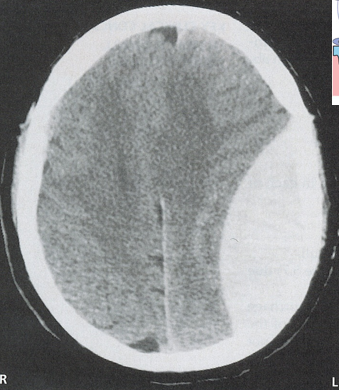
epidural hematoma
tearing of vein across the subdural space causing gradual seepage of blood
subdural hematoma
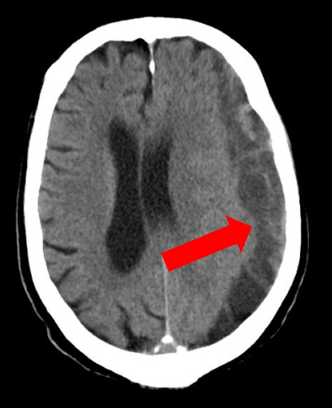
subdural hematoma
common signs of elevated intracranial pressure
headache, altered mental status, nausea, visual loss/changes
differences between epidural and subdural hematoma
epidural - rapidly expanding with arterial blood. lemon shape on imaging
subdural - slowly expanding with venous blood, banana shape lol
inflammation of meninges from infection (virus/bacteria/etc). flu symptoms, stiff neck
meningitis
viral vs bacterial meningitis
viral - mild
bacterial - damages cranial nerves and brain. can be fatal