Objective 2
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Describe the structure and function of carbohydrates
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What are monosaccharides? How do we identify them?
Smallest unit of a carbohydrate containing carbon molecules ranging from 3-7
We identify them using the formula
(CH2O) in a 1:2:1 ratioExample: C6H12O6
What are Pentoses?
Pentoses are monosaccharides that are an important part of DNA, RNA, and ATP
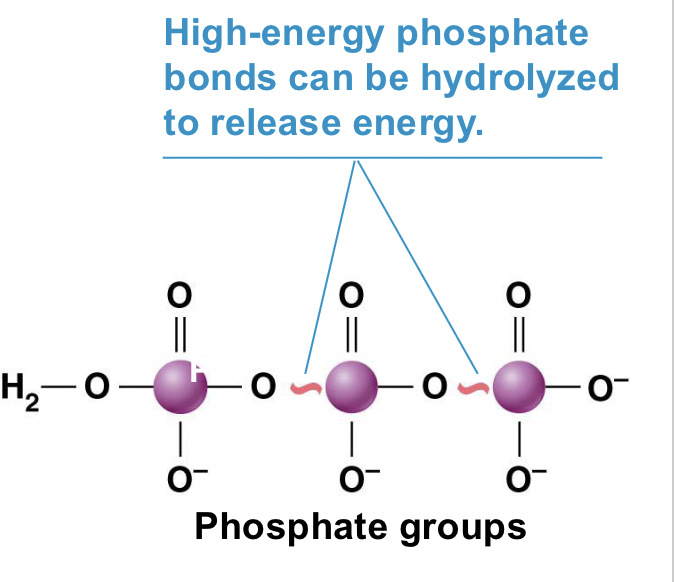
High energy phosphate bonds can be hydrolyzed to release energy
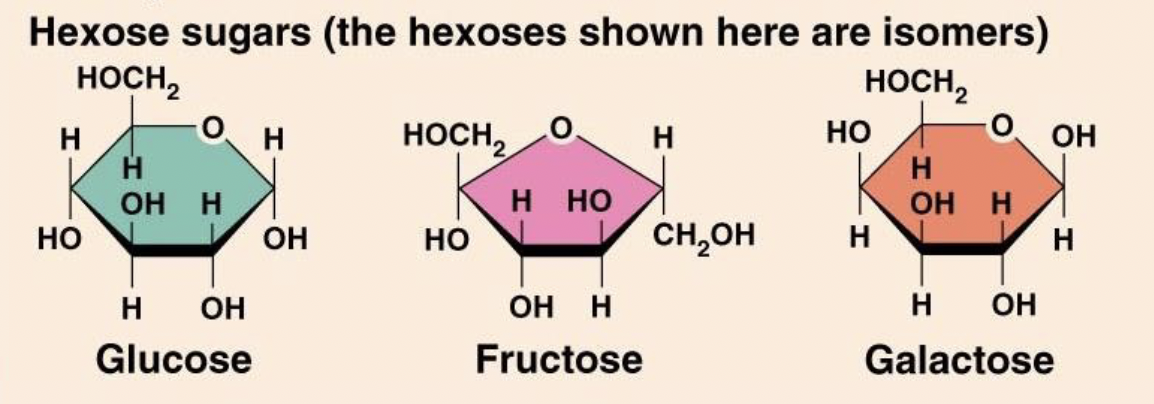
What are the three dietary Hexoses?
GFG
Glucose (main blood sugar, found in most fruit and honey)
Fructose (found in fruit and honey)
Galactose (milk and sugar)
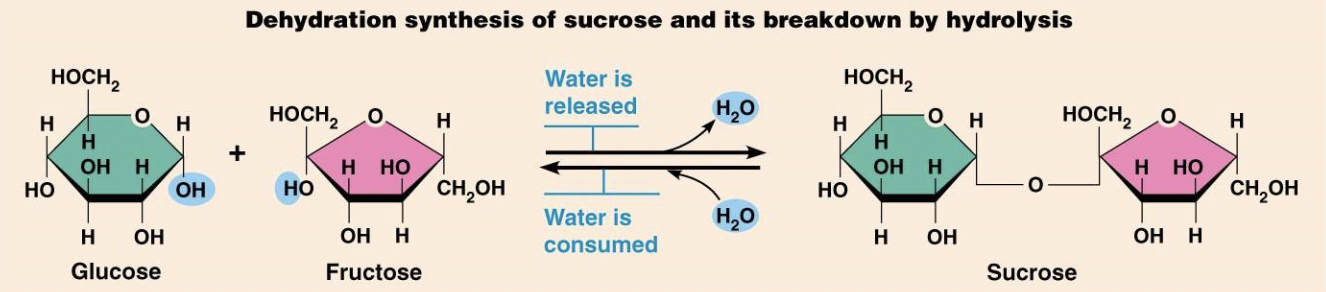
What are Disaccharides and how are they formed?
Formed by the combination of two monosaccharides through dehydration synthesis
What are the three important dietary Disaccharides?
Maltose
Composed of glucose and glucose
Sucrose
Composed of glucose and fructose
Lactose
Composed of glucose and galactose
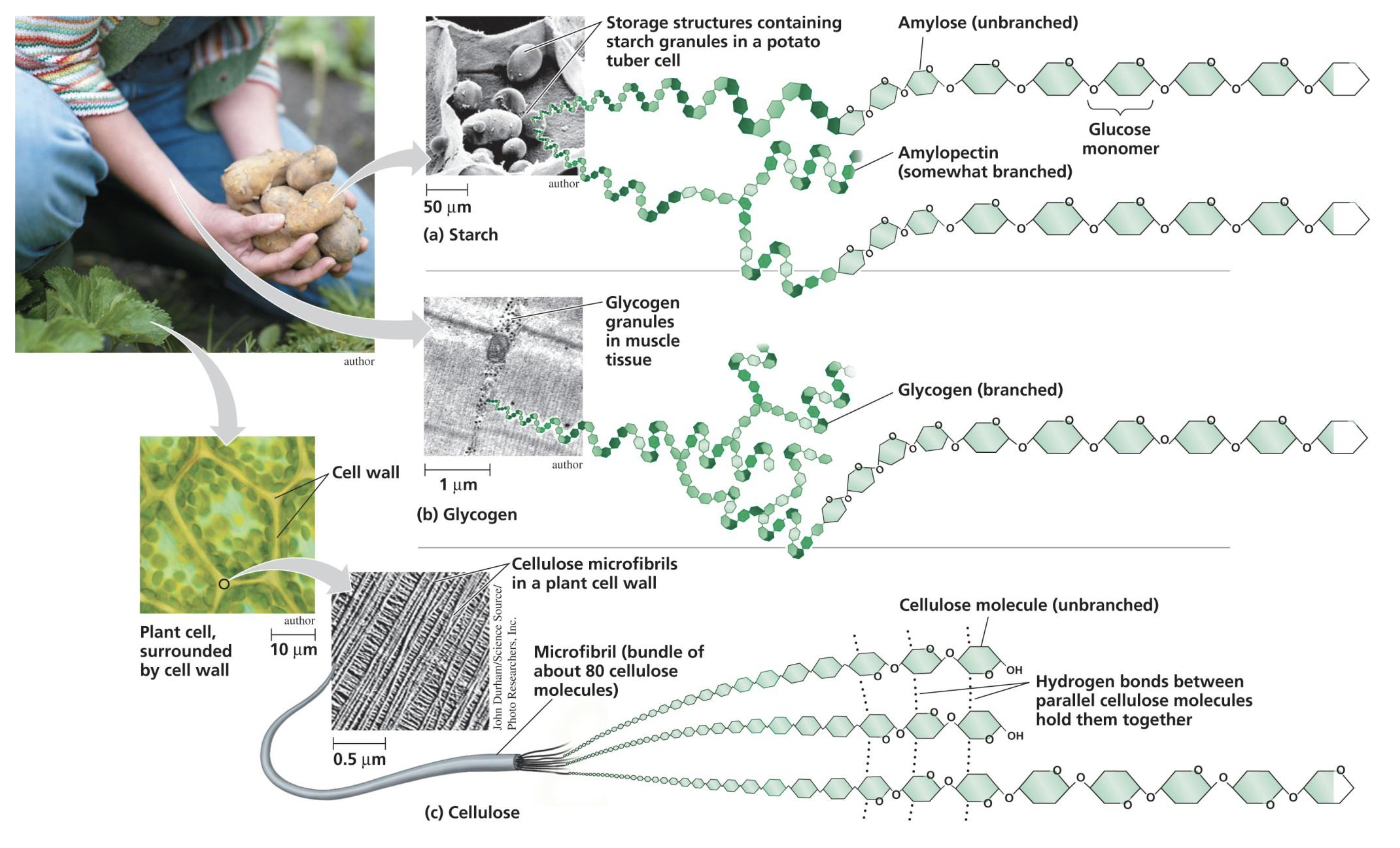
What are Polysaccharides?
Starch (unbranched chains)
Glycogen (branched chains)
Cellulose (unbranched chains but has hydrogen bonds connecting chains)
What are the functions of Carbohydrates?
Cellular respiration
ATP Production
Structural components
(RNA, DNA, ATP)
Glycolipids
present in myelin sheath in nervous system
Glycoproteins
part of connective tissue, some enzymes, some hormones