Anatomy of the Heart, Lungs, and Digestive System
1/307
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
308 Terms
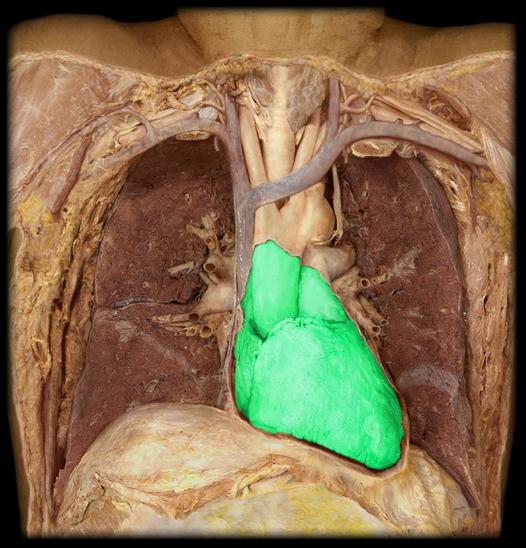
fibrous pericardium
outer memembrane of the heart
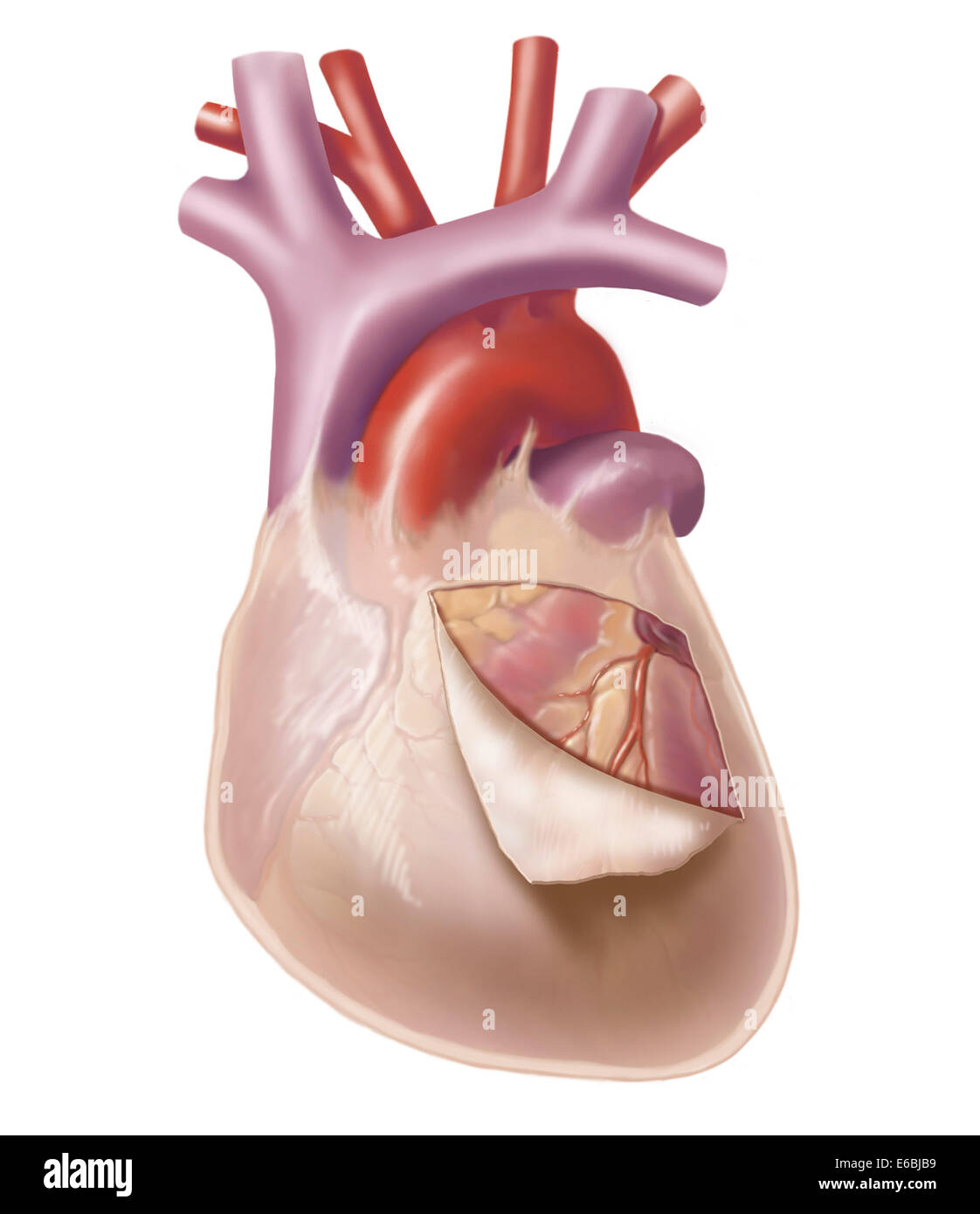
Parietal pericardium
Visceral pericardium
Coronary (atrioventricular) sulcus
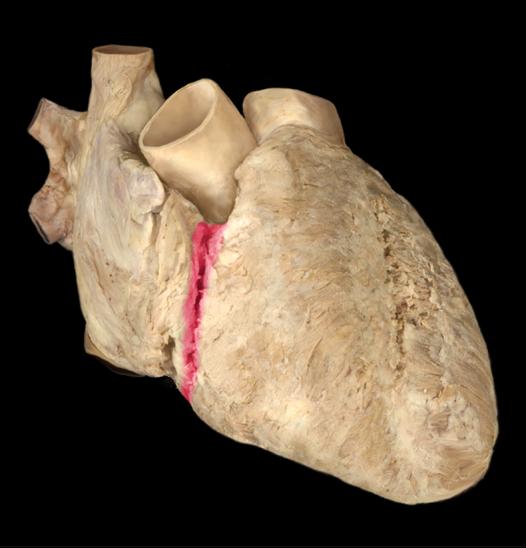
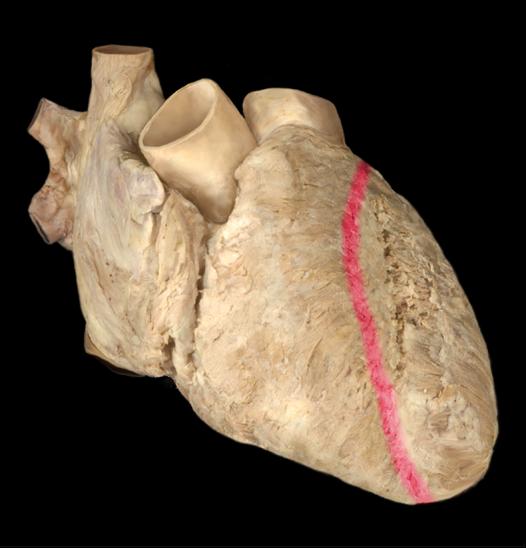
Anterior interventricular sulcus
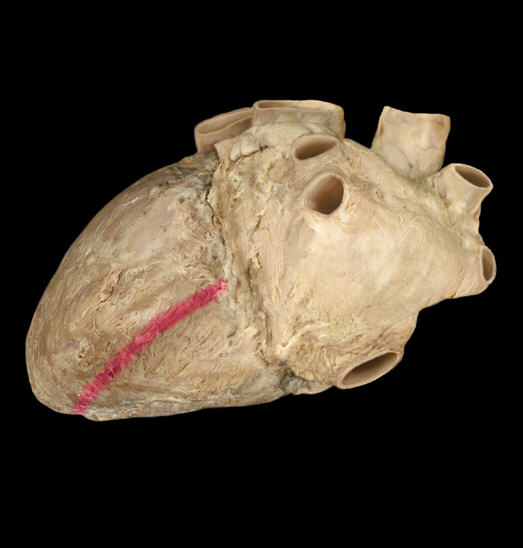
Posterior interventricular sulcus
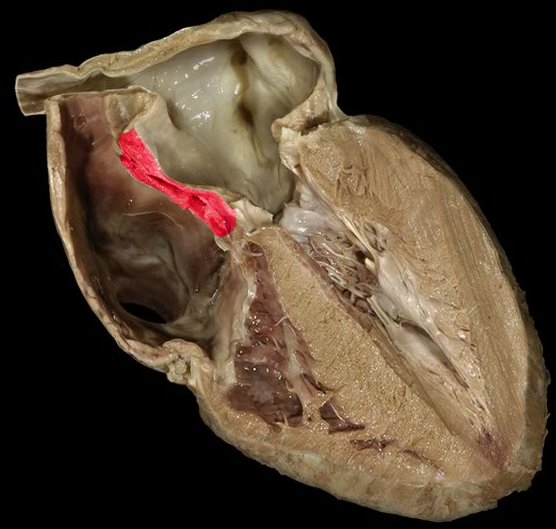
Interatrial septum
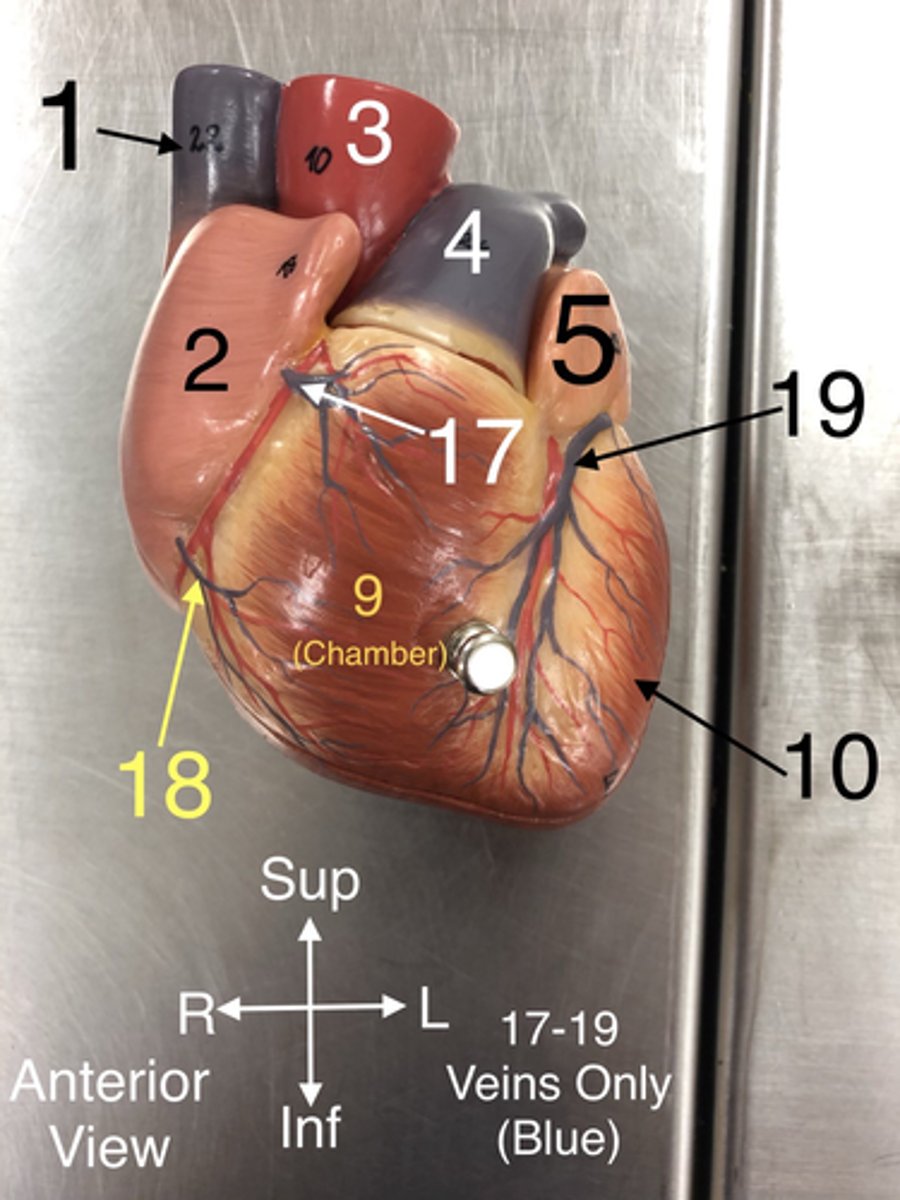
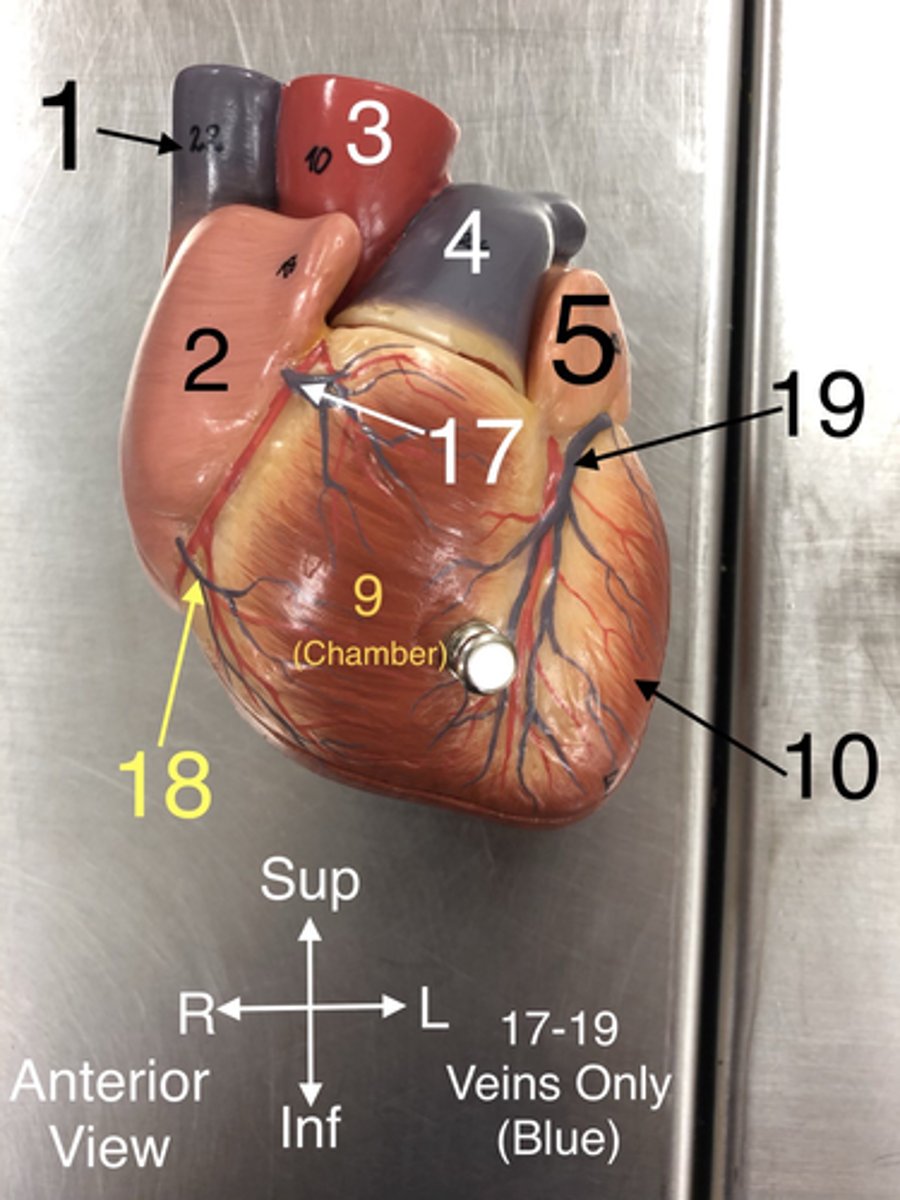
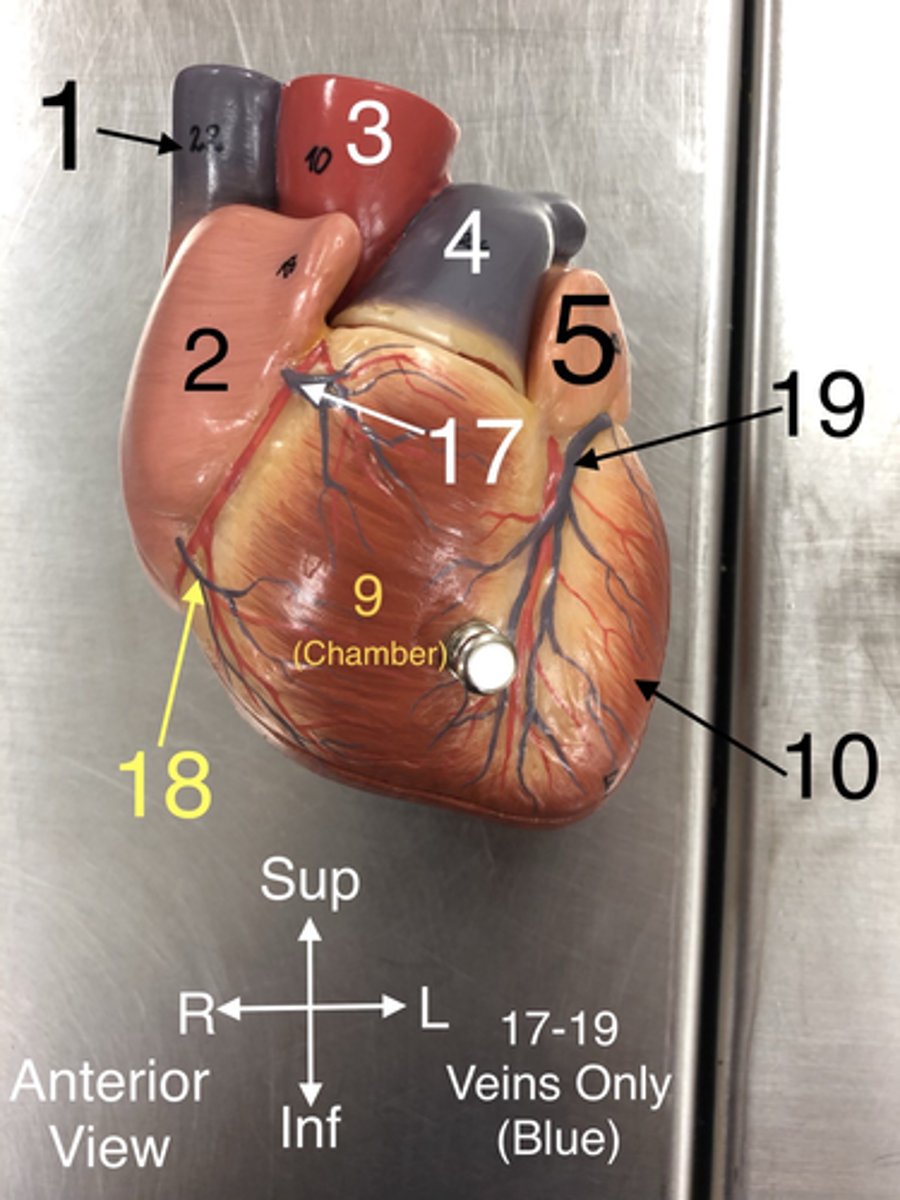
Superior Vena Cava
1. A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart
R Auricle
2.The right upper chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
Ascending Aorta
3.The part of the aorta that rises from the heart, carrying oxygenated blood to the body.
Pulmonary Trunk
4.The large vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
L Auricle
5. The left upper chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
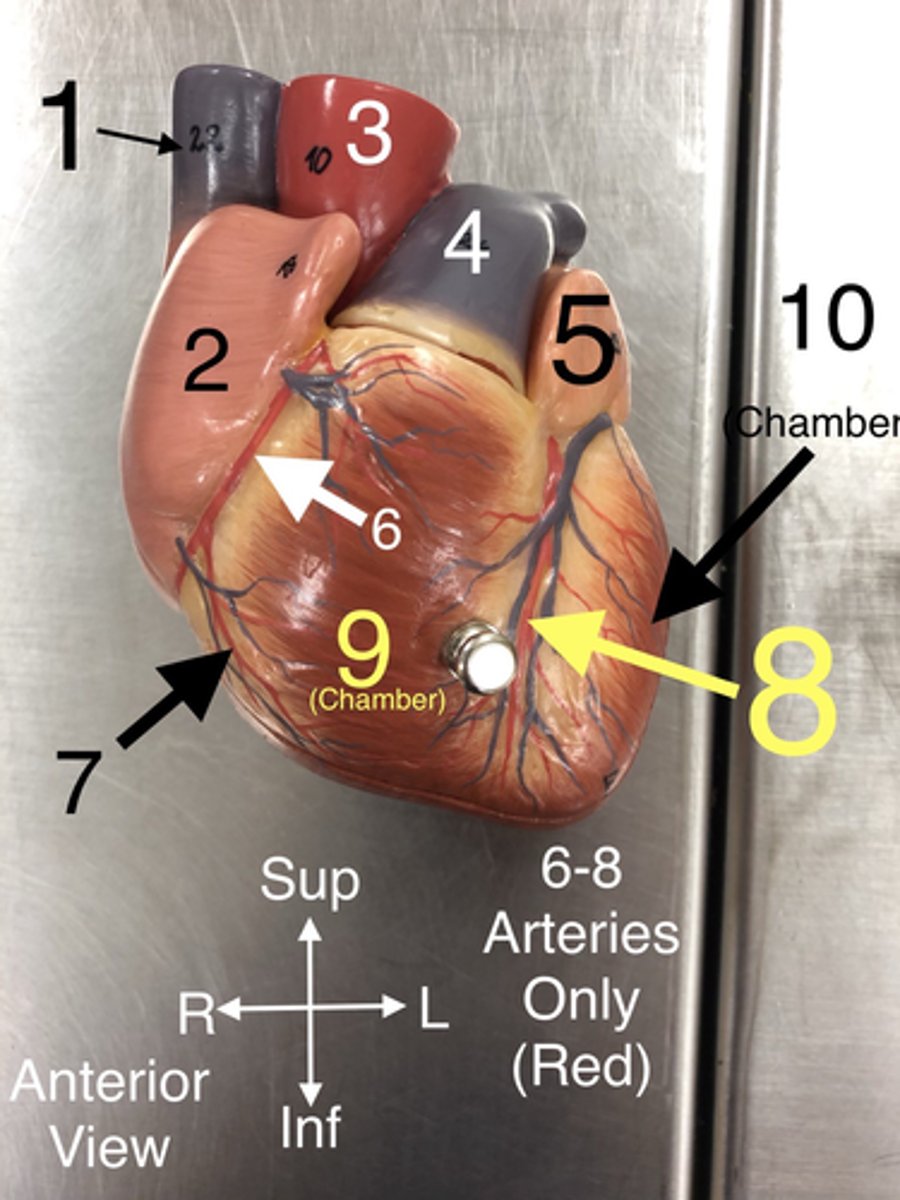
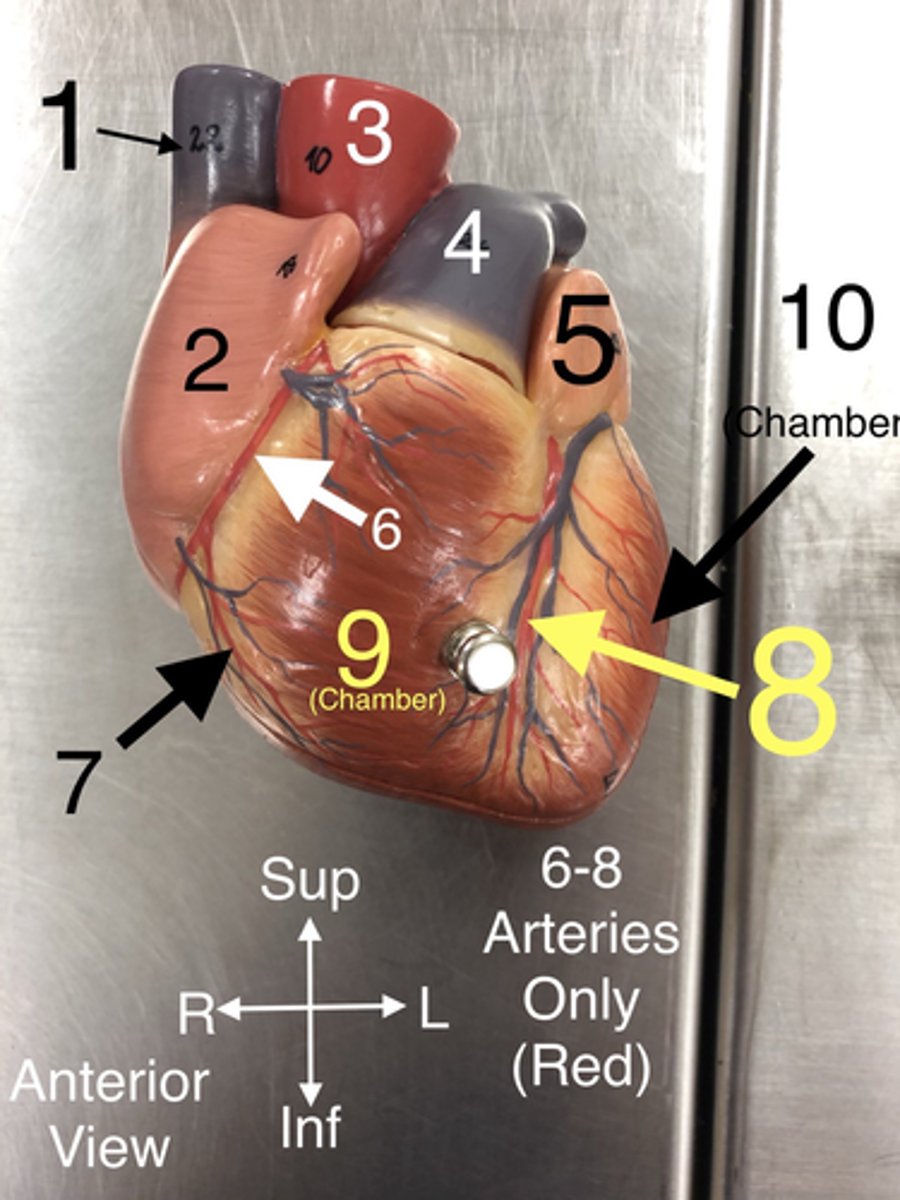
R Coronary a.
6.An artery that supplies blood to the heart muscle.
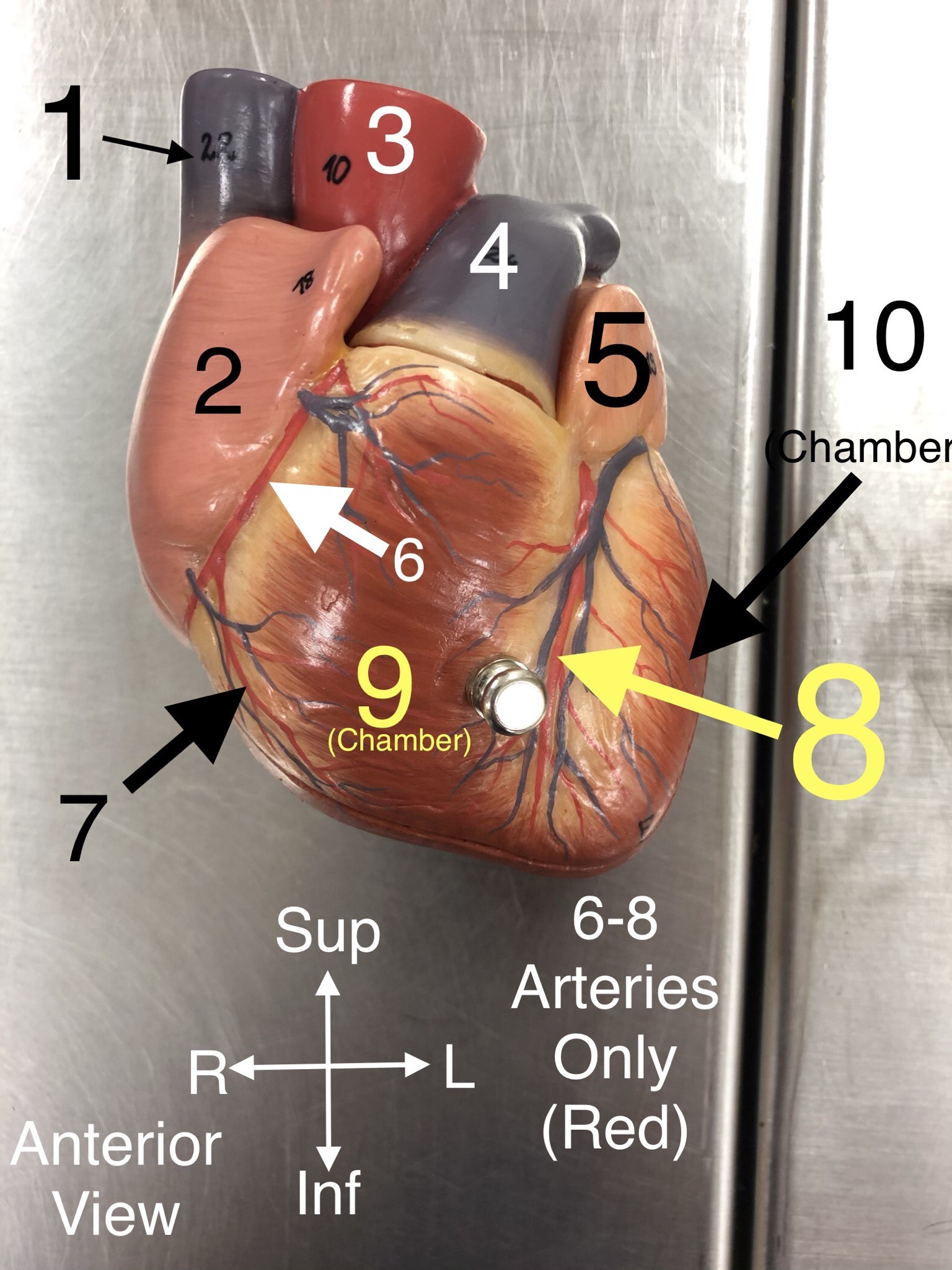
Right marginal branch of the right coronary artery
7. An artery that supplies blood to the right side of the colon.
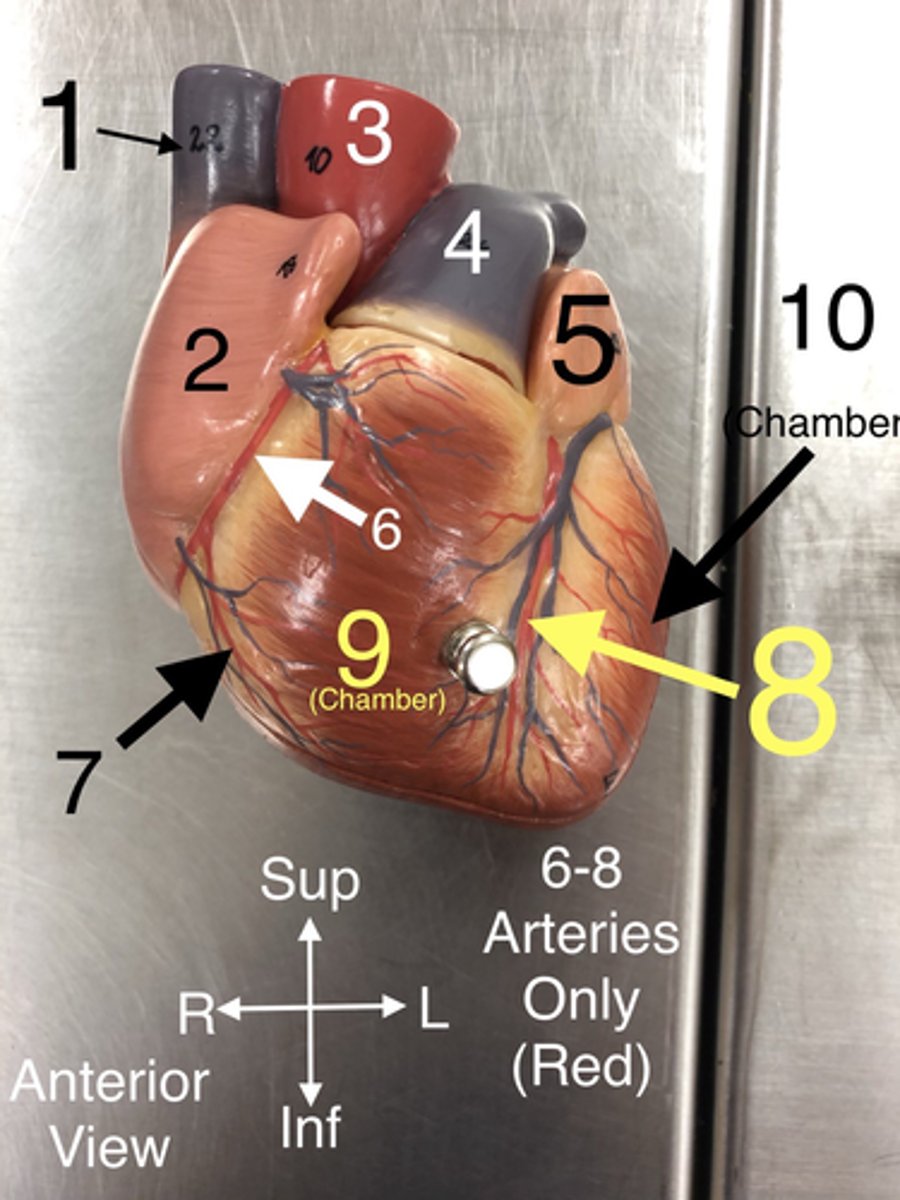
Anterior Interventricular branch of left coronary (L Anterior Descending) a.
8An artery that supplies blood to the anterior portion of the left ventricle and the interventricular septum.
R Ventricle
9. The right lower chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
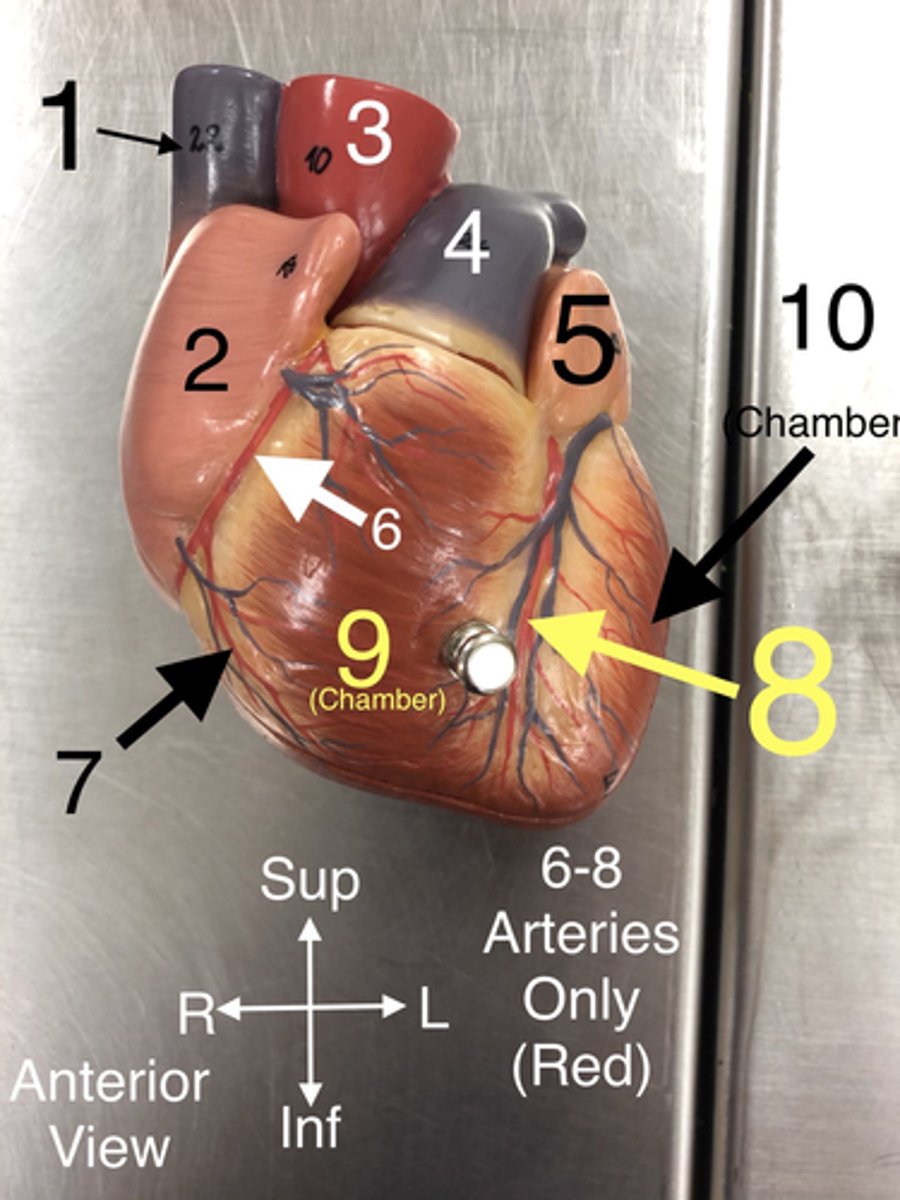
L Ventricle
10.The left lower chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
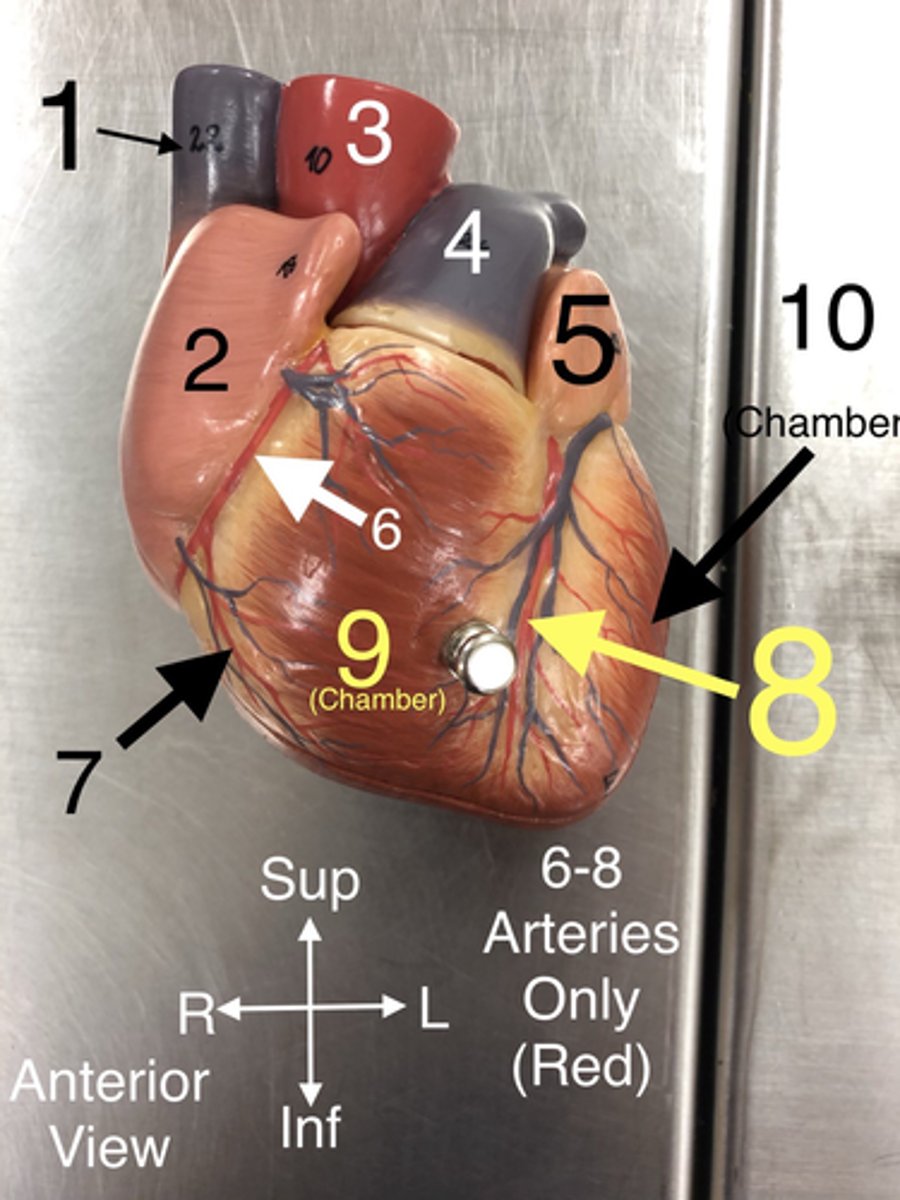
L Atrium
11.The left upper chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Circumflex a.
12.An artery that supplies blood to the heart muscle and branches from the left coronary artery.
Posterior Interventricular a.
13.An artery that supplies blood to the posterior portion of the heart.
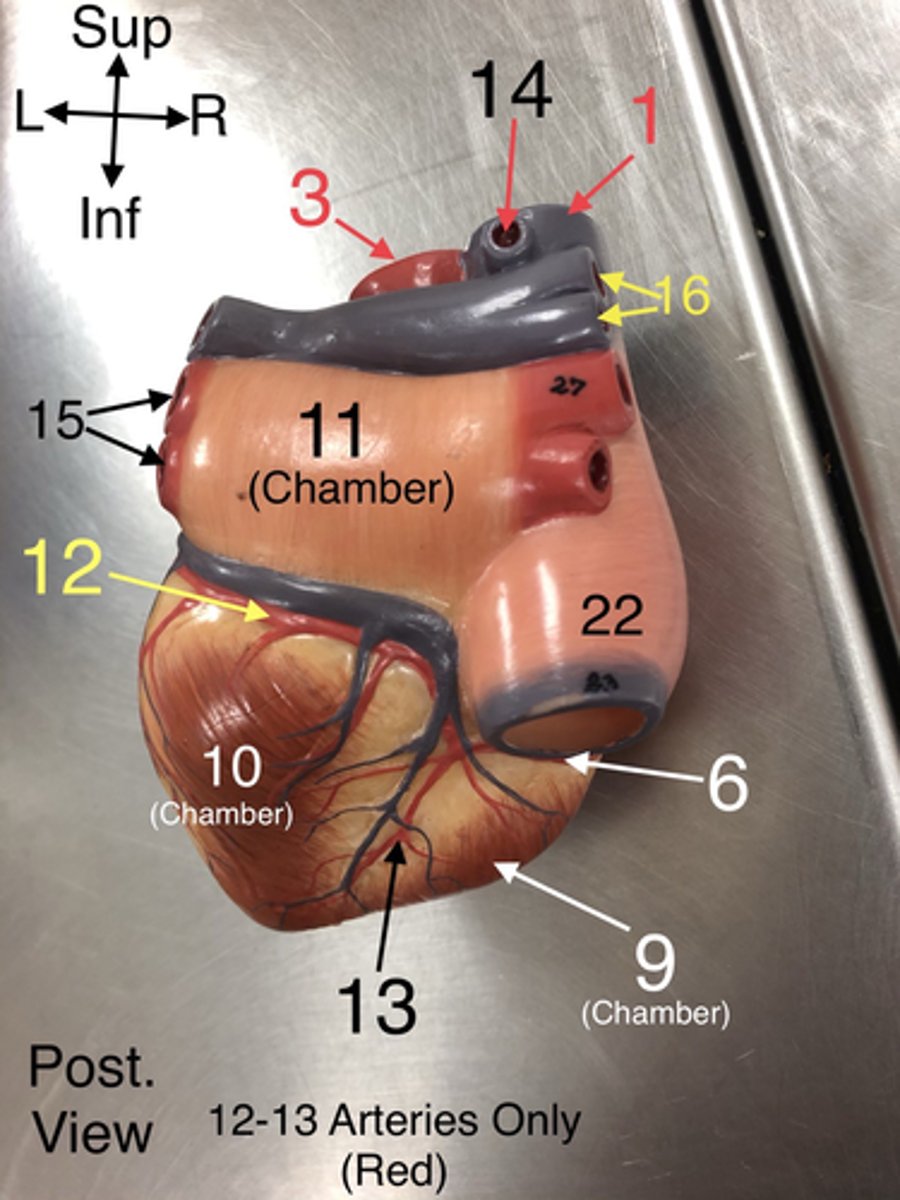
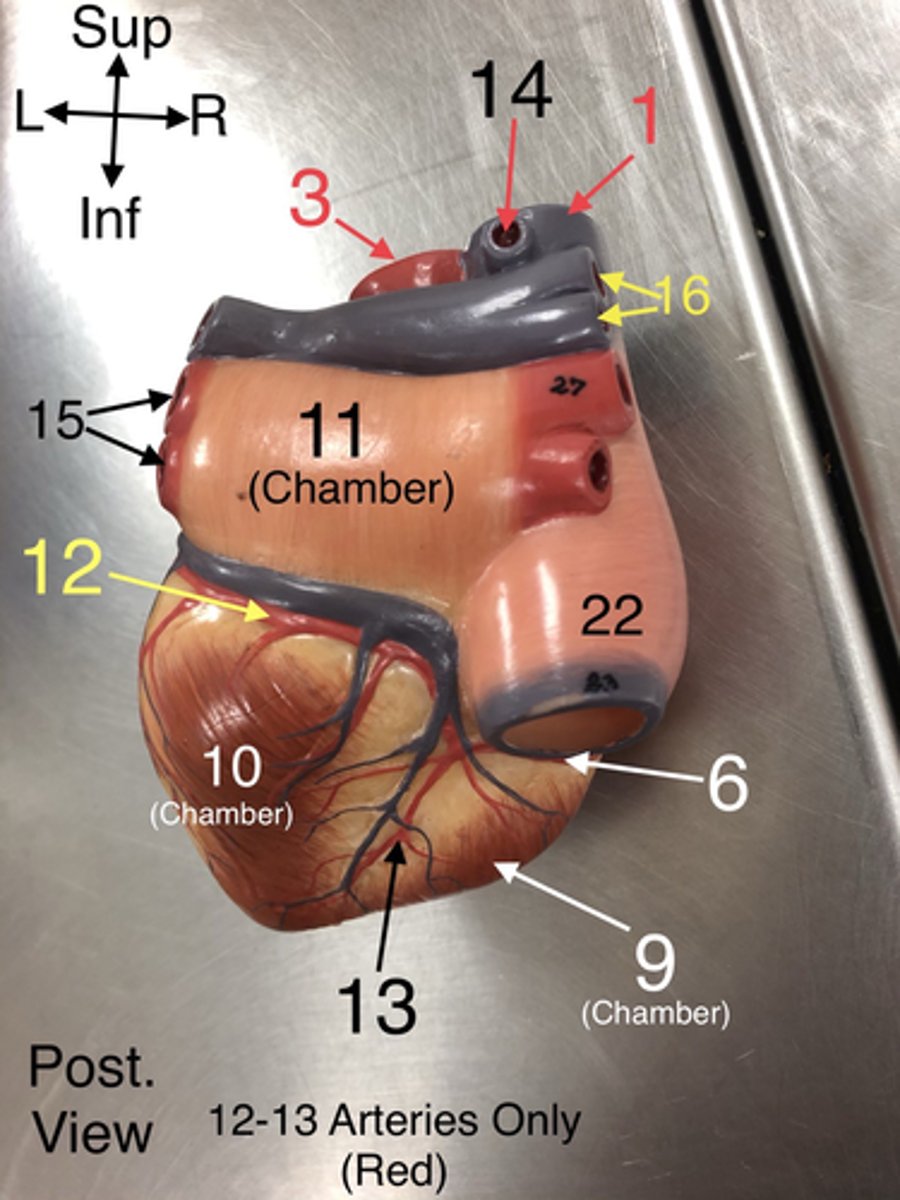
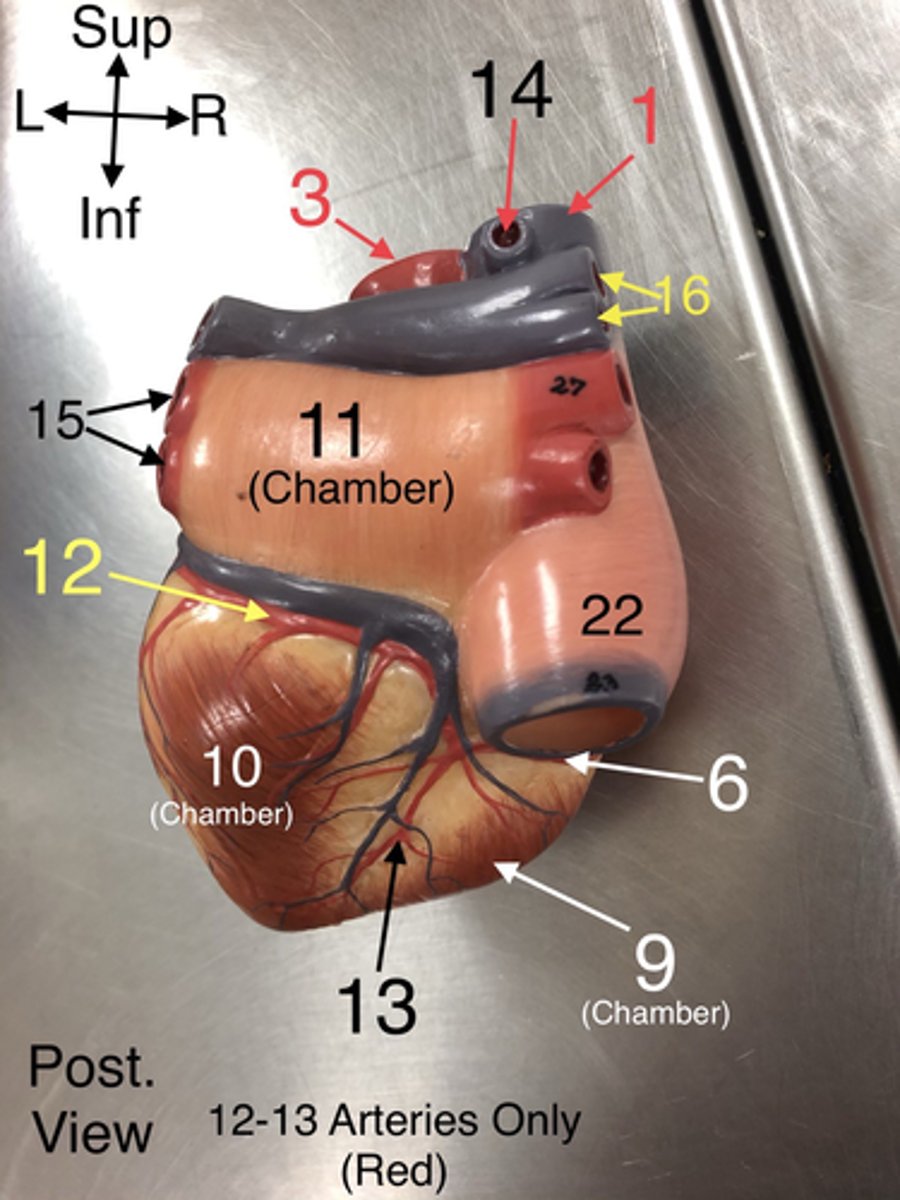
Azygos v.
14. A vein that drains blood from the thoracic wall and empties into the superior vena cava.
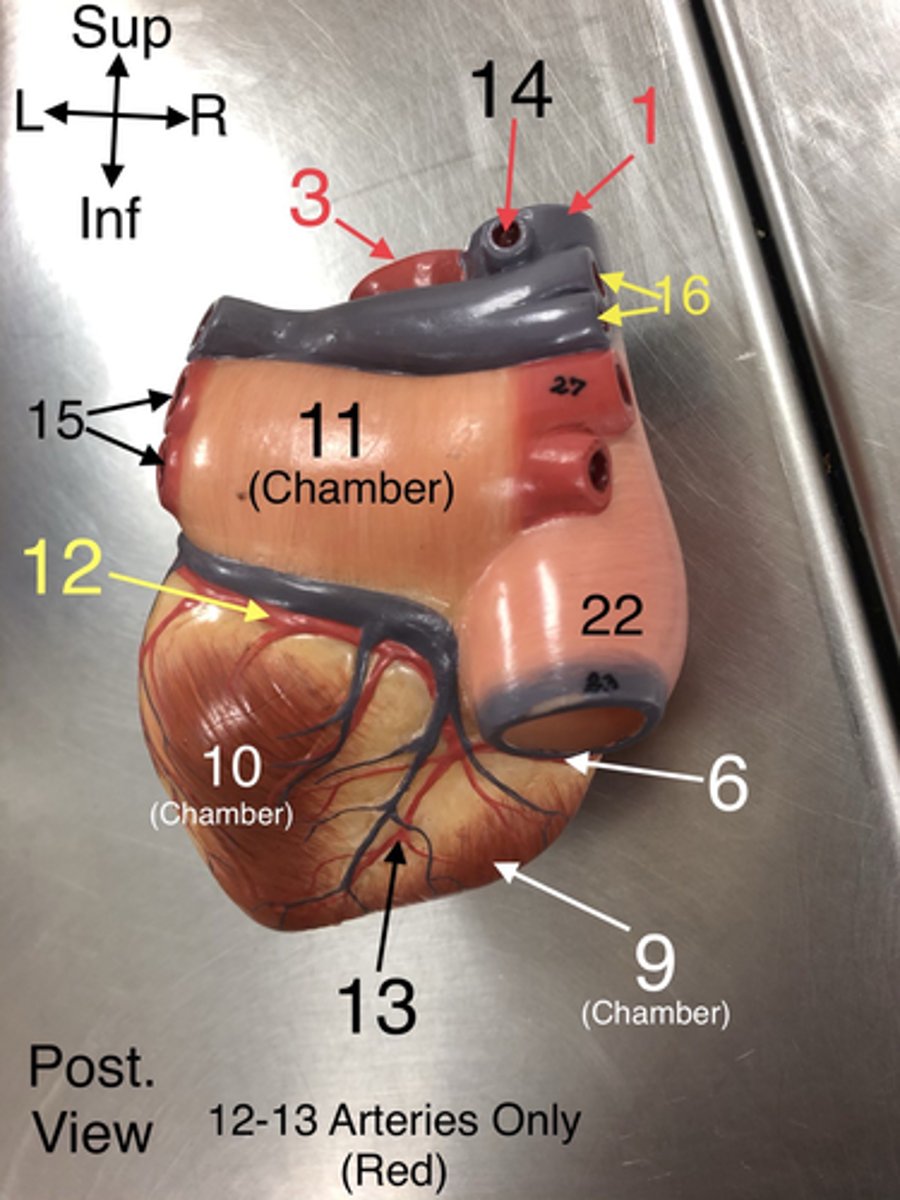
Pulmonary veins
15. Veins that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
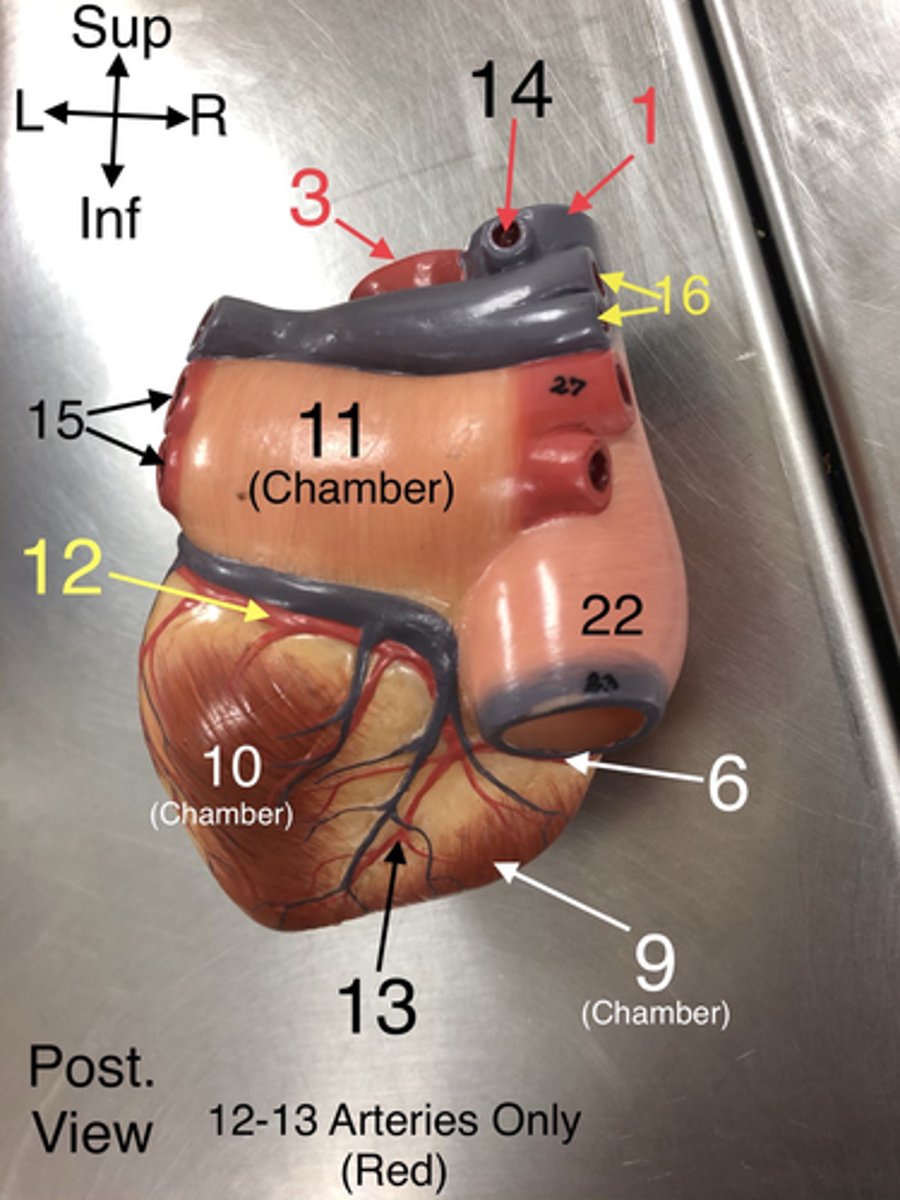
Pulmonary arteries
16. Arteries that carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
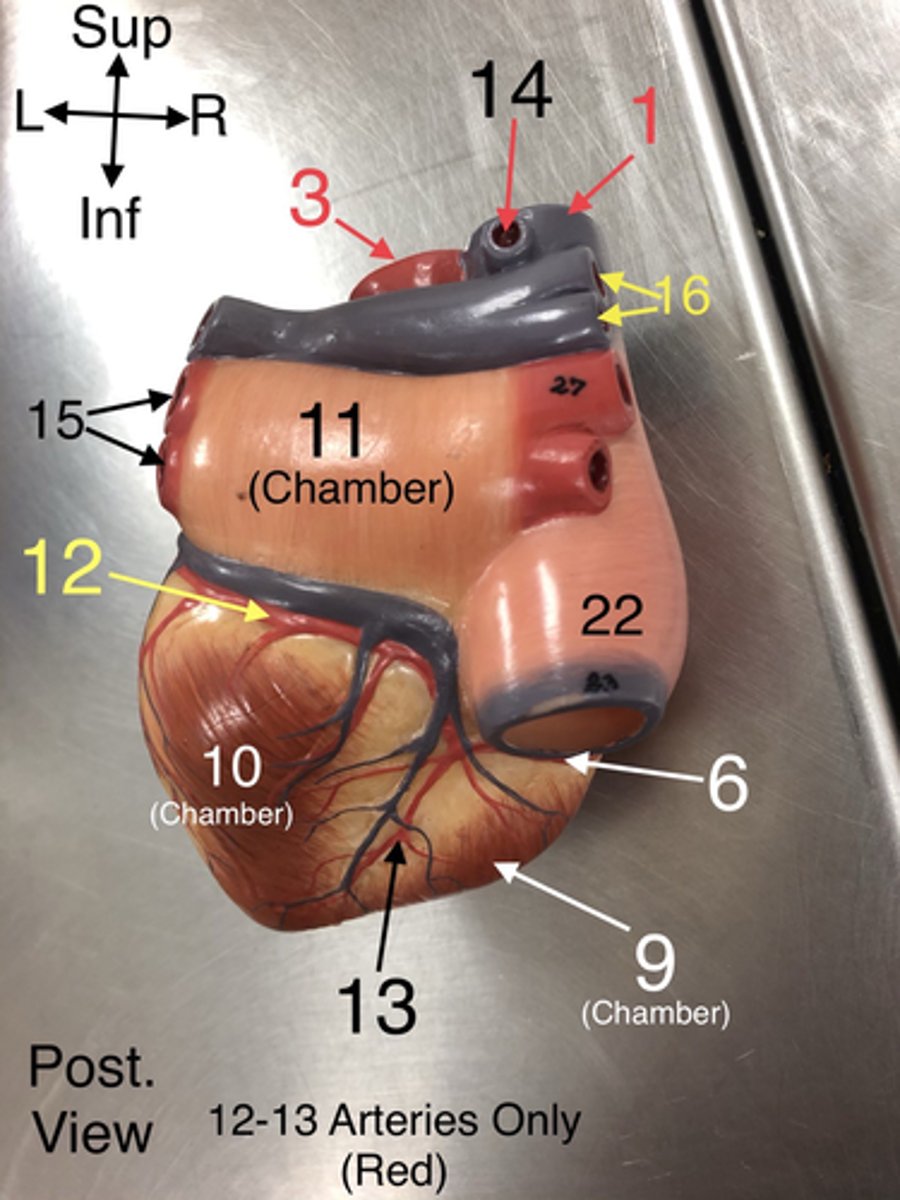
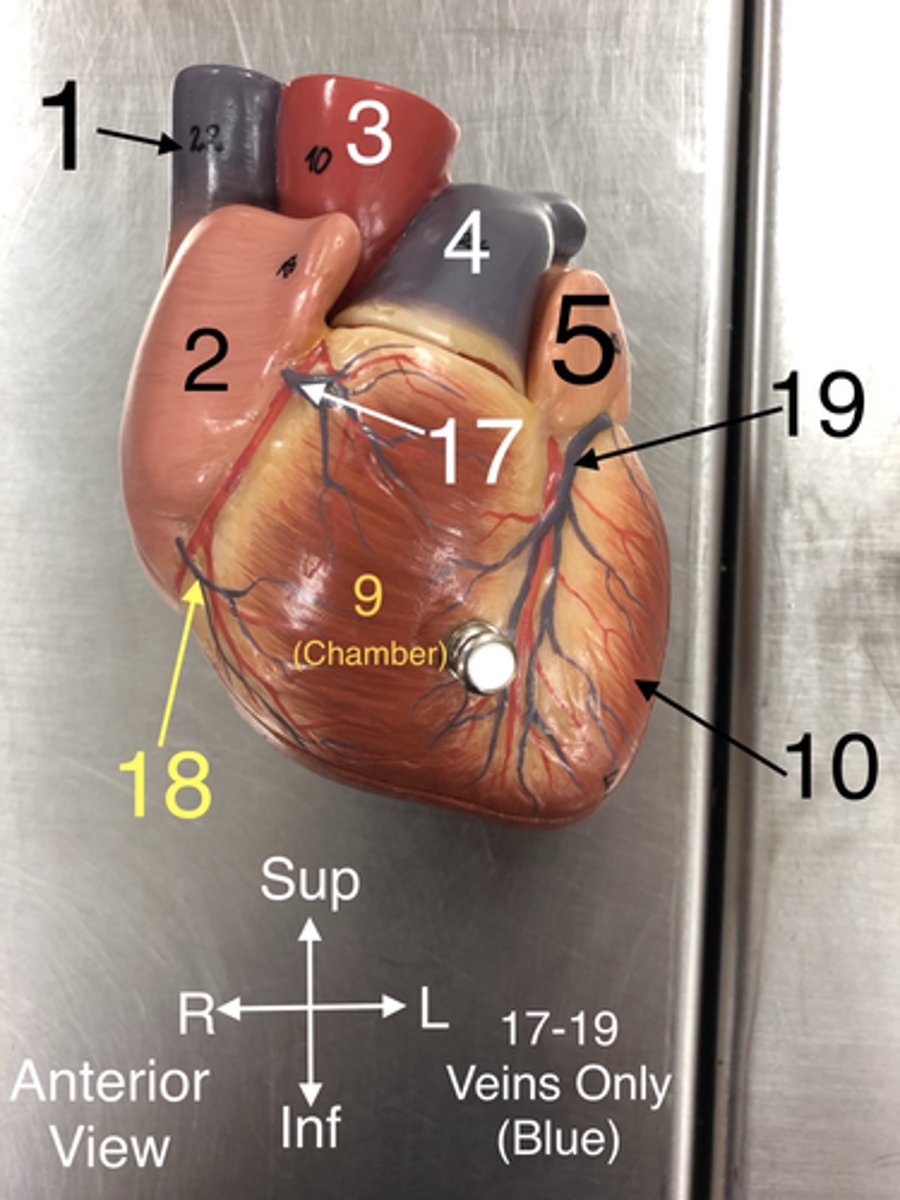
Anterior Cardiac veins
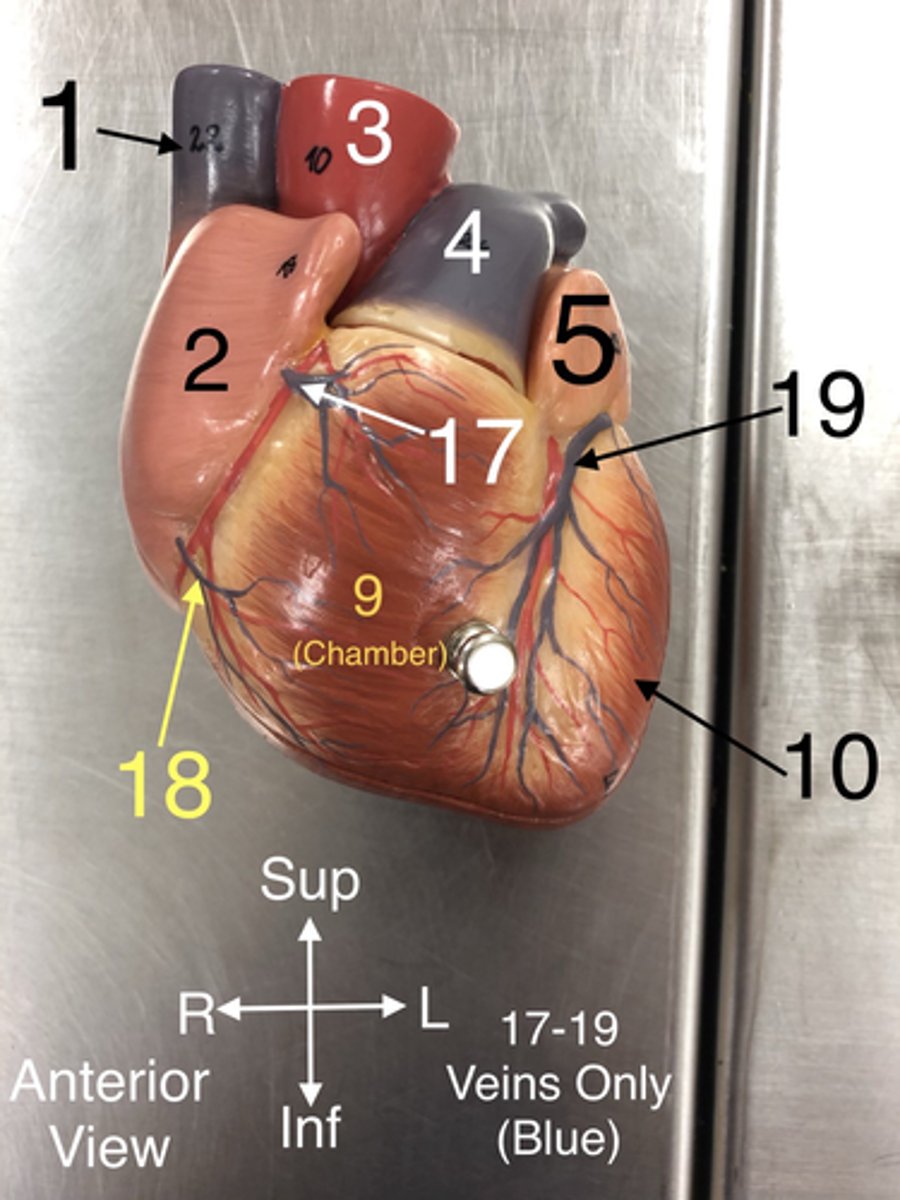
17. Veins that drain blood from the anterior part of the right ventricle into the right atrium.
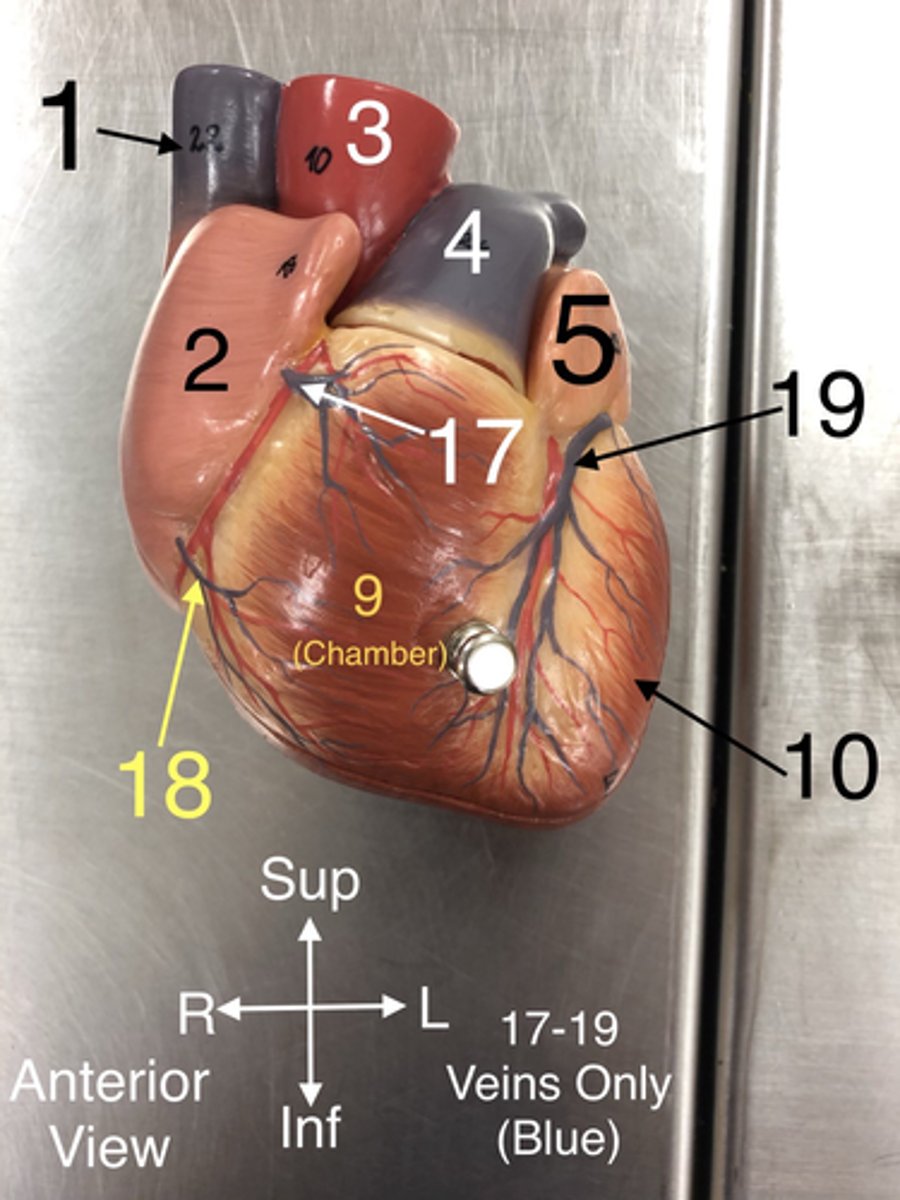
Small Cardiac v.
18.A vein that drains the right atrium and the right ventricle.
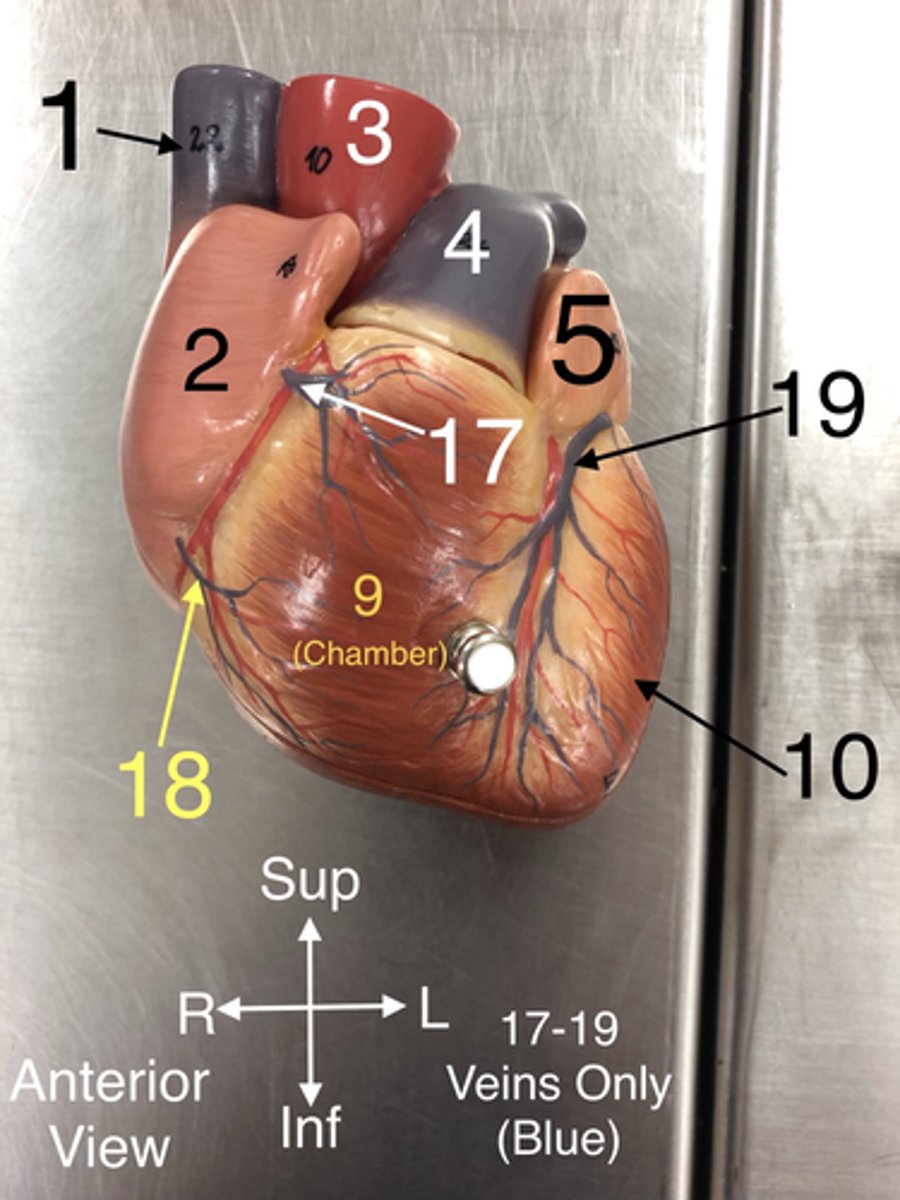
Great Cardiac v.
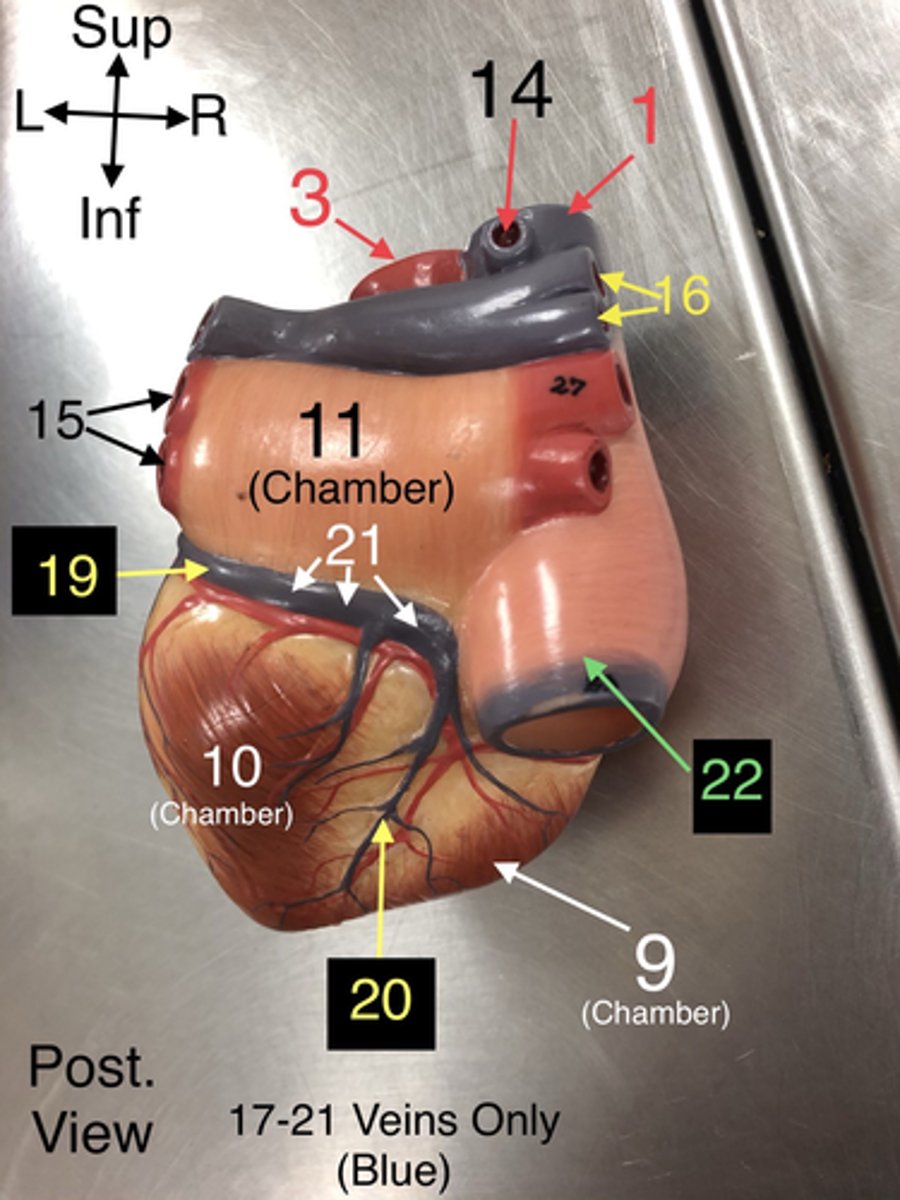
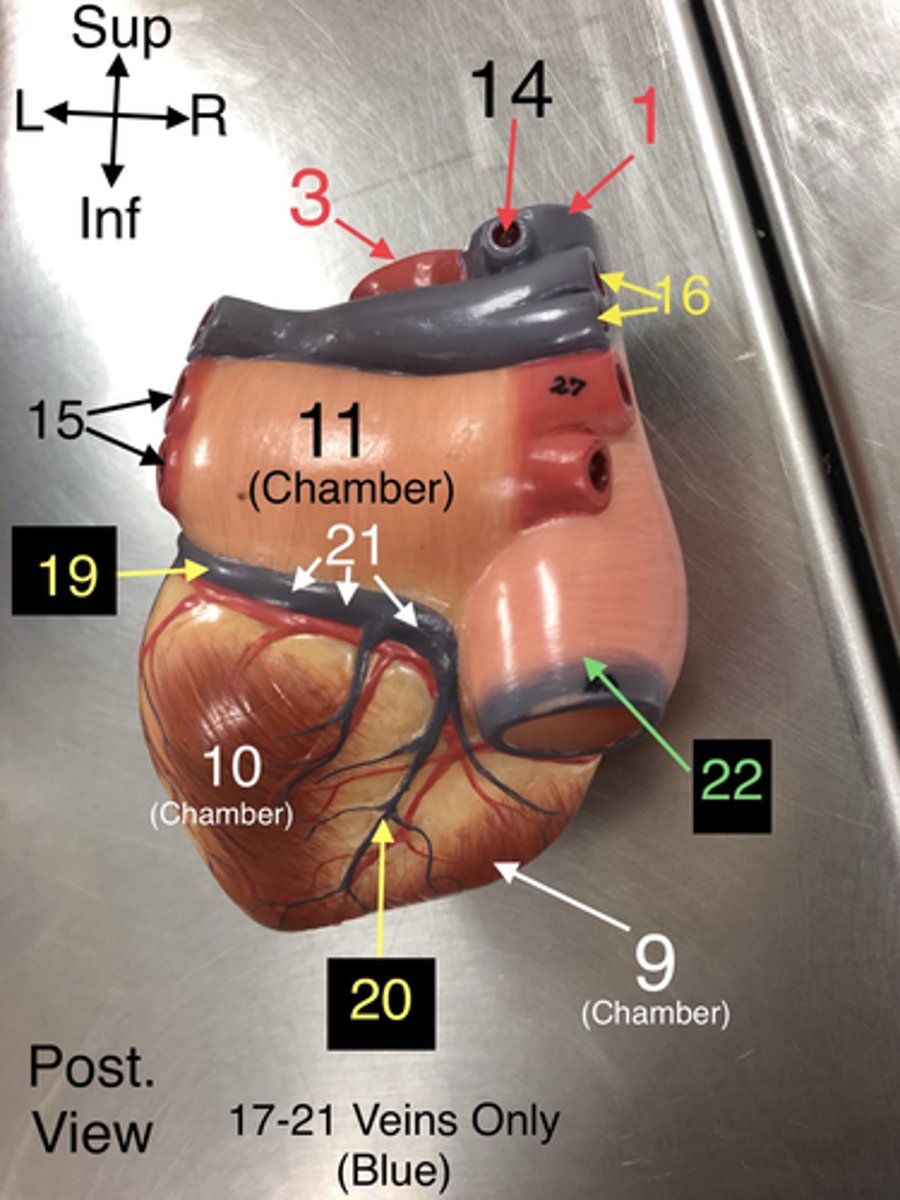
19.A vein that drains the left side of the heart.
Middle Cardiac v.
20.A vein that drains the right ventricle and the interventricular septum.
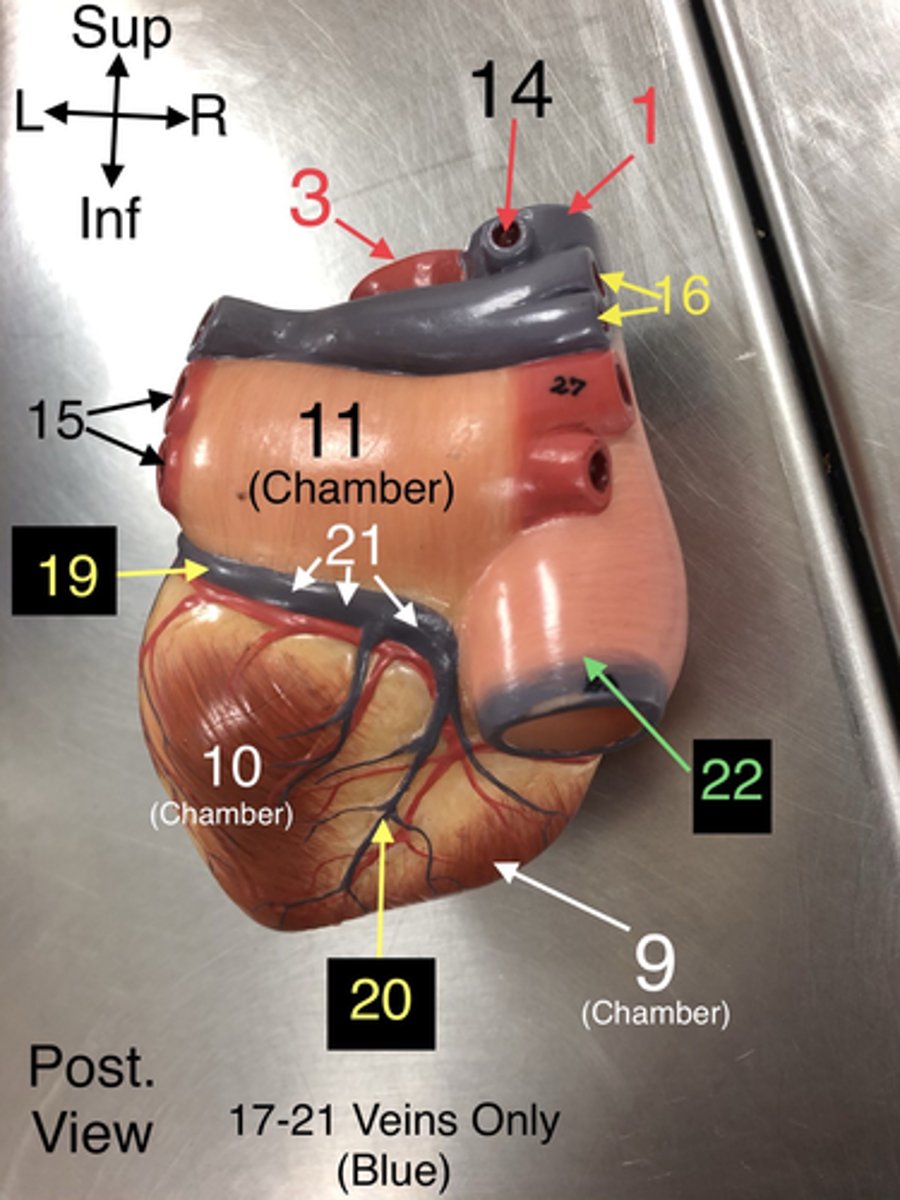
Coronary Sinus
21. A large vein that collects deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle and drains into the right atrium.
Inferior Vena Cava
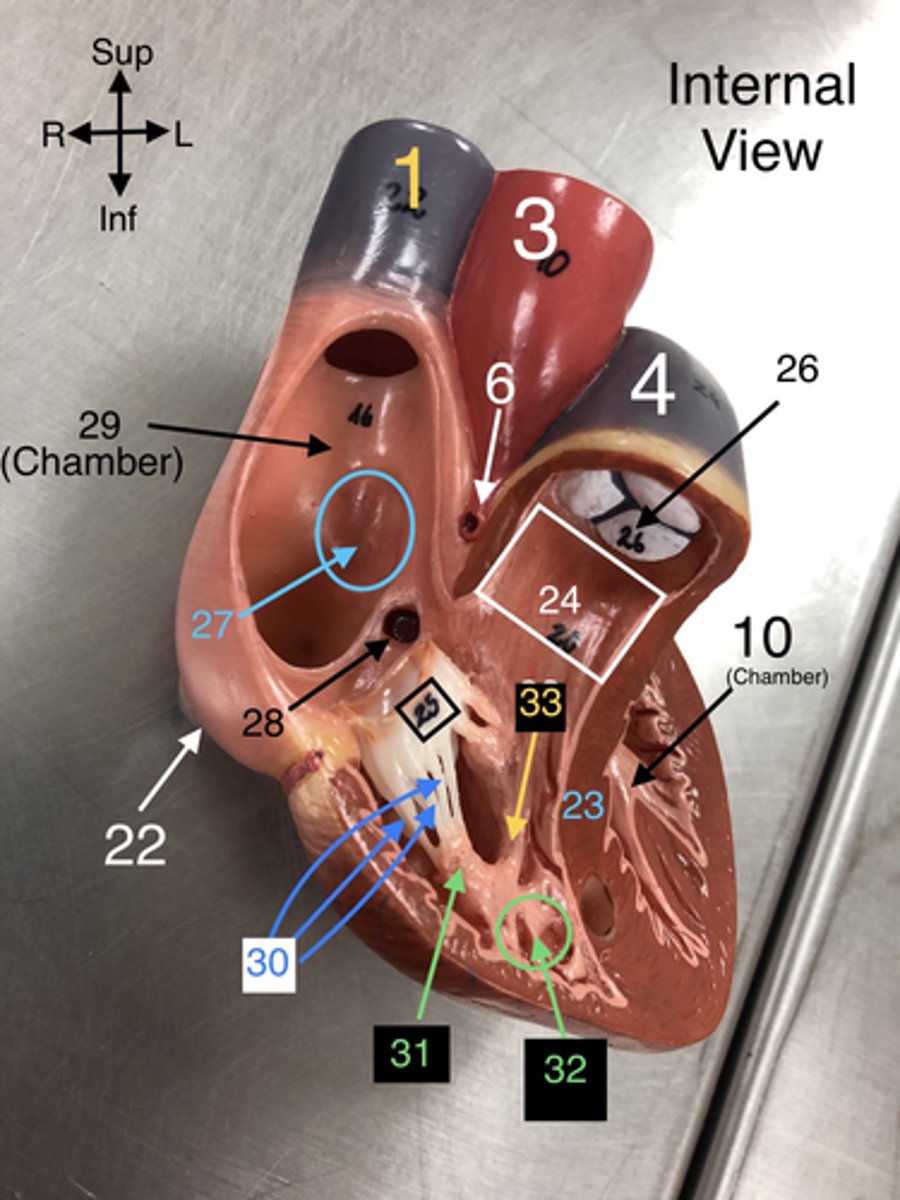
22. A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium.
Interventricular Septum
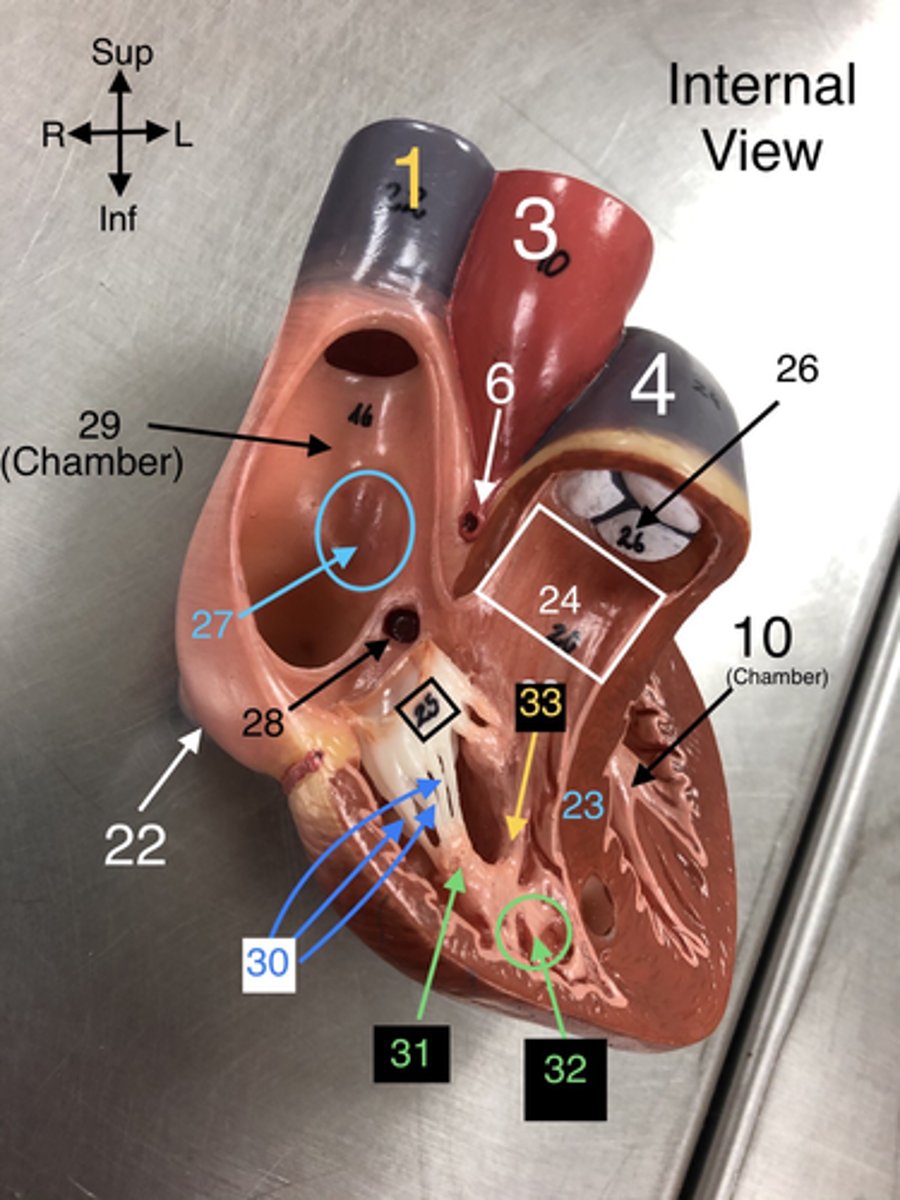
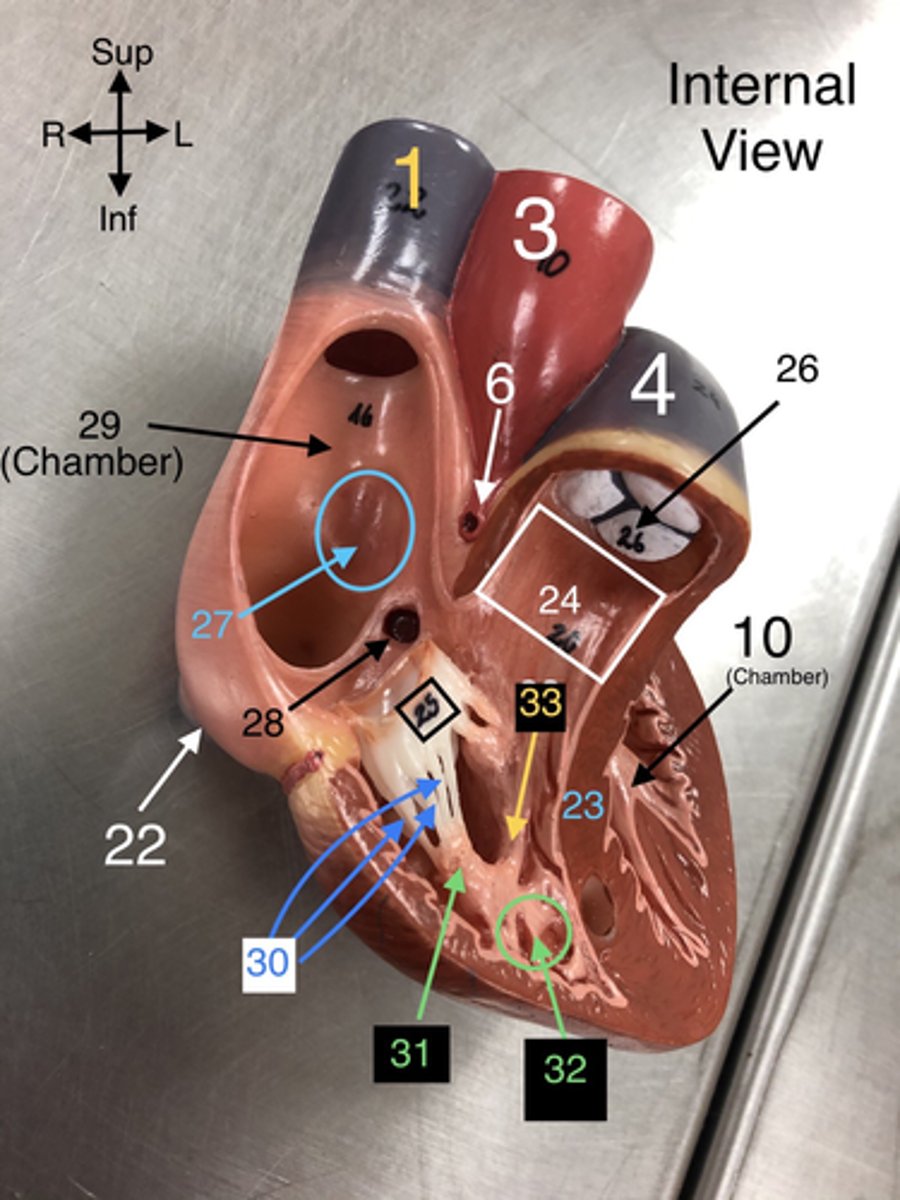
23. The wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart.
Conus Arteriosus (internal view)
24. The outflow tract from the right ventricle leading to the pulmonary trunk.
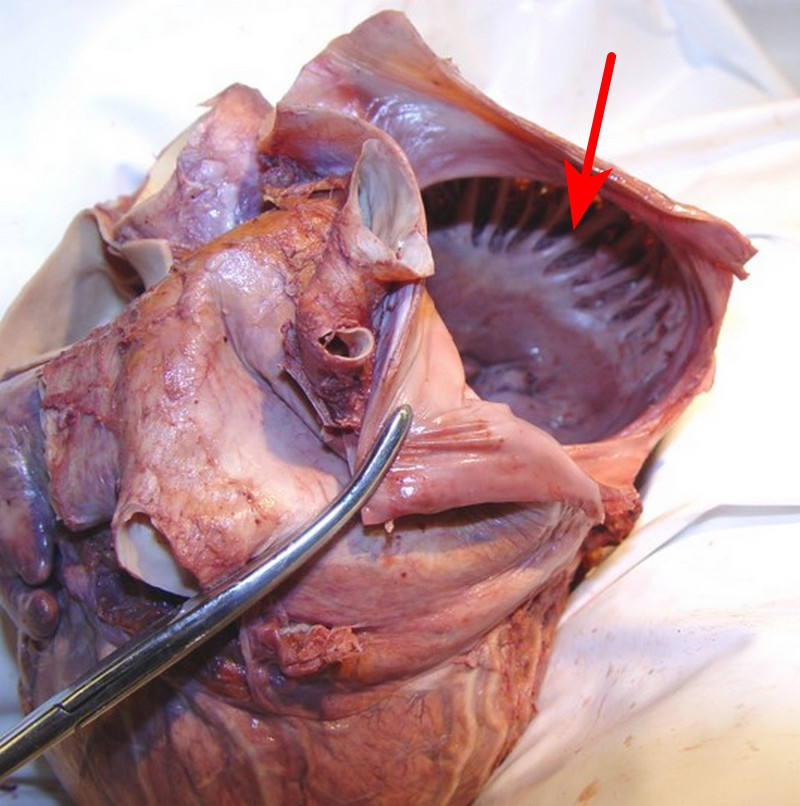
Tricuspid valve
25. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle that prevents backflow.
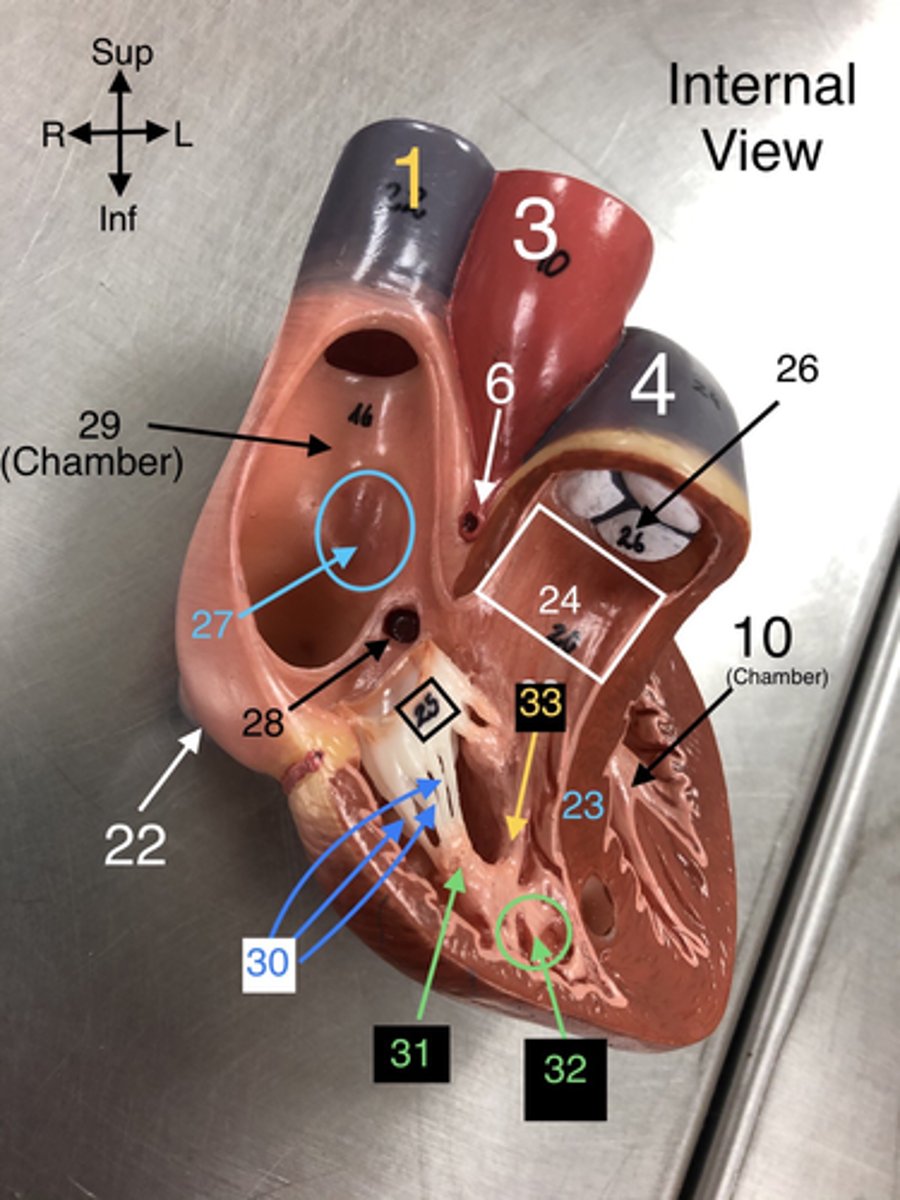
Pulmonary Semilunar valve
26. The valve that prevents backflow from the pulmonary trunk into the right ventricle.
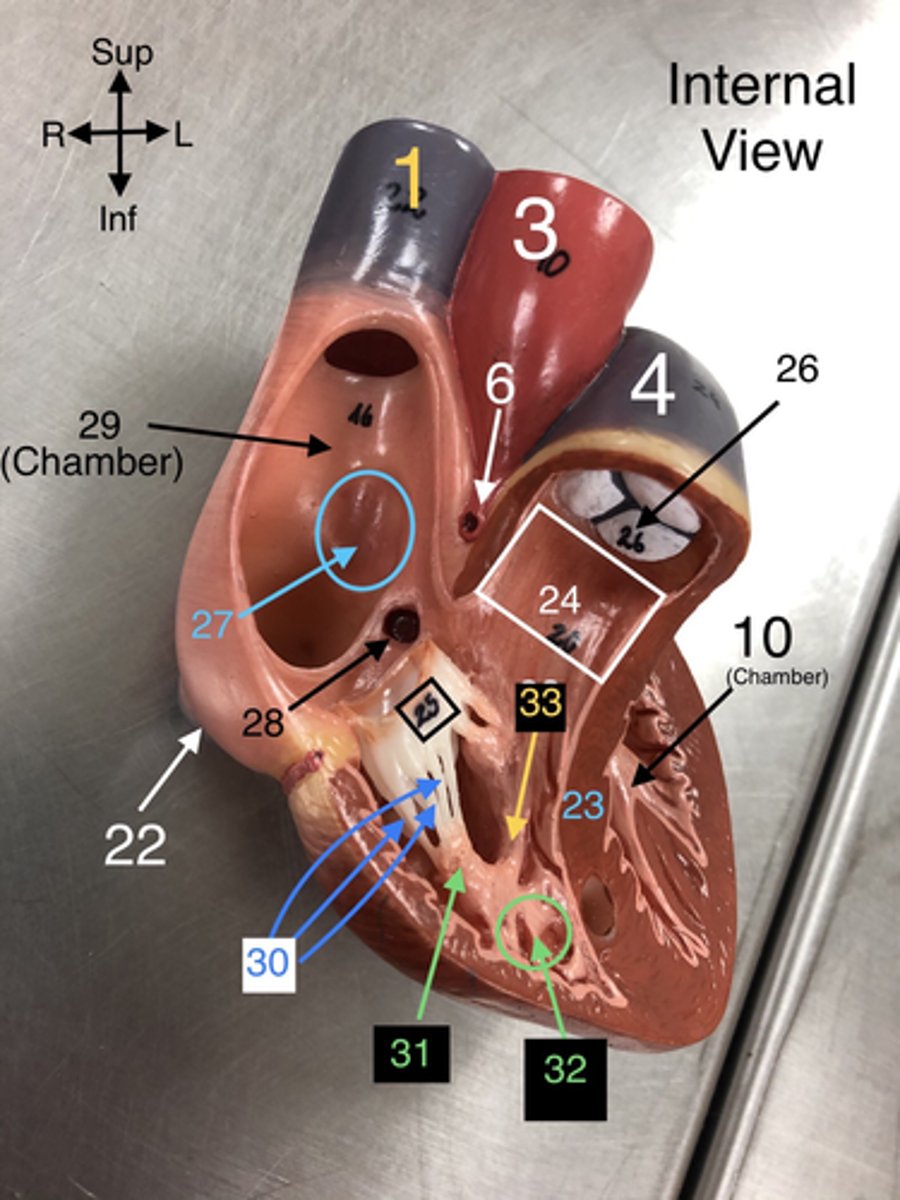
Fossa Ovalis
27. A depression in the right atrium that is a remnant of the foramen ovale from fetal development.
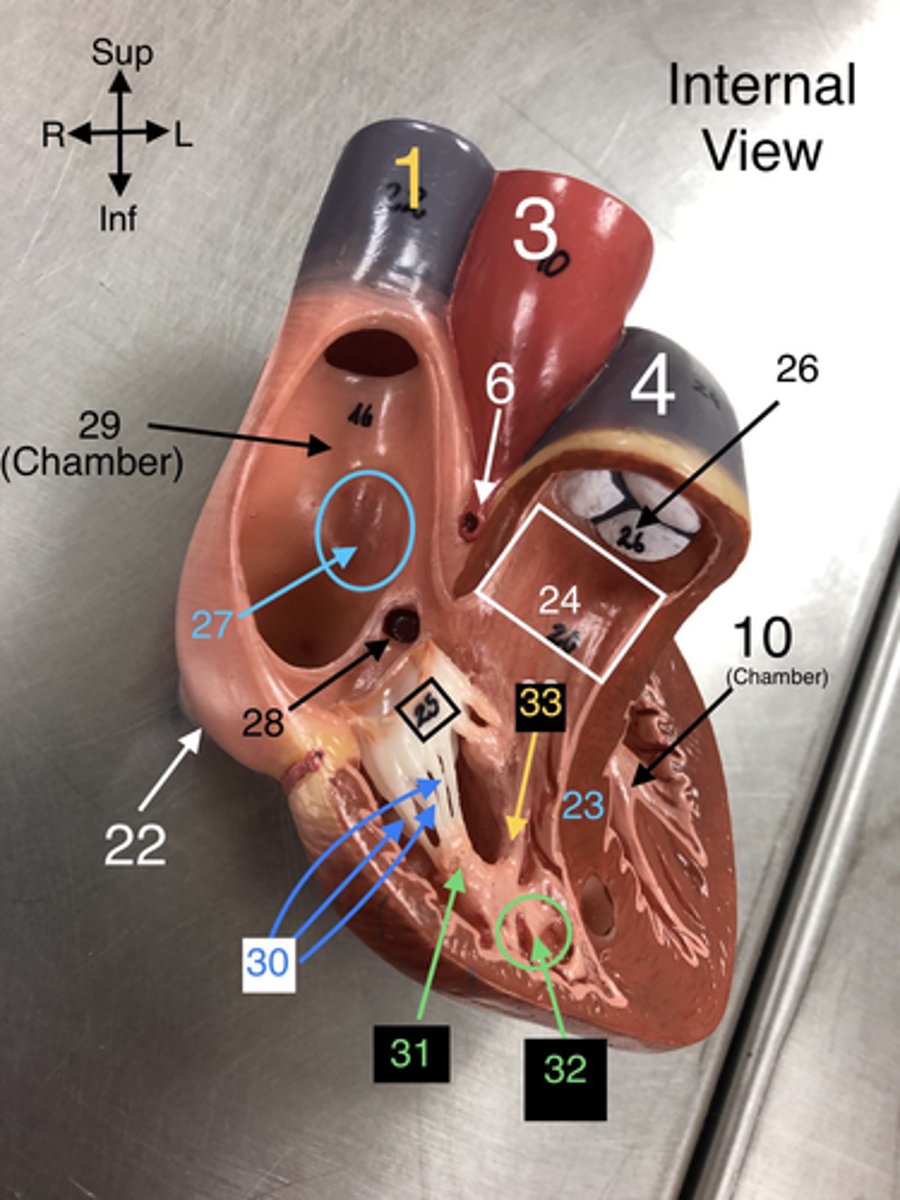
Coronary Sinus Orifice
28. The opening through which the coronary sinus drains into the right atrium.
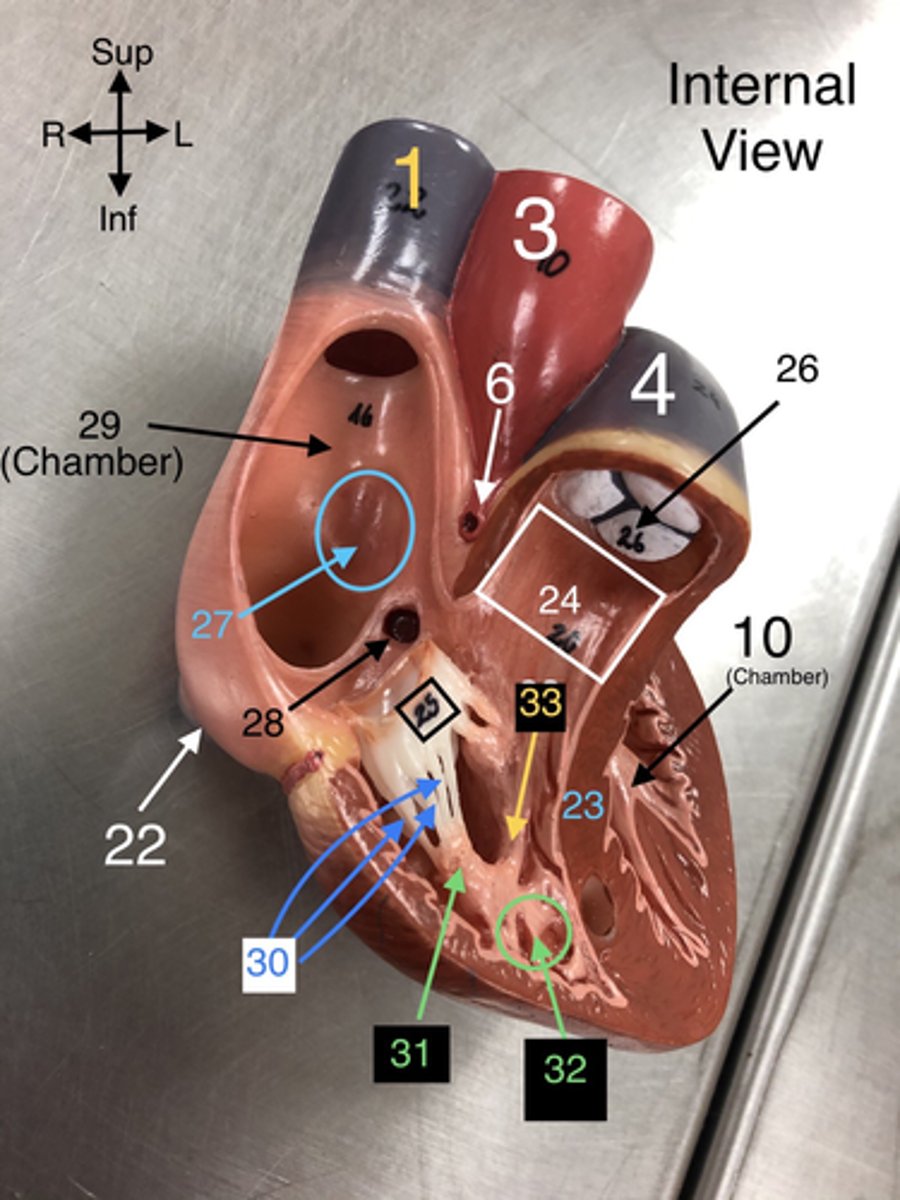
R Atrium
29. The right upper chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
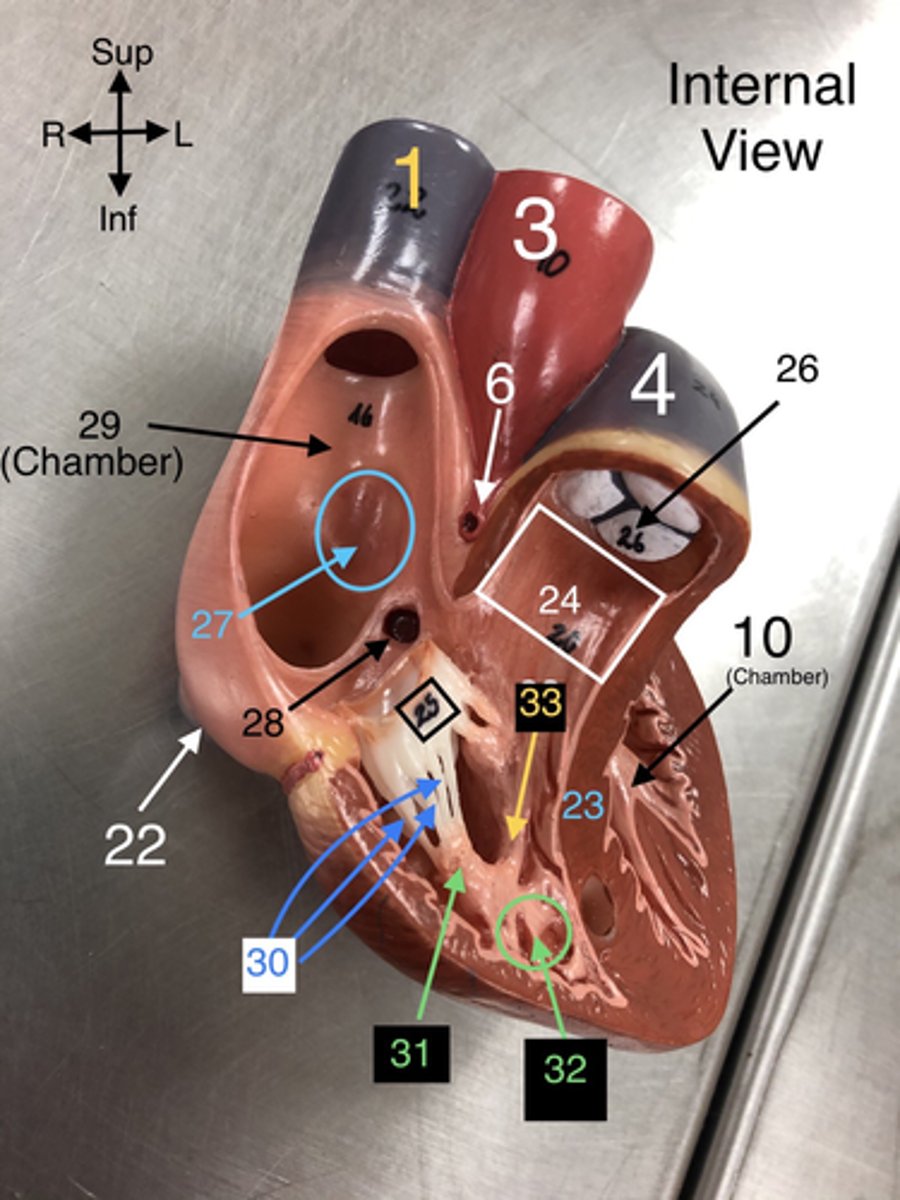
Chordae Tendineae
30. Fibrous cords that anchor the atrioventricular valves to papillary muscles in the ventricles.
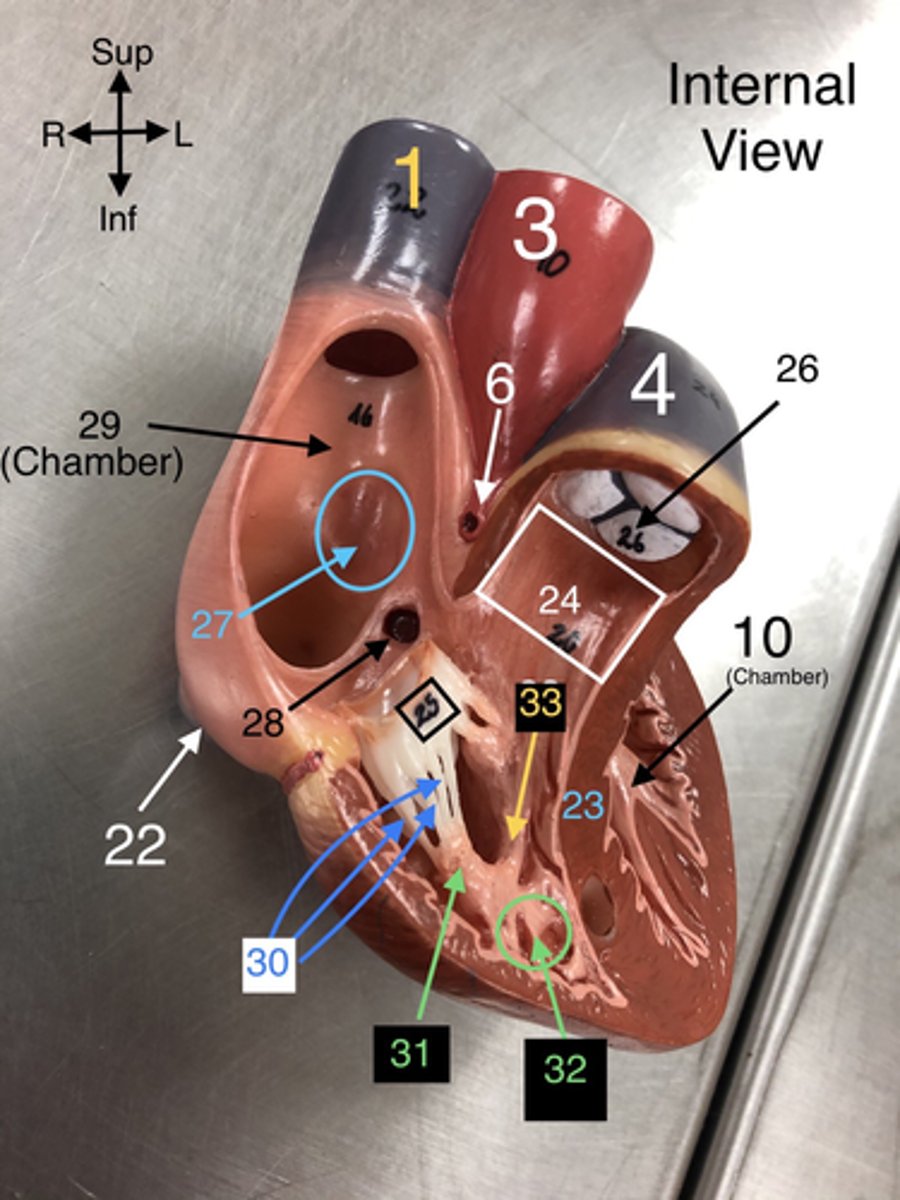
Papillary m.
31. Muscles located in the ventricles that contract to prevent backflow of blood through the valves.
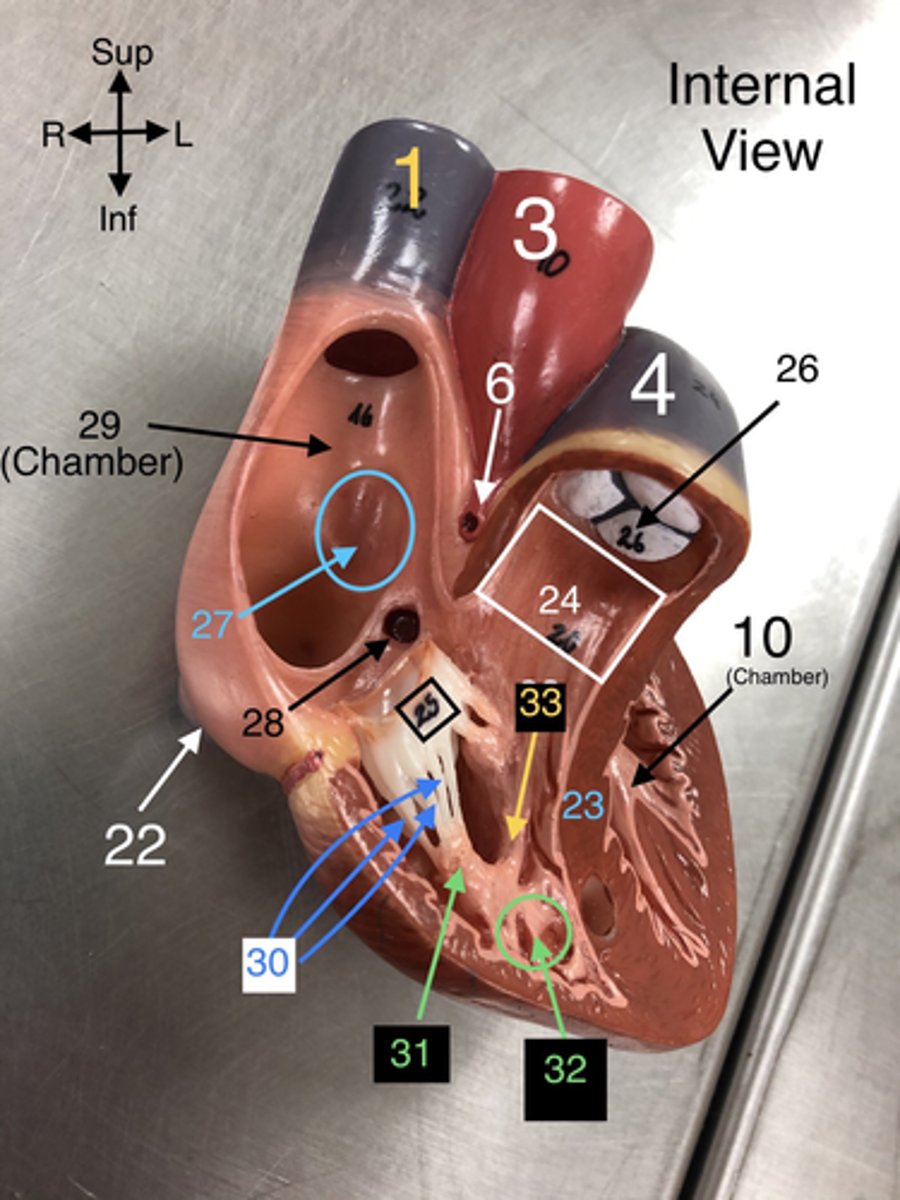
Trabeculae carneae
32. Muscular ridges on the internal surface of the ventricles.
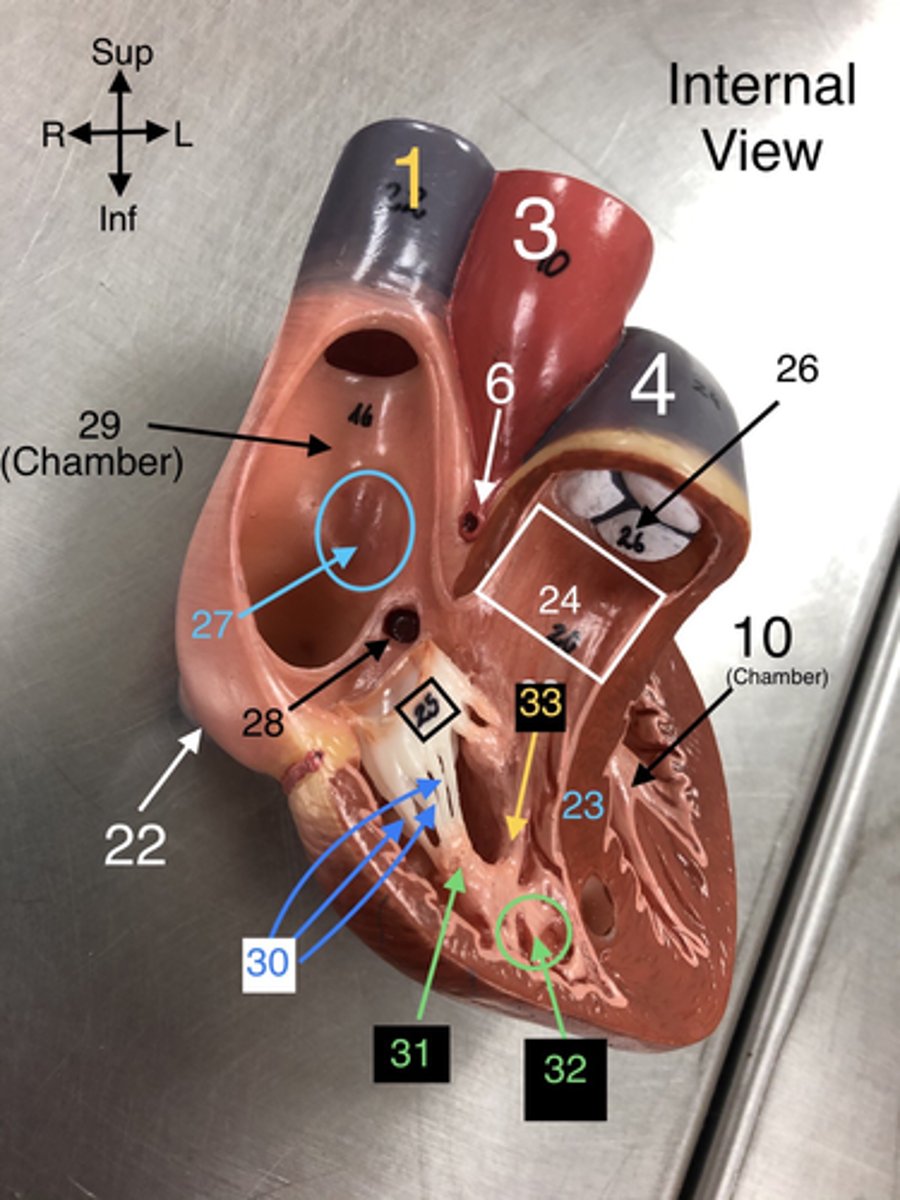
Moderator Band
33.A band of cardiac muscle found in the right ventricle that carries part of the conduction system.
L Coronary a.
34.An artery that supplies blood to the left side of the heart.
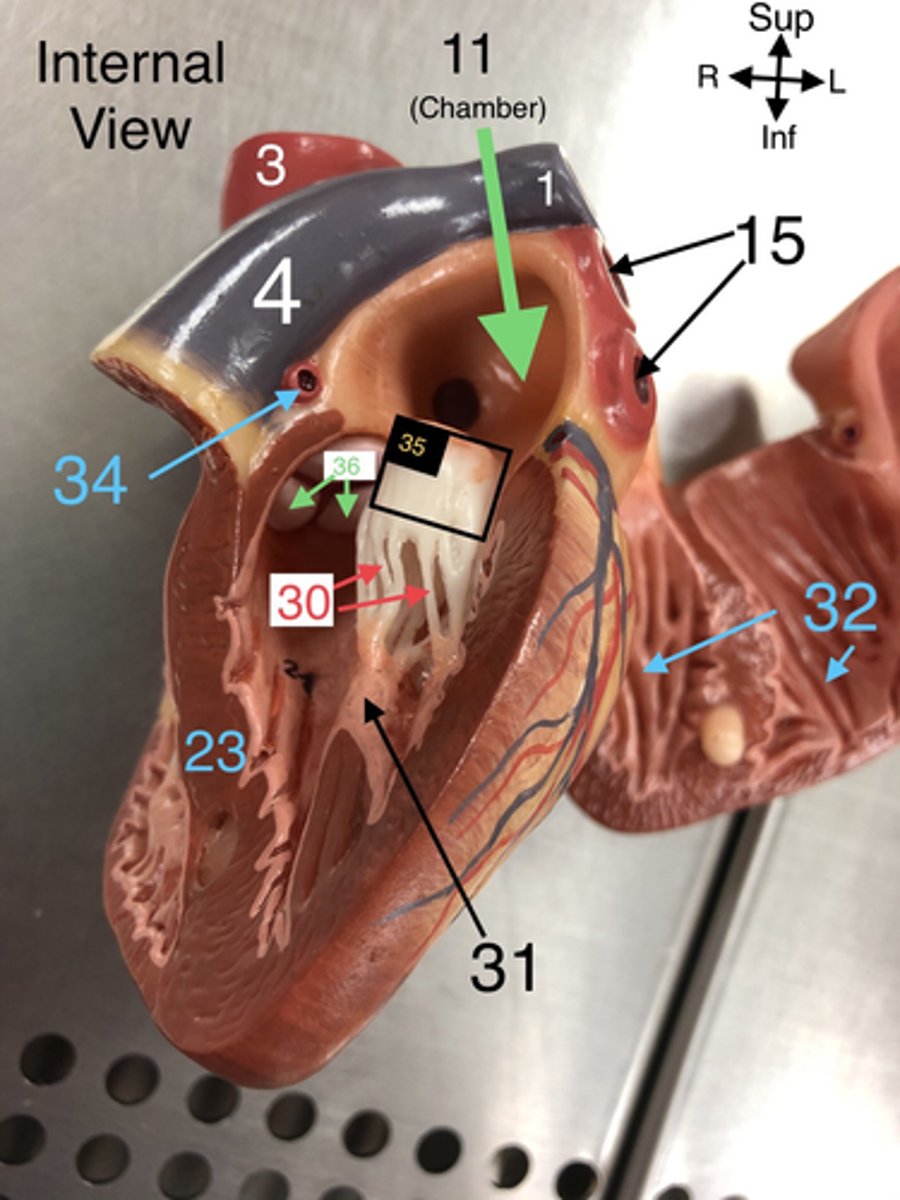
Bicuspid (Mitral) valve
35.The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle that prevents backflow.
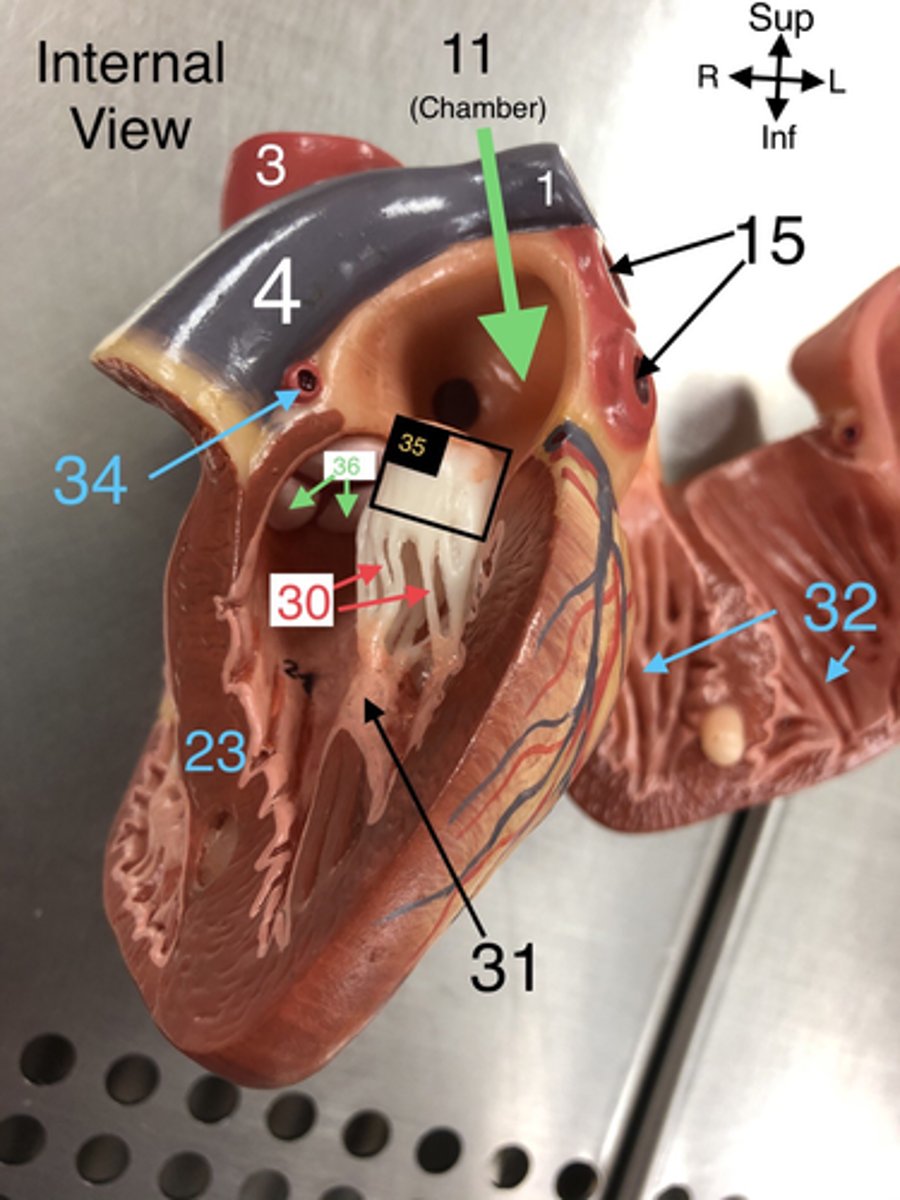
Aortic Semilunar valve
36. The valve that prevents backflow from the aorta into the left ventricle.
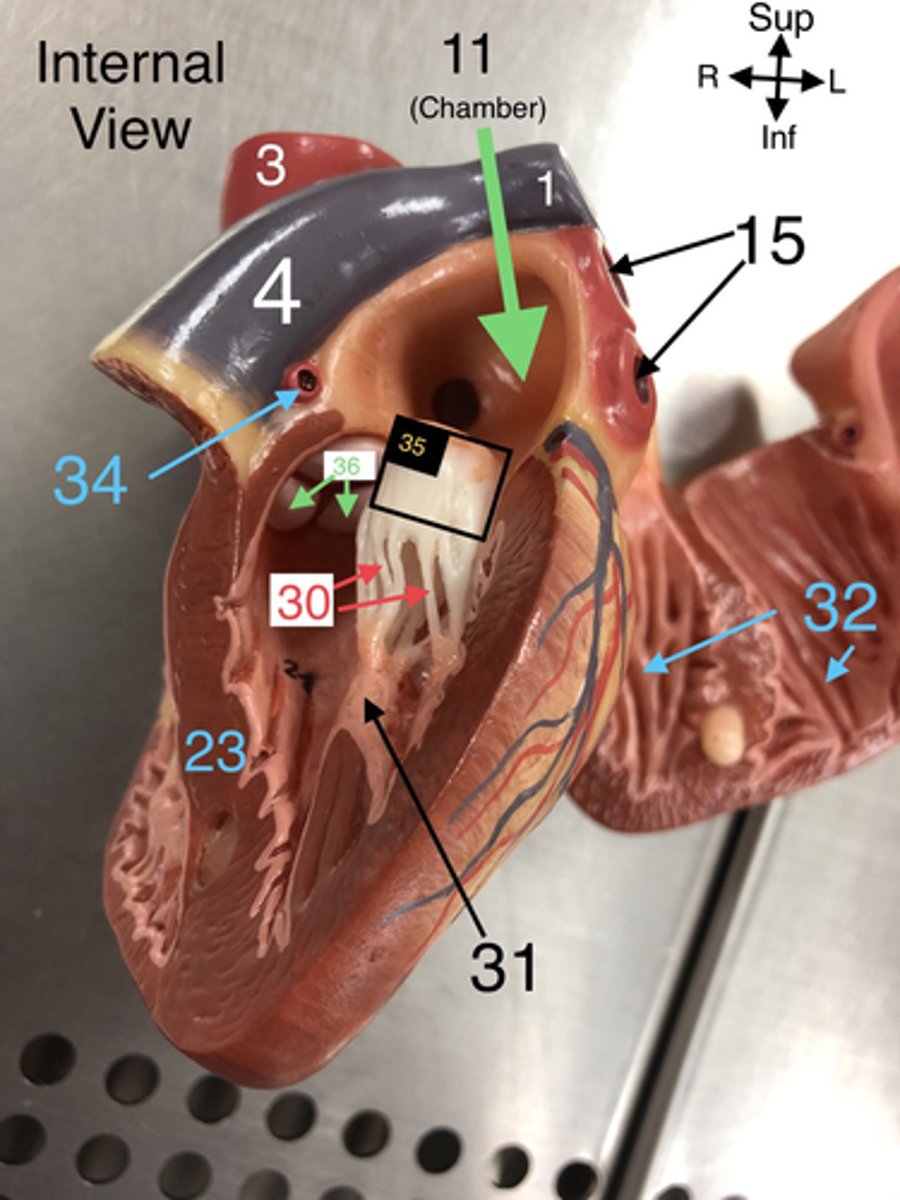
pectinate mm
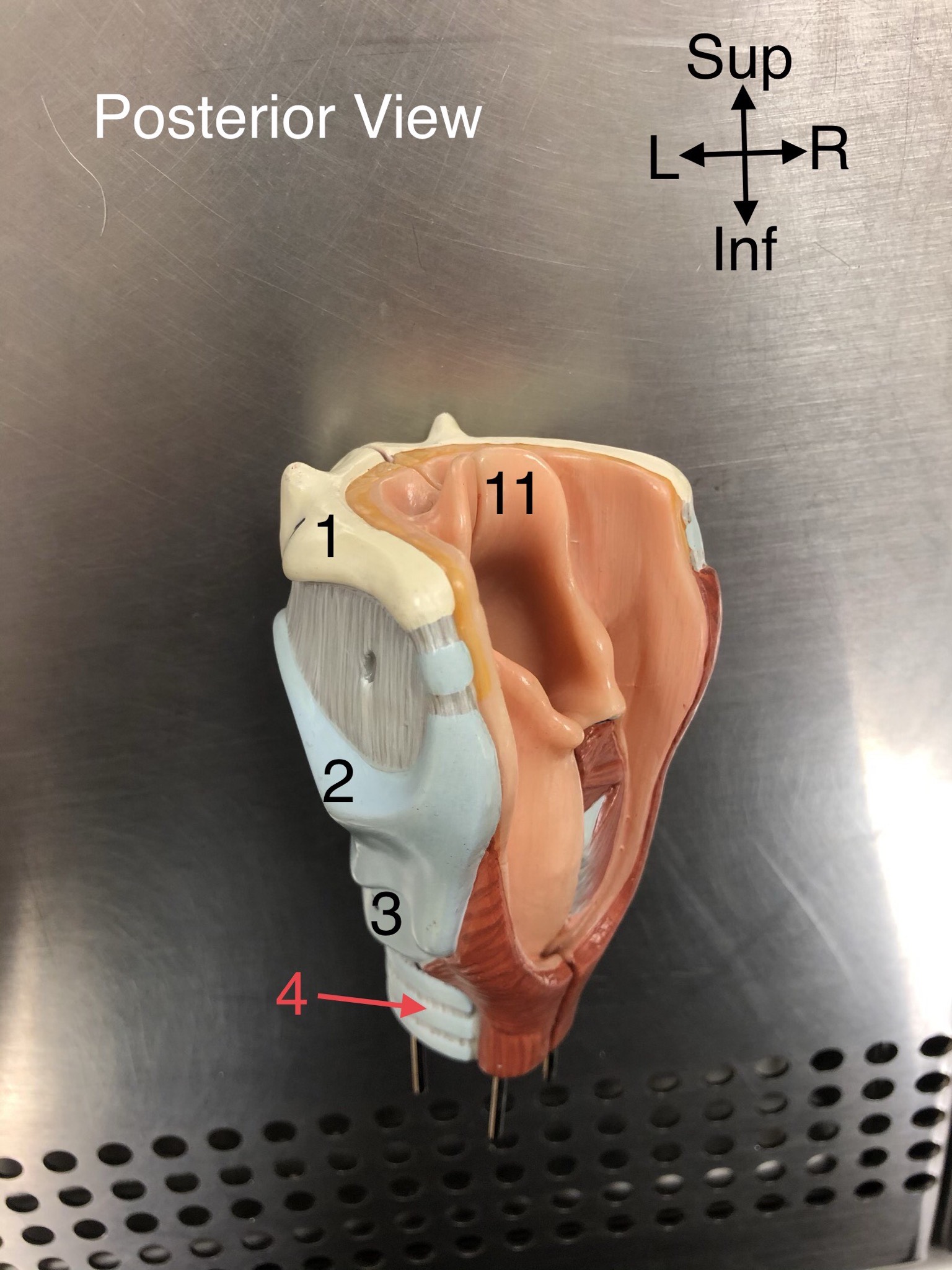
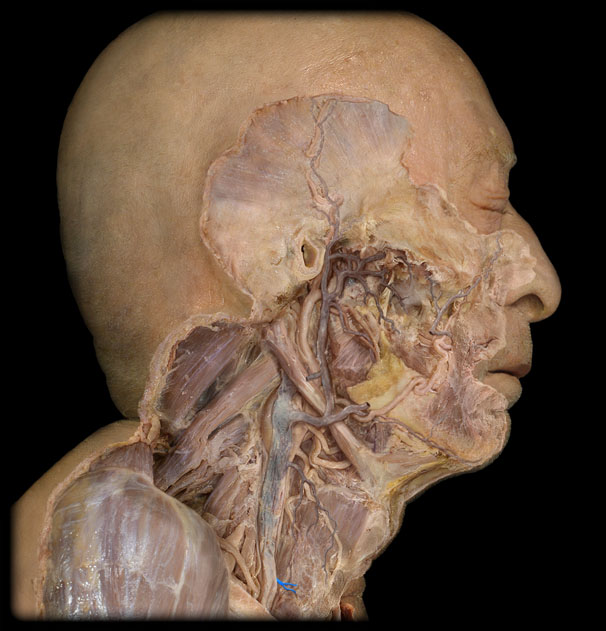
Hyoid b.
1.A U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
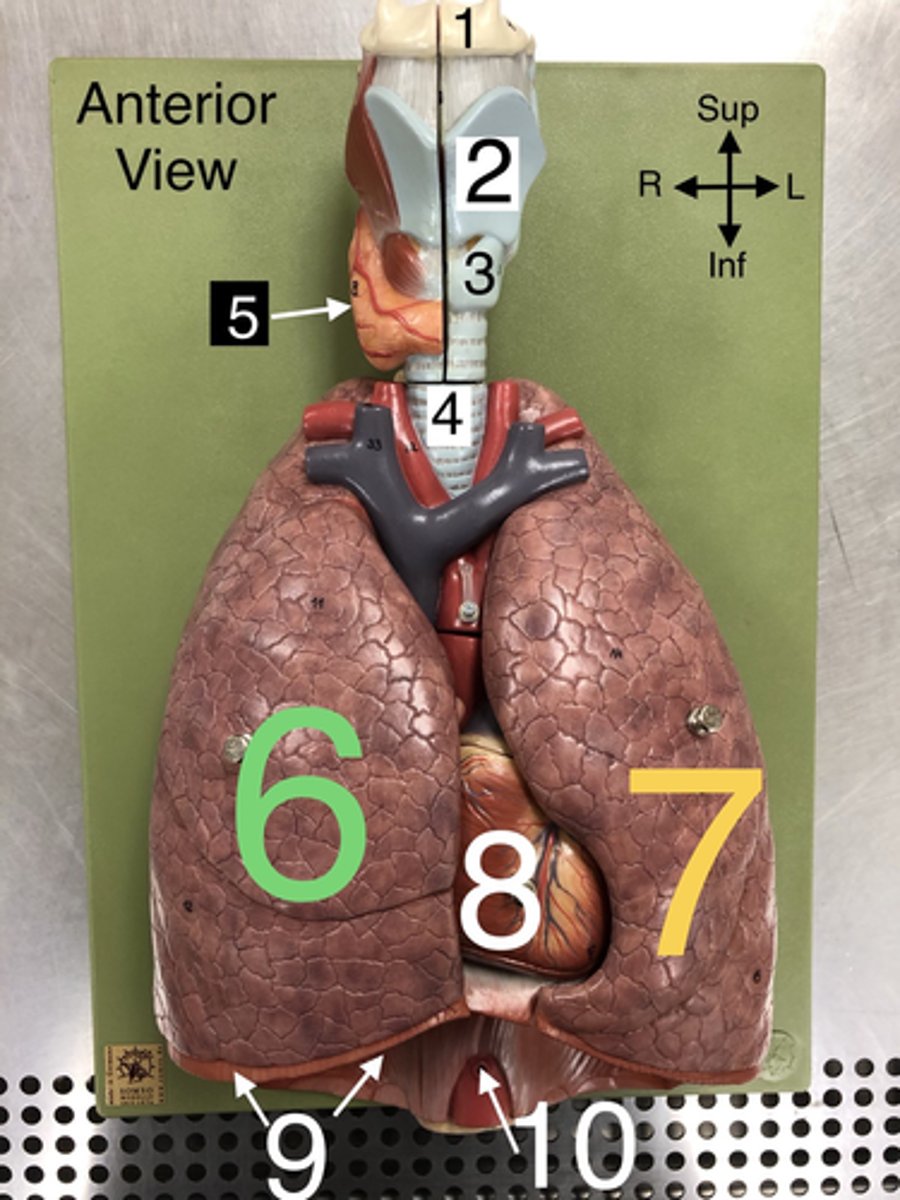
Thyroid cartilage
2. The largest cartilage of the larynx, often referred to as the Adam's apple.
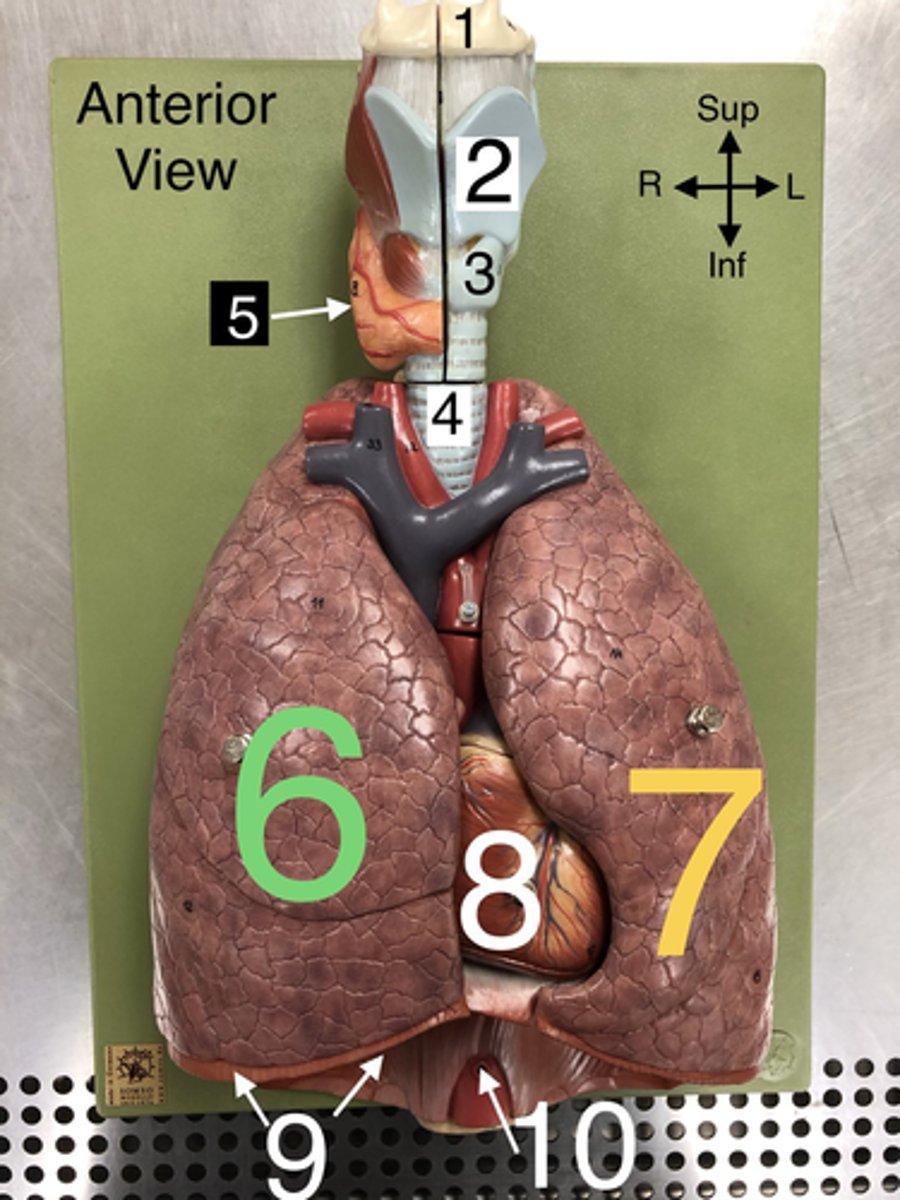
Cricoid cartilage
3. A ring-shaped cartilage located below the thyroid cartilage in the larynx.
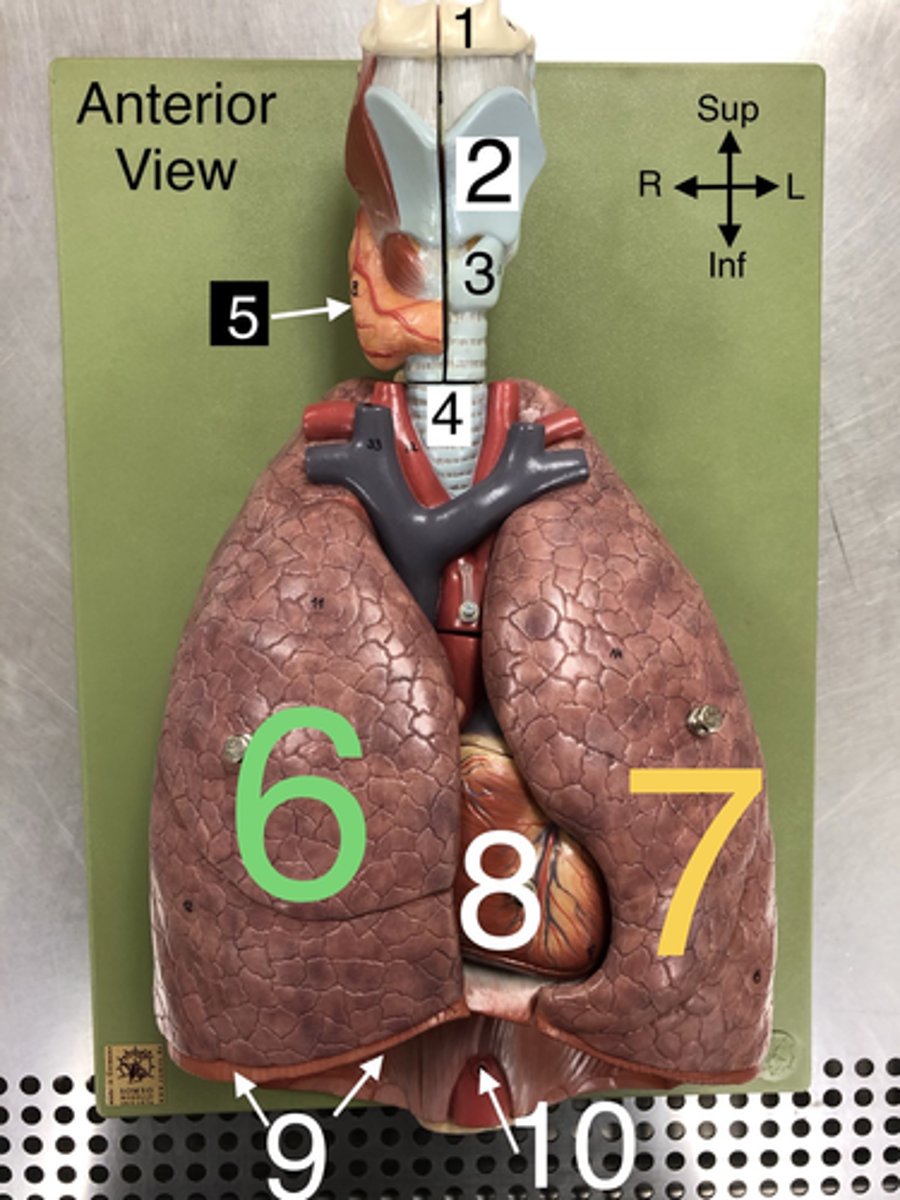
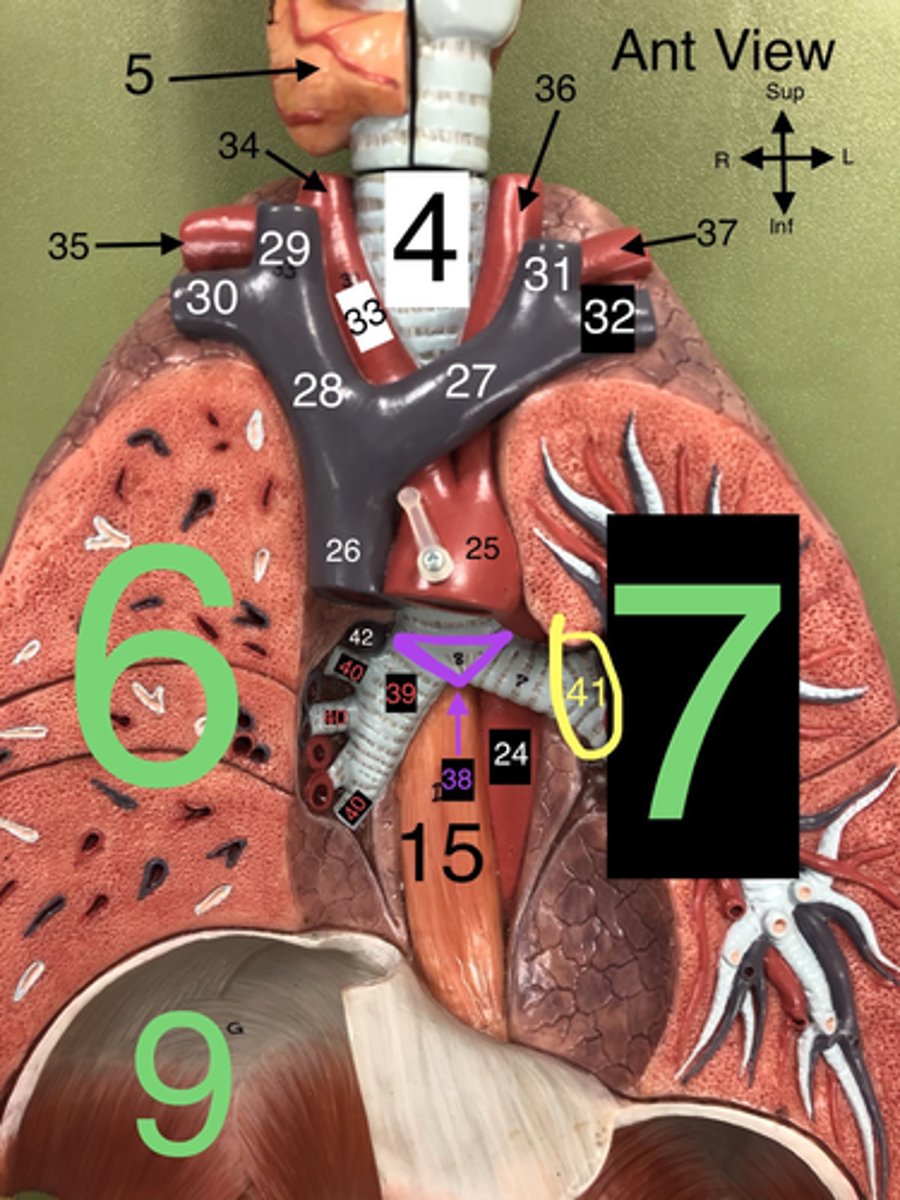
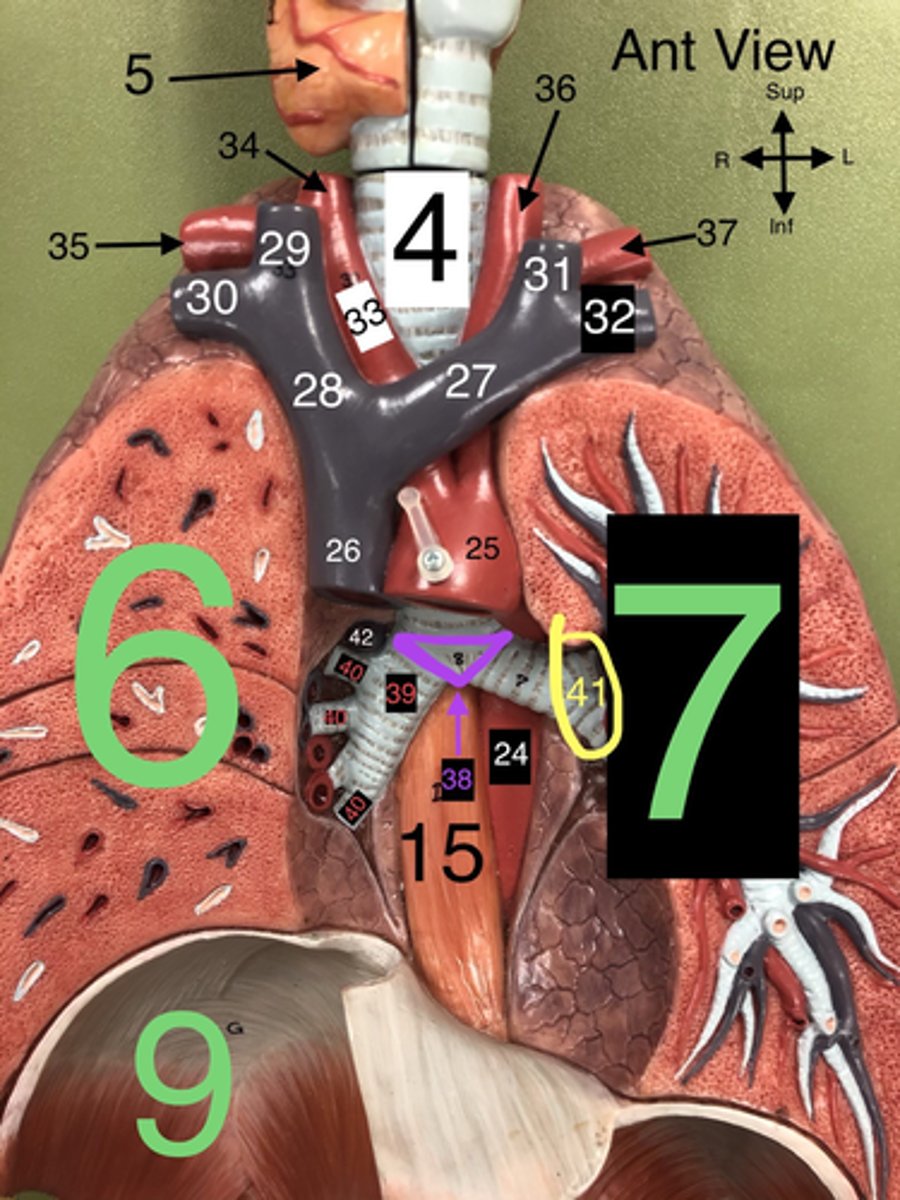
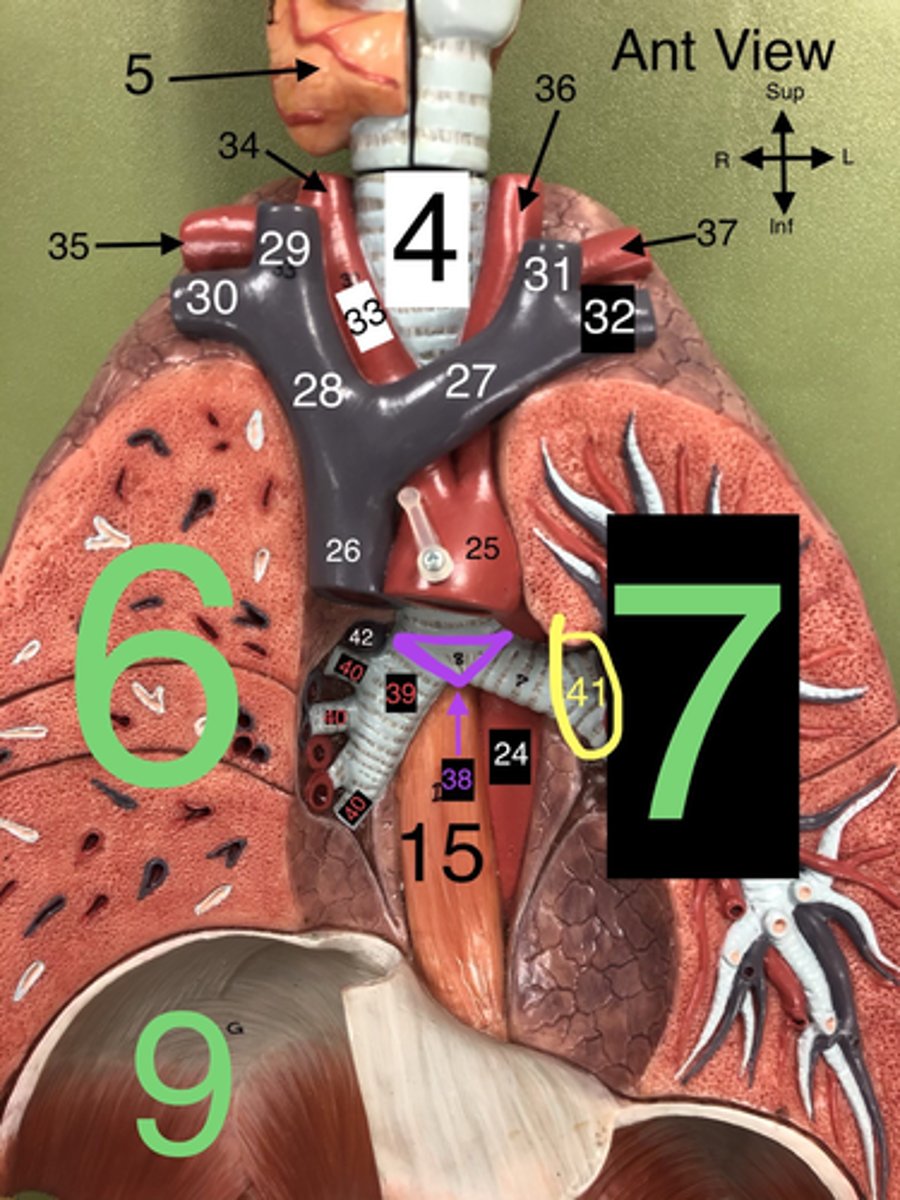
Trachea
4. The windpipe that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs.
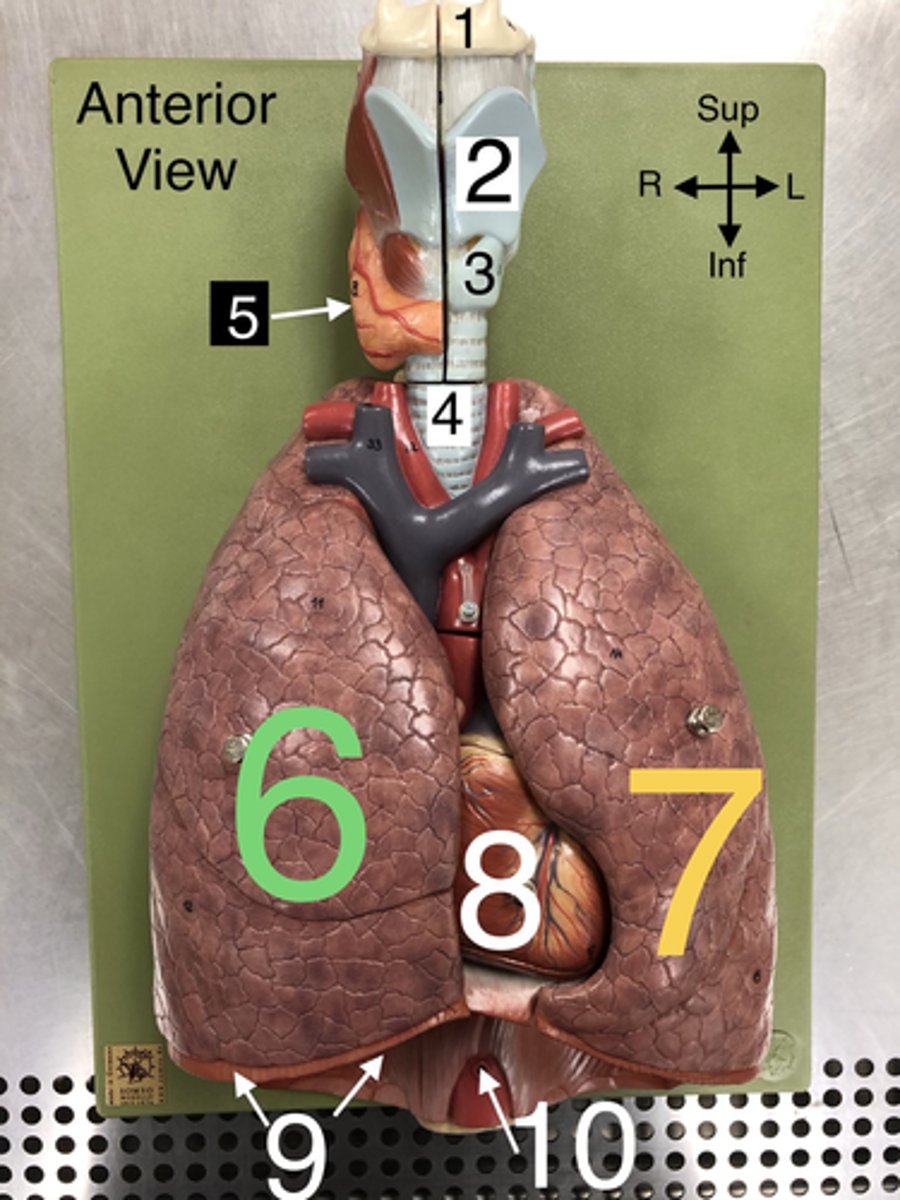
Thyroid gland
5. An endocrine gland located in the neck that produces hormones regulating metabolism.
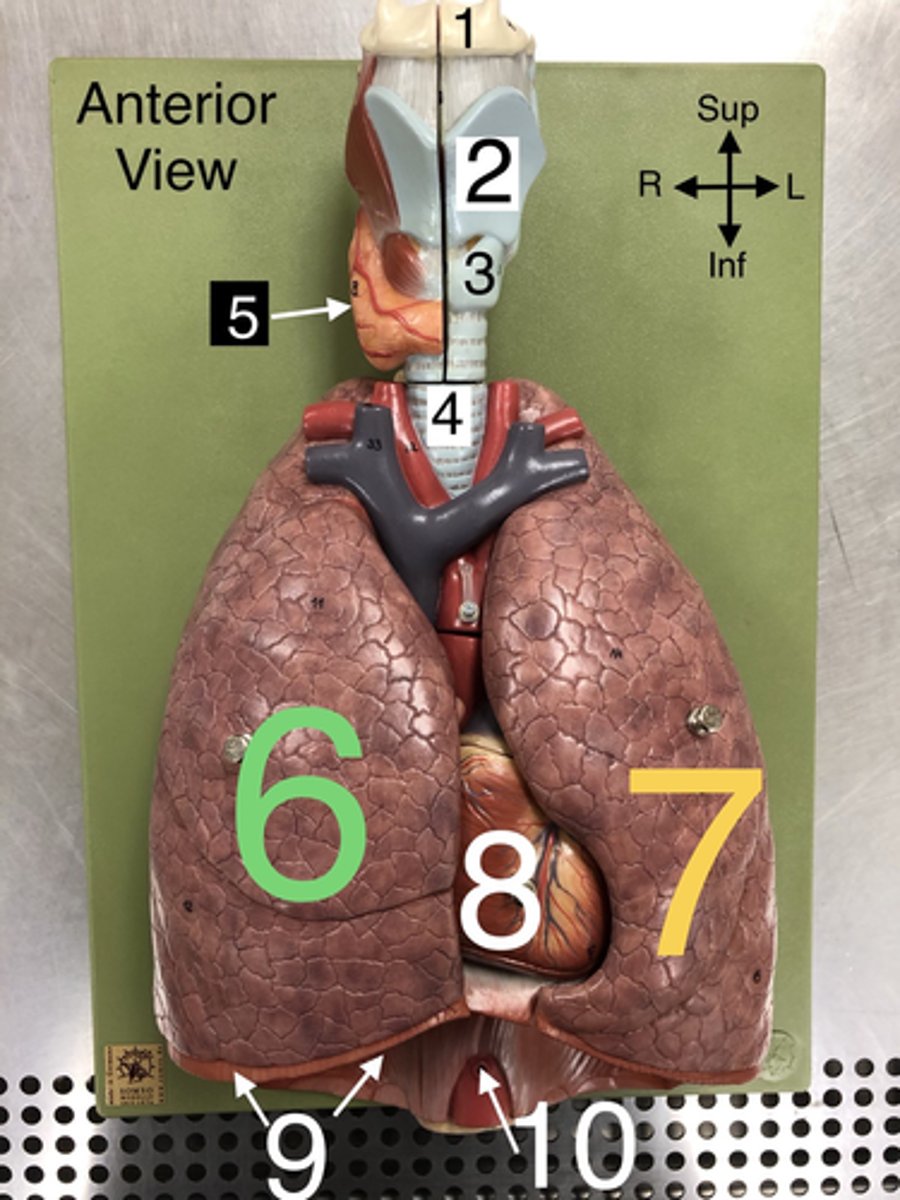
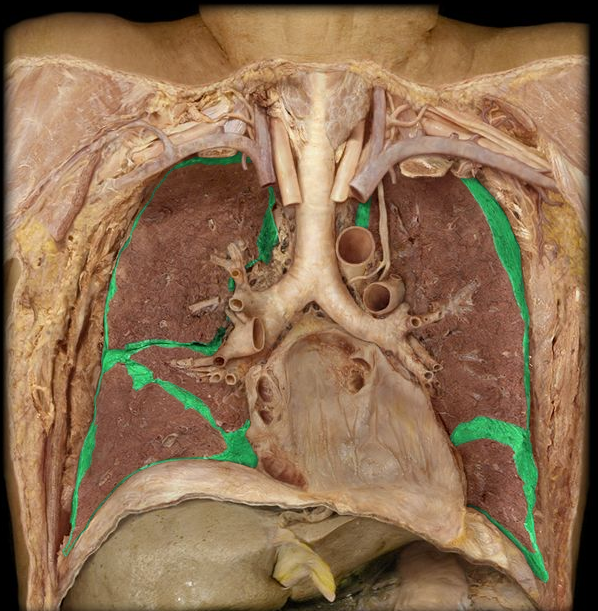
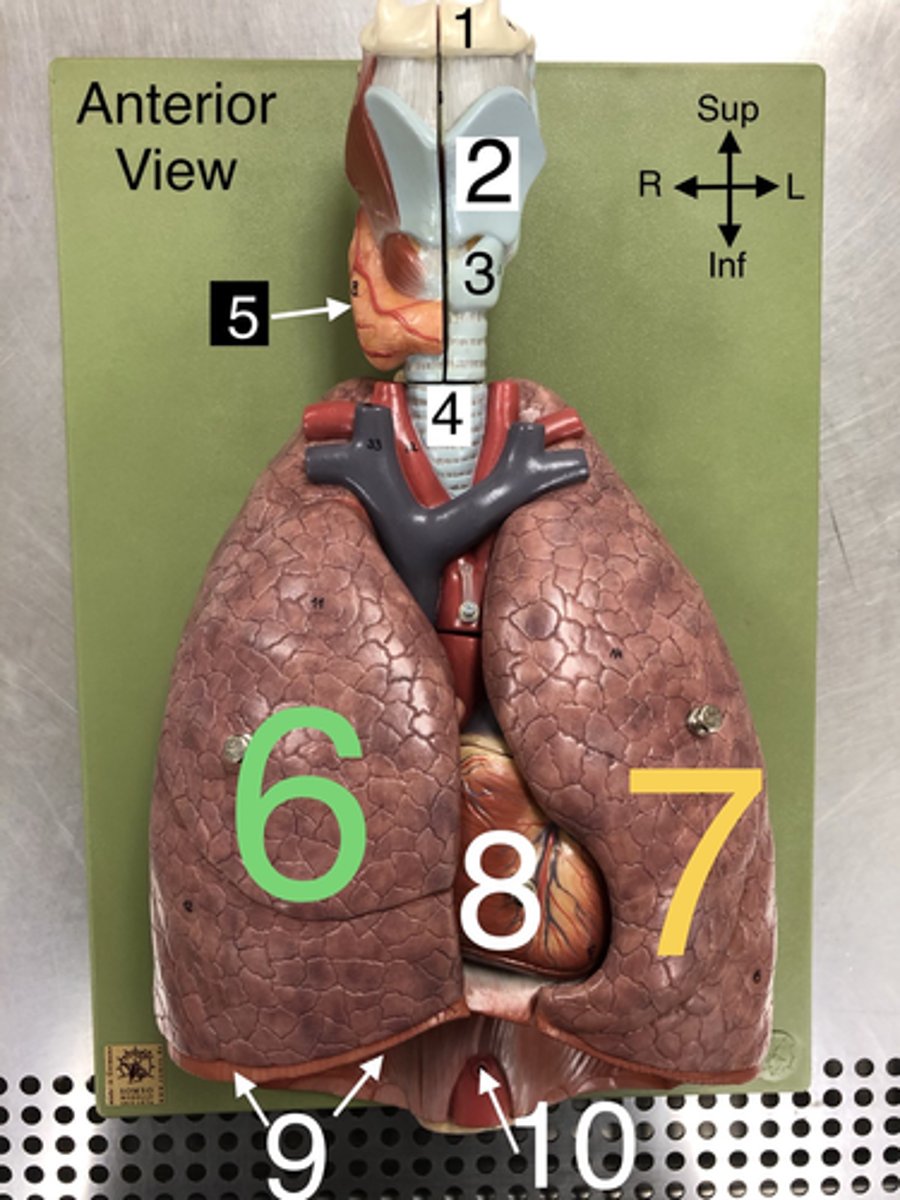
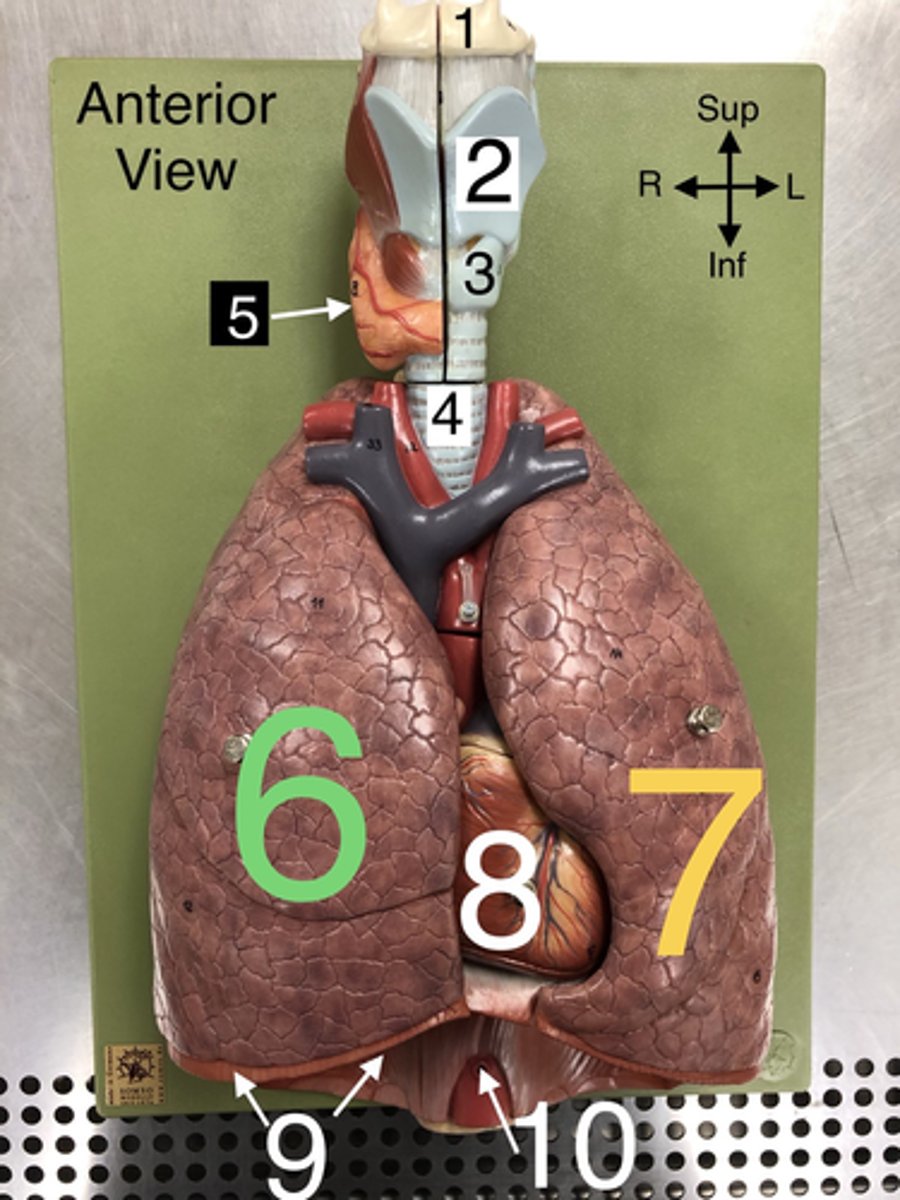
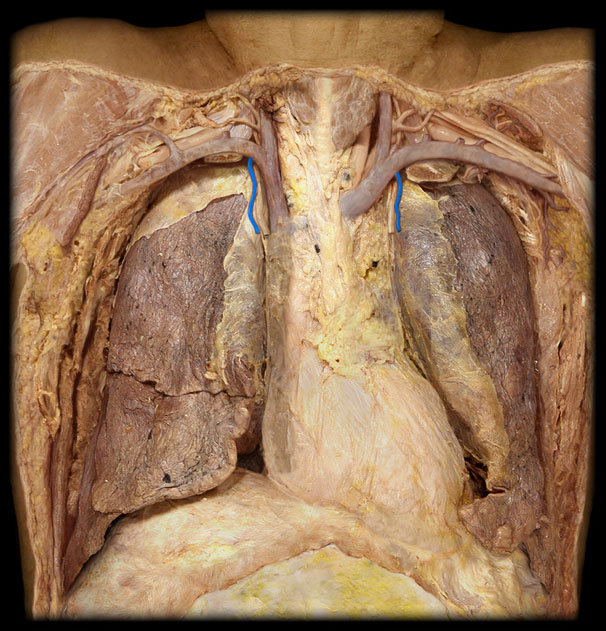
R Lung
6. The right lung, which is divided into three lobes: upper, middle, and lower.
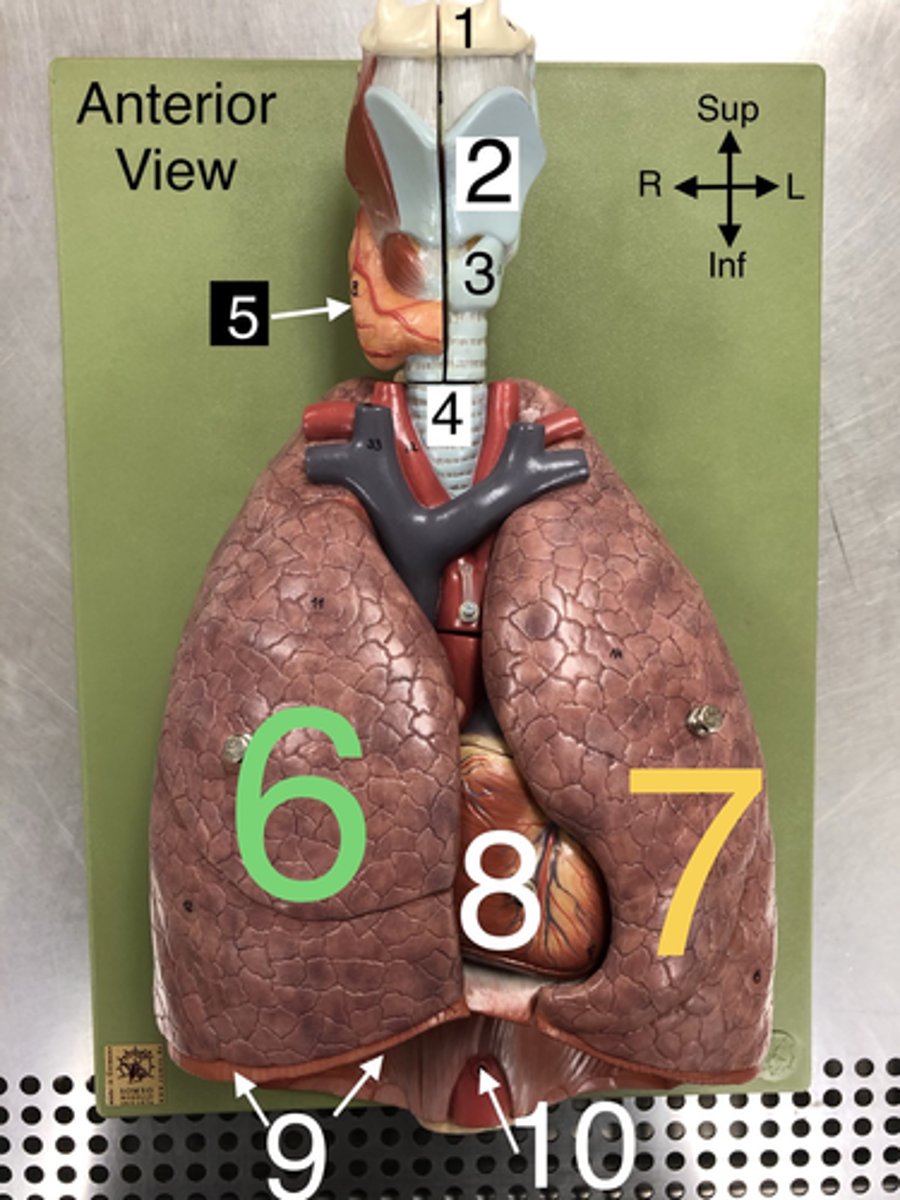
L Lung
7. The left lung, which is divided into two lobes: upper and lower.
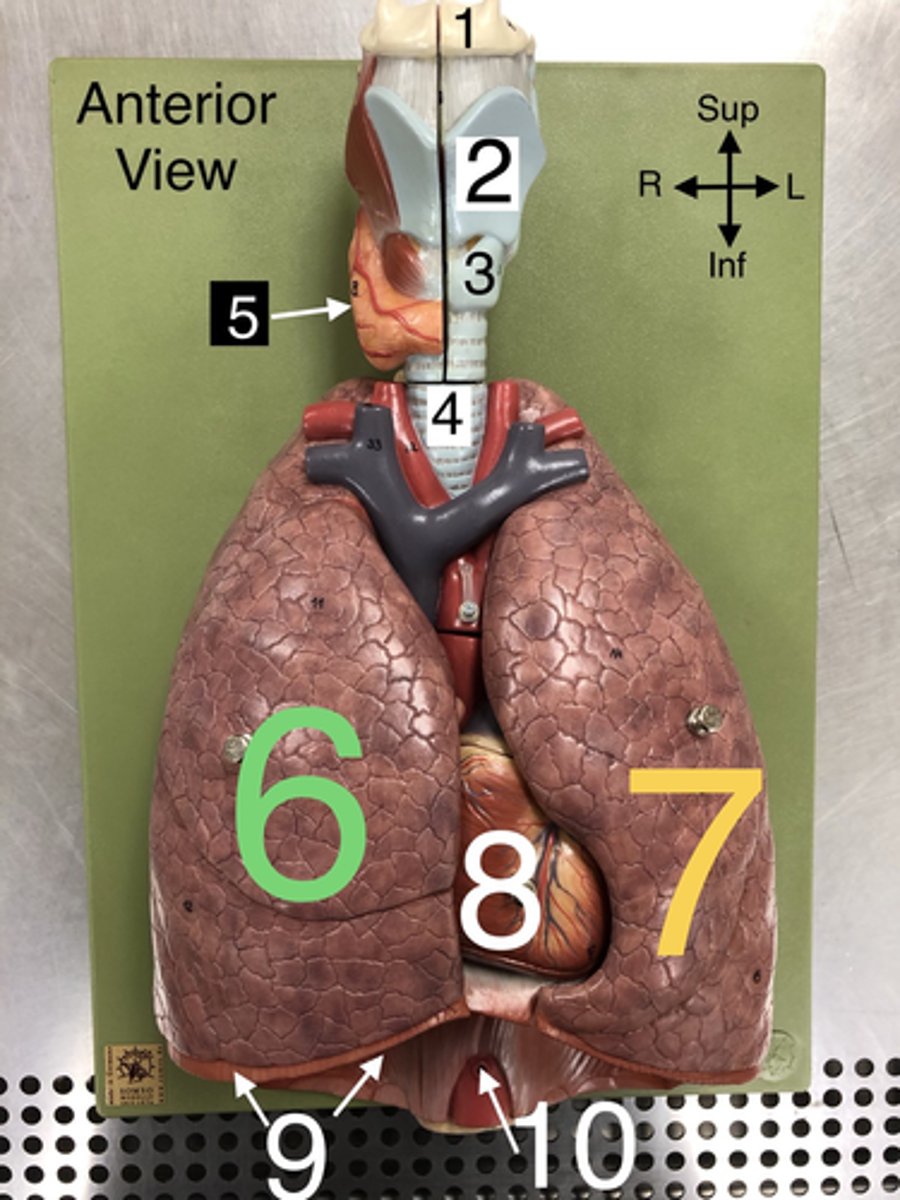
Heart
8. The muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system.
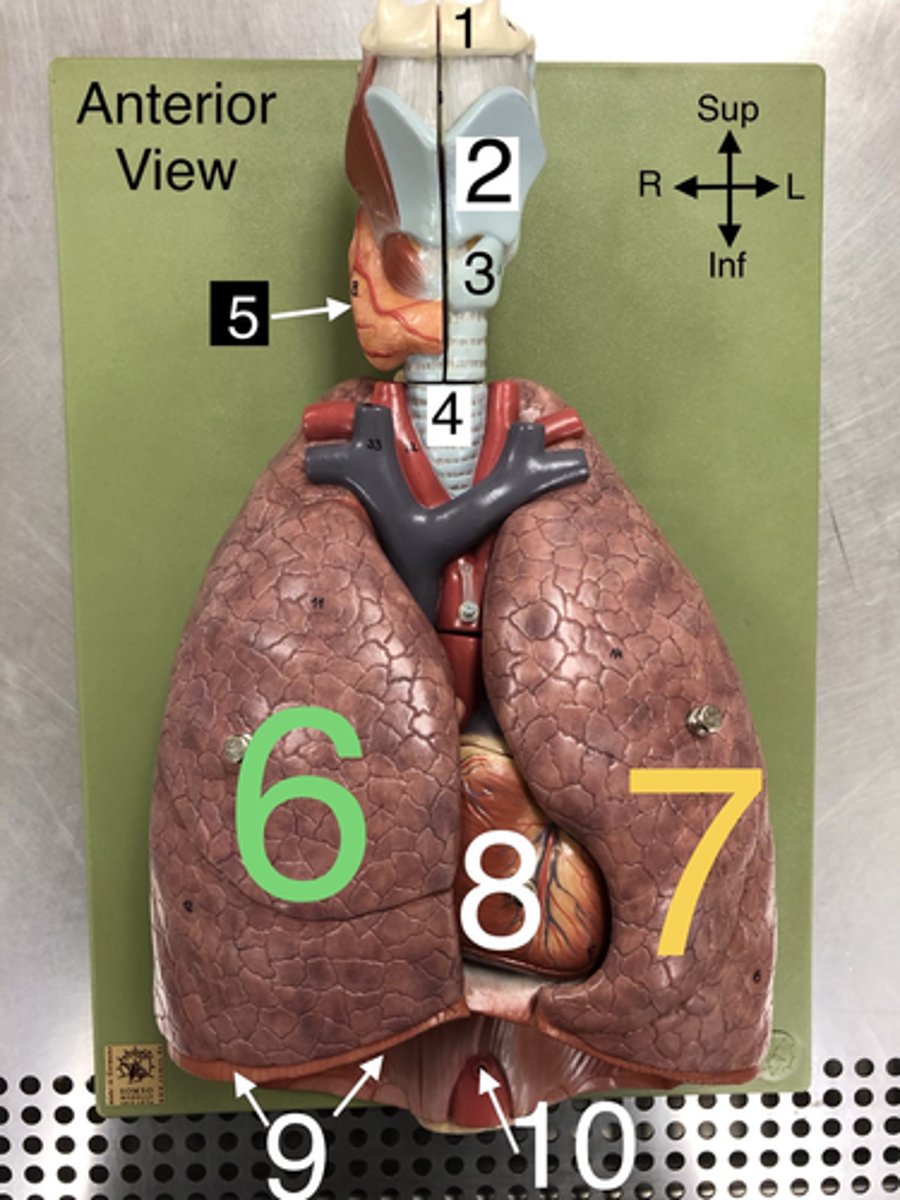
Diaphragm
9. A dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, playing a major role in breathing.
Abdominal Aorta
10. The section of the aorta that runs through the abdomen, supplying blood to the abdominal organs.
Epiglottis
11. A flap of cartilage that covers the windpipe during swallowing.
False Vocal Cord (fold)
12. The upper pair of vocal cords that do not produce sound but serve to protect the true vocal cords.
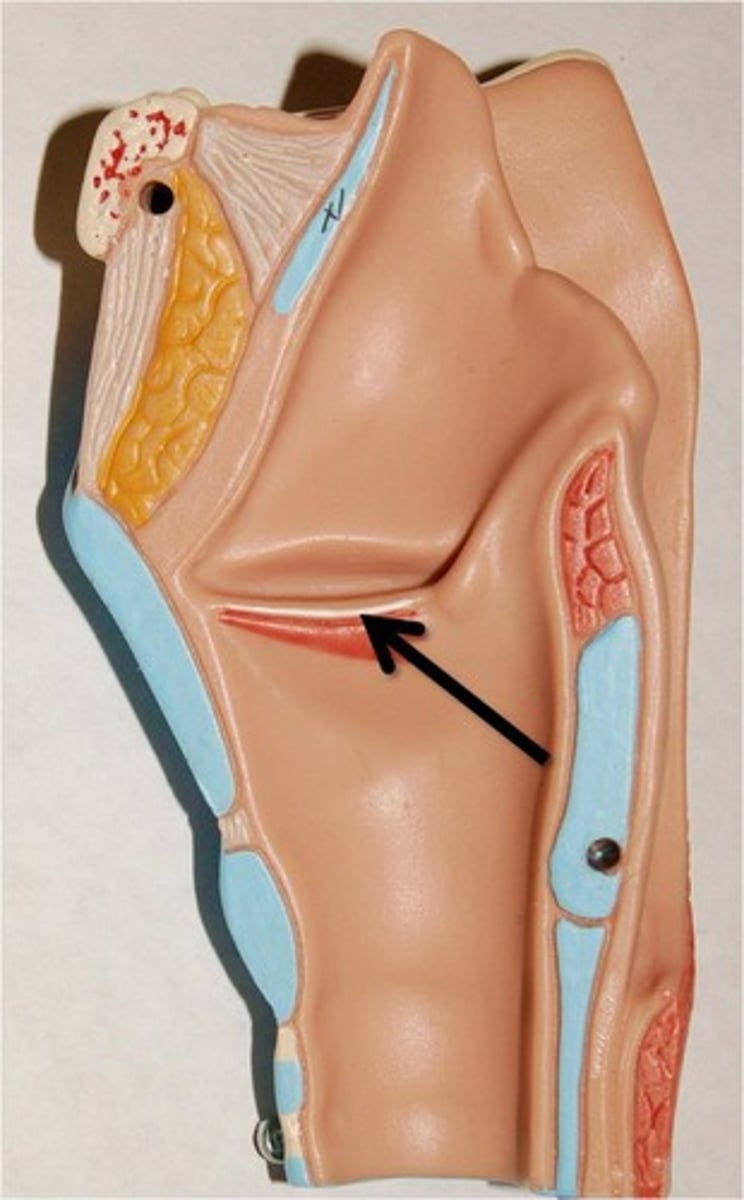
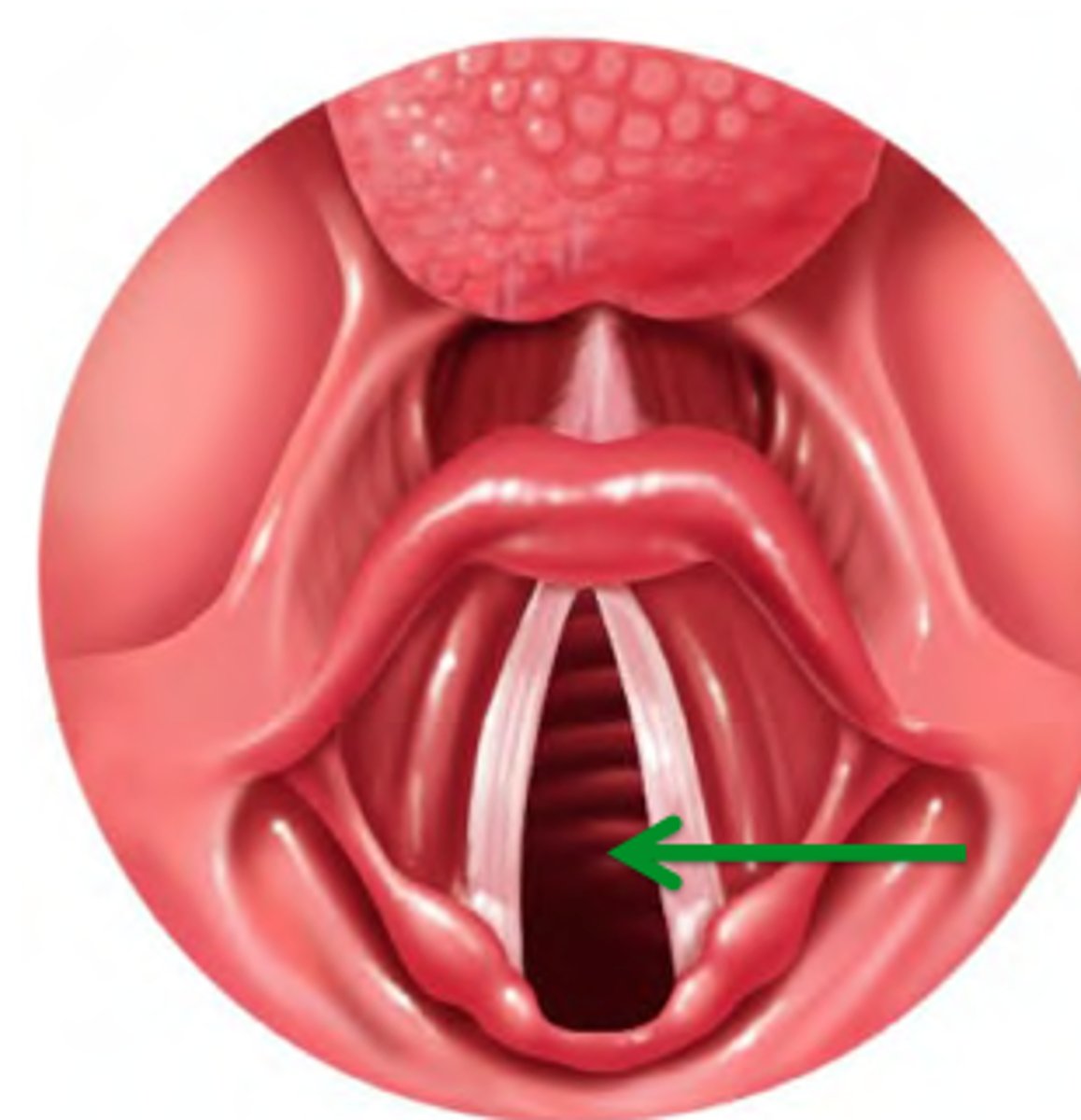
True Vocal Cord
13. The lower pair of vocal cords that vibrate to produce sound.
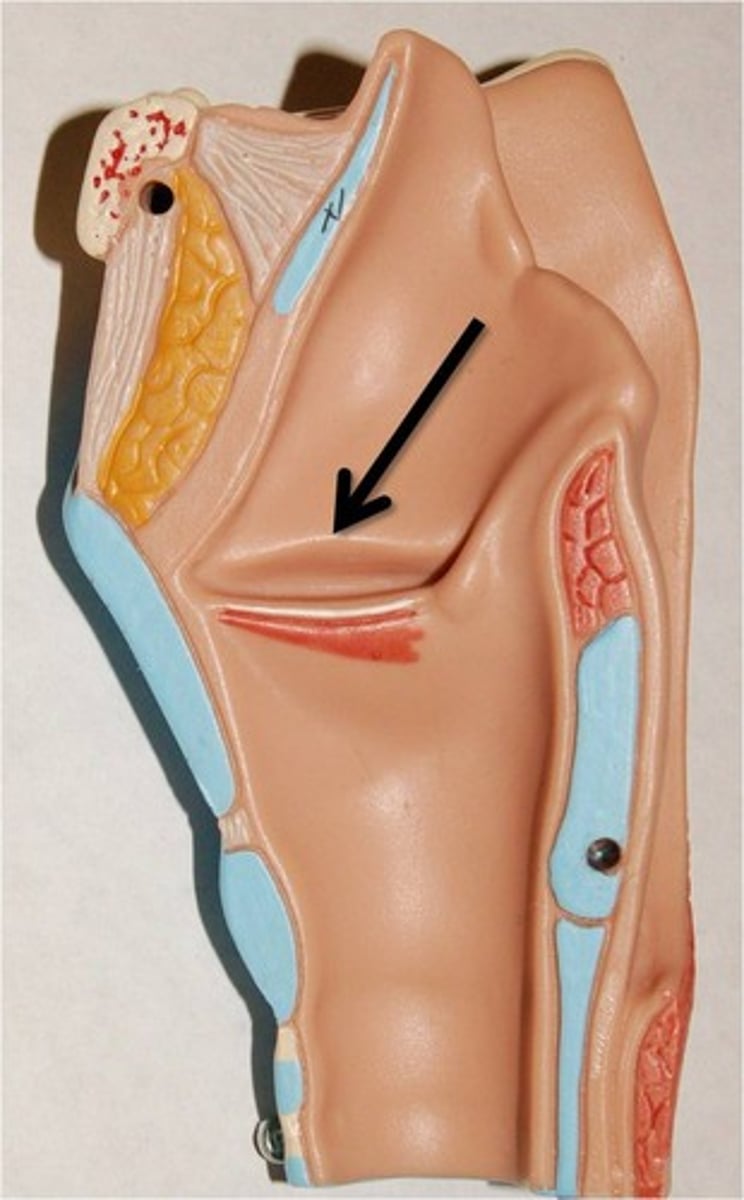
Glottis (the space between)
14. The opening between the vocal cords in the larynx.
Esophagus
15. The muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
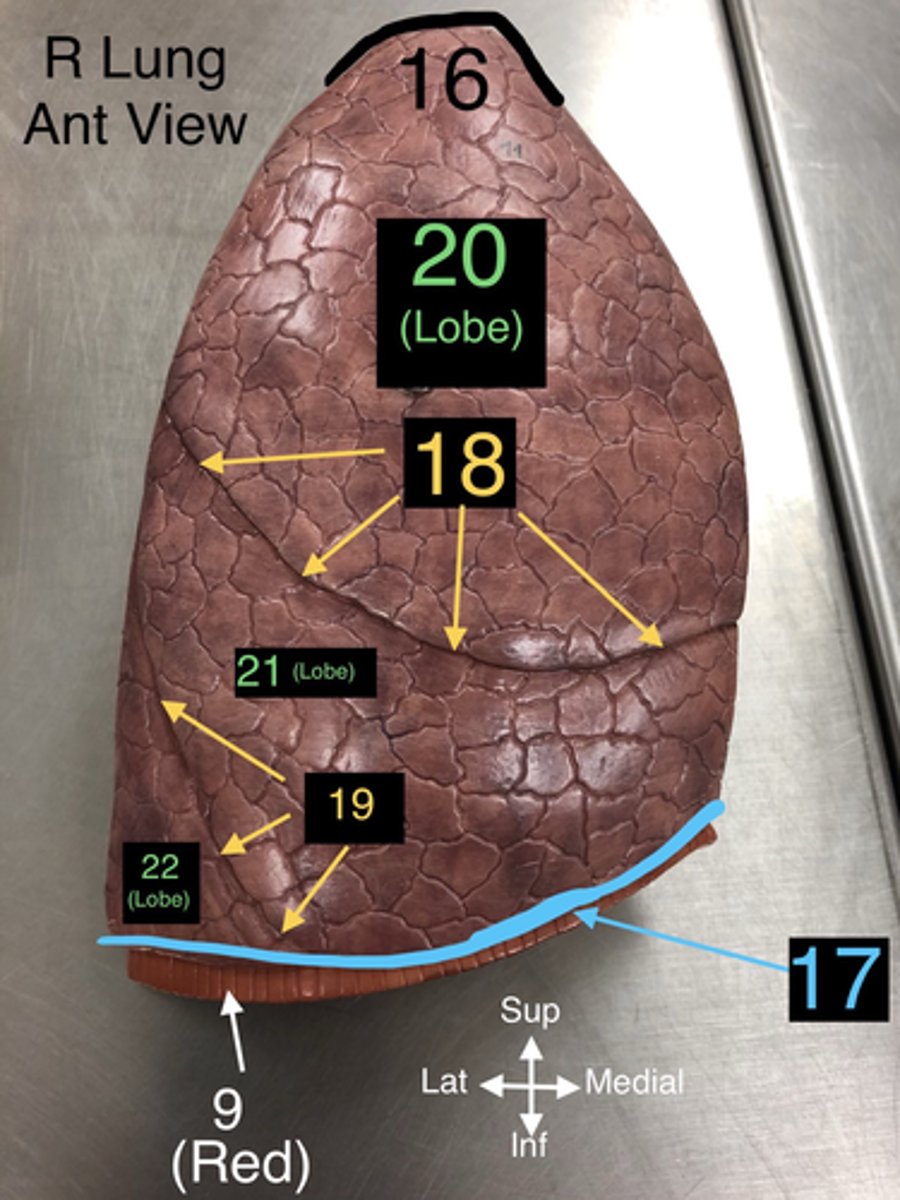
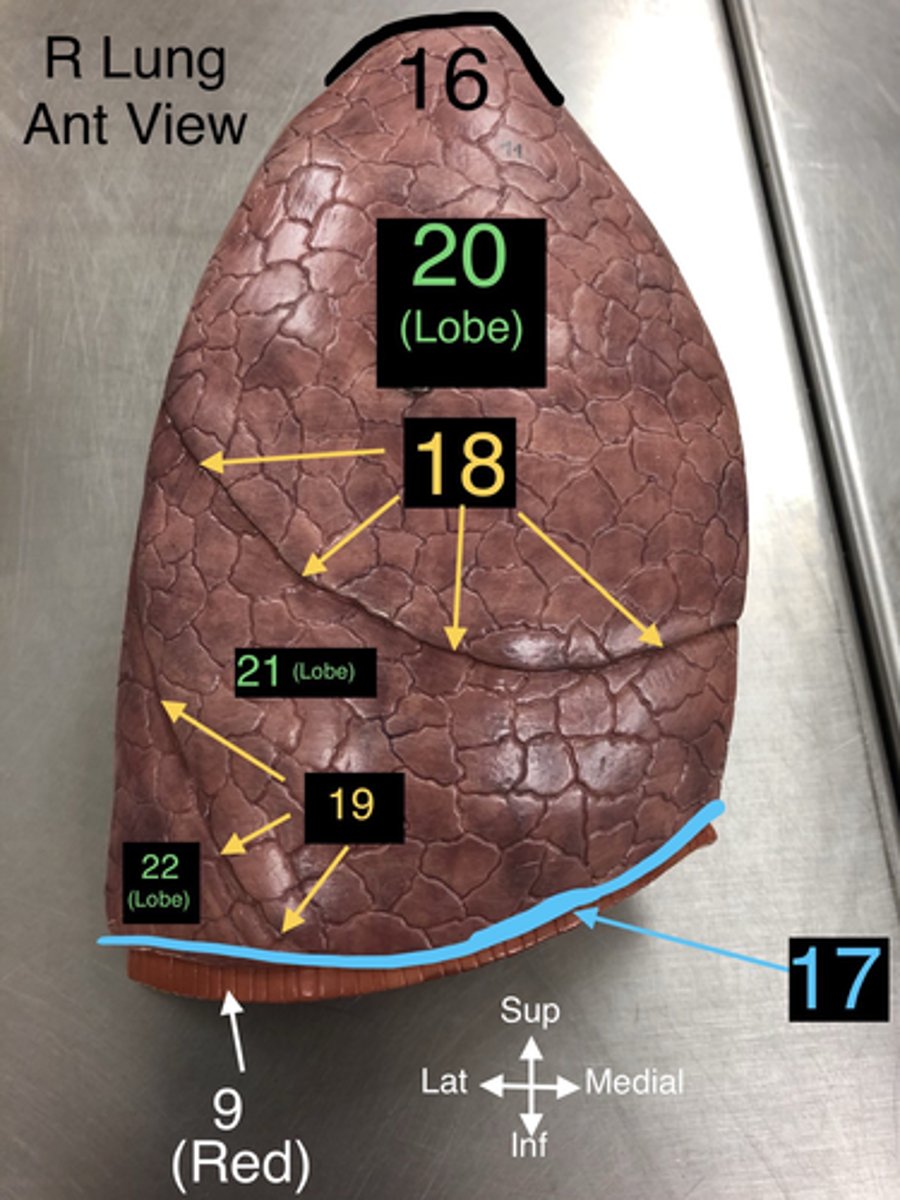
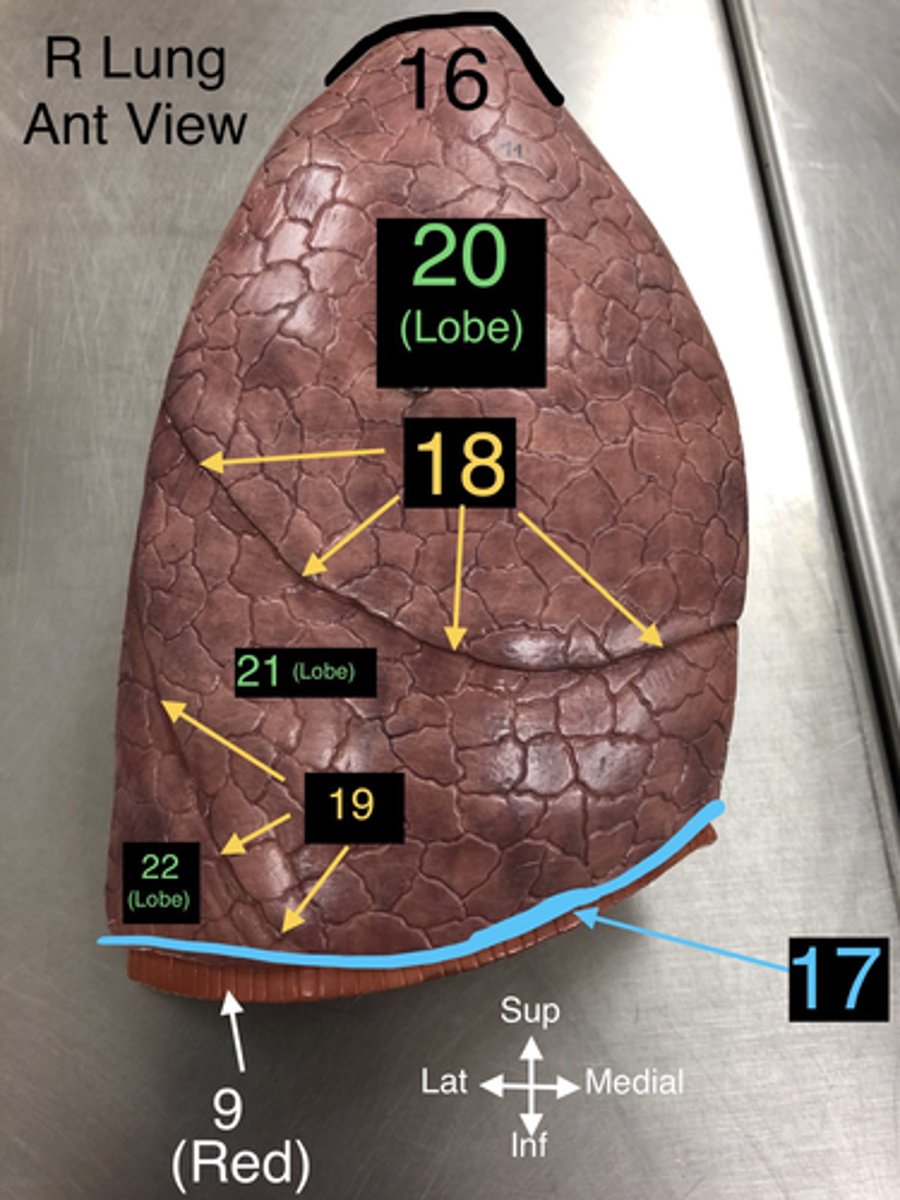
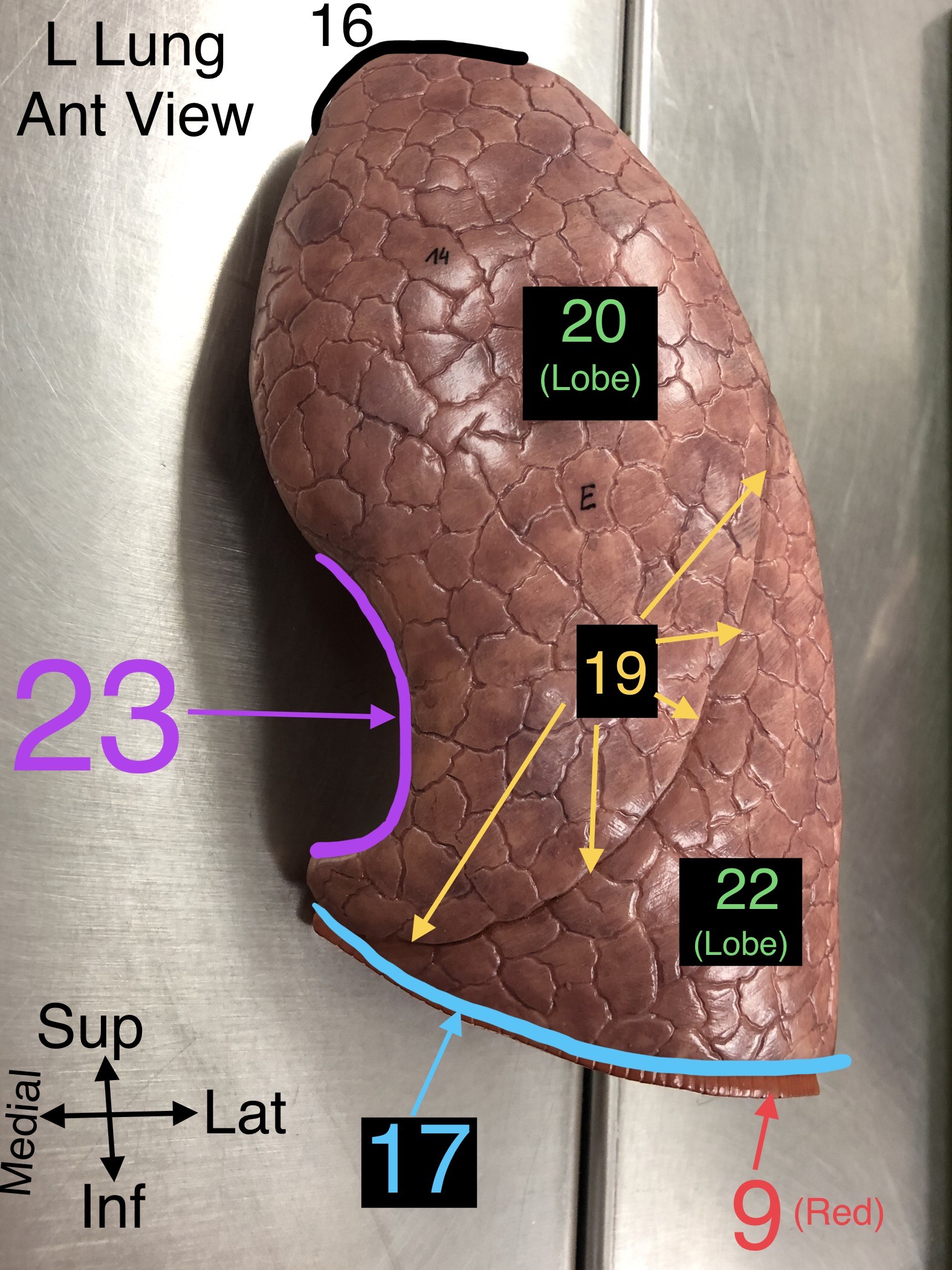
Apex of Lung
16. The topmost part of the lung, located above the level of the first rib.
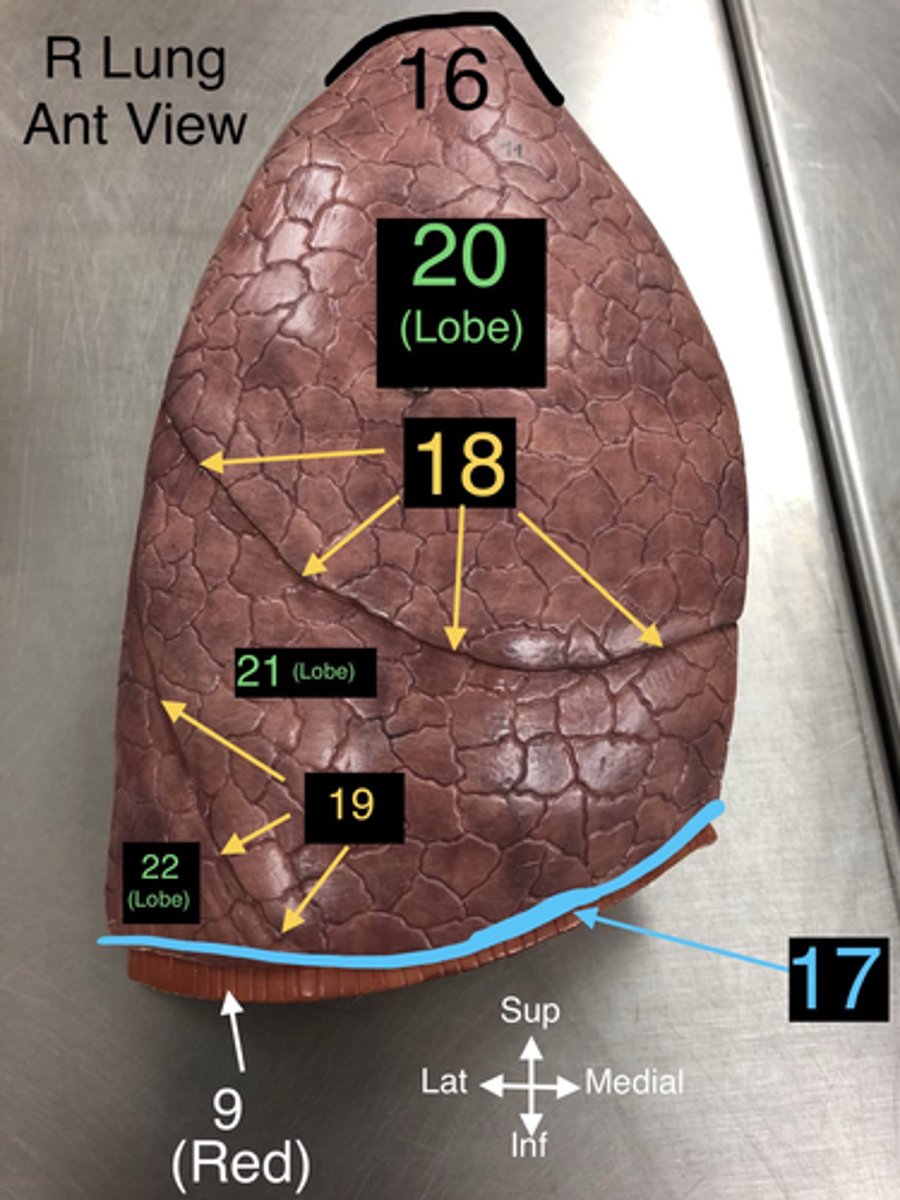
Base of Lung
17. The lower part of the lung that rests on the diaphragm.
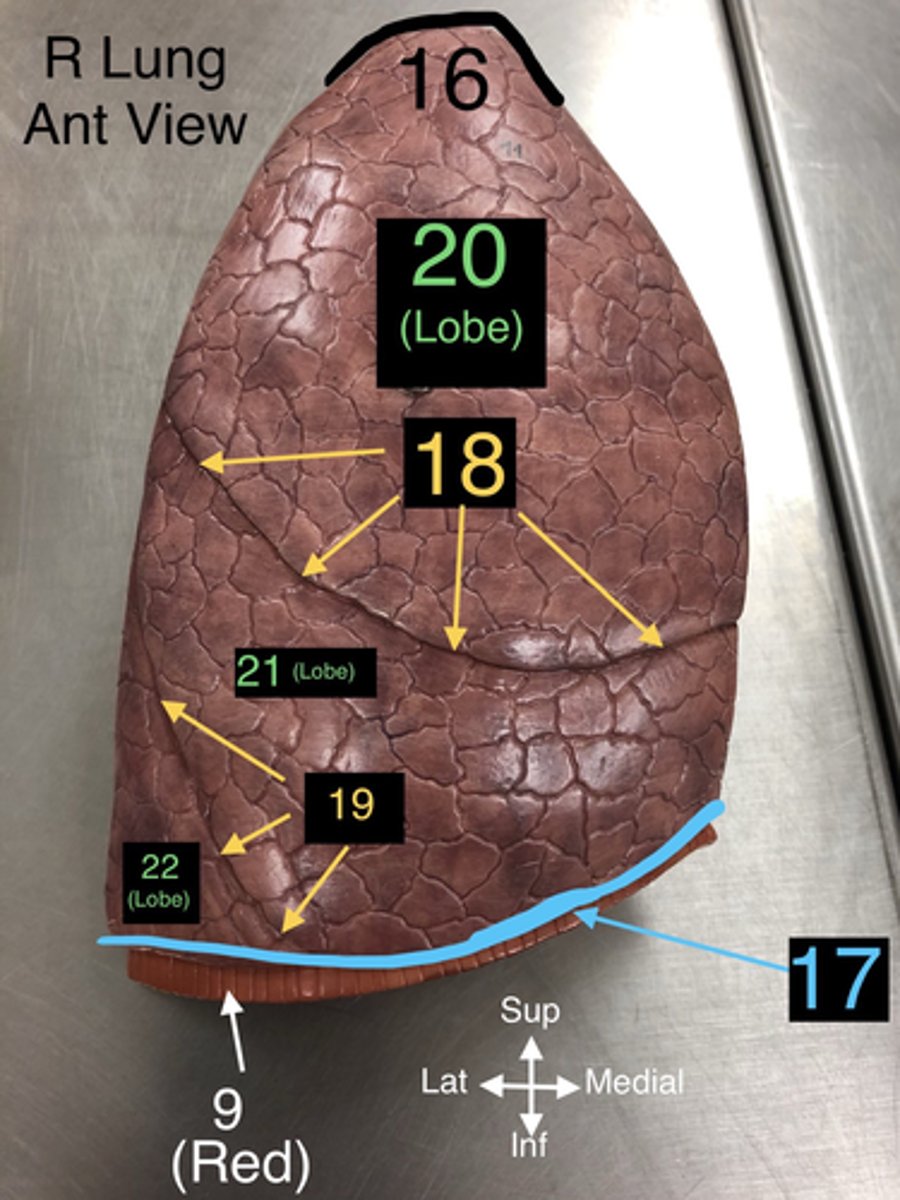
Horizontal Fissure
18. A fissure that divides the right lung into upper and middle lobes.
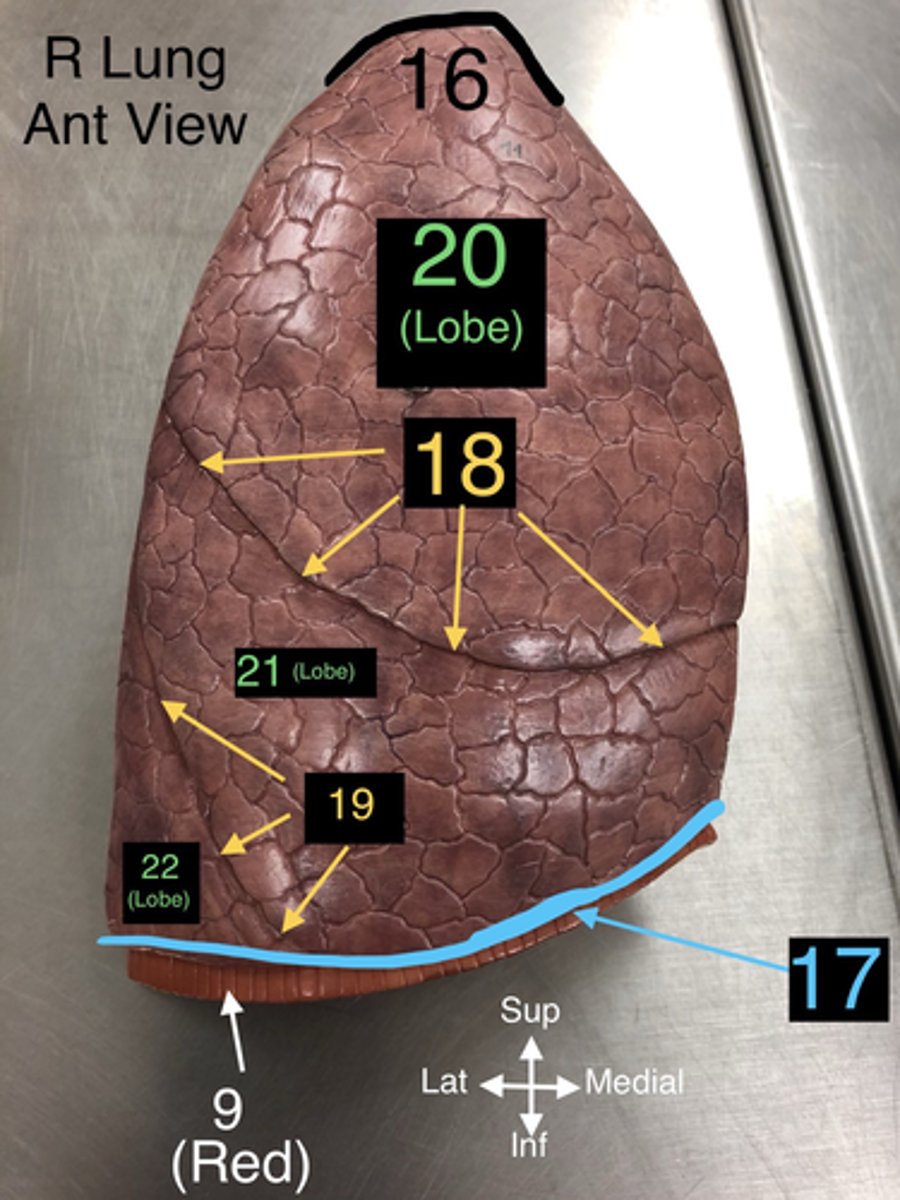
Oblique Fissure
19. A fissure that divides both the right and left lungs into lobes.
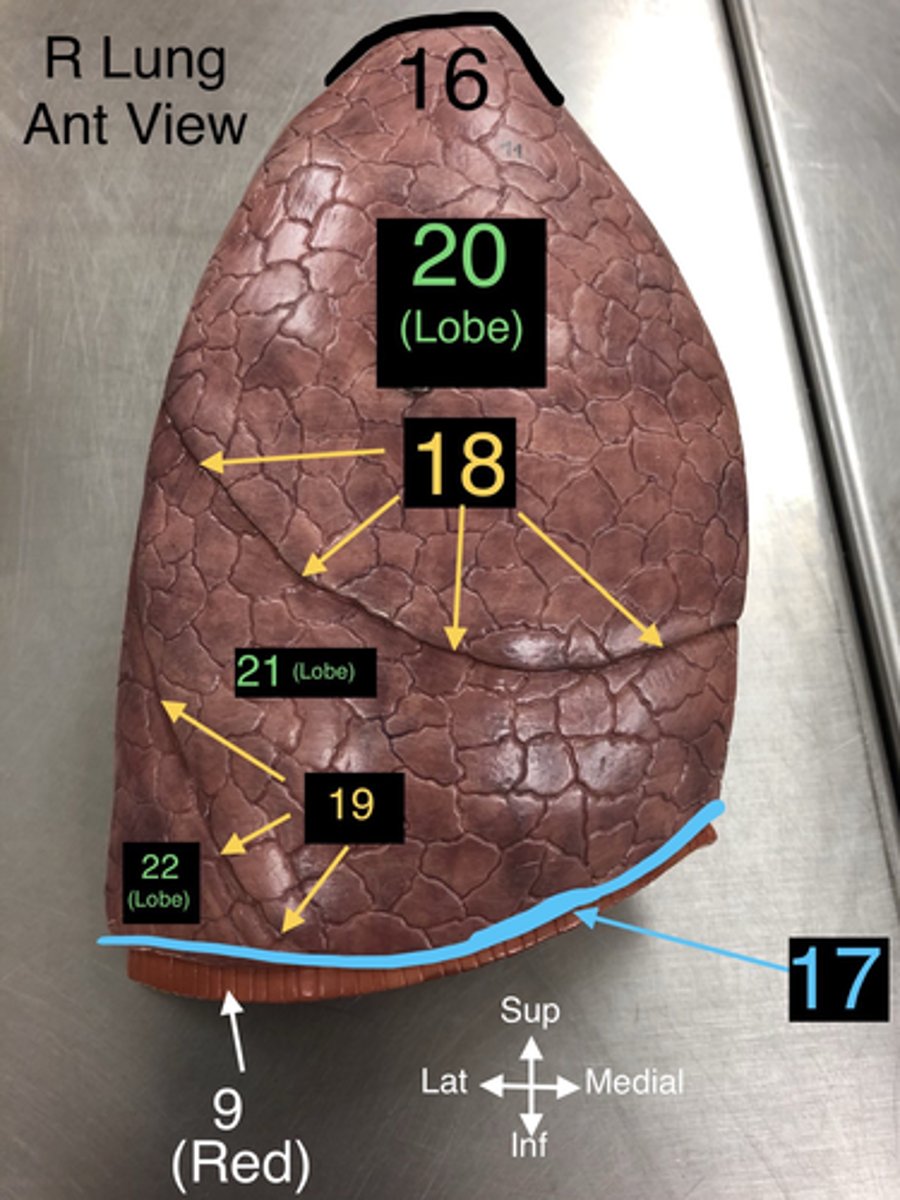
Superior Lobe
20. The upper lobe of the lungs, both right and left.
Middle Lobe
21. The lobe located only in the right lung.
Inferior Lobe
22. The lower lobe of the lungs, both right and left.
Cardiac Notch
23. A notch in the left lung where the heart accommodates.
Thoracic Aorta
24. The part of the aorta that runs through the thoracic cavity.
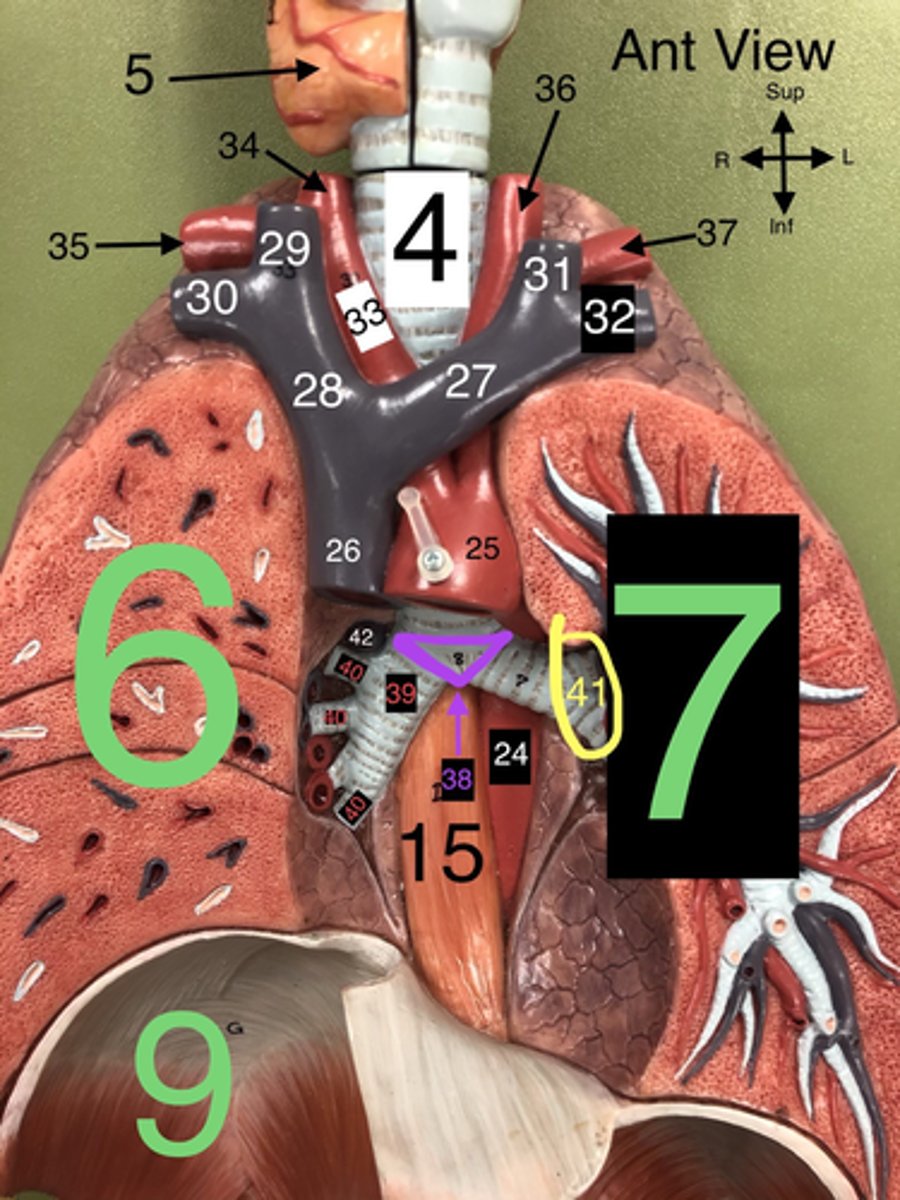
Arch of the Aorta
25. The curved portion of the aorta that gives rise to major arteries supplying the head and arms.
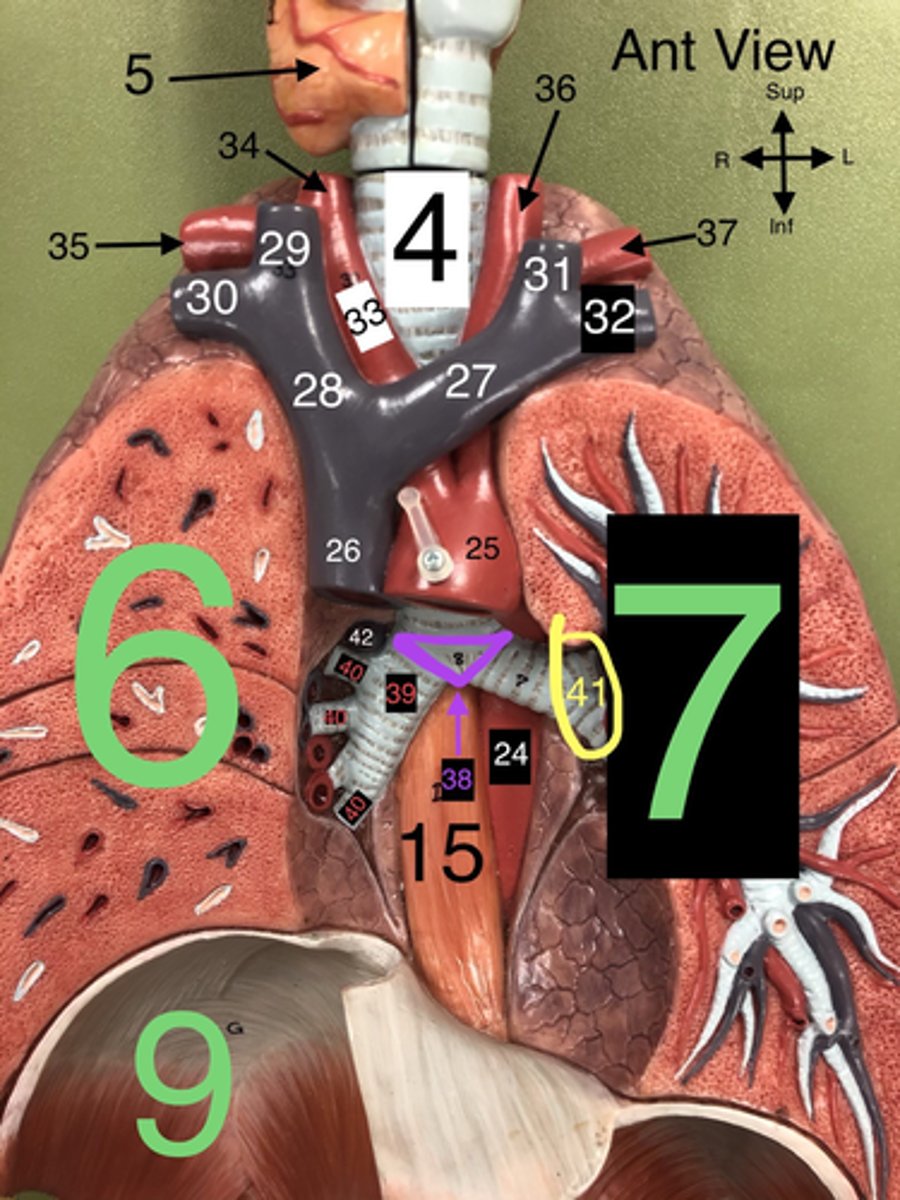
Superior Vena Cava
26. A large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart
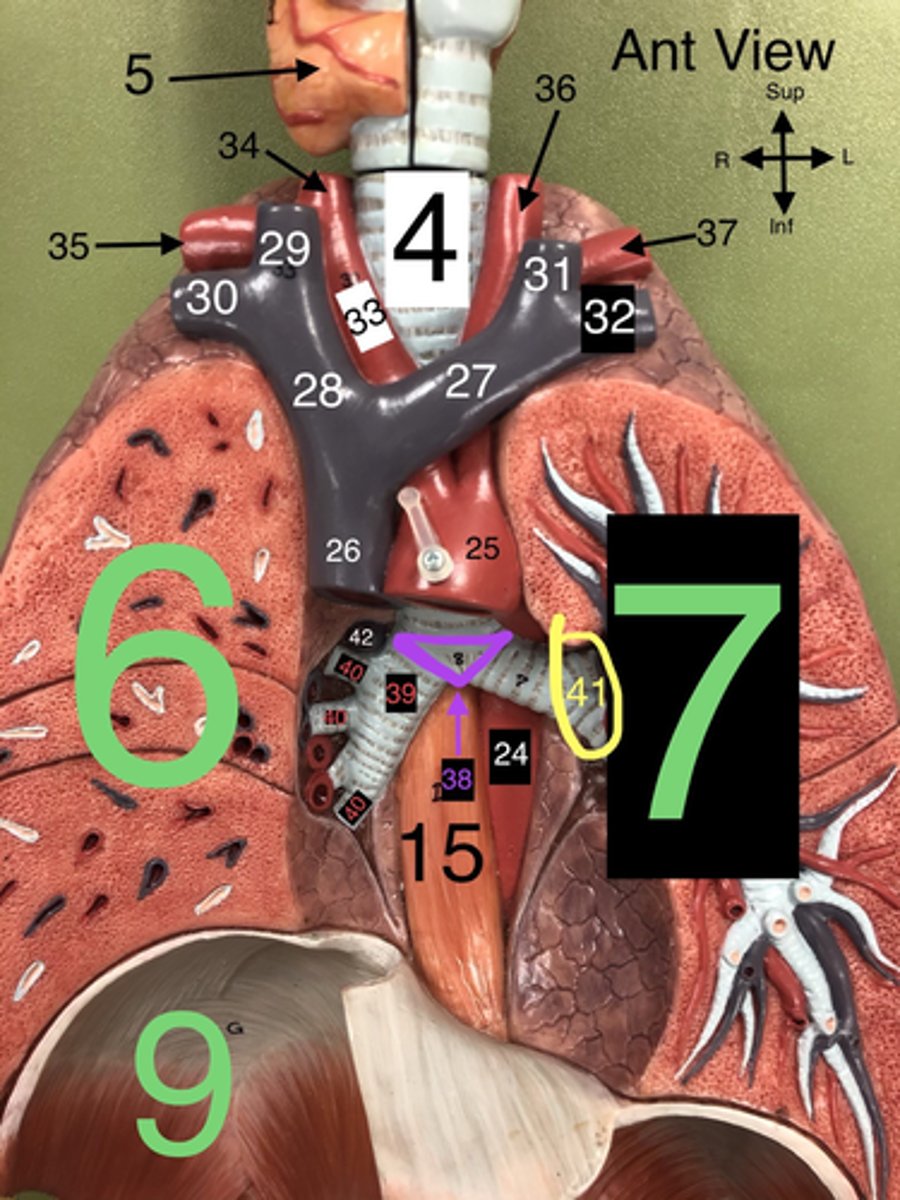
L Brachiocephalic v.
27. A vein that drains blood from the left arm and the left side of the head and neck into the superior vena cava.
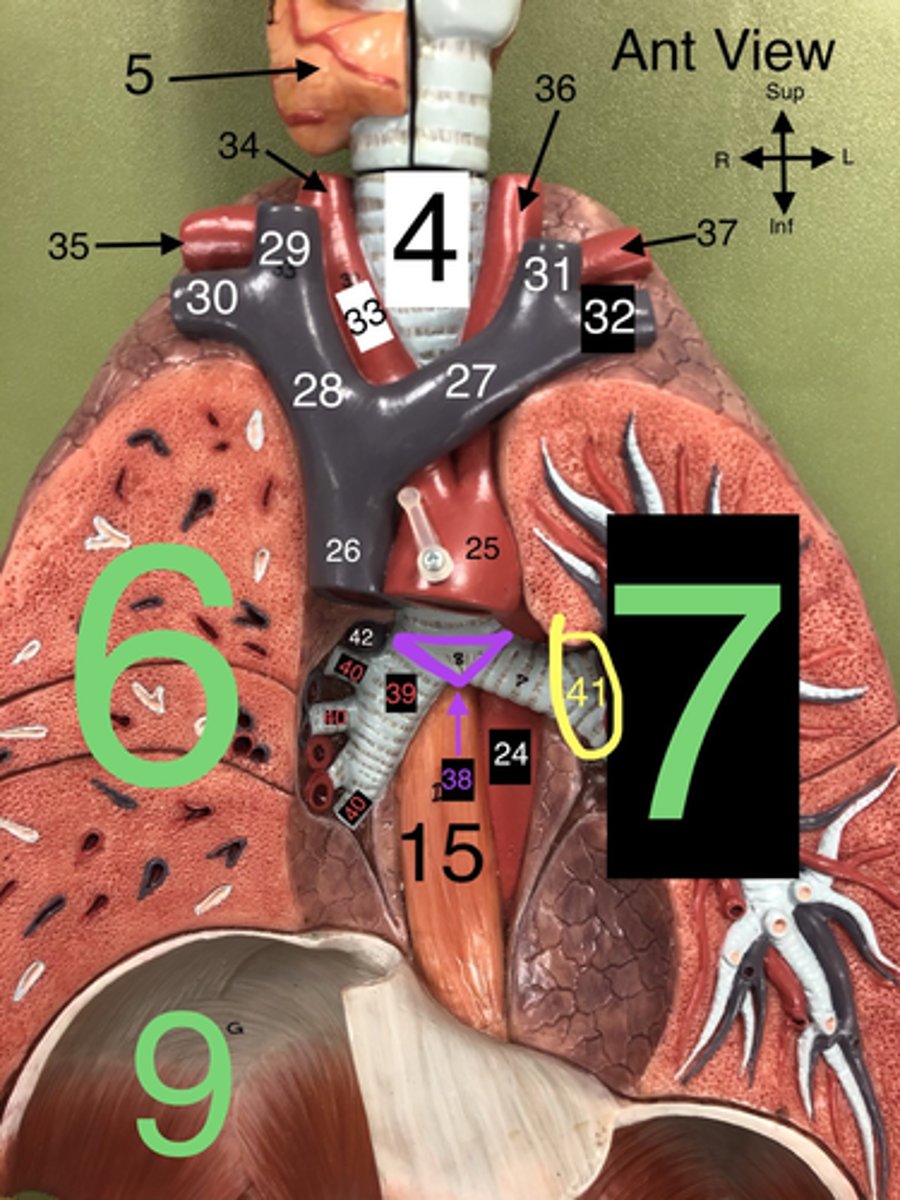
R Brachiocephalic v.
28. A vein that drains blood from the right arm and the right side of the head and neck into the superior vena cava.
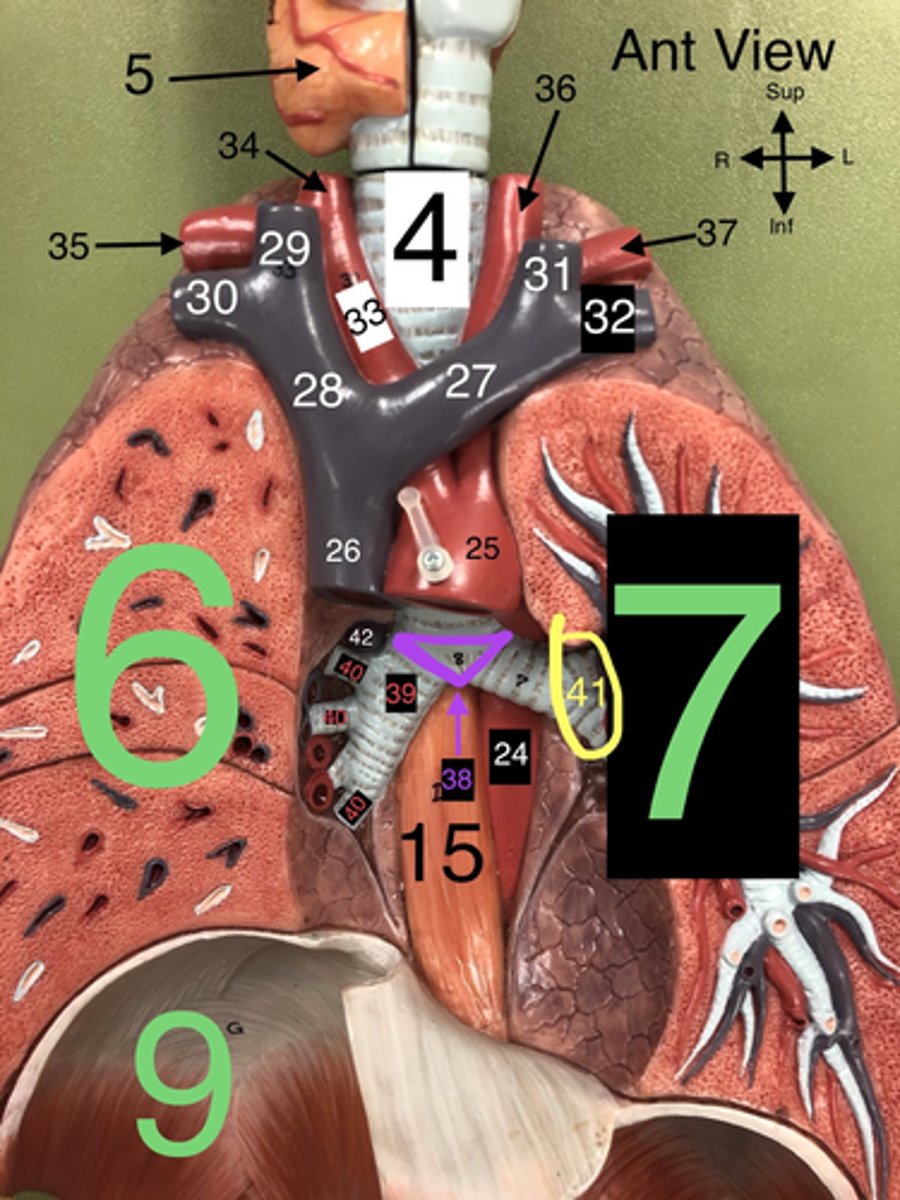
R Internal Jugular v.
29.A vein that drains blood from the brain, face, and neck into the brachiocephalic vein.
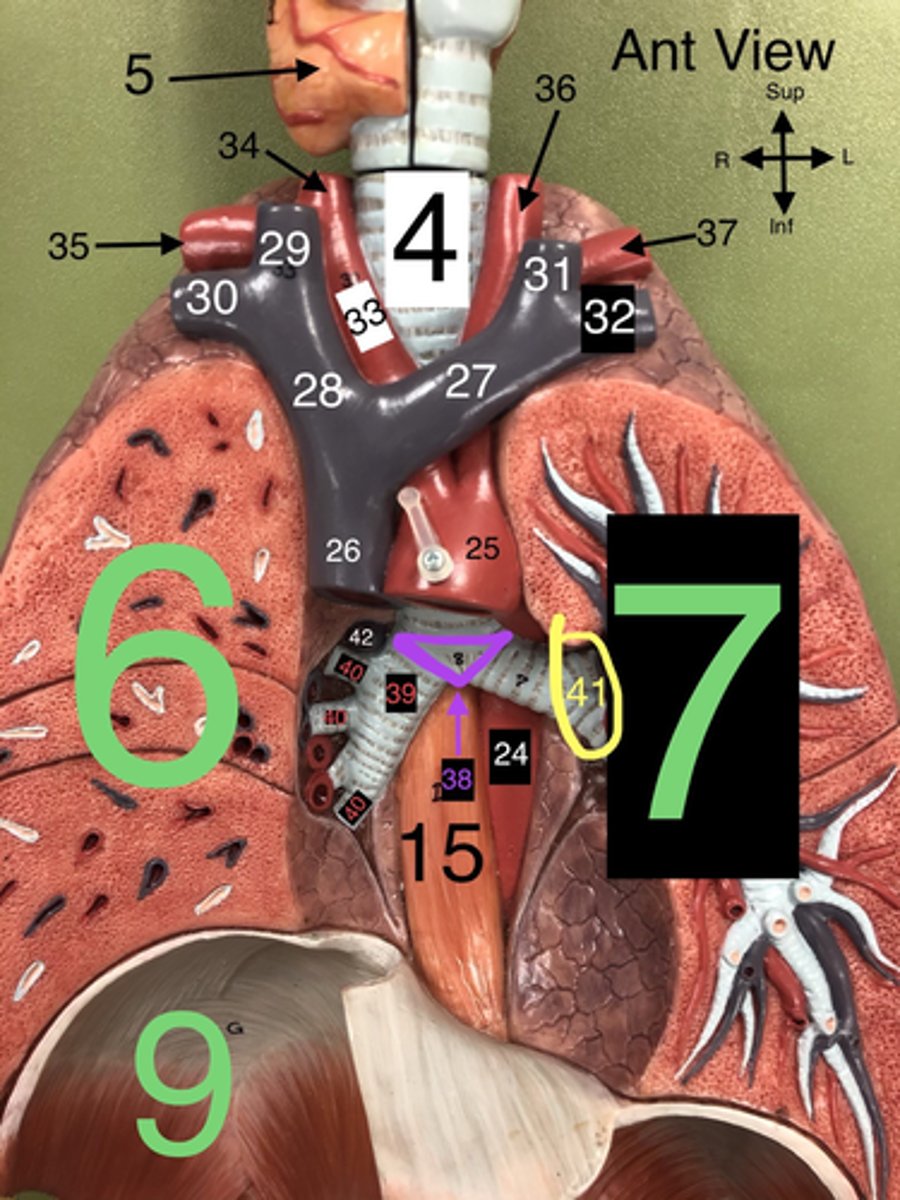
R Subclavian v.
30. A vein that drains blood from the right arm into the brachiocephalic vein.
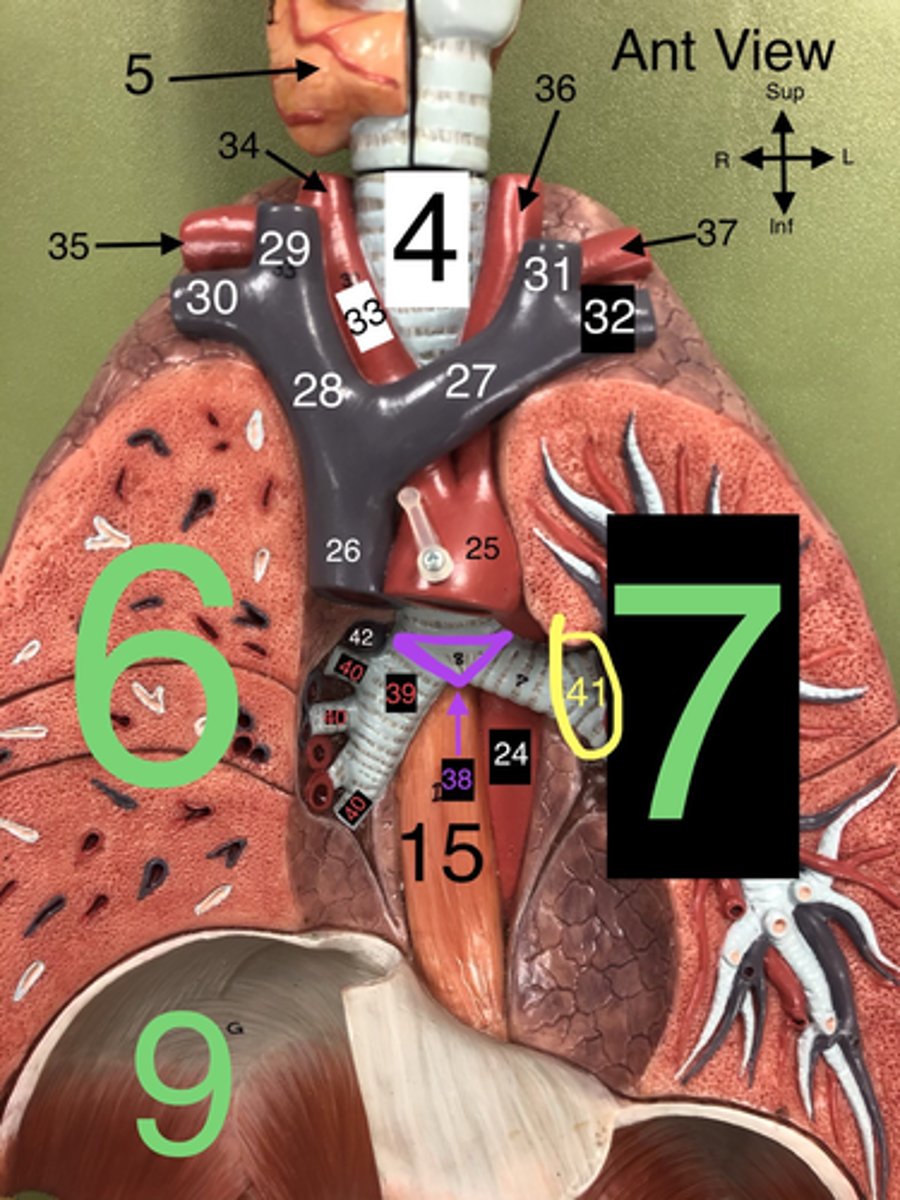
L Internal Jugular v.
31. A vein that drains blood from the left side of the brain, face, and neck into the left brachiocephalic vein.
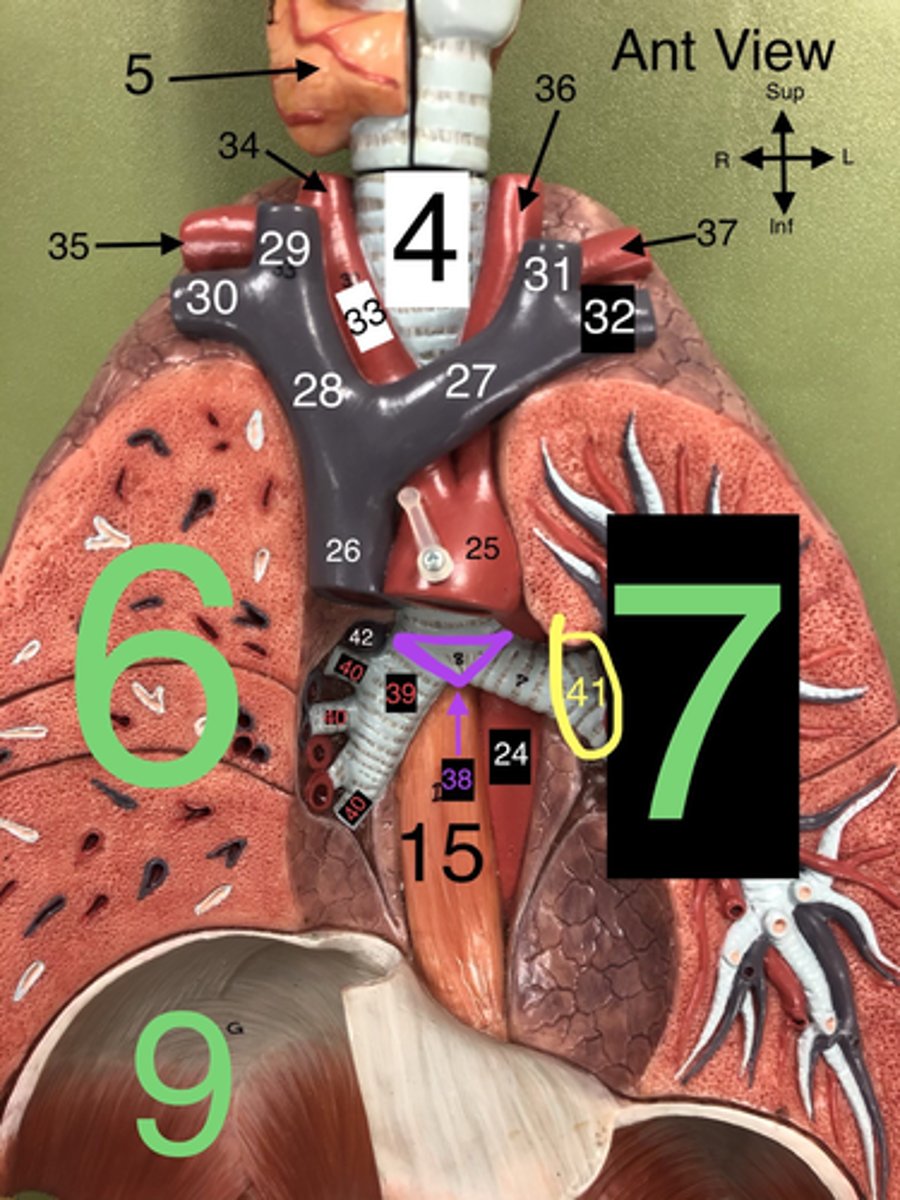
L Subclavian v.
32. A vein that drains blood from the left arm into the left brachiocephalic vein.
Brachiocephalic Trunk (innominate a)
33. The first major branch of the aorta that splits into the right common carotid artery and right subclavian artery.
R Common Carotid a.
34. An artery that supplies blood to the right side of the head and neck.
Internal carotid a
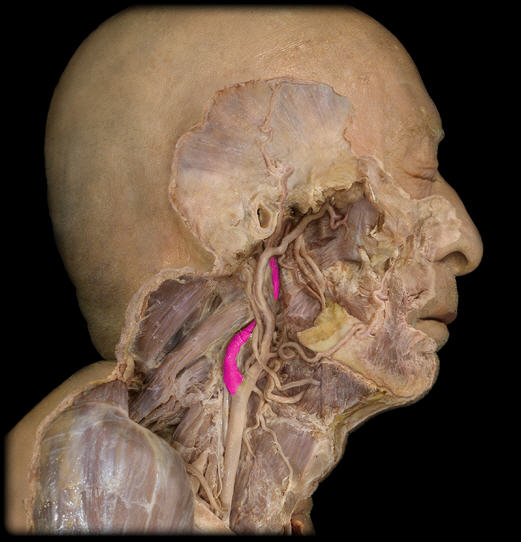
Carotid sinus
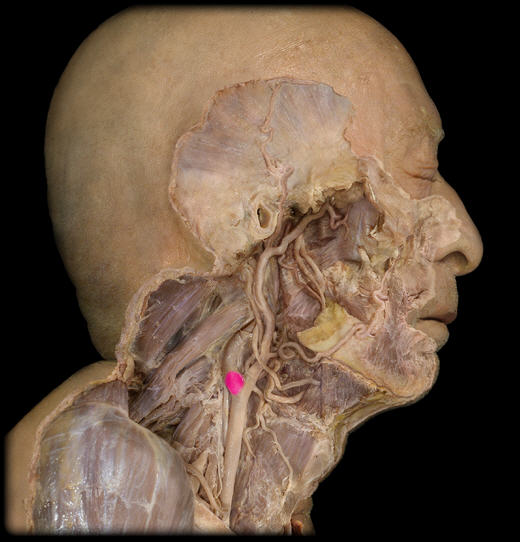
External carotid a
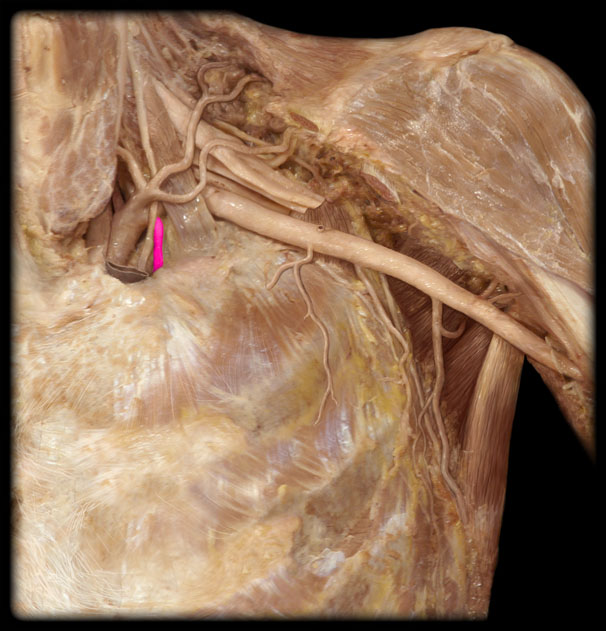
Thyrocervical trunk and branches
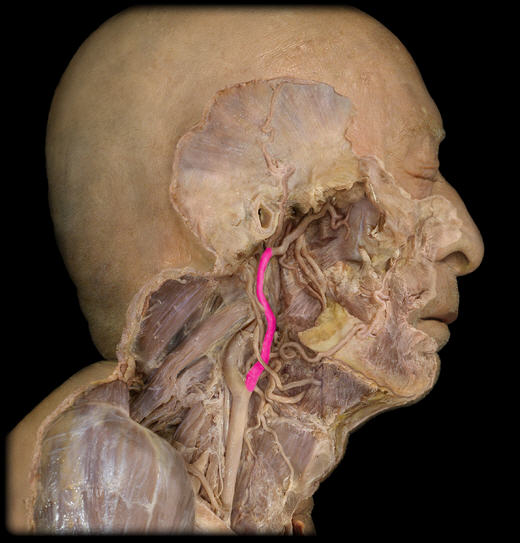
Vertebral a
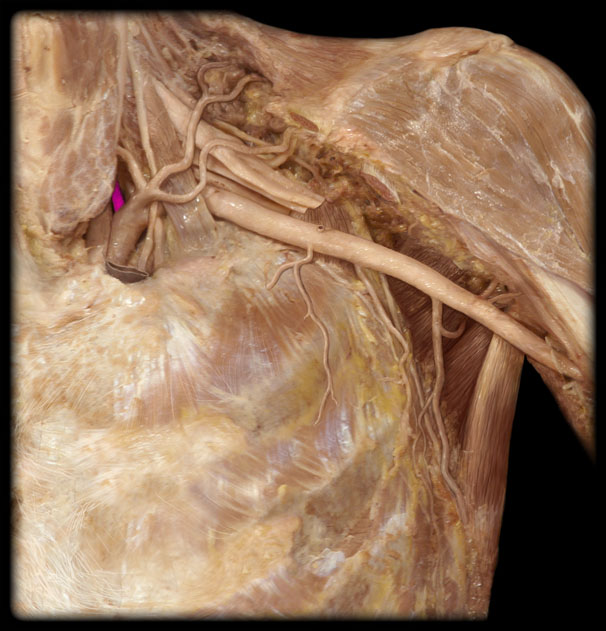
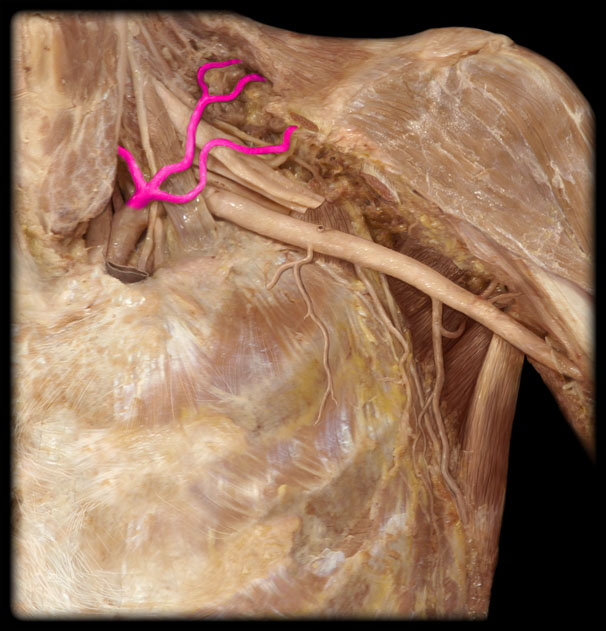
Costocervical trunk
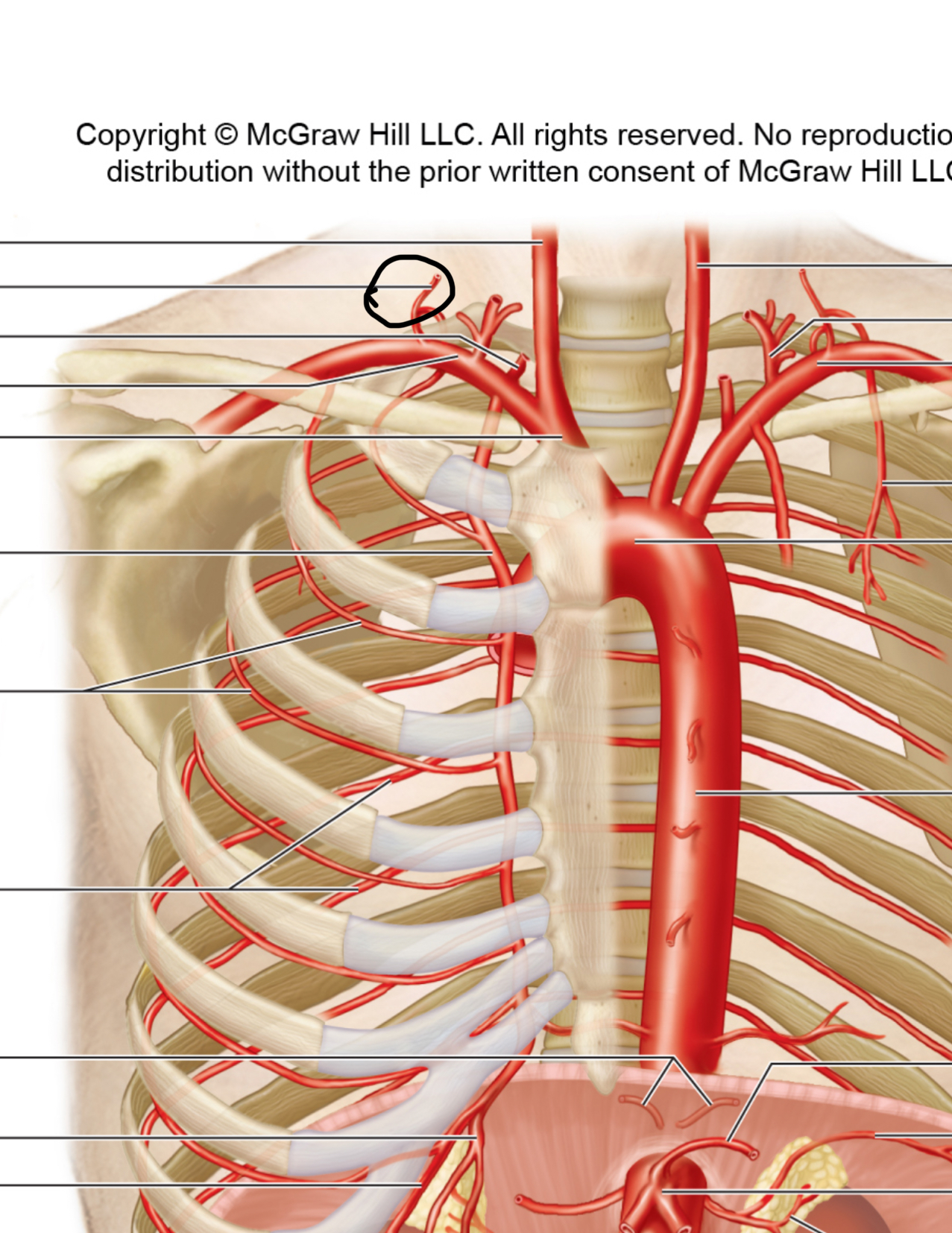
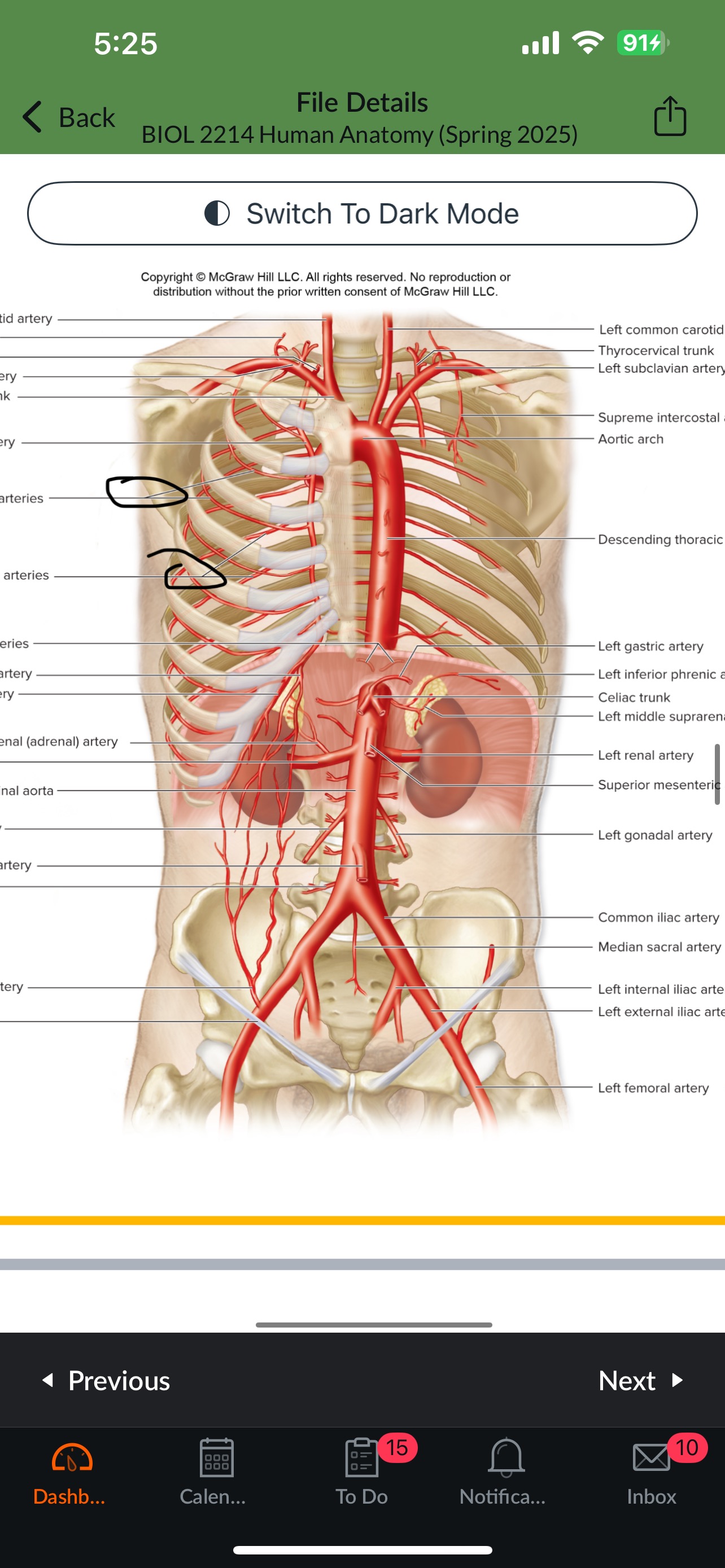
Internal thoracic a (internal mammary a)
Intercostal arteries
Vertebral v
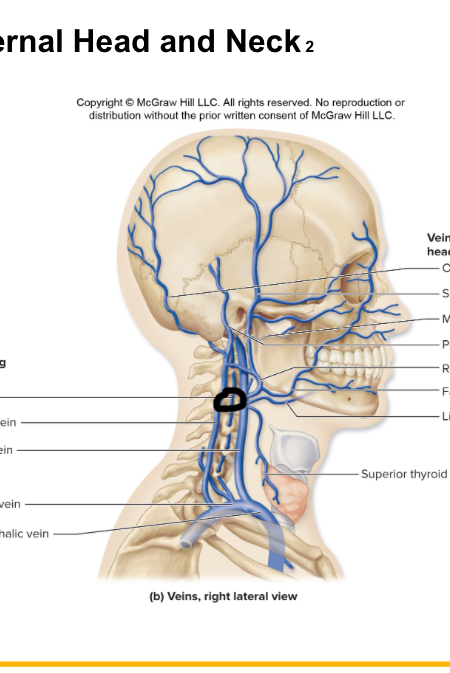
Internal thoracic veins
Middle thyroid v
Accessory hemiazygos v
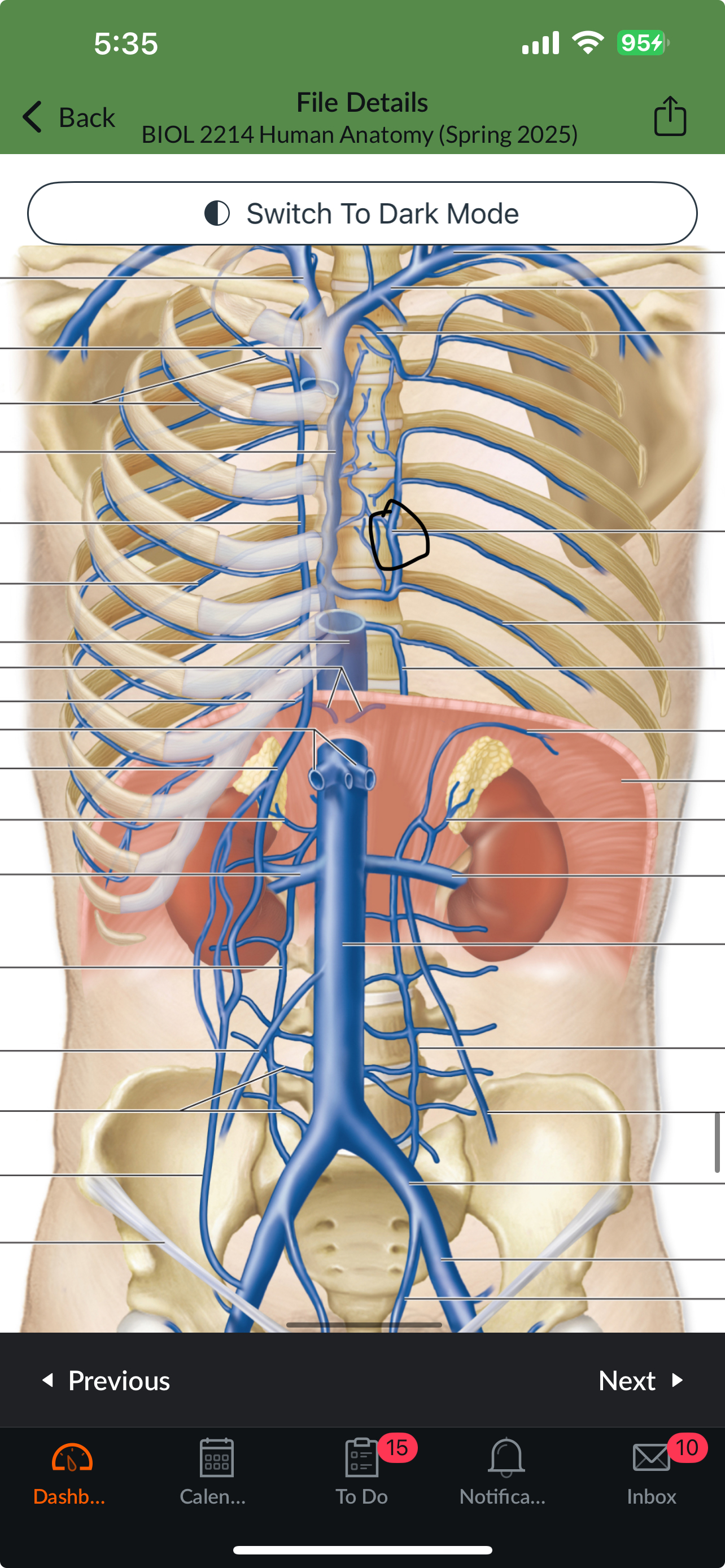
Hemiazygos v
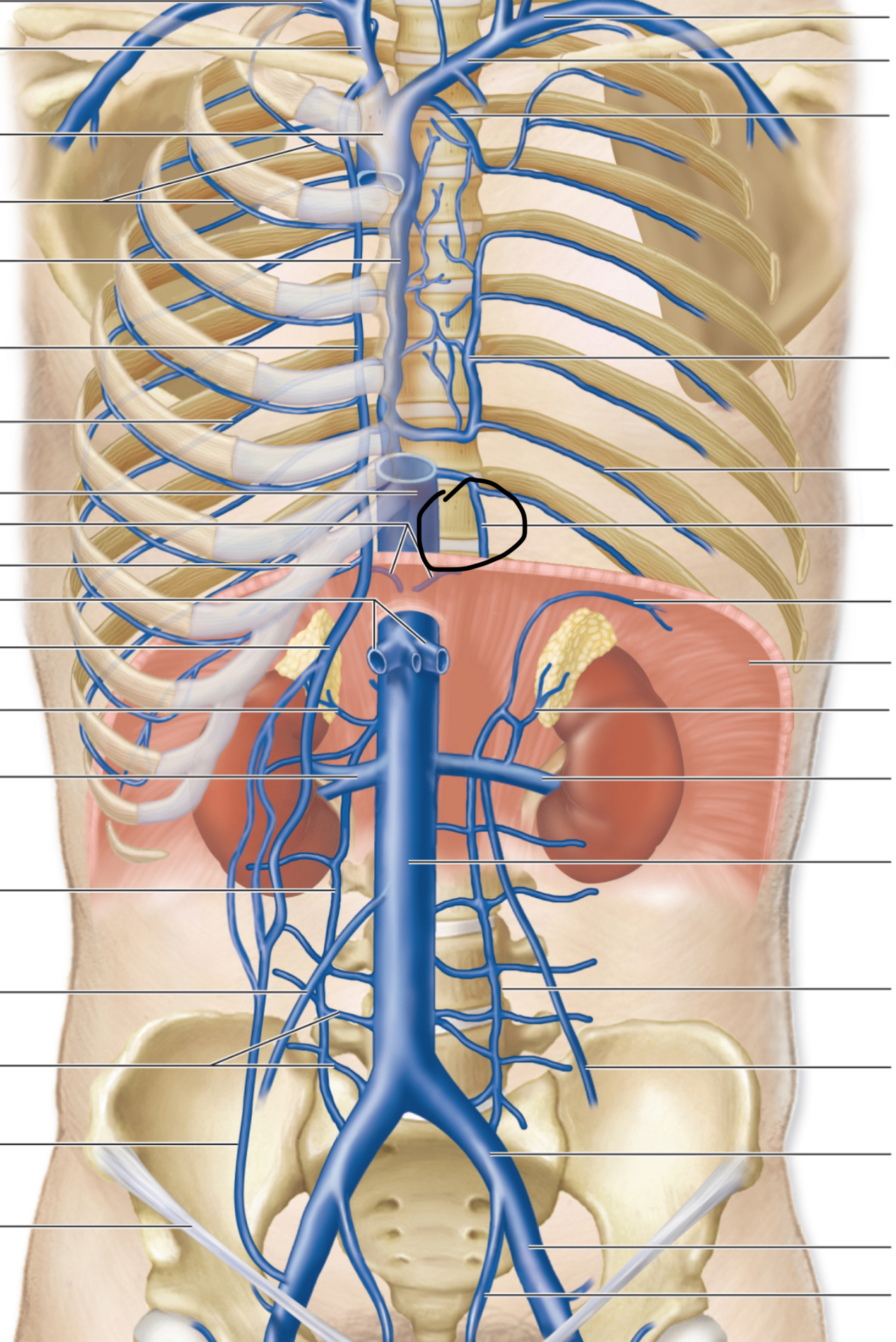
Posterior Intercostal veins
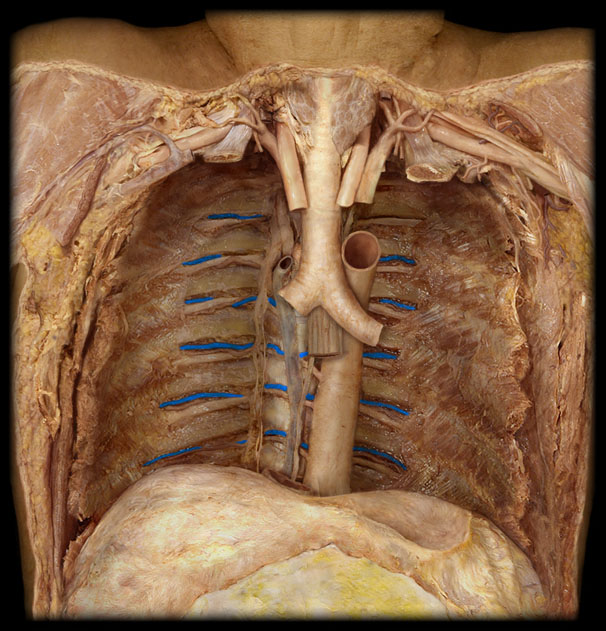
R Subclavian a.
35. An artery that supplies blood to the right arm and parts of the thorax.
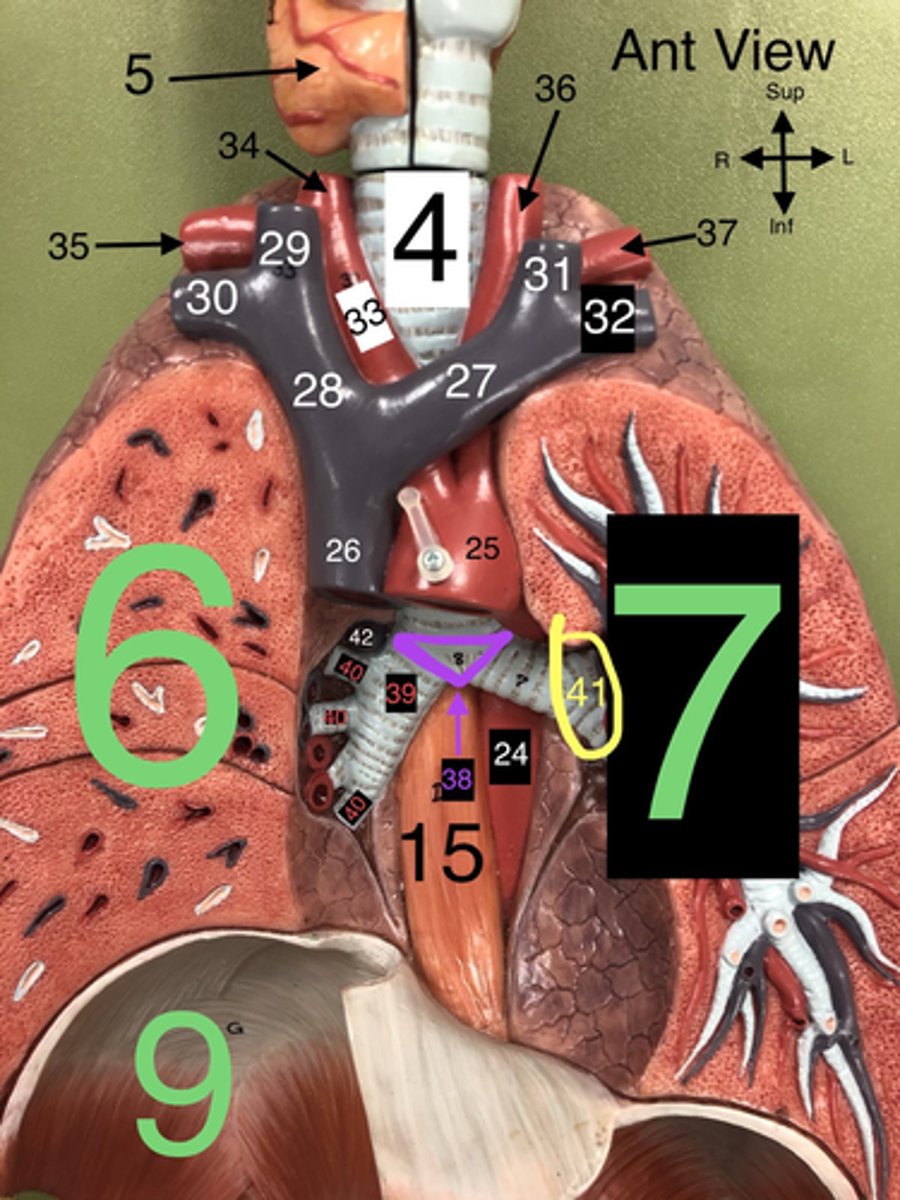
L Common Carotid a.
36. An artery that supplies blood to the left side of the head and neck.
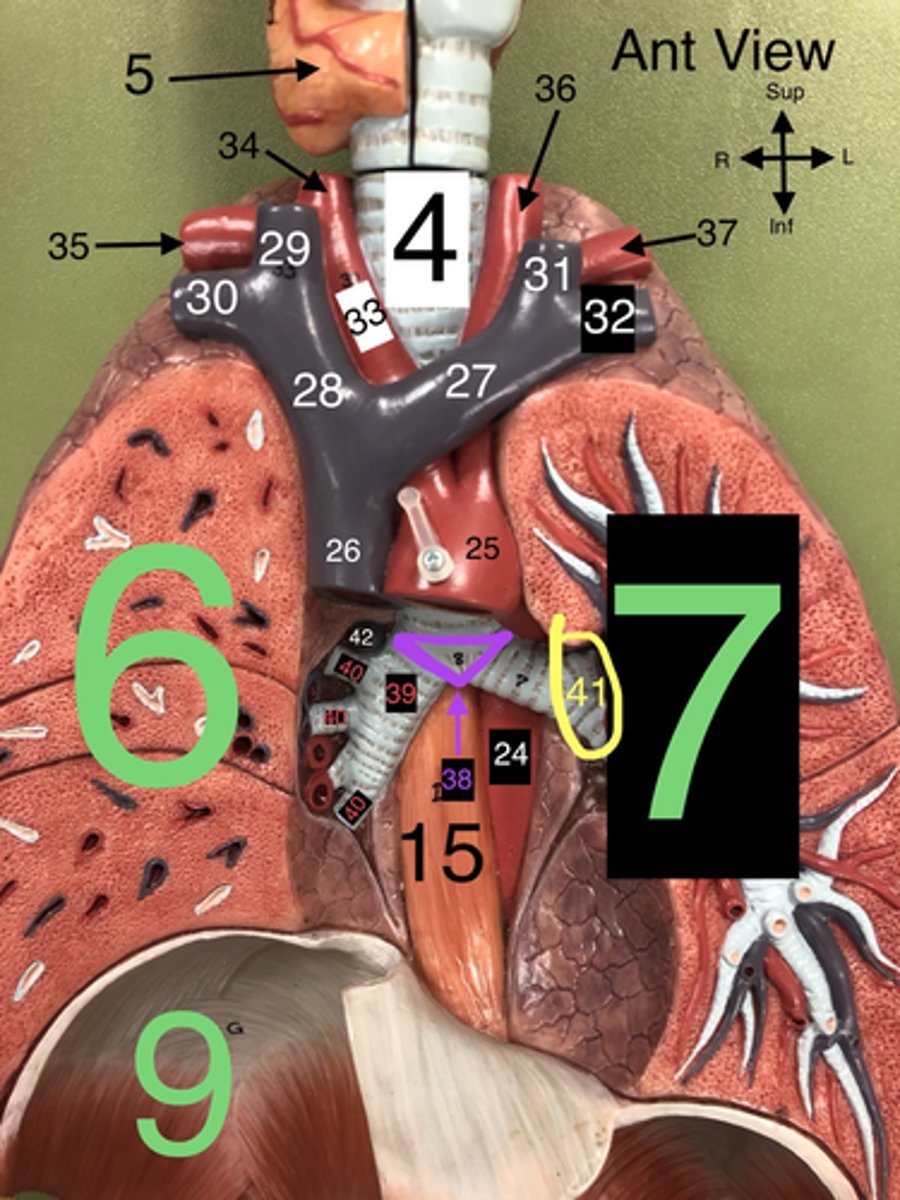
L Subclavian a.
37. An artery that supplies blood to the left arm and parts of the thorax.
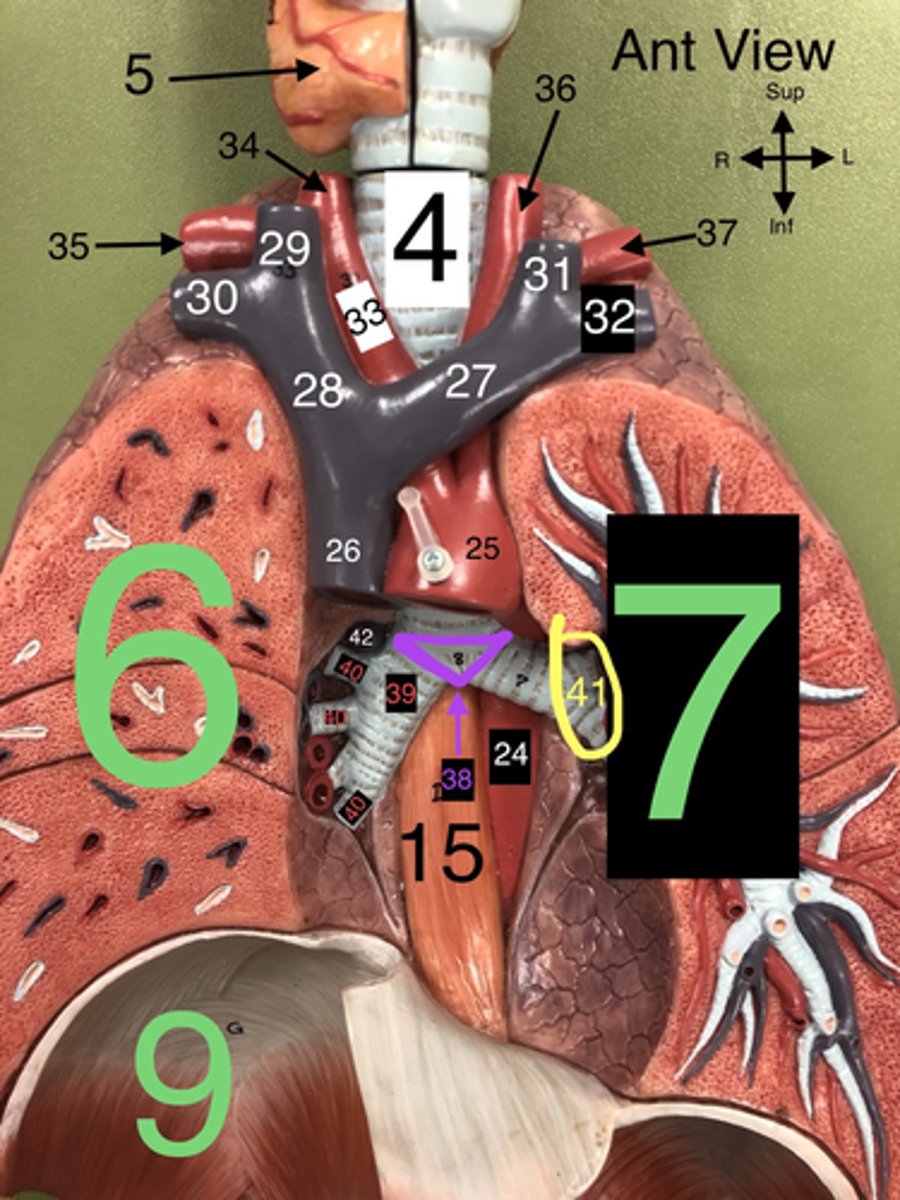
Carina
38. The ridge at the base of the trachea where it splits into the right and left primary bronchi.
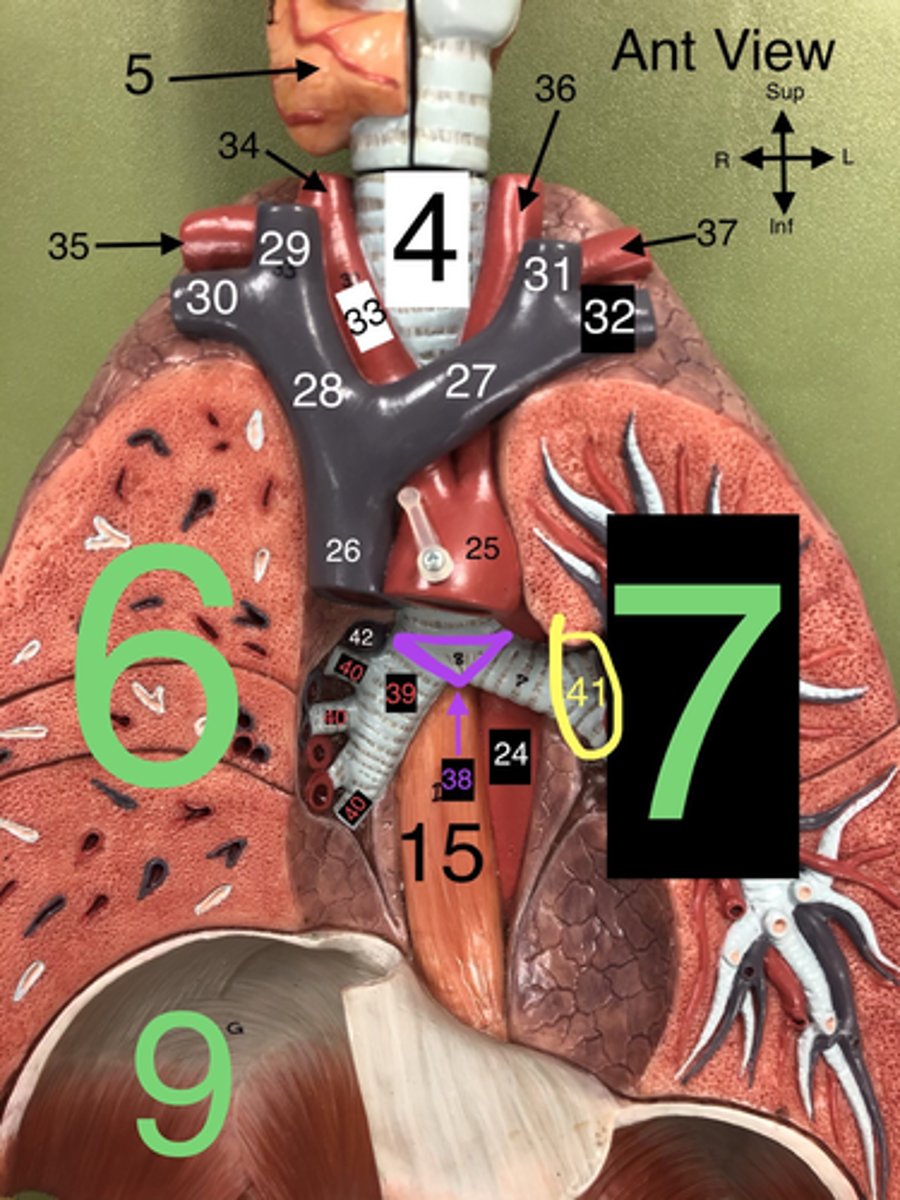
R Primary Bronchus
39. The bronchus that leads directly into the right lung.
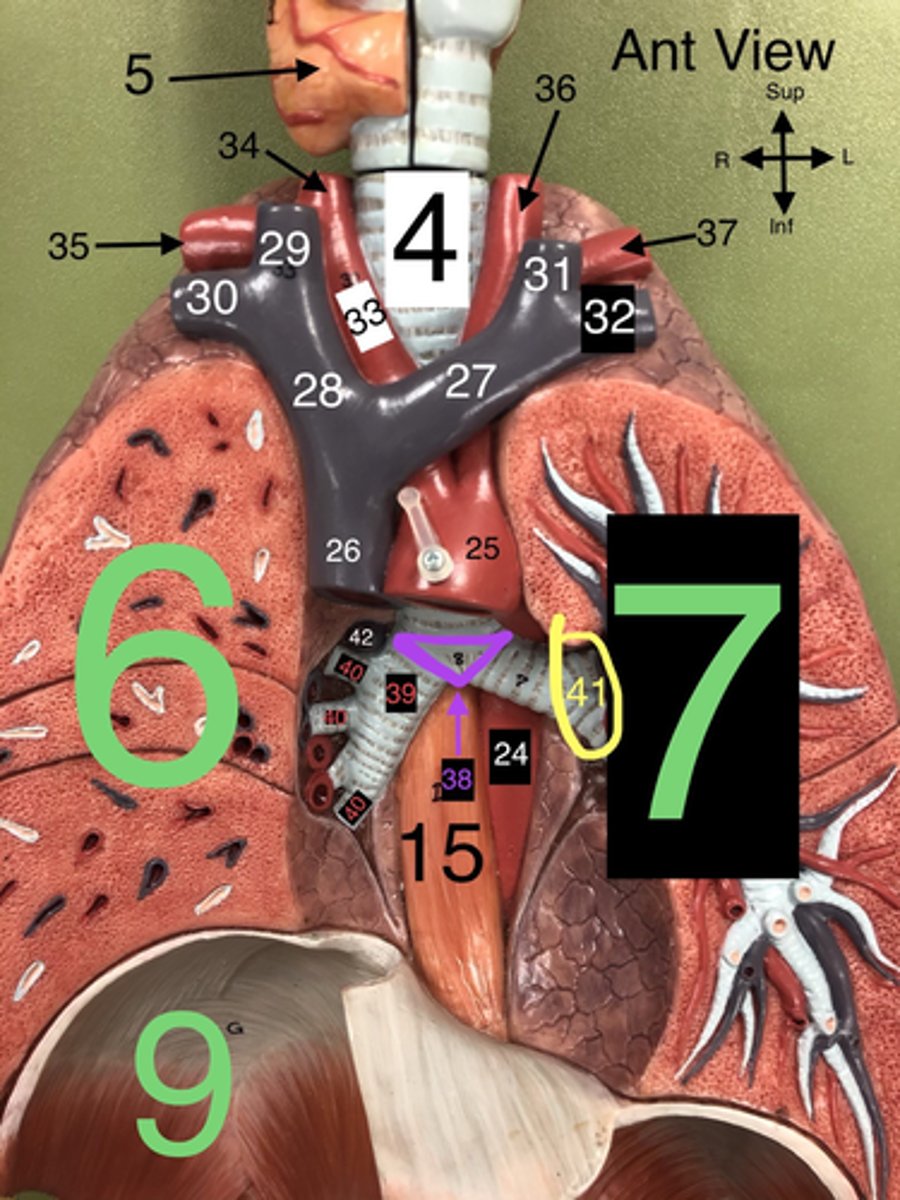
R Secondary (Lobar) Bronchi
40.The bronchi that branch from the right primary bronchus into the lobes of the right lung.
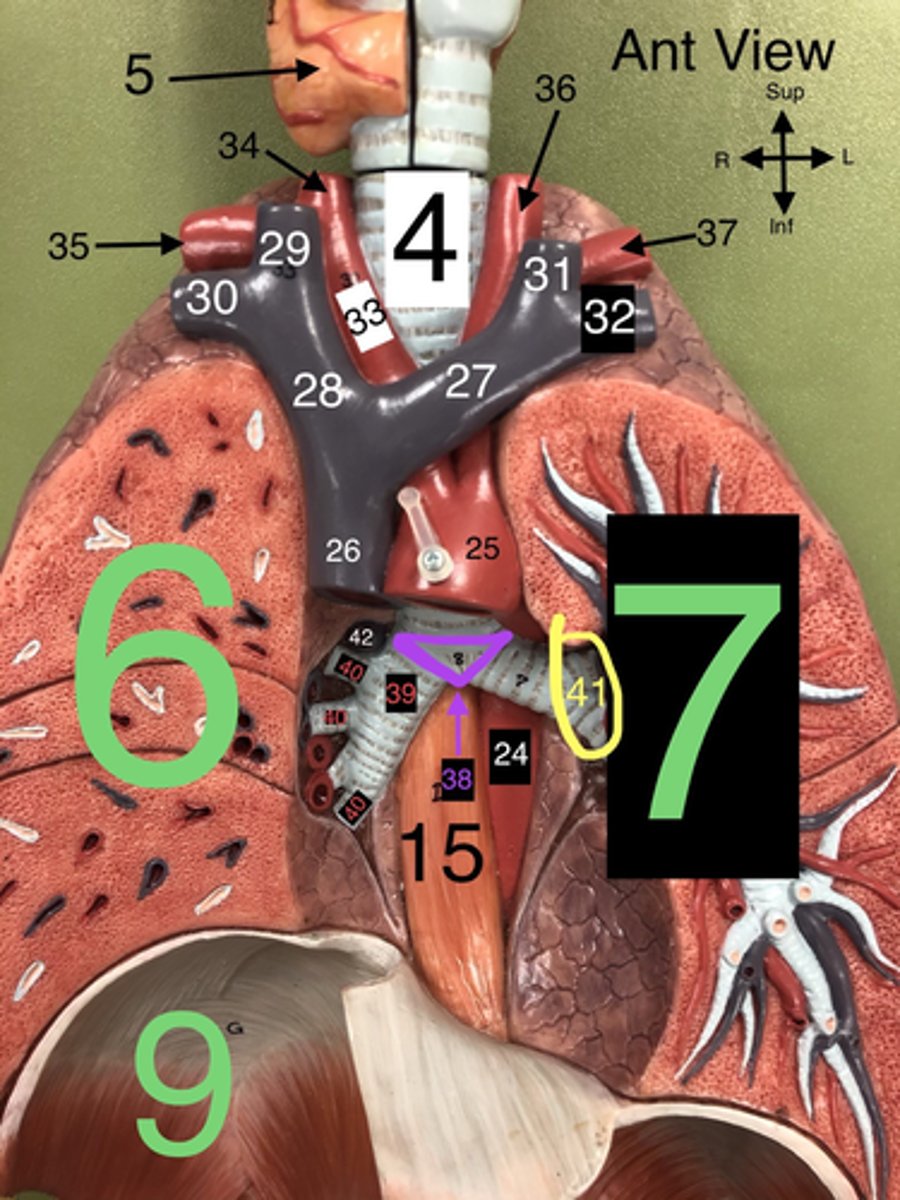
Segmental bronchi
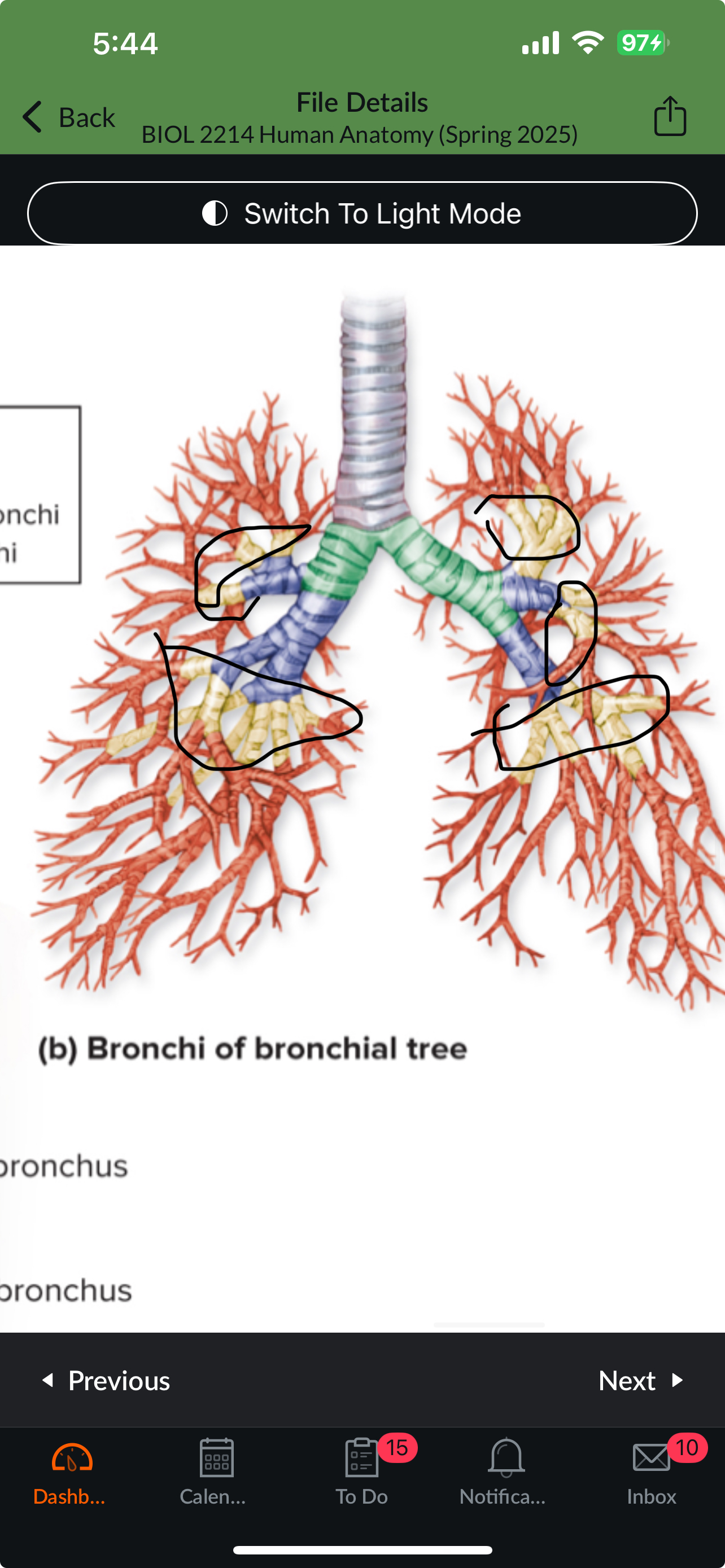
Visceral pleura