Grnd-54 Theory of Flight 7 Hydraulic Systems
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Hydraulic Theory
Hydraulic systems use an incompressible fluid to transmit force from one location to another within the fluid. A large mechanical advantage can be obtained.
Pascal’s Law
Pressure applied to a confined liquid at any point is transmitted without loss in every direction in that it acts at right angles to each portion of the entire area of that container.
Mechanical Advantage
The ratio between the effort (input force) required to move a load (output force). In other words, it is the multiplying of force.
Makeup of Basic Hydraulic System
Hydraulic Fluid
Pressure Generator (pump)
Plumbing (reservoir, lines, and valves)
Hydraulic motor or actuator
Desirable qualities of hydraulic fluid
High flash point
Adequate viscosity
Lubricant properties
Thermal capacity/conductivity
Hydraulic fluid warning
May cause skin irritation, avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin and ingestion and contact with eyes.
Types of hydraulic pumps
Manual
Engine driven
Electric
Pneumatic
Hydraulic
Ram Air Turbine
Hydraulic plumbing components
Reservoir
Filters
Valves (shut-off, control, pressure relief)
Accumulators
Hydraulic Motors
Converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque or rotation. Most often used to drive jackscrews which power flaps, stabilizer trim, and some vertically extending landing gear applications.
Hydraulic Actuator
Provide a reversible force in a single direction. Landing gear extension and retraction, cargo door operation and movement of flight control surfaces.
Aircraft Hydraulic Systems operating pressure
May vary from 200 - 5000 psi, typically 3000 - 5000 psi.
Advantages of hydraulic sources for operating aircraft systems
Light weight
Ease of installation
Simplification of inspection
Minimum maintenance requirements
Almost 100% efficient
Hydraulic Aircraft Components
Wheel brakes, NWS
Landing gear retraction/extension
Flaps and slats, spoilers and speed brakes
Flight control surfaces
Propeller pitch control, thrust reversers
Cargo doors, loading ramps/bomb bay doors
Hoist/winches
System redundancy
Multiple pressure sources (pumps), multiple hydraulic systems (actuators)
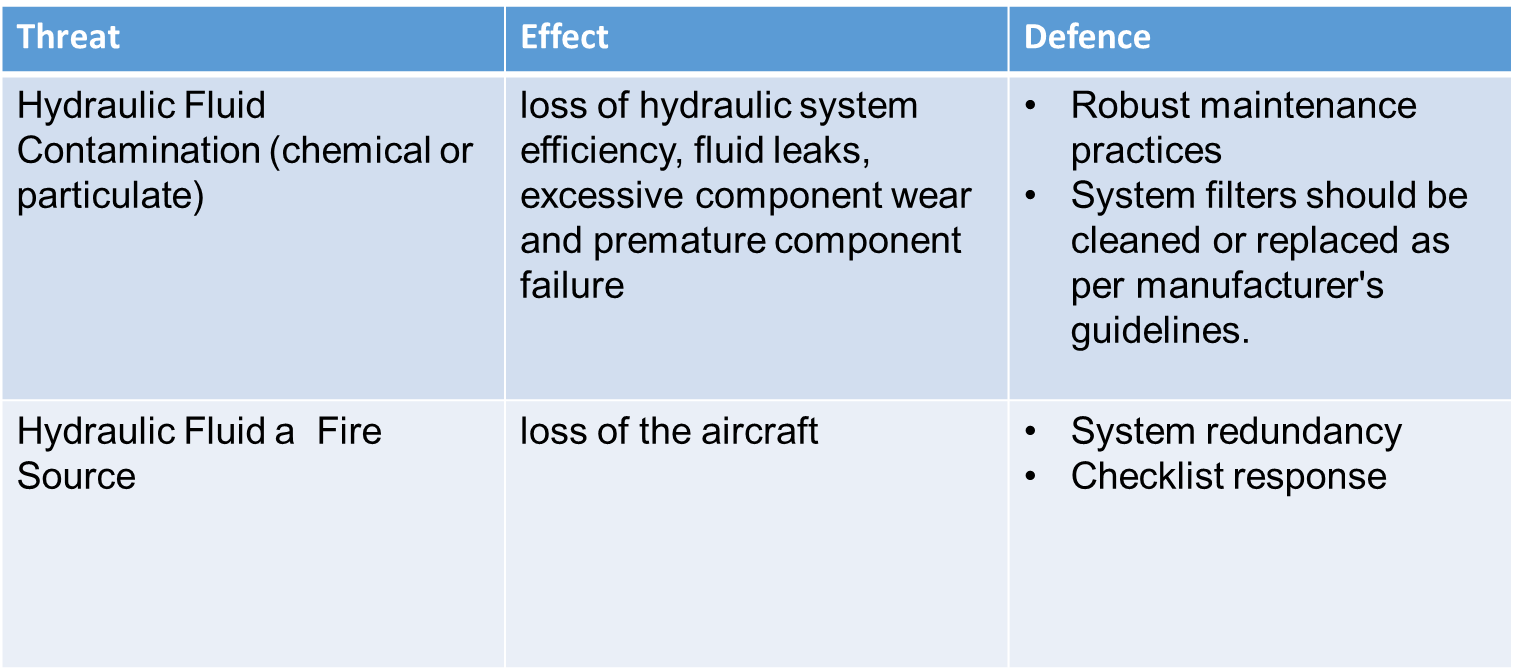
Hydraulic System Threats 1
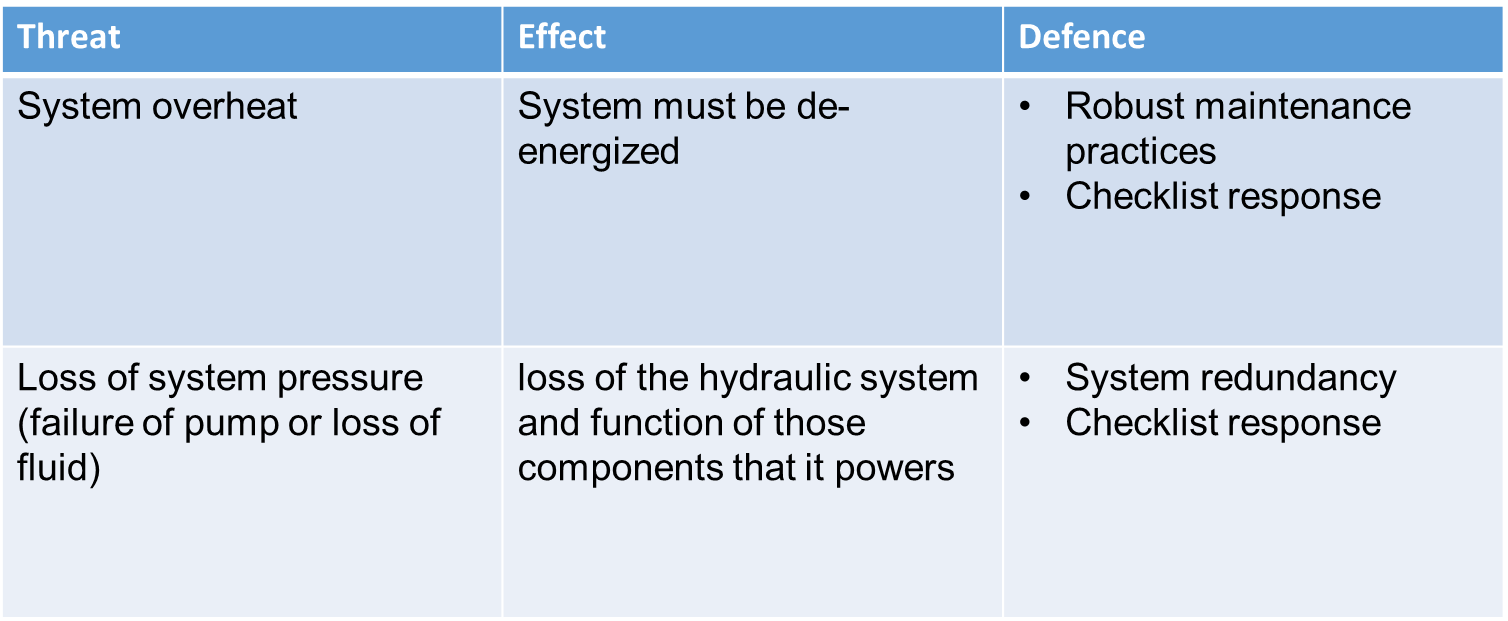
Hydraulic System Threats 2