Medical Anatomy and Physiology Precision Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IT STARTEED WITH A WHISPERRRRRRR (Standard 1, 2, 3, & a little bit of 4).
Last updated 6:10 AM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Contrast the sciences of anatomy and physiology.
Anatomy refers to the internal and external structures of the body and their physical relationships, whereas physiology refers to the study of the functions of those structures.
3
New cards
Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and give an example of each level.
move onto the next cards.
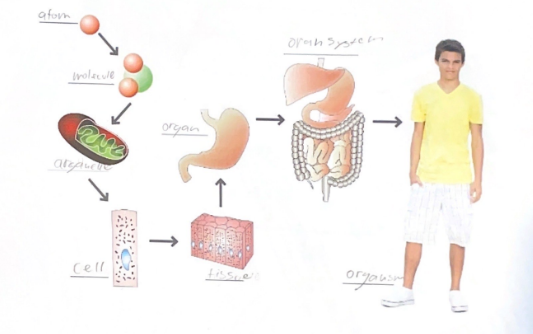
4
New cards
Chemical
a compound or substance that has been purified or prepared, especially artificially.
Ex: Oxygen, CO2, and H2O
Ex: Oxygen, CO2, and H2O
5
New cards
Cellular
The first and most basic level of organization is the cellular level. A cell is the basic unit of life and the smallest unit capable of reproduction.
Example: Red Blood Cells
Example: Red Blood Cells
6
New cards
Tissue
A group or layer of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Example: Nerve tissue
Example: Nerve tissue
7
New cards
Organ
A part of the body that performs a specific function. Ex: The heart.
8
New cards
System
An organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs so arranged that together they can perform complex functions for the body.
Example: Respiratory System
Example: Respiratory System
9
New cards
Organism
An individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form.
Example: Human
Example: Human
10
New cards
Describe Metabolism
**The chemical processes that take place as your body converts foods and drinks into energy**.
11
New cards
What is an Anabolic process?
The process by which the body utilizes the energy released by catabolism to synthesize complex molecules.
12
New cards
What is a Catabolic process?
Takes larger structures like proteins, fats, or tissues and breaks them down into smaller units such as cells or fatty acids. Occurs when you're digesting food.
13
New cards
Apply directional terms used in human anatomy.
sheesh.
14
New cards
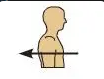
Posterior (dorsal)
Behind, or toward \n the back of the \n body \n (The heart is \n posterior to the \n breastbone.)
15
New cards
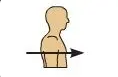
Anterior (ventral)
In front of, toward \n the front of the \n body \n (The breastbone \n is anterior to the \n spine.)
16
New cards
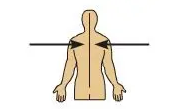
Medial
Toward, or at the \n midline of the \n body, on the inner \n side of (The heart is \n medial to the \n arm.)
17
New cards
Lateral
Away from the \n midline of the \n body, on the outer \n side of \n (The arms are \n lateral to the \n chest.)
18
New cards
Proximal
Close to, or \n toward the point of \n attachment to the \n trunk of the body \n (The elbow is \n proximal to the \n wrist (it is closer \n to where the arm \n connects to the \n trunk).)

19
New cards
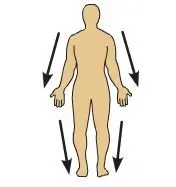
Distal
Farther from, or \n away from the \n point of \n attachment to the \n trunk of the body (The knee is \n distal to the \n thigh.)
20
New cards
\
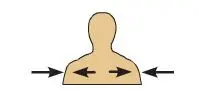
Superficial
Superficial
\
Toward the body \n surface (The skin is \n superficial to the \n skeleton.)
Toward the body \n surface (The skin is \n superficial to the \n skeleton.)
21
New cards
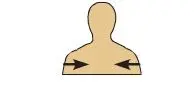
Deep
Away from the \n body surface, \n more internal (The lungs are \n deep to the rib \n cage.)
22
New cards
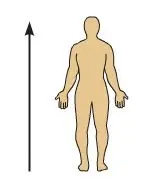
Superior
Above, or toward \n the head or upper \n part of the body \n (The forehead is \n superior to the \n nose.)
23
New cards
Inferior
Below, or toward the lower part of a structure of the body (The hips are \n inferior to the \n ribs.)
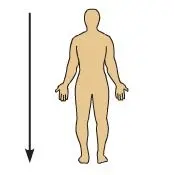
24
New cards
Apply commonly used planes to divide the body.
ye.
25
New cards
Sagittal plane
Divides body into right and left \n portions
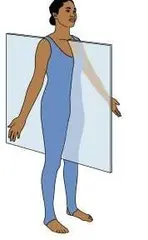
26
New cards
Midsagittal plane
Divide the right and left sides of the brain into two equal parts, like cutting down the middle of a baked potato before you put on the toppings. While sagittal is just dividing into right and left side portions.
27
New cards
Transverse plane (horizontal)
Divides body into top and bottom \n portions.
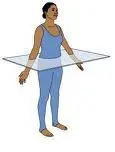
28
New cards
\
Frontal plane (coronal)
Frontal plane (coronal)
\
Divides body into front and back \n portions.
Divides body into front and back \n portions.
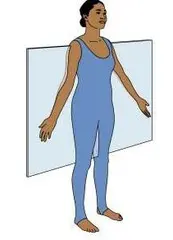
29
New cards
Identify the body cavities and locate the following organs within each cavity.
yuh
30
New cards
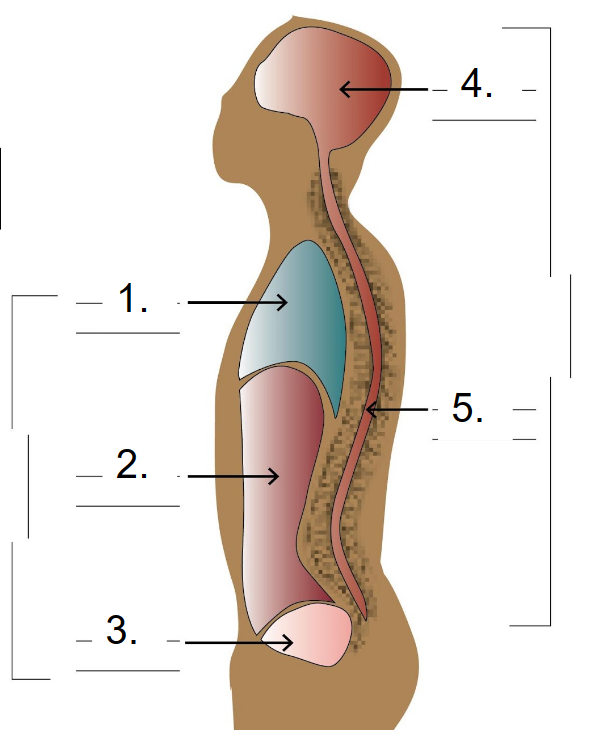
Dorsal Cavity
Cranial-brain (4) and Vertebral-spinal cord (5).
31
New cards
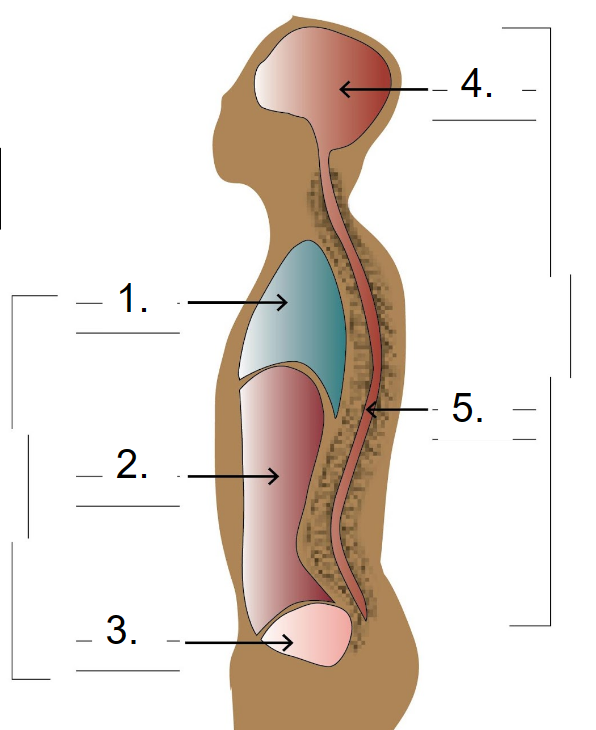
Ventral Cavity
1\. Thoracic-heart, lungs
\-Mediastinum-heart, bronchi, esophagus, thymus
\-Pericardial-heart
\-Pleural-lungs
2. Abdominal-liver, spleen, intestines, kidneys, stomach
3. Pelvic-intestines, urinary bladder, sex organs
\-Mediastinum-heart, bronchi, esophagus, thymus
\-Pericardial-heart
\-Pleural-lungs
2. Abdominal-liver, spleen, intestines, kidneys, stomach
3. Pelvic-intestines, urinary bladder, sex organs
32
New cards
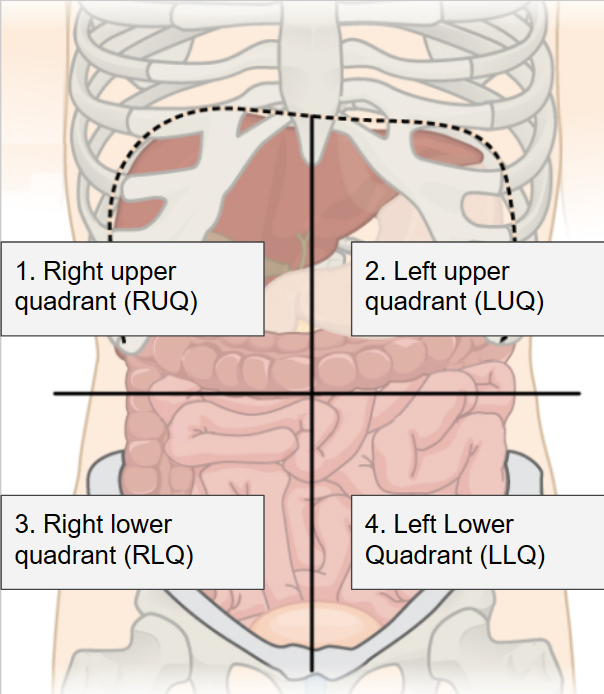
Identify the major organ(s) in each abdominal quadrant.
33
New cards
RUQ-right upper quadrant
Liver, gallbladder, right kidney
34
New cards
RLQ-right lower quadrant
Cecum, appendix, right ovary.
35
New cards
LUQ-left upper quadrant
Spleen, stomach, left kidney.
36
New cards
LLQ-lower left quadrant
Left ovary.
37
New cards
What are the 5 Steps of a feedback Loop?
Stimulus --> Receptor --> Control Center --> Effector--> Response \n Example of Glucagon: Low Glucose levels (stimulus), Pancreas are triggered and detects disease (receptor), Alpha Cells receives signals from the pancreas and release glucagon (control center), Glucagon acts on the glycogen and sent to the liver and broken down to the blood (effector), and glucose levels start to rise (response). See other examples in notes.
38
New cards
Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress.
Stress constitutes a state of threatened homeostasis triggered by intrinsic or extrinsic adverse forces (stressors) and is counteracted by an intricate repertoire of physiologic and behavioral responses aiming to maintain/reestablish the optimal body equilibrium (eustasis).
39
New cards
What is a negative feedback loop?
Negative feedback counteracts with the stimulus and the changes of properties from their target values (set points). Example would be body temperature rising, or under body temperature.
40
New cards
What is a positive feedback loop?
\
Positive feedback is amplifying the stimulus or pushes away from the normal state. Example would be childbirth or a fruit rotting.
Positive feedback is amplifying the stimulus or pushes away from the normal state. Example would be childbirth or a fruit rotting.
41
New cards
Describe the relationship between homeostasis and childbirth.
The neurons send a signal that leads to release of the hormone oxytocin from the pituitary gland. Oxytocin increases uterine contractions, and thus pressure on the cervix. This causes the release of even more oxytocin and produces even stronger contractions. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born.
42
New cards
Describe the relationship between homeostasis and breastfeeding.
Homeostatic adjustments in lactation are influenced by milk composition, the substrates used for milk synthesis, the partitioning of nutrients between body tissues and organs, the mechanisms controlling milk synthesis, the energy output in milk, the efficiency of milk synthesis as well as dietary energy intake and level of physical exercise.
43
New cards
Describe the relationship between homeostasis and Blood clotting.
Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps. This cascade culminates into the formation of a “plug” that closes up the damaged site of the blood vessel controlling the bleeding.
44
New cards
States of Matter
Solids, liquids and gases are three states of matter. In solids, the particles are tightly packed together. In liquids, the particles have more movement, while in gases, they are spread out. Particles in chemistry can be atoms, ions or molecules.
45
New cards
Elements
Each of more than one hundred substances that a not be broken down into something else by a chemical reaction, they do not change.
46
New cards
Basic components of the atom
1\. Nucleus 2. Electrons 3. Protons 4. Neutrons
47
New cards
Ion
Charged particles, and unbalance of the protons and electrons in the nucleus. Cations are the positively charged ions giving electrons away, while anions are negatively charged ions that are attracted to electrons. Ex: Electrolyte
48
New cards
Identify the four major elements in the body.
1\. Carbon 2. Hydrogen 3. Oxygen 4. Nitrogen
49
New cards
Compound
Chemical formulas that hold lots of information, and a molecule that has more than one element in it. Example of a compound would be Carbon Dioxide, CO2 = 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms.
50
New cards
Molecule
A combination of atoms that interact with each other.
51
New cards
Cation
Atom or group of atoms that bears a positive electric charge.
52
New cards
Anion
A negatively charged ion, i.e. one that would be attracted to the anode in electrolysis.
53
New cards
Ionic
**Form when two or more ions come together and are held together by charge differences.**
54
New cards
Covalent
Involves the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms.
55
New cards
Hydrogen
A weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other.
56
New cards
Define pH
Stands for power of hydrogen, or potential hydrogen. Essentially, it's a measure of how readily a chemical solution will accept H+ ions.
57
New cards
What is Acidic?
When the pH level is lower than 7, and there are more hydrogen ions.
58
New cards
What is Basic?
When the pH level is more than 7, and there are less hydrogen ions or more hydroxide ions.
59
New cards
What is Neutral?
When the pH level is 7, meaning not too acidic or too basic.
60
New cards
Distinguish between “neutral” pH and the “average” pH range of the blood.
1\. Neutral pH=7.0
2\. Average pH of blood=7.35 to 7.45
2\. Average pH of blood=7.35 to 7.45
61
New cards
Describe the properties of water and how it is utilized in the human body.
move to uh the next cards ye.
62
New cards
Universal solvent
Water, described as the "universal solvent" for its ability to dissolve many substances.
63
New cards
Transport
The cohesion and adhesion property of water support the binding of other molecules with water so as to transport the molecules in the body.
64
New cards
Lubricant
lubricants that are water-based, without the use of oil, silicone, or grease to offer additional lubrication.
65
New cards
Heat capacity
One of water's most significant properties is that it takes a lot of energy to heat it. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature.
66
New cards
Chemical reactions
Water undergoes various types of chemical reactions. One of the most important chemical properties of water is its ability to behave as both an acid (a proton donor) and a base (a proton acceptor), the characteristic property of amphoteric substances.
67
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Do not contain carbon, small molecules, usually form ionic bonds.
68
New cards
Organic compounds
Usually contain carbon, large molecules, form covalent bonds, flammable
69
New cards
Carbohydrates
The main source of energy for everything your body does. All your tissues can use this source for energy and are the only molecule our brains can use. Example: Glucose
70
New cards
Proteins
Provide the building blocks for new proteins and enzymes that make many of your cellular functions possible. Some examples of proteins are Keratin, Myosin and Hemoglobin.
71
New cards
Lipids
Become stored energy but can also become parts of cell membranes and protective tissues. Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E and K), hormones and most of the cell membrane that is not made up of protein.
72
New cards
Nucleic acids
Carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the RNA and proteins by which living things function. The well-known structure of the DNA double helix allows this information to be copied and passed on to the next generation. Example: 1. RNA 2. DNA
73
New cards
Amino acids
Building blocks of polypeptides and proteins play important roles in metabolic pathways, gene expression, and cell signal transduction regulation. A single organic amino acid molecule contains two functional groups – amine and carboxyl – and a unique side chain.
74
New cards
Describe how the body produces energy during cellular respiration.
ATP ↔ ADP + P + ENERGY.
75
New cards
Identify the four principle parts of a generalized animal cell and their functions.
1\. Nucleus 2. Cytosol 3. Organelles 4. Cell membrane
76
New cards
Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane.
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
77
New cards
Describe a selectively permeable membrane and factors which influence permeability.
The permeability of a membrane is affected by temperature, the types of solutes present and the level of cell hydration. Increasing temperature makes the membrane more unstable and very fluid. Decreasing the temperature will slow the membrane
78
New cards
Contrast intracellular and extracellular fluid in terms of location and composition.
While intracellular fluid is only found on the inside of cells, a majority of extracellular fluid is found in all of the spaces of the body located outside of the cells, while a small percent is located within the blood plasma.
79
New cards
Diffusion (passive)
A physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration.
80
New cards
Osmosis (passive)
Is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane.
81
New cards
Facilitated diffusion (passive)
The diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane.
82
New cards
Dialysis (passive)
Separation of substances in solution by means of their unequal diffusion through semipermeable membranes. The process of separating larger molecules from smaller molecules that occurs in kidney dialysis for example, where a machine takes a role of a kidney and filtrates blood.
83
New cards
Filtration (passive)
The process of separating suspended particles from the fluid through a porous material in which the fluid can pass while the suspended particles are retained. It refers to the process of segregating solids from the fluid (liquid or a gas) by passing it through a filtering device.
84
New cards
Phagocytosis (active)
The process by which a phagocyte (a type of white blood cell) surrounds and destroys foreign substances (such as bacteria) and removes dead cells.
85
New cards
Exocytosis (active)
The fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and results in the discharge of vesicle content into the extracellular space and the incorporation of new proteins and lipids into the plasma membrane.
86
New cards
Active Transport
A substance goes from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, and this requires energy.
87
New cards
Isotonic solution
When a red blood cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there will be no net movement of water. Both the concentration of solute and water are equal both intracellularly and extracellularly.
88
New cards
Hypotonic solution
A cell placed into a hypotonic solution will swell and expand until it eventually burst through a process known as cytolysis.
89
New cards
Hypertonic solution
A cell placed into a hypertonic solution will shrivel and die by a process known as plasmolysis.
90
New cards
Contrast the following: 1. Exocrine glands 2. Endocrine glands
Exocrine: A gland that makes substances such as sweat, tears, saliva, milk, and digestive juices, and releases them through a duct or opening to a body surface. \\
Endocrine: An organ that makes hormones that are released directly into the blood and travel to tissues and organs all over the body.
Endocrine: An organ that makes hormones that are released directly into the blood and travel to tissues and organs all over the body.