Liver ARDMS Review
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Amebic Hepatic Abscess
an abscess that develops from a parasite that grows in the colon and invades the liver via the portal vein
Anastomosis
the surgical connection between two structures
Arteriovenous Fistula
An abnormal passageway between an artery and a vein
Autoimmune Disorders
Disorders in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy tissues and/or organs
ADPKD (autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease)
An inherited disease that results in development of renal, liver and pancreatic cysts late in life
Bare Area
Region of the liver not covered by peritoneum
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
a growth disorder syndrome synonymous with enlargement of several organs including the skull, tongue, and liver
Caput Medusa
recognizable dilation of the superficial veins of the abdomen
Cavernous Hemangioma
the most common benign liver tumor
Cirrhosis
condition defined as hepatocyte death, fibrosis and necrosis of the liver, and the subsequent development of regenerating nodules
Cystic Fibrosis
genetic disorder linked with the development of scar tissue accumulation within the lungs, liver, pancreas, kidneys, and/or intestines
Diaphragmatic Slip
A pseudomass of liver seen on sono resulting from hypertrophied diaphragmatic muscle bundles
Dysentery
Infection of the bowel which leads to diarrhea that may contain mucus and/or blood
Echinococcus Granulosus
A parasite responsible for the development of hydatid liver cysts
Epstein-Barr Virus
The virus responsible for mononucleosis and other potential complications
Fibrosis
The development of scar tissue within an organ
Focal Fatty Infiltration
Manifestation of fatty liver disease in which fat deposits are localized
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia (FNH)
A benign liver mass composed of a combination of hepatocytes and fibrous tissue that typically contains a central scar
Glisson's Capsule
The thin fibrous casing of the liver
Hematemesis
Vomiting blood
Hemochromatosis
An inherited disease characterized by disproportionate absorption of dietary iron
Hemopoiesis
The formation and development of blood cells
Hepatic Candidiasis
A hepatic mass that results from the spread of fungus in the blood to the liver
Hepatic Encephalopathy
A condition where a PT becomes confused or suffers from intermittent loss of consciousness secondary to overexposure of brain to toxic chemicals that the liver would normally remove
Hepatocellular Adenoma
A benign liver mass often associated with the use of oral contraceptives
Hyperlipidemia
Abnormally high levels of fats within the blood (i.e. high cholesterol and high triglycerides)
Hypovolemia
Decreased blood volume
Idiopathic
No recognizable cause; from an unknown origin
Kernicterus (bilirubin encephalopathy)
Brain damage from bilirubin exposure in a newborn with jaundice
Kupferr Cells
Specialized macrophages within the liver that engulf pathogens and damaged cells
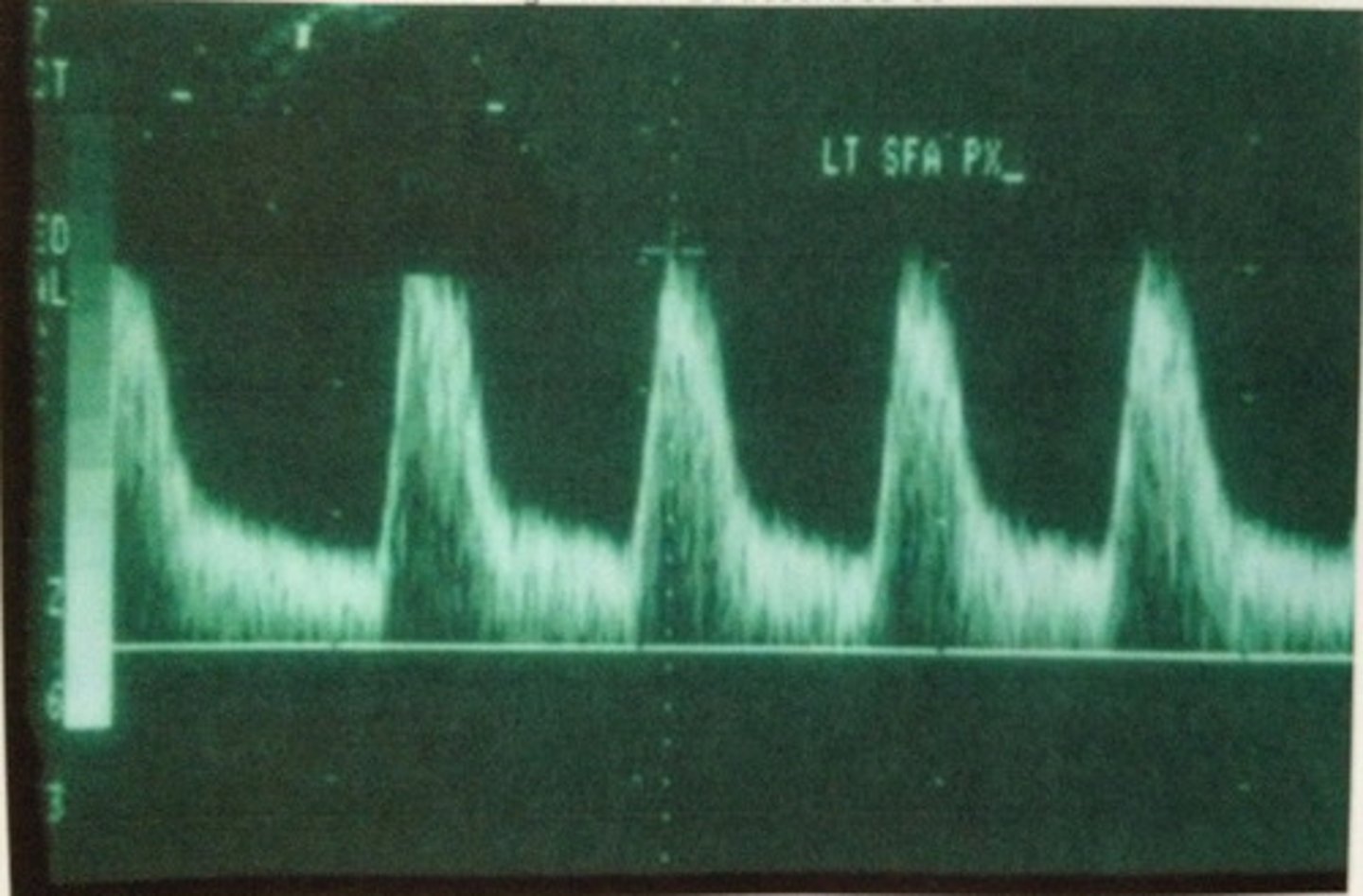
Low-Resistance Flow
a flow pattern that characteristically has antegrade flow throughout the cardiac cycle
Malaise
a vague feeling of physical discomfort or uneasiness
Malignant Degeneration
the deterioration of a benign mass into a malignancy
Monophasic
vascular flow yielding a single phase
Pseudocirrhosis
nodular appearance of the liver caused by multiple metastatic tumors
Quadrate Lobe
Another name for the medial segment of the left lobe of the liver
Riedel Lobe
A tongue like extension of the right hepatic lobe
Sequela
An illness resulting from another disease, trauma or injury
Serpiginous
Twisted or snake like pattern
Total Parental Hyperalimentation
Procedure where an individual receives vitamins and nutrients through a vein often the subclavian vein
TIPS
The therapy for portal HTN that involves the placement of a stent between the portal veins and hepatic veins to reduce pressure in portal system
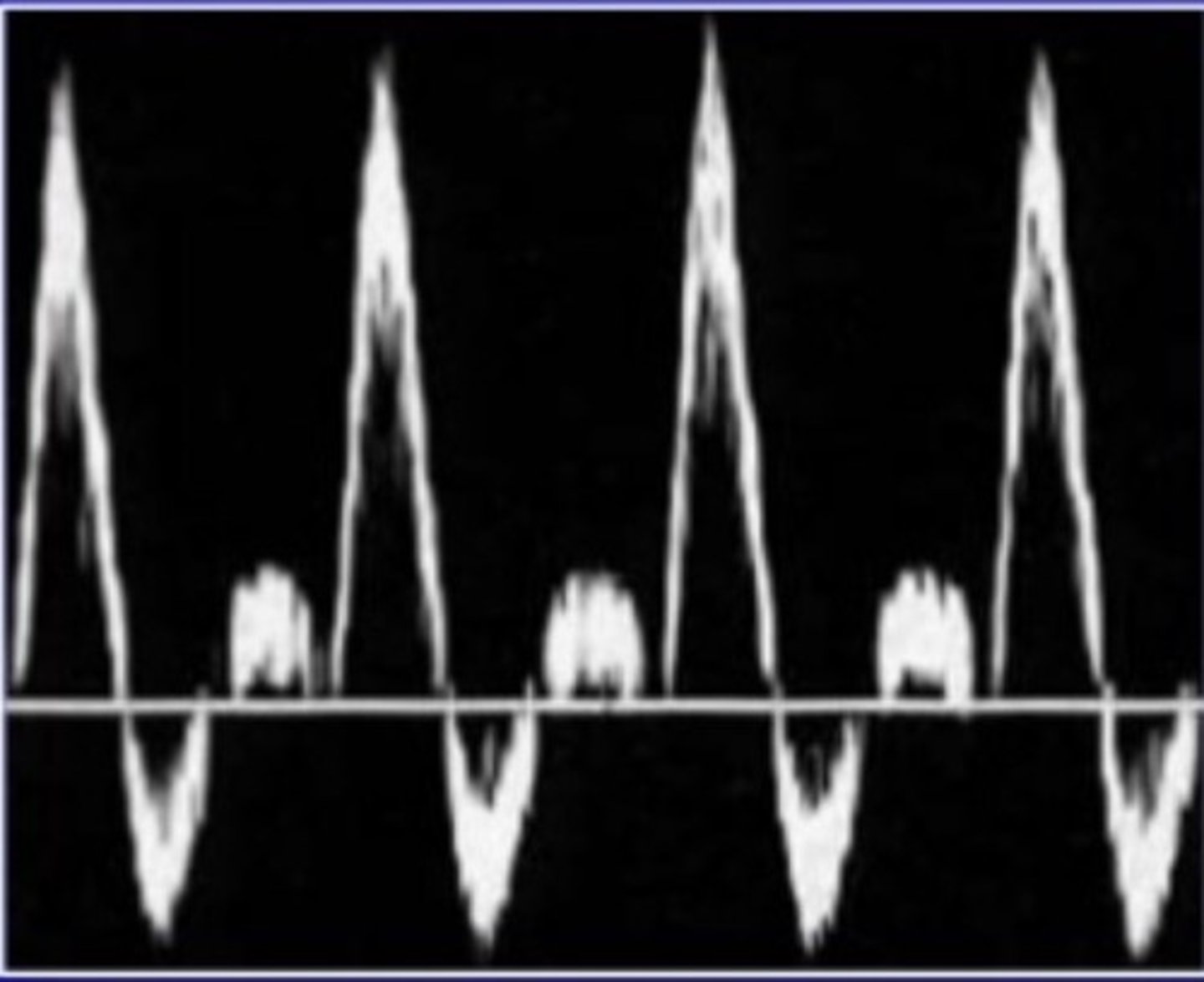
Triphasic
vascular flow yielding three phases
Von Gierke disease (type I glycogen storage disease)
Condition in which the body does not have the ability to break down glycogen
Von Hippel-Lindau Disease
Inherited disease that includes development of cysts within the liver, pancreas and other organs
Wilson Disease
Congenital disorder that causes body to accumulate excess copper
Hemopoeisis/Hematopoeisis
In early embryonic life, the liver is responsible for:
Medial segment of left lobe
The quadrate lobe of the liver is AKA
Hepatics= Triphasic
Portals= Monophasic
Describe blood flow pattern of hepatic veins vs portal veins
Right sided heart failure
Enlargement of hepatic veins and IVC is seen in
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
MC liver disorder in the Western World that is both acquired and reversible
6 months
Chronic hepatitis persists beyond what time frame?
Hep A: fecal oral route
Hep B: contaminated body fluids/mom->infant at birth
How are hep A and hep B spread?
Hepatitis C
Leading indication for liver transplantation in the US
Hemochromatosis
hereditary disorder with an excessive buildup of iron deposits in the body
Wilson's Disease and Hemochromatosis
What 2 inherited disorders would prompt a sonographer to assess the PT for signs of chronic hepatitis?
Less than 1cm (Micronodular)
Cirrhosis caused by alcoholism will lead to development of nodules that measure:
1-5cm (Macronodular)
Cirrhosis caused by hepatitis will lead to development of nodules that measure:
-Monophasic flow in hepatic veins
-Hepatofugal flow in portal vein
Possible blood flow changes seen in liver with Cirrhosis
Enlarges to help bring blood into liver
What may happen to the hepatic artery in presence of portal HTN?
Cruveilhier-Baumgarten Syndrome
the development of paraumbilical collateral flow in cases of portal hypertension
TIPS procedure
Relives portal hypertension by shunting blood from portal vein to hepatic vein (bypassing liver)
Cavernous Transformation of the portal vein
Term for a mesh of tiny blood vessels in the area of the portal vein that develop as a response to portal vein thrombosis
Development of portal venous gas (typically fatal)
How might an ischemic bowel disease affect the portal system?
Cavernous Hemangioma, Right lobe
MC benign liver tumor and where is it usually found?
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia (FNH)
Benign liver mass that may grown in size with oral contraceptive use due to its estrogen sensitivity
Hepatocellular Adenoma (Liver Cell Adenoma)
Rare, benign liver tumor often associated with oral contraceptive use
AFP
Tumor marker for HCC
Metastases
MC form of liver cancer
Lung
MC primary source of liver mets
Infantile Hemangioendothelioma
MC benign childhood liver tumor
Hepatoblastoma
MC malignant childhood tumor
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Hepatoblastomas are associated with what syndrome?