Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Chapter 6: Gymnosperms
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
seed
provide a much better protection to the plant embryo; produced by gymnosperms and angiosperms
spermatophytes
gymnosperms and angiosperms; produces seeds
seed production; wood production
two major improvements of previous plant lineages that are found in gymnosperms
wood production
allow gymnosperms and angiosperms to grow taller and become better competitors in their habitats
gymnosperm
literally means “naked seed” in reference to their seeds being borne out in the open on cone scales of a sporophyte plant
excurrent branching pattern
trunk only divides when the terminal bud is removed
terminal bud
a bud located at the apex of the stem where most of the plant growth occurs
evergreen leaves
most gymnosperms have _________ ______, in which foliage remains green and functional all throughout the year
2; 5
conifers may have a total change of leaves every - years
Cycadophyta (cycads); Ginkgophyta (maidenhair tree); Pinophyta (conifers); Gnetophyta (gnetophytes)
four major phyla of gymnosperms; follow this format: Phylum (subset/group)
Late Devonian period (375-400 MYA)
when gymnosperms arose
Mesozoic Era - late Cretaceous Period (70 MYA)
when gymnosperms dominated land vegetation
65; 720
known number of genera and species to exist at present
Phylum Cycadophyta
a relatively ancient group of plants that were once much more common than today and served as fodder for plant-eating non-avian dinosaurs
cycads
seed plants that typically have a stout and woody trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and pinnate leaves
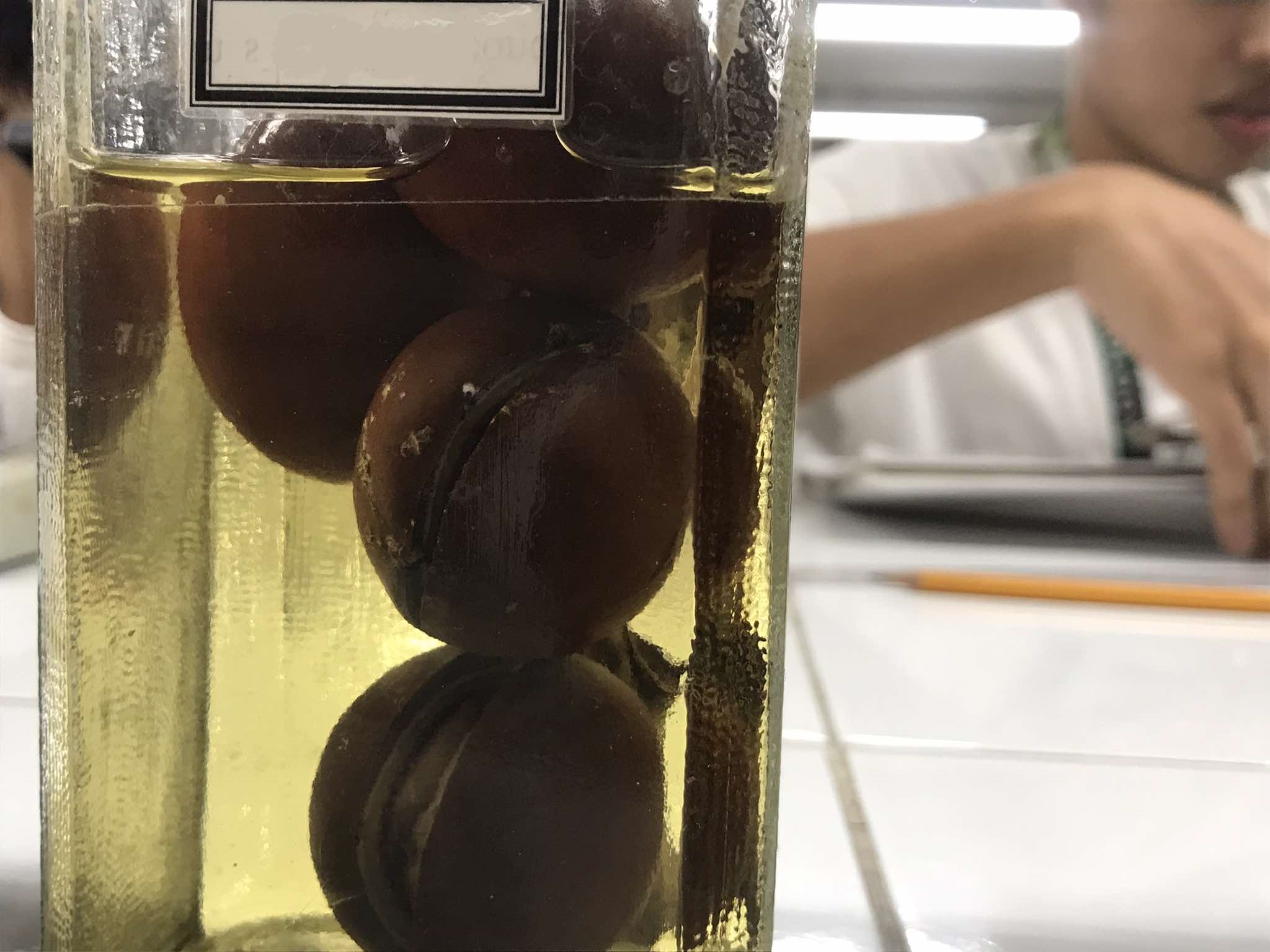
cycad (male cone)
a microsporophyll; produce pollen, which is carried by wind to female cones (borne on separate plants), where fertilization occurs
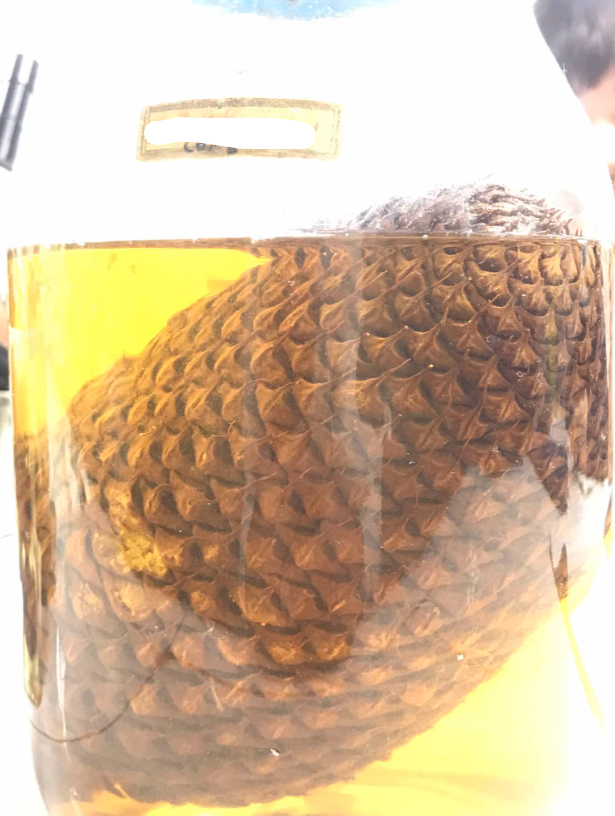

cycad (seed)
produced by female cycads; edible

Cycas revoluta (sago palm)
under Cycadophyta

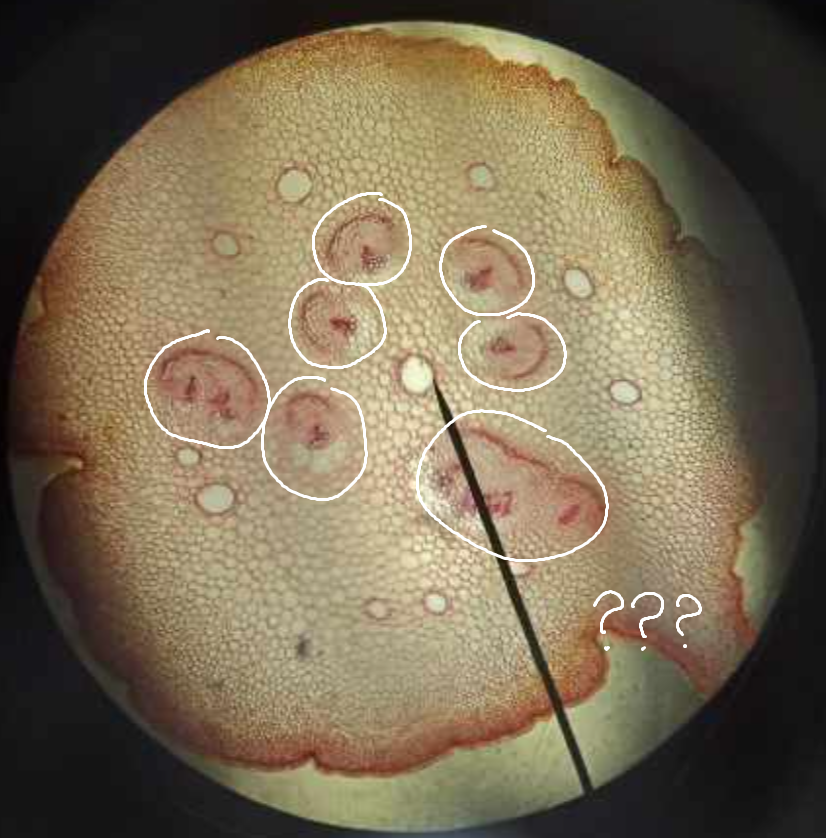
x-s midrib Cycas revoluta
identify the prepared slide
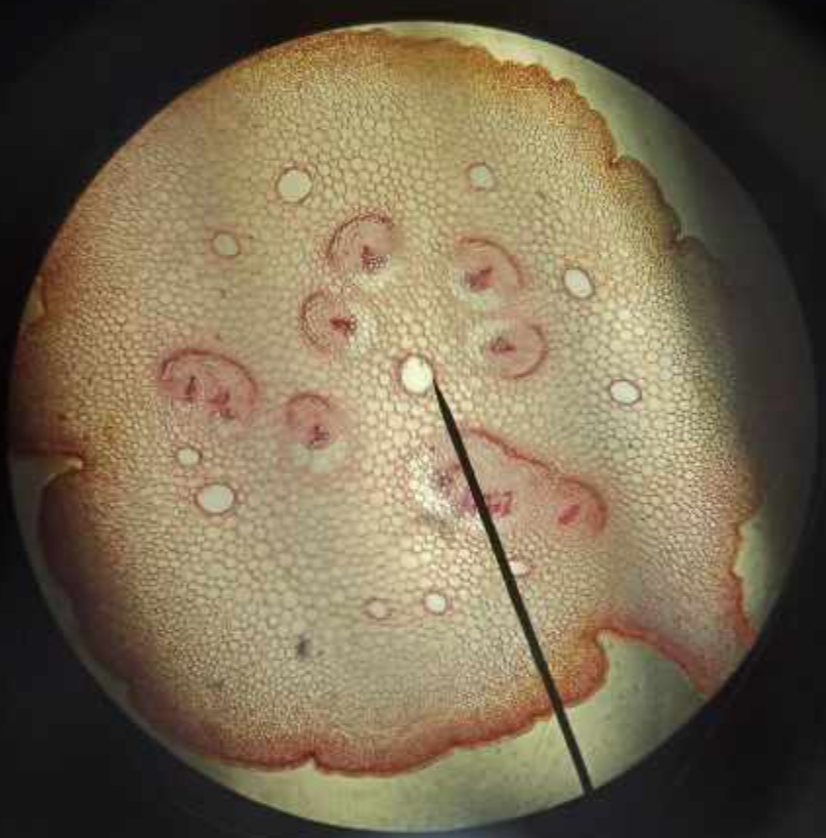
vascular tissues
what is the encircled part of the x-s midrib Cycas revoluta called?
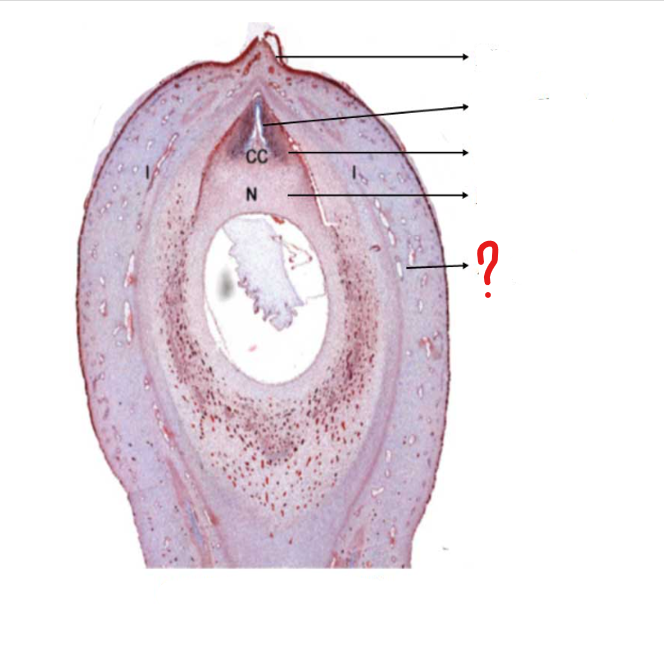
mature ovule
a small structure present in the ovary of Cycas; forms the seed; consists of a food tissue covered by one or two future seed coats, known as integuments
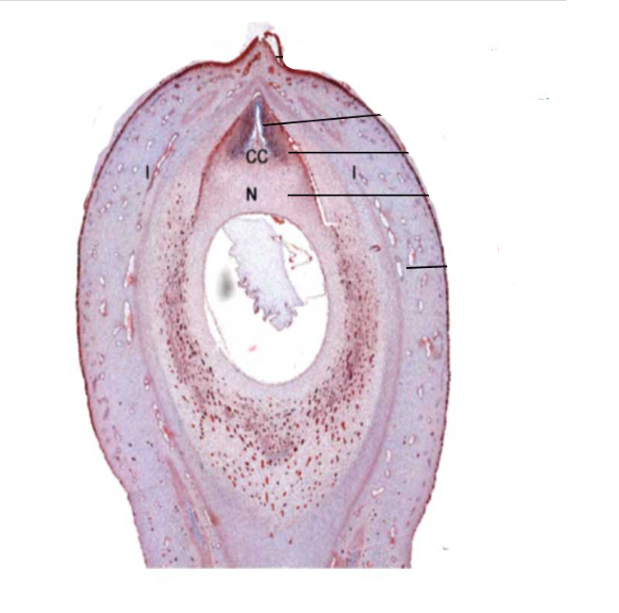
micropyle
identify the part labeled with a question mark; a small opening in the surface of an ovule, through which the pollen tube penetrates, often visible as a small pore in the ripe seed
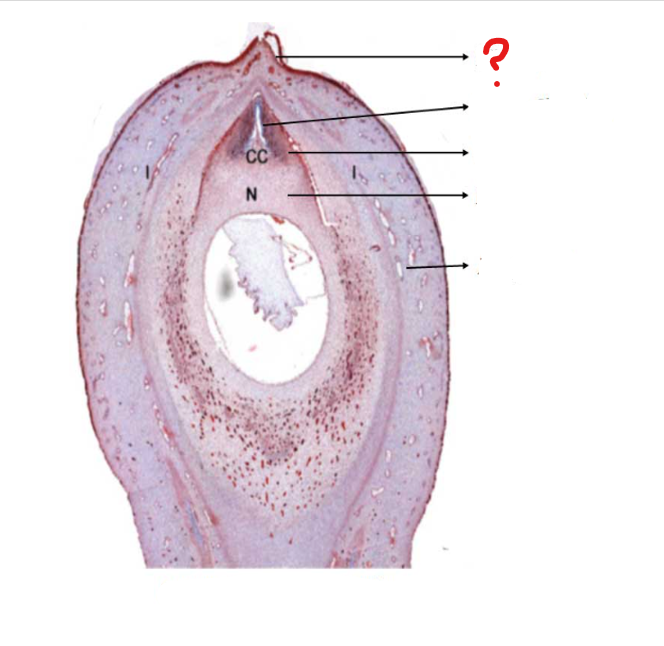
pollen chamber
identify the part labeled with a question mark; a small chamber at the apex of the nucellus in some plants (as most gymnosperms) for the reception of the pollen
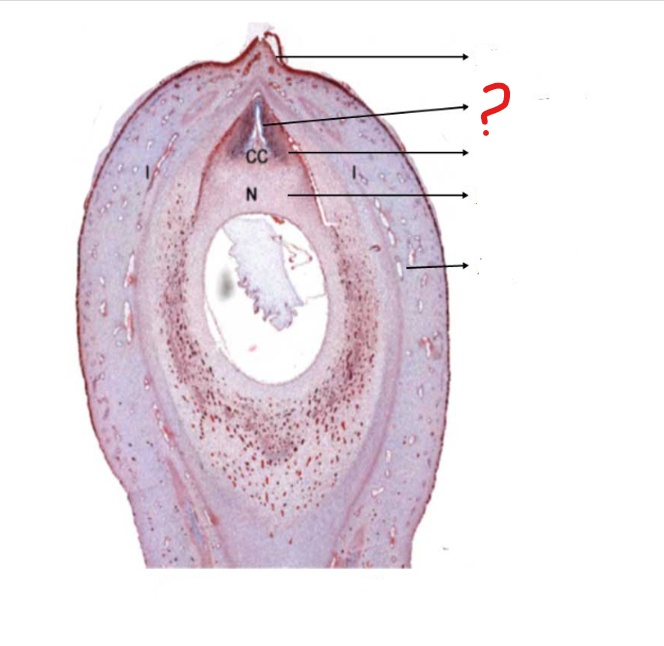
nucellar beak
identify the part labeled with a question mark; a proboscis-like outgrowth of the nucellus at the micropylar end, being the obligatory path for the pollen tube entering the ovule
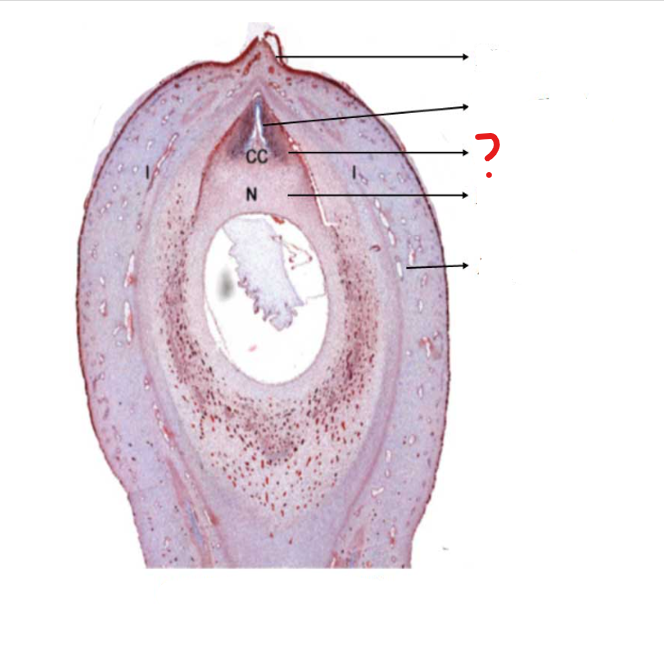
nucellus
identify the part labeled with a question mark; the central part of an ovule, containing the embryo sac
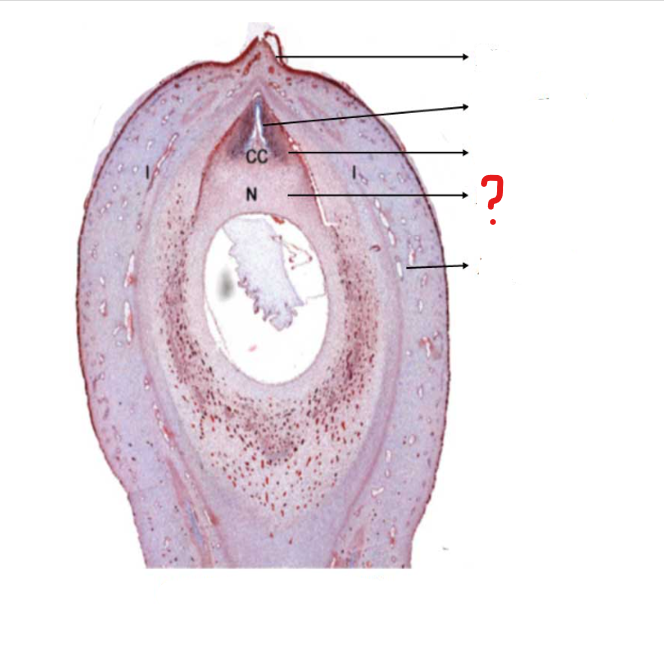
integument
identify the part labeled with a question mark; a tough outer protective layer, especially that of an animal or plant
10
number of extant genera of cycads
extant
opposite of extinct; still in existence; surviving
100
number of species of cycads
palm trees
what cycads resemble superficially; belonging to the family Arecaceae
pinnate leaves
attached to short stems; a type of compound leaf that has a central stem with small leaves arranged on either side of it
dioecious
having the male and female reproductive organs in separate individuals
microsporophyll
part of the male cycad cone that bear pollens containing motile sperms
motile sperm
sperm that have the ability to move or swim efficiently through the female partner’s reproductive system in order to fertilize an egg
megasporophyll
part of the female cycad cone that is modified to bear the ovules which eventually become seeds
integument
a tough outer protective layer, especially that of an animal or plant
archegonium
where the egg is borne inside in
megasporangium
where the archegonium is found
Phylum Ginkgophyta
a phylum consisting of only one living species (Ginkgo biloba)
Ginkgo biloba
an ancient plant dating back to the Carboniferous times (290 MYA) with very little change; this species is a temperate species originating from China; fan-shaped leaves with dichotomous venation; dioecious
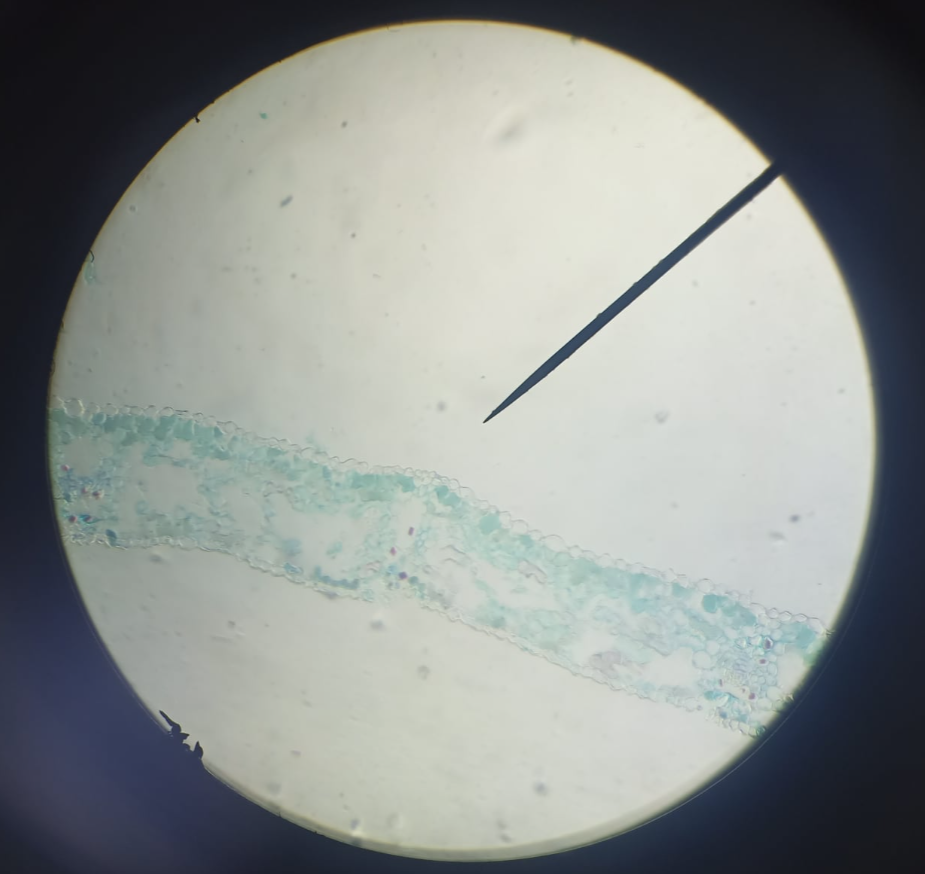
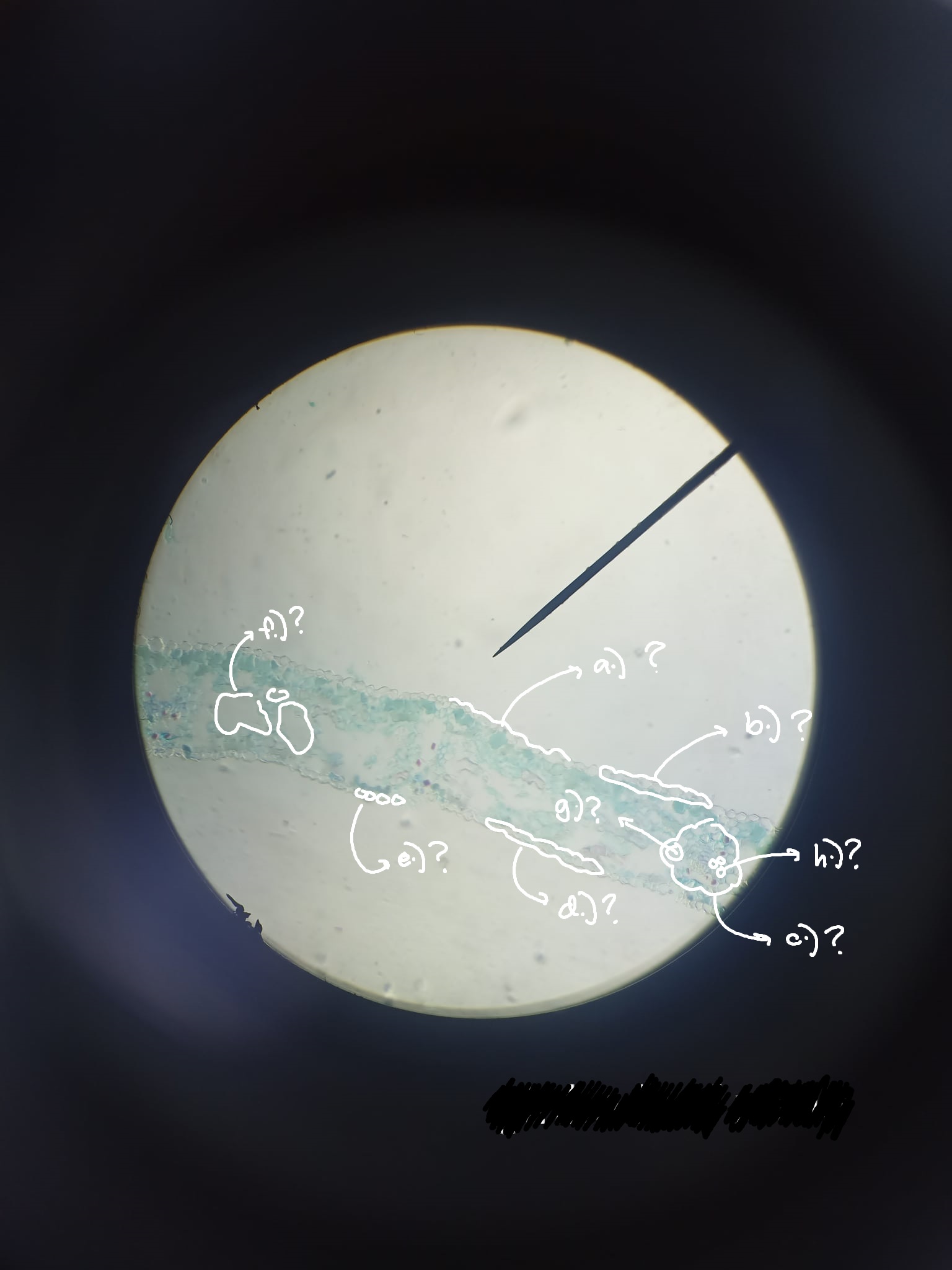
x-s leaf Ginkgo
identify the prepared slide
a.) cuticle; b.) upper epidermis; c.) vascular tissues; d.) lower epidermis; e.) guard cells; f.) spongy parenchyma cells; g.) xylem; h.) phloem
label the parts of the Ginkgo leaf; use this format: a.) answer; b.) answer; etc etc
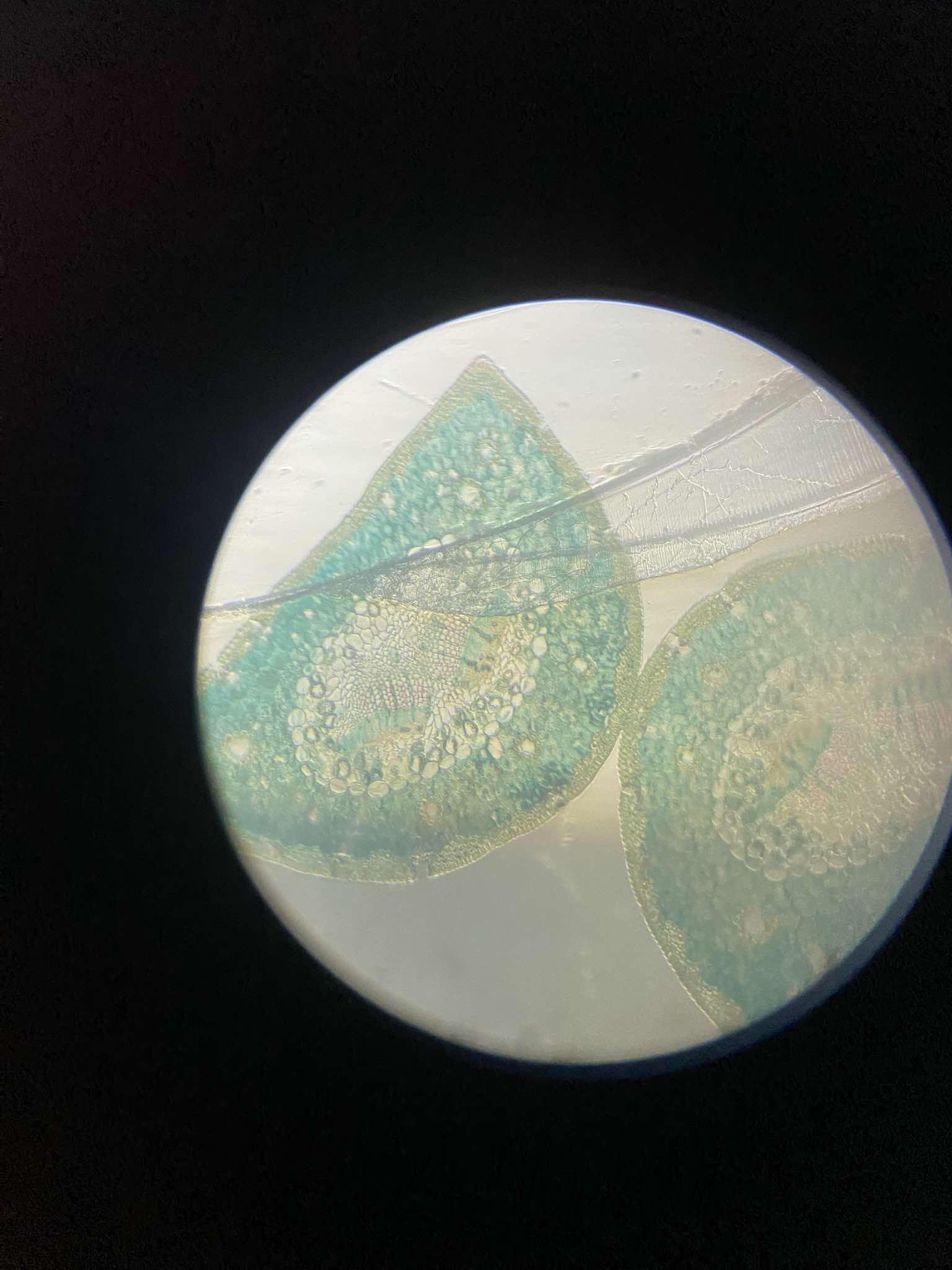
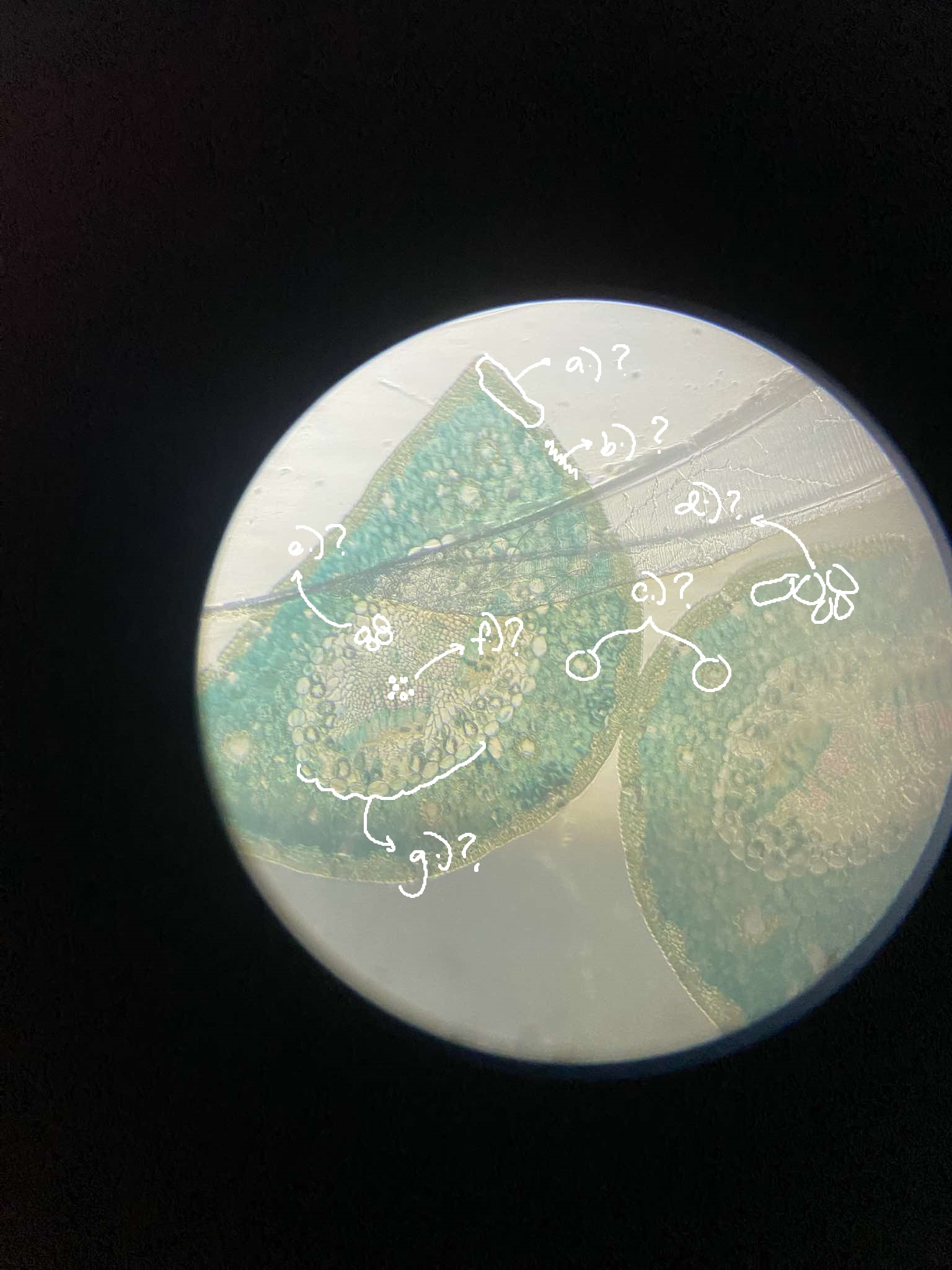
x-s leaf (stalk) Ginkgo
identify the prepared slide
a.) epidermis; b.) stomata; c.) resin ducts/canals; d.) mesophyll; e.) xylem; f.) phloem; g.) endodermis
label the parts of the Ginkgo leaf stalk; use this format: a.) answer; b.) answer; etc etc
deciduous
shreds leaves annually
Carboniferous times (290 MYA)
from when the ancient ginkgo plant dates back to with very little change
China
country of origin of ginkgo
dichotomous venation
of ginkgo; veins fork by twos extending from a common point forming a “y” pattern fanning out
hypodermal sclerenchyma
tissue that makes the plant hard and stiff
hypodermis
lies beneath the epidermis
ginkgo leaf
contains a thin-walled epidermis and lacking a hypodermal sclerenchyma
guard cells
of ginkgo; slightly depressed and occur only on the abaxial side; pairs of epidermal cells that control gas diffusion by regulating the opening and closure of stomatal pores
abaxial side
the underside or side facing away from the stem
stomata
a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spaces of the leaf and the atmosphere
mesophyll
consists of one-cell layer palisade of short lobed cells and a spongy parenchyma
parenchyma
tissue typically composed of living cells that are thin-walled, unspecialized in structure, and therefore adaptable, with differentiation, to various functions
lumen
the compartment where molecular oxygen is produced from water during photosynthetic light-dependent reactions
palisade
a layer of plant cells containing chloroplasts right below the epidermis in plants
lignified endodermis
plant tissue in the roots of vascular plants between the periderm and the cortex
tannins
of ginkgo; abundant in the endodermal sheath; complex chemical substances derived from phenolic acids
transfusion tracheids
of ginkgo; to transport water and inorganic salts, and to provide structural support for trees
mucilage ducts
of ginkgo; found alternating with the vascular bundles; distributed in a ring within the cortex and may also be found in the pith region
mucilage
plays a role in the storage of water and food, seed germination, and thickening membranes
resin ducts/canals
of ginkgo and conifers; elongated, tube-shaped intercellular spaces surrounded by epithelial cells which secrete resin into the canal; occur in the mesophyll and its number varies with the species
resin
of ginkgo and conifers; a mixture of organic compounds that protect tissues from microbial disease
Phylum Coniferophyta/Pinophyta
conifers; mostly woody, evergreen shrubs and trees; group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms; an important source of lumber and wood for fuel
Thuja orientalis (oriental arborvitae)
Platycladus; a monotypic genus of evergreen coniferous trees in the cypress family Cupressaceae

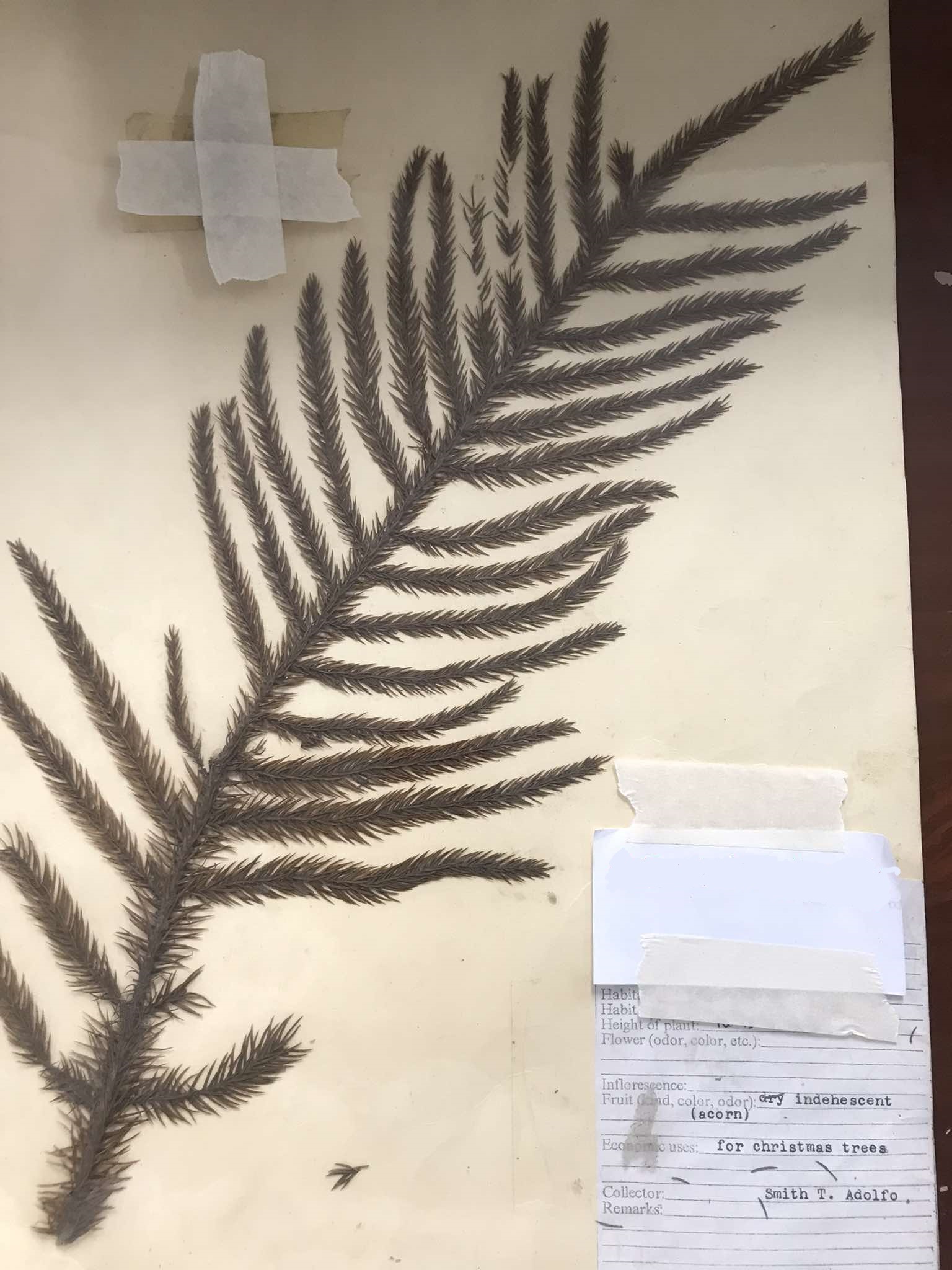
Araucaria heterophylla (Norfolk pine)
Pinophyta; used for Christmas trees

Pinus kesiya (Benguet pine tree)
Pinophyta; one of the most widely distributed pines in Asia

Pinus sp. conifer cone
a seed-bearing organ on gymnosperm plants; usually woody, ovoid to globular, including scales and bracts arranged around a central axis, especially in conifers and cycads
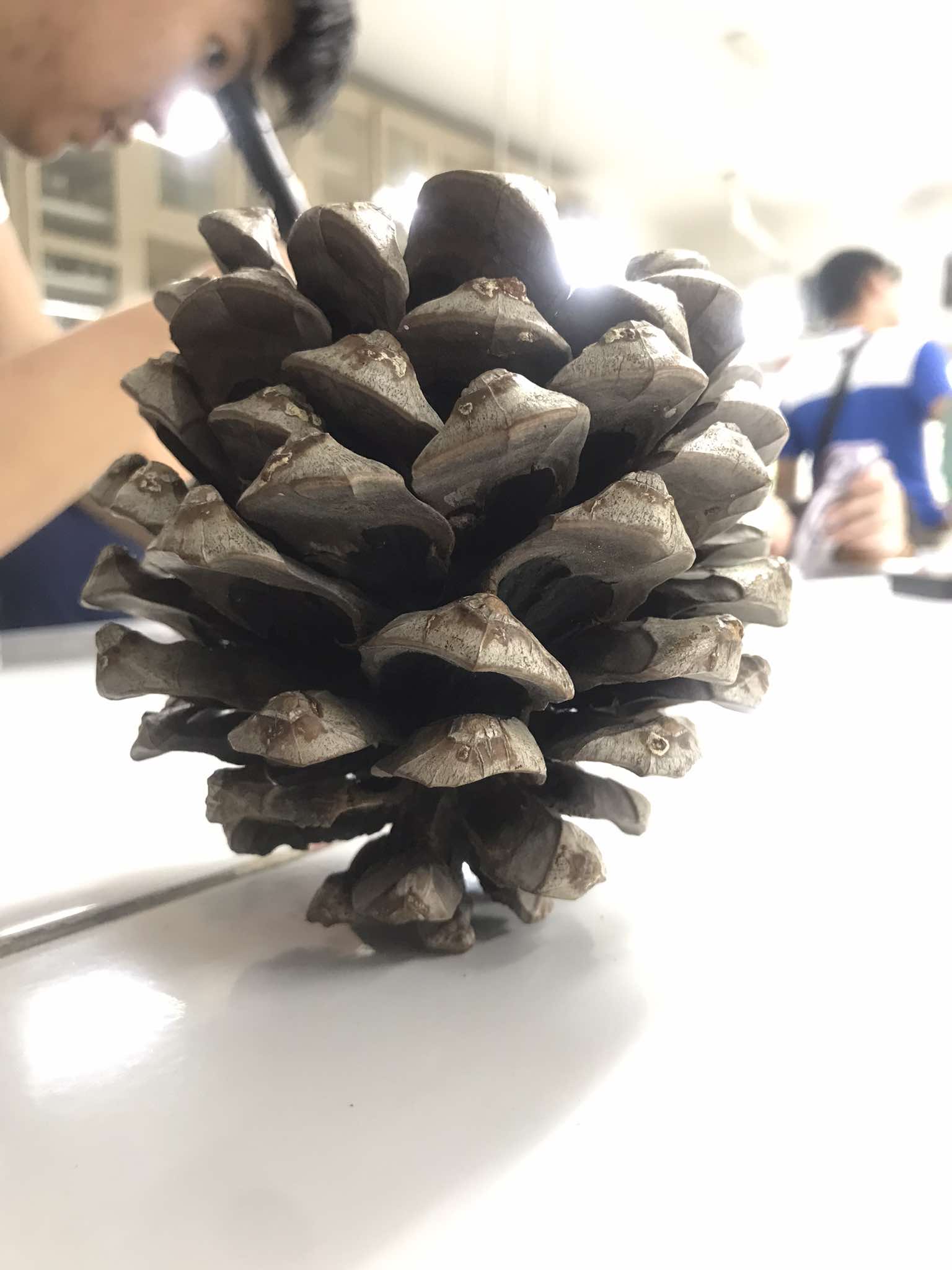

Pinus resinosa (red pine)
Pinophyta; native to Eastern North America
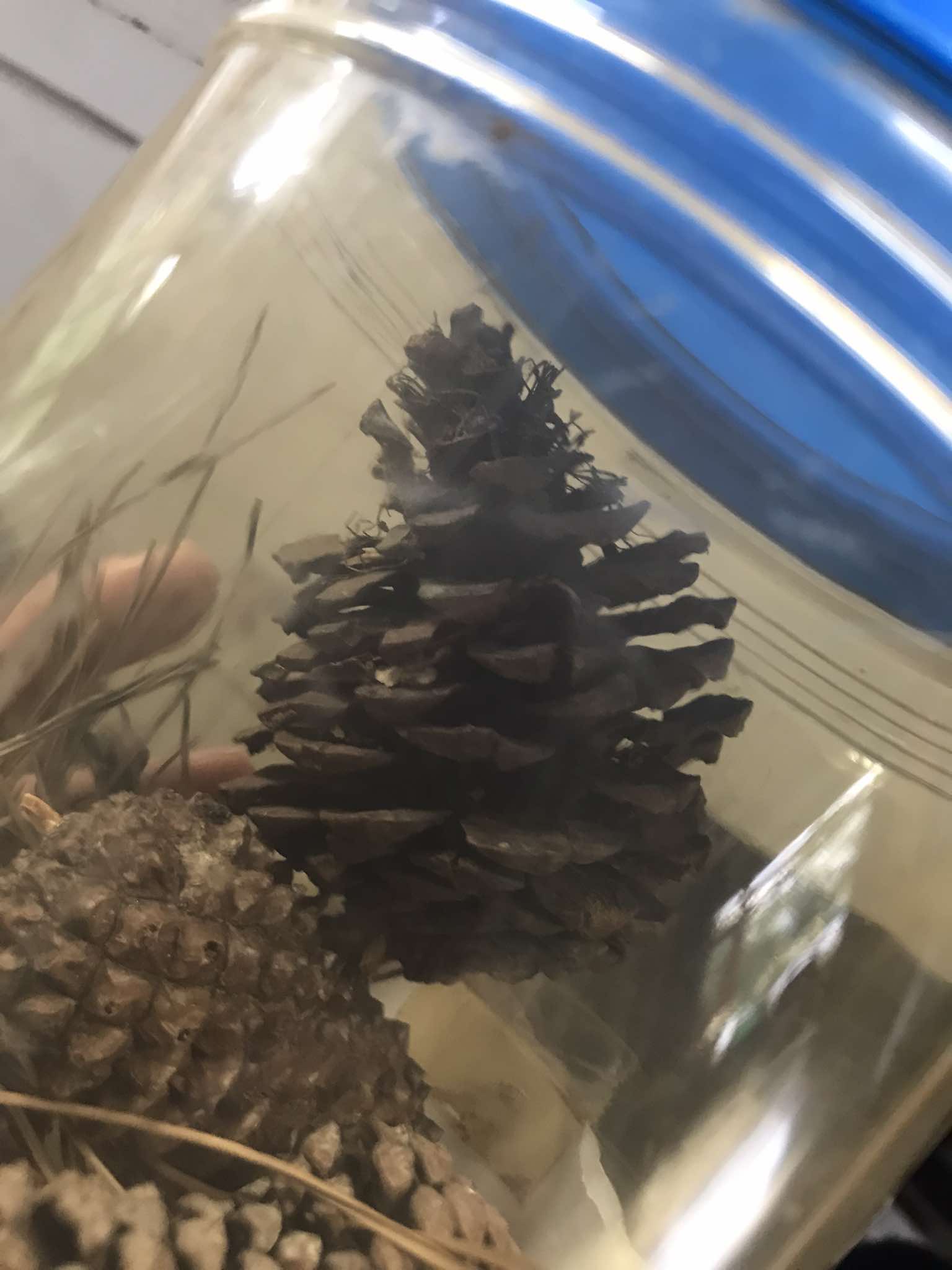

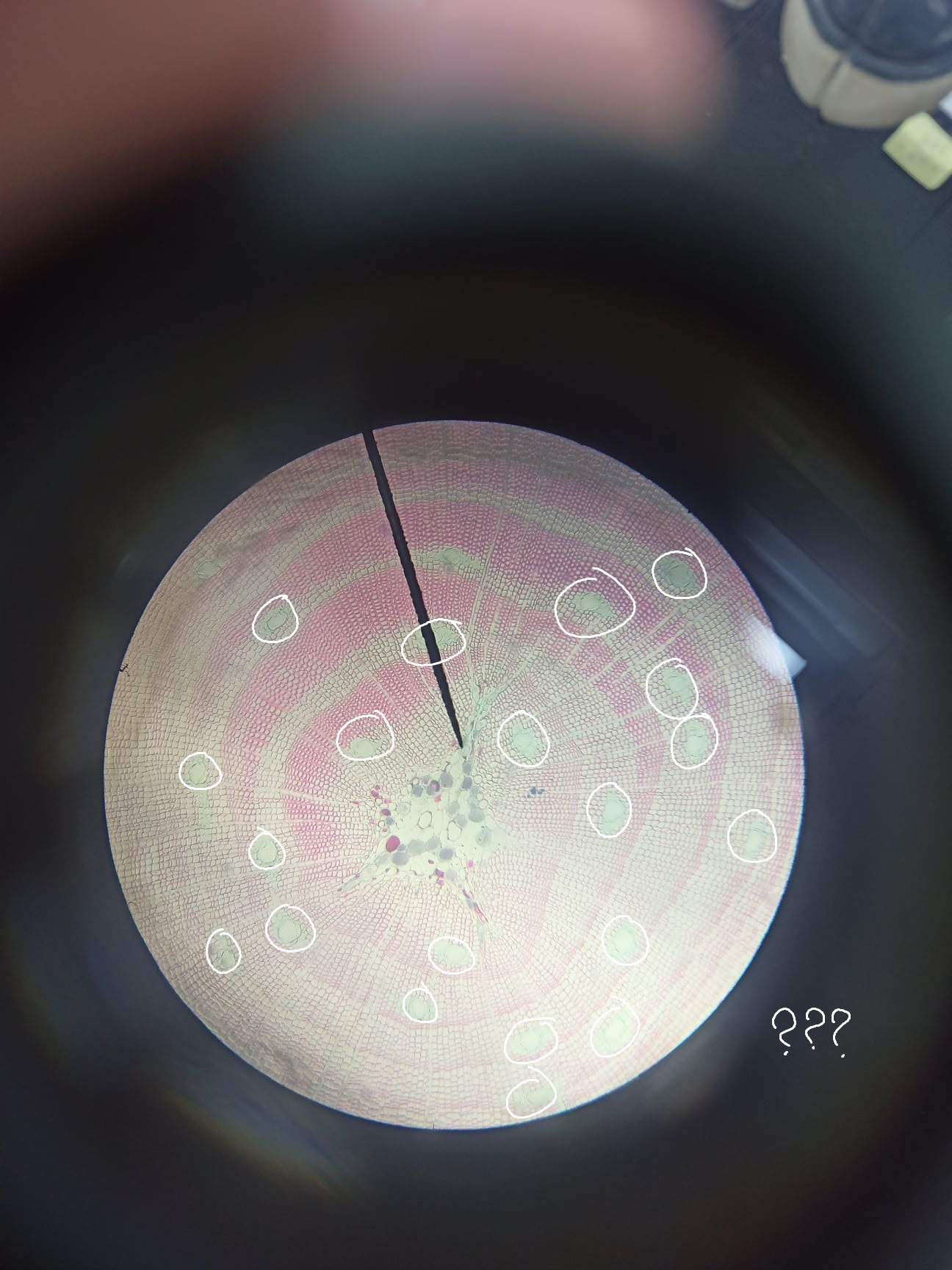
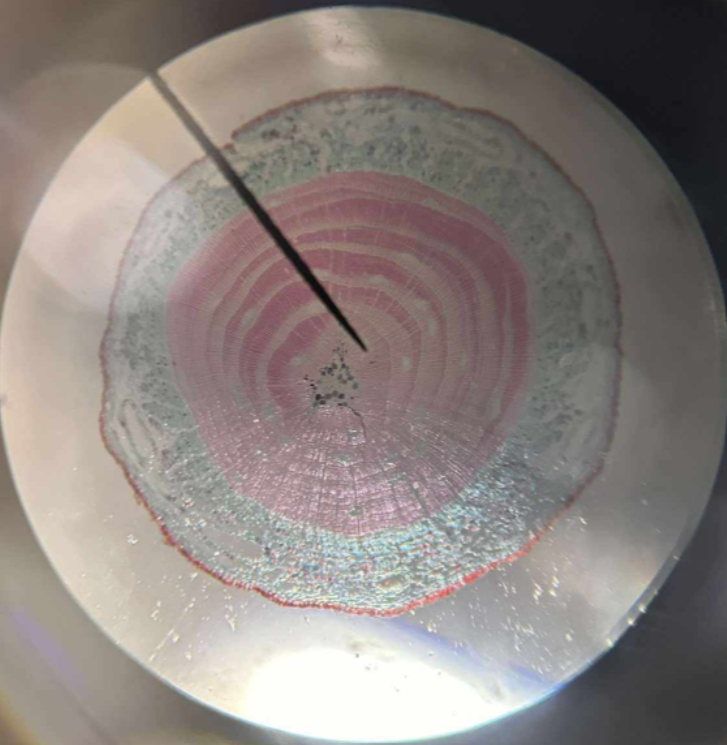
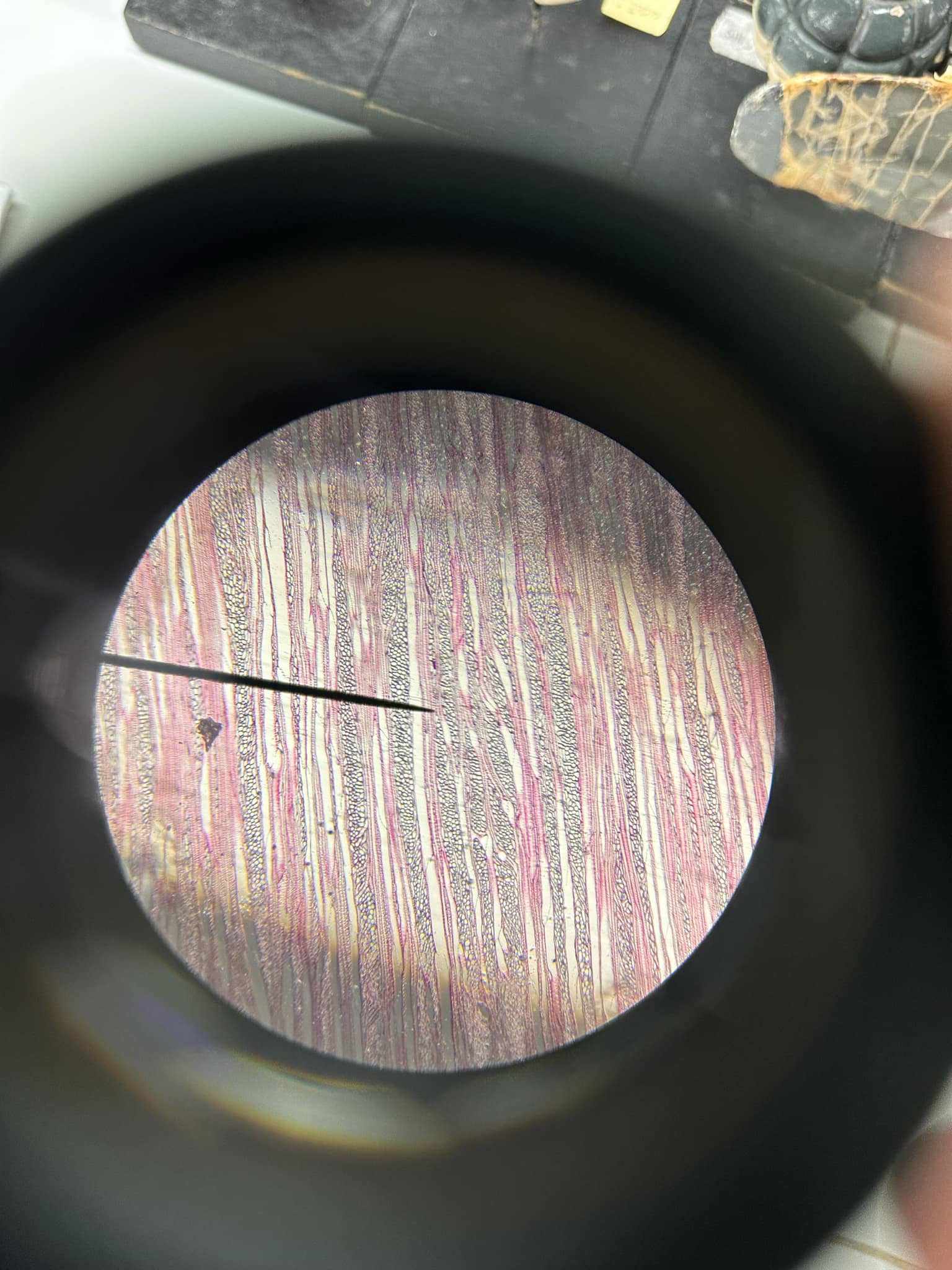
Pinus stem (older)
identify the prepared slide
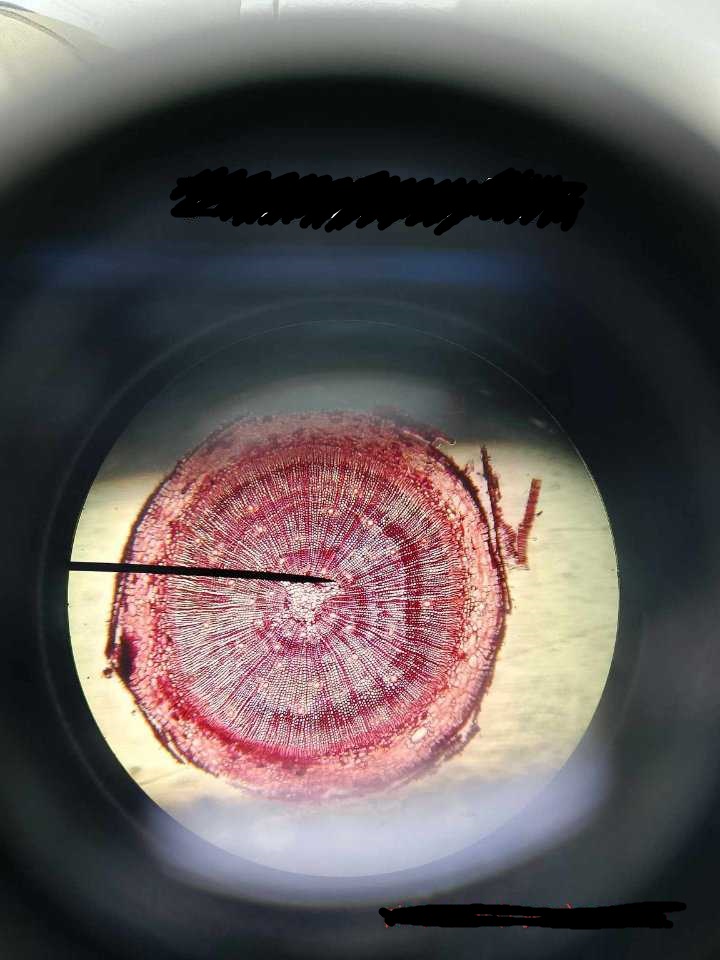
Pinus stem (younger)
identify the prepared slide
50; 550
amount of genera and living species under Coniferophyta; most thriving in colder regions of the world
needle-shaped
shape of conifer leaves
sunken stomata
of conifers; stomata that are buried or not directly visible to the surface
sclerified fibrous hypodermis
of conifers; occurs beneath the epidermis; except under the rows of stomata
sclerification
thickening of the cell wall, increasing rigidity
transfusion tissue
of conifers; composed of tracheids and parenchyma cells; bordered by a thick-walled endodermis
ring/circle
conifer stems behave similarly to woody dicots in the sense that their vascular tissues are arranged in a ____/______ around the pith
apical meristem
give rise to the primary plant body and are responsible for the extension of the roots and shoots
vascular cambium
the main meristem in the stem, producing undifferentiated wood cells inwards and bark cells outwards
growth rings
in a cross section of the stem of a woody plant, the increment of wood added during a single growth period; tell us how old the tree is
annual rings
the layer of wood that is formed during a single growing season
softwood
lacking fibers, giving the wood a smooth, light texture
hardwood
numerous resin ducts are distributed not only in the cortex but also in the wood region
wings/air bladders
of conifers; found in Pinus pollen grain; help with the dispersal of the pollen; allow the pollen to travel farther on the wind and reach new areas and other plants
Phylum Gnetophyta
a small group of gymnospermous vascular plants that are represented by three living genera: Ephedra, Gnetum, and Welwitschia
Gnetum latifolium
an evergreen plant in the family Gnetaceae with a broad distribution across South East Asia
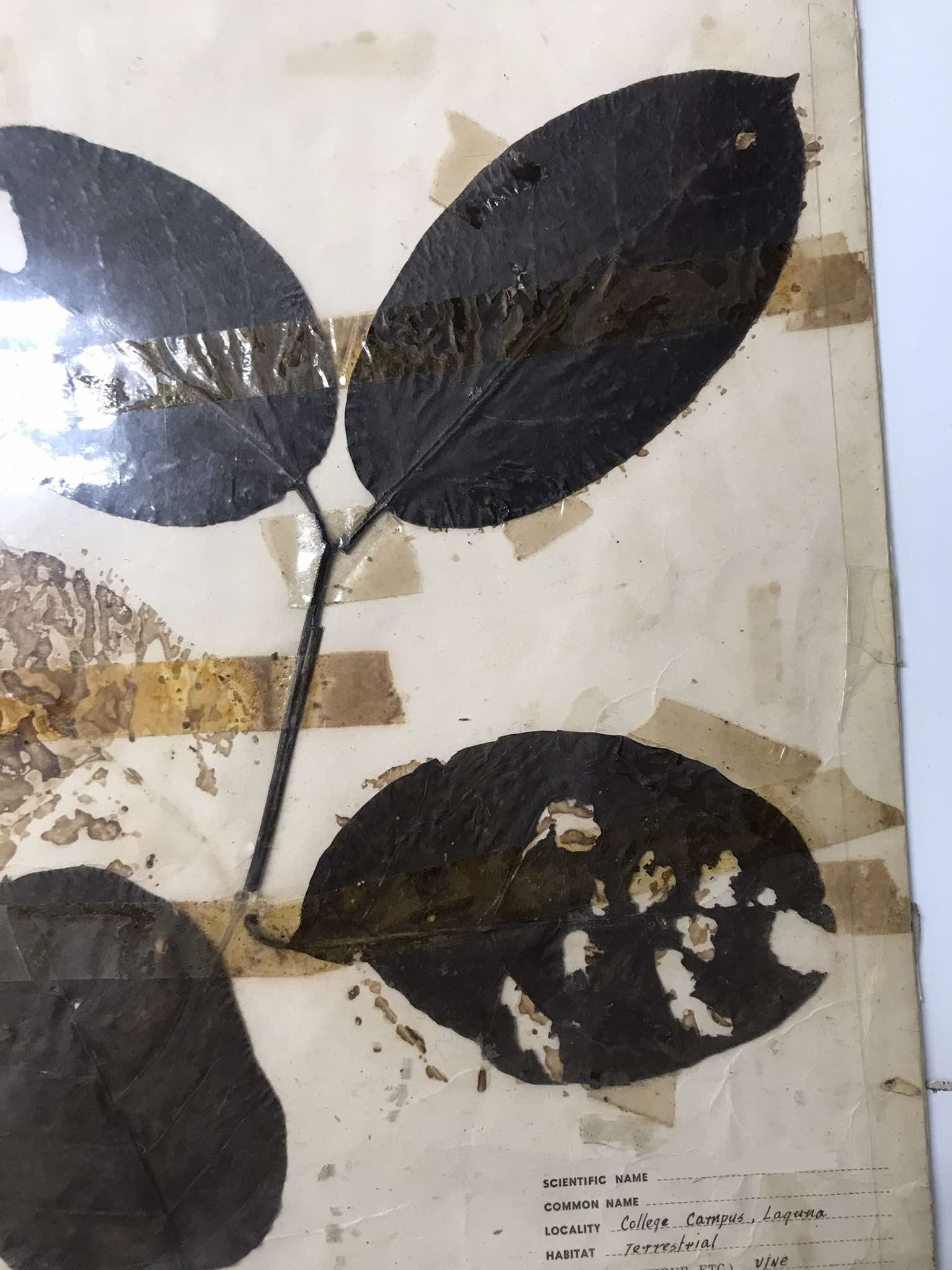

Ephedra foliata (shrubby horsetail)
Gnetophyta; a species of gymnosperm in the Ephedraceae family
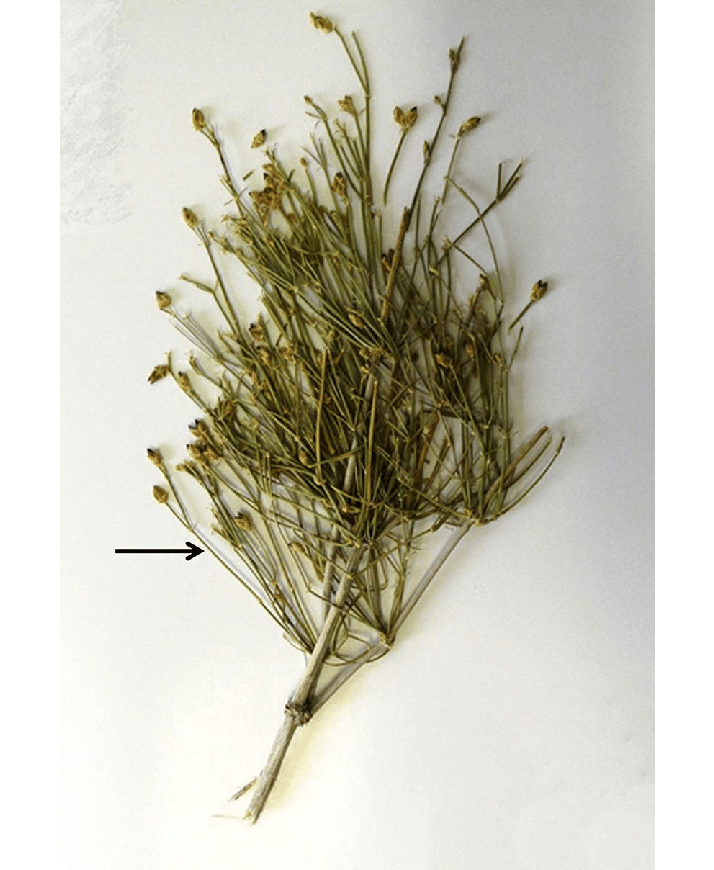

Ephedra foliata (transverse section)
identify the prepared slide
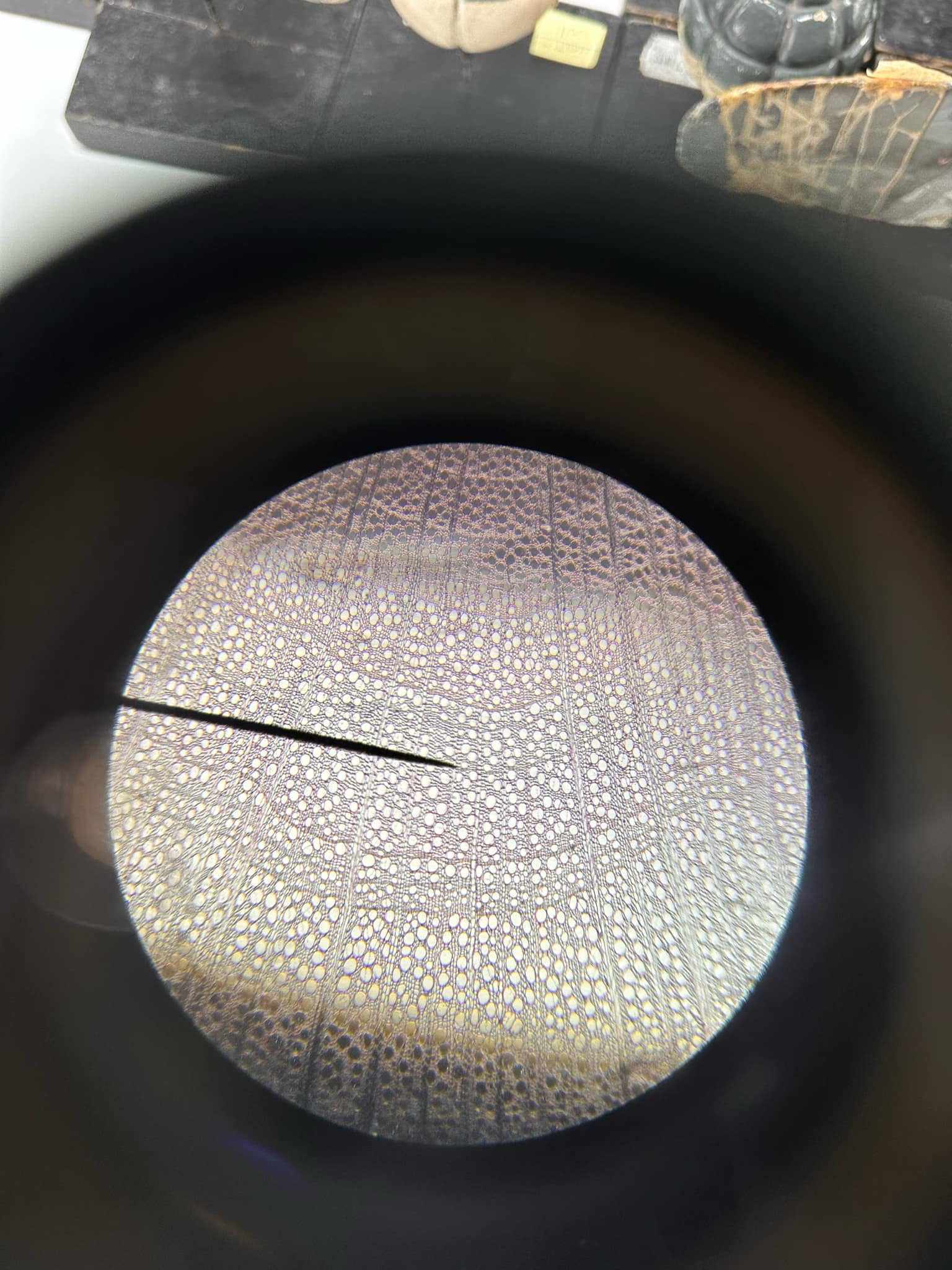
Ephedra foliata (tangential section)
identify the prepared slide
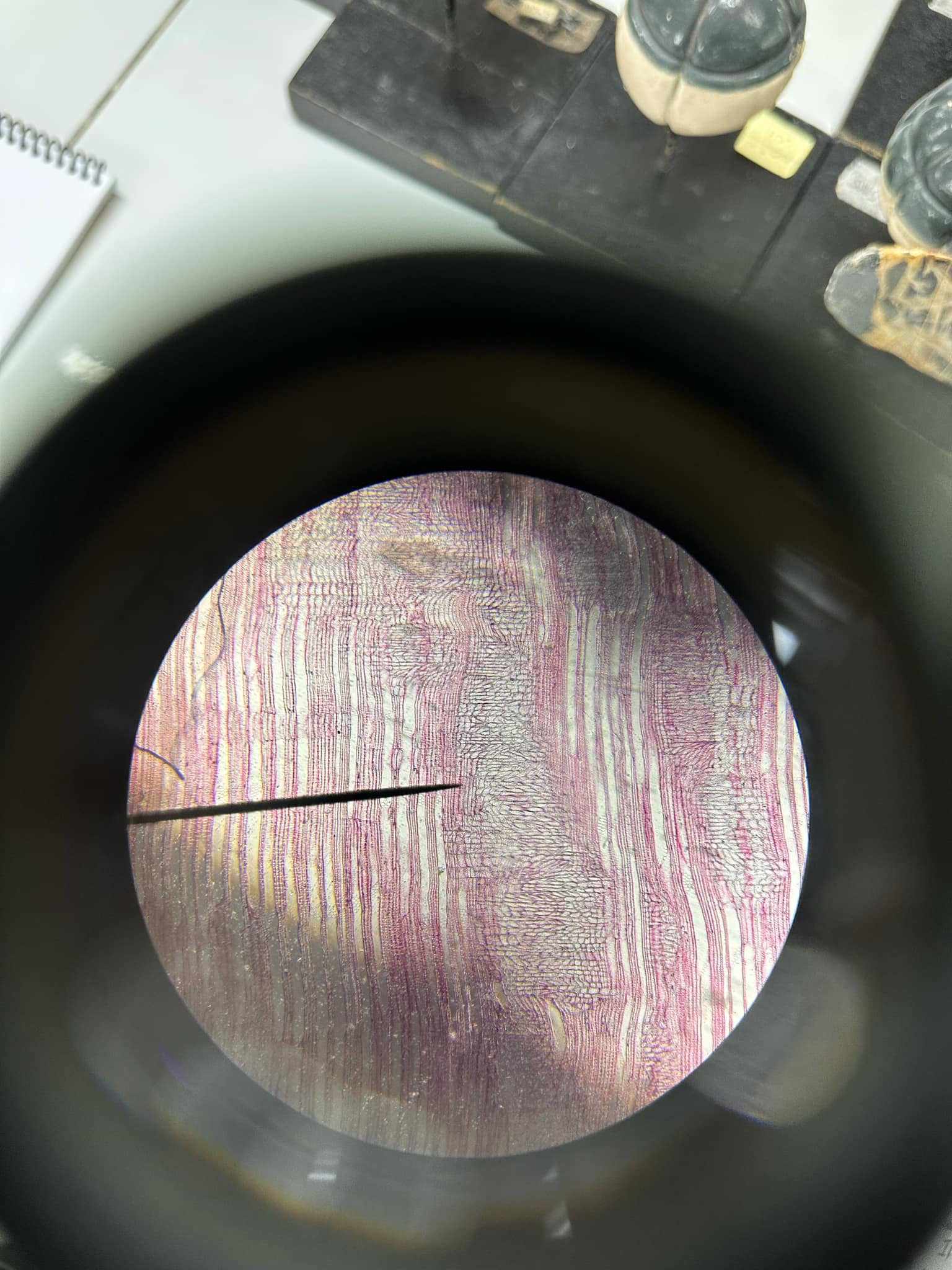

Ephedra foliata (radial section)
identify the prepared slide
3; 70
number of genera and species in Phylum Gnetophyta
Gnetum
have broad leaves and live mostly in the tropics as vines or trees