Psychological Disorders(Module 41-46)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
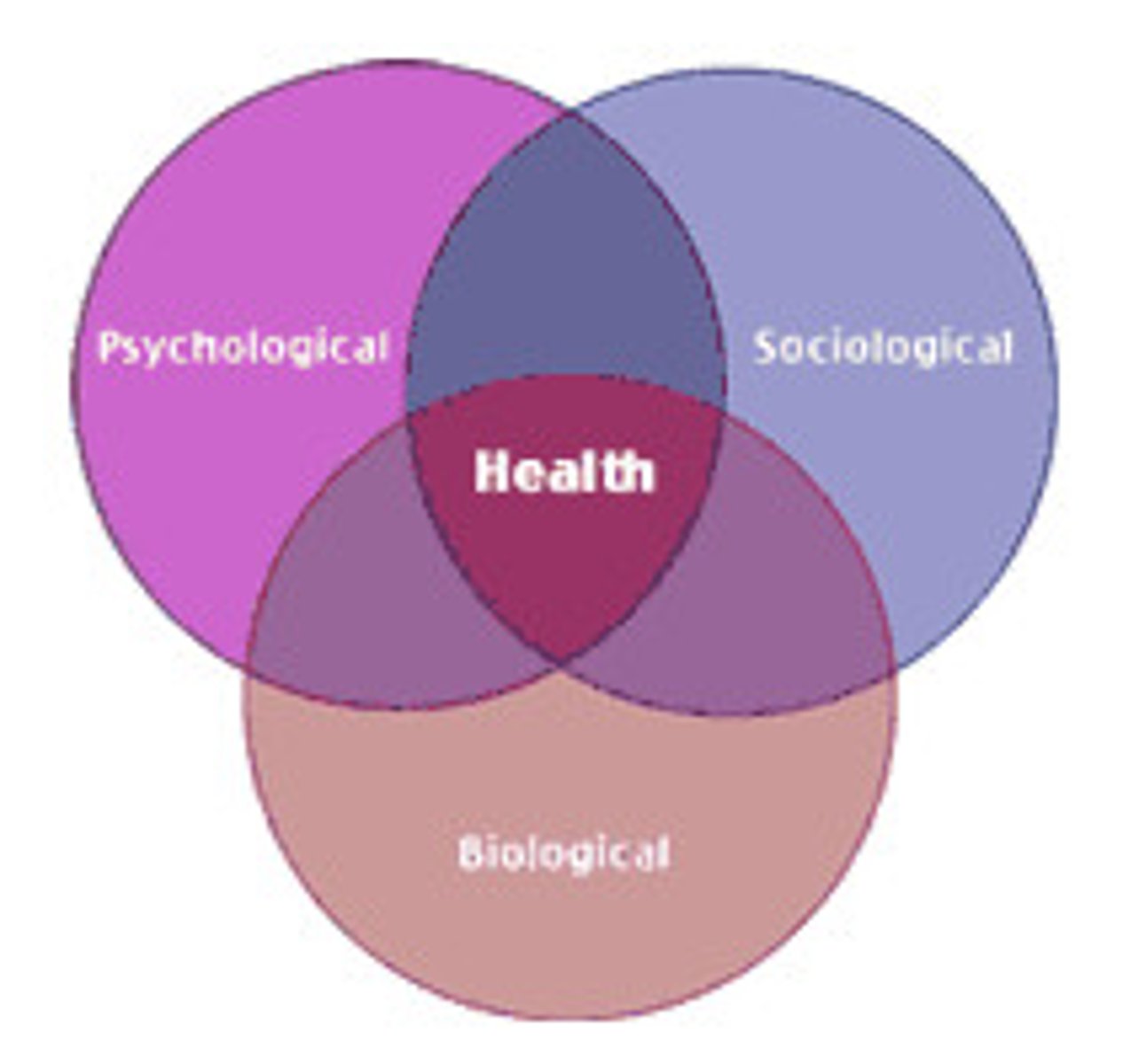
biopsychosocial model
a view of mental disorders as caused by a combination of interacting biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors
psychological disorder
a syndrome marked by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior
medical model
the concept that diseases, in this case psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and, in most cases, cured, often through treatment in a hospital.
Labeling Disorders Cons
-overly prejudicial
-"psychology student's syndrome"
sociocultural model
a way of looking at mental disorders in relation to gender, age, ethnicity, and other social and cultural factors
anxiety disorder
a condition in which intense feelings of apprehension are long-standing and disruptive

phobia
an anxiety disorder involving strong, irrational fear of an object or situation that does not objectively justify such a reaction
post-traumatic stress disorder
a pattern of adverse reactions following a traumatic and threatening event
social phobia
an anxiety disorder involving strong, irrational fears relating to social situations
agoraphobia
an anxiety disorder involving strong fear of being alone or away from the security of home
generalized anxiety disorder
a condition that involves relatively mild but long-lasting anxiety that is focused on any particular object or situation; also called free-floating anxiety
panic disorder
an anxiety disorder involving sudden panic attacks
panic attacks
attacks marked by intense heart palpitations, pressure or pain in the chest, dizziness or unsteadiness, sweating, and a feeling of faintness
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
an anxiety disorder involving repetitive thoughts and urges to perform certain rituals
obsessions
persistent, upsetting, and unwanted thoughts
compulsions
ritualistic, repetitive behaviors
Somatic Disorders
psychological problems in which there are symptoms of a physical disorder without a physical cause

dissociative disorders
rare conditions that involve sudden and usually temporary disruptions in a person's memory, consciousness, or identity
illness anxiety disorder
a disorder in which a person interprets normal physical sensations as symptoms of a disease
dissociative identity disorder (DID)
a dissociative disorder in which a person reports having more than one identity; also called multiple personality disorder

mood disorder
conditions in which a person experiences extreme moods, such as depression or mania; also called affective disorder
major depressive disorder
a mood disorder in which a person feels sad and hopeless for weeks or months
delusions
false beliefs, such as those experienced by people suffering from schizophrenia or extreme depression
mania
an elated, very active emotional state
bipolar I disorder
a mood disorder in which a person alternates between deep depression and mania; also called manic depression
bipolar II disorder
a mood disorder in which a person alternates between major depressive episodes and hypomania episodes

seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
during months of shorter daylight, patients experience severe depression, accompanied by irritability and excessive sleeping

schizophrenia
a severe and disabling pattern of disturbed thinking emotion, perception, and behavior

hallucinations
a symptom of disorder in which people perceive voices or other stimuli when there are no stimuli present

positive symptoms
schizophrenic symptoms such as disorganized thoughts, hallucinations, and delusions
negative symptoms
schizophrenic symptoms such as absence of pleasure, lack of speech, and flat effect

paranoid schizophrenia
a form of schizophrenia characterized by delusions (of persecution or grandeur or jealousy); symptoms may include anger and anxiety and aloofness and doubts about gender identity; unlike other types of schizophrenia the patients are usually presentable and (if delusions are not acted on) may function in an apparently normal manner
disorganized schizophrenia
a form of schizophrenia characterized by severe disintegration of personality including erratic speech and childish mannerisms and bizarre behavior; usually becomes evident during puberty; the most common diagnostic category in mental institutions
catatonic schizophrenia
a form of schizophrenia characterized by a tendency to remain in a fixed stuporous state for long periods; the catatonia may give way to short periods of extreme excitement
undifferentiated schizophrenia
a form of schizophrenia characterized by having positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia but do not meet the specific criteria for the paranoid, disorganized, or catatonic subtypes

personality disorders
long-standing, inflexible ways of behaving that create a variety of problems
paranoid personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by suspiciousness and distrust of others, all of whom are assumed to be hostile
schizotypal personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by detachment from, and great discomfort in, social relationships; odd perceptions, thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors
obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, and control

avoidant personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by inhibition in social situations; feelings of inadequacy; oversensitivity to criticism

narcissistic personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by exaggerated ideas of self-importance and achievements; preoccupation with fantasies of success; arrogance
borderline personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by lack of stability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotion; impulsivity; angry outbursts; intense fear of abandonment; recurring suicidal gestures
antisocial personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by shameless disregard for, and violation of, other people's rights
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
patients diagnosed with this disorder are impulsive and unable to concentrate on an activity as well as other children their age can
Down Syndrome
a condition of intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by significant deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviors
DSM-IV
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual; resource for diagnosing disorders, uses a 5 axis system

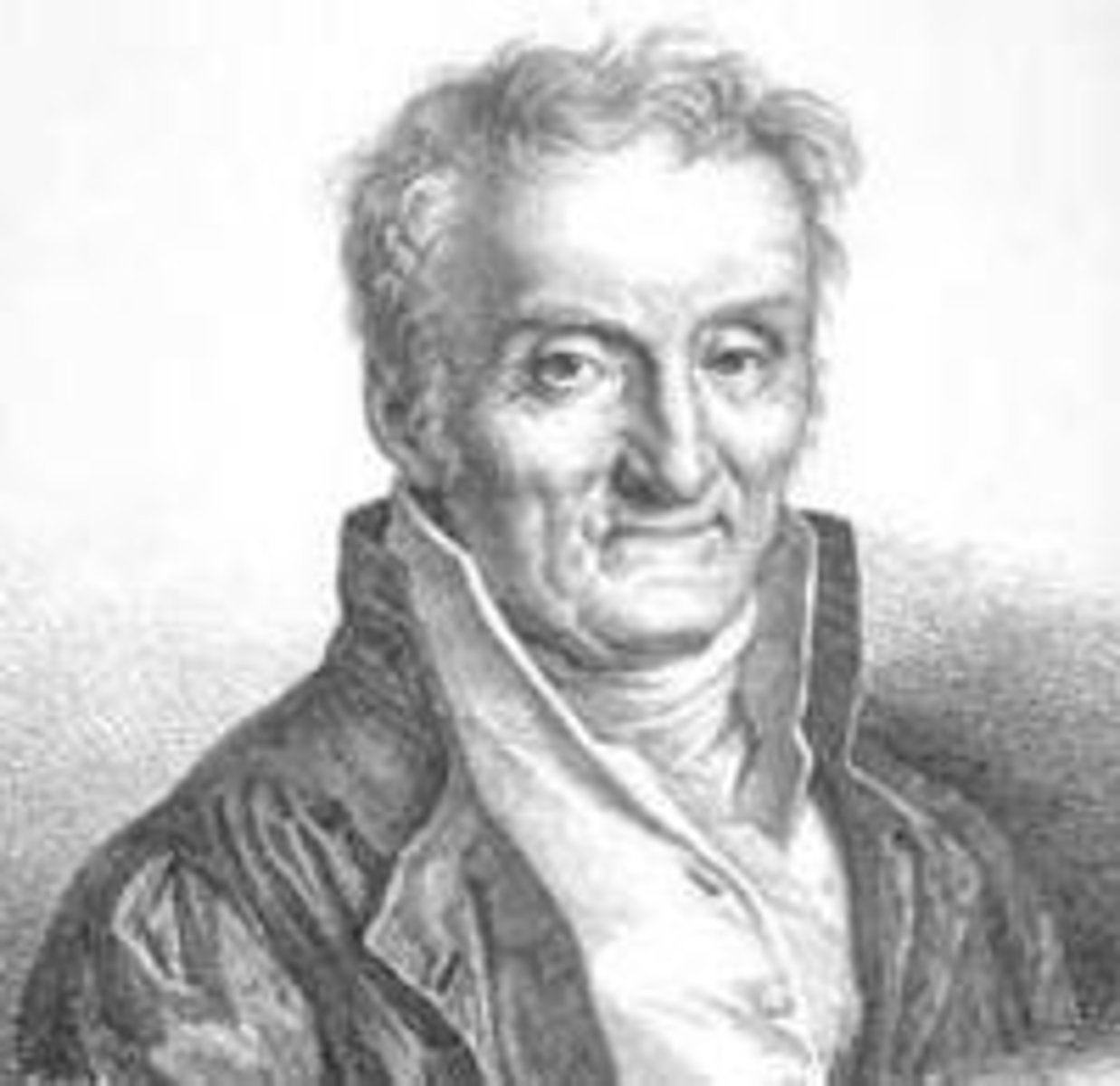
Philippe Pinel
In 1795 Pinel assumed the responsibility for the mental patients at l'Hôpital de la Salpêtrière, where he continued his policy of nonrestraint and brought about many significant and far-reaching reforms in the care and treatment of mental patients. Humane treatment under the watchful eye of trained and compassionate personnel in the institution made possible the recovery of many otherwise doomed patients. Pinel also introduced the practice of keeping case histories, which proved a valuable source of information in later efforts to understand insanity.

medical model
the concept that diseases, in this case psychological disorders, have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and, in most cases, cured, often through treatment in a hospital.