Lecture 1/8/2025
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pharm 120
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What it the basic organization of the human body?
Atoms, Molecules, Organelles, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ, Organ Level, Organ Level System, Organismal Level
Integumentary System
Skin, Nails, Hair - Forms external body covering, provides protection
Skeletal System
Shape for form, protection, calcium, produces red blood cells
Muscular System
protection, generates heat
Nervous System
control system of the body
Endocrine System
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes - growth, reproduction
norepinephrine
chemical messenger system
Heart
Blood vessels transport blood, carrying oxygen
Lymphatic System
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood
houses white blood cells involved in immunity
Respiratory
keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
digestive system
breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood
Urinary System
eliminates nitrogenous waste from the body
reproductive system
production of offspring
Cell Theory
that organismal functions depend on individual and collective cell functions
Human cells have three basic parts
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
What molecules can passively diffuse through the plasma membrane?
oxygen and CO2 - due to hydrophobic properties
what is the plasma membrane comprised of?
phospholipids (lipid bilayer) - 75%
Phosphate heads = hydrophilic
Fatty Acid Tails = Hydrophobic
5% Glycolipids - important for recognition
20% Cholesterol
Allows for membrane stability
Glycolipids are used for?
specific biological markers for cell to cell recognition
Cell Junctions - Name the 3
Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, Gap Junctions
Tight Junctions
Nothing can get in between cells
Desmosomes
allows for cells to slide, tension reducing
Gap Junctions
Nutrients are able to move cell to cell
What are the two types of passive transport?
Diffusion - simple diffusion, channel mediated facilitated diffusion
Filtration - for the lungs or kidneys
usually across capillary walls
Molecule will passively diffuse through membrane if…
is lipid soluble, small enough to pass through membrane channels, assisted by carrier molecules
Leakage Channels are,,
always open
Gated channels are…
controlled by chemical, electrical, or physical signals
Water diffuses through specific water channels called..
aquaporins
Osmosis
diffusion of a solvent through a specific channel protein
What is the importance of osmosis in cells?
can cause shrinkage or swelling, and changes in cell volume disrupts cell function
Isotonic
solution with same non-penetrating solute concentration as cytosol
Hypertonic
solution with higher non-pentrating solute concentration than cytosol
Hypotonic
solute with lower non-penetrating solute concentration than cytosol
What are the 2 types of active transport
vesicular transport, active transport
both require ATP
Endocytosis
transport into cell
Exocytosis
Transport out of cell
Transcytosis
transport into, across, and then out of cell
Vesicular trafficking
transport from one area or organelle in cell to another
Cilia
contains microtubules and motor molecules, move substances across cell surfaces
in throat
Flagella
tail on sperm
Microvilli
increases surface area
Tissues
Groups of cells similar in structure that perform common or related function
Histology
study of tissues
Haematoxylin
Stains nuclei purple
Eosin
stains cytoplasm, red blood cells, muscle fibers
What are the 4 types of primary tissues?
Epithelial - Covers
Connective - Protects
Muscle - Moves
Nerve - Contols
What are the functions of Epithelial tissues
PSAFE
Protection
Absorption
Filtration
Excretion
Secretion
What are the characteristics of Epithelial Tissue?
Avascular but Innervated, high regnerative capacity
Simple Epithelia
Single Layer
Stratified Epithelia
two or more layers of cells
Squamous
flattened and scale like
cubodial
cube, boxlike and nucleus round
Columnar
tall; nucleus elongated
simple squamous epithelium
location: air sacs of lungs and lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphmatic vessels
Simple cuboidal epithelium
in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
Simple columnar
ciliated tisses are in bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much fo the upper respiratory tract
stratified squamous epithelium
lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
stratified cuboidal epithelium
sweat glands, salivary glands, and mamory glands; protective
transitional epithelium
lines the bladder, uretha, and the ureters
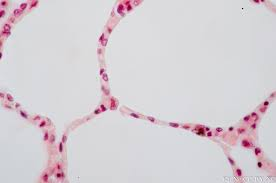
simple squamous epithelium
L: Air sacs of linds, kidney glomeruli
F: allows materials to diffuse and filtrate
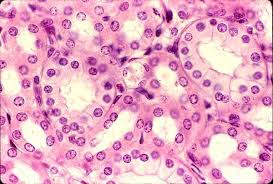
simple cuboidal epithelium
L': Kidney Tubules
F": Secretion and Absorption
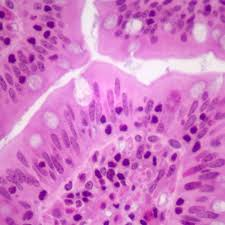
Simple columnar Epithelia
F: Absorption, secretion of mucus
L: GI Tract, small intestine
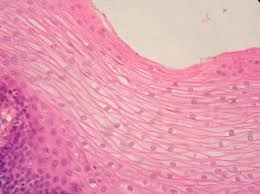
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
F: Protects underlying tissues subjected to abrasion
L: Non Keratinized = esophagus, vagina, mouth, Keratinized = skin