Anatomy- Nasal Cavity and Palate
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
clean; warm; humidify
the three functions of the nasal concha are to .... air
pharyngeal
the .... tonsil in the nasal cavity works to pick up dust
tympanic
the .... tube allows air into the ear cavity from the nasal cavity
mucosal
the nasal concha are bone covered by .... epithelium
superior; middle
which concha are part of the ethmoid bone
inferior
which concha is its own bone
maxillary
which bone supports most of the weight of the nasal cavity
hyaline
what type of cartilage are the cartilages of the nose
anterior
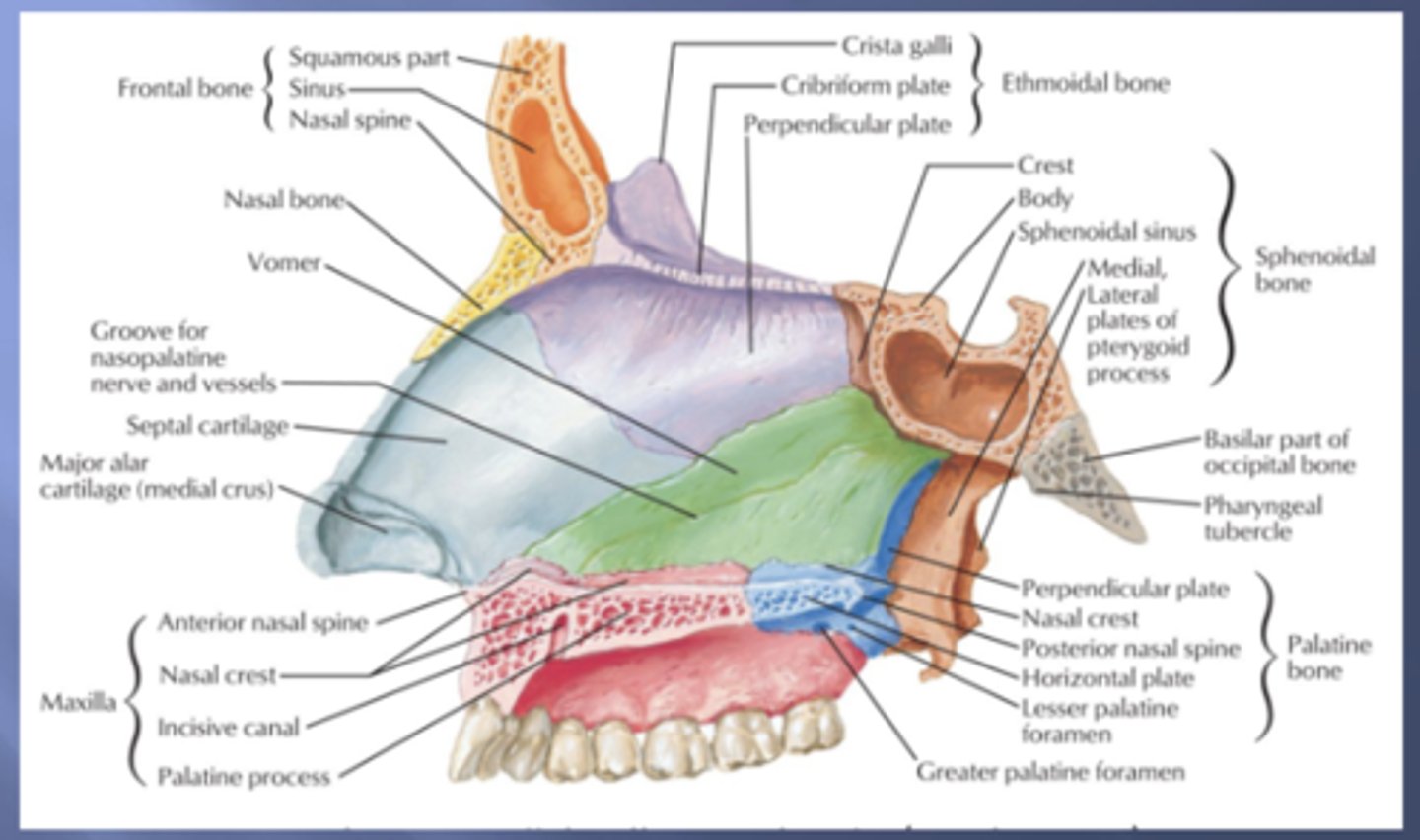
which part of the nasal septum:
- nasal septal cartilage
- alar cartilage
- lateral nasal cartilage
superior
which part of the nasal septum:
- ethmoid bone
inferior
which part of the nasal septum:
- vomer bone
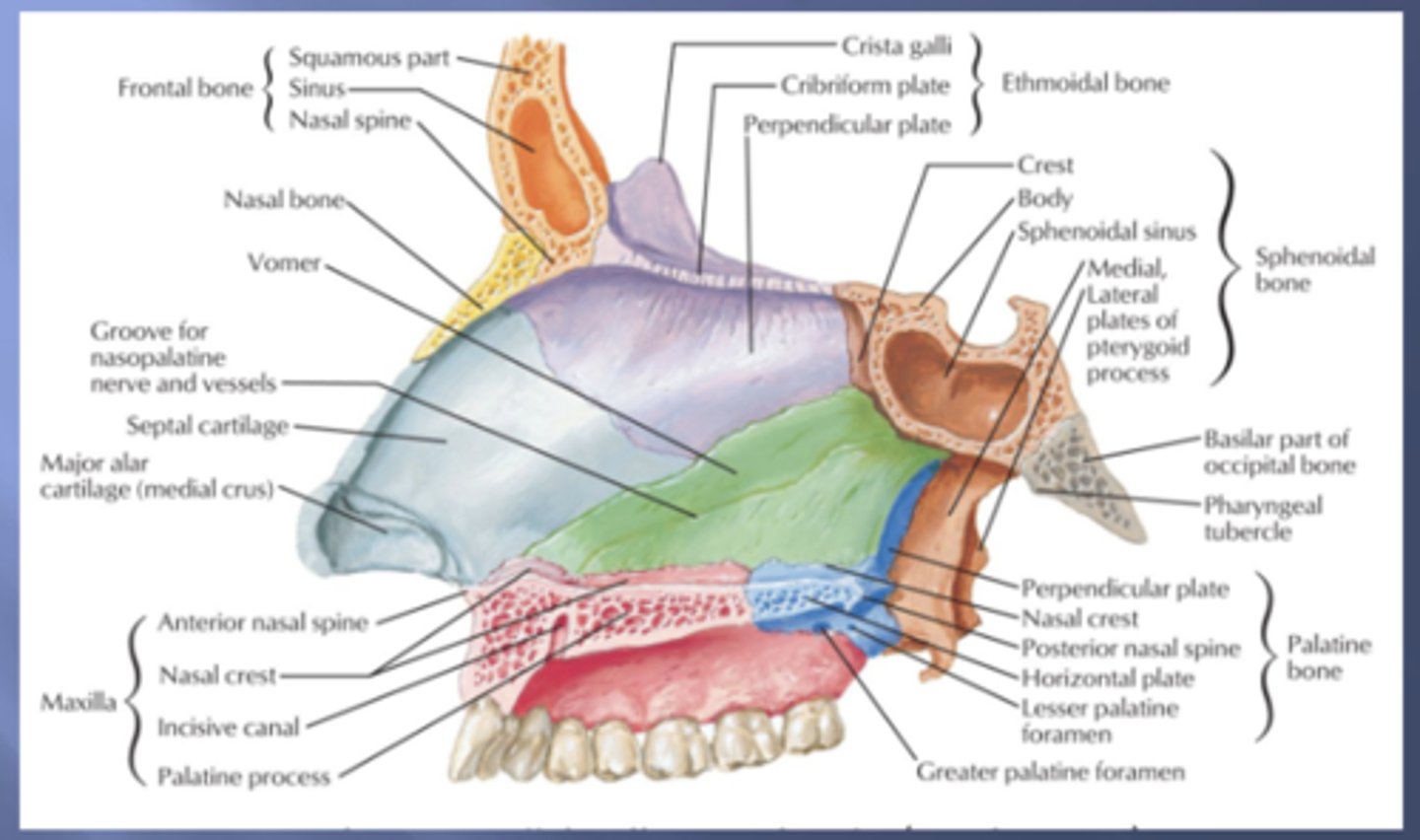
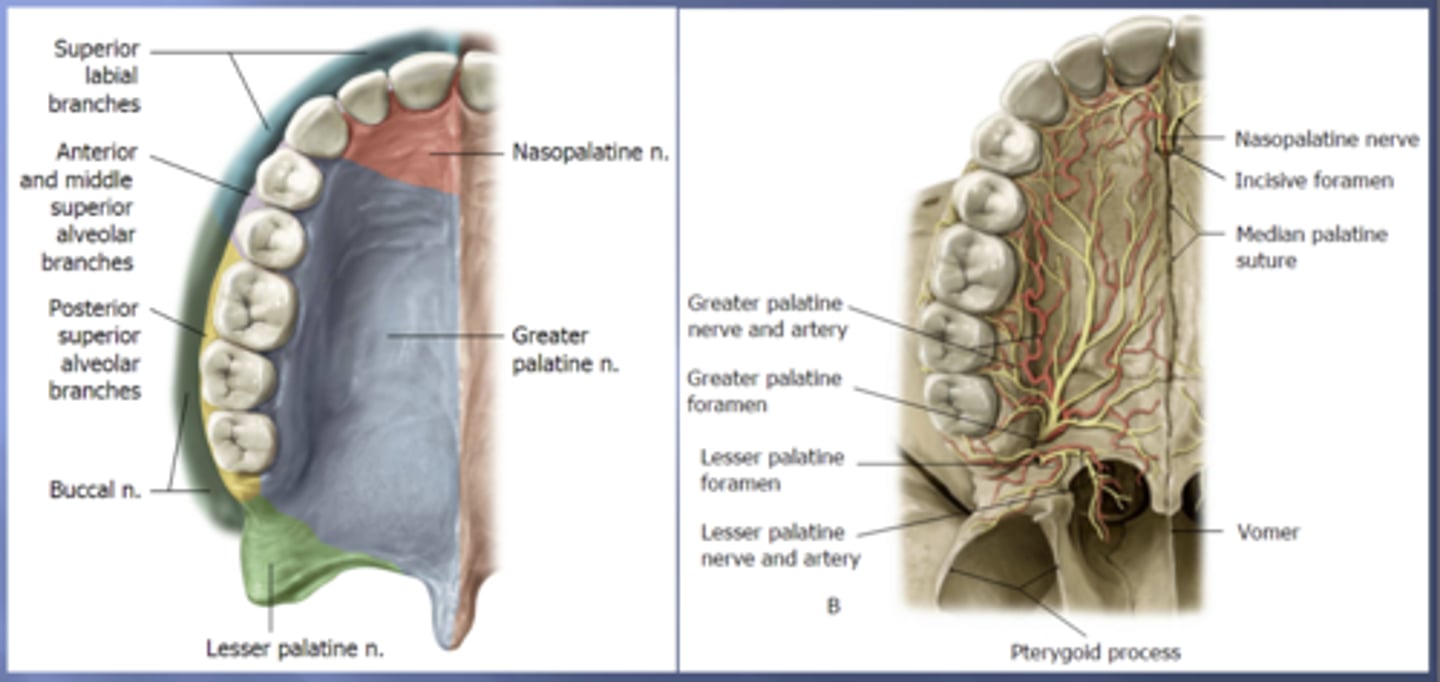
nasopalatine
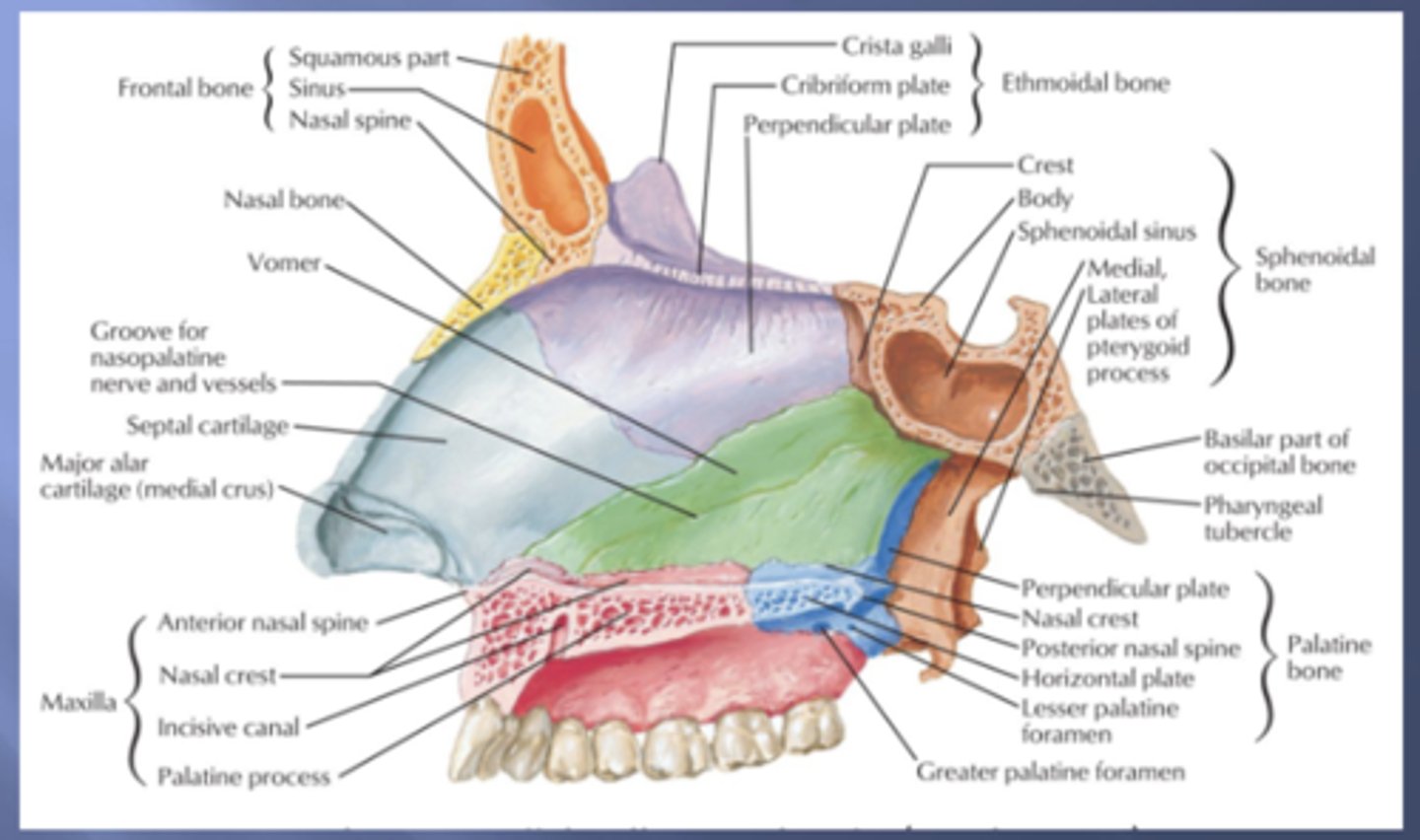
the vomer bone has a groove for the .... nerve and vessels which provide innervation to the hard palate
lighten
a main function of the sinuses of the skull are to .... the skull
maxillary
what is the largest sinus of the skull
ostea; semilunar hiatus
the maxillary sinus drains into the nasal cavity through the maxillary ... to the .... which is located in the middle meatus
semilunar hiatus
the frontal sinus drains into the nasal cavity through the .... which is located in the middle meatus
semilunar hiatus
the anterior ethmoid air sinus drains into the nasal cavity through the .... which is located in the middle meatus
middle
the middle ethmoid air cells drain into the nasal cavity directly into the .... meatus
superior
the posterior ethmoid air cells drain into the nasal cavity directly into the ..... meatus
sphenoethmoidal
the sphenoid sinus drains into the nasal cavity through the .... recess which is just superior to the superior nasal concha
inferior meatus
the nasolacrimal duct drains into the nasal cavity's .....
maxillary
most of the nasal blood supply comes from the .... artery, a branch off the external carotid artery
pterygopalatine
in the ..... fossa, the maxillary artery branches into the:
- sphenopalatine artery
- descending palatine artery
- infraorbital artery
- posterior superior alveolar artery
- pharyngeal artery
sphenopalatine
the maxillary artery branches into the ... artery which supplies the posterior of the nasal cavity
greater palatine
the maxillary artery branches into the ... artery which supplies the inferior of the nasal cavity
ethmoid
the superior of the nasal cavity is supplied blood through the ..... arterys
septal
the anterior of the nasal cavity is supplied blood through the ... branch of the superior labial artery from the facial artery
kiesselbachs
.... areas is the meeting of these arterys in the nasal cavity:
- sphenopalatine
- greater palatine
- superior labial
- ethmoid
nasopalatine
the ..... nerve is a branch off the maxillary nerve (V2) which innervates the posterior of the nasal cavity
parasympathetic
the nerve of the pterygoid canal from the facial nerve brings ..... information to the pterygopalatine ganglion which control mucous secretions from the nasal glands
ethmoid
the superior nasal cavity is innervated by the .... nerves which are branches of the nasociliary nerve from the ophthalmic nerve (V1)
middle
the pterygopalatine ganglion is located just posterior to the .... nasal concha
SVA
..... innervation of the nasal cavity is provided through the olfactory nerve for smell
GSA
.... innervation of the nasal cavity is provided through the pterygopalatine ganglion from the trigeminal nerve
GVE
.... innervation of the nasal cavity is provided through the pterygopalatine ganglion from the facial nerve
nasopalatine
the anterior portion of the hard palate that contains the 4 incisors is innervated by the .... nerve
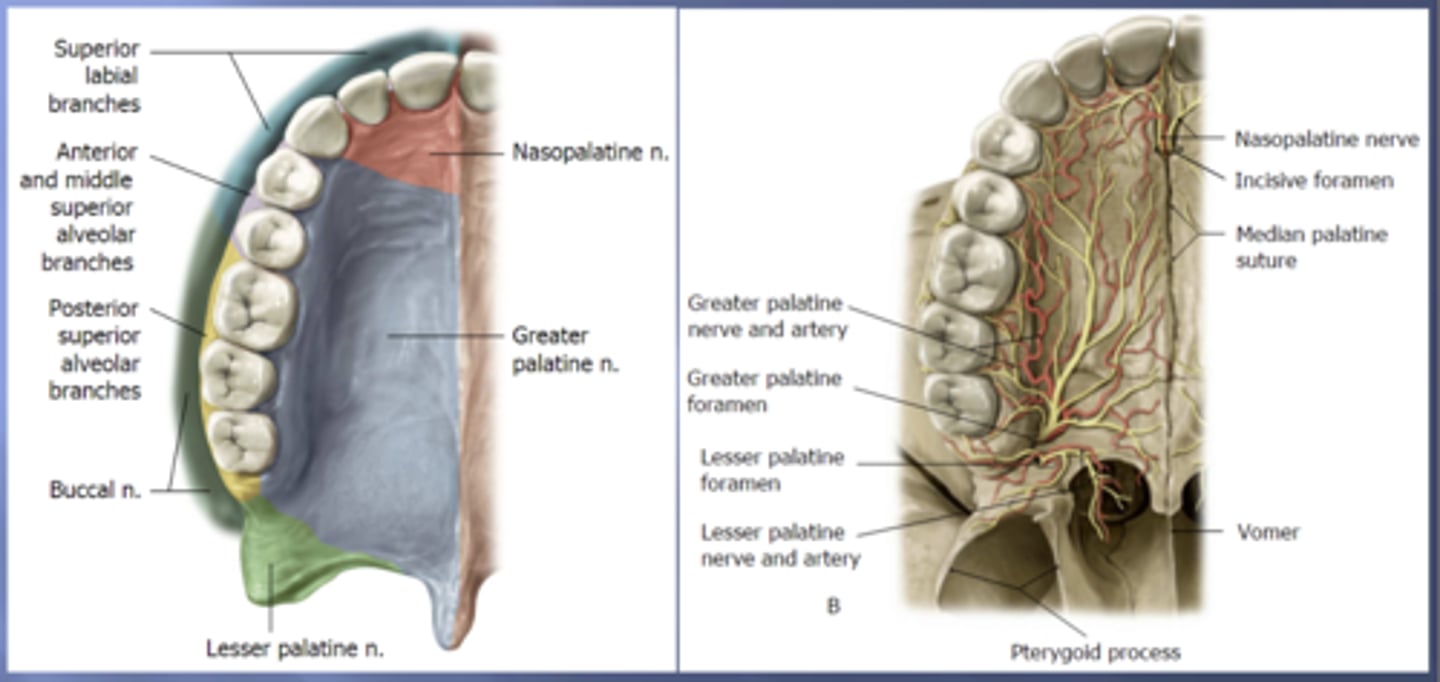
greater palatine
the majority of the hard palate including the molars and premolars is innervated by the .... nerve
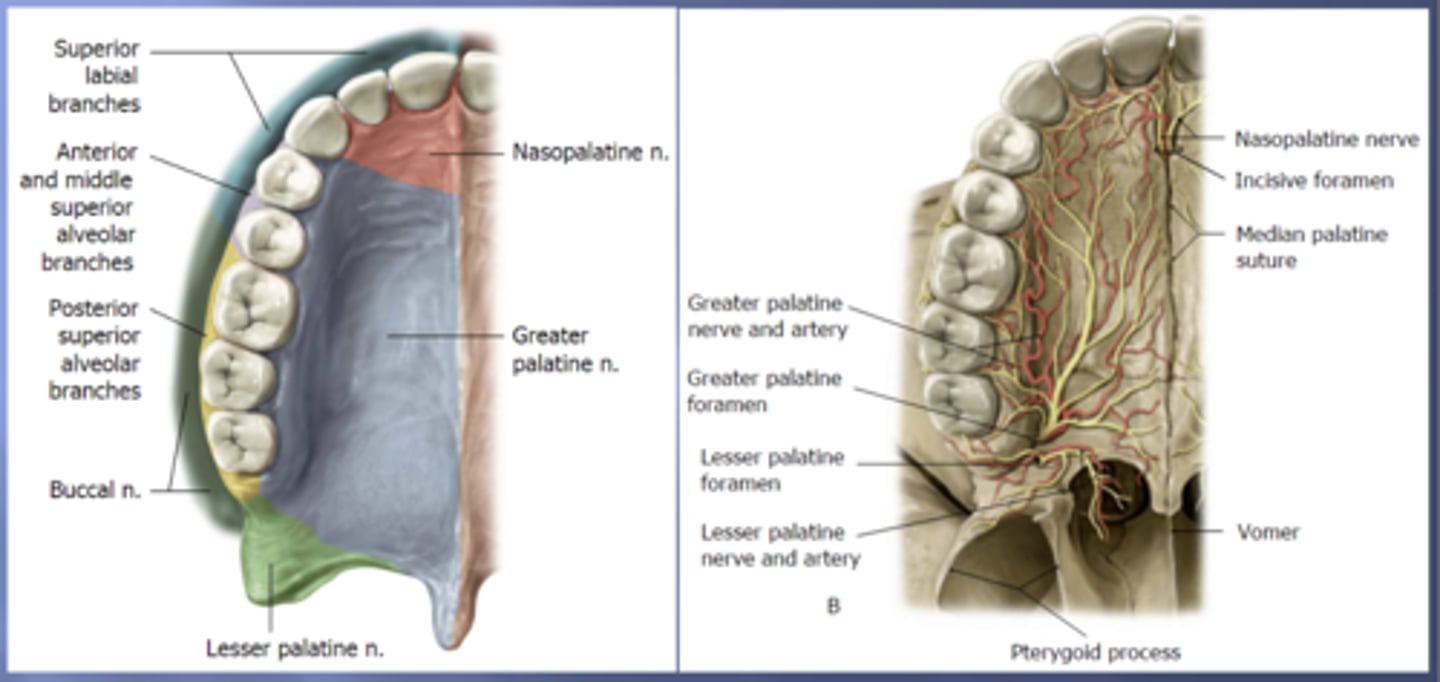
posterior superior alveolar
the portion of the alveolar arch that contains maxillary molars is innervated by the ..... nerve
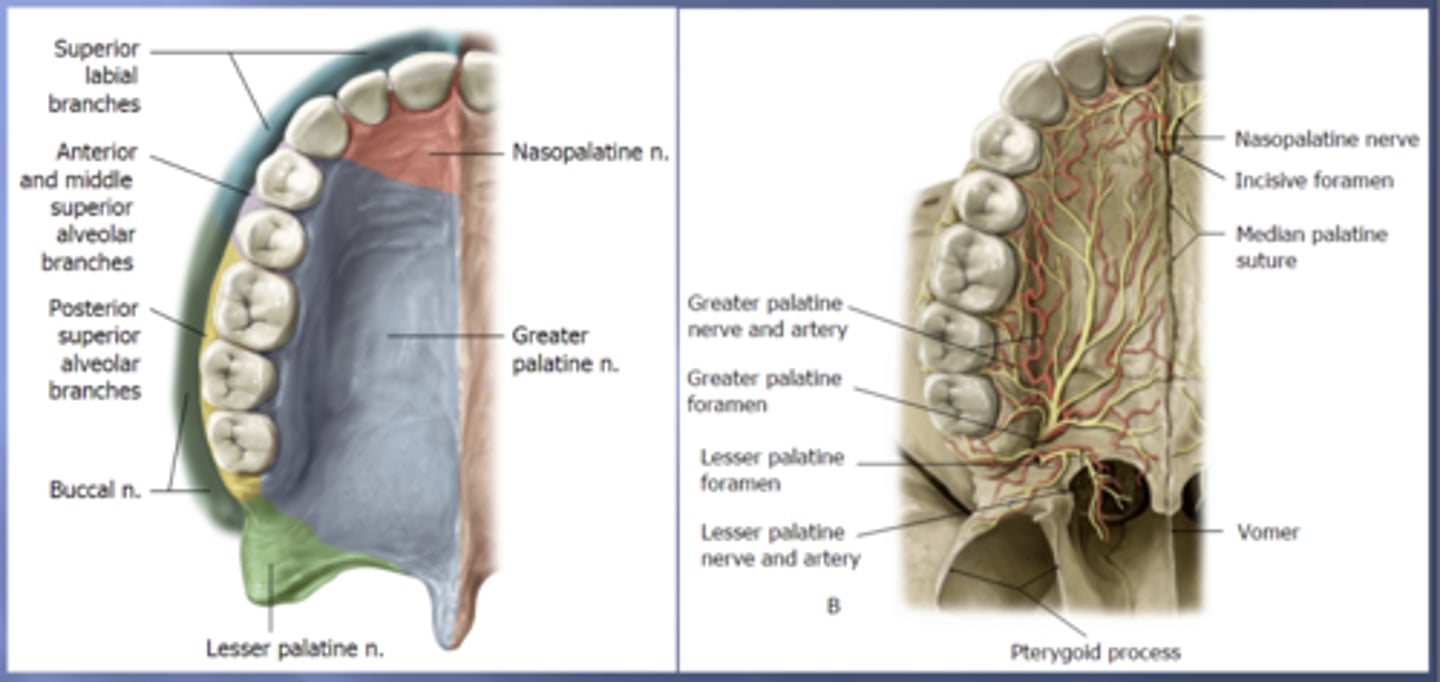
middle superior alveolar
the portion of the alveolar arch that contains maxillary premolars is innervated by the ..... nerve
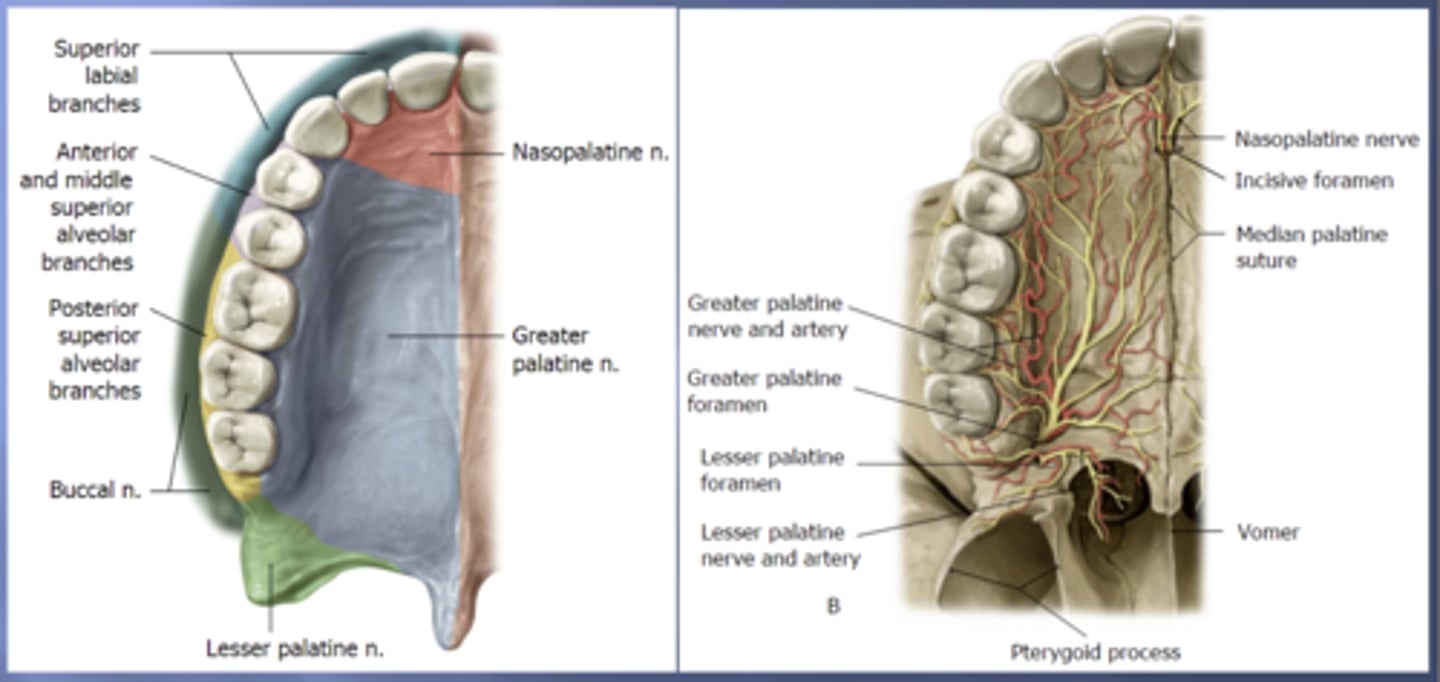
anterior superior alveolar
the portion of the alveolar arch that contains maxillary canines and incisors is innervated by the ..... nerve
superior labial
the anterior portion of the upper lip is innervated by the ..... nerve which are branches of the infraorbital nerve from the maxillary (V2) nerve
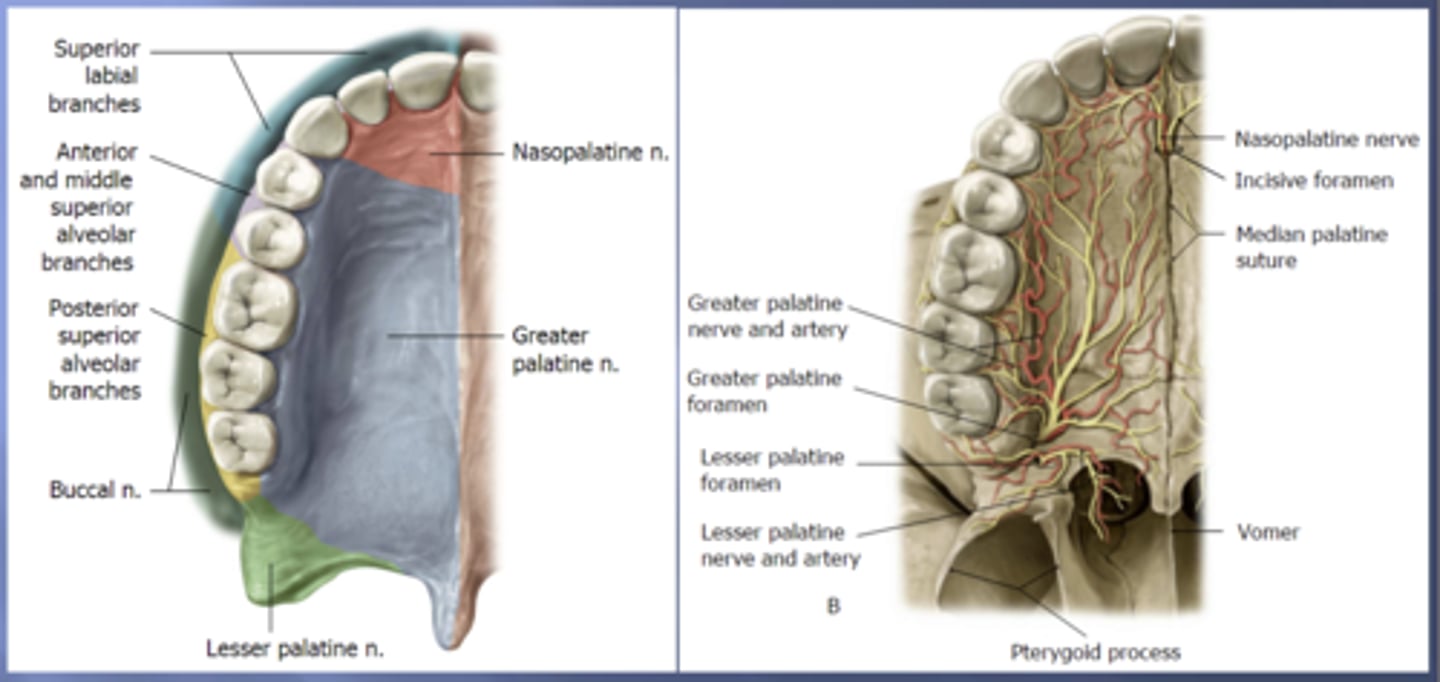
long buccal
the posterior portion of the upper lip is innervated by the ..... nerve which is a branch of the mandibular (V3) nerve
uvula
the muscular ... on the floor of the soft palate directs fluid from the oral cavity down towards the pharynx
palatine
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- around pharyngotympanic tube
- make soft palate and uvula
- stop food from going into nasal cavity
tensor veli palatini
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- runs from pterygoid hanulus in towards soft palate laterally
- tenses the soft palate laterally
- opens pharyngotympanic tube when swallowing and yawning
- innervated by the medial pterygoid nerve from the otic ganglion from V3
- originates from 1st pharyngeal arch
levator veli palatini
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- from pharyngotympanic tube into soft palate posteriorly
- elevates soft palate
- innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus
- originates from 4th pharyngeal arch
salpingopharyngeus
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- trumpet end to pharyngotympanic tube
palatoglossus
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- elevates posterior part of tongue
- draws soft palate onto tongue
- innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus
palatopharyngeus
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- tenses soft palate
- pulls walls of the pharynx superior, anteriorly, and medially during swallowing
- innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus
musculus uvulae
which muscle of the nasopharynx:
- shorten uvula and pulls it superiorly
- innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus
frontonasal prominence
the primary hard palate originates from the ....
first pharyngeal arch
the secondary hard palate originates from the ....
incisive
the nasopalatine nerve travels through the .... canal to innervate the primary hard palate
GVE
the infraorbital nerve contains .... fibers for controlling face vasculature and sweat
anterior; middle
the infraorbital artery branches into which superior alveolar arteries
palatoglossal arch
which aspect of the soft palate:
- made by palatoglossus muscle
- runs from uvula to the tongue
- depress soft palate and elevate the tongue
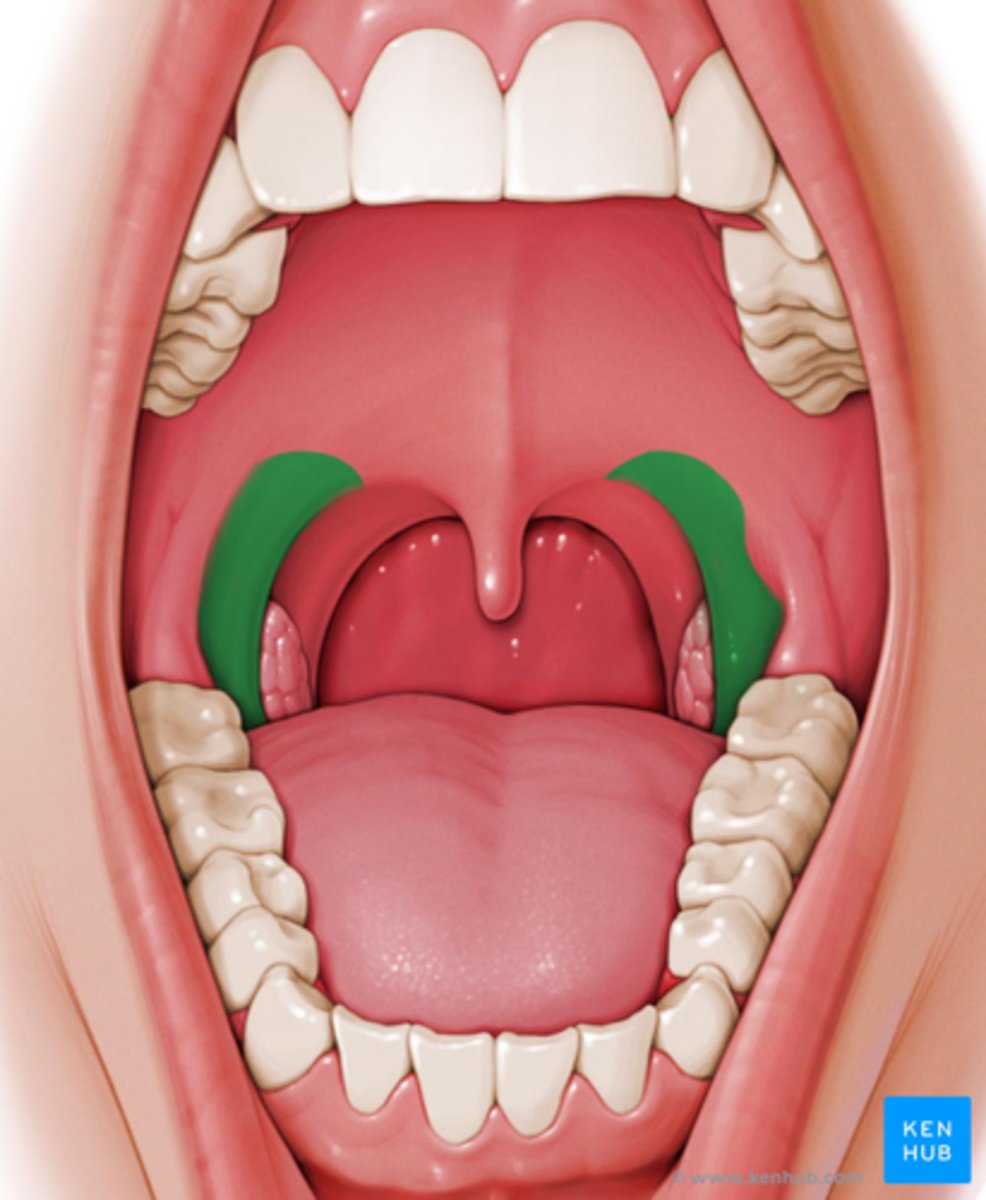
palatine tonsil
which aspect of the soft palate:
- lymphatic system for pathogens in food/drink

palatopharyngeal arch
which aspect of the soft palate:
- made by palatopharygneus mucles
- runs from soft palate to the pharynx
- depress soft palate elevate pharynx
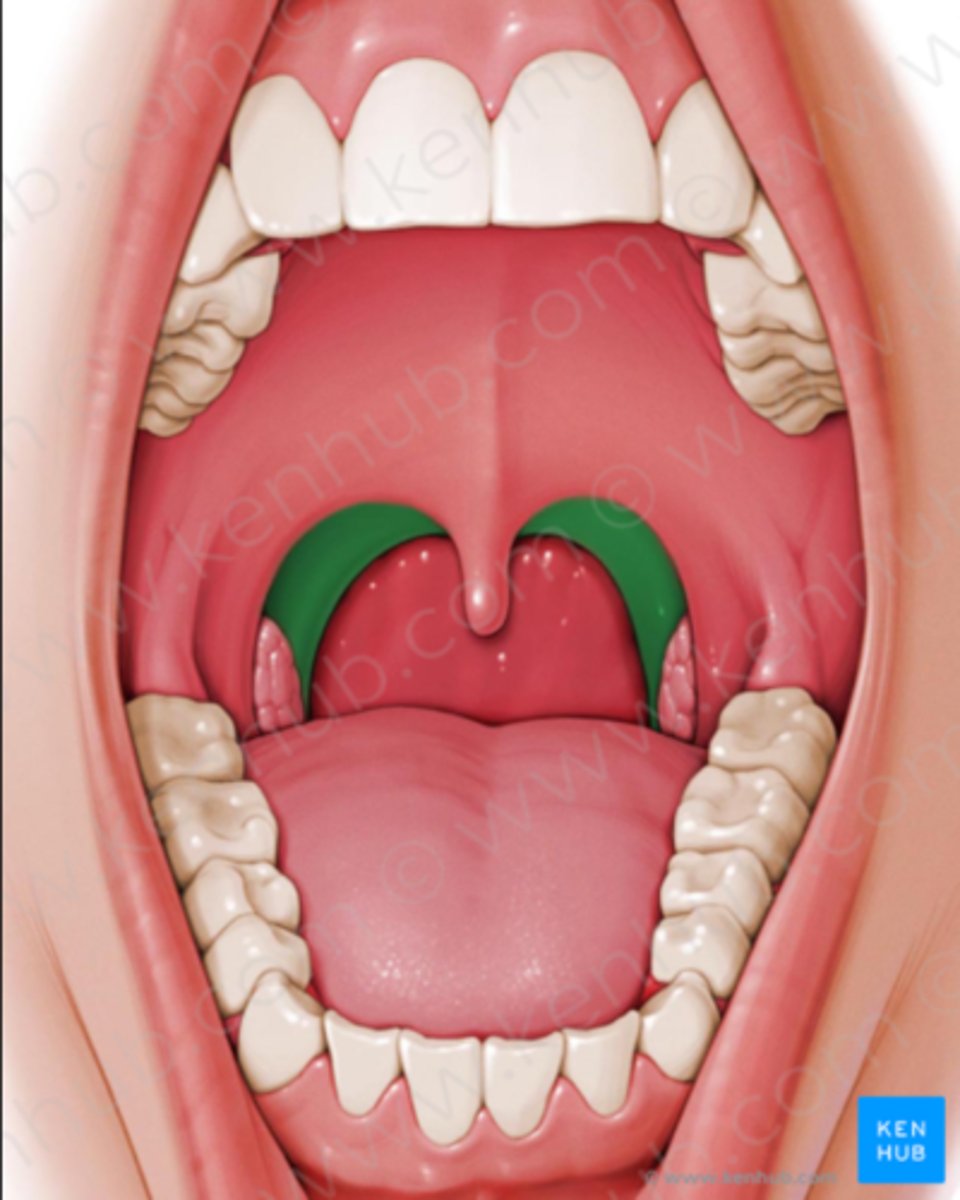
palatine tonsils
what is located between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
1 pharyngeal arch
what does the tensor veli palatini originate from
4 pharyngeal arch
what does the levator veli palatini originate from
glossopharyngeal
the ..... nerve provides sensation to the palatine tonsil
maxillary
the soft palate receives blood from above through the ... artery
ascending pharyngeal
the soft palate receives blood from below through the ... artery
SVE
most of the muscles of the soft palate (other than the tensor vili palatini) originate from the 4th pharyngeal arch and are provided innervation through .... fibers from vagus nerve
prep; transit
which phases of deglutition are under voluntary control
esophageal; pharyngeal
which phases of deglutition are under autonomic control