IB Chemistry HL - CHAPTER 5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:13 PM on 3/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
2
New cards
The law of conservation of energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of a process cannot change.
3
New cards
Exothermic (-∆H)
A reaction is exothemic (-∆H) when the products have less enthalpy than the reactants.
4
New cards
Endothermic (+∆H)
A reaction is endothermic (+∆H) when the products have more enthalpy than the reactants.
5
New cards
Standard conditions
* A pressure of 100 kPa
* A concentration of 1 mol dm^{-3} for all solutions
* Each substance involved is in its standard state
* A temperature of 298 K
* A concentration of 1 mol dm^{-3} for all solutions
* Each substance involved is in its standard state
* A temperature of 298 K
6
New cards
The standard enthalpy change of reaction
The standard enthalpy change of reaction (∆H_{r}^{⦵}) is the enthalpy change when the reactants in the stoichiometric equation react to give the products under standard conditions.
7
New cards
The standard enthalpy change of formation
The standard enthalpy change of formation (∆H_{f}^{⦵}) is the enthalpy change when one mole o a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
8
New cards
The standard enthalpy change of combustions
The standard enthalpy change of combustion (∆H_{c}^{⦵}) is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is burnt completely in excess oxygen under standard conditions.
9
New cards
The standard enthalpy change of neutralization
The standard enthalpy change of neutralization (∆H_{neut}^{⦵}) is the enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed by reacting an acid and alkali under standard conditions.
10
New cards
The specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity (c) is the amount o heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Kelvin.
11
New cards
Q
mc∆T
12
New cards
The principle of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
Carry out the reaction with an excess of one reagent and measure the temperature change over the course of a few minutes.
13
New cards
The setup of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
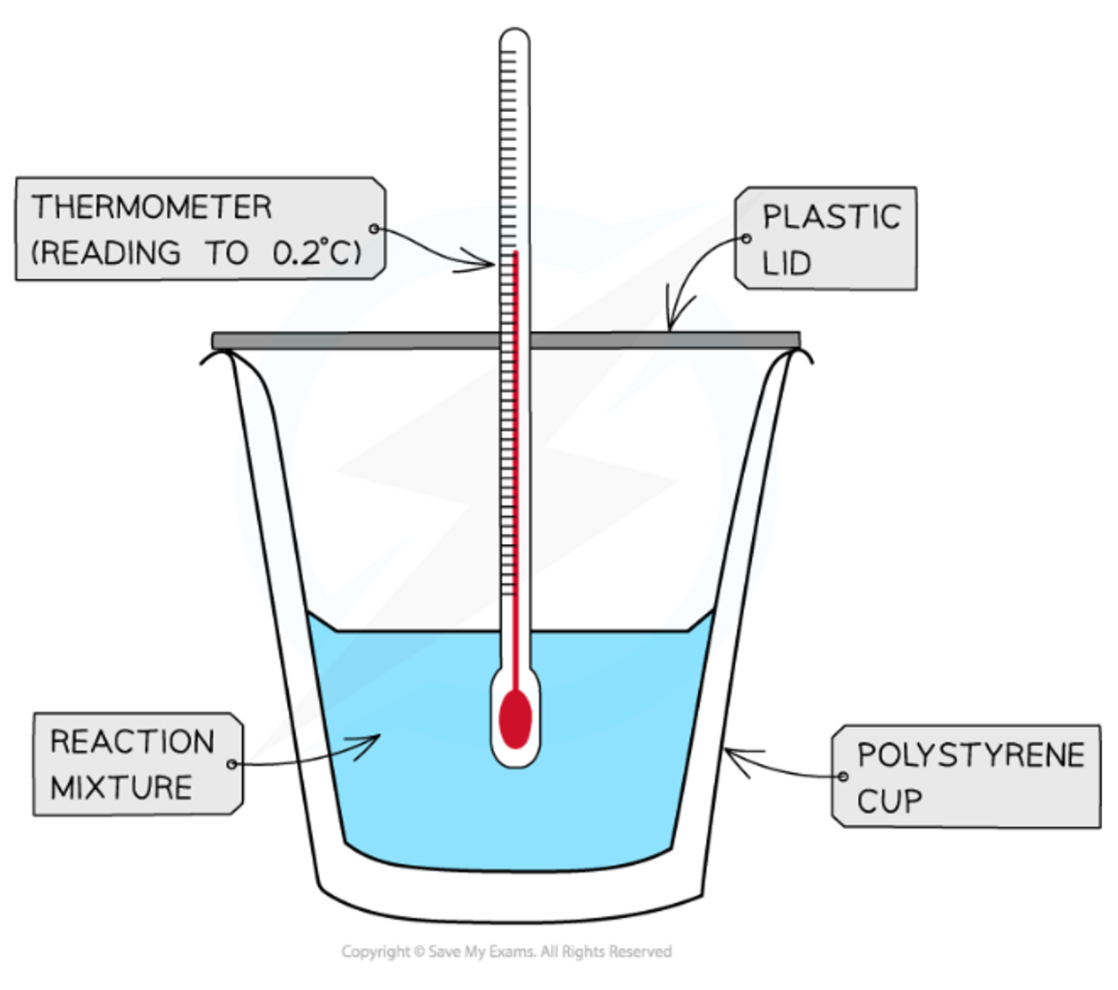
14
New cards
The errors of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
* The density of the solution is assumed to be 1 g cm^{-3}
* Incomplete reaction
* Heat losses
* Incomplete reaction
* Heat losses
15
New cards
Temperature correction graphs
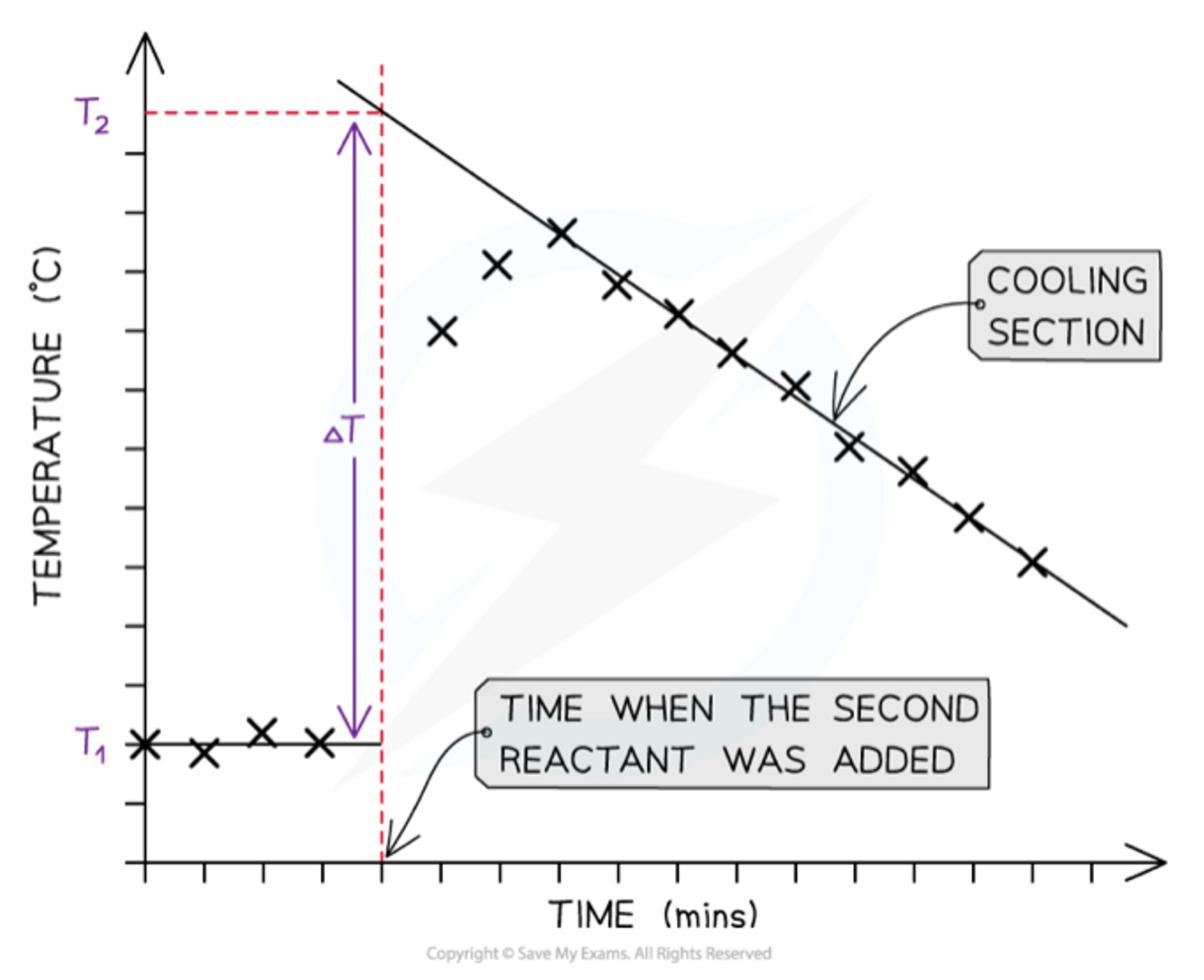
16
New cards
The principle of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
Use the heat released by a combustion reaction to increase the heat content of water.
17
New cards
The setup of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
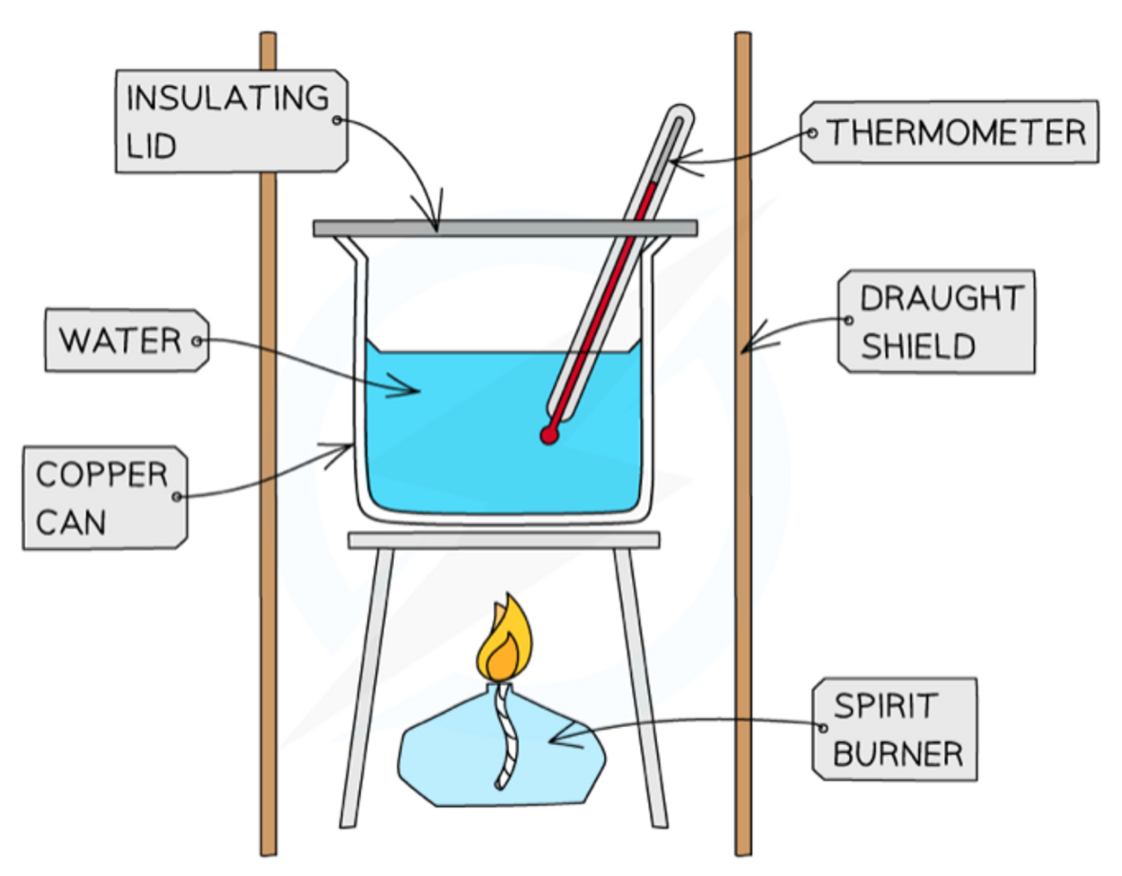
18
New cards
The errors of experiments to find enthalpy changes for reactions in solutions
* Heat loss to the surroundings and the calorimeter
* Minimised by placing a lid over the calorimeter and having a small distance between the coppor calorimeter and the flame.
* Incomplete combustion
* Minimised by placing a lid over the calorimeter and having a small distance between the coppor calorimeter and the flame.
* Incomplete combustion
19
New cards
Enthalpy equation
∆Hr = Σ∆Hf(products) - Σ∆Hf(reactants)
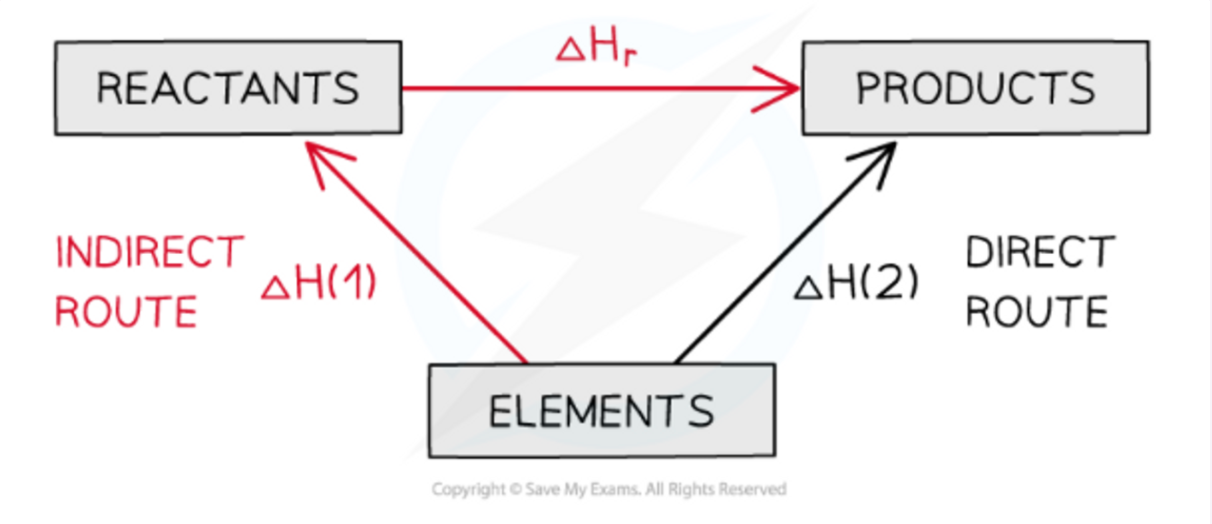
20
New cards
Two important rules for solving Hess’s Law-cycles.
1. If you follow the direction of the arrow you add the quantity
2. If you go against the arrow you subtract the quantity
21
New cards
The steps to solve Hess’s law-equations
1. Identify which given equation contains the product you want.
2. Adjust the equation if necessary, to give the same product. If you reverse it, reverse the sign of the ∆H value.
3. Adjust the equation if necessary, to give the same number of moles of product.
4. Identify which given equation contains your reactant.
5. Adjust the equation if necessary,to give the same reactant.If you reverse the ∆H value.
6. Adjust the equation if necessary, to give the same number of moles of reactant.
7. Add the two equations together.
8. Cancel the common items.
9. Add the two ΔH values together to get the one you want.
22
New cards
The standard enthalpy of formation
The standard enthalpy of formation (∆H_{f}^{⦵}) is defined as the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
23
New cards
Average bond energy
The average bond energy is the energy needed to break one mole of bonds in a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds.
24
New cards
Stability in endothermic processes
In endothermic processes (+∆H) reactants are more stable than the products.
25
New cards
Stability in exothermic processes
In exothermic processes (-∆H) reactants are less stable than the products.
26
New cards
Bond enthalpy calculations
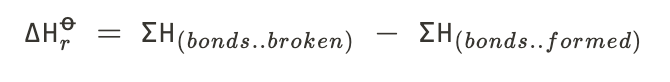
27
New cards
Transition state
The transition state is a stage during the reaction at which chemical bonds are partially broken and formed. The transition state is vey unstable.
28
New cards
Activation energy
The activation energy (E_a) is the minimum amount of energy needed for reactant molecules to have a successful collision and start the reaction.
29
New cards
Does endothermic or exothermic reactions have higher activation energies?
Endothermic reactions have a higher activation energy compared to exothermic reactions.
30
New cards
The steady state of the ozone cycle

31
New cards
Increased depletion of ozone when other chemicals are introduced
