blood coagulation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is haemostasis
body’s natural process for stopping bleeding after an injury which involves forming clot and seal damaged blood vessel
what is the main purpose of haemostasis
to control blood loss following vascular injury
what happens if haemostasis is overactive
thrombosis (blood clot)
what happens if haemostasis is underactive
haemorrhage (excessive bleeding)
difference between thrombosis and haemorrhage
thrombosis is blockage of blood flow from within blood vessel (blood clot inside blood vessel)
haemorrhage is loss of blood from blood vessel (leakage of blood)
what are the main stages in haemostatic process after vascular injury
1) Local vasoconstriction
2) Platelet plug formation
3) Stabilisation of platelet plug by fibrin (thrombus formation)
4) Thrombus dissolution (fibrinolysis)
1) local vasoconstriction - why does the injured blood vessel immediately narrow
to reduce blood flow to damaged area
2) platelet plug formation - how do platelets stick together in the site of injury to exposed collagen
they stick by a protein called von Willebrand factor (vWF) which forms a bridge between collagen platelets
3) thrombus formation - what happens
fibrin forms from the coagulation cascade which is a tough sticky protein
the fibrin mesh turns soft platelet plug into stable clot (thrombus)
4) thrombus dissolution - how is the clot removed once healed
enzyme plasmin breaks down fibrin into soluble fragments
plasmin is made from plasminogen and activated by tPA
prevents clots from blocking blood vessel permanently
what drug classes can modulate haemostasis
Antiplatelet drugs
Anticoagulant drugs
Fibrinolytic/thrombolytic drugs
Anti-fibrinolytic drugs (e.g. tranexamic acid)
what triggers platelet adhesion
exposure of collagen
von Willebrand factor (vWF acts as a bridge)
name key substances that activate platelets
thrombin
thromboxane A2
ADP
fibrinogen
what are the main functions of platelets in haemostasis
adhere to exposed collagen via vWF
aggregate with other platelts
provide surface for coagulation cascade
what is contained in platelet dense granules
ADP and serotonin
what is contained in platelet alpha granules
vWF, fibrinogen, Factor V, fibronectin, platelet factor 4, platelet-derived growth factor
true or false: there is only a single layer of endothelium cells so when damaged, this exposes underlying structures to the blood. via vWF, tethering between structures and surface of platelets
true
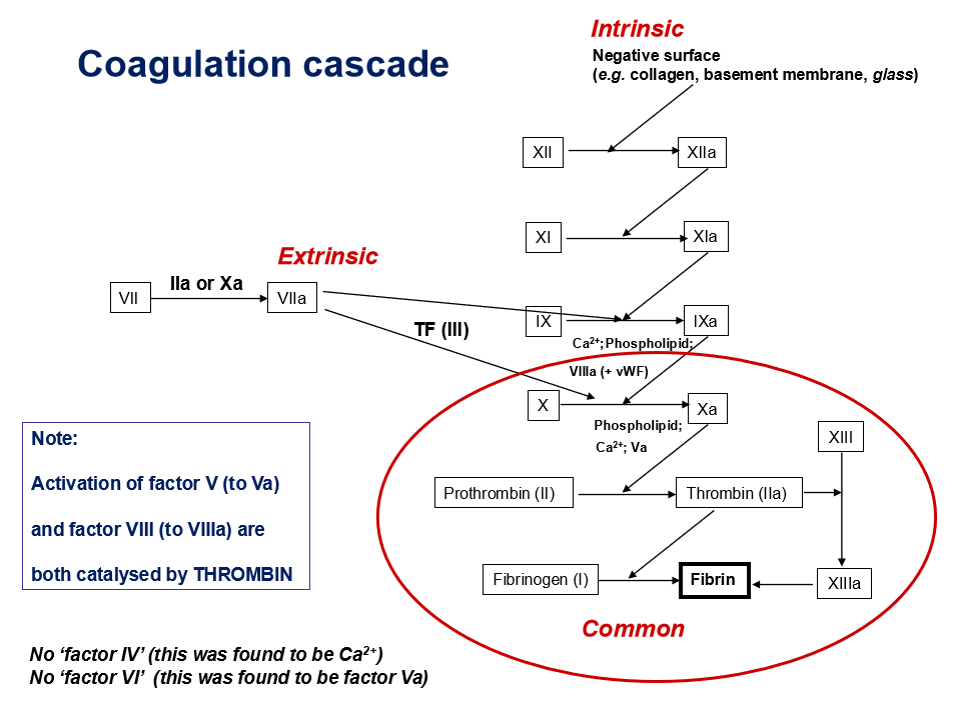
what is the purpose of coagulation cascade
production of fibrin to stabilise clot
what triggers the intrinsic pathway (intrinsic = internal damage to blood vessel)
contact with a negatively charged surface e.g. collagen, glass
what triggers extrinsic pathway (extrinsic = external injury releasing tissue factor)
exposure to tissue factor during vascular injury
which factor marks start of common pathway
factor Xa
which ion is essential for coagulation reactions
Ca2+
what activates factor V and factor VIII
thrombin
why is there no factor IV and factor VI
“Factor IV” was found to be Ca²⁺ and “Factor VI” is actually Va
what is inactive precursor of plasmin
plasminogen
how is plasminogen activated
by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) released from damaged endothelium
what does plasmin do
digests fibrin into soluble degradation products
what is the mechanism of fibrinolytic drugs
activate plasminogen to plasmin promoting fibrin breakdown
examples of fibrinolytic agents
Streptokinase: Antigenic; can cause allergic reactions (1–4% incidence).
Alteplase: Recombinant tPA; used in MI and ischaemic stroke.
Reteplase: Longer-acting tPA mutant; bolus administration (MI).
Tenecteplase: Longer-acting tPA mutant; bolus administration (MI).
antiplatelet drugs
aspirin
clopidogrel
tirofiban
what enzyme does aspirin inhibit
cyclooxygenase (COX)
true or false: aspirin’s inhibition is reversible
false - irreversible
how does aspirin reduce platelet activation
inhibits thromboxane AT synthesis → less platelet activation and vasoconstriction
what receptor does clopidogrel block
P2Y12 receptor (ADP receptor)
what effect does clopidogrel have on platelets
Inhibits ADP-induced platelet aggregation and GPIIb/IIIa expression
what drug class does clopidogrel belong to
thienopyridines (same as prasugrel)
what other drug has similar mechanism to clopidogrel
ticagrelor
what is the target of tirofiban
GPIIb/IIIa complex on platelets
what is the role of GPIIb/IIIa complex
platelet receptor for fibrinogen binding — crucial for platelet aggregation
name other drugs that inhibit GPIIb/IIIa
eptifibatide (peptide inhibitor)
bciximab (monoclonal antibody; no longer available)
what is the GPIIb/IIIa complex
glycoprotein receptor found on the surface of platelets important for platelet aggregation
true or false: haemophilia is X-chromosome linked
true
which sex is usually affect by haemphilia
males because females are usually carriers
what factor is deficient in haemophilia A
factor VIII
which factor is deficient in haemmophilia B
factor IX
which factor deficiency has less clinical significance
factor XI deficiency
what is the main clinical problem in untreated haemophilia
internal bleeding