Orgo Exam 3: pKa Values, Bases + Nucleophiles, IUPAC Names of Common Alkenes
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms

-10

-9

-8
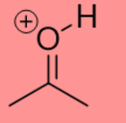
-8
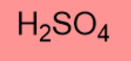
-3.0
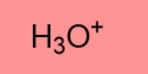
-1.7

-1.4
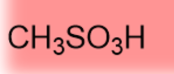
-1.2
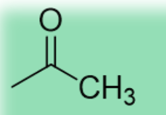
19.2

25

35
38
41-43
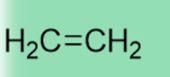
44
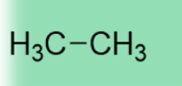
50

3.2

4.7
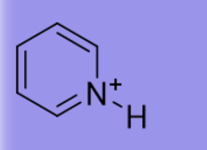
5.3
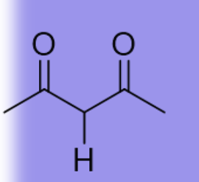
9
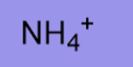
9.3
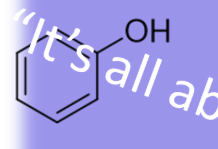
10

10
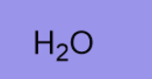
15.7
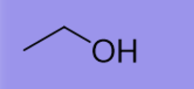
16
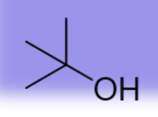
18
NaH
Strong base
Weak nucleophile
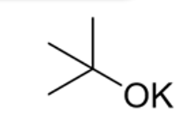
t-BuOK (pronounced “t-butoxide” or potassium tert-butoxide
Strong base
Weak nucleophile
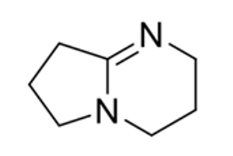
DBN
Strong base
Weak Nucleophile
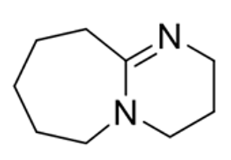
DBU
Strong base
Weak nucleophile
OH-
Strong base
Strong nucleophile
OMe-
Strong base
Strong Nucleophile
OEt-
Strong base
Strong nucleophile
I-
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
Br-
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
Cl-
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
RS-
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
HS-
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
RSH
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
H2S
Weak base
Strong nucleophile
H2O
Weak base
Weak nucleophile
MeOH
Weak base
Weak nucleophile
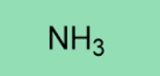
NH3
Weak base
Weak nucleophile
EtOH
Weak base
Weak nucleophile
LDA
bulky, strong base that removes protons but doesn’t act as a nucleophile — perfect for controlled deprotonation and E2 reactions
Ethylene

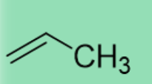
Propylene
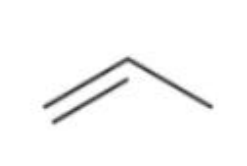
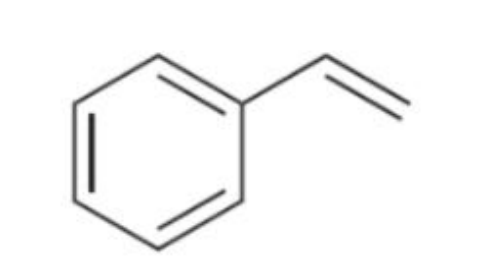
Styrene
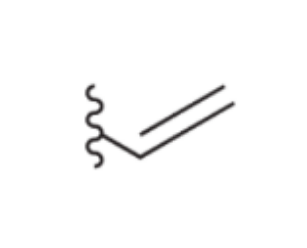
Vinyl
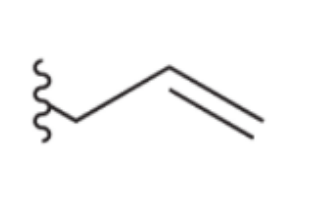
Allyl
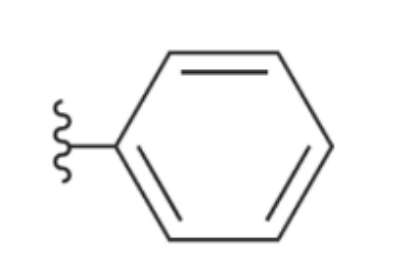
Phenyl
Methylene
Reaction of Alkenes (11 mechanisms)
Hydrohalogenation
Anti-Markonikov
Acid-Catalyzed hydration
Oxymercuration-Memercuration
Hydroboration-Oxidation
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Halogenation
Halohydrin Formation
Anti-Dihydroxylation
Syn-Dihydroxylation
Oxidative cleavage
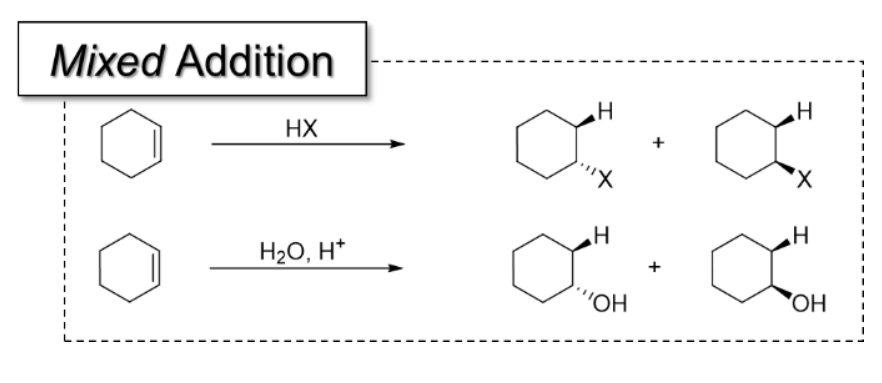
1) Hydrohalogenation
Alkene + HX (X = halide, such as Cl, Br, I)
Halide is added onto MORE SUBSTITUTED carbon
Markonikov additions
Formation of carbocation
Racemization and rearrangement are possibilities
RING EXPANSION can also be a result (form of rearrangement)
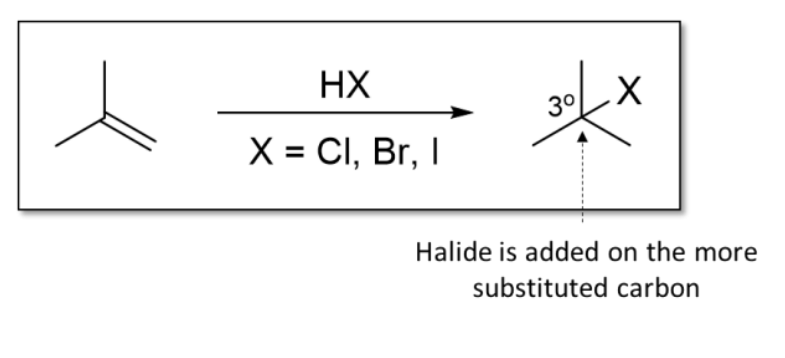
Markonikov’s rule
In the addition of HX or H2O to an alkene, H adds to the less substituted C
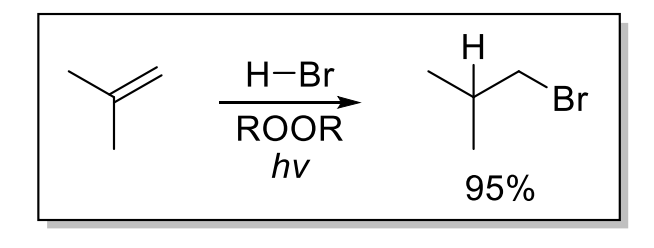
2) Anti-Markonikov
Only occurs with ROOR (peroxide), HBr, and hv (radical)
HCl and HI do not undergo rxn because racial reactions of HCl and HI are not spontaneous
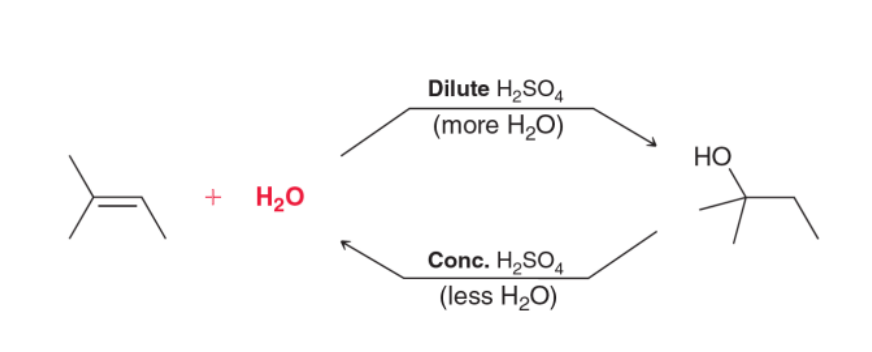
3) Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
OH group added to MORE substituted carbon in alkene
When the carbon is MORE substituted, reaction rate INCREASES
Catalysts
1) cat. H2SO4
2) H2O
The addition and elimination of water are in equilibrium
Carbocation forms in reaction mechanism, so rearrangement is possible!!!!!
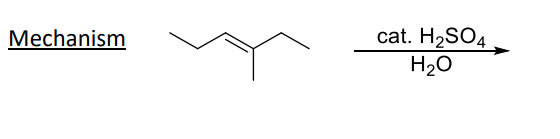
Equilibrium in acid-catalyzed hydration reaction
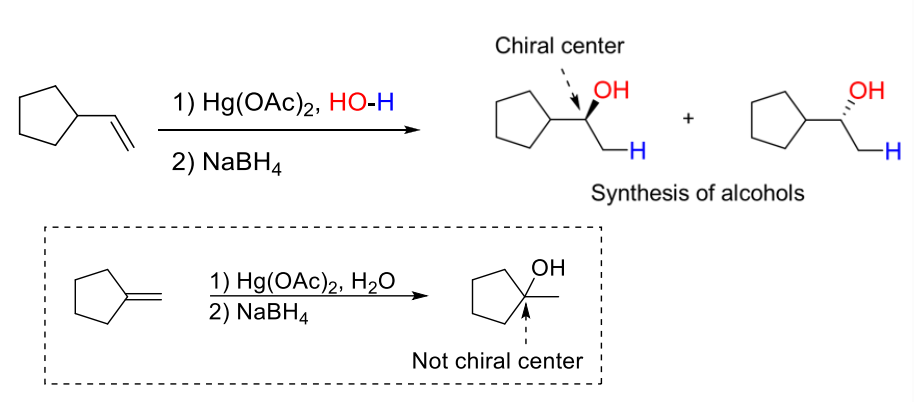
4) Oxymercuration-Demercuration
Alternative hydration to alkene (different from acid-catalyzed hydration because there is NO formation of carbocation intermediate, so there will never be rearrangement)
Regiospecific: OH will ONLY be added to the more substituted C in the alkene
If addition of OH creates chiral center —> enantiomers will form
1) Hg(OAc)2, HO-H
2) NaBH4
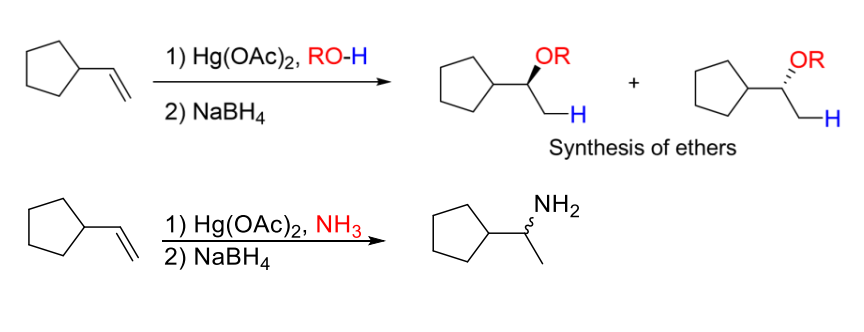
4B) Alkoxymercuration-Demercuration
Instead of water as reagant, alcohols and amines can be used
Basically same thing as oxymercuration-demercuration
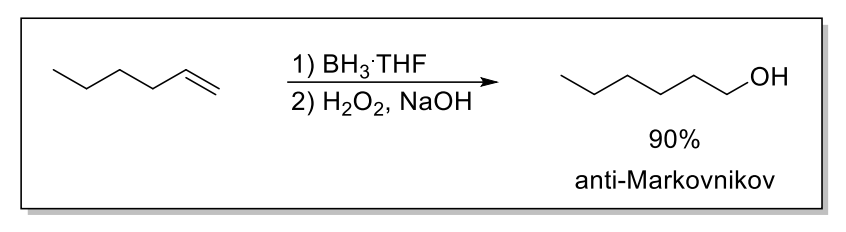
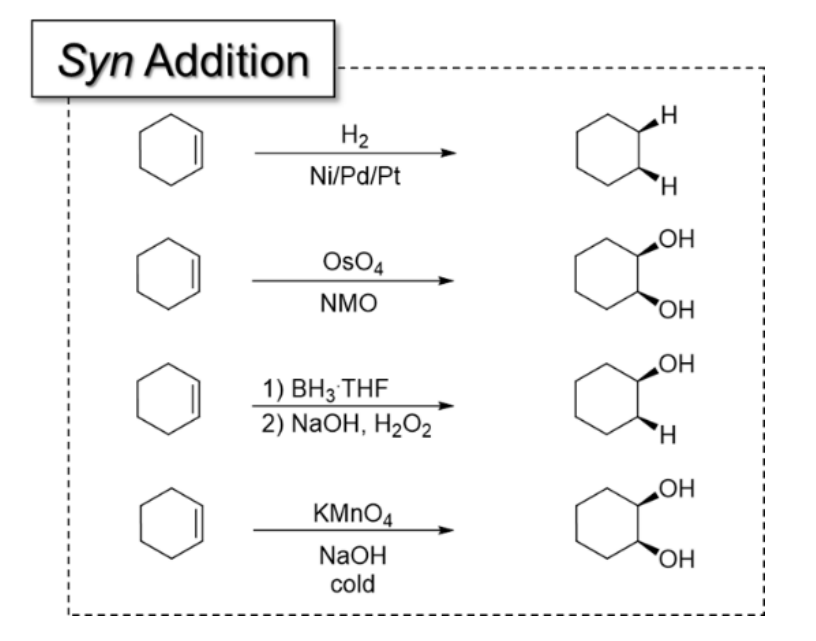
5) Hydroboration-Oxidation
1) BH3, THF
2) H2O2
Result: Anti-Markonikov addition of OH (because anti-Markonikov allows less steric hindrance)
Boron has similar structure to carbocation —> forms dime
NO REARRANGEMENT in Hydroboration-Oxidation reaction
Stereospecificity: Syn-addition of H and OH
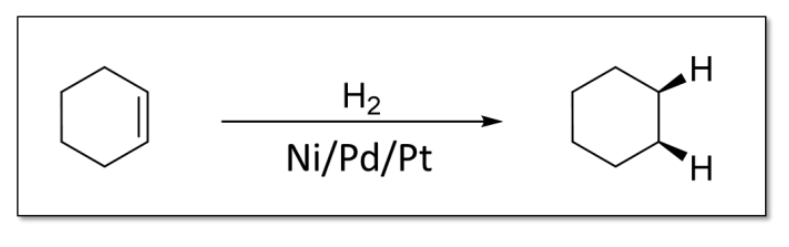
6) Catalytic Hydrogenation
Syn addition because two flat surfaces interacting
Less steric hindrance with syn addition
Possible metal catalysts: Pt, Pd, Ni
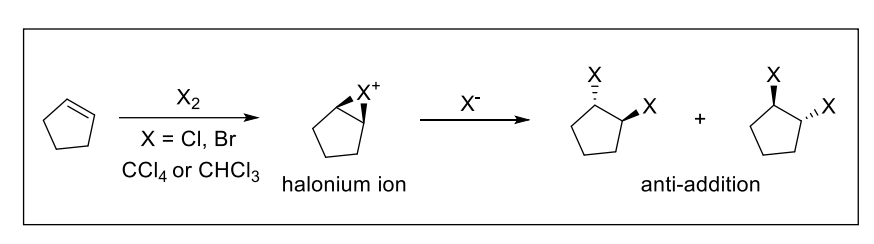
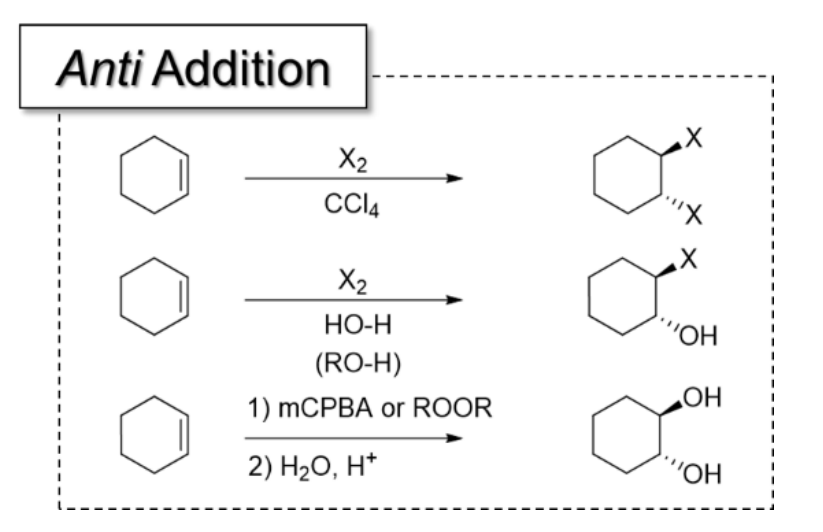
7) Halogenation
Result: anti-addition of 2 halogens across alkene
1) X2
2) CCl4 or CHCl3 ← NON-nucleophilic solvent
Can form cis or trans isomer depending on the configuration of starting alkene
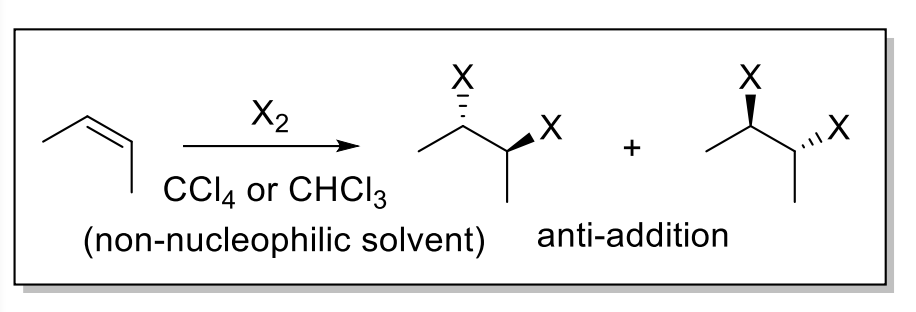
8) Halohydrin Formation
When bromination reaction performed in NUCLEOPHILIC solvent such as H2O or ROH, the bromination is “captured” by the solvent
Result: anti-addition of X and OH/OR
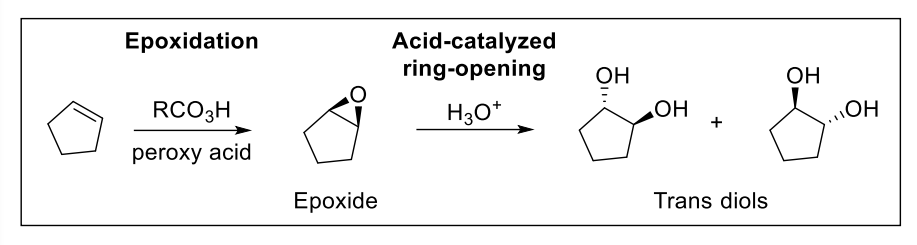
9) Anti Dihydroxylation
Result: anti-addition of 2 OH groups —> forms trans diols
Epoxide controls the stereochemistry
mCPBA is popular reagant
Common peroxides
Acetic acid
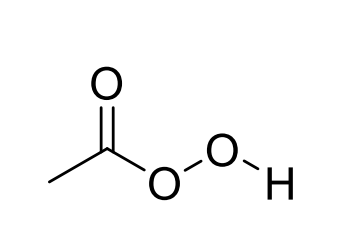
Peroxyacetic acid
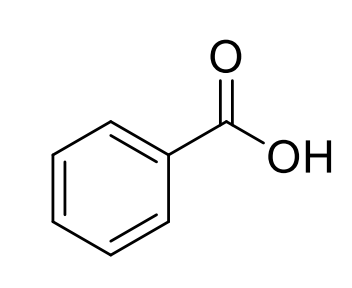
Benzoic acid
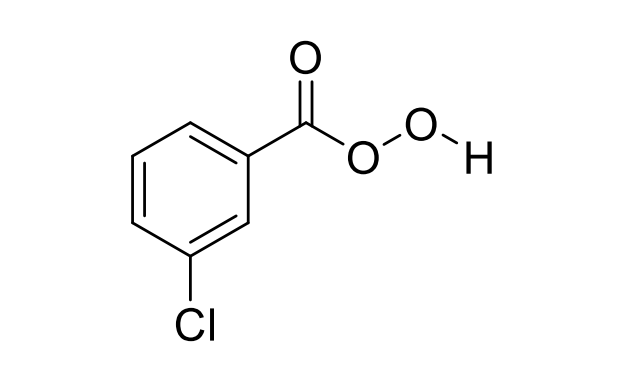
Meta-chloroperoxy benzoic acid (mCPBA)
Acetic acid
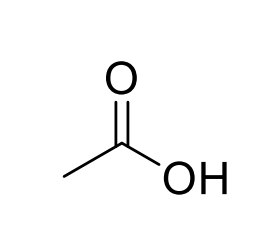
Peroxyacetic acid
Benzoic acid
meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA)
Commonality between anti-addition reactions:
Reactions go through 3-membered ring intermediate
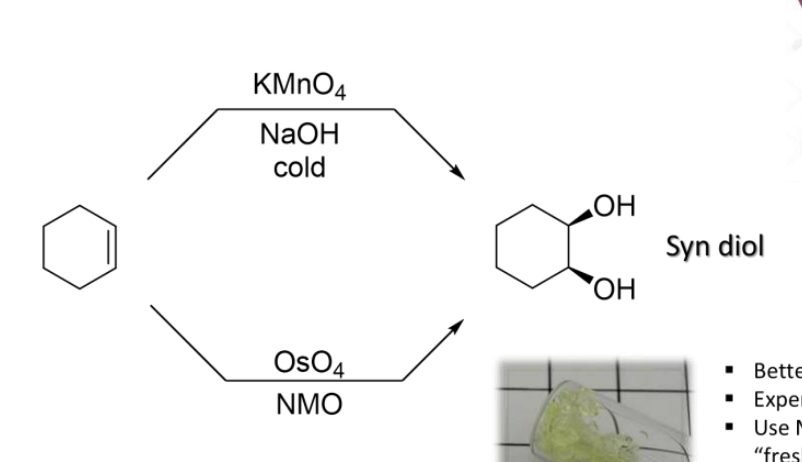
10) Syn Dihydroxylation
Reagants:
Either:
1) KMnO4, NaOH, cold
2) OsO4, NMO
All syn-addition reactions and what they add:
All anti-addition reactions and what they add:
All mixed addition reactions and what they add
11) Oxidative Cleavage: 2 possible reactions
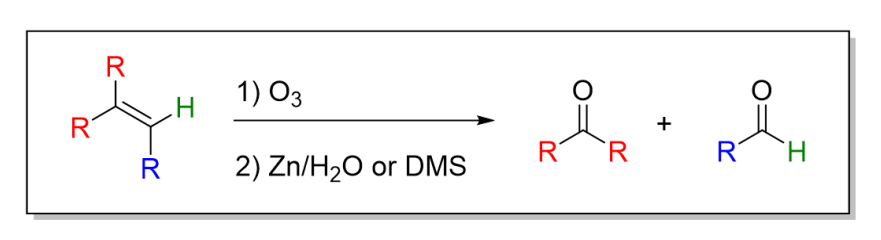
11.1 Ozonolysis
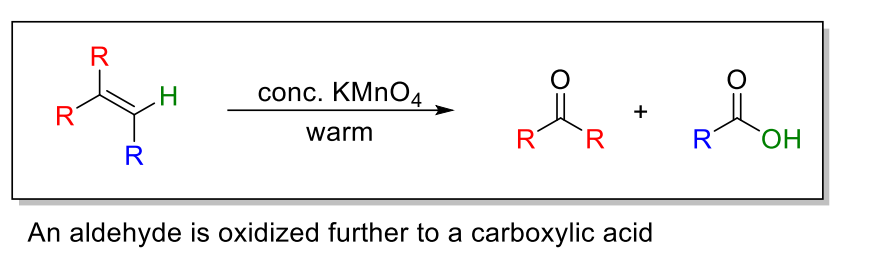
11.2 By KMnO4, warm condition: an aldehyde is further oxidized to a carboxylic acid
11.1) Ozonolysis
11.2) Oxidative Cleavage By KMnO4
How to deprotonate terminal alkyne
Equilibrium favors WEAK ACID so conjugate acid of the reactant base must be weaker than reactant acid (alkyne). Basically, the base is only strong enough if its conjugate acid has a pKa HIGHER THAN 25.
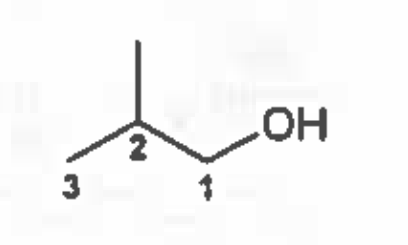
Isobutyl alcohol
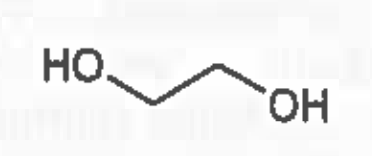
Ethylene glycol
1) excess NaNH2
2) H2O
Elimination
Vicinal or geminal dibromide converted to alkyne
HX
Hydrohalogenation
Alkyne + HX —> Markonikov addition (excess HX gives TWO addition rxns, forming geminal dihalide)
H2SO4, H2O, HgSO4
Acid Catalyzed Hydration
Terminal alkyne + ____ —> Markonikov addition of H and OH to create enol —> quickly tautomerizes to ketone
1) R2BH (9-BBN)
2) H2O2, NaOH
Hydroboration-Oxidation
Terminal alkyne + ___ —> anti-Markonikov addiiton of H and OH —> enol —> tautomerizes to aldehyde
X2 + non-nucleophilic solvent
Halogenation
Alkyne + _____ —> addition of two halogens across the double bond
1) O3
2) H2O
Ozonolysis (alkyne)
Oxidative cleavage of C-C triple bond
Internal alkyne converted into two carboxylic acid
Terminal alkynes converted into carboxylic acid and carbon dioxide
H2, Lindlars Catalyst (Pd/BaSO4, quinoline)
Hydrogenation
When treated with these reactants, alkyne → cis alkene
H2, Pt
Hydrogenation
Alkyne → alkane
Na(s), NH3 (l)
Dissolving metal reduction
When treated with these reagents, internal alkyne converted to trans alkyne
Br2, hv
Radical bromination
Alkane (CC single bond) undergoes bromination with installation of Br at most substituted position
Cl2, hv
Radical chlorination
Alkane (CC single bond) undergoes Chlorination
Less selective than bromination but faster → most useful in situations where monochlorination results in ONLY ONE regiochemical outcome
HBr, ROOR (peroxide)
Hydrobromination
Alkene undergoes anti-Markonikov addition of H and Br
NBS, hv
Allylic bromination
Install bromine atom at allylic position of alkene
Consider rearrangement!
NaH
Very strong base used to deprotonate alcohols —> alkoxide ion
Na
Will react w/ alcohol to liberate hydrogen gas → Alkoxide ion
NaBH4, MeOH
Reduces once
Reducing agent (source of nucleophilic hydride) → can be used to reduce ketones or aldehydes to alcohols
1) LiAlH4
2) H3O+
Strong reducing agent (source of nucleophilic hydride)
Can be used to reduce ketones, aldehydes, or carboxylic acids
H2, Pt
Reduces alkenes and alkynes to alkanes
Mg
Make Grignard Reagant
TMSCl, Et3N
Protecting group