KIN 1Y03: Lecture 9 - Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
integrative
analyze incoming sensory information, store some aspects, and make decisions
⤷ eg. putting on a fuzzy sweater in the morning but throughout the day, brain gets used to it, doesn't recognize the sensory anymore
⤷ eg. mental activities, thinking, memories, emotions
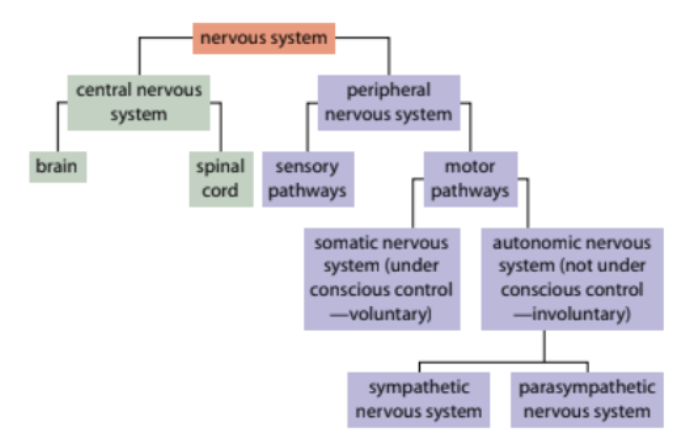
divisions of NS
CNS, PNS
central NS
brain and spinal cord
peripheral NS
sensory receptors and nerves (basically, everything thats not CNS)
⤷ nerves can be grouped depending on where they originate/terminate (eg. cranial nerves, spinal nerves)
sensory receptors
ending of neurons, that gather info internally/externally
⤷ specialized cells that detect things like temp, pain etc.
nerve
a bundle of axons and their sheaths that connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles, and glands
cranial nerve
nerves that enter (envir → brain) and exit (brain → target) structures in the brain
⤷ 12 pairs ("pairs" are bilateral - left and right side)
spinal nerve
nerves that originate from spinal cord
⤷ 31 pairs
ganglion
collection of neuron cell bodies in PNS
⤷ when nerve is in a bundle of axons, the resulting neuron's cell body forms ganglion (if outside CNS)
↳ sensory info from spinal nerves will be in ganglion
↳ ganglion can also be the connection point between 2 neuron
plexus
extensive network of axon and sometimes neuron cell bodies
⤷ located in PNS
sensory
(afferent): transmit action potentials from receptors to CNS
⤷ gathers info from internal/external envir and bring info back to CNS
⤷ eg. light, touch, taste etc - detected by sensory receptors
dorsal root side of SC
if the electrical signal is sent to the dorsal root of the spinal nerve, then sensory info is carried - travelling from the stimulus → spine → CNS
^^ HAS THE GANGLION
action potential
gets created by sensory info/stimuli from envir → trigger receptors
⤷ become electrical signal
motor
(efferent) transmit action potentials from CNS to effectors (target tissues - muscles, glands)
ventral root side of SC
if electrical signal is sent to the ventral root of the spinal nerve, then motor info is carried - travelling from spinal cord to target muscle
somatic NS
allow for voluntary control from CNS to skeletal muscles (eg. moving your body, talking)
⤷ single neuron system (from neuron to target, NO MIDDLEMEN)
⤷ synapse with skeletal muscles @ neuromuscular junction:
autonomic NS
allows for involuntary control (eg. digestion, heartrate, pupil dilation)
⤷ from CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands
⤷ two neuron system: first from CNS to ganglion, second from ganglion to effector
>> Divisions of ANS -- (sympathetic NS and parasympathetic)
sympathetic NS
prepares body for physical activity or a change from the regular "resting position"(fight or flight)
⤷ eg. seeing a bear: ↑ heart rate, ↑ breathing, pumps epinephrine
parasympathetic NS
regulars resting or vegetative functions (rest-and-digest)
⤷ active when youre not doing much physical activities
⤷ eg. digesting food: ↓ heart rate
enteric NS
series of plexuses within the walls of the digestive tracts
↳ controls the digestive tract independently of CNS, but still communicates with the CNS via the ANS (para and symp)
⤷ brain doesn't always need to know whats happening in the digestive system, in order for it to happen ⇒ ∴ the ENS allows for digestion to happen without the CMNS actively knowing
organization of nervous system