Chapter 6 - Chemical kinetics: the rates of reactions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
The average reaction rate
The average rate of change of the concentration in a time interval adjusted for differences in the stoichiometric coefficients
Instantaneous reaction rate
the rate of change of the concentration of a species involved in the reaction, divided by the stoichiometric coefficient
Can be obtained from the slope of the graph of concentration [A] versus time, again corrected for the stoichiometric coefficient.
![<ul><li><p>the rate of change of the concentration of a species involved in the reaction, divided by the stoichiometric coefficient</p></li></ul><ul><li><p>Can be obtained from the slope of the graph of concentration [A] versus time, again corrected for the stoichiometric coefficient.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8584f965-96bc-46c6-a940-b9965f2f4da2.png)
Rate law
The proportionality constant k is called the rate constant. It depends on the temperature.
r = k[A]p[B]q
Reaction order
The powers p and q are the reaction order.
Shows how the reaction rate depends on the concentration of the species involved.
The relation between the reaction rate and the reactant concentrations must be obtained from experiment.
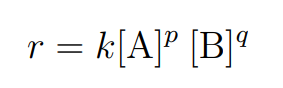
Overall order
The sum p + q = overall order
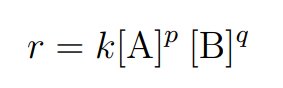
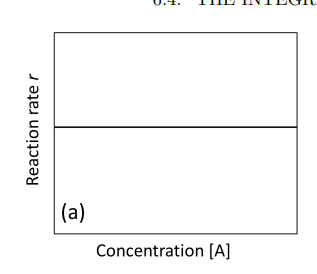
Graph rate vs. concentration [A] zero order
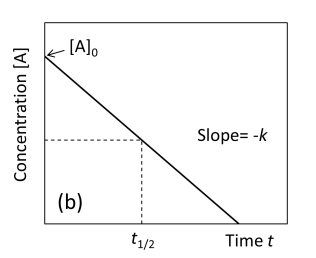
Graph concentration [A] against Time zero order
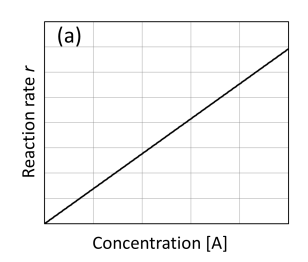
graph rate against concentration [A] first order
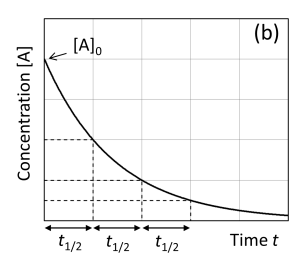
Graph concentration [A] against time first order
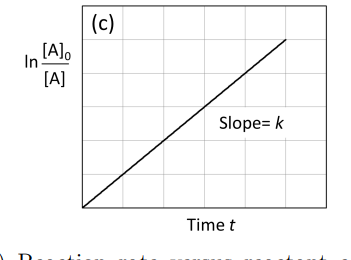
graph ln [A]0/[A] against time first order
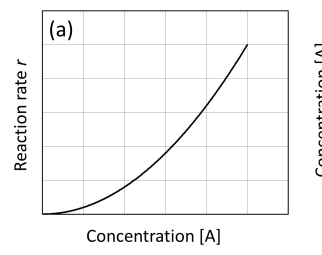
Graph rate against concentration [A] second order
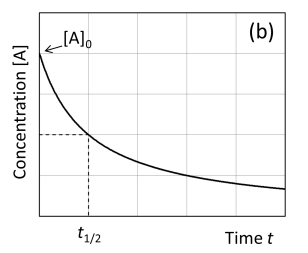
Graph concentration [A] against time second order
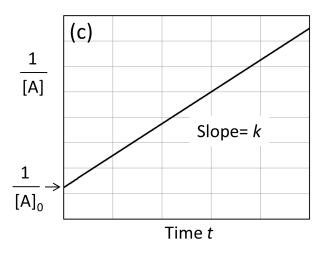
Graph 1/[A] against time t second order
What does the differential form give us?
Expresses the rate of change of the concentration of a reactant with respect to time
Shows how the reaction rate depends on the concentration of the reactant
What does the integrated form give us?
This is derived from the differential rate law by integrating with respect to time
Provides a direct relationship between the concentration of the reactant and time.
What does the half-life equation give us?
This is the time required for the concentration of the reactant to decrease to half of its initial value.
It is derived from the integrated rate law and depends on the order of the reaction.
Determining the rate law from the integrated rate law graph.
If a plot of [A] versus time gives a straight line, then the reaction is zeroth order with respect to A
If a plot of ln[A] versus time gives a straight line, then the reaction is first order with respect to A
If a plot of 1/[A] versus time gives a straight line, then the reaction is second order with respect to A.
How to determine reaction order from half-life
Plot ln t1/2 against ln[A]0 which should give a straight line.
The slope equals -(p-1) with p being the reaction order.