[17] MORE FREQUENCY COLLISIONS
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what is needed for a reaction to take place
particles need to collide in excess of the activation energy
what is the minimum amount of energy needed for particles to react
activation energy
what does the rate of reaction depend on?
the frequency of collisions between particles
the energy of which particles collide
what happenes if particles collide under the activation energy
nothing
how does increased temperature effect reactions
increased the energy of which particles collide
how does increased concentration/pressure of gaseous reactans effect the reaction
increases the frequency of collisions between particles
how does increased surface area of solid reactans effect reactions
increased frequency of collisions between particles
name of factors that increase the rate of reactions
increased temperature
increased concentration of dissolved reactants
increased pressure of gaseous reactants
increased surface area of solid reactants
use of a catalyst
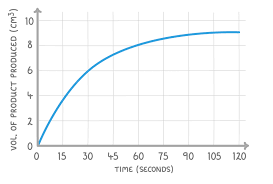
describe the first middle and end points of the graph of a reaction of magnesium and hcl
first - steep gradient because high concentration of acid
middle - some reactants formed products, gradient starts to decline because lower concentration of hcl
end - plateaus because all hcl has been used up

why is the cotton plug there??
so co2 can come out but not acid/water
when doing an experiment combining calcium carbonate and hcl in a conical flask how can we make it more reliable?
using a cup in concical flask containing calcium carbonate tip it over by shaking conical flask
word equation for hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulphate
sodium thiosulphate + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + sulphur dioxide + water + sulphur
what happens with a rate of reaction graph if one reaction is higher temp than another
they plateau at the same level but initial gradient of higher temperature is steeper than lower temperature line
what would a line on a rate of reaction graph look like if the reaction had a half the concentration of acid and why?
line would be half the y axis lower because half the co2 would be produced, it would level off at half the volume
define a catalyst
not used up in a reaction
speeds up rate of reaction
provides an alternation reaction path with a lower activation energy
what does an exothermic graph look like and why
goes from high reactant energy to lower product energy because reaction has given out the energy
what does an endothermic graph look like
low reactant energy to high product energy because reaction has absorbed in energy
How can you investigate the effects of surface area on the rate of reaction?
Use different sizes of solid reactants in a reaction with acid. You should observe that the reaction rate is faster with a larger surface area because more particles are exposed to collide with the acid.
how can you investigate the effects of concentration on the rate of reaction?
React same surface area solids with different concentrations of acid, the reaction rate increases with a higher concentration of acid, as there are more particles to collide.
How can you investigate the effects of temperature on the rate of reaction?
React a solid with acid at different temperatures. you should observe that the reaction rate increases as the temperature increases because particles move faster, leading to more frequent collisions.
How can you investigate the effects of a catalyst on the rate of reaction?
do decomposition of hydrogen peroxide with and without manganese dioxide.
How does pressure affect the rate of reaction (for gases)?
Increasing the pressure compresses the gas molecules, increasing the frequency of collisions, which speeds up the reaction.
how do you draw exothermic and endothermic graphs (do in book)
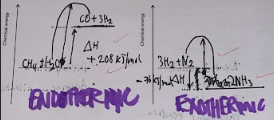
How can you investigate the effect of changing the surface area of marble chips on the rate of reaction with hydrochloric acid?
react powdered, small pieces and larges marble chips with a fixed concentration of hydrochloric acid. Measure the volume of carbon dioxide produced
How can you investigate the effect of changing the concentration of hydrochloric acid on the rate of reaction with marble chips?
Use different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and react each with the same amount of marble chips. Measure the volume of gas (CO₂) produced over time. you will observe that the reaction rate is faster with a higher concentration of hydrochloric acid because there are more acid particles to collide with the marble chips.
What is the reaction between marble chips and hydrochloric acid?
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O(l) + CO2 (g)
What is the balanced chemical equation for the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
2H2O2 (aq)→ 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
with the reaction with magnesium and htdlorchloric acid use the particle collision theory to explain why the rate of reaction decreases during the experiment
At the start of the reaction, there are many hydrochloric acid particles in the solution, which frequently collide with the magnesium surface As the reaction progresses, the acid is gradually used up, so the concentration of acid particles decreases. This leads to fewer collisions per second, so the rate of reaction slows down over time.
explain why an increase in the concentration of the acid causes an increase in the rate of reaction you should use the particle collision theory in your answer
Increasing the concentration increases the frequency of collisions between particles, as there are more particles in the same volume which leads to more frequent successful collisions increasing the rate of the reaction.
describe a method to show that solid manganese (IV) oxide is a catalyst in this reaction and not a reactant
weigh a know mass of manganese(IV) oxide before reaction
after reaction, filter it and dry it
reweigh it, if the mass is unchanged it is a catalyst
to calculate rate of reaction at a point what do you do?
draw tangent at point and calculate gradient
how do you find the mean/average rate of reaction
total volume of gas / time