Plasma Membrane
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
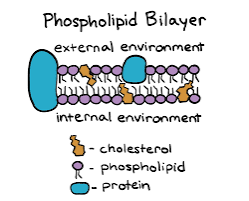
Cell Membrane
A phospholipid bilayer with proteins that separate the internal contents from its surroundings environment, which regulates the ins and outs of organic molecules, ions, and water with its selective permeability
Key Figures in Cell Membrane
Phospholipid, Protein, Cholesterol, Carbohydrates
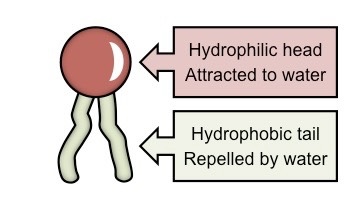
Characteristics of Phospholipid
It creates a nonpolar environment in between phospholipids (away from the water) and poplar environment outside of the phospholipids
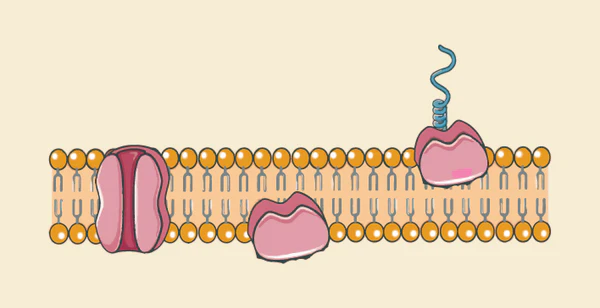
Characteristics of Protein
It can be found on or in the cell membrane. The integral proteins (those inside of the membrane) open or close, allowing larger molecules to be in or out. The peripheral proteins (those outside of the membrane) acts as enzymes that speed up reaction
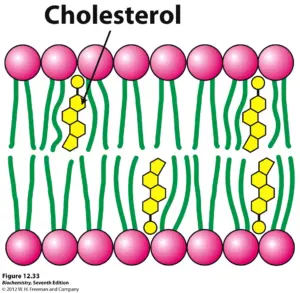
Characteristics of Cholestrol
It influences the movement of phospholipids, like pushing phospholipids away if they are too close in a cold environment or pulling phospholipids in if they are too far away in a hot environment
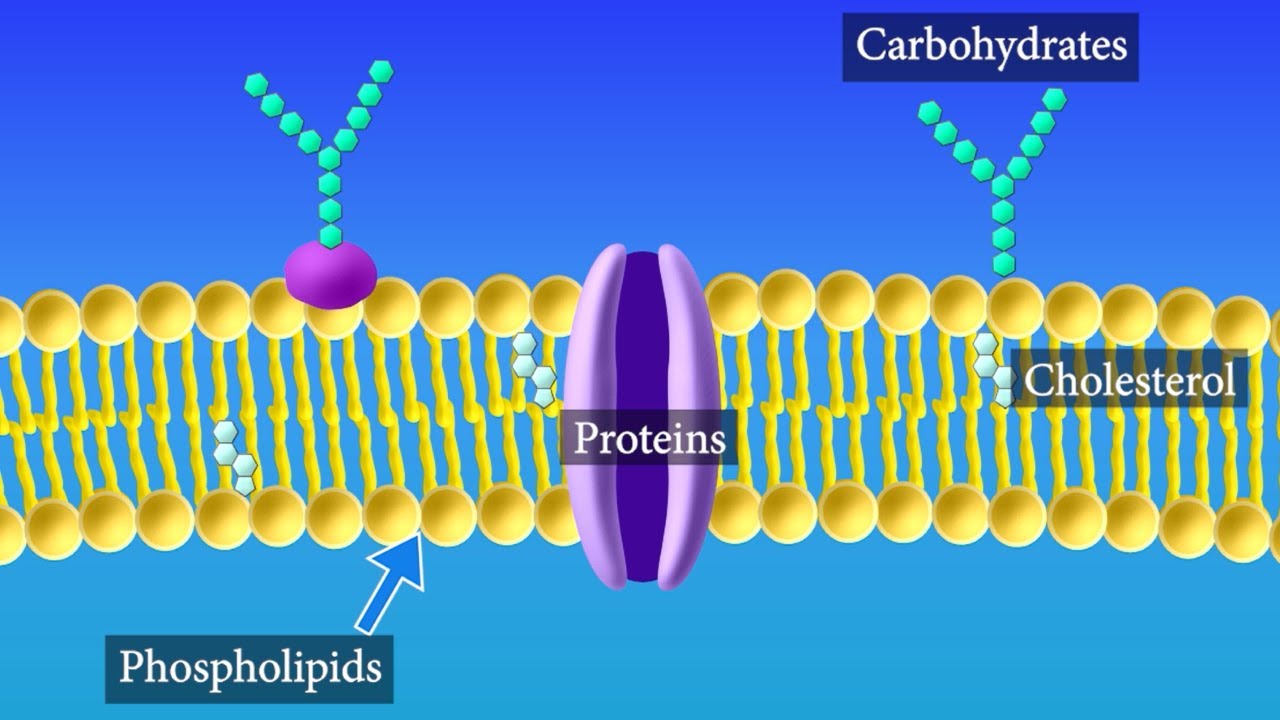
Characteristics of Carbohydrates
It allows cells to recognize each other to allow the molecules in by either binding to proteins (glycoproteins) or lipids (glycolipids), which becomes essential in terms of blocking pathogens
Passive Transport
Naturally occurring phenomenon that does not require energy for cell movement
Active Transport
Mechanisms that require energy (ATP) for cell movement
Examples of Passive Transport
Osmosis, Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
The transport of water through a semipermeable membrane from a high concentration to low across the membrane
Diffusion
Net of movement of a substance that travels down from high concentration to low across its concentration gradient
Facilitated Diffusion
Similarly to diffusion, it’s a movement of substances that travels down from high concentration to low, but it uses integral proteins as channels to pass thtough
Active Transport
Movement of molecules that uses ATP to force the direction the molecules are moving, which disrupts the natural flow of movement
Tonicity
Amount of solutes in a solution, which correlates to osmolarity; solutes (salt) can be dissolved by water, which attracts water to higher solute concentration
Hypertonic
High concentration of solutes and Low concentration of water
Isotonic
Equal concentrations of solutes and water
Hypotonic
Low concentration of solutes and High concentration of water
How does Tonicity affect Red Blood Cells?
Hypertonic water + RBC = shriveling
Isotonic water + RBC = no effect
Hypotonic water + RBC = bursting
Endocytosis
Active transport that takes particles inside the cell
Examples of Endocytosis
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, Receptor Mediated Endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Process of cells stretching out to engulf large particles (vore)
Pinocytosis
The process of “drinking cells” by taking multiple small molecules all at once (polyamorous + size difference vore)
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Has receptors that only specific molecules to then engulf the molecules (demisexual vore)
Exocytosis
Active transport that takes molecules out of the cell by opening the plasma membrane to release them