Unit 4: Transoceanic Interconnections
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Land-based Powers
A shift in land based powers where governments controlled lands by building armies, bureaucracies, road, canals, and walls that unified and protected
Sea-based Powers
Sea people built their power by controlling water routes, developing technology to cross the seas, and gaining wealth from trade and land claims.
New Monarchies
Monarchies that emerged that differed from their medieval predecessors in having greater centralization of power, more regional boundaries, and stronger representative institutions
Reconquest
the retaking of land in Iberia by Spain and Portugal in a religious crusade to expand. This conquest advanced in waves over several centuries.
Phillip II
ruled Spain at the height of its power in the 15th century
Capitalism
an economic system based on private ownership of property and business that provide goods to be bough and sold in a free manner
Mercantilism
the responsibility of government to promote the states economy to improve the revenues and limit imports to prevent profits from going to outsiders (allows industry to develop their own business)
Joint-stock Companies
these companies organized commercial ventures on a large scale by allowing investors to buy and sell shares. The new capitalist system largely replaced the old guild system of the middle ages.
Zheng He
led expiditions in Chinese junks across the atlantic ocean, with one goal being to assert Chinas power after the demise of the Yuan dynasty.
Yongle
something of a renegade who supported a series of seven maritimes expeditions. Chinese vessels started to take tribute from those they encountered.
Henry the Navigator
the third son of the portuguese king; devoted his life to navigation, creating a navigation school, which became a magnet for the cartographers of the world
Caravel
a new ship developed by the portuguese, which was much smaller than the junk, but size allowed for exploration of shallower coastal areas
Vasco da Gama
set out to find the tip of Africa and connect it to the Indian Ocean, and discovered the fastest and safest ways to travel to Portugal
Christopher Columbus
A Genoese mariner who convinced Isabella and Ferdinand to sponsor a voyage across the Atlantic after he was turned down by the Genoese and Portugal. He believed he could reach east Asia by sailing West.
Treaty of Tordesillas "Tortillas"
a treaty making Spain and Portugal land claim boundary. Portugal pushes its explorations to India and beyond.
Magellan
Spanish explorer had a ship that was first to circumnavigate the globe, even though Magellan himself died in the phillipines
Conquistadors
went to search for gold and convert the natives to Christianity in the interior of Mexico
Cortes
sought to find the Aztec capital, and took over the Aztec land - with help of Amerindians, disease, and technology
Moctezuma
the Aztec emperor, who welcome the Spaniards at Tenochtitlan, seeing them as god-like. This was a mistake, as this allowed everyone to conquer him.
Francisco Pizzaro
led a group of soldiers to the Andes to find the Inca. The Incas were weak; Pizzaro conquered and got gold.
Atahualpa
the leader of the Incas, who was seized by Pizzaro and gave gold to him, first baptized as a Christian, than strangled
Ethnocentrism
the term that describes the tendency of human beings to view their own culture as superior
De La Casas
a conquistador priest who dedicated himself to protecting Amerindian rights
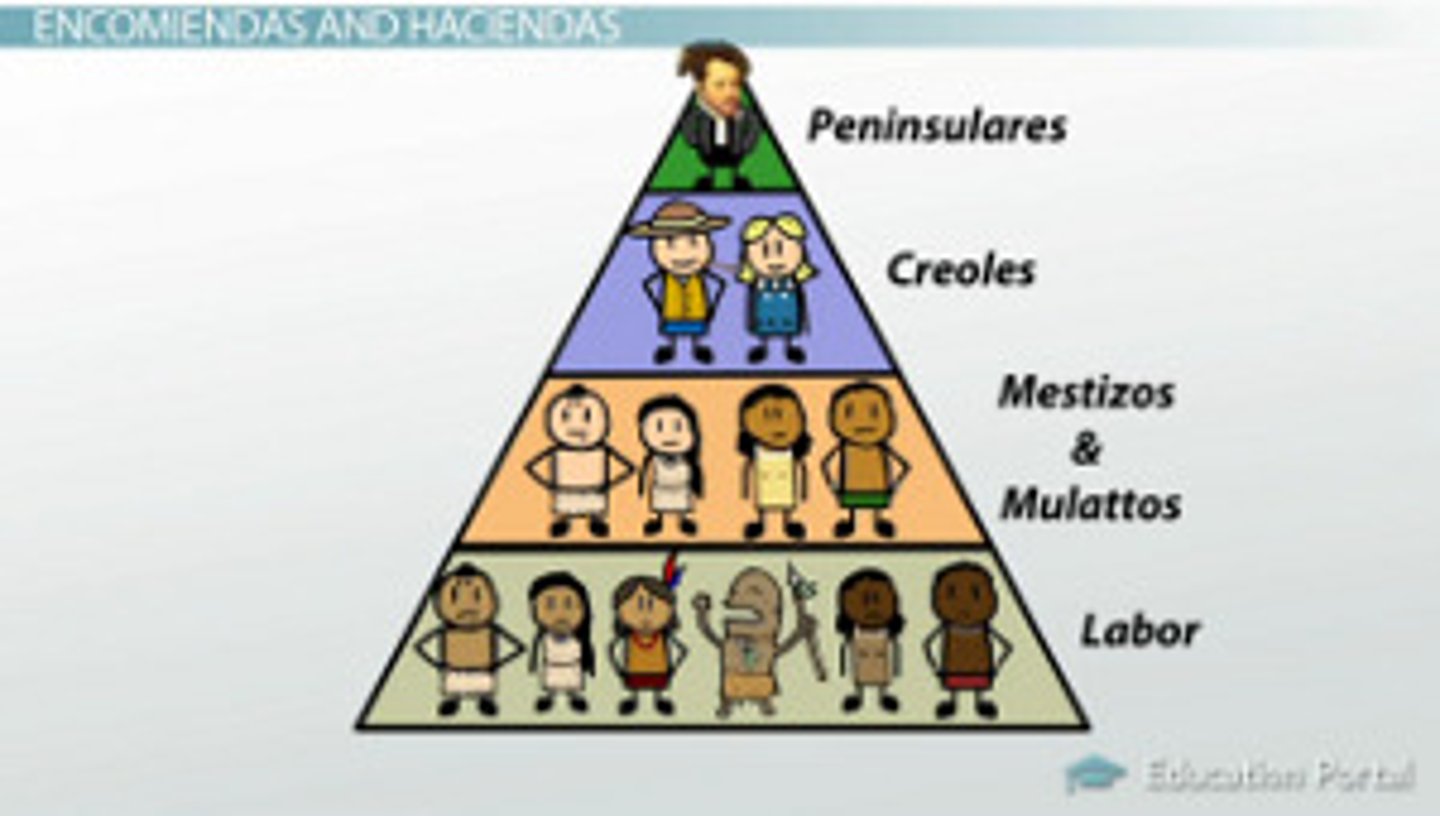
Peninsularies
a fading social class in the new world, composed of the people born in the old world
Mestizos
composed of European and Amerindian children, part of the castas
Mulattoes
composed of European and African children, also part of the castas
Council of Indies
supervised all government and commercial activity in the Spanish colonies
Bartholomew Dias
set out to find the tip of Africa and connect beyond it to the Indian Ocean, as well as discovering the fastest and safest ways back to Portugal
Encomienda
the system in which conquistadors had forced natives to do work for them
Creoles
composed of those born in the new world; a quickly growing class
Casta System
rigid social structure, a middle-level status between Europeans at the top; and Amerindians and blacks at the bottom
Dutch East India Company
a joint stock company that specialized in the spice and luxury trade of the East Indies and quickly gained control of Dutch Trading in the Pacific
Mercantilism
a system in which the government is constantly intervened in the market, with the understanding the goal of economic gain and to benefit the mother country
Indentured Servitude
a system which was usually ethnically the same as a free settler, but he or she was bound by an "indenture" (contract) to work for a person for four to seven years, in exchange for payment of the new world voyage
Columbian exchange
the global diffusion of crops, other plants, human beings, animals, and distance that took place after the European exploring voyages of the New World
Triangle Trade
a network of sea routes in the Atlantic Ocean (connected Afrcia, the Americas, and Eurasia)
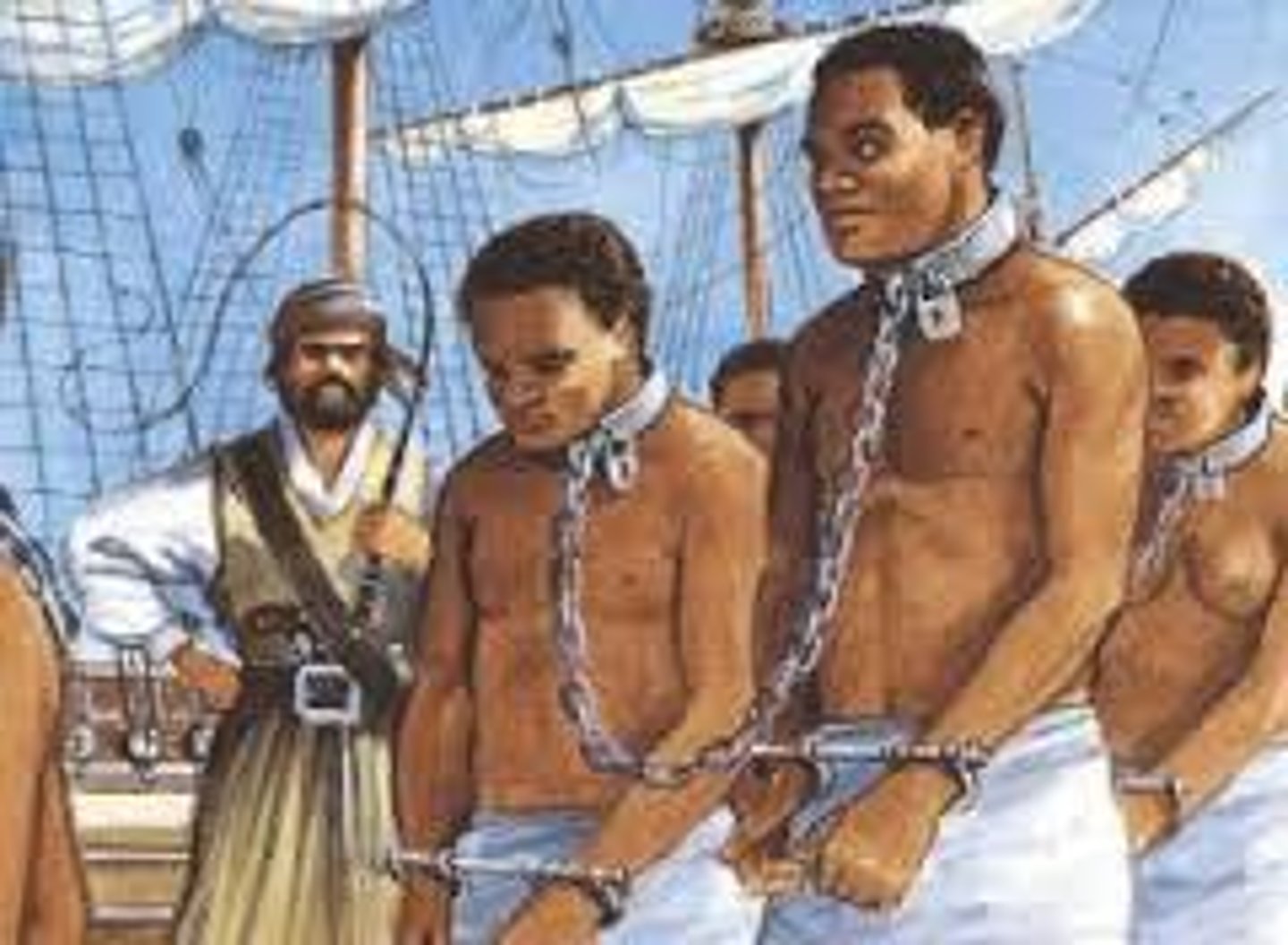
Middle Passage
the first leg of the atlantic circuit, where ships took slaves to the new world
Manumission
legal grant of freedom to an individual slave
Maroons
runaway slaves in the Carribean
Kongo
Christian missionaries went to this kingdom just south of the Congo River, where Christian Missionaries converted its inhabitants to Christianity
African Diaspora
The spreading of Africans to many other parts of the world, especially the Americas. This is one of the most important demographic changes during 1450 - 1750
Asante
Produced insignificant amounts of gold and Kola nuts, they rose in West Africa on the Gold Coast.
Ana Nzinga
queen of Africa known for resisting Portuguese encroaching on her land
Cape Colony
one of the two beachland colonies established by the Europeans in the 16th century, functioned as a major coastal for travelers.
Tokugawa Shogunate
unified Japan after infighting and the warring time. a centralized government established in 1603 in present day Tokyo. led restrictive or isolated trade policies during age of exploration
Forbidden City
was the home of the emperor and his family, which expanded service people to 20,000; as the government returned to Beijing from Manjing
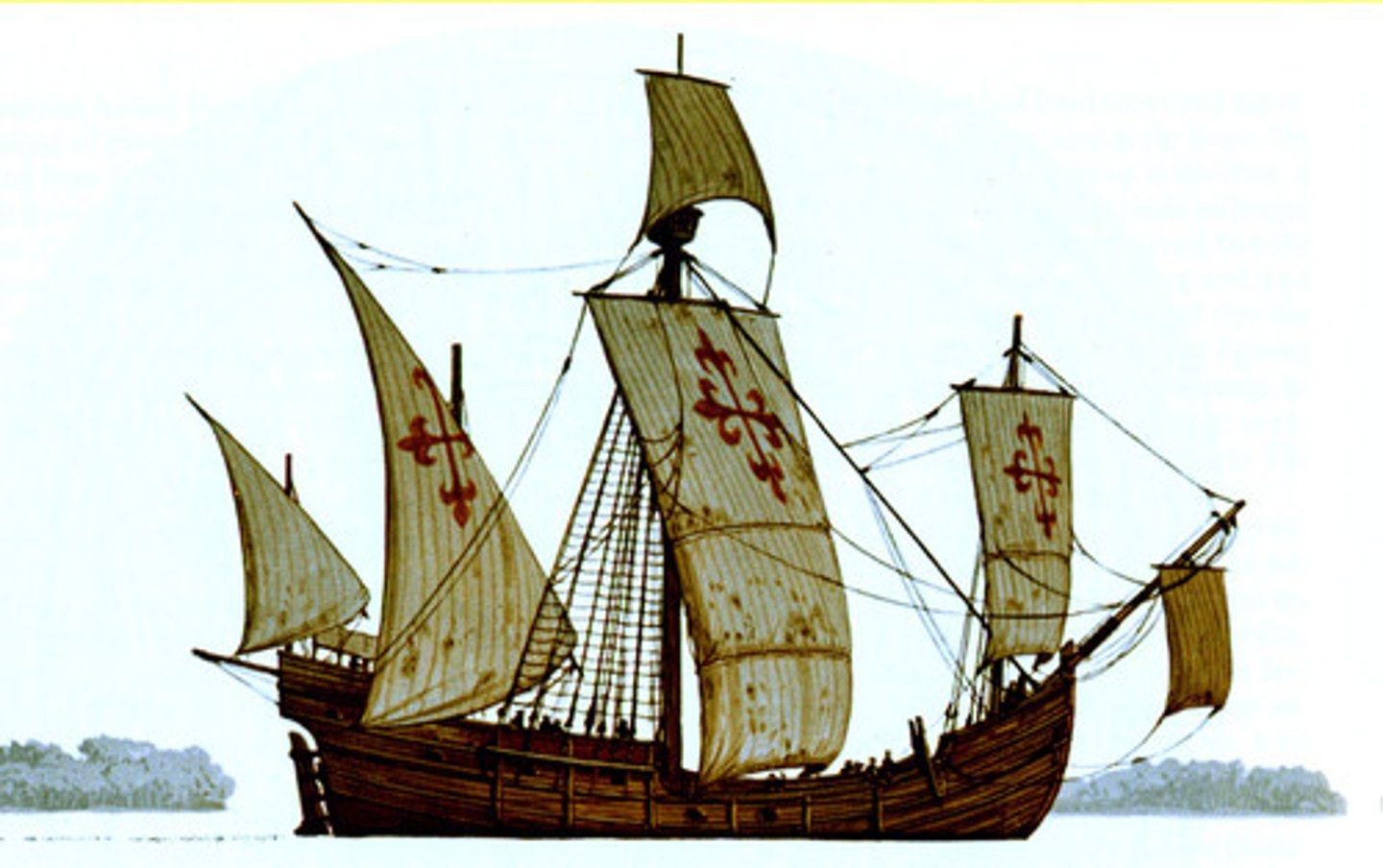
Carrack
Large Portuguese ship used for ocean travel which was a mode of trade during the Columbian Exchange

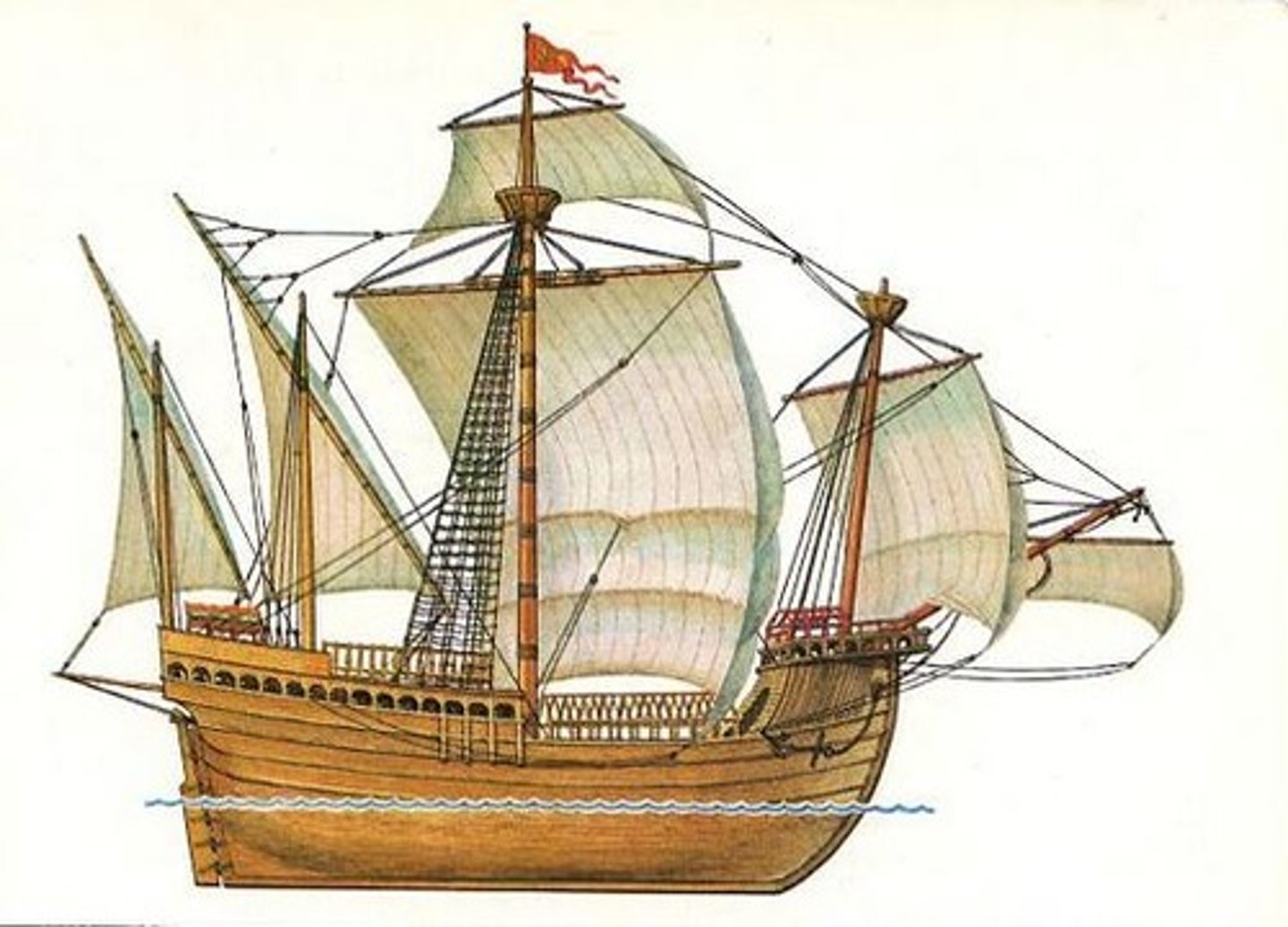
Fluyt
a Dutch type of sailing vessel originally designed as a dedicated cargo vessel.

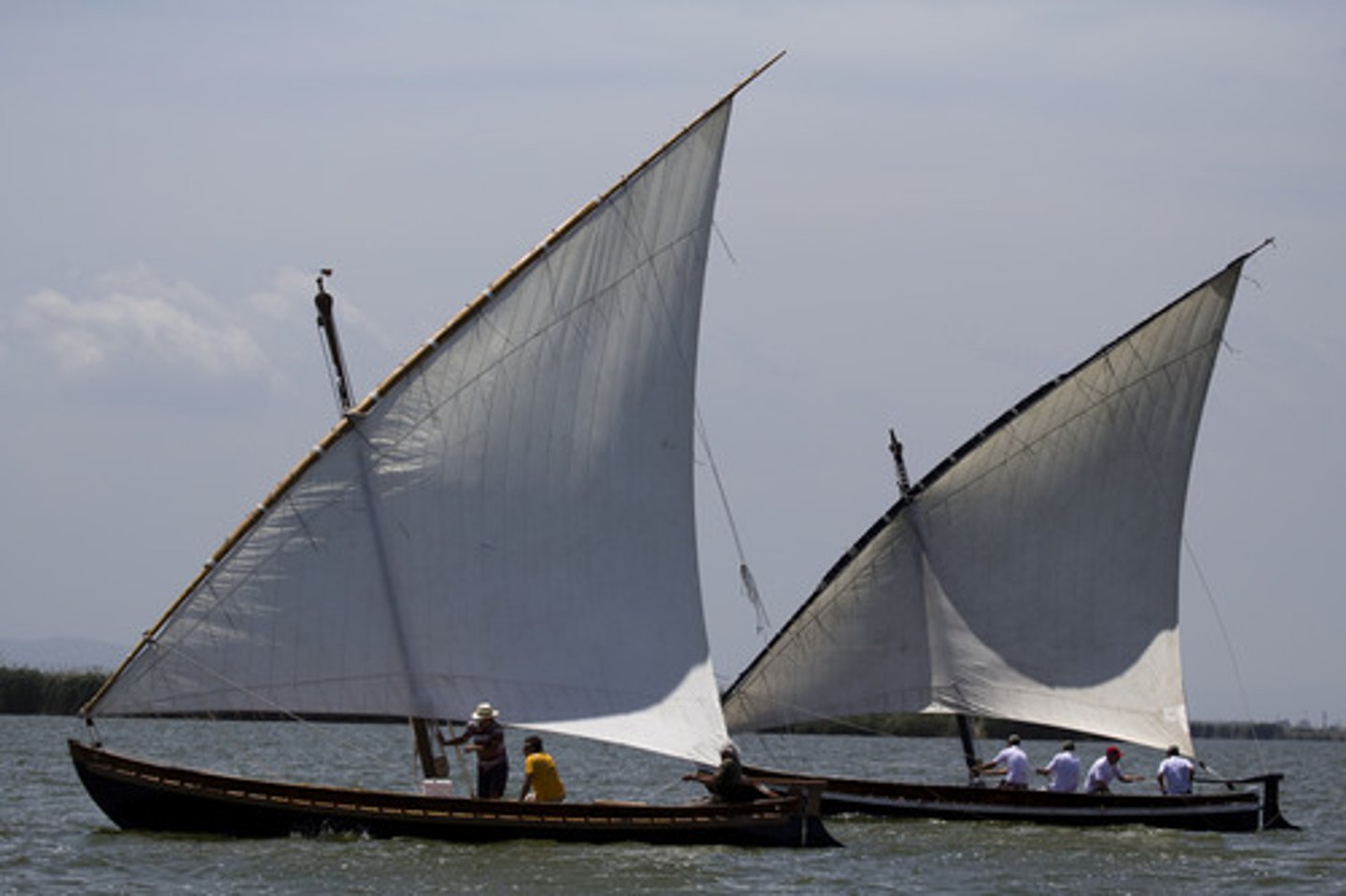
Lateen Sail
triangular sail that made it possible to sail against the wind; used in the Indian Ocean trade

European technology influenced by Classical, Islamic, and Asian world
lateen sail, compass, astronomical charts

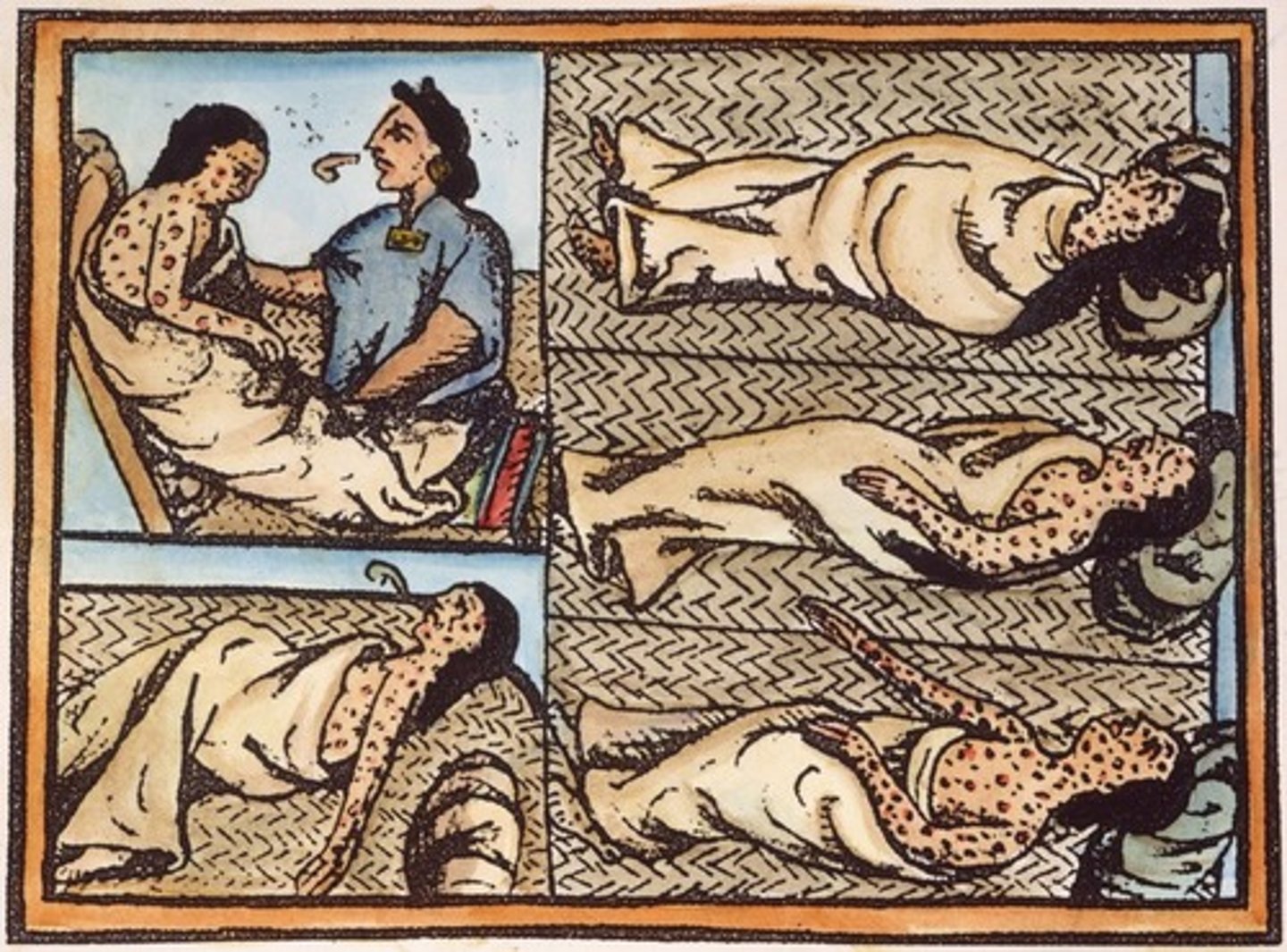
Smallpox
The overall deadliest known disease in the history of the world. In the 20th century alone there were approximately 500,000,000 people who died of this disease. Spread by Europeans in the Columbian Exchange to native peoples
Cash crops
crops, such as tobacco, sugar, and cotton, raised in large quantities in order to be sold for profit. Often raised on plantation with coerced labor for export to Europe and the Middle east

Okra and Rice
Columbian Exchange--foods brought by African slaves

Horses, PIgs, Cattle
European animals that were transferred to the New World during the Columbian Exchange
Ming China
A major dynasty that ruled China from the mid-fourteenth to the mid-seventeenth century. It was marked by a great expansion of Chinese commerce into East Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. 1368-1644. Often adopted restrictive policies to limit cultural effects of Europe

Swahili city-states
Waring states that were always competing for control of trade routes in Indian Ocean and each other. established by swahili., Many of these city-states were Muslim and very cosmopolitan.
Javanese
the largest ethnic group in Indonesia, despite European disruption many groups in Indian Ocean continued existing trade routes.
Indian Ocean Asian Merchants
despite European disruption many groups in Indian Ocean continued existing trade routes.
examples: Swahili Arabs, Omanis, Gujaratis, Javanese
Hacienda
Spanish estates in the Americas that were often plantations. They often represent the gradual removal of land from peasant ownership and a type of feudalistic order where the owners of Haciendas would have agreements of loyalty to the capital but would retain control over the actual land. This continued even into the 20th century.

Indentured Servitude
A contractual system in which someone sells his or her body (services) for a specified period of time in an arrangement very close to slavery, except that it is voluntary entered into.

Labor Systems
large colonial economies were largely agricultural and relied heavily on systems of forced labor
examples) Inca Mi'ta system, Chattel Slavery, indenture servitude, encomienda, and hacienda systems

Competition over trade routes
as the world expanded economies sought to control trade in various regions
examples: Muslim-European rivalry in the Indian Ocean, Moroccan conflict with Songhai Empire

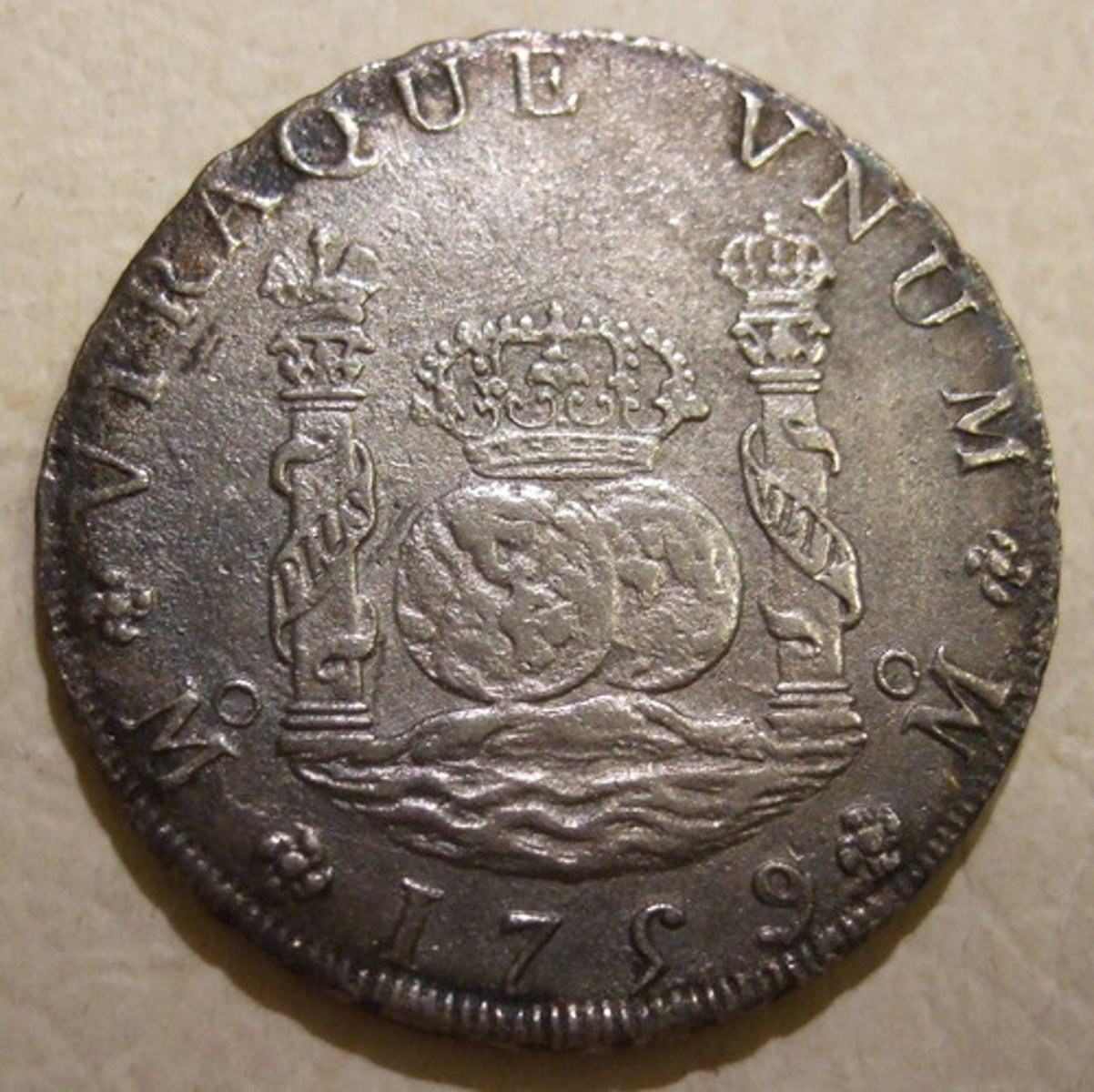
Potosi
City that developed high in the Andes (in present-day Bolivia) at the site of the world's largest silver mine and that became the largest city in the Americas, with a population of some 160,000 in the 1570s. Spanish colonies controlled a monopoly on the global flow of silver

Peasant and Artisan Labor
Peasants and artisans continued to intensify in regions and consumer goods increased
examples: Western Europe--wool and linen, India--cotton, China--silk

Maroon Societies
Communities formed by escaped slaves in the Caribbean, Latin American. and the United States.

Slave Resistance
Many slaves sought to resist and challenge authority in the Americas
examples: Maroon Societies, Turners Rebellion in Virginia
Ana Nzinga
17th century Angolan queen who fought off the Portuguese colonizers by pretending to accept Christianity, but actually was partnered with their enemies, the Dutch, and also developed a powerful trade nation instead of waging internal war.
Fronde
A series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV triggered by growing royal control and increased taxation

Pueblo Revolts
1680- revolted in the southwest when spaniards tried to suppress their religious rituals. revolt was successful, they captured santa fe, and drove spaniards out. spaniards reconquered pueblos 12 years later and put down 2nd revolt in 1696. spaniards realized colonial policies had to be changed. pueblos- own land, stopped forced indian labor, and tolerated religious rituals.
Maratha Conflicts with Mughals
group in center of India who rise up against the Mughul empire, British step in to help Mughal regain order but Britain takes over by seeping in to protect economic interests
Castas
middle-level status between Europeans and pure minorities (made up of mezitos and mulattoes)
Differential Treatment of Ethnic groups
Jews were expelled from Spain and Portugal but accepted in the Ottoman Empire
Han Chinese experienced restriction in Qing China
Status of Women differed within the Ottoman Empire
Russian Boyars
Russian nobles
Existing elites
Many groups experienced preferiential treatment and continued to experience this such as the Ottoman Timars, Russian boyars, European nobles
Ottoman Timar System
land granted by the Sultain in exchange for military service often to groups like the Janissaries from conquered lands. Allowed upward mobility for those granted it
Tupac Amaru II
(1738-1781) Mestizo leader of Indian revolt in Peru; supported by many among lower social classes; revolt eventually failed because of Creole fears of real social revolution

Mita System
The system recruiting workers for particularly difficult and dangerous chores that free laborers would not accept.

Potosi
Located in Bolivia, one of the richest silver mining centers and most populous cities in colonial Spanish America.
Gold, Glory and God
the desire for these three things prompted European exploration

Trading Post Empire
This is the type of empire established by the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean trading arena./The Portuguese sought to control the commerce in the area and did not want to control large areas of land.