Hamster diseases
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are the names and stain characteristics of Lawsonia Intracellularis
Proliferative enteritis, transmissible ileal hyperplasia, wet tail, gram negative, obligate intracellular rod
What age hamsters are most sensitive to lawsonia infection?
weanlings less than 10 weeks
What other species does lawsonia infect?
Infects swine, guinea pigs, ferrets, horses, deer, rabbits
Clinical signs of lawsonia in hamster?
Hamster: proliferative lesions epithelium terminal ileum (ileitis). Most common gross findings are Watery diarrhea w/moist, matted fur on tail/perineum/ventral abdomen, hence wet tail/
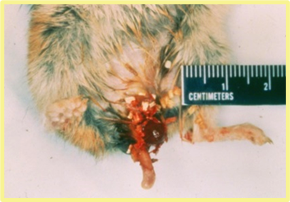

There is high mortality in weanlings, the clinical signs show these photos, what microbe is likely?
lawsonia intracellularis
DDX for lawsonia?
Tyzzers Disease, Salmonellosis, Clostridium difficile


Prevention and control Lawsonia?
DEPOP/SANITIZE/REPOPSeparate, supportive care, Tetracycline/Enrofloxacin/TMS combos in H20 (only moderate success
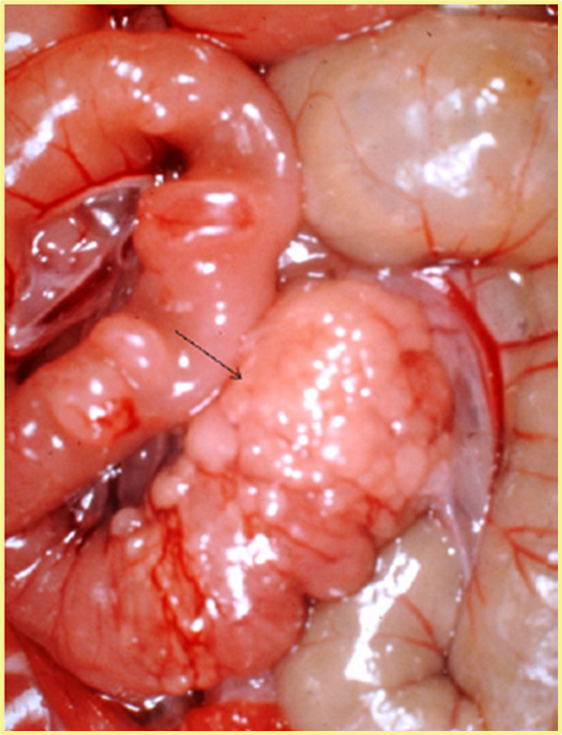
You do a necropsy on high mortality event of hamsters and see this? What can cause this? And is this lesion always seen with this microbe?
Lawsonia, and no not always seen.
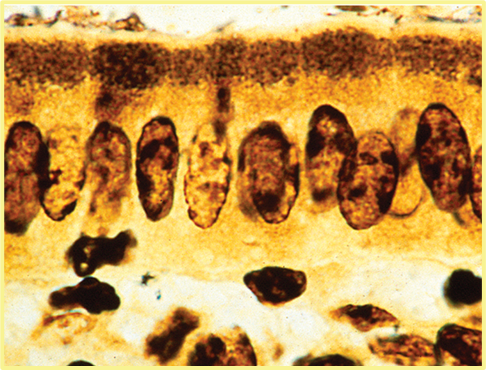
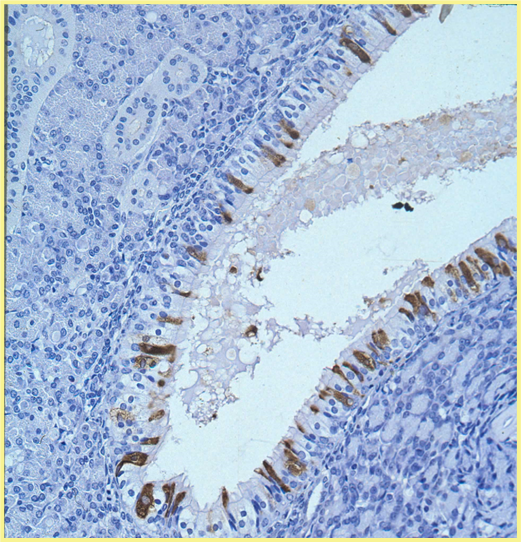
What stain is this, and what is it showing?
Warthin starry stain, showing intracellular small bacteria at apical cytoplasm of enterocytes. It is lawsonia.
What is the common name for Clostridium piliforme, what are the characterisitics of it?
Tyzzers disease, gram negative spore forming intracellular bacteria.
What species can get tyzzers?
rats, rabbits, cats, rhesus, dog, horse, GP
What age in hamsters are most affected, and what are the clinical signs?
Rough hair coat, diarrhea, high mortality weanlings/immunocompromised
What three systems do you typically see lesions of tyzzers?
intestine/liver/cardiac m.
Preferred diagnostic for tyzzers?
Serology/Fecal PCR assays available
Prevention and control of tyzzers?
Prevention key - sanitize, isolate, eliminate spores
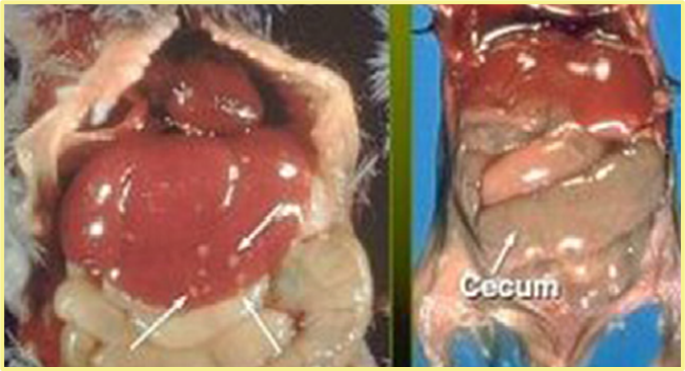
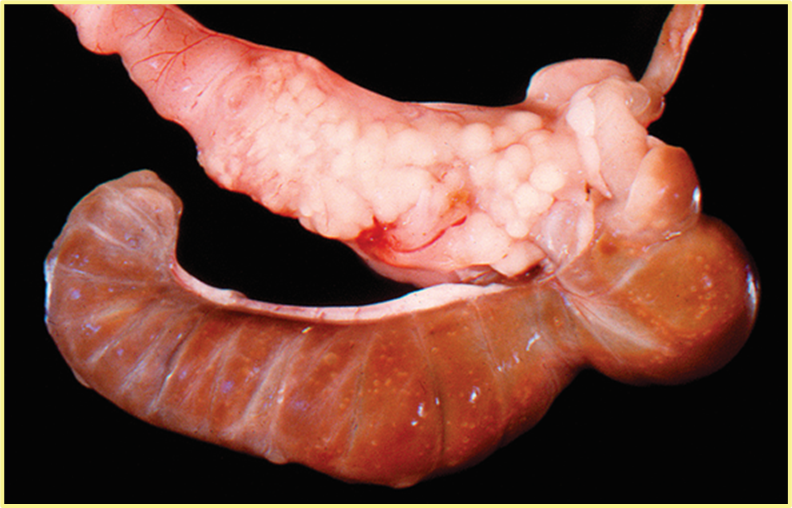
What are the arrows showing and what pathogen commonly causes this as well as lesions on SI and cardiac SM?
Tyzzers, Multifocla necrotizing hepatitis
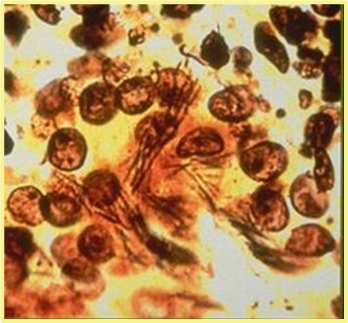
What are those filamentous bacteria “ pick up sticks”? What is the stain?
Warthin starry stain, Clostridium piliforme. Can also use giemsa stains.
Most common bacteria proliferation after certain ABs are given?
Clostridium deficile
What ABs cause bacterial dysbiosis in hamsters?
Ampicillin, Penicillin, Cephalosporins, Clindamycin, Erythromycin, Gentamicin, Lincomycin, Vancomycin
PORe Cilly Cins
Clinical signs and most common age group affected for C. deficile?
Juveniles to adults
unexpectedly die w/or w/o diarrhea, cecitis
+/- typhlitis, colitis
Are hamsters good models for C diff?
Yes
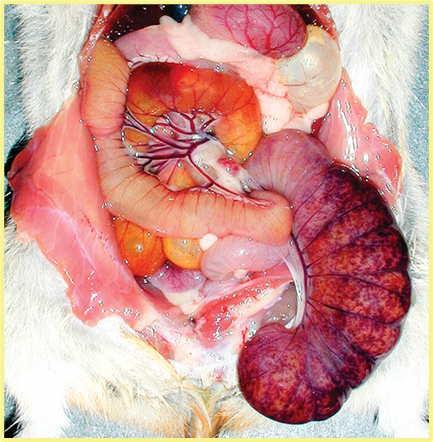
What disease do you commonly see diarrhea with severely hemorrhagic cecum after giving penicillin to a hamster?
C. deficile
Differentiate toxins A and B for C diff in cytologic preference?
Toxin A = mucosal damage, Toxin B = cytotoxic
Prevention / control of C diff in hamsters?
DEPOP / DECON w/chlorine dioxide / REPOP
Diag of C diff?
PCR
Is salmonella common in lab hamster pops?
No
Most common source of transmission of salmonella in hamster pops?
bedding
Most common Salmonella serovars in hamsters?
Enteriditis and typhimerium
One benefit of having a sentinal animal with contaminated bedding in regards to salmonella?
often silently shed from healthy animals chronically
Common pathology of salmonella in hamsters?
Multifocal pinpoint sized pale areas in liver (hepatic necrosis) w/o enteritis (white spots). Patchy pulmonary hemorrhage with septic thrombi (very unique to hamsters)
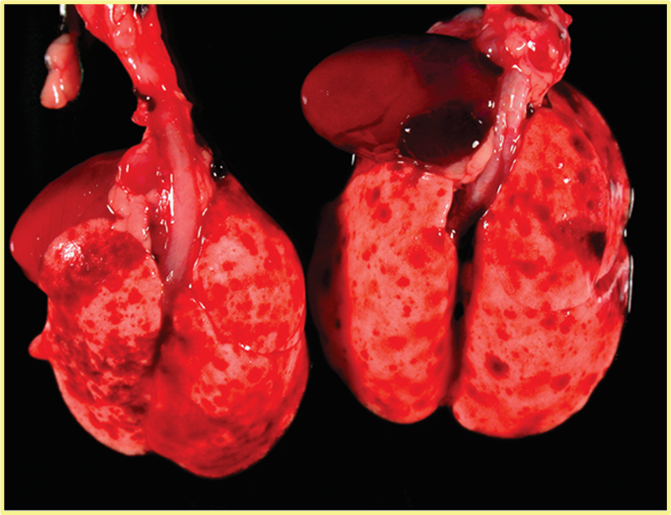
Found on necropsy of a sentinal animal exposed to bedding from colony animals, what is the pathogen?
Salmonella
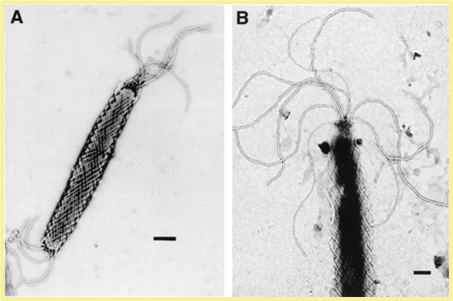
What pathogen?
helicobacter
Characteristics of helicobacter?
gram negative, motile spiral bacteria, normal commensal in hamsters
Which helicobacter species of hamsters can cause disease in immunocompromised people?
H. cinaedi => pathogenic humans
source of infection for humans, esp. immunocompromised
Most common disease in hamsters?
diarrhea
Second most common disease in hamsters?
pneumonia
What bacteria cause pneumonia in hamsters?
Rodenibacter pneumotropicus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, other Streptococcus spp., Corynebacterium paulometabulum
Common clinical signs of bacterial pneumonia ?
depression, anorexia, nasal/ocular discharge, “chattering”, resp distress
Prevention of bacterial pneumonia?
Avoid stress, isolate infected, +/- ABCs
Characteristics of lymphocytic choriomenengitis virus?
RNA enveloped Arenavirus
Why are hamsters so important regarding zoonosis on LCMV?
Most common cause of zoonosis to humans
What species is the primary host of LCMV?
Mus musculus
Clinical signs of LCMV in hamsters?
rarely any, often silent shedders
Transmission of LCMV in hamster and what is the most common?
Vertical OR Horizontal transplantable tumors (most common), direct contact, fomites, aerosols Viral shedding primarily in urine/saliva – persists longer in urine
What ABSL do hamsters with LCMV require?
ABSL 3
What pathogen causes this, in the liver lung pancreas brain and spleen? Found incidentally after necropsy of a hamster that received a transplant tumor in the cheek pouch.
LCMV
DDX and diagnostic for LCMV?
Amyloidosis, PCR
Sendai virus (respirovirus) characteristics?
Parapoxviridae, respirovirus, RNA enveloped.
natural host of respirovirus?
Mouse
Age group most affected?
newborn pups
Diagnosis of respirovirus
PCR, IFA, ELISA
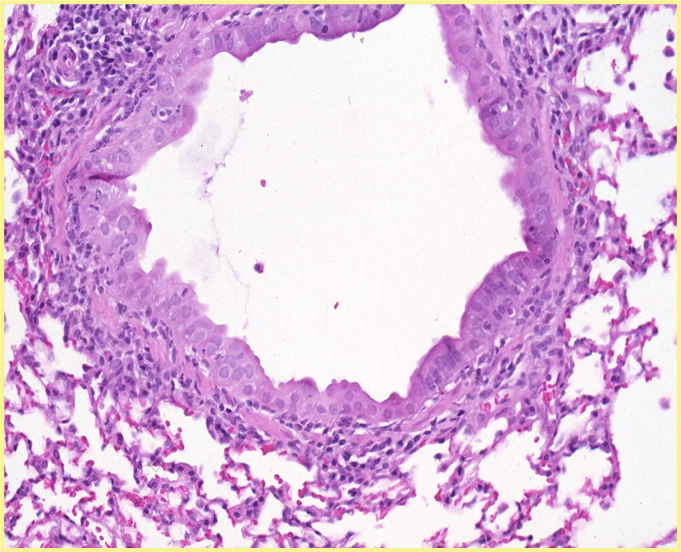
You do histo on a newborn hamster pup that died suddenly. See peribronchial cuffing and these Ag accumulations in the lungs?
respirovirus
Can hamsters get adenovirus?
Yes, they can get mouse adenovirus (DNA nonenveloped)
What is hamster polyomavirus common name and what are its characteristics?
Transmissible lymphoma and are DNA nonenveloped.
What is the tropism for hamster polyomavirus?
keratinocytes and lymphocytes
What are the two syndromes of polyomavirus in hamsters?
Naïve juveniles: Multisystemic lymphoma mesentery, intestines, liver, kidney, thymus
3mos-1yr: Trichoepitheliomas on face, feet, neck, back, flank, abdomen
Common clinical presentation of hamster polyomavirus?
thin with palpable masses in the abdomen

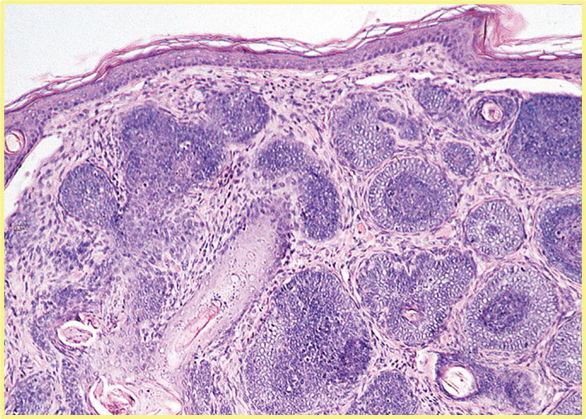
You have a 1 year old hamster with this presentation and histologically shows this, what is the pathogen?
Hammster polyomavirus
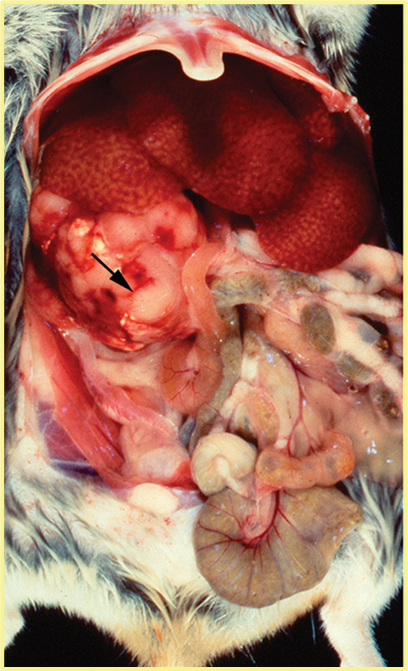
Juvenile hamster < 3 mo presents with palpable masses and low BCS, on necropsy you find enlarged mesenteric LNs. What disease is this?
Hamster polyomavirus
What are the characterisitcs of hammster parvovirus?
DNA nonenveloped
What do you see with weanling hamsters with parvovirus?
Suckling/weanling hamsters (2-4weeks old): runted, malformed or missing incisors, enamel hypoplasia of the incisor
Can animals be reinfected with parvovirus?
No, humoral immunity protects
Are adults clinically affected by parvovirus?
No
You find a weaning hamster with missing incisors and enamel hypoplasia, what is the pathogen?
Hamster parvovirus
Three most common protozoa found in hamsters
Spironucleus muris, Tritrichomonas muris, Giardia muris
Do protoza cause disease in hamsters?
None have been shown to be associated with significant lesions

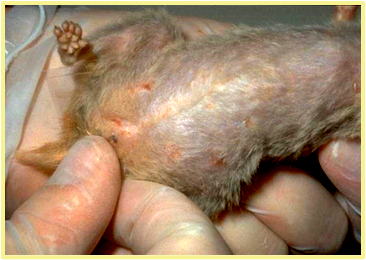
What diagnostic is being shown, what are you trying to diagnose?
tape test, pin worm
Are hamsters susceptible to pin worm infection, and do they typically show clinical signs?
Infection very common, but no clinical signs usually occur.
Common pinworms in hamsters?
Syphacia mesocriceti, S. criceti, S. stroma, S. peromysci, S. obvelata (from mice), S. muris (from rats), Aspicularis tetraptera (esp. Siberian dwarf hamsters) and Dentostomella translucida
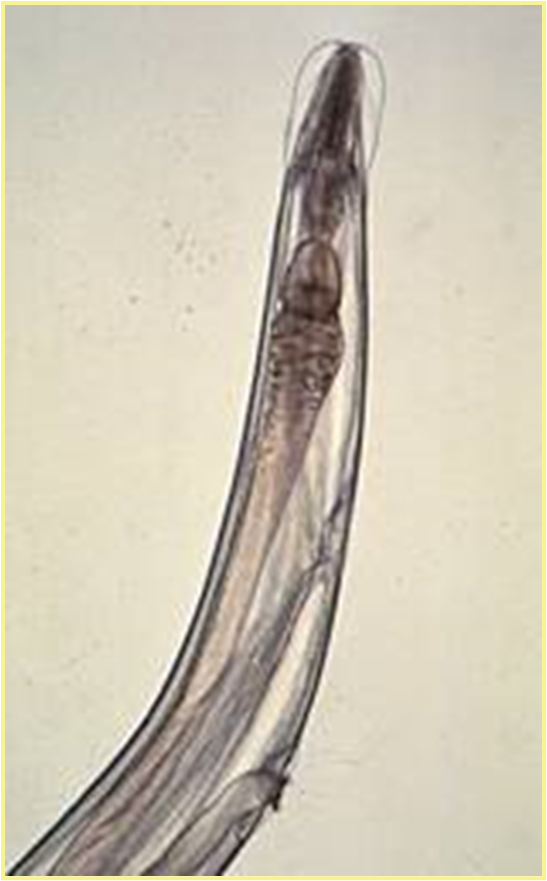
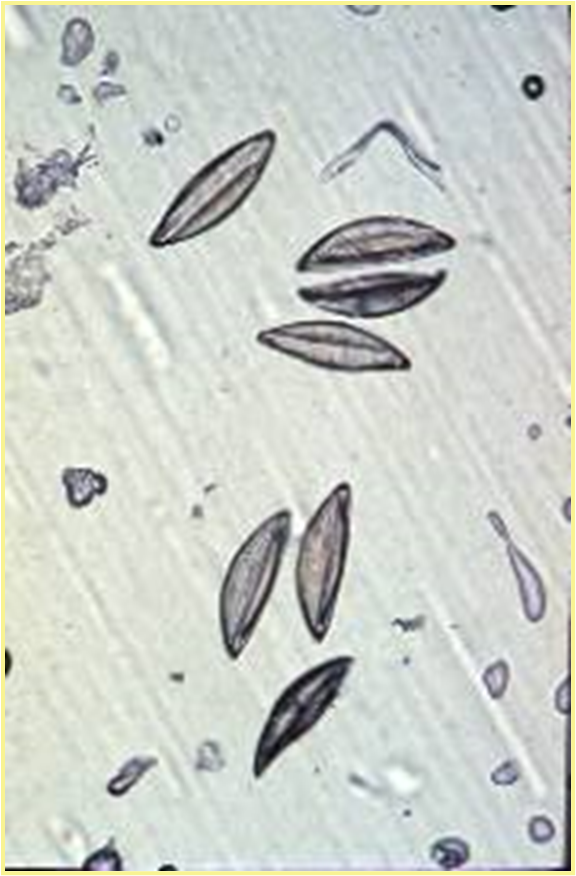
What is the species?
Syphacia mesocriceti
Most common zoonotic tapeworm in hamsters?
Rodentolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm)
Life cycle information for rodentolepis nana?
Direct (14-16 dys) OR Indirect LC – flour beetle/flea intermediate host
Which is larger? Hymenolepis diminuta or R. nana?
Hymenolepis diminuta Larger than R. nana
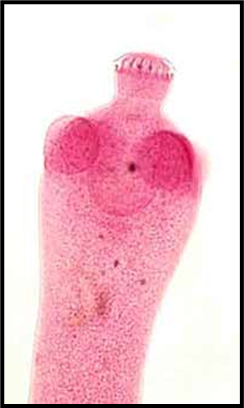
Which parasite and where does it preference?
R. nana, prefer lower intestine.
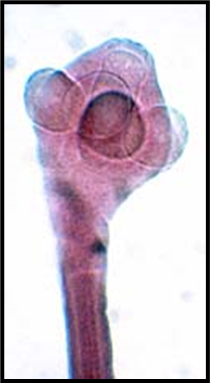
what pathogen? and where does it preference?
H. Diminuta, upper SI
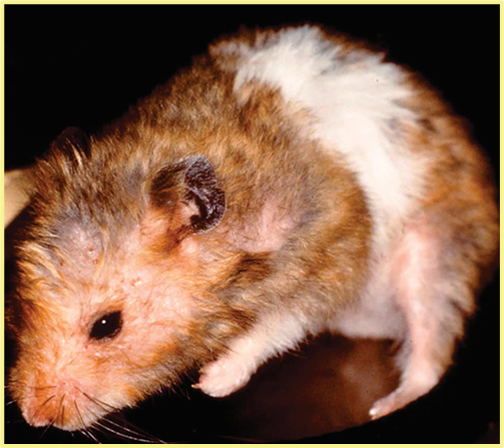
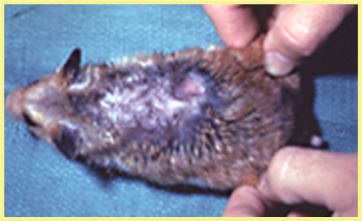

What pathogen is causing this? And how would you treat?
Likely demodex species, alopecia on rump and back with dry, scaly skin
TX: Topical amitraz, oral ivermectin/weekly cleaning w/selenium and benzoyl peroxide shampoo
Which demodex species in C shaped in hamster and where does it infect on skin?
Demodex criceti, invade epidermal pits, 24 hour life cycle
Which demodex species is A shaped in hamsters and where does it like to infect on the skin?
Demodex aurati, invades the hair follicles.
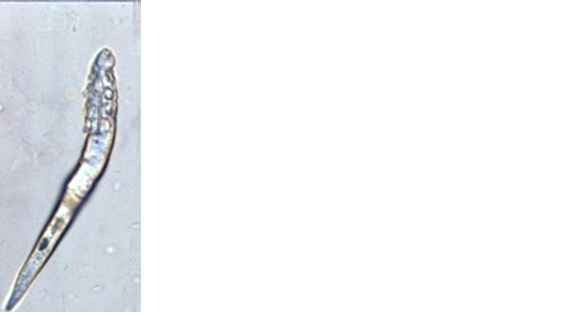
Which species is this in hamsters?
Demodex aurati, pointy A end
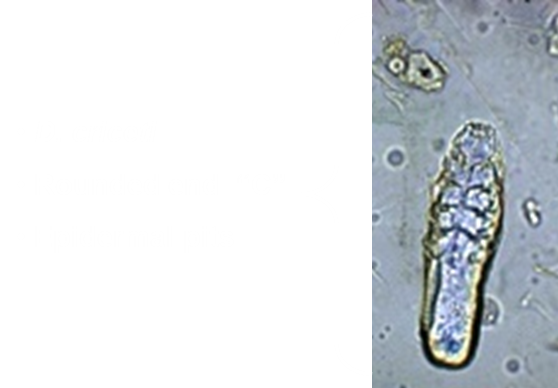
What species is this in hamsters?
D. criceti, round end
Are females or males more likely to get neoplasia in hamsters?
Females, but still very rare
Most common malignant neoplasia of hamsters
Malignant Lymphosarcoma
Which cancer is polyomavirus most associated with in hamsters?
malignant lymphosarcoma
Most common benign cancers in hamsters?
intestinal polyp, adrenal adenoma, splenic hemangioma, islet cell pancreatic, hepatic ademona, mammary fibroadenoma
What two diseases are the most common cause of death in older hamsters?
Amyloidosis and nephrotic syndrome
Is amyloidosis sex dependent?
Yes, predominantly females
Two amyloid proteins of concerns of hamsters?
AA and AP
Which hormone is important for inactivation of which amyloid protein in hamsters?
Testosterone inhibits growth of AP amyloid. Thats why females are more predisposed to disease.
Organs involved in amyloidosis in hamsters?
liver, kidney, stomach, adrenal, thyroid, spleen
Clinical signs of amyloidosis in hamsters?
Extensive SQ edema, ascites, hydrothorax, ↓ albumin, ↑globulin, proteinuria, hypercholesterolemia, ↑ creatinine
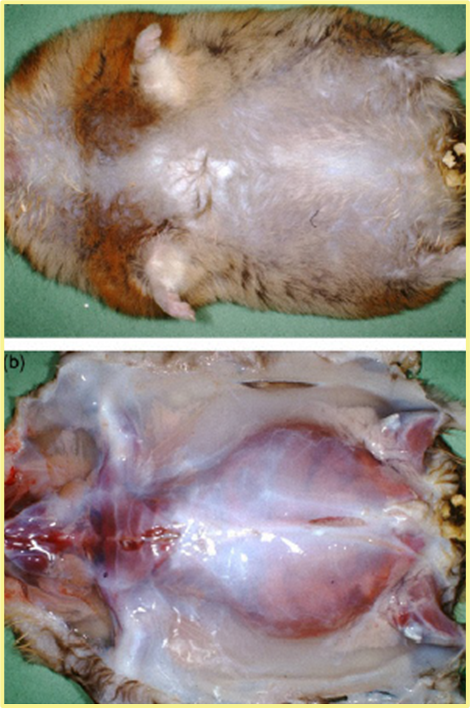
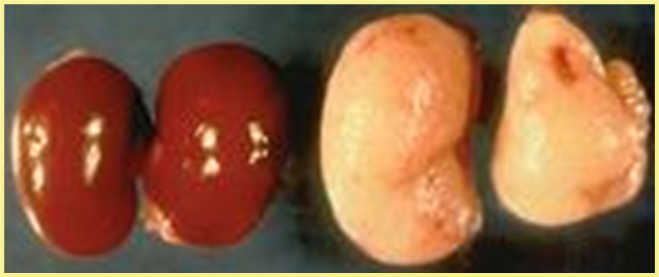
What is being described here and what is the disease in hamsters?
SQ edema and pallor congested kidneys associated with amyloidosis.
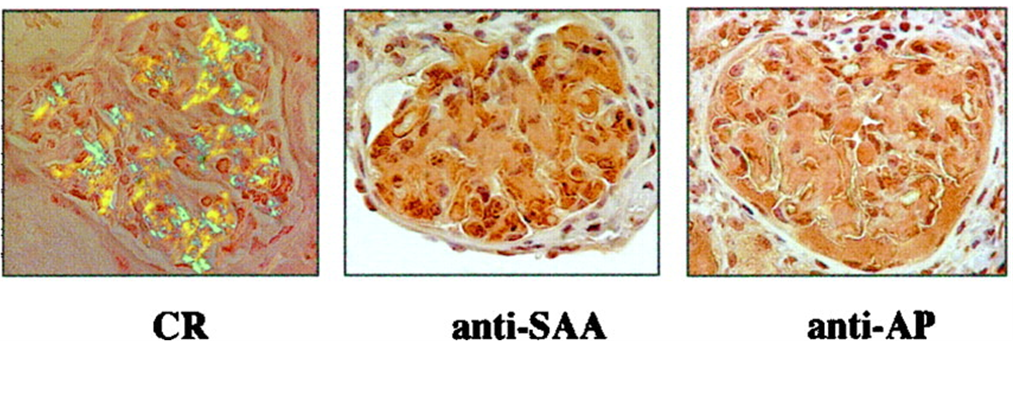
What is the stain and what is being shown here?
Congo red stain for amyloidosis
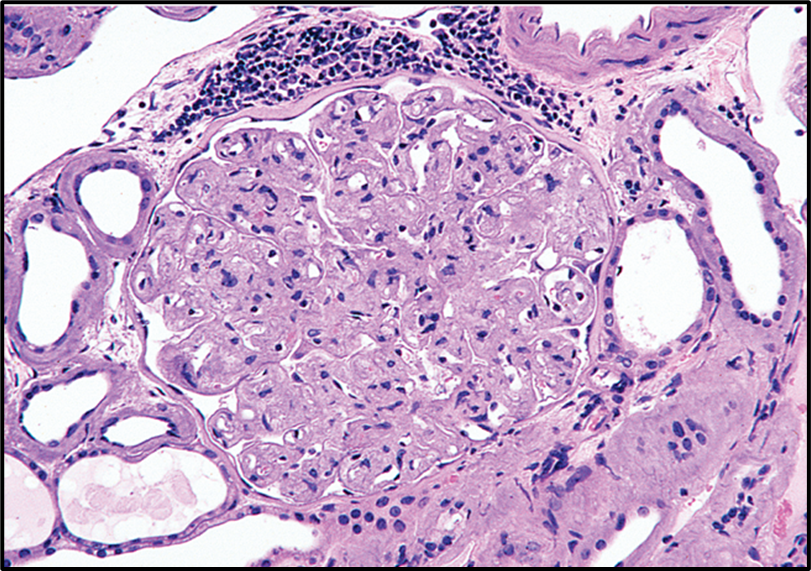
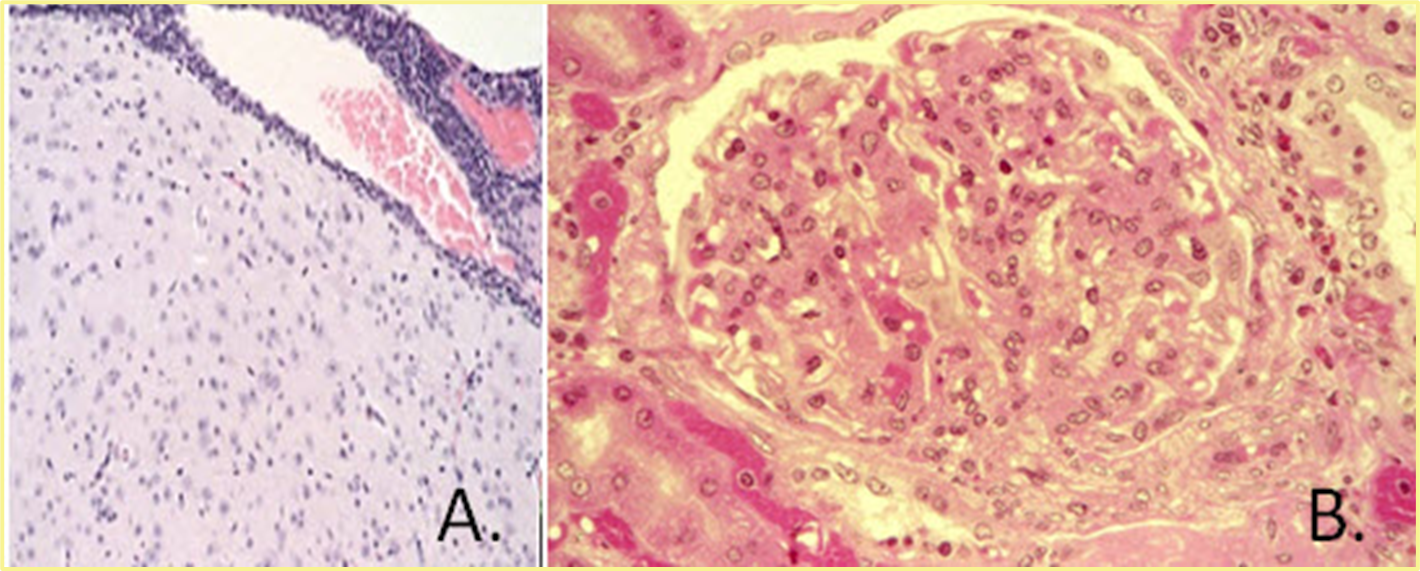
What organ system is this, and what is being shown?
glomeruli of kidney with amyloid deposits
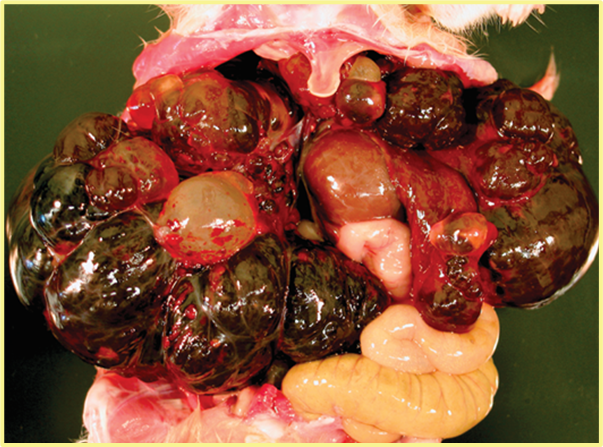

What is being shown here?
Polycystic disease in an aged hamster. Common in hamsters over 1 year of age
Most common areas affected by polycystic disease in hamsters?
liver and epididymis
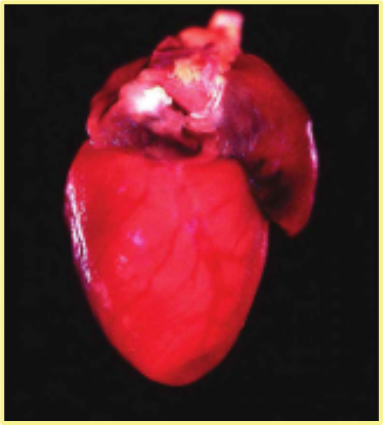
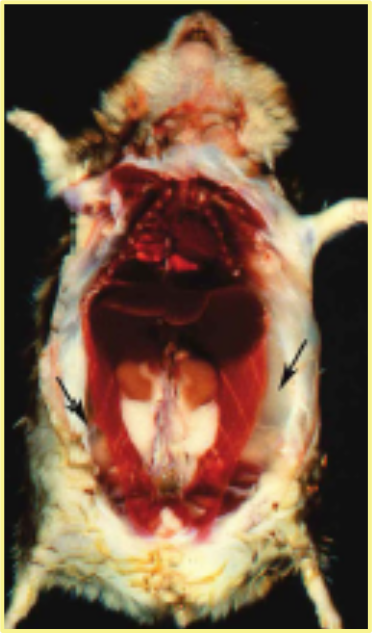
Find these cardiac and abdominal findings on necropsy of an aged APA hamster? What is it?
Thromvbi in the left atrium due to blood stasis, results in jelly hams or SQ edema in abdomen.