Kingdom Plantae Classification Review
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
kingdom plantae classification
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Botany
the study of the plant kingdom
Divisions
Plantae is divided into 12 phyla, known as _______
12 phyla divided into 3 smaller groups:
Nonvascular: Bryophyta, Hepatophyta, and Anthocerophyta
Vascular w/o seeds: Pteridophyta, Sphenophyta, Lycophyta, and Psilotophyta
Vascular w/ seeds: Ginkgophyta, Anthophyta, Coniferophyta, Cycadophyta, and Gnetophyta
Bryophyta (the mosses)
non-vascular
A leafy shoot on top and tiny root anchors (rhizoids)
Non-vascular
plants do not have veins/true tissues to transport water and nutrients
diffusion to move particles — must be small & close to water
Rhizoids
tiny root anchors
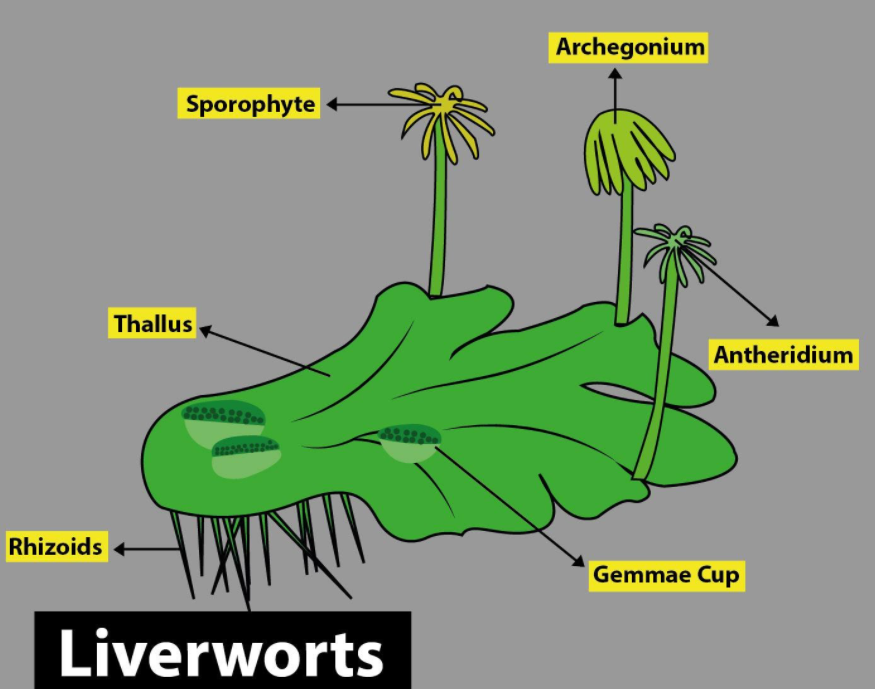
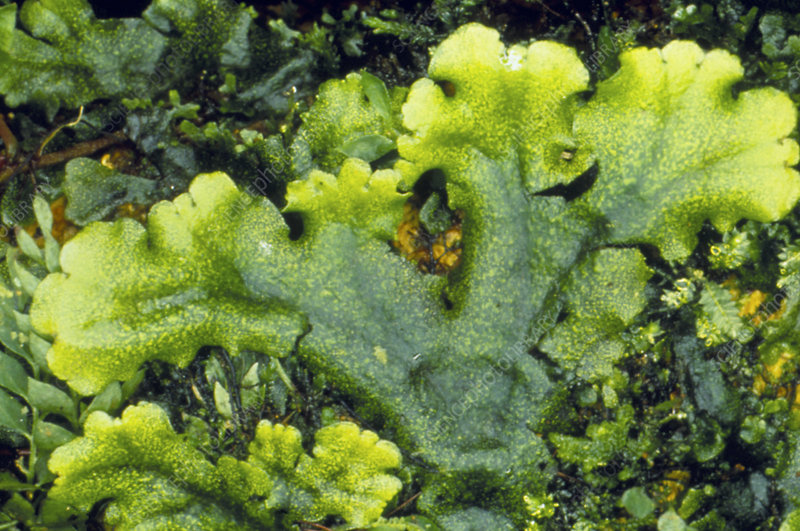
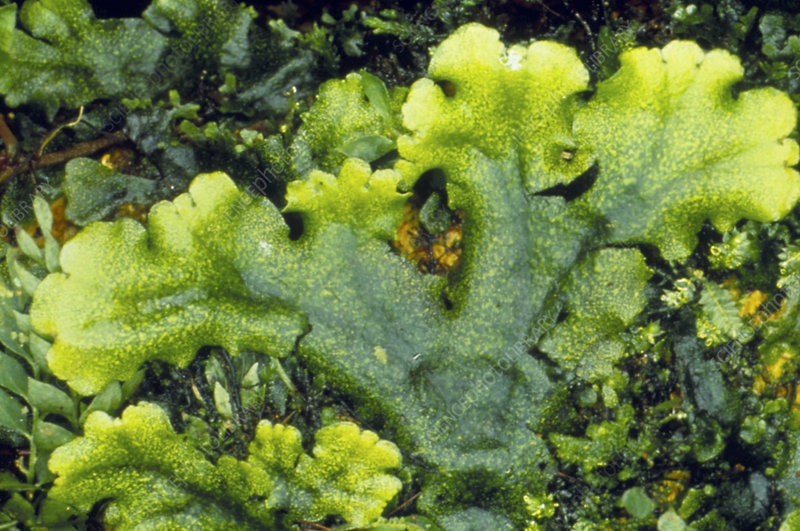
Hepatophyta (liverwort)
Nonvascular
Gametophytes are a flattened leathery structure —- thallus
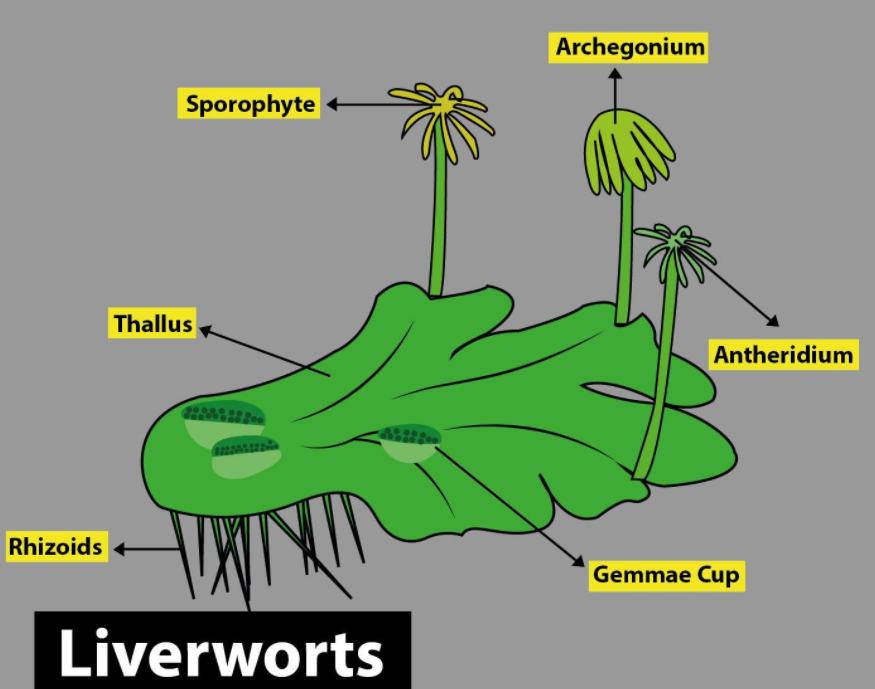

Thallus
simple, flat plant body not divided into roots, stems or leaves
In liverworts, the ______ is the flattened leathery structure gametophyte

Anthocerophyta (Hornworts)
Nonvascular
Flattened along the ground, but sporophyte looks like a horn growing out of the plant
Xylem
Tissues that transport water
Phloem
Tissues that transport nutrients
Pteridophyta (the ferns)
Vascular w/o seeds (grow large and survive in drier environments due to veins)
Found in all climates, prominent in cool, shady areas
Uses spores
Frond
A fern leaf
Sori (Sporangia)
A collection of sporangia, releasing spores via wind that grows and germinates.
Prothallus
As a spore germinates, it grows into a heart shaped _____ —> fiddlehead —> unfurls as a frond
gametophyte stage in life cycle of ferns
Fiddlehead
Young, uncoiled fern frond
Sphenophyta (Horsetails)
Vertical w/o seeds
Hollow, vertical stems, producing whorls of thin leaves
Uses spores
American settlers used it to clean pans, rigid and rough
Lycophyta (Club Mosses)
Vascular w/o seeds
Looks like large moss plants
Use spores
Have erect stems w/ cone-like structures for releasing spores on the ends
Psilotophyta (Whisk ferns)
Vascular w/o seeds
Rare and unusual
Use spores
May grow a thick stem covered with rhizoids (like fungi) underground to spread
Gymnosperm
non flowering plants with seeds: coniferophyta, cycadophyta, ginkgophyta, and gnetophyta
Angiosperm
flowering plants with seeds: anthophyta
Coniferophyta (Cone-bearing plants)
Vascular plants
Gymnosperm & largest type
Two cone types:
pollen cone: numerous. small, produce large amounts of pollen to increase the chance of reaching the seed cone. pollen travels via air
seed cone: small and green. After trapping pollen, they close scales, and ova is fertilized. Seeds grow —> brown and woody —> opens to release mature seeds
Cycadophyta (Cycads)
Vascular w/seeds
Gymnosperms
Native to tropical areas, look like palm trees
Ginkgophyta (Ginkgos)
Vascular w/ seeds
Gymnosperms
Broad leathery leaves
Trees either male, producing pollen (sperm) or female, producing yellow cherry-sized foul-smelling fruit
Gnetophyta (Gnetophytes)
Vascular w/seeds
Gymnosperms
Grow pollen & seeds in cones that look like flowers
Two unusual members: Ephedra plants, Welwitschia plants
Anthophyta (The Flowering Plants)
Vascular w/ seeds
Angiosperms
Pollen fertilizes an ovule inside the ovary of a flower, ovary —> fruit w/ seed(s)
Most plants, trees, shrubs and grasses you think of are angiosperms
2 groups: Monocots, Dicots
Cotyledon
first leaf or leaves from a germinating seed, serving as a food source and nutrient storage, until true leaves develop
Main characteristics of all plants
Eukaryotic, autotrophic, multicellular, chloroplast, large vacuoles, cellulose walls, sexual and asexual reproduction, evolved from algae
What did plants evolve from? What adaptations were required for life on land
Algae
Land requires: water conservation— waxy cuticle on leaves, transport of water & nutrients— vascular system, reproduction (sexual) — pollen in higher plants, and support — woodiness.
How do non-vascular plants transport water and nutrients within the plant
Diffusion - the natural passive movements of particles from a high concentration area to a low one.
Describe the Bryophyte life cycle and define gametophyte and sporophyte
Gametophyte produces sperm and eggs at the top of a moss’ leafy shoot
Water triggers the release of sperm, traveling to eggs, and growing into a new shoot
This shoot produces a stalk with spores in the sporophyte generation.
When the spores are released, they will germinate into a new leafy shoot and the gametophyte generation will begin again.
Gametophyte: haploid stage in life cycle that produces gametes (egg & sperm) via mitosis for sexual reproduction, forming the next sporophyte generation after fertilization
Compare monocots and dicots
Monocot:
one cotyledon (seeds), parallel veins in leaves (leaves), fibrous root system (roots), xylem and phloem are scattered throughout the stem (stems), flower petals are in 3’s or 6’s (flower parts)
Dicot: two cotyledons, branched veins in leaves, tap root, xylem and phloem are arranged in a ring throughout the system, flower parts in 4’s or 5’s