Ch 21- Artifacts
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
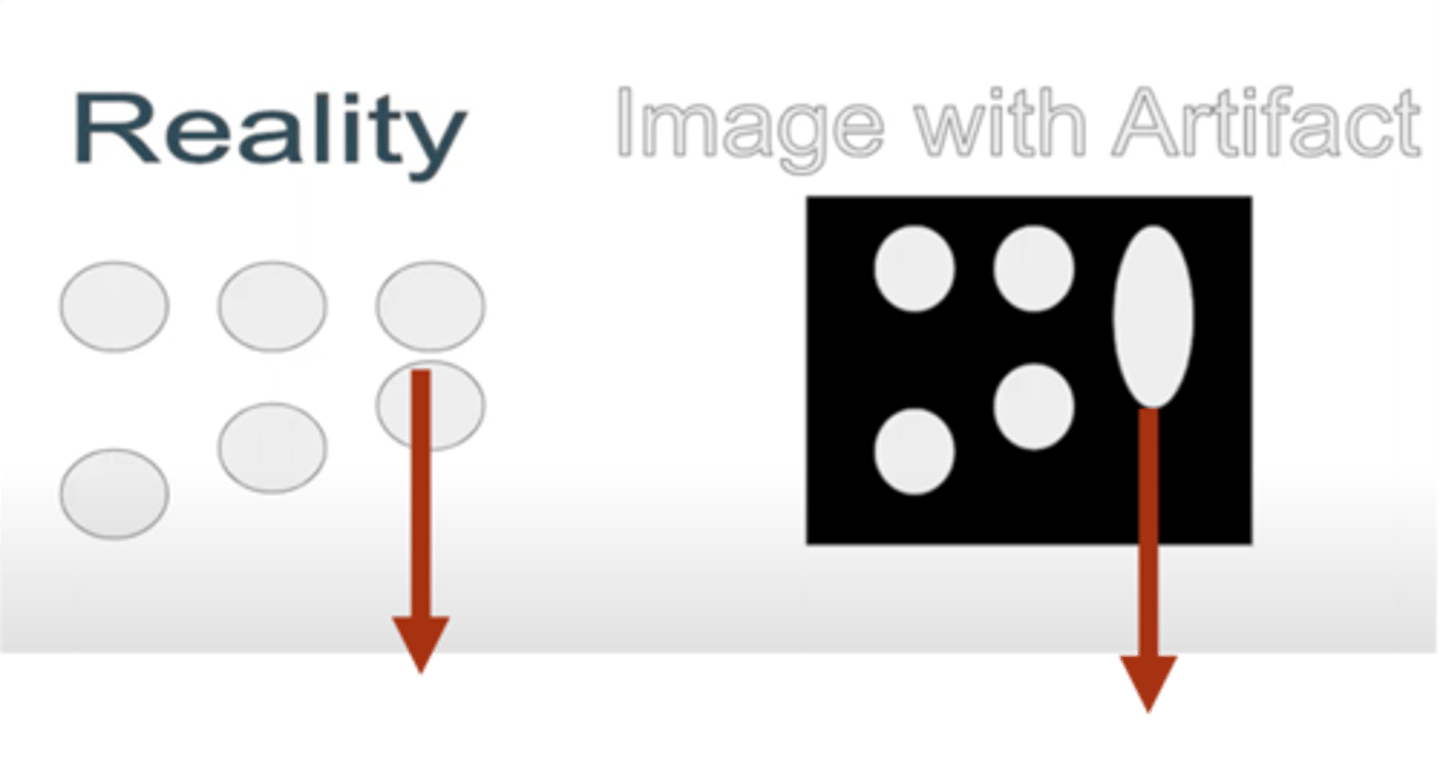
What is an artifact?
an error in imaging
Artifacts include reflections that are described as:
1. ____
2. ____
3. ____
4. ____
5. ____
1. not real
2. not seen on the image
3. incorrect shape or size
4. incorrect position
5. incorrect brightness
What are causes of artifacts?
- violation of assumptions
- equipment malfunction or poor design
- physics of ultrasound
- operator error
What terms are used to describe ultrasound images?
- hyperechoic
- hypoechoic
- anechoic
- isoechoic
- homogenous
- heterogenous
There are __ assumptions incorporated into the design of every ultrasound system. What appears when these assumptions are not true?
6; artifacts
What are the 6 assumptions of imaging systems?
1. sound travels in a straight line
2. sound travels directly to a reflector and back
3. sound travels in soft tissue at exactly 1,540 m/s
4. reflections arise only from structures positioned in the beam's main axis
5. the imaging plane is very thin
6. the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
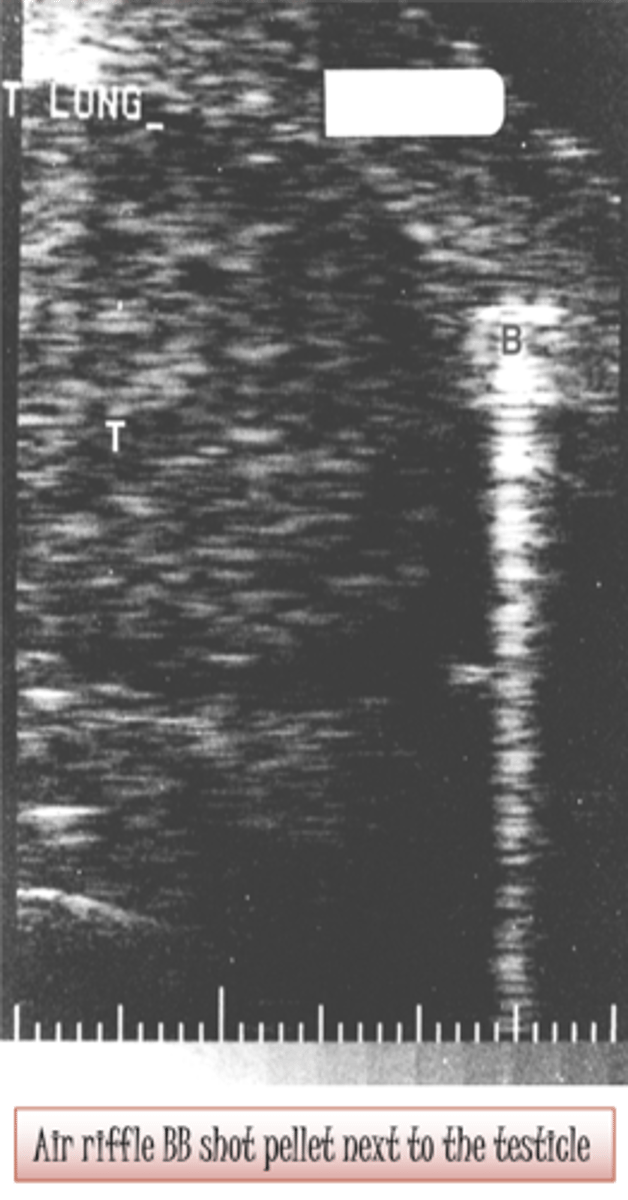
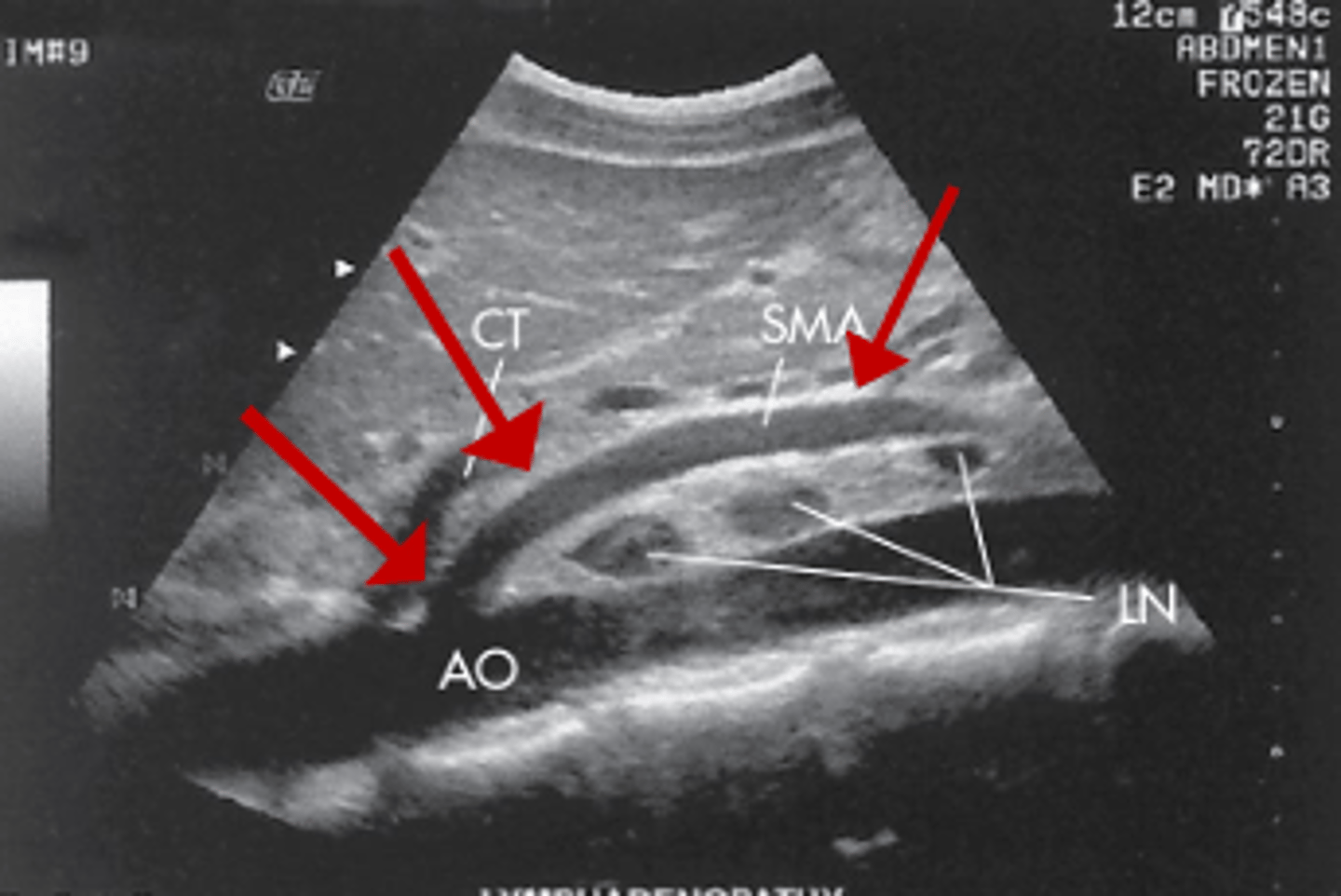
Reverberation is caused by ___ bouncing between the ___ and a ___
multiple reflections; transducer; strong reflector
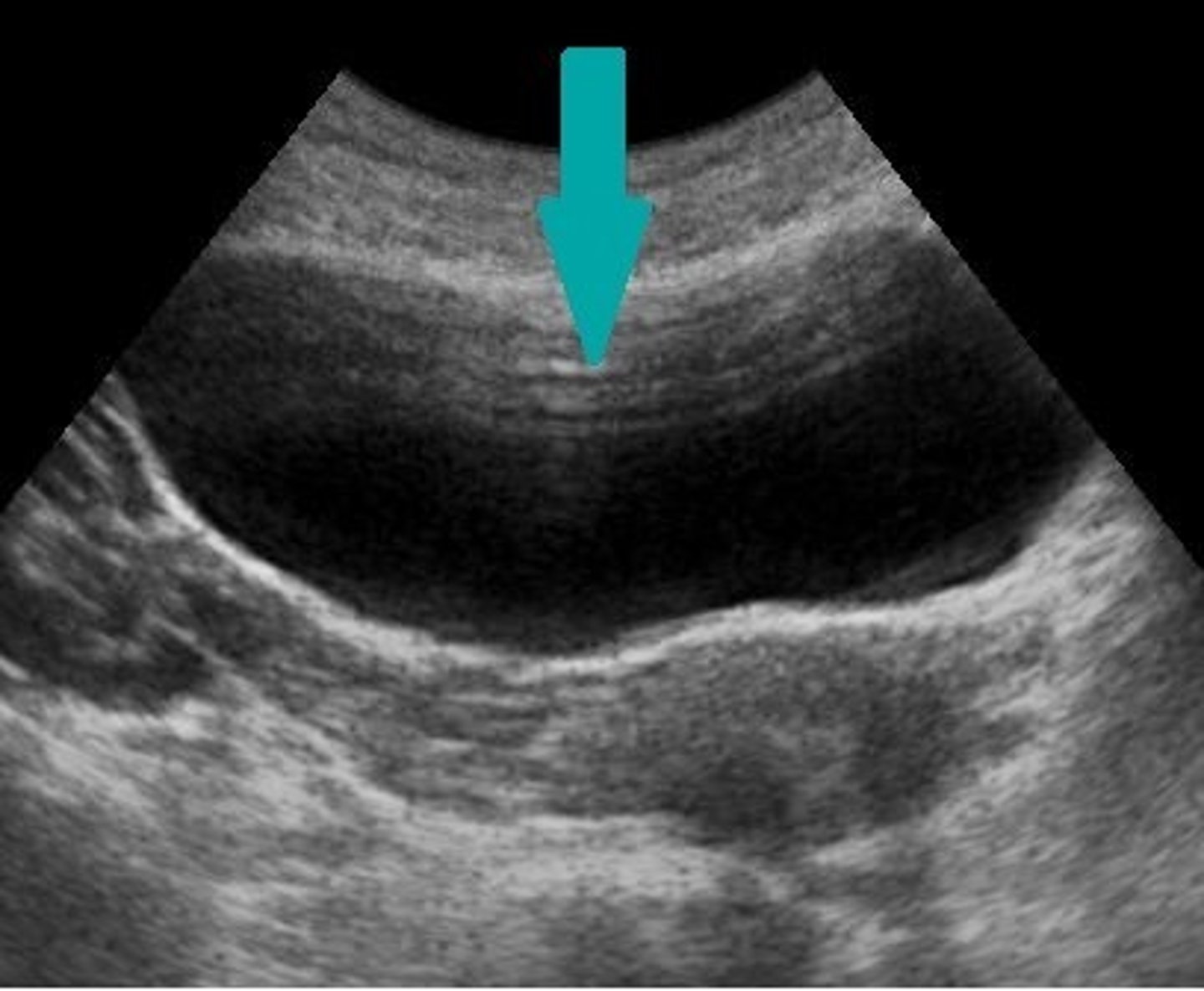
Reverberations appear as ___, ___ spaced echoes
multiple; equally
Reverberation produces ___ echoes of ___ brightness
parallel; decreasing

Which assumption causes reverberation?
sound travels directly to a reflector and back
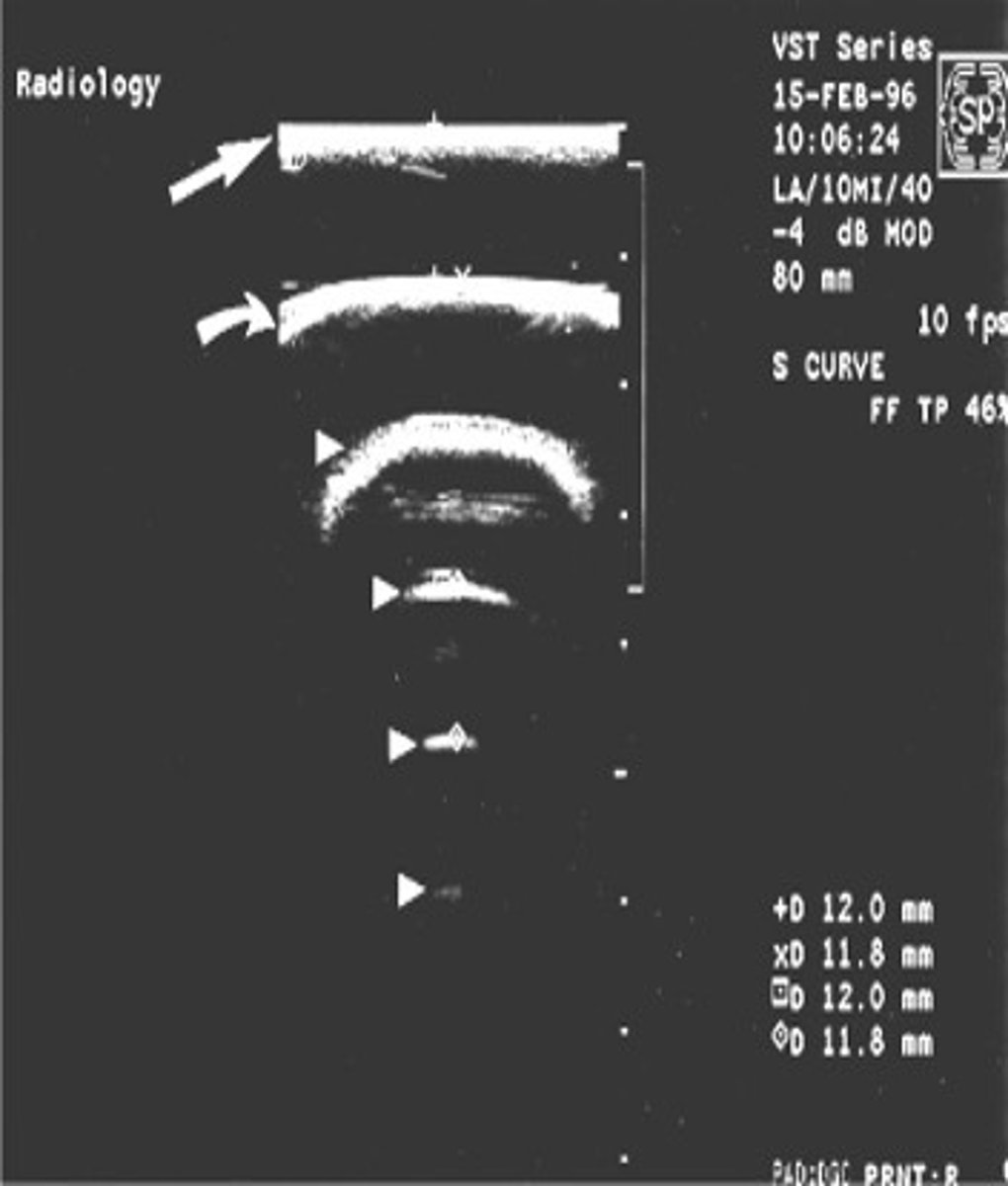
Comet tail is caused by ___ of ___ or ___ hit by a ___
vibration; small gas bubbles; air; sound beam
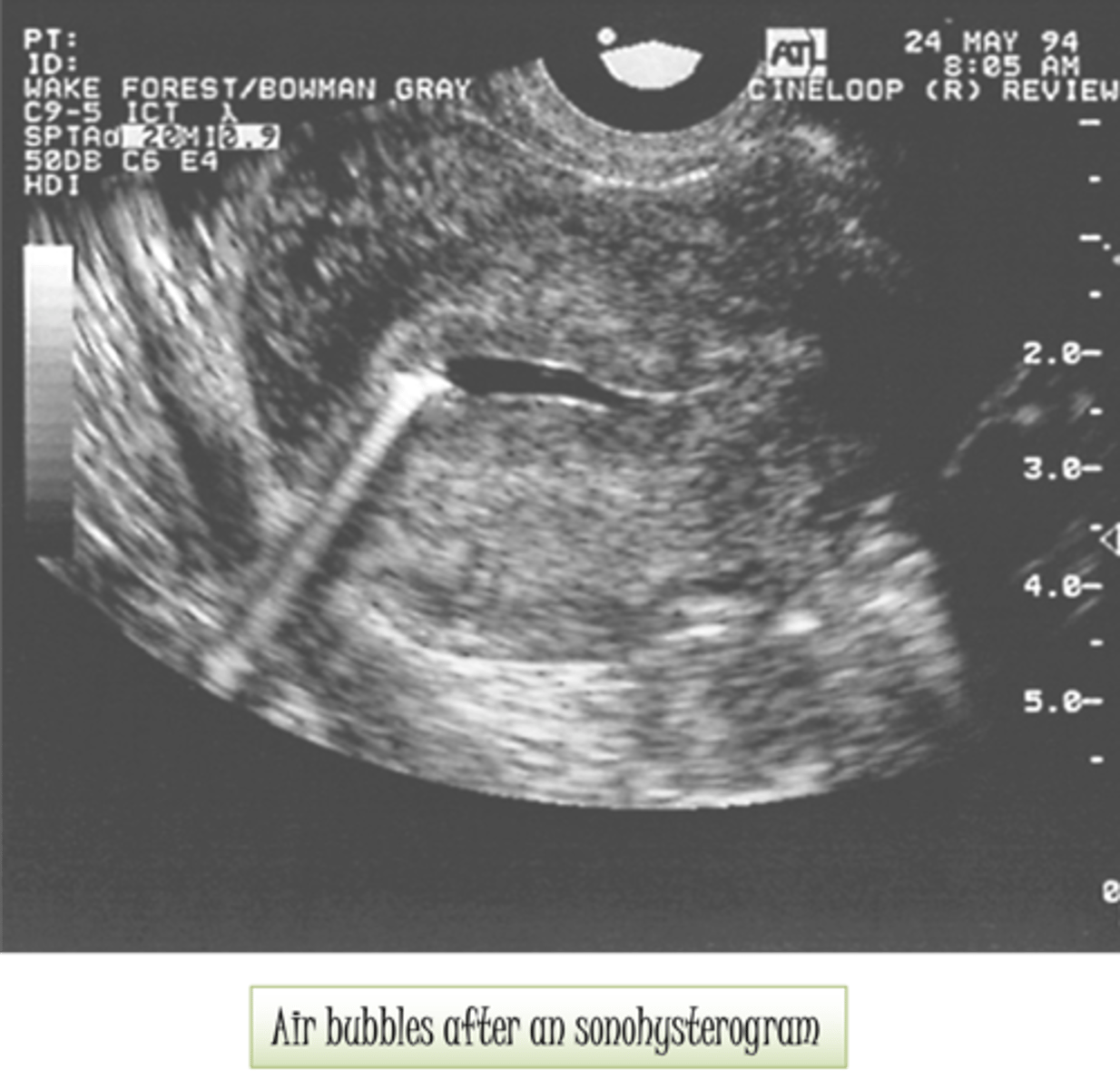
When is comet tail artifact created?
when closely spaced reverberations merge
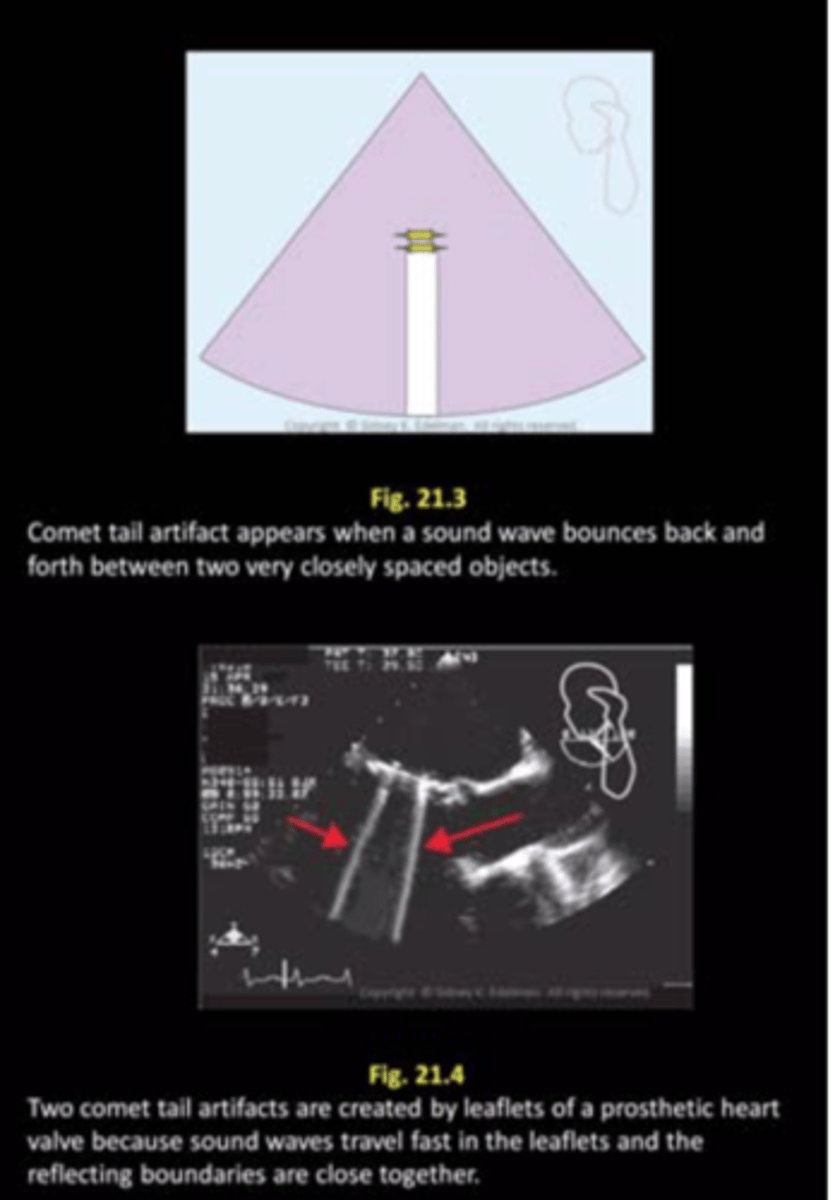
What is comet tail also called?
ring down artifact
Comet tail appears as a ___, ___ line directed ___
solid; hyperechoic; downward
What assumption causes comet tail?
sound travels directly to a reflector and back
Refraction occurs when a sound pulse ___ during ___
changes direction; transmission
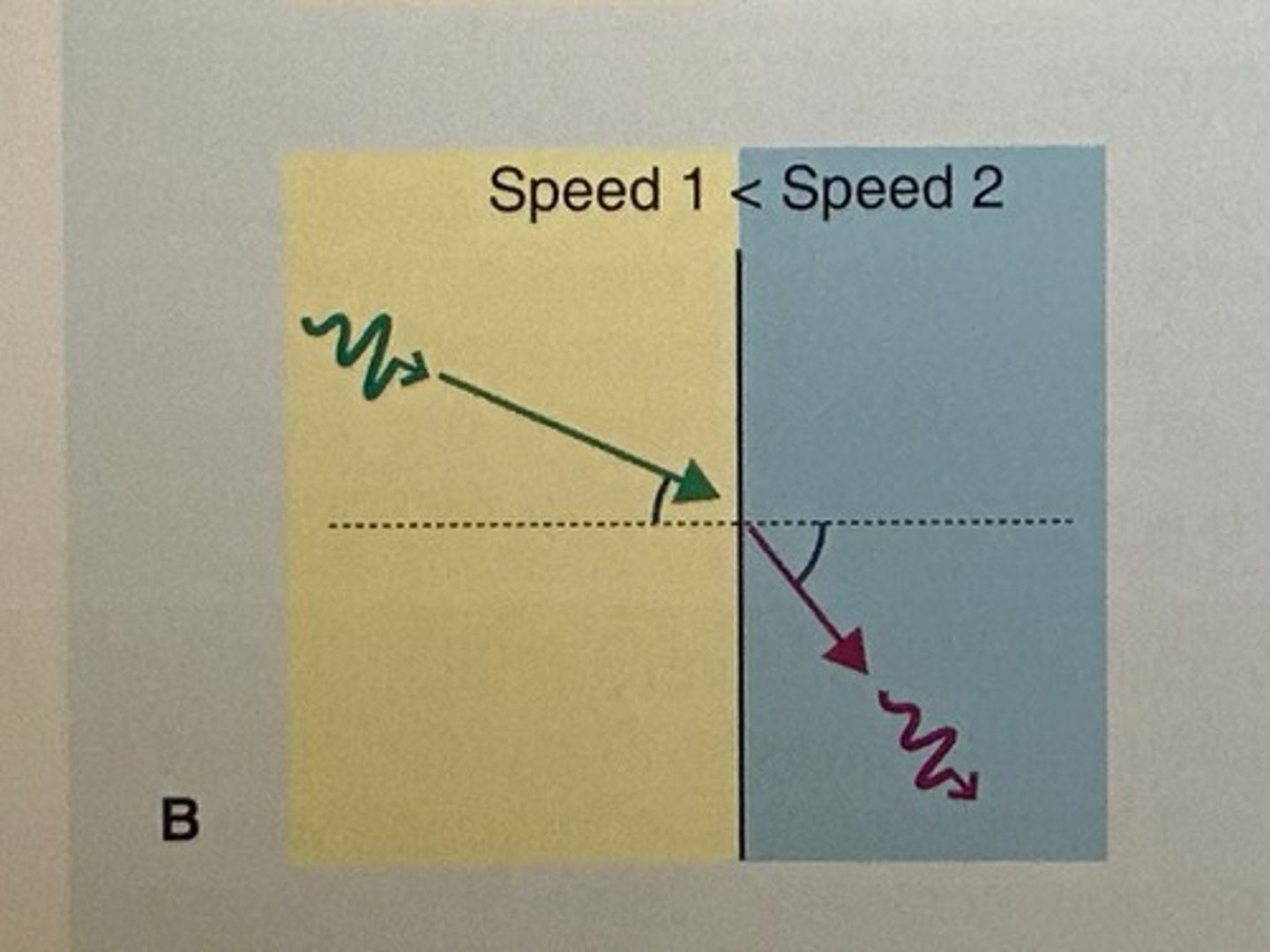
Refraction produces a ___ copy of the reflector
side by side
Refraction is ___ with a ___
transmission; bend
What does refraction degrade?
lateral resolution
Which assumption causes refraction?
sound travels in a straight line
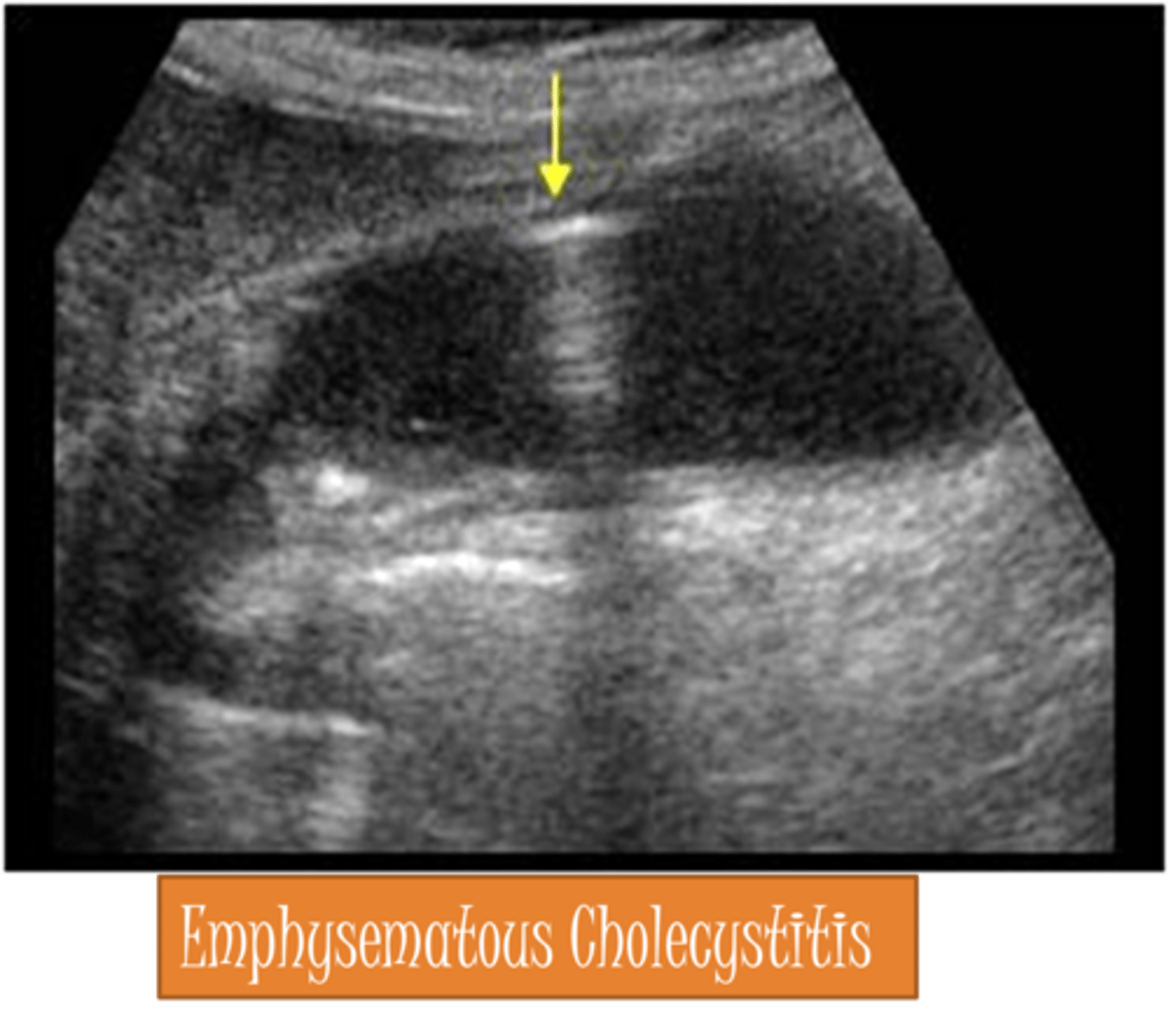
Shadowing occurs when sound hits a ___ structure and cannot ___, leaving a ___
highly attenuating; penetrate; shadow
Shadows appear when the attenuation is ___ in the tissue above the shadow than in the surrounding tissue
higher
Shadowing appears as a ___ or ___ region extending ___
hypoechoic; anechoic; downward
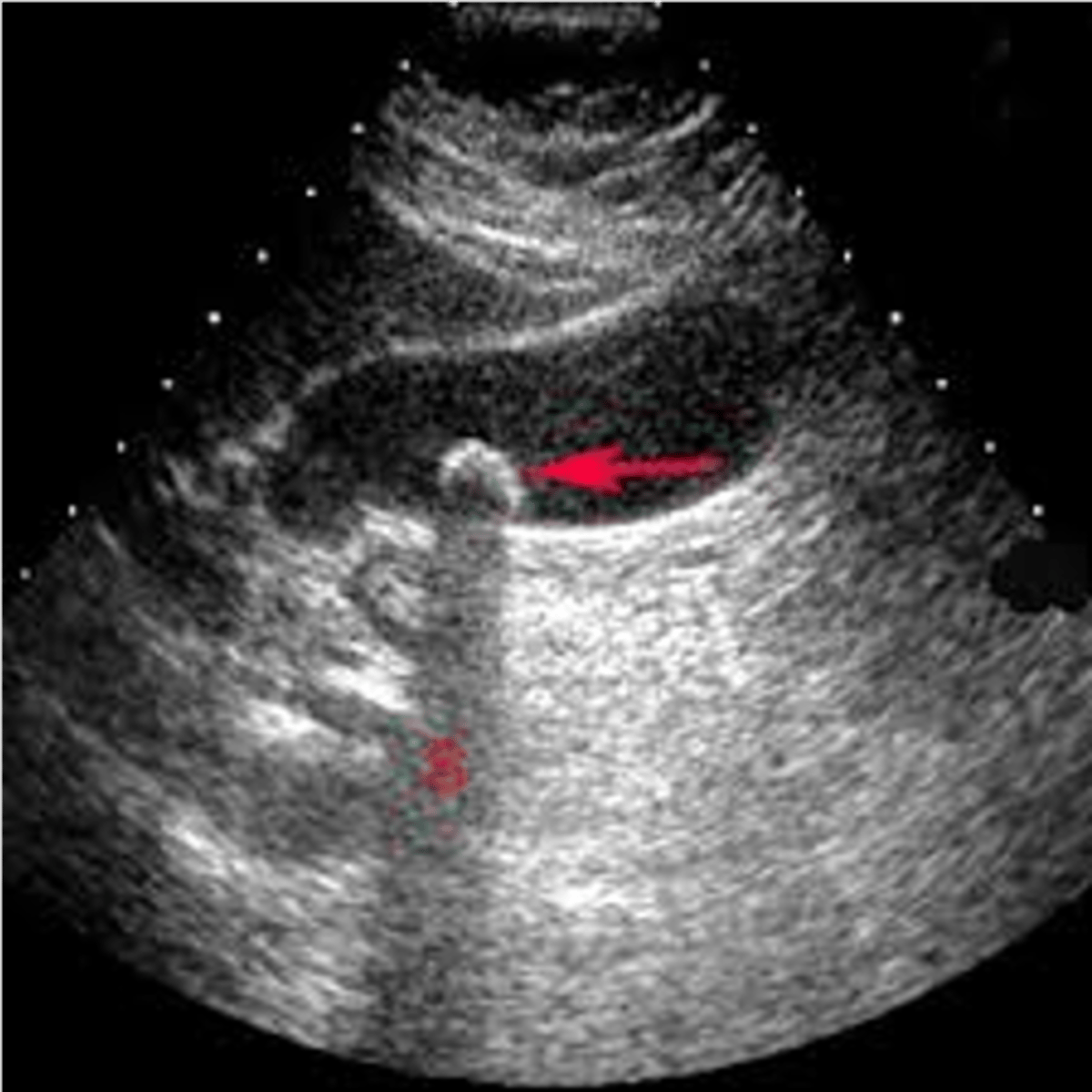
When can shadows be useful?
when characterizing tissue (Ex. bone, gallstones)
Which assumption causes shadowing?
the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
Edge shadow is a ___ artifact caused by sound ___ off of a ___ surface
refraction; refracting; curved
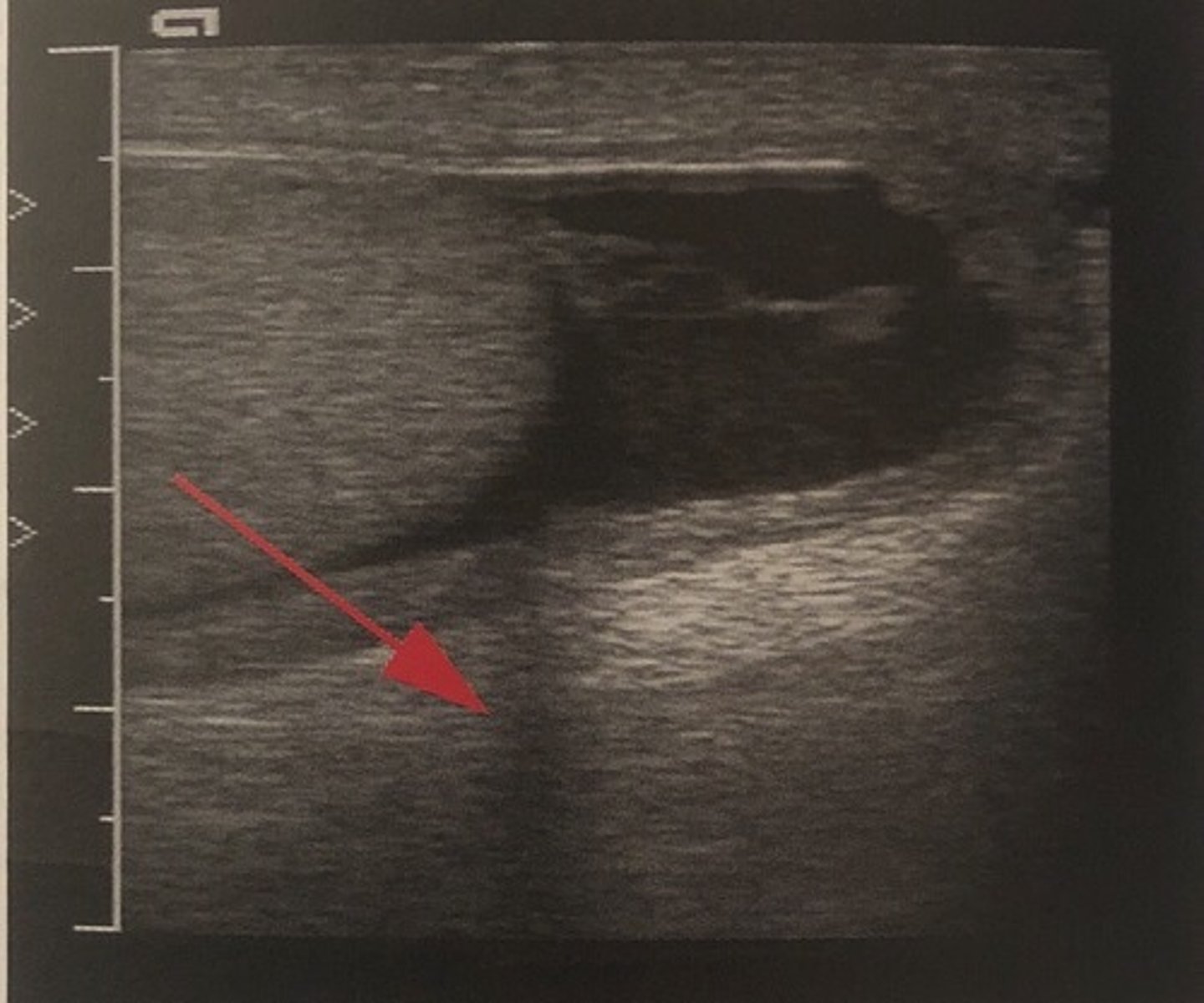
With edge shadow, the sound beam refracts at the edge of a curved reflector
The beam simultaneously ___, resulting in a drop in ___
This decrease causes edge shadowing
diverges; intensity
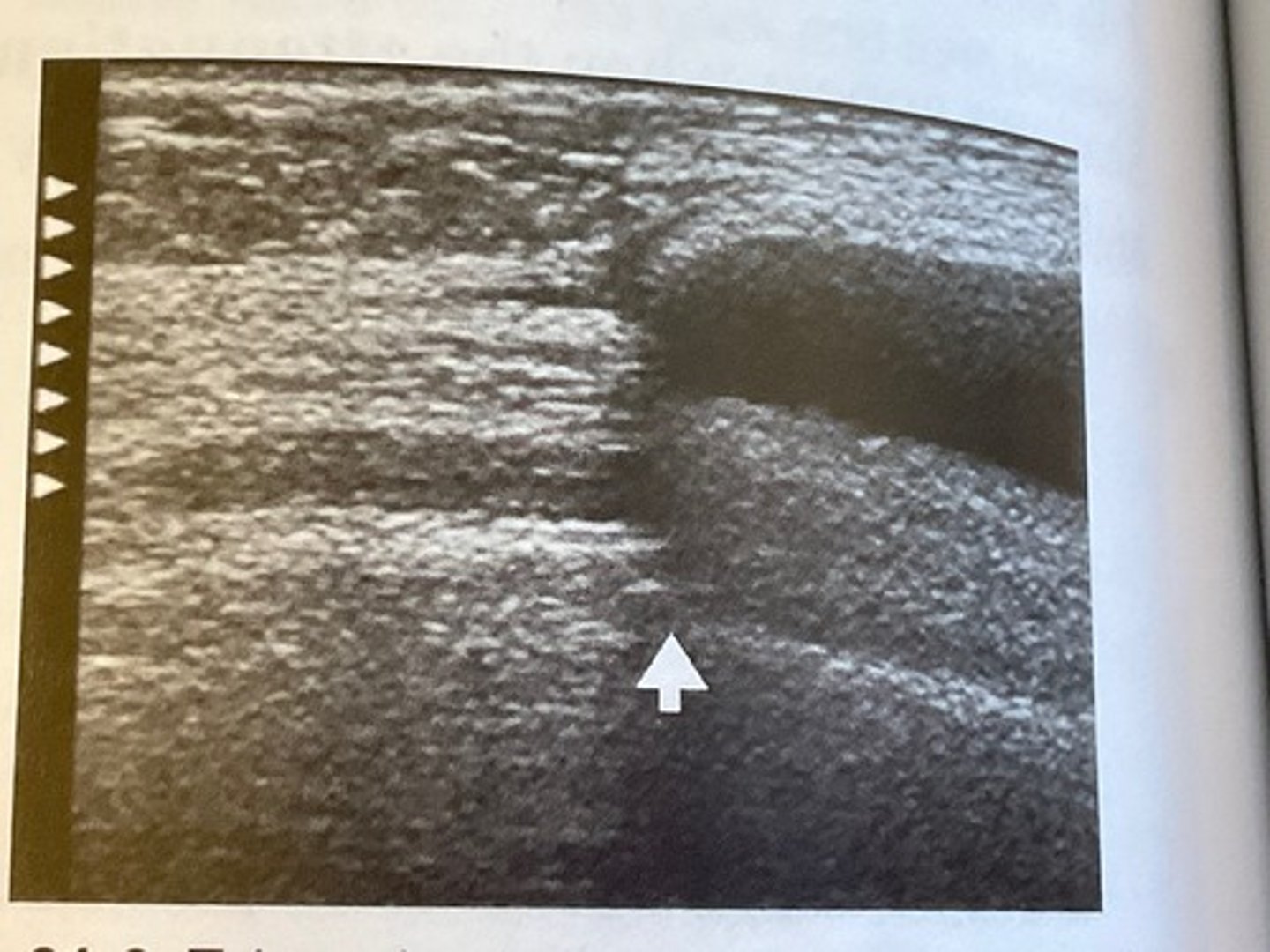
Edge shadow appears as a ___ region extending along the ___ of a ___ reflector
hypoechoic; edges; curved
Which assumption causes edge shadow?
the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
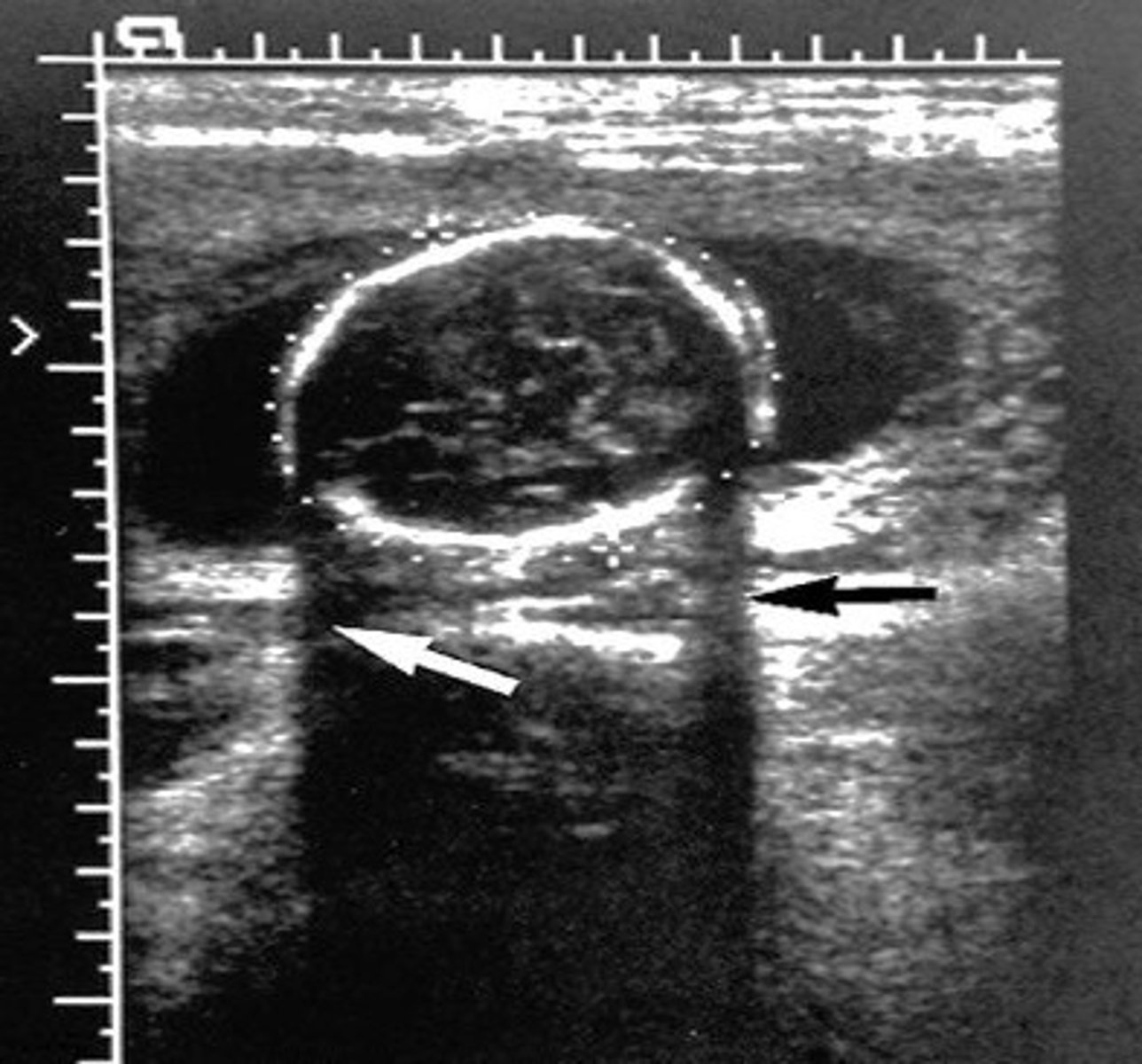
Enhancement occurs when sound travels through a ___ structure
weakly attenuating
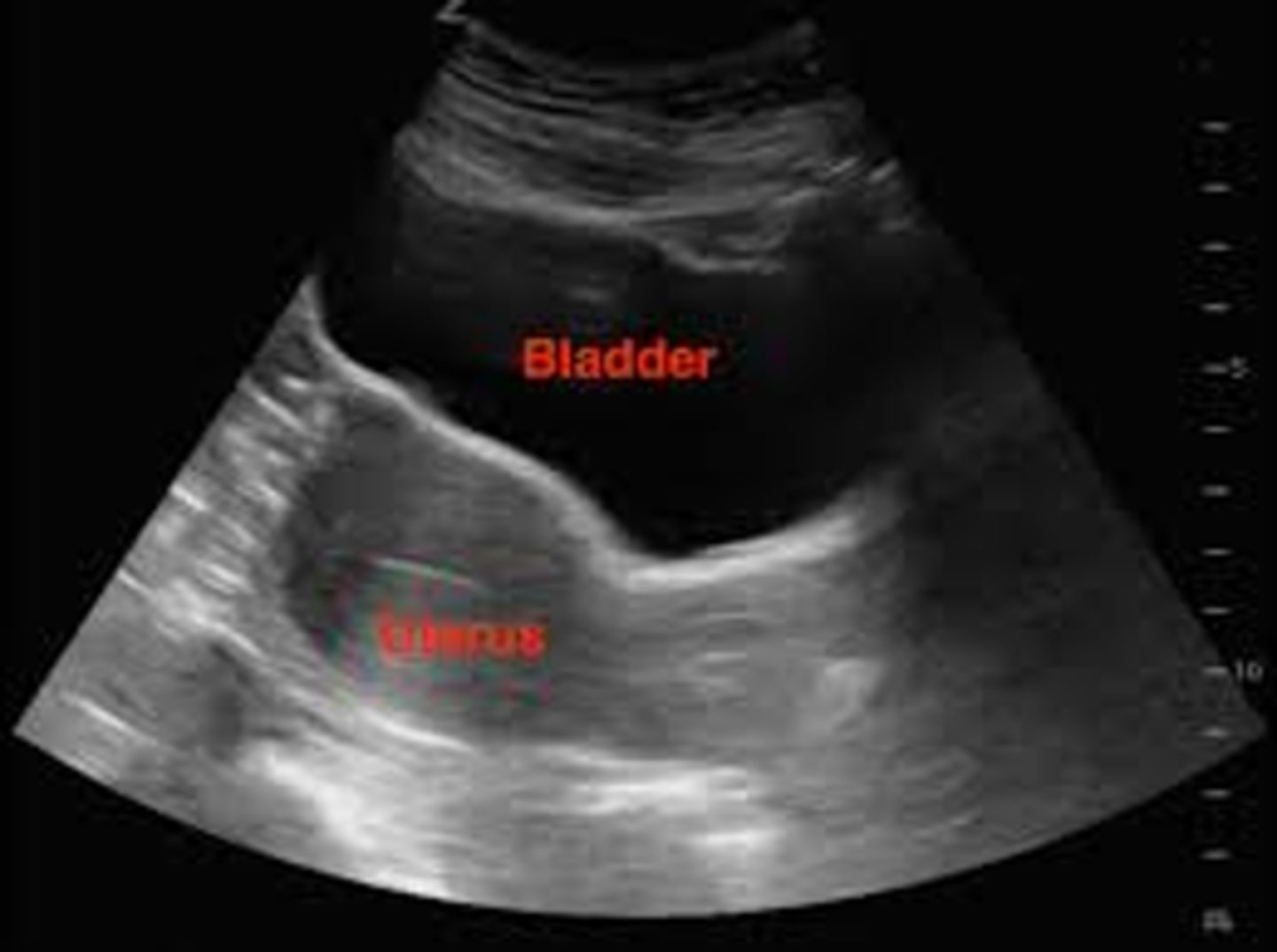
Enhancement appears as a ___ area beneath ___
hyperechoic; weak reflectors
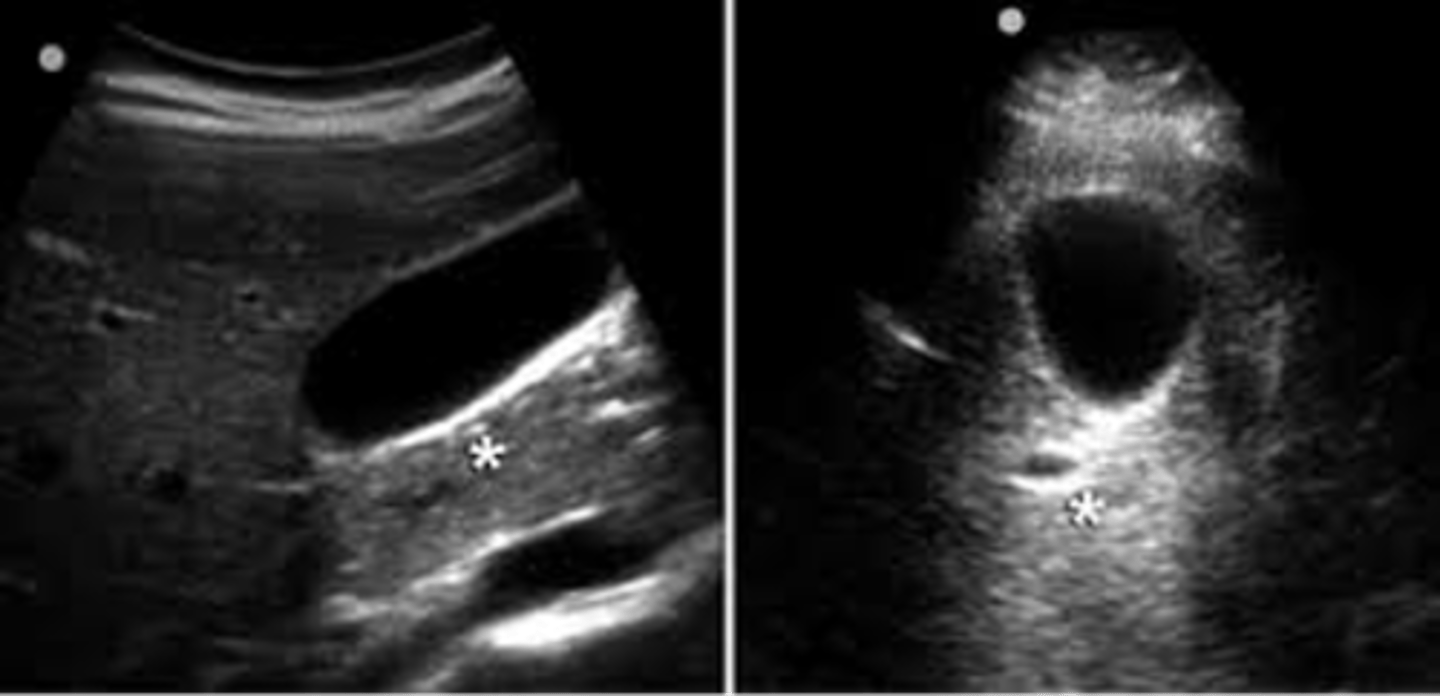
Weak reflectors are tissues with ___ attenuation
low
Enhancement is a ___ artifact
useful
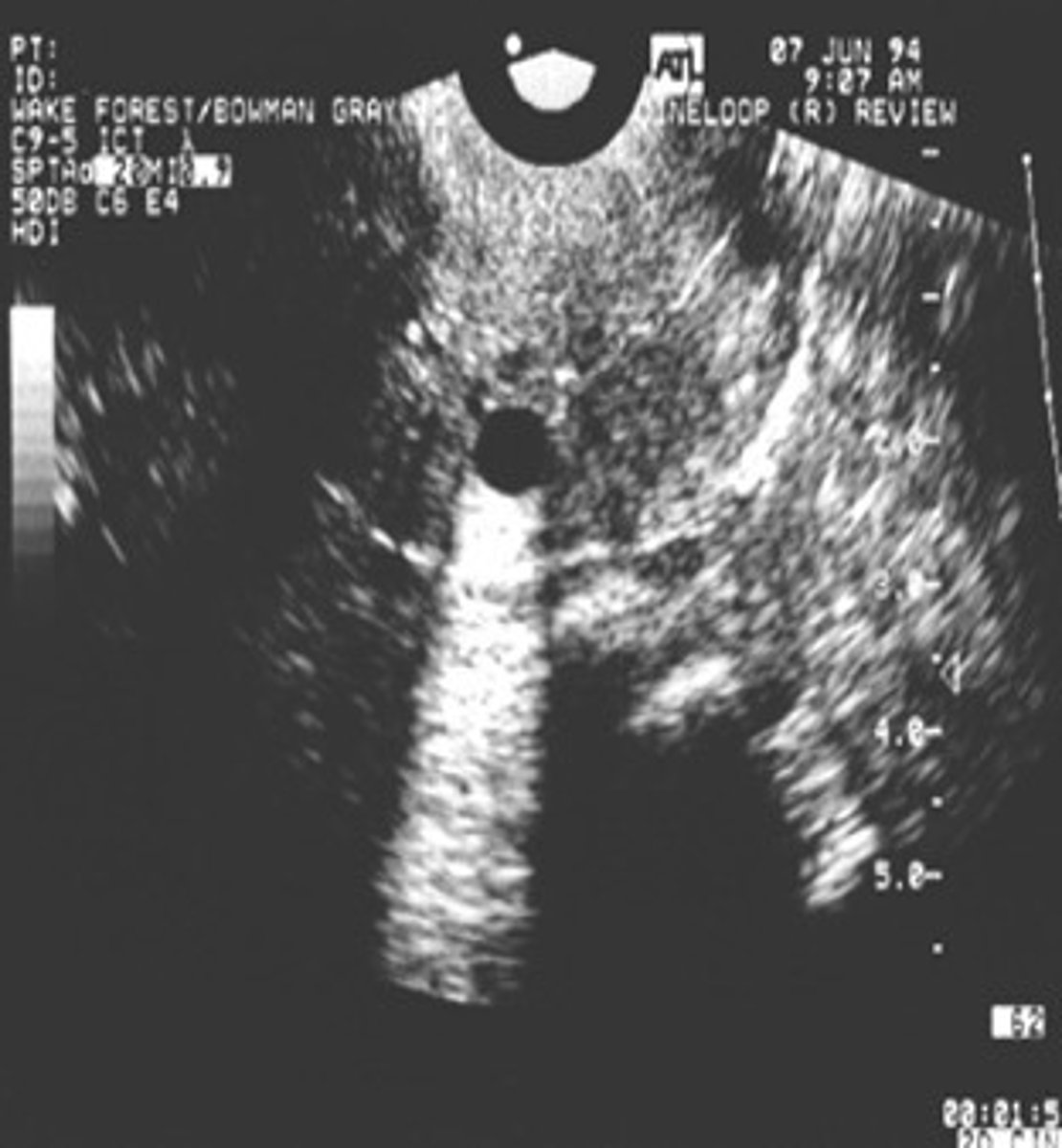
Which assumption causes enhancement?
the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
Focal enhancement is a ___ enhancement
side to side / horizontal
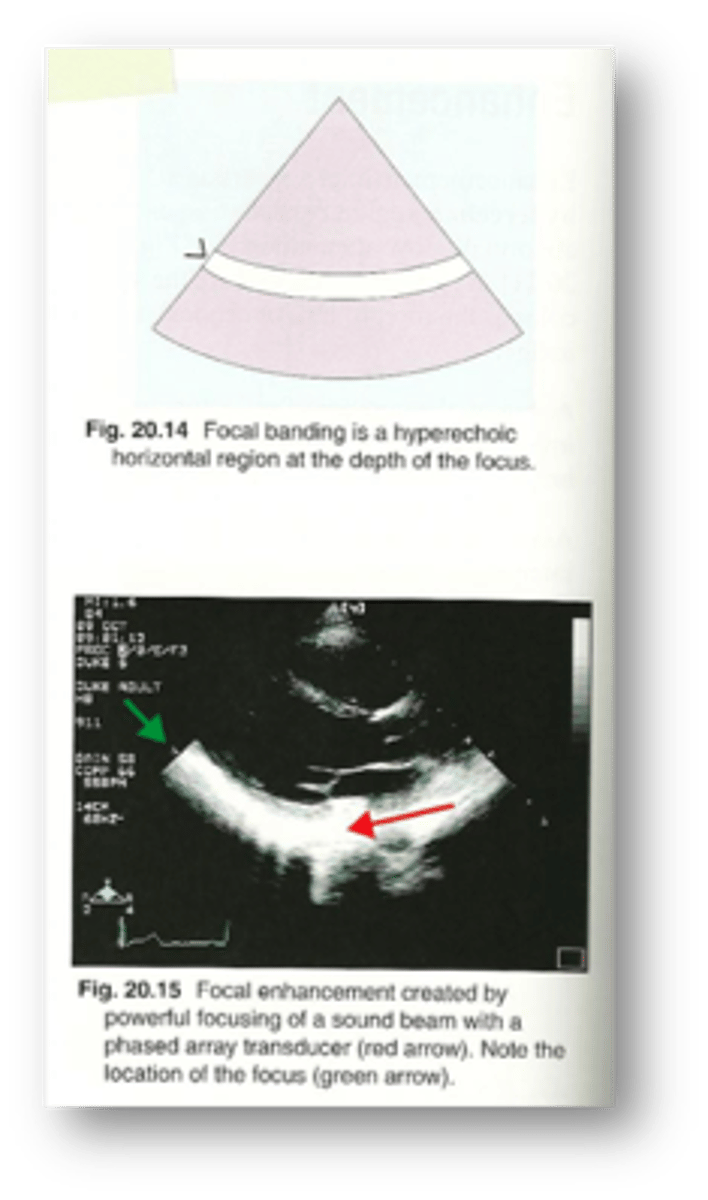
What is focal enhancement also called?
focal banding
Focal enhancement is caused by a ___ beam
strongly focused
When a beam is strongly focused, the ___ in the focal zone is increased
intensity
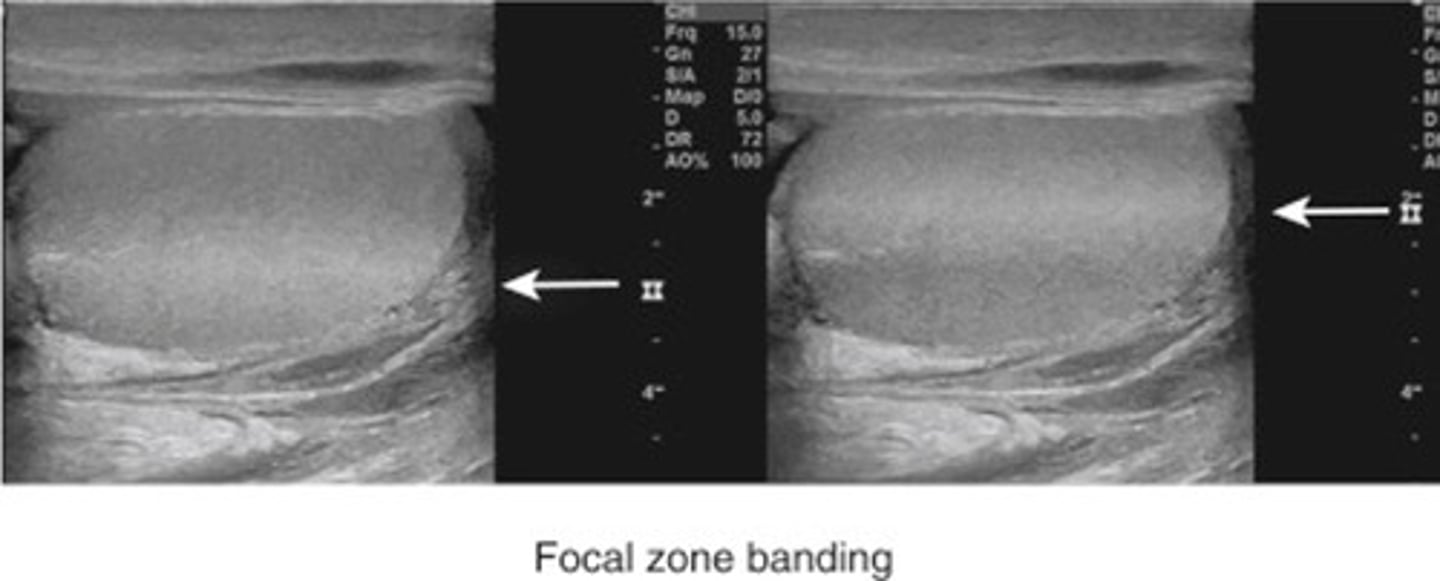
Which assumption causes focal enhancement?
the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
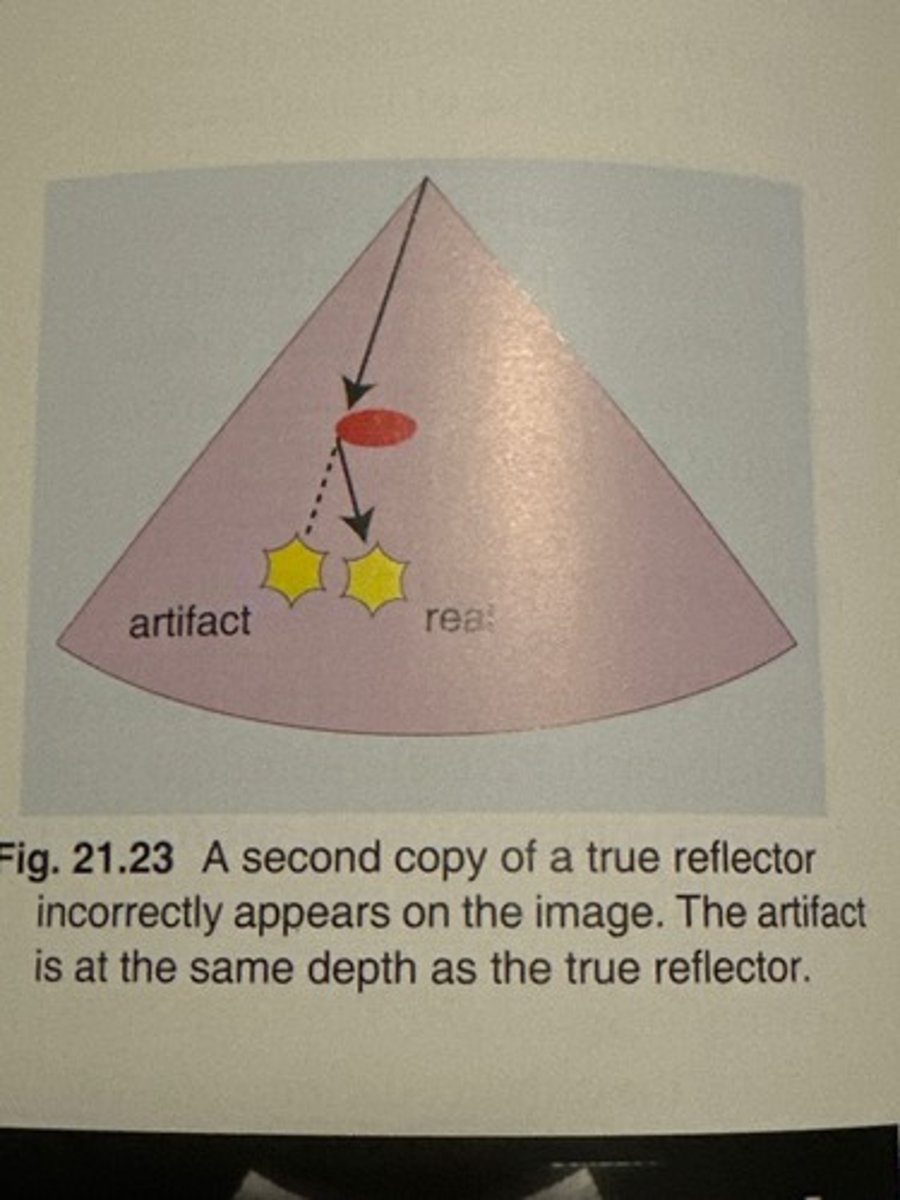
Mirror image is created when sound reflects off of a ___ and is ___ toward a ___
strong reflector; redirected; second structure
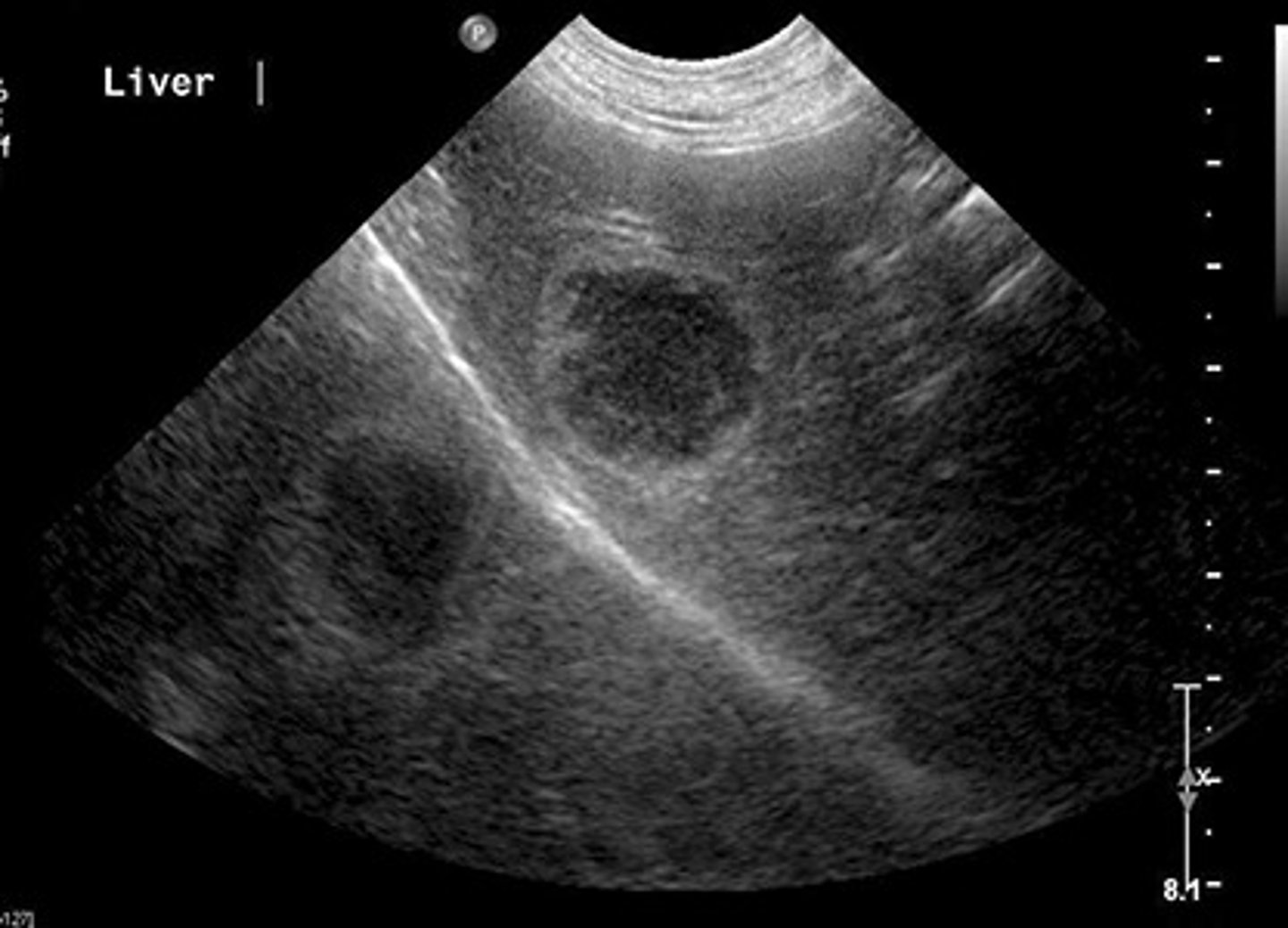
Mirror image artifact is located ___ than the real structure
deeper
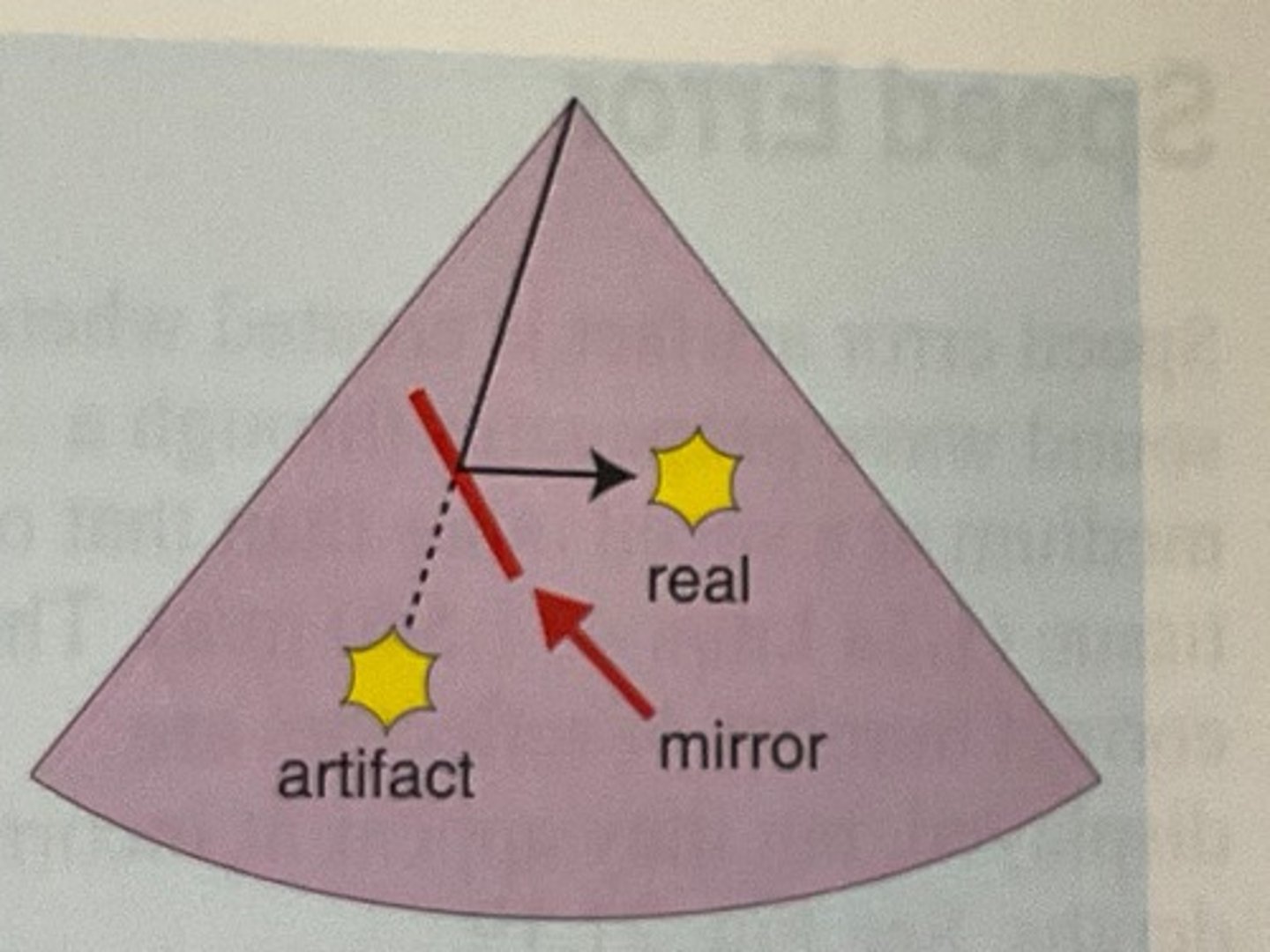
What is the mirror image artifact of spectral display?
crosstalk
Which assumption causes mirror image?
1. sound travels in a straight line
6. the strength of a reflection is related to the characteristics of the tissue creating the reflection
Multipath is created when sound pulses ___ off a ___ structure on the way to or from the ___ reflector
bounce; second; primary
Multipath is when the beam makes ___ changes in direction
2 or more
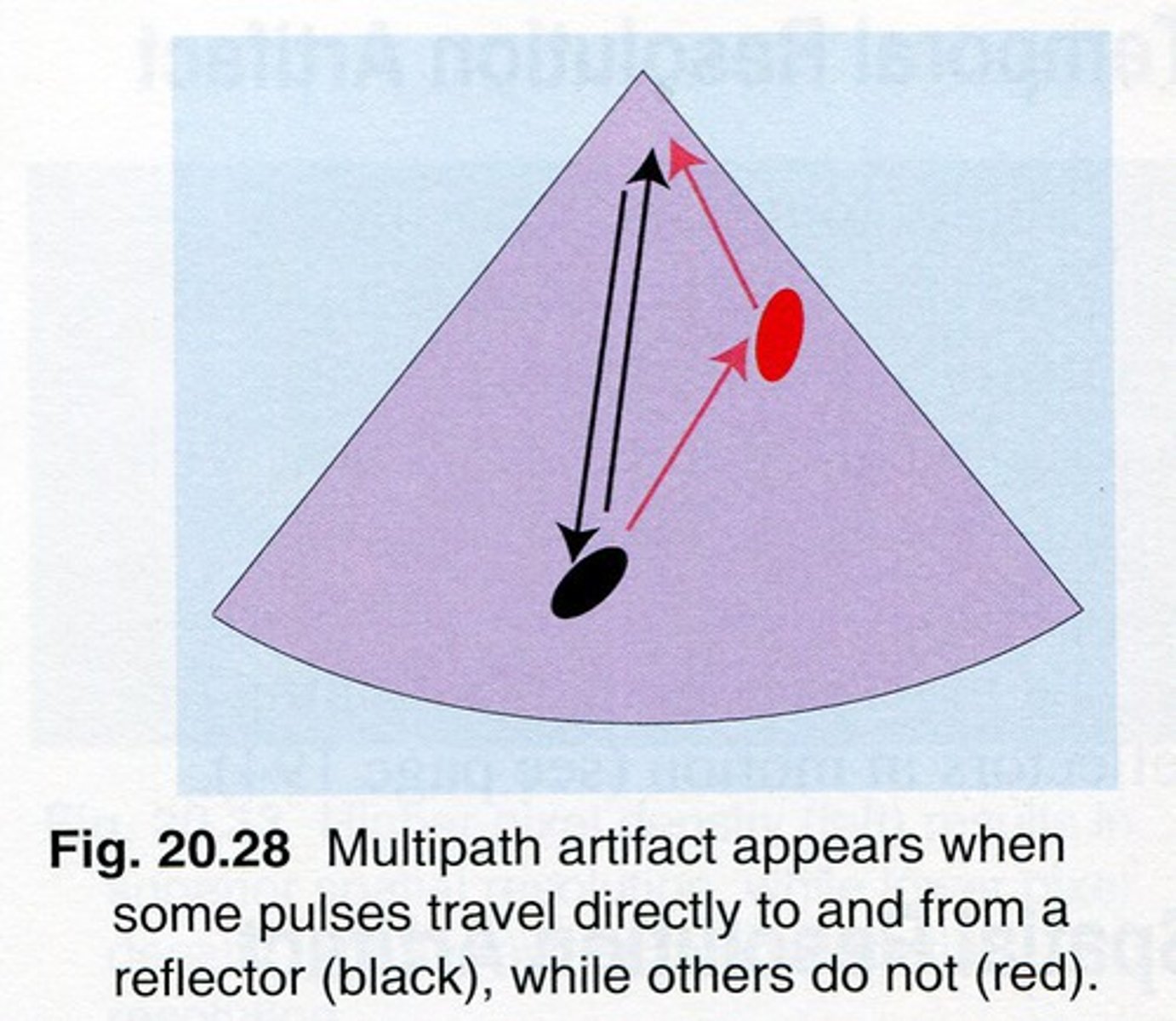
With multipath, the ___ path length differs from the ___ path length
transmit; receive
Multipath often results in ___, ___ changes that can not be identified on the image
subtle; nonspecific
Which assumption causes multipath?
2. sound travels directly to a reflector and back
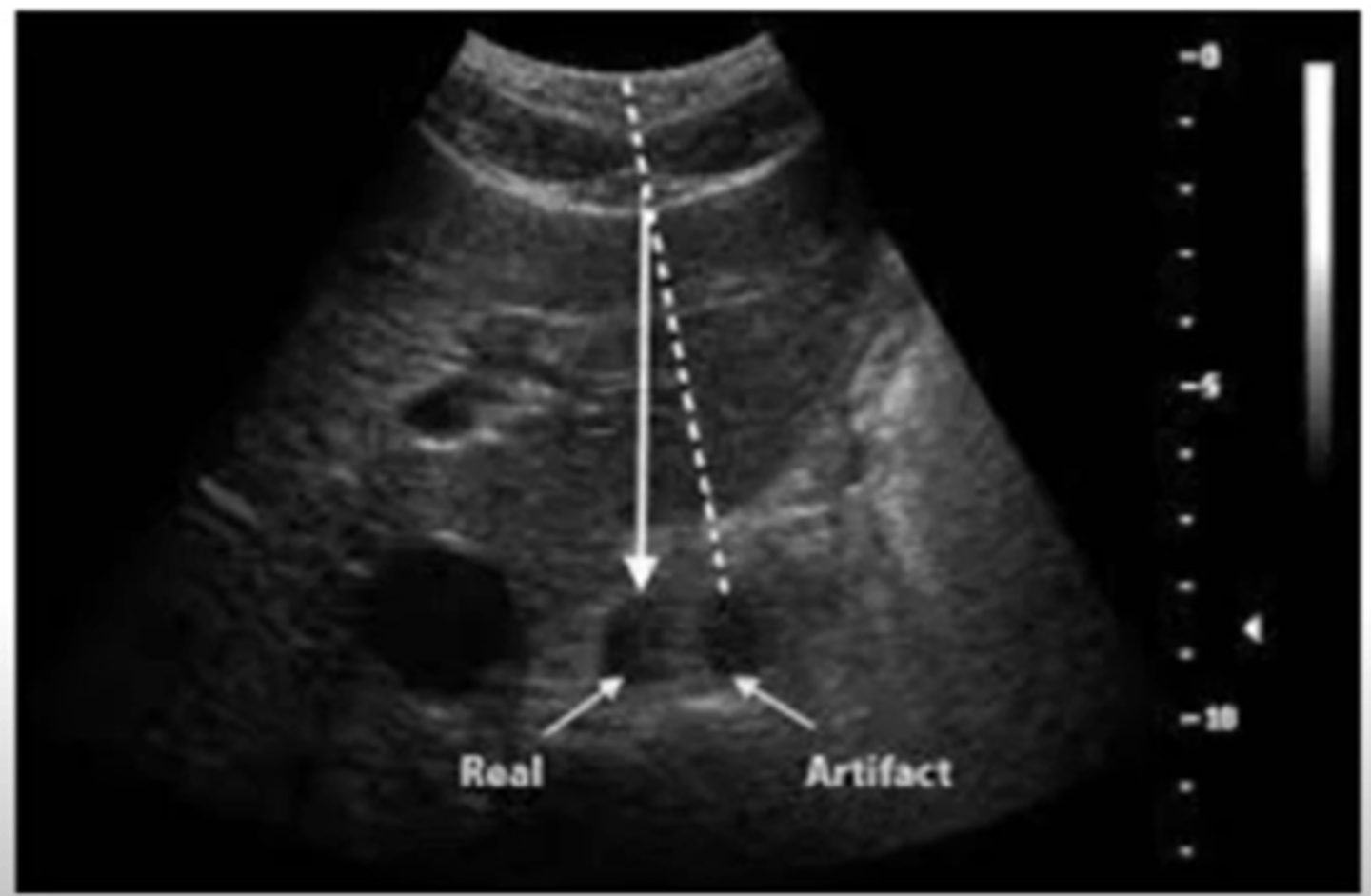
Speed error is created when a sound wave moves through a medium at a speed other than that of ___ (___)
soft tissue (1.54 km/s or 1540 m/s)
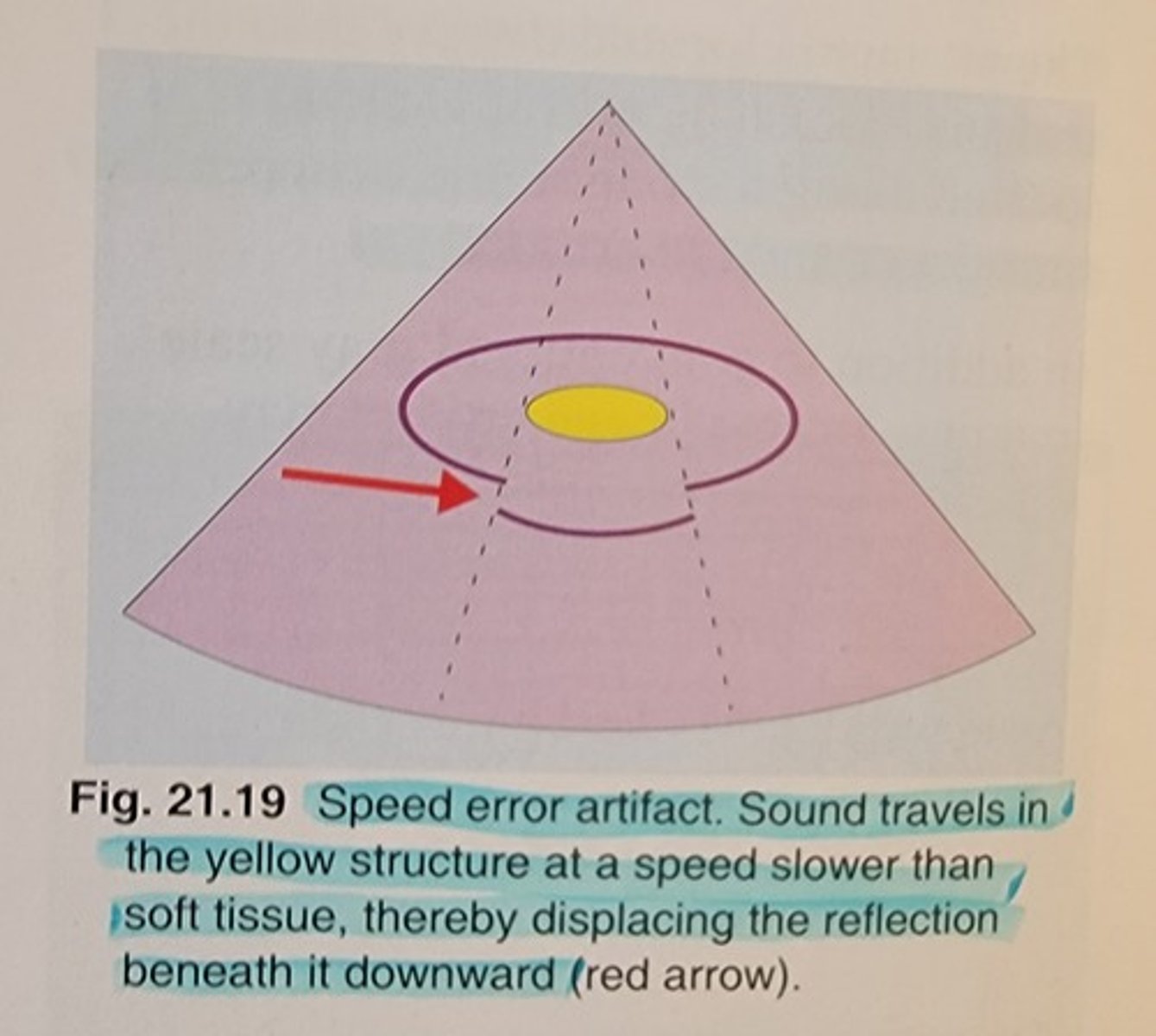
Speed error is created when a sound wave moves through a medium at a speed other than that of soft tissue (1.54 km/s or 1540 m/s).
The correct ___ of reflectors are displayed, but appear at incorrect ___
number; depths
Speed errors appear as a ___, as if structures are ___ or ___
step-off; split; cut
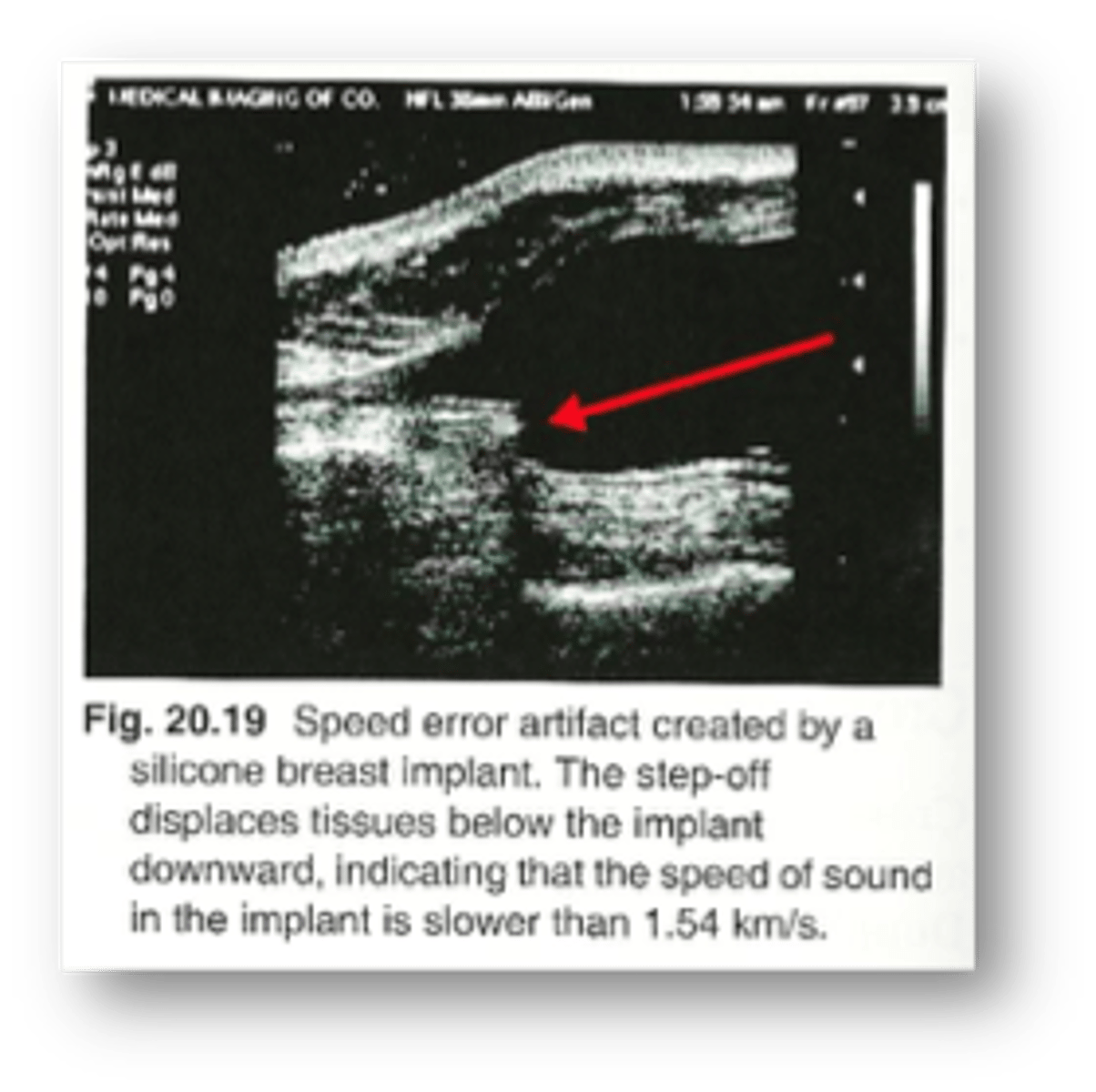
What is another name for speed error?
range error artifact
Which assumption causes speed error?
3. sound travels in soft tissue at exactly 1540 m/s
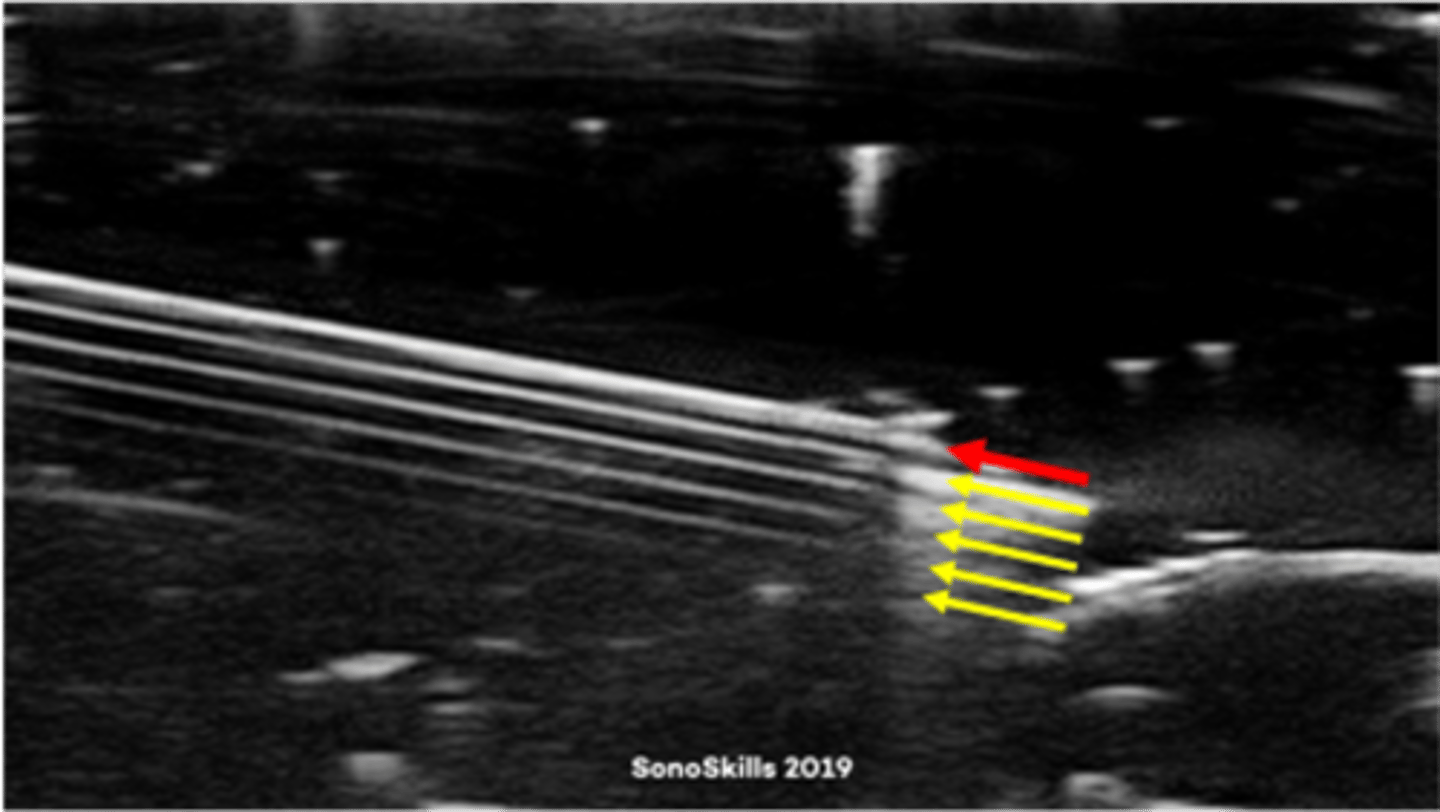
Lobe artifact appears when sound energy is ___ in a direction other than along the beam's ___
transmitted; main axis
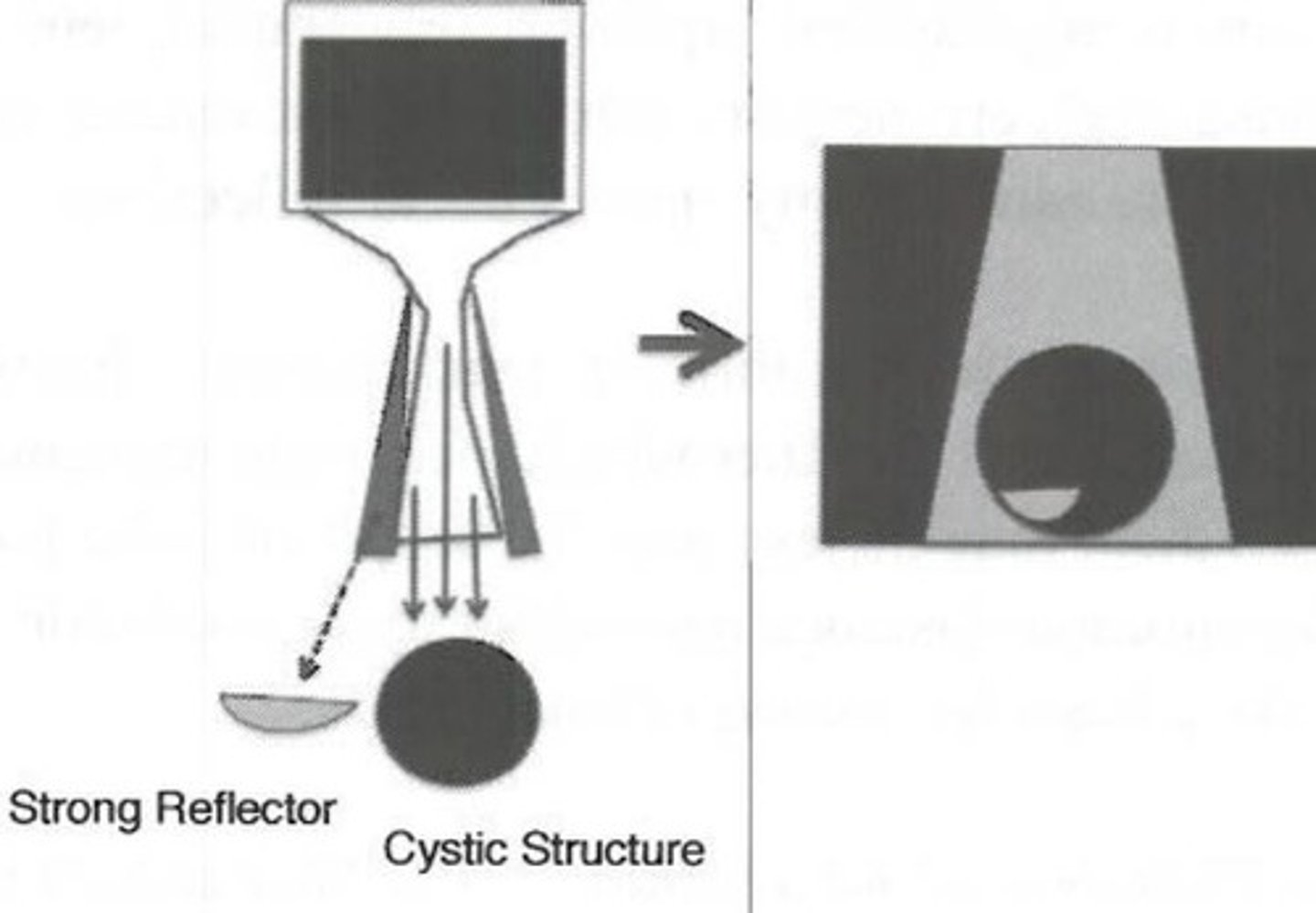
What does lobe artifact degrade?
lateral resolution
Lobes are created when a ___ is in the path of the ___
strong reflector; off-axis lobe
The lobe artifact and the true reflector are located ___
side by side
Which assumption causes lobes?
4. reflections arise only from structures positioned in the beam's main axis
What type of transducer causes side lobes?
mechanical
What type of transducer causes grating lobes?
array
What methods reduce lobes?
subdicing
tissue harmonics
apodization
What is subdicing?
dividing each PZT element into small pieces
What is apodization?
the process of reducing the strength of side and grating lobes- it alters the electrical spike voltages
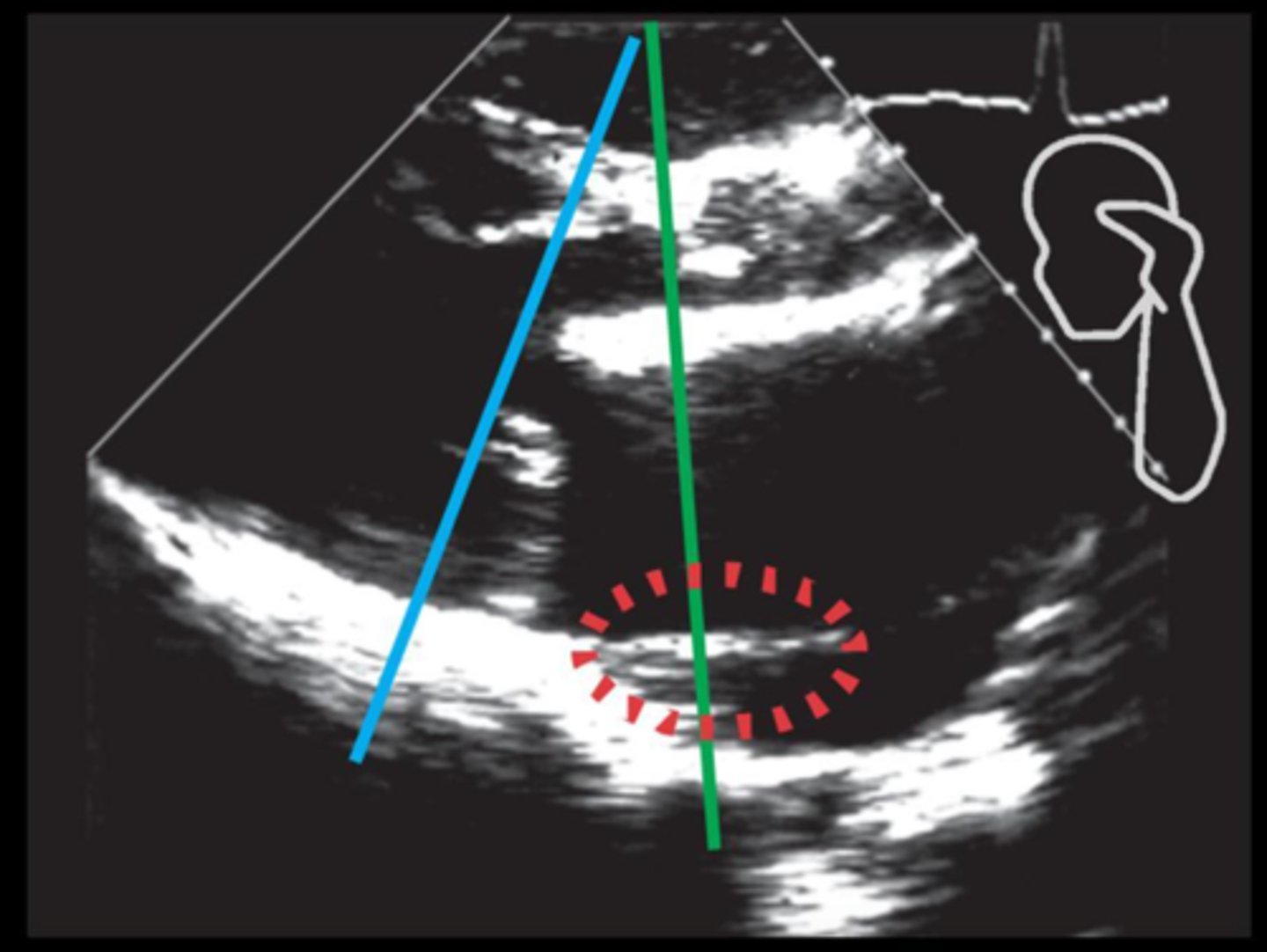
With slice thickness, reflections from structures ___ or ___ the ___ may appear in the image
above; below; imaging plane

Slice thickness is the result of the beam not being ___
razor thin
With slice thickness, ___ appear in the image as the beam slices through structures ___ to intended reflectors
unintended echoes; adjacent
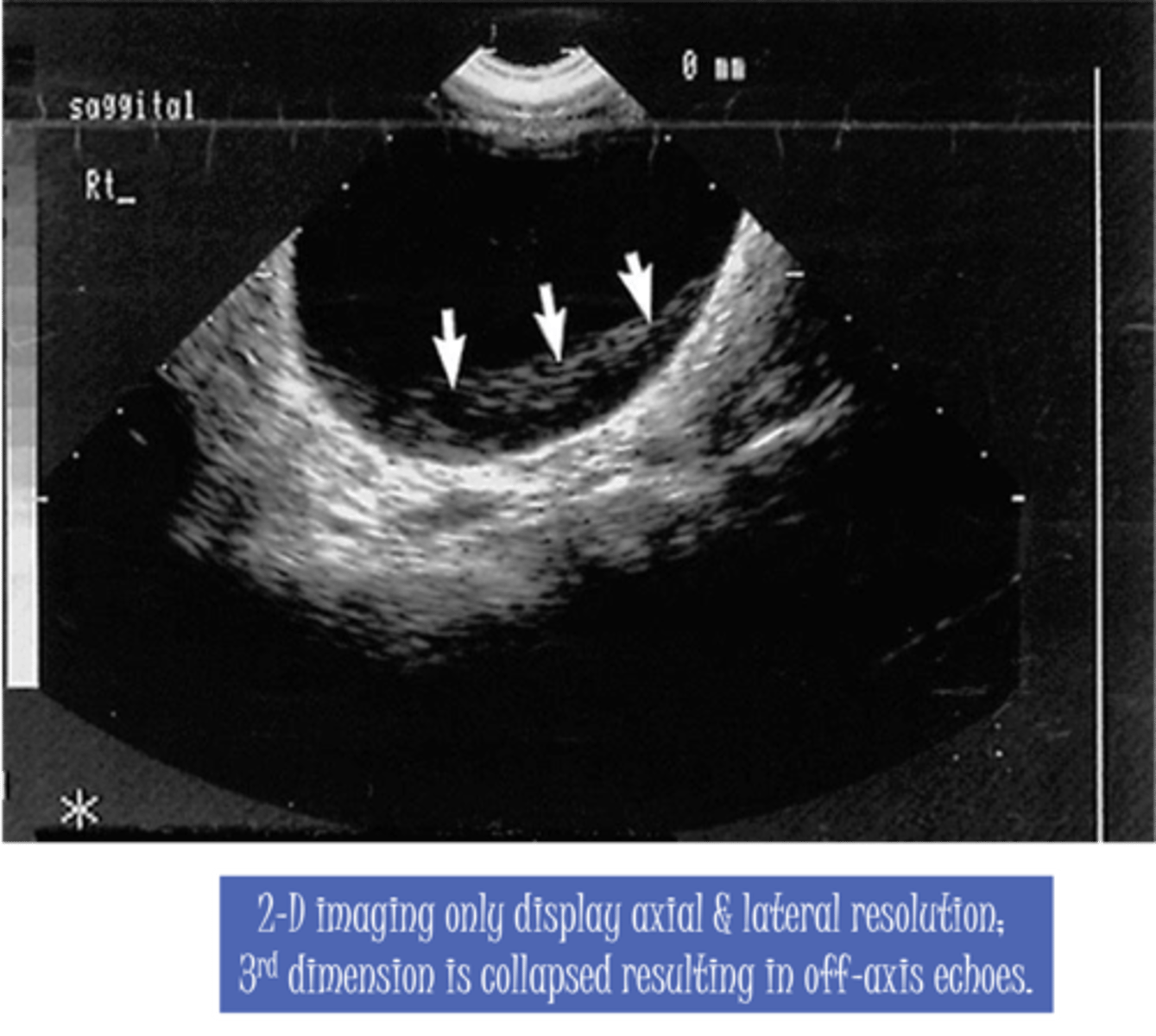
With slice thickness, cystic structures appear ___
filled in
How is slice thickness artifact reduced?
thinner imaging planes, such as those created by 1 1/2-dimensional array transducers
Which assumption causes slice thickness artifact?
5. the imaging plane is very thin
Lateral resolution artifact occurs when a pair of ___ reflectors are closer than the ___ of the sound beam
side by side; width
Lateral resolution artifact occurs when reflectors are ___ to the beam
perpendicular
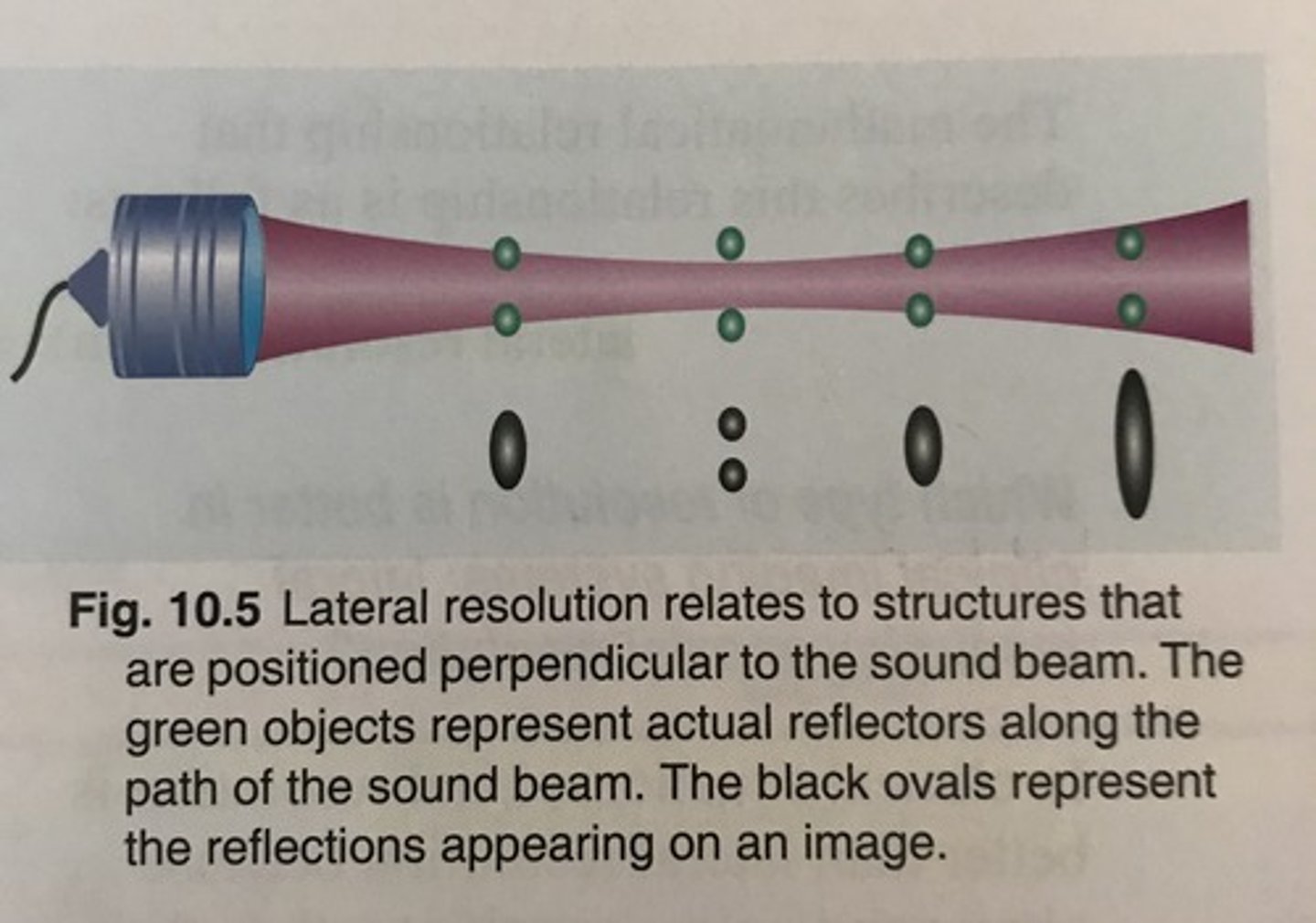
With lateral resolution, 2 objects appear as one ___ reflection on the image
horizontal
Axial resolution artifact is created when a long pulse strikes two ___ structures that are ___ of each other or ___ to the beam
closely spaced; in front; parallel
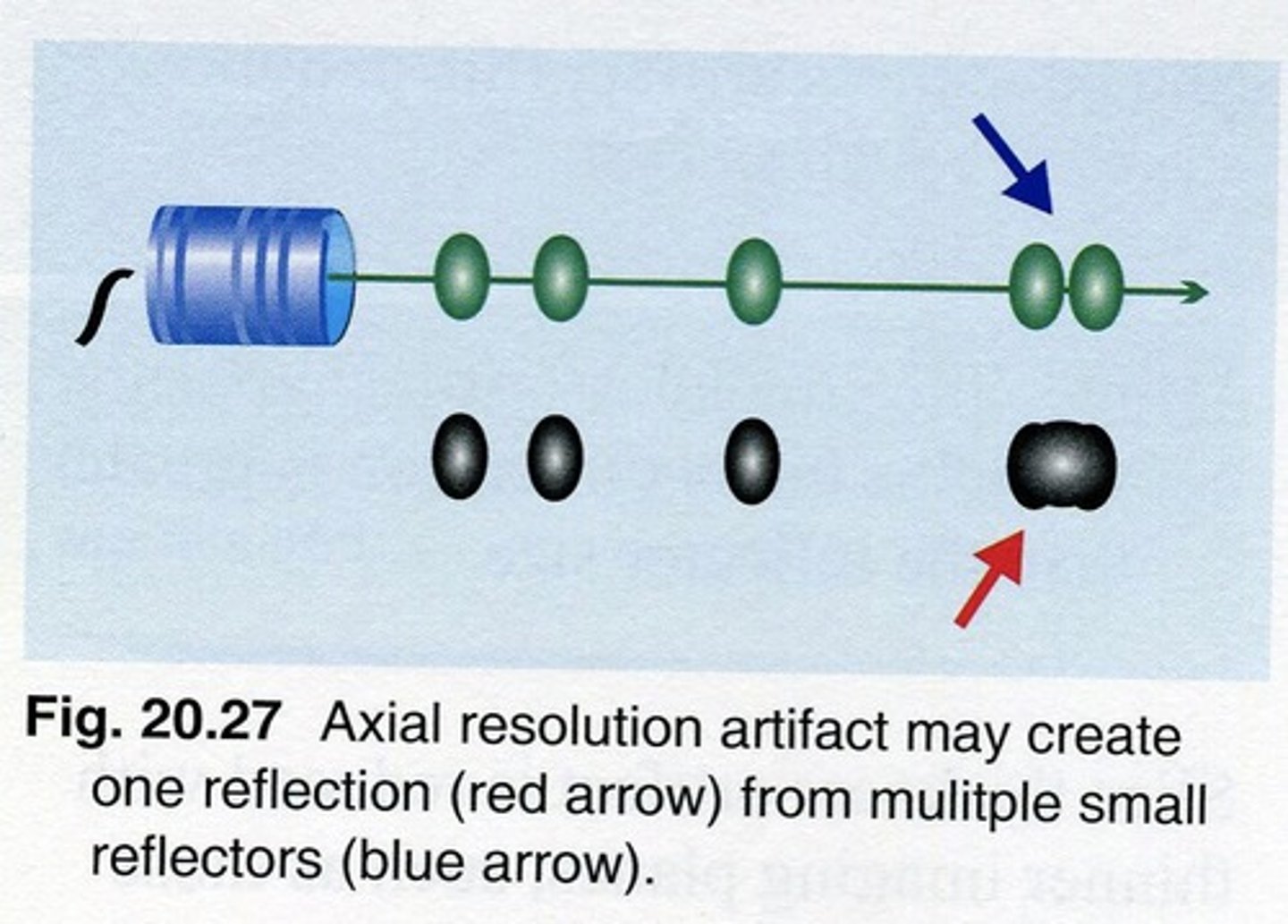
With axial resolution, 2 objects appear as one ___ reflection on the image
vertical
Curved and oblique reflectors are caused by a sound beam striking a ___
curved reflector
With curved and oblique reflectors, a portion of the ___ sound is directed ___ from the transducer
reflected; away
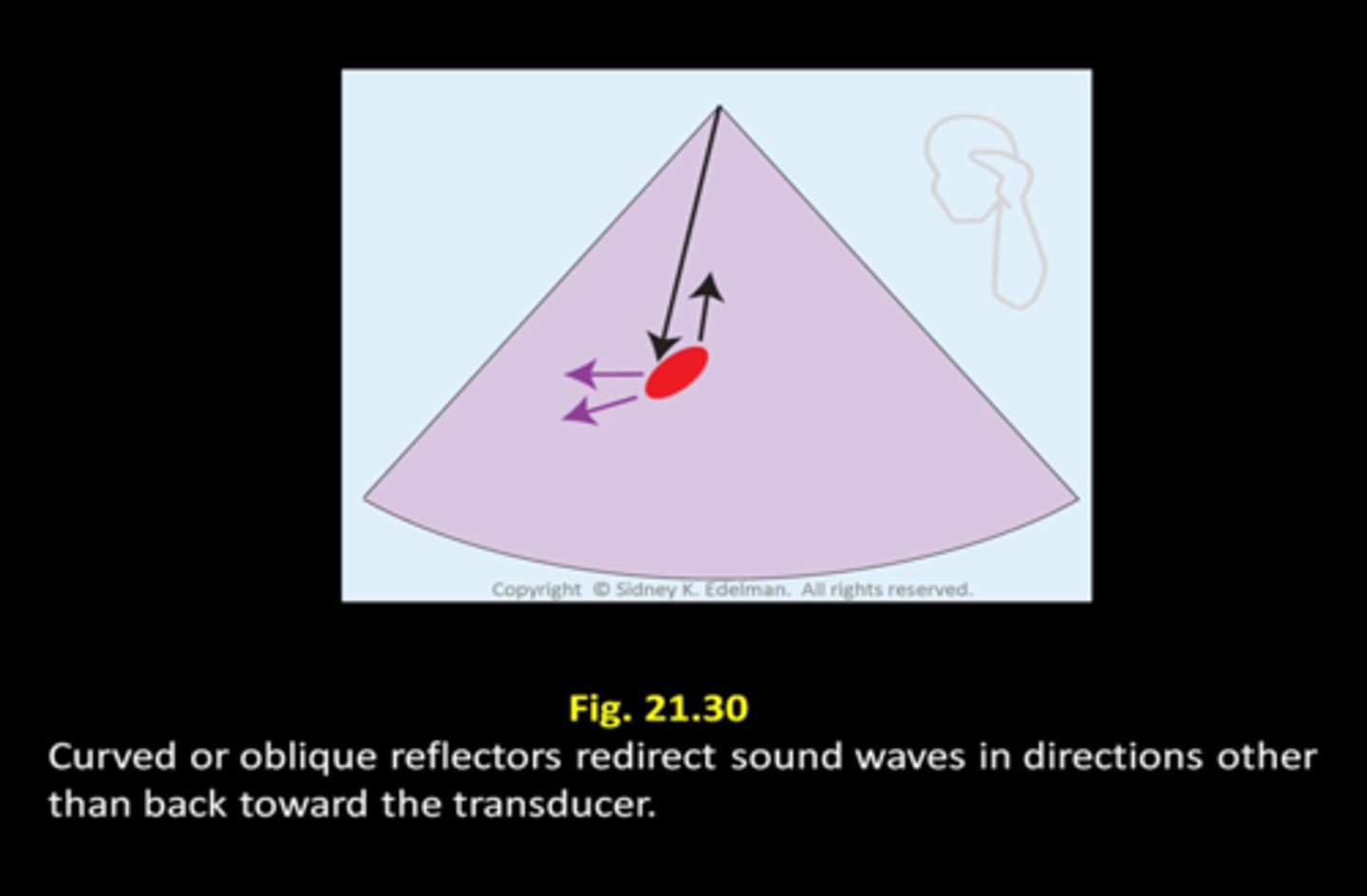
With curved and oblique reflectors, the received sound may be ___ intense than expected
less
What causes temporal resolution artifact?
slow frame rates
Poor temporal resolution results in less accurate ___ of ___
positioning; moving reflectors
What causes spatial resolution artifact?
low line density

Less reflector detail causes ___ spatial resolution
inferior
How do you correct spatial resolution?
use more line density or more pixels
How does noise appear?
as small amplitude echoes
What is noise caused by?
electrical interference
signal processing
spurious reflections
What is speckle caused by?
small amplitude waves interfering with each other
Speckle appears as tissue texture that does not directly correspond to ___
true anatomic scatterers
Speckle causes a ___ appearance of ultrasound images
grainy
What reduces speckle?
harmonic imaging
Clutter is a form of noise in ___
spectral doppler
Ghosting is a form of noise in ___
color doppler
Electronic interference is a ___ on display that appears as ___ moving bands
disturbance; arc-like
What is electronic interference caused by?
ultrasound machine being too close to unshielded electrical equipment