Chapter 13 - Properties of Solutions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Last updated 2:48 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Solutions
Homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances
2
New cards
Solute
Part being dissolved
3
New cards
Solvent
Thing that dissolves
4
New cards
Solvation
Dissolving process
5
New cards
Hydration
The dissolving process with water as the solvent
6
New cards
Substances depend on what to form solutions
Intermolecular forces and their natural tendency to mix
7
New cards
Solute-solute interactions
Must be overcome to disperse these particles when making a solution
8
New cards
Solvent-solvent interactions
Must be overcome to make room for the solute
9
New cards
Solvent-solute interactions
Occur as the particles mix
10
New cards
ΔH solvent
Energy required to vaporize
11
New cards
Solubility
How much solute can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature

12
New cards
Saturated solutions
Cant add more solute
13
New cards
Unsaturated solutions
Can add more
14
New cards
Supersaturated solutions
Temporary situation where the solution is cooled slowly and for it to react, a crystal from the solute is added
15
New cards
Factors that affect solubility
* Solute-solvent interactions
* Temperature
* Pressure (for gas solutes only)
* Temperature
* Pressure (for gas solutes only)
16
New cards
pressure effects on solids and liquids
the solubility isn’t affected
17
New cards
pressure effects on gases
Solubility is affected by pressure
18
New cards
Henrys Law
The solubility of a gas is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the solution

19
New cards
Henry’s Law for two points
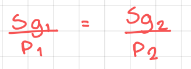
20
New cards
Temperature effects on solid’s solubility
for most solids, as temperature increases, solubility increases
21
New cards
Temperature effects on gases’s solubility
As temeprature increases, solubility decreases
22
New cards
Mass percentage (% m/m)
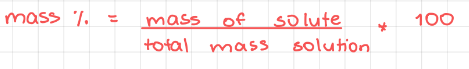
23
New cards
Parts per million (ppm)
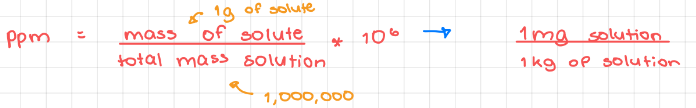
24
New cards
Parts per billion (ppb)

25
New cards
Mole fraction (X)

26
New cards
Molarity (M)

27
New cards
Molality (m)

28
New cards
Colligative properties
They depend only on the quantity, not on the identity of the solute.
29
New cards
what are the colligative properties
vapor pressure reduction
boling point elevation
freezing point depression
osmotic pressure
boling point elevation
freezing point depression
osmotic pressure
30
New cards
Vapor pressure reduction (Raoult’s Law)

31
New cards
Boiling point elevation
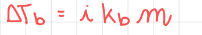
32
New cards
i
Van-Hoff factor, the number of ions you get when dissolving the compound
33
New cards
Freezing point depression

34
New cards
Osmosis
The net movement of solvent molecules from a solution of low to a high concentration of solute across a semipermeable membrane
35
New cards
Semipermeable membrane
Smaller particles pass through it, but it blocks larger particles
36
New cards
Osmotic pressure
The applied pressure to stop bigger particles

37
New cards
Colloids
Suspension of particles larger than individual ions or molecules, but too small to be settled by gravity.