Unit 5- Work, Energy, Power, Momentum, Impluse
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is Work?
What is the formula?
what are its Units?
Is it a Scalar or a Vector?
Work is how much energy (J) is applied to something
W = Fd
The Units for work is Joules (J) cus Fd = Nm
Work is a SCALAR
How can you tell if no work is done?
If the displacement is 0 (lifting something up and bringing it back down to initial point)
What are the 3 conditions for Work?
A force must be exerted on an object (F)
The object must be displaced by the force (Δd)
At least part of the force must be in the same direction as displacement
What is Work Proportional to?
Work is basically proportional to the two Units in its formula:
W = FD
W is proportional to F (force)
W is proportional to D (displacement)
Who do you calculate Work for when something is pulled at an angle?
Basically find the horizontal (x-axis) Force/movement of the pulled object
—> Will depend if it is Force or Displacement based on the Q

Name all metric conversion prefixes and symbols from 10^1 to 10^12(yes you need to go that high)
*WHAT ARE THE SYMBOLS FOR EACH???*
10^1 = deca (da) - remember this
10^2 = hecto (h)
10^3 = kilo (k)
10^6 = mega (M) - becomes a capital letter
10^9 = giga (G) - becomes a capital letter
10^12 = tera (T) - becomes a capital letter
Note: all units from 10^3 to 10^12 follow computer storage (kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, terabyte)
Name all metric conversion prefixes and symbols from 10^ -1 to 10^ -12
*WHAT ARE THE SYMBOLS FOR EACH???*
10^ -1 = deci (d)
10^ -2 = centi (c)
10^ -3 = mili (m)
10^ -6 = micro (μ)
10^ -9 = nano (n) - haha like ipod na-no
10^ -12 = pico (p)
What is Momentum?
What is the formula?
what are its Units (what MUST you not forget)?
Is it a Scalar or a Vector?
Momentum a quantity of movement of smth
P = mv, yes P is used to rep Momentum
the Unit is kg x m/s
DO NOT mistake this for accelerate and write N
Momentum is a VECTOR
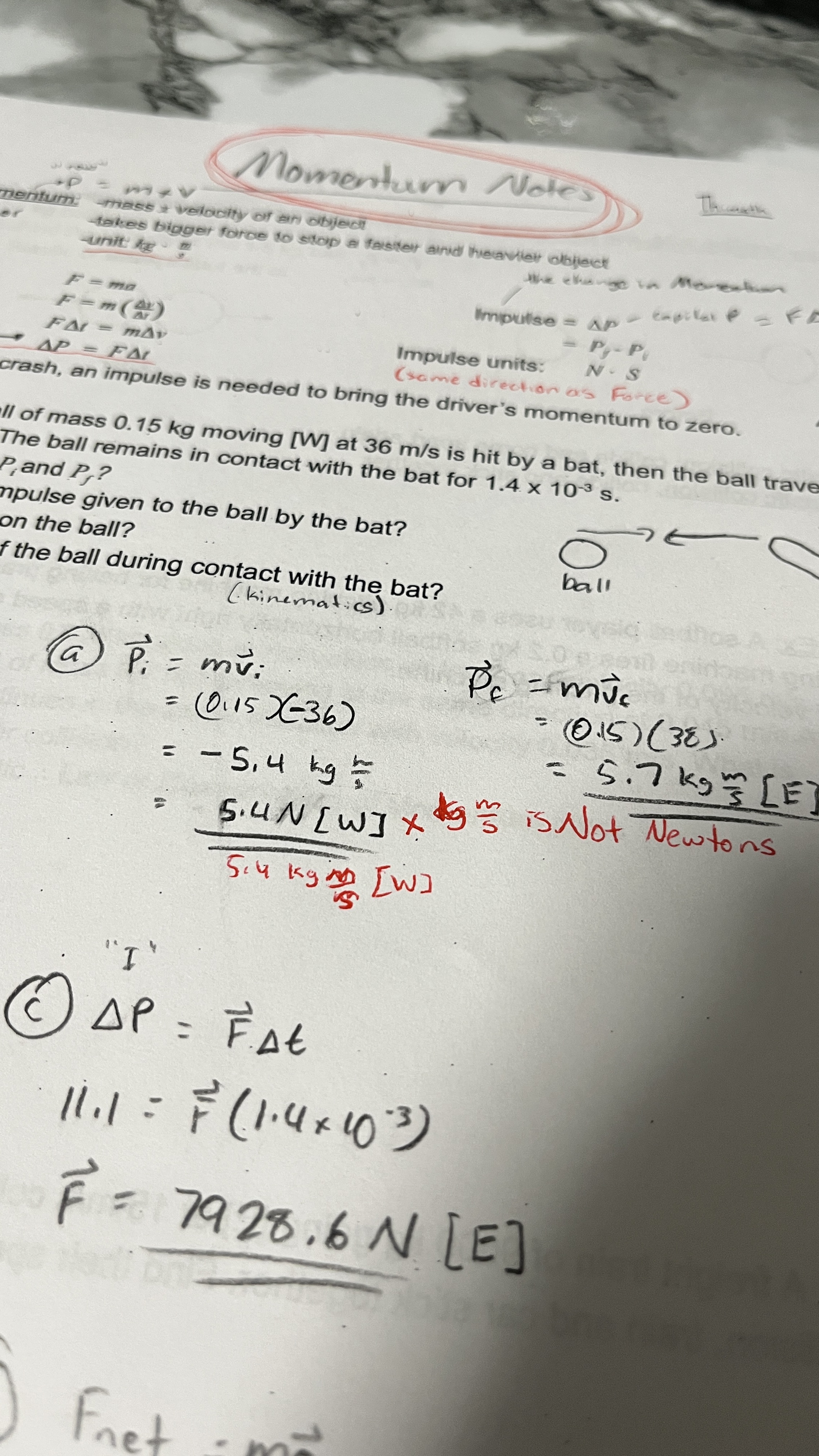
What is Impulse?
What is the formula?
what are its Units?
Is it a Scalar or a Vector?
Impulse is the change in Momentum (ΔP)
impulse is ΔP = Pf - P i
The units are Ns
Impulse is a VECTOR (will be in same direction as Force given in the Q)
What is the Law of Conservation of Momentum?
The Law of Conservation of Momentum = total P (momentum) in an isolated system remains constant
(Pin = Pout)
How can you identify an Elastic Q?
What are some examples?
What is the formula???
Elastic Q = collide and come apart again (or everything that does not get stuck together after a collision🤯)
EX: ball bounces off a table, bullet getting shot (gun and bullet both move), or faster object moving in same dir as a slower object hits the slow object and speeds it up 😳
The formula is: m1v1o + m2v2o = m1v1f + m2v2f
How can you identify an Inelastic Q?
What is the formula???
Inelastic Q = collide and then stick together (usually “sticks“ is said in the Q)
Formula is: m1v1o + m2v2o = (m1+ m2)vf
Since velocity is a vector, what should you put for the direction if no compass dir is given?
Say left/right or up/down if compass directions like north/south or east/west are not given
—> Usually in the Q, it will say right/left or compass directions and that is what you’ll use in the answer.
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only change from one form to another, but the total amount of energy in the universe is conserved.
What are the formulas for:
Kinetic Energy (KE)
Potential Energy (PE)
Total Mechanical Energy (ME or Etotal)
KE = 1/2mv² —> v² = vo² + 2ad
PE = mgΔh
ME or Etotal = PE + KE = mgΔh + 1/2mv²
What 3 things should you remember about Kinetic Energy (KE) and Potential Energy (PE) when dropping something?
What MUST you remember about Total Mechancial Energy?
Before you drop it KE = 0, and PE = mass x 9.8 x height
When you drop it, at a specific point, KE = ½ mv² where you use the kinematic formula v² = vo² + 2gd, where d= distance the thing has fallen from the start point.
PE = mass x 9.8 x height remaining to the ground
TOTAL ENERGY = PE + KE
On the ground, PE = 0, and KE will be total height (basically right before touching ground)
—> Total mechanical energy is always KE + PE so it remains the SAME no matter where the rock is falling (PE before drop = total ME during drop cus KE = 0 before dropping)
What is N = ?
What is p = ?
What is ΔP = ?
What is W =?
N = kg m/s²
p = kg m/s
ΔP = N s (multiplication)
W = Joule
What is Power?
Is it a vector or scalar?
What is the general formula?
What are the 3 specific formulas?
Power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is used.
Power is a SCALAR
The general formula is work(J)/ΔT OR energy (J)/ ΔT
The 3 specific formulas are:
P= W / ΔT or P= E / ΔT
P = mgd / ΔT OR mad / ΔT
P = F Vav OR P = maVav
What is a Watt?
1 Watt (W) = 1 Joule/second (J/s)
What are 6 applications of LCE (Law of Conservation of Mass)
Gas car needs to burn fuel to move
You need energy form food to move
To lift a box: increases box’s PE
Energy in a machine (dishwater, washing machine)
Harmonic oscillator
Whole universe (including dark energy)