EKG rhythms
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
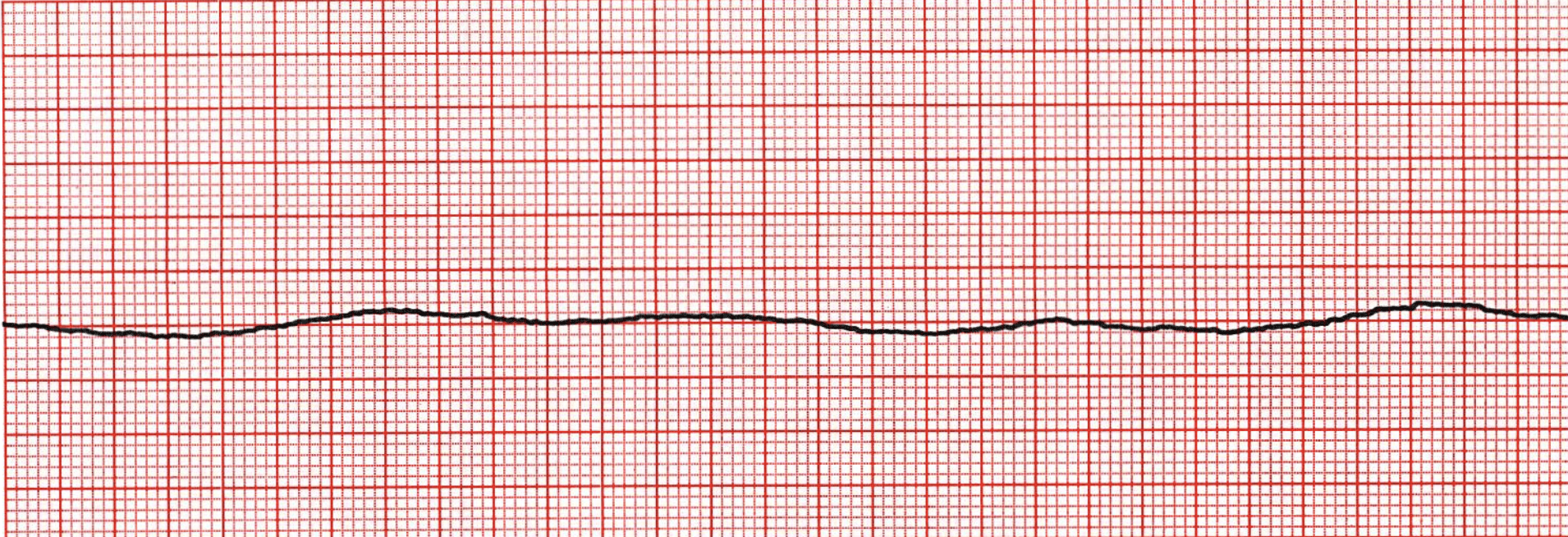
asystole
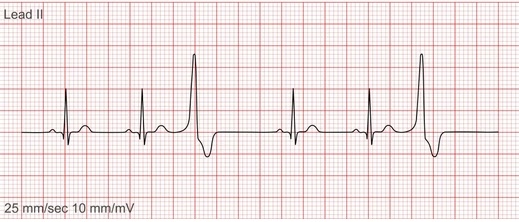
normal sinus rhythm
-P wave for every QRS
-PR: 0.12-0.2
-QRS: 0.04-0.1
-QT: 0.4
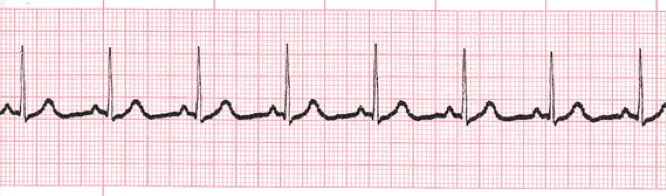
PVCs (premature ventricular contractions)
Extra, abnormal heartbeats that begin in one of the heart's two lower chambers.
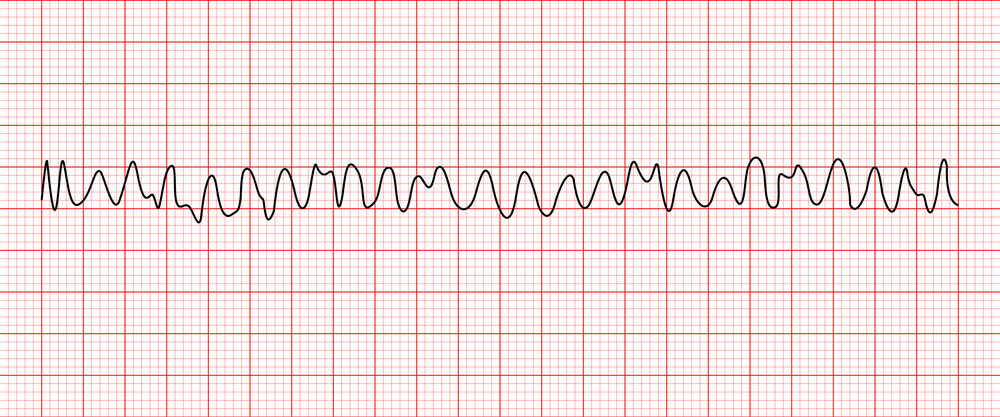
Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib)
With this irregular heart rhythm, your heart's lower chambers (ventricles) beat in an erratic way. They quiver or twitch instead of expanding and squeezing.
V-fib = D-fib (you want to shock this rhythm)
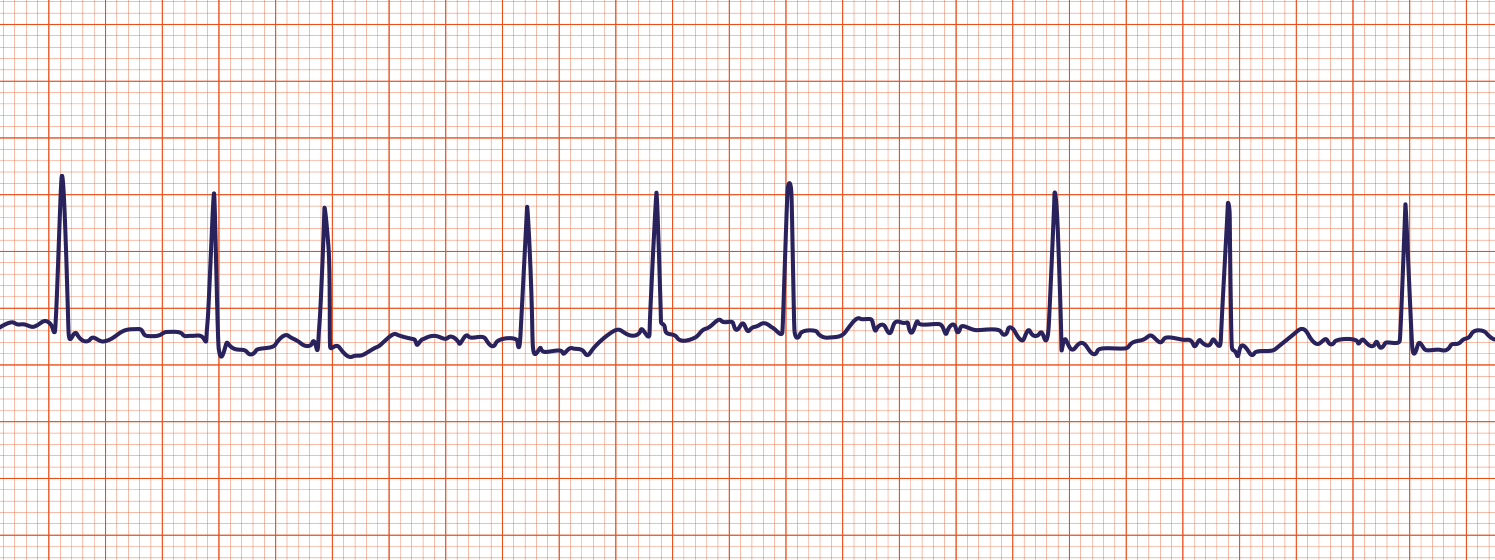
Atrial Fibrillation (A-fib)
An irregular, often rapid heart rate that commonly causes poor blood flow.
The heart's upper chambers (atria) beat out of coordination with the lower chambers (ventricles).
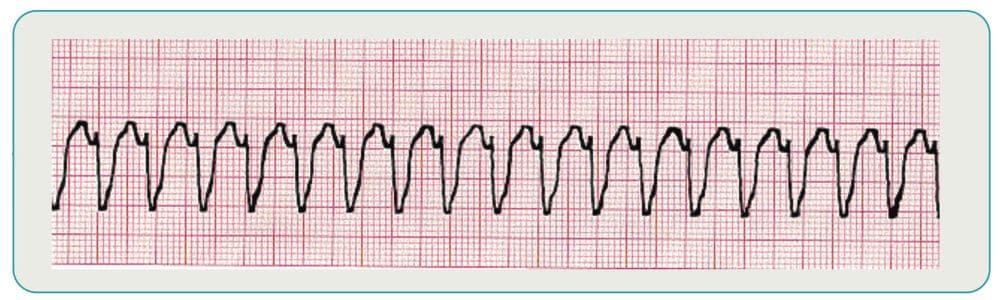
ventricular tachycardia
No P waves, wide QRS.
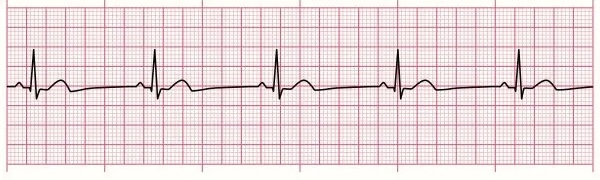
Sinus bradycardia
similar to NSR but slower. common in some athletes. HR<60bpm.
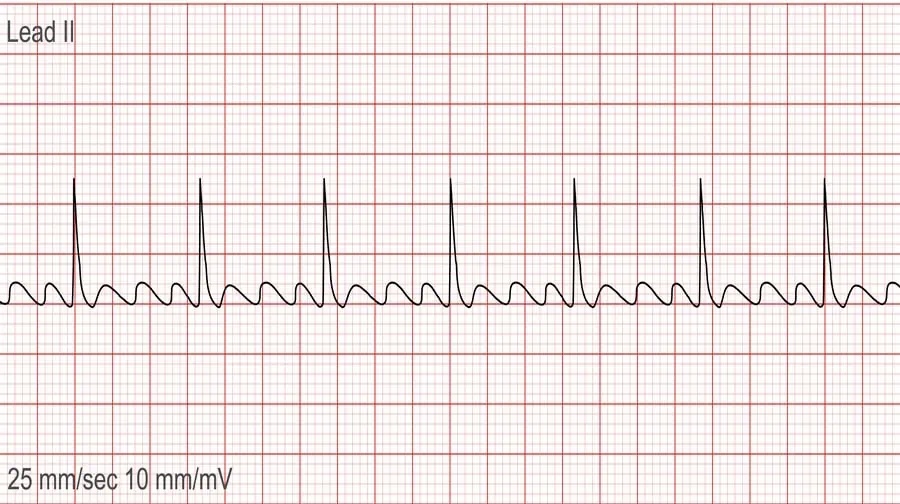
Atrial flutter
A condition in which the heart's upper chambers (atria) beat too quickly.
Rapid contractions of the upper chambers of the heart may spread to the lower chambers, resulting in rapid heartbeats.
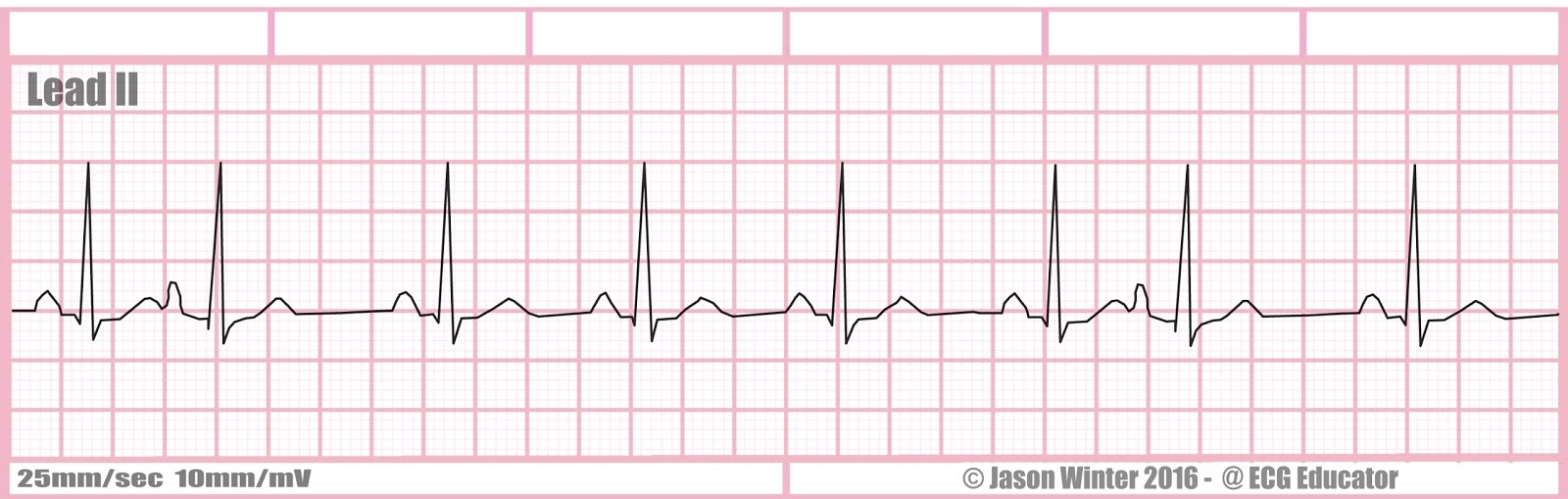
PACs (premature atrial contractions)
A premature atrial contraction (PAC) is an extra heartbeat that originates in the atria (upper chambers of the heart) and disrupts the normal heart rhythm.
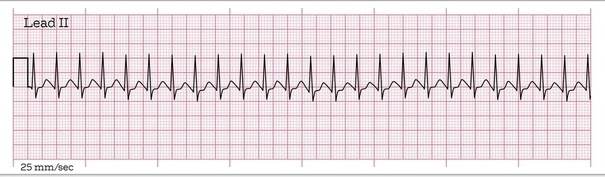
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
Rhythm is regular, rate is 180. P-wave is buried in the preceding complex, PR is unmeasurable, QRS is 0.07 seconds.
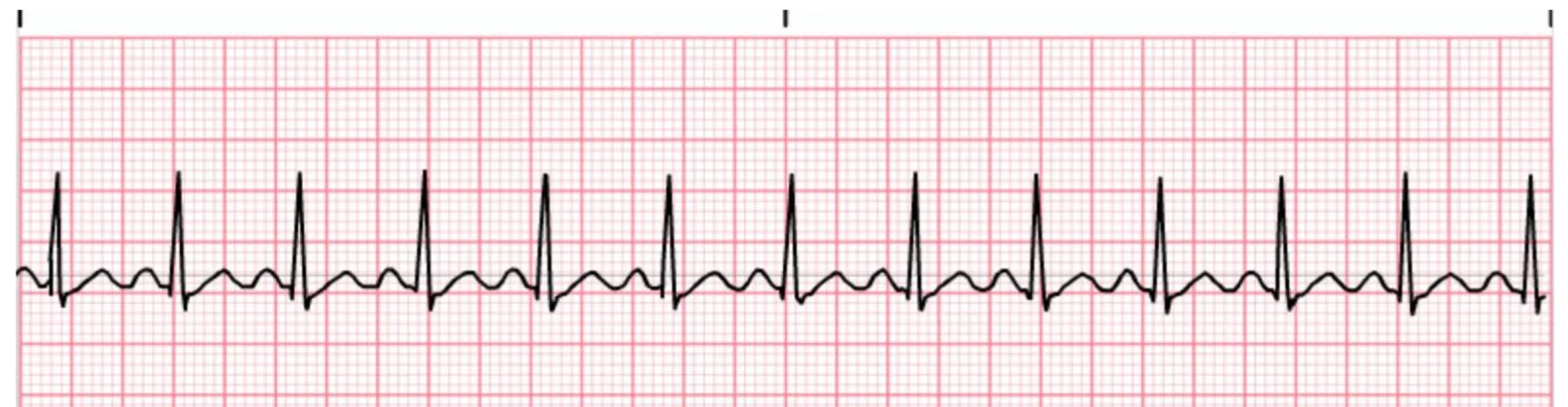
Sinus tachycardia
rate greater than 100, usually less than 120.
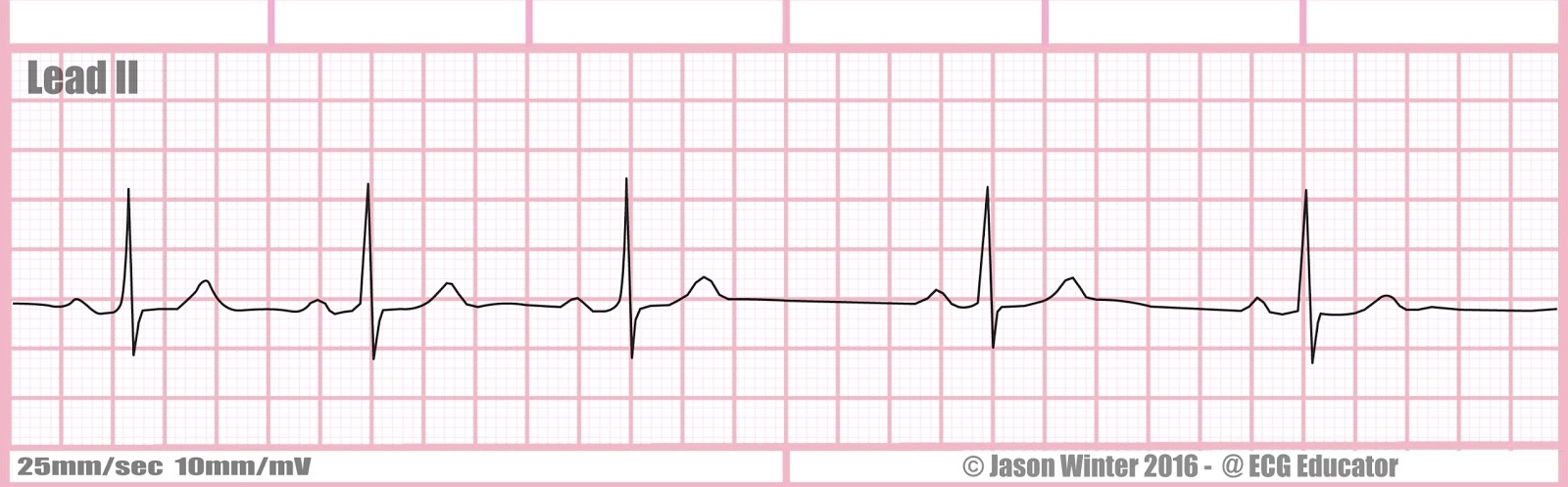
Sinus arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia on an ECG shows a normal sinus rhythm with a varying P-P interval (the time between consecutive P waves).