Skin integrity and wound healing
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Structures of the integumentary system
3 layers: epidermis, dermis, SUBQ
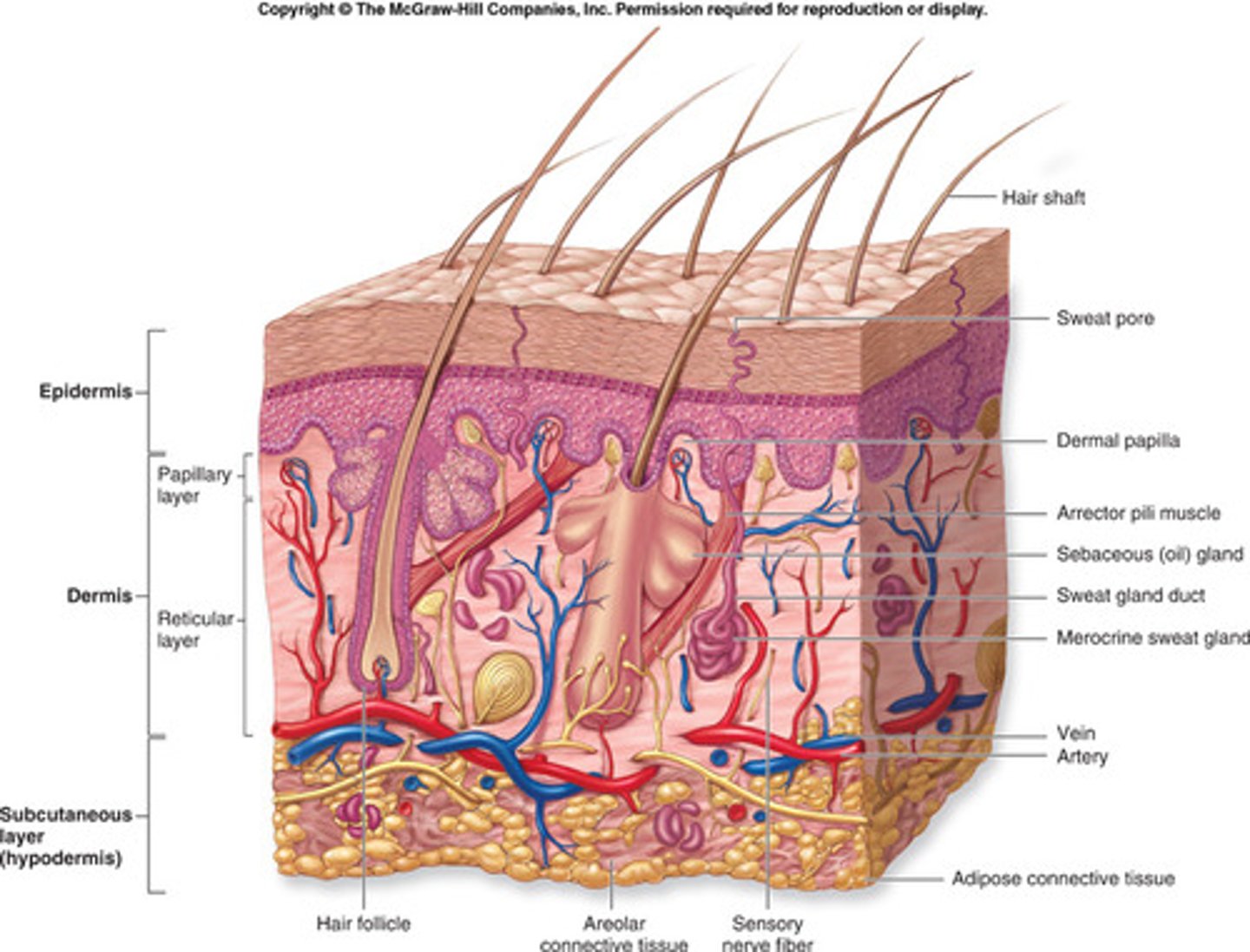
epidermis
- outer layer
- avascular
- relies on the epidermis for nutrients
- sheds and regrows every month
dermis contains
plenty of functions: nerve endings, sweat glands, hair follicles
SUBQ
fat + connective tissue
Protection from the skin 3
- from physical and chemical injury
- sebum
- normal flora that combat microorganisms
Metabolism from the skin
Vitamin D
Thermoregulation from the skin done by?
- dilation and constriction of blood vessels
- shivering and sweating
Elimination from the skin includes
Water, electrolytes, wastes eliminated through sweat
Sensation from the skin come from? what do they do?
Nerve endings in skin provide valuable info and protection
Psychosocial functions of the skin
- facial expressions
- hair distribution
Absorption of the skin due to?
substances absorbed due to vascularity of the skin
Factors that affect integumentary function
- Circulation
- Nutrition
- Condition of the epidermis
- Allergy
- Infection
- Abnormal growth rate (ex. psoriasis)
- Systemic diseases (ex. PVD, renal failure, neuropathy)
Most common skin infections in the hospital
- streptococcus
- staphylococcus
Manifestations of Altered Integumentary Function
- Pain
- Pruritus
- Rash
- Lesions
What causes itching?
- histamine release
- buildup of toxins
Alterations in Integumentary Structure
- Intentional or Unintentional
- Open or Closed
- Acute or Chronic
Intentional vs Unintentional integumentary injury
Intentional= planned and under sterile conditions ex. surgical incision
Unintentional= accidental injury that is more prone to infection and takes longer to heal ex. bed sore, fall
open vs closed integumentary injury
Open= break in skin integrity ex. animal bite
Closed= intact skin integrity, but trauma underneath skin layer ex. bruise
acute vs chronic integumentary injury
Acute= short term w/ better healing
Chronic= long term problem and prone to infection that may lead to further complications
Skin in children below the age of two
- Skin is thinner and weaker
- An infant's skin and mucous membranes are easily injured and subject to infection
- Becomes increasingly resistant to injury and infection
Skin in the elderly
- Maturation of epidermal cells is prolonged, leading to thin, easily damaged skin
- Circulation and collagen formation are impaired, leading to decreased elasticity and increased risk for tissue damage from pressure.
Causes of pressure injuries
- Pressure intensity on a bony prominence that decreases blood flow (ex. heels, elbows, coccyx, back of head)
- Pressure duration
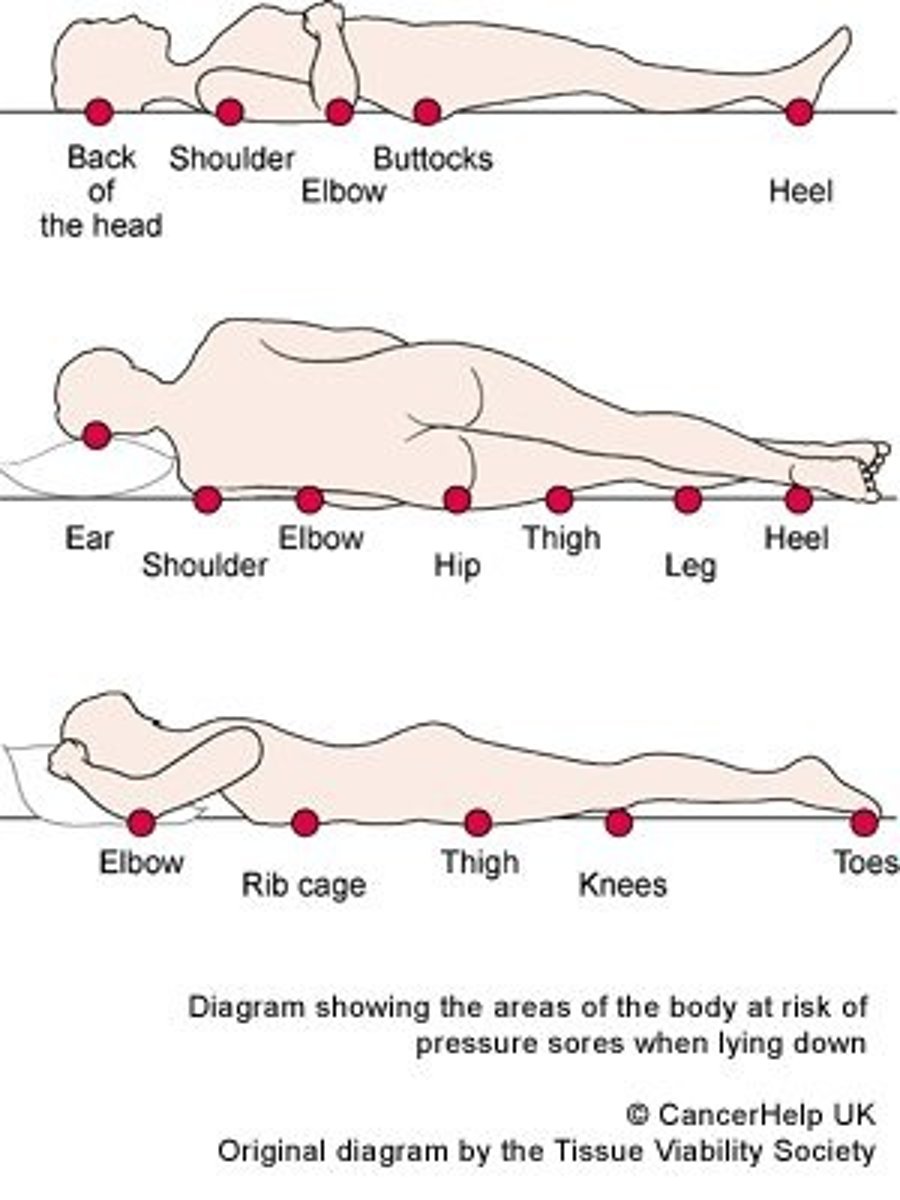
Predisposing factors for pressure injuries
- diabetes
- malnourishment
- cachectic/small stature
- previous pressure injury
Primary Intervention for Pressure Injuries
- turn q2h, mobilize
- nutrition
- prevent moisture accumulation and friction
- place padding on bony prominences if individual will be in same position
- barrier creams
Risks for pressure injuries include:
- Impaired tissue tolerance
- Nutrition
- Moisture
- Age
- Friction/shear
Comorbid conditions w/ pressure injuries
- Altered level of consciousness
- Sensory impairment
- Impaired mobility
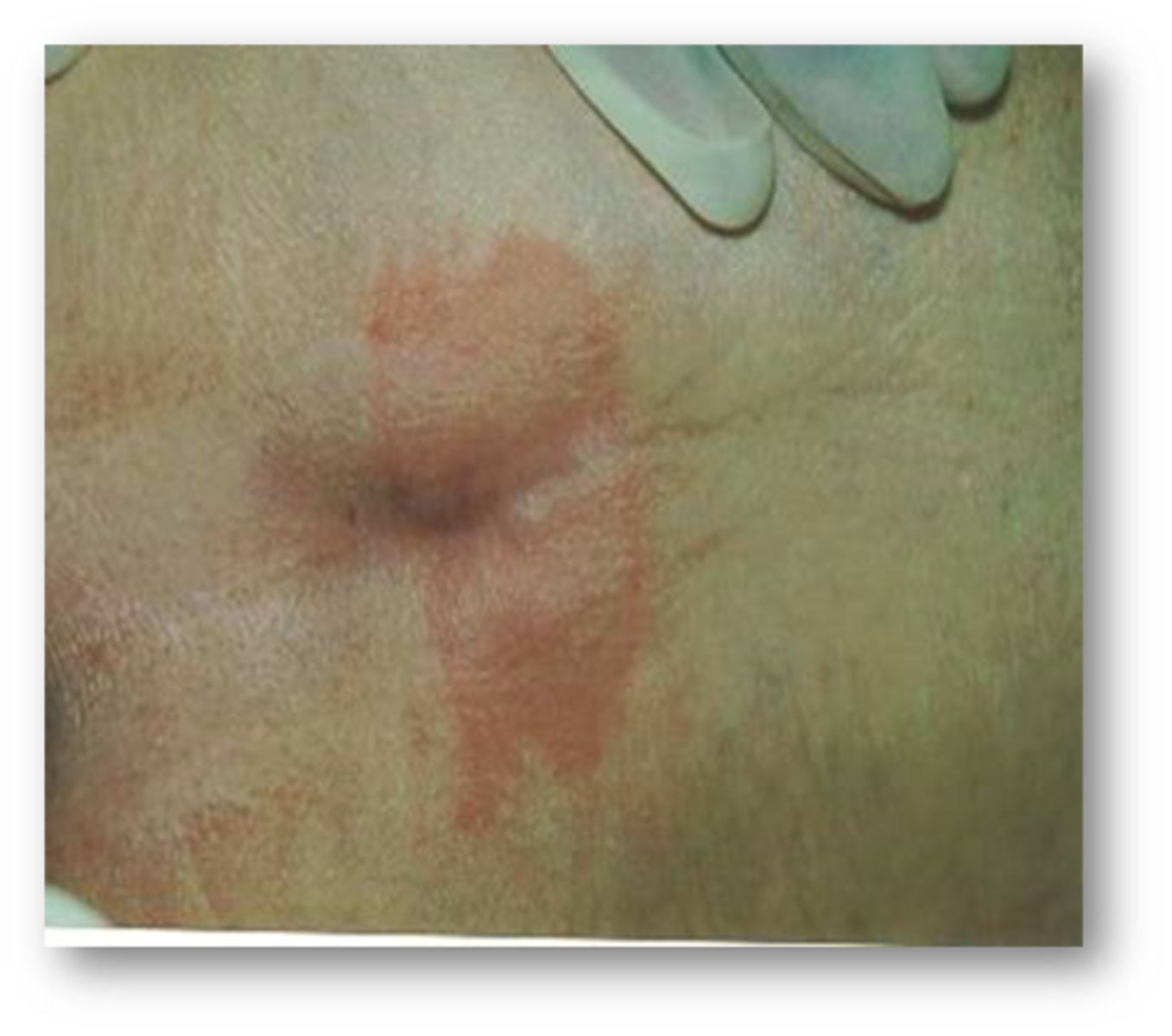
Stage 1 pressure injury + interventions
- Non-blanchable erythema of intact skin
- Apply barrier cream or padding on site, keep pt off site
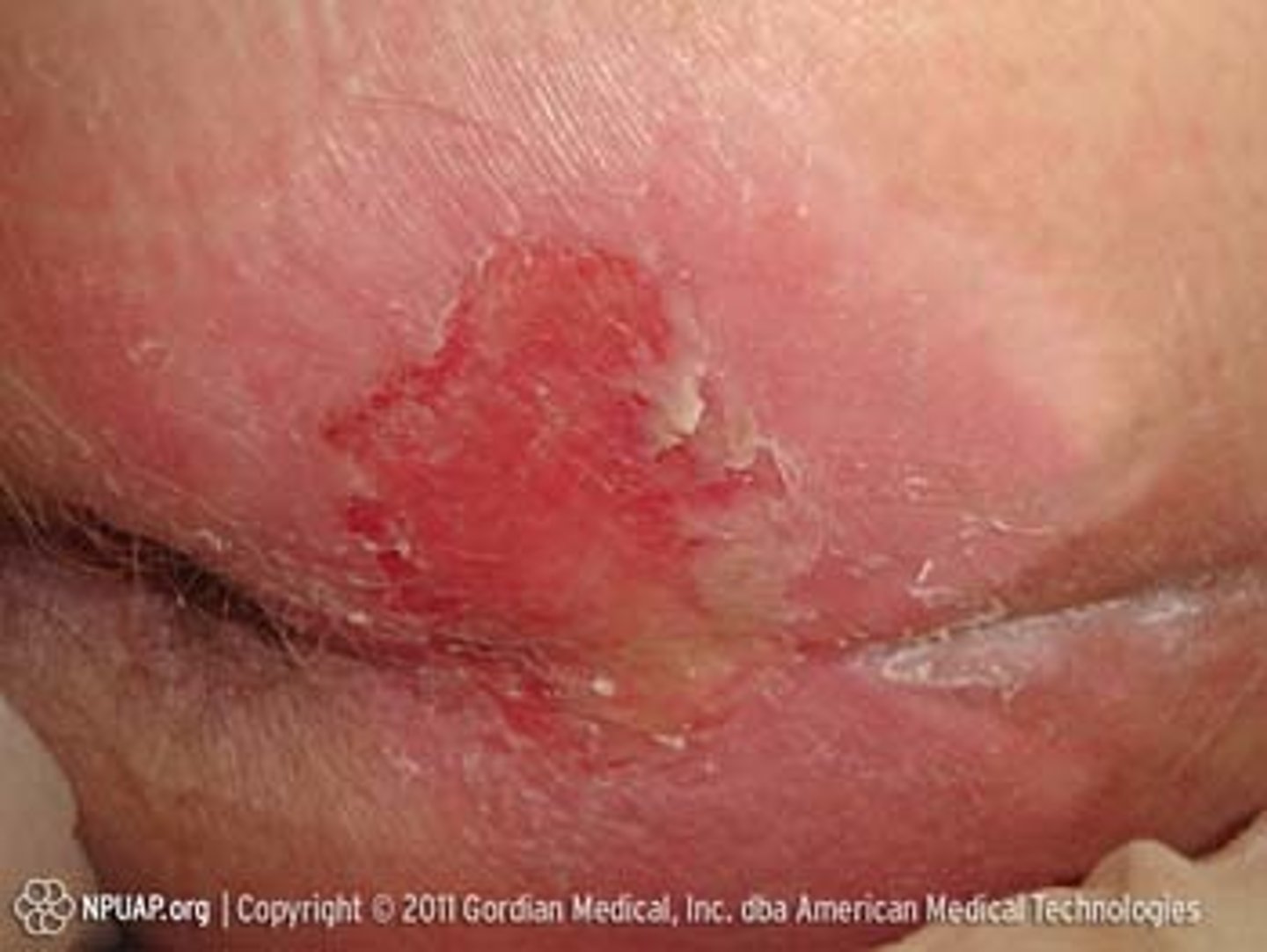
Stage 2 pressure injury + interventions
- partial thickness skin loss
- presents as an abrasion or blister
- keep area clean and dry, utilize mechanical lifts
Stage 3 pressure injury + interventions
- full thickness skin loss with damage or necrosis of subq
- presents as a deep crater (may be tunneling and undermining)
- frequent dressing changes, pack wound
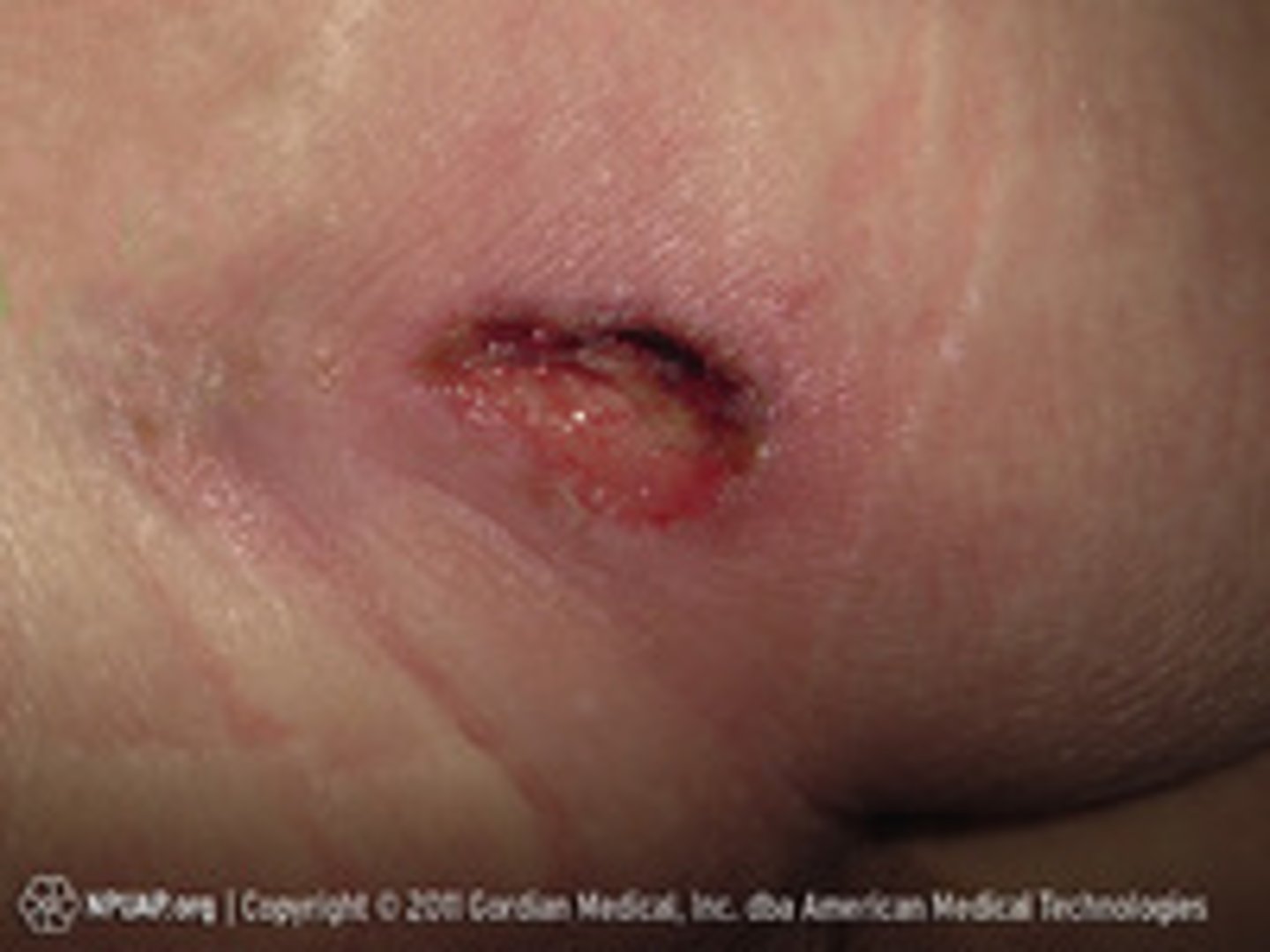
Stage 4 pressure injury + interventions
- Full-thickness skin and tissue loss with extensive destruction, necrosis, or damage to muscle, bone, or tendons
- Can take years to heal/may never heal
- May need surgical debridement, wound vac
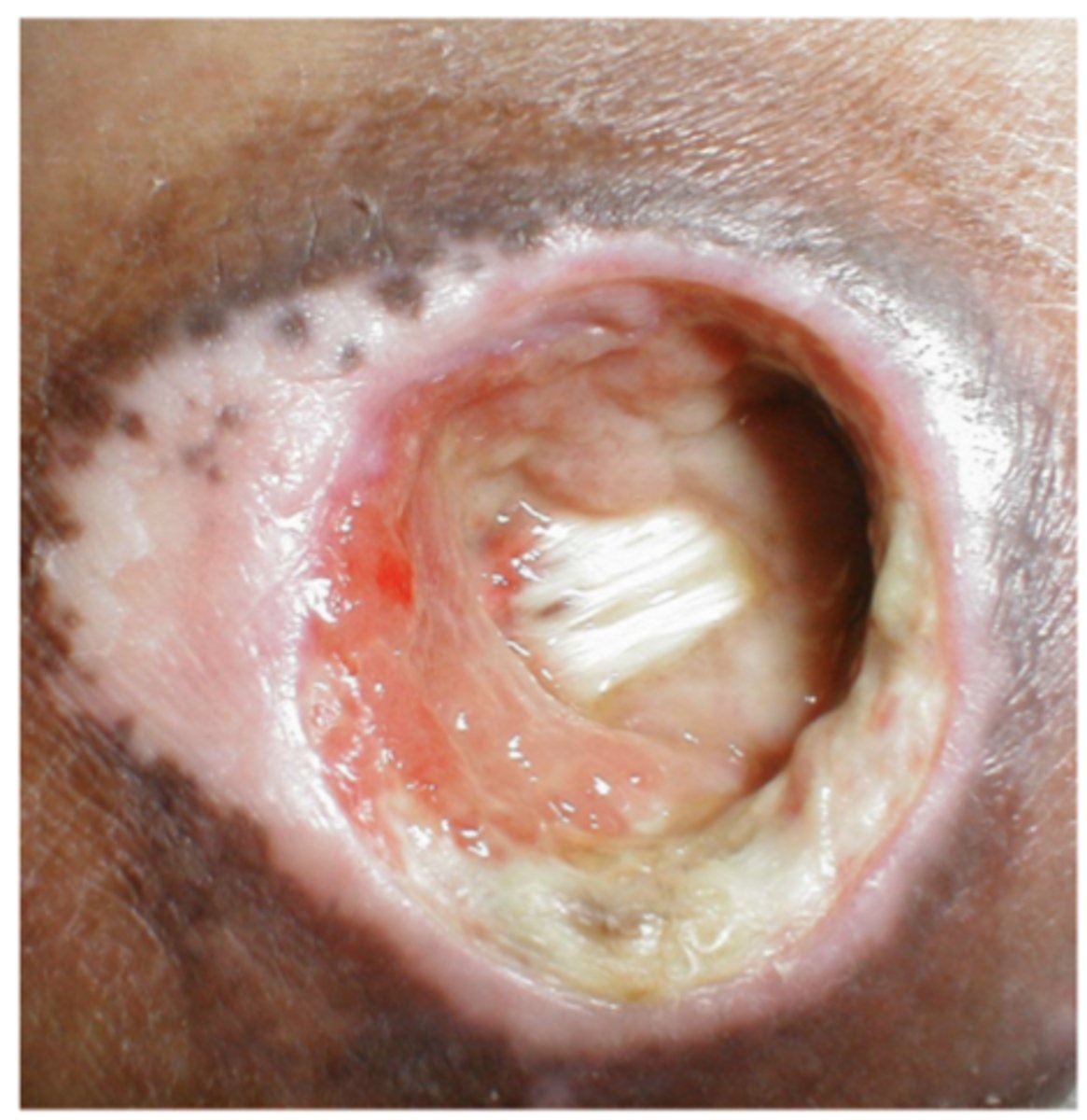
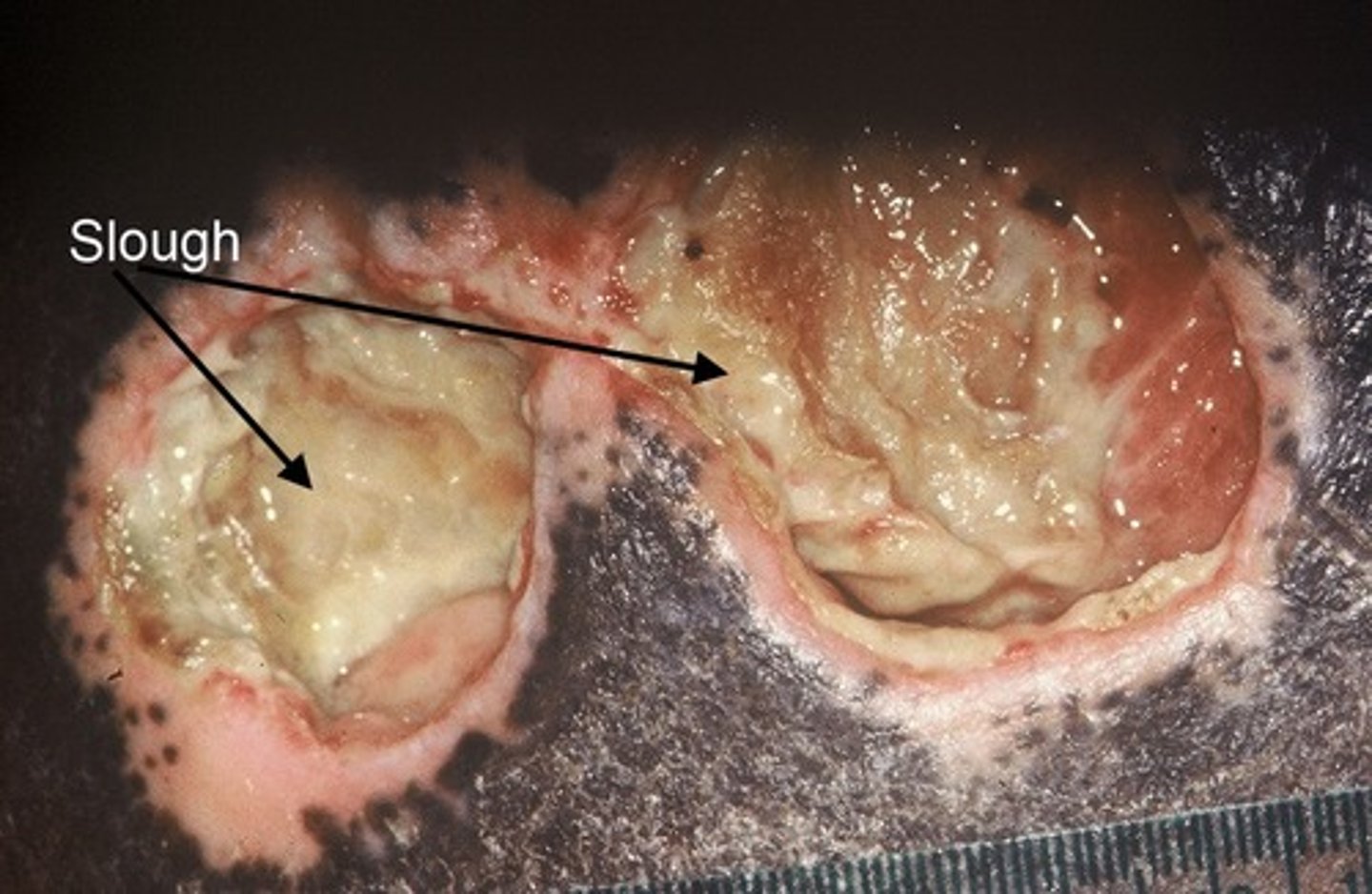
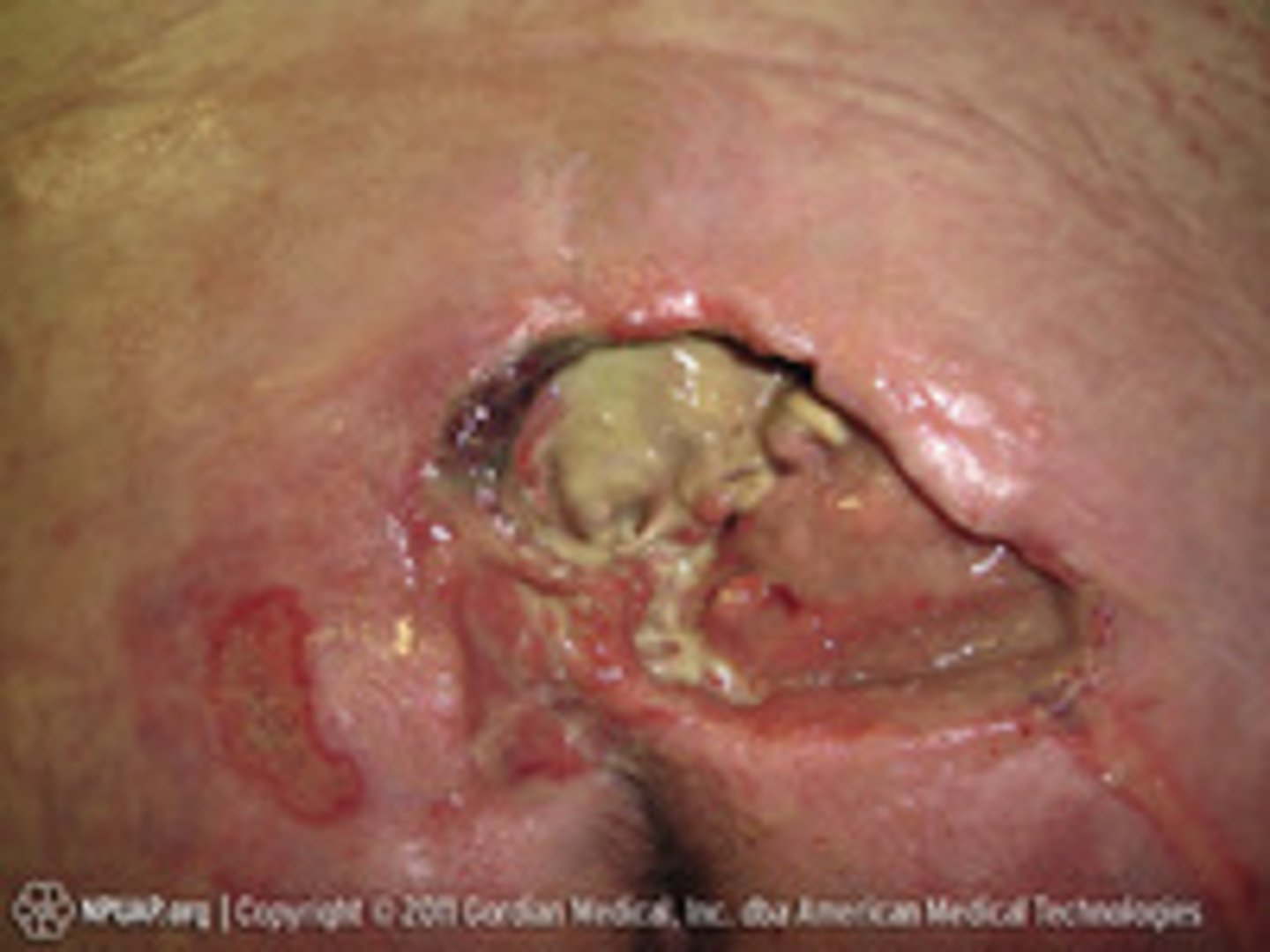
Slough
- yellow, tan, gray, green, brown
- nonviable tissue/needs removed
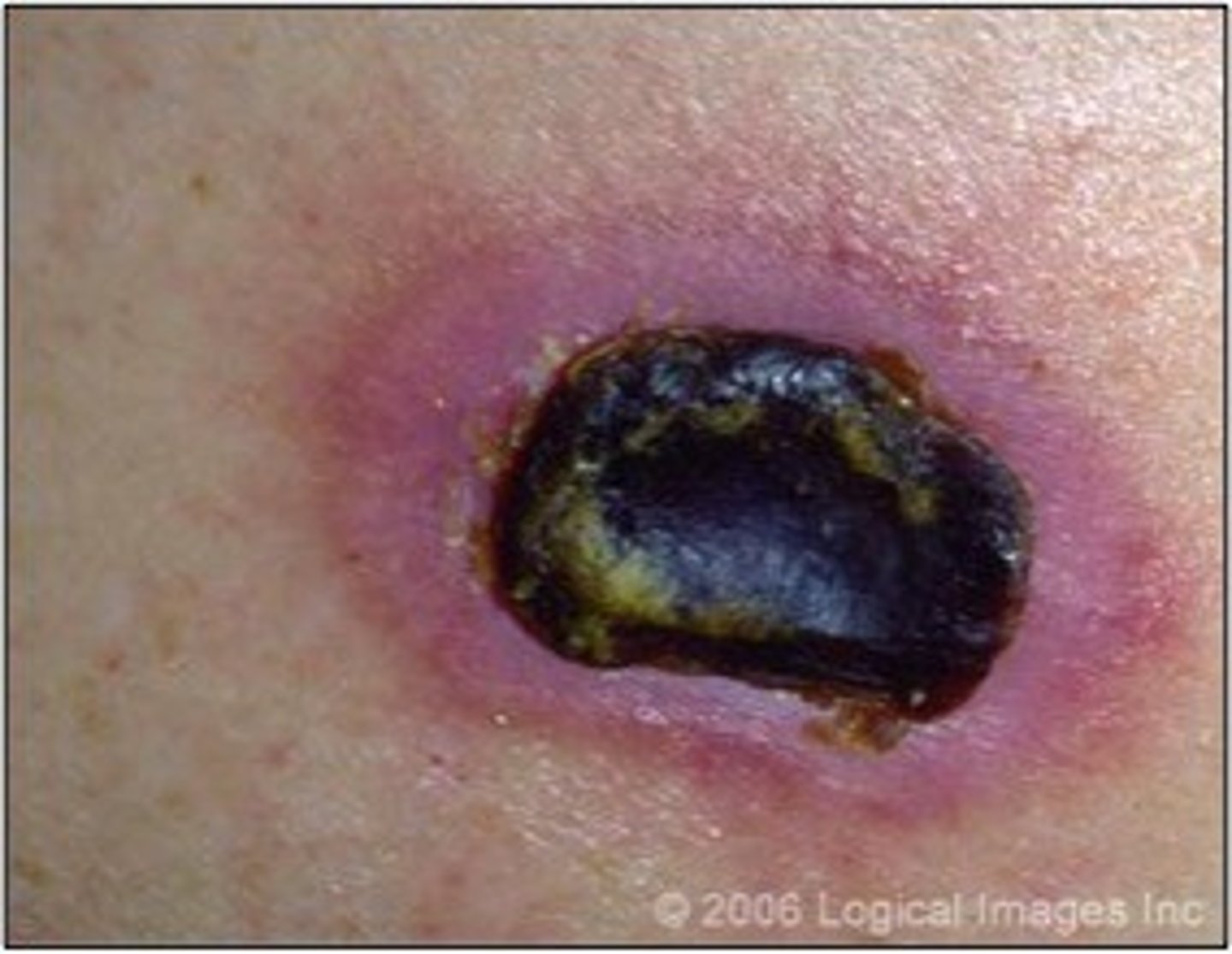
Eschar
- dark brown or black
- crust-like, non-viable tissue
- DO NOT remove, done by physician
unstageable pressure injury
- full thickness tissue damage
- base of the wound is covered by slough or eschar
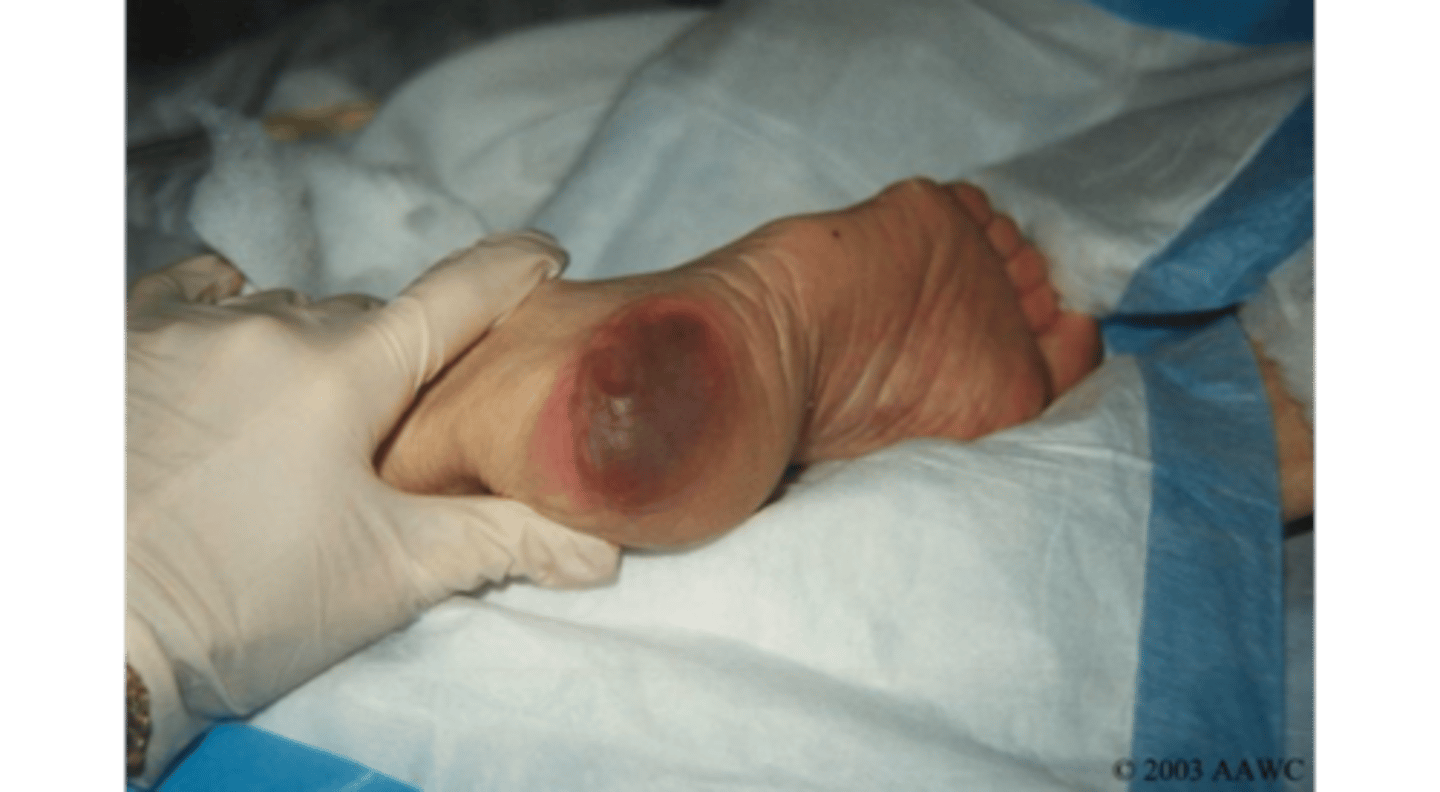
Suspected deep tissue injury (SDTI)
purple or maroon localized area of intact skin
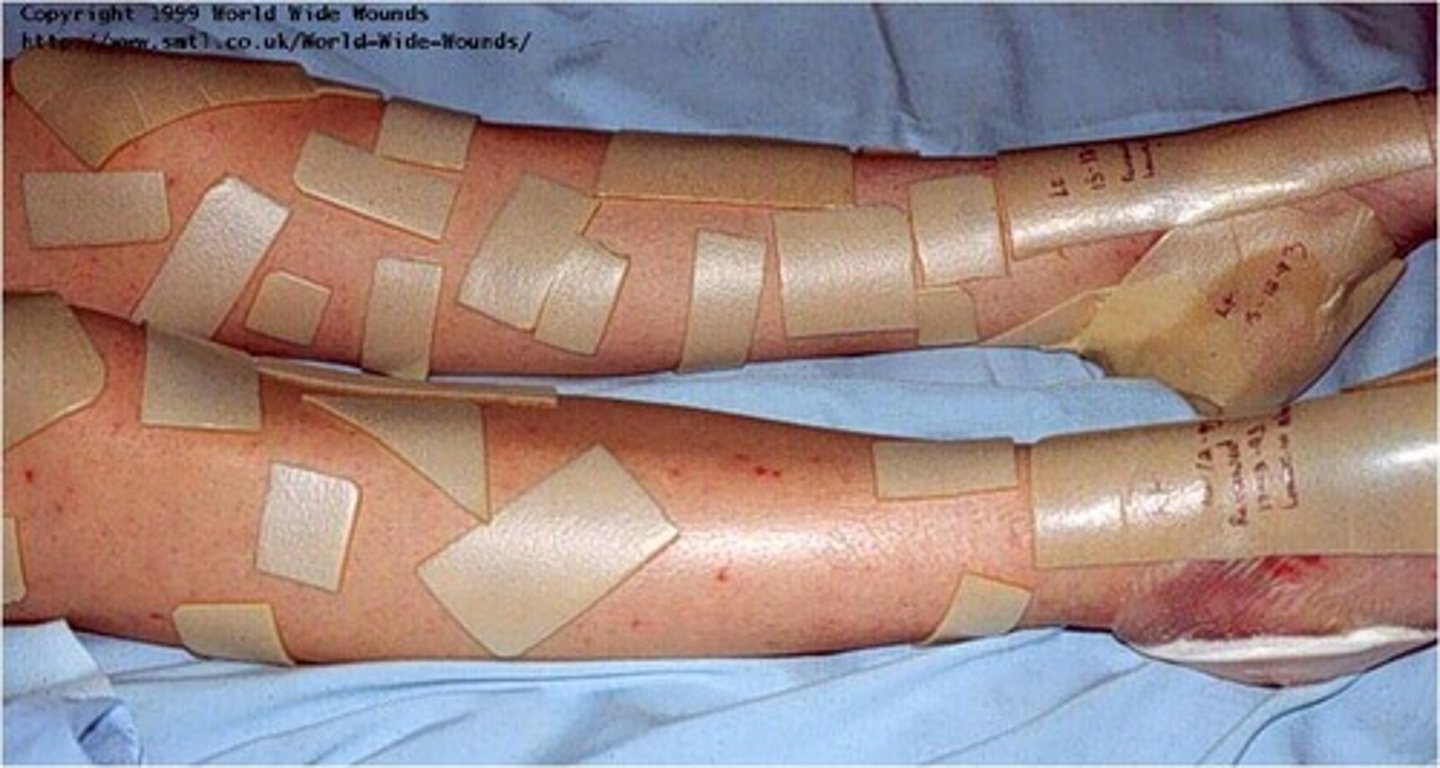
Autolytic debridement
- use of hydrocolloid or foam dressings
- body's own enzymes and defensive mechanisms to loosen and liquefy necrotic tissue
Bio-surgical debridement
- Use of surgical grade/sterile fly larvae
- Larvae secrete enzyme that liquefies necrotic tissue, then larvae consume liquid and infectious material in the wound
Enzymatic debridement
- application of commercially prepared enzymes to speed up the body's autolytic process
- prescribed by a provider
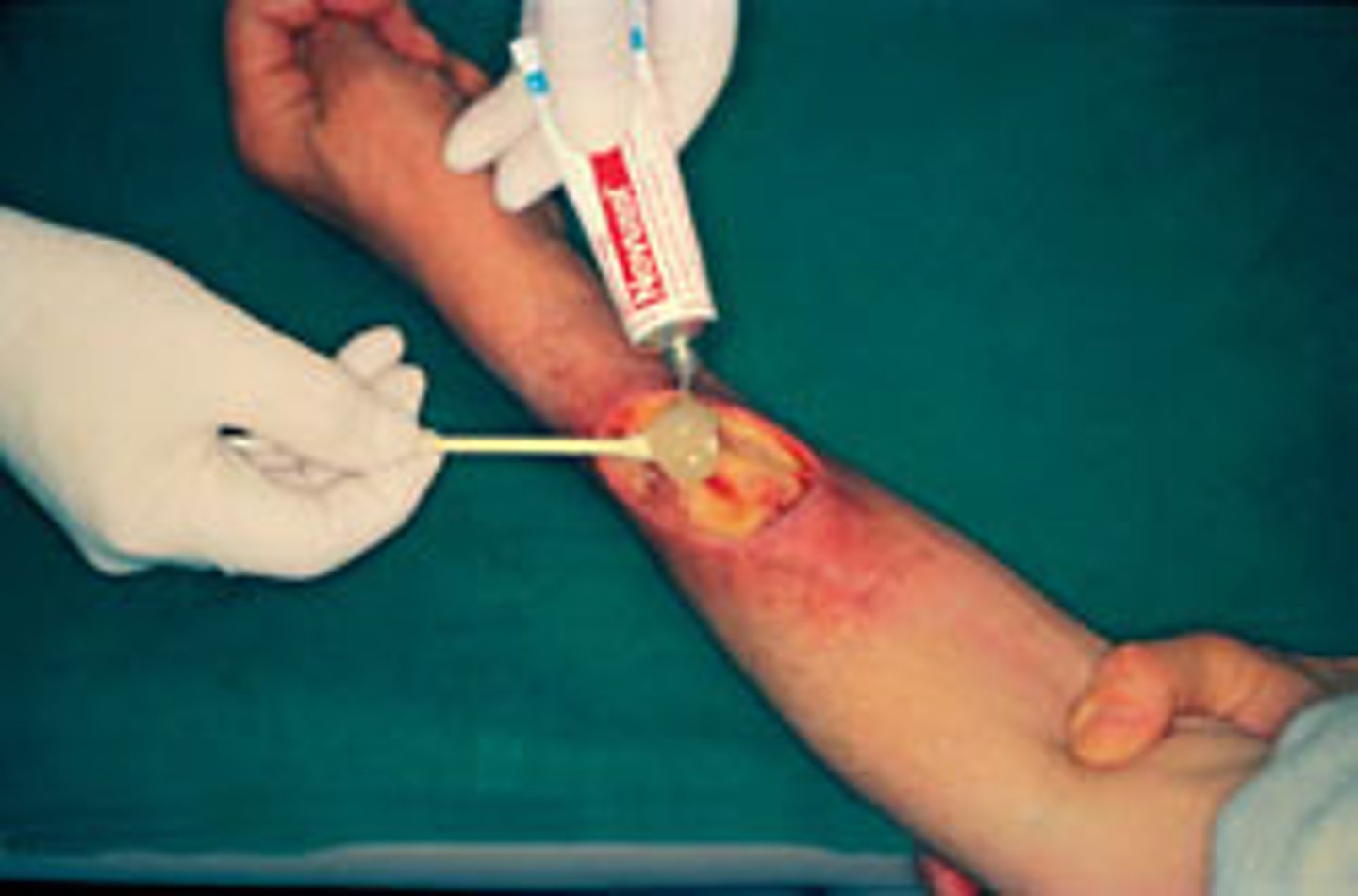
Mechanical debridement
- use of an external physical force (W-> D drg, H2O2, irrigation)
- painful method of debridement
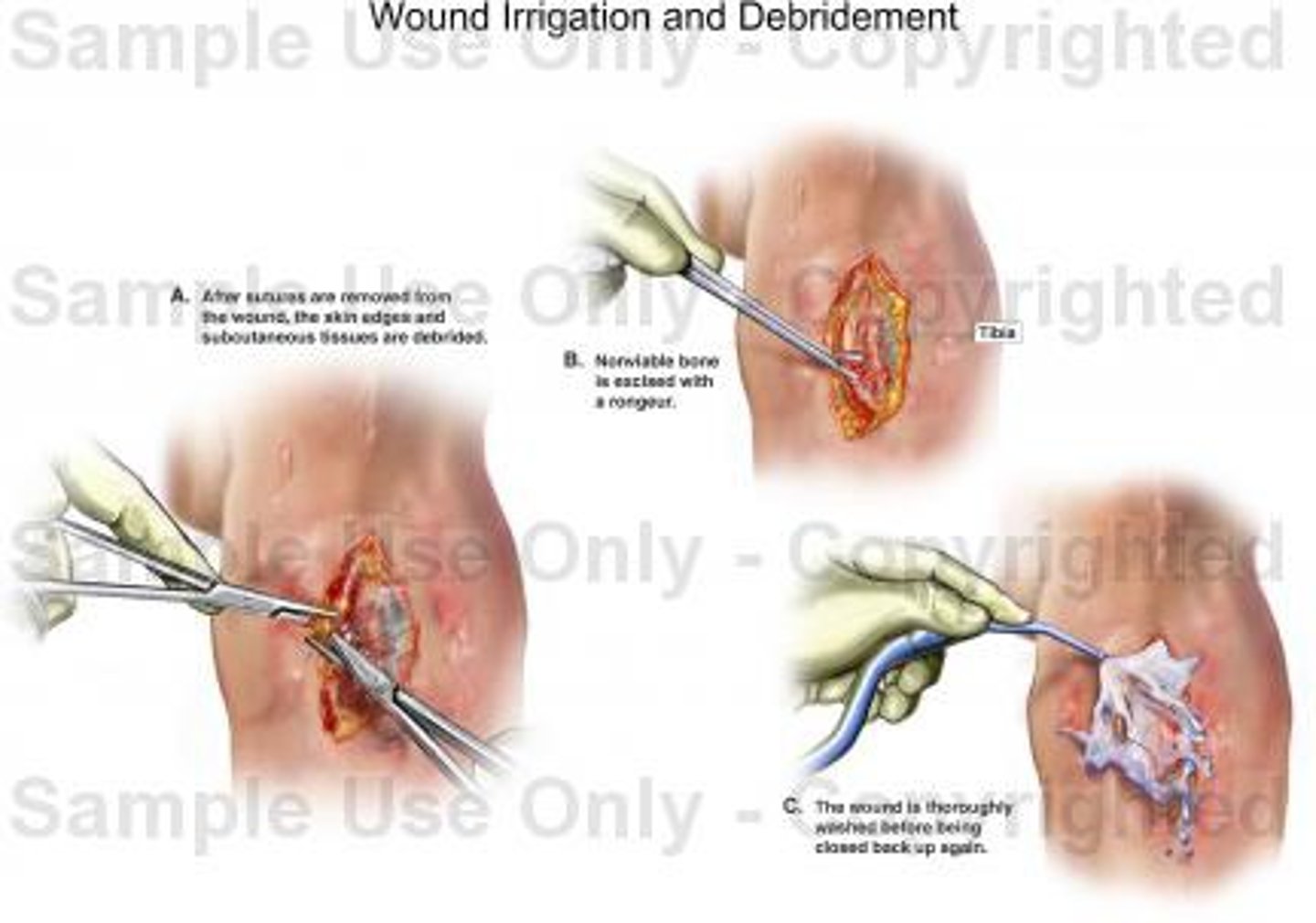
Sharp/surgical debridement
- use of scalpel
- performed by physicians and advance practice nurses
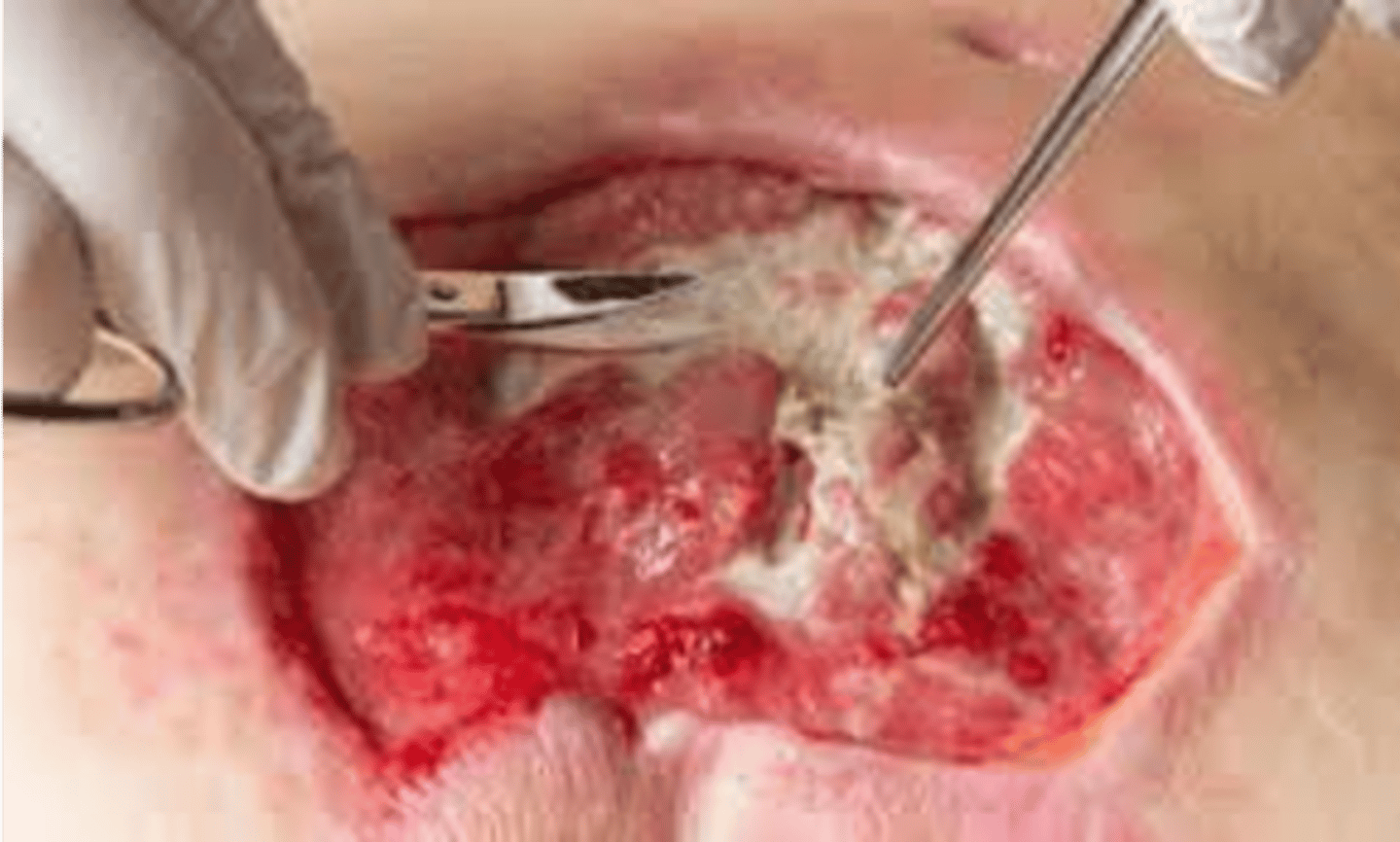
4 stages of wound healing
hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, maturation
Hemostasis wound healing steps include?
- Vasoconstriction to slow bleeding on outside
- Exudate production
- Clot formation
Inflammatory wound healing steps include
- Vasodilation increases bloodflow
- Phagocytosis get rid of bacteria
- Localized inflammatory response redness swelling tender warm
- Lasts 4-6 days
Proliferative wound healing steps
- Lasts 3-24 days
- Fibroblasts and Growth Factor create collagen and blood vessels
- Granulation tissue formation
Maturation wound healing steps
- Can take up to 2 years
- Collagen matures
- Scar tissue is created
Describe Primary intention wound healing
- clean incision
-> early suture -> "hairline scar"
- edges are well approximated, can't see granulation tissue
- best healing
Describe Secondary intention wound healing
- gaping irregular wound -> granulation tissue -> epithelium grows over scar
- full thickness, deep laceration (ex. burn, pressure injury)
- can develop infections due to more area for infection
Tertiary intention wound healing
- wound -> granulation -> closure w/ wide scar
- delayed closing
- increased risk of infection and pressure injuries
Systemic factors that affect wound healing
- Age
- Nutrition
- Circulation/ Oxygenation
- Health Status
Nutrition that is helpful for wound healing
- Protein
- Vitamins A & C
- Zinc
Health statuses that impact wound healing
- Diabetes
- Shock
- Immunosuppression
- Obesity
7 Local factors that affect wound healing
- Moisture
(Desiccation, Maceration)
- Trauma
- Edema
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Necrosis
- Biofilm
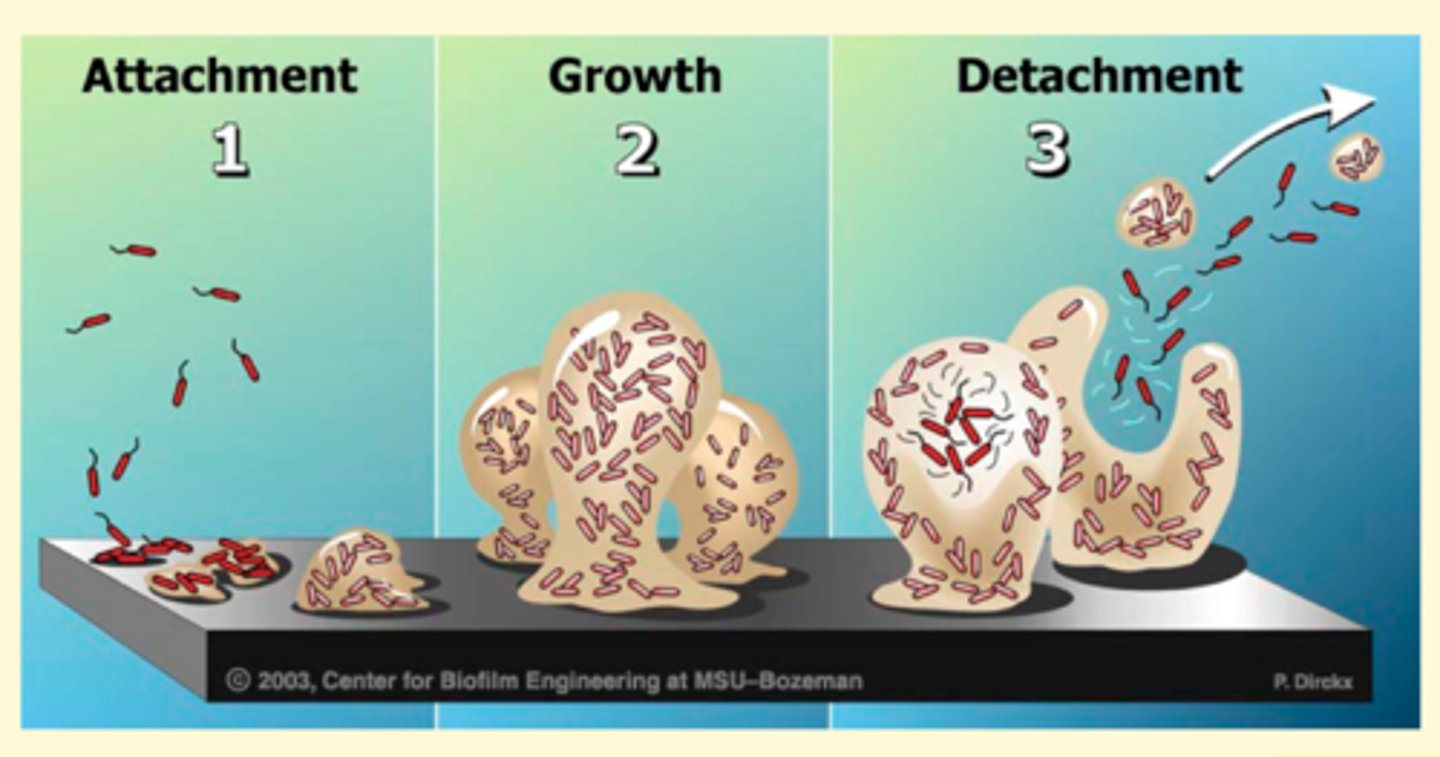
Biofilm
sugar protein film that feed bacteria for protection
Complications of wound healing
- Hemorrhage
- Hematoma
- Dehiscence
- Evisceration
- Infection
- Fistula
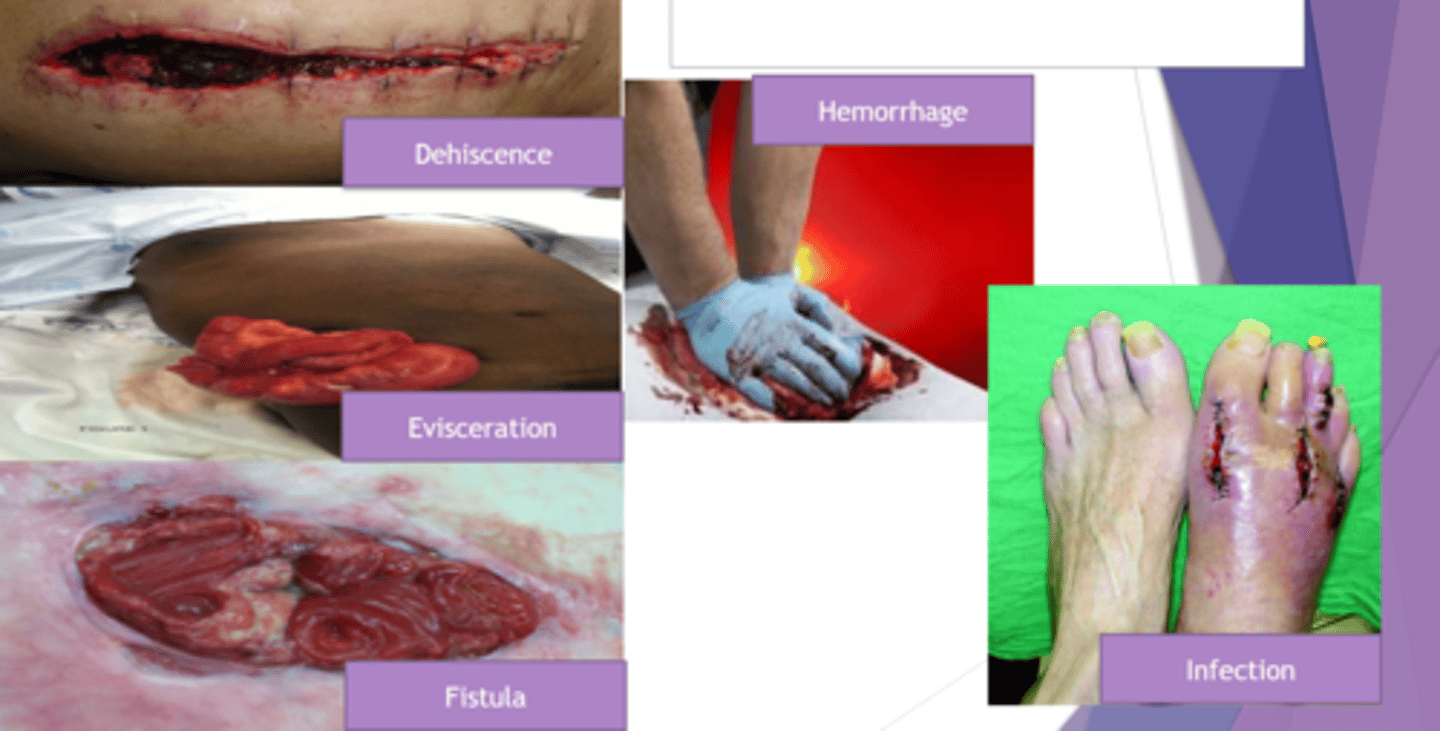
Dehiscence
partial or total separation of wound layers
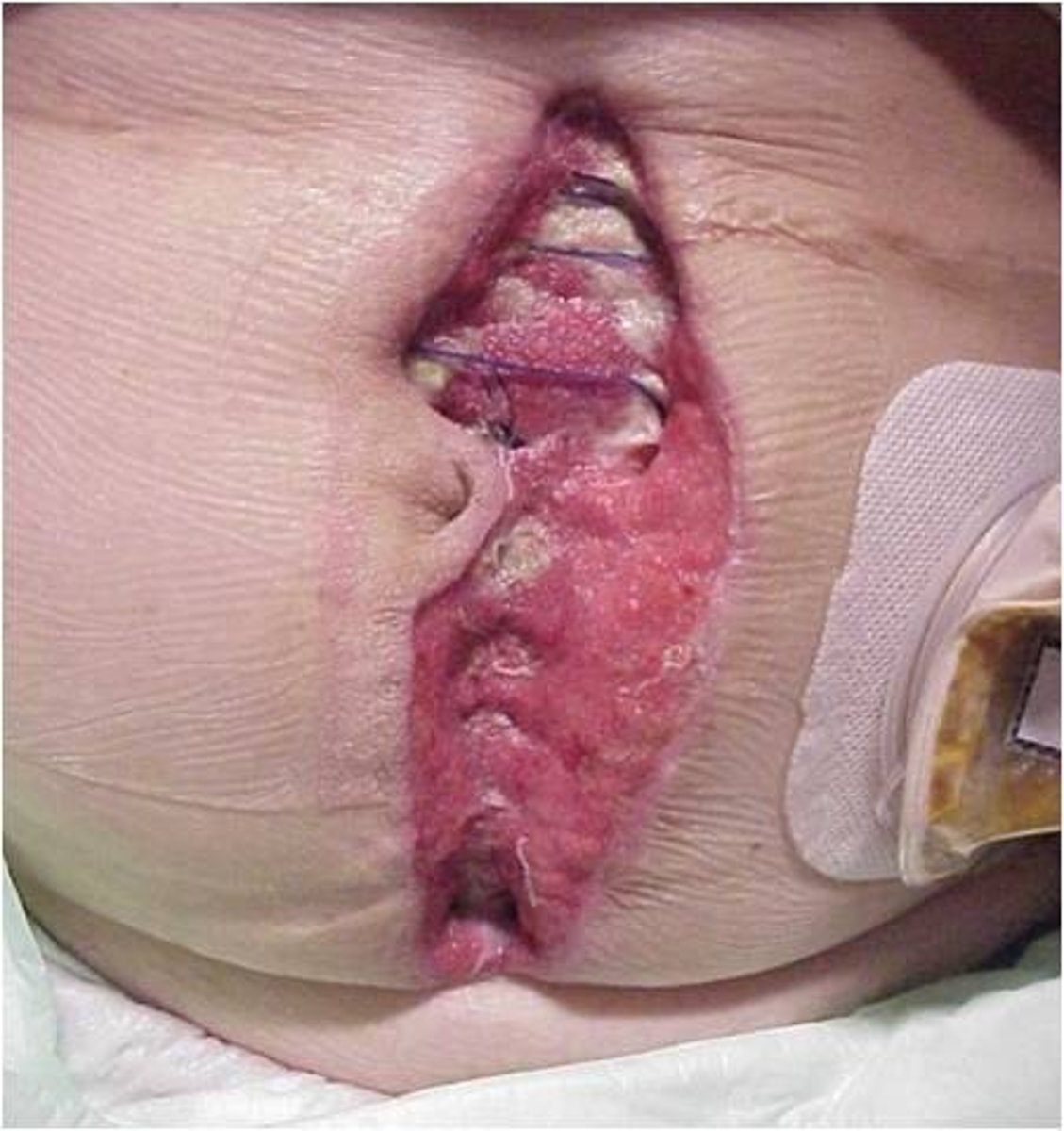
Evisceration
The displacement of organs outside of the body.
What to do if an organ comes out w/ evisceration?
- sterile saline to keep it moisturized
- cover with sterile gauze
- notify the physician
Fistula
abnormal passageway between two organs
Maceration
softening or dissolution of tissue after lengthy exposure to fluid
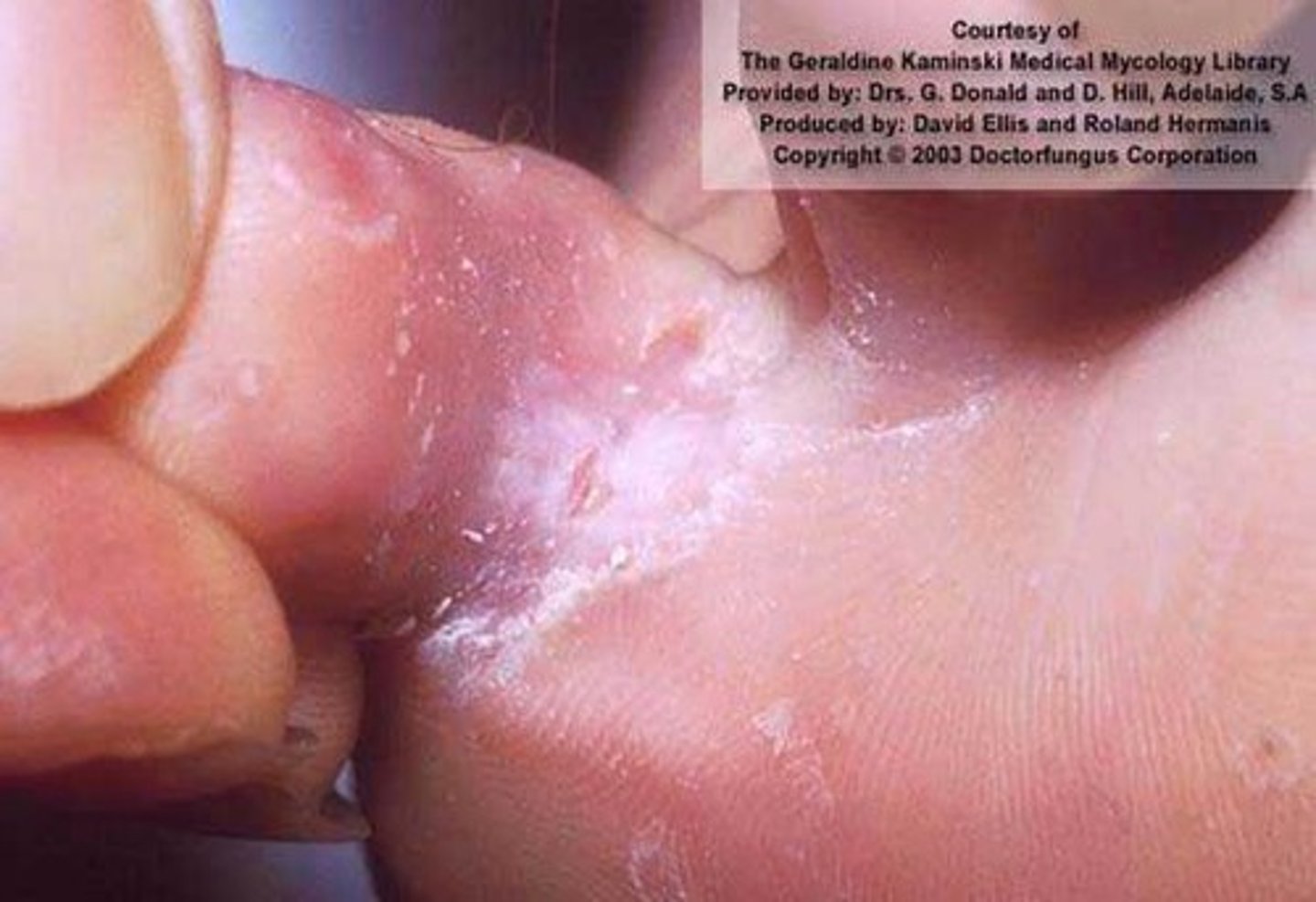
5 signs of localized infection
1.Redness
2.Heat
3.Edema
4.Pain
5.Altered Function
Subjective assessment data
- Normal skin condition
- Hx of skin conditions, wounds
- Psychosocial effects of impaired skin integrity
Psychosocial effects of impaired skin integrity
Pain, Anxiety, Fear, Impact on ADLs, Change in Body Image
Objective assessment data
- Visual, tactile and olfactory assessment
- Wound assessment
- Presence of tubes or devices
- Areas of pressure
- Nutritional Status
- Risk Scoring Tools
- Diagnostic Tests
6 Typical findings of intact skin
- Color
- Temperature
- Moisture
- Texture
- Odor
- Turgor
5 Potential nursing diagnosis
- Impaired Skin Integrity
- Impaired Tissue Integrity
- Risk for Infection
- Imbalanced Nutrition: less than body requirements
- Pain
Implementation
- Health promotion
- Prevention of pressure ulcers
- Patient teaching
- Prevent & manage wounds
- Protect wounds (dressings)
- Monitor lab values (WBC)
- Provide nutritional support
- Teach patient appropriate wound care
Preventing pressure injuries
- Positioning & skin care
- Pressure reducing surfaces
Patient teaching for wound care
- Hygiene and Handwashing
- Pressure ulcer prevention
- Symptoms of infection
How to prevent and manage wounds
- Remove nonviable tissue
- Manage wound exudate
Non blanchable means
push on skin and the skin does not whiten or change color