DNA Polymorphisms and ID: Exam 3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Polymorphism
presence of two or more inherited variant forms of a specific DNA sequence (genetic mutations in a population)
- can occur among different individuals or populations
- variations occurring in > 1% of population can be considered useful polymorphisms
Types of Polymorphisms
SNPS, polymorphic repetitive elements, microsatellites, small INDELS, and RFLPS
SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphisms
- most common type; each individual has 11 million
- 99% have no biological effect
- each SNP represents difference in single nucleotide in DNA sequence
Polymorphic Repetitive Elements
large or short blocks of repeated sequences
- may be inverted, deleted, duplicated from one individual to another
- LINEs or SINEs
- LINEs: long elements 6-8kbp
- SINEs: short elements 0.3kbps
Microsatellites
VNTRS or STRS
- variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs): 10-50bp
- short tandem repeats (STRs): 1-10bp
Small INDELs
insertion or deletion variations among individuals
- cause of similar levels of variations as SNPS
RFLPs
restriction fragment length polymorphisms
- one or more nucleotide change that affects the size of restriction enzyme products
RFLP Typing
differences in the sizes and number of fragments generated by RE digestion of DNA
- change in nucleotide sequence alters restriction site
RFLP Typing Steps
create a restriction map and compare the number and sizes of fragments
- detects polymorphisms by observing the number and size of fragments
RFLP Inheritance
offspring inherit a combination of parental polymorphisms
- single locus will have several alleles/versions
- band patterns represent combination of RFLPs inherited from each parent
- can test for paternity; 8 loci needed
STR (short tandem repeat) Typing by PCR
uses a polymarker system to amplify loci; set of primers complementary to sequences
- used in forensics
- number of repeats within an STR is referred to as an allele
Y-STR Identification
AMEL locus (amelogenin) is used to identify male individuals
- amplification and electrophoresis reveals two bands for males and one band for females
Genotyping
peak or band patterns must be converted to genotype for allele identification
- represents homologous chromosomes when repeated on both chromosomes
- if one has a repeat in one chromosome and a different one in another then it would be heterologous
Partial Repeat Units
microvariant alleles indicated by the number of complete repeat units followed by a decimal point indicating the number of incomplete units
- 9.3 locus; full 9 TCAT and one 3bp repeat
Genetic Concordance
all alleles from two sources are the same
- indicates inclusion of a single individual as the donor of both genotypes
Genotyping Considerations
stutter: error due to pol missing a repeat during amplification
intragel precision: comparing bands in same gel
intergel precision: comparing bands between separate gels
Match Probability
the more loci tested, the higher the probability that the locus genotype positively identifies an individual
Product Rule
the frequency of a set of alleles or genotype in a population
OF = F1 x F2 x F3 X…
- OF is overall frequency
ex. calculate OF for penta D (1 in 10) and D7S829 (1 in 50) = 1/500
National DNA Index System (NDIS)
important to consider whether database is representative of a population or subpopulation
- 13 million offender profiles
Allelic Frequencies in Paternity Testing
H0 and H1
- an individual will share one allele of every locus with the paternal parent
- H0: not the father
- H1: is the father
Paternity Index (PI)
likelihood of paternity calculated for each locus which both the father and child share an allele
Combined Paternity Index (CPI)
product of all PI of each loci tested
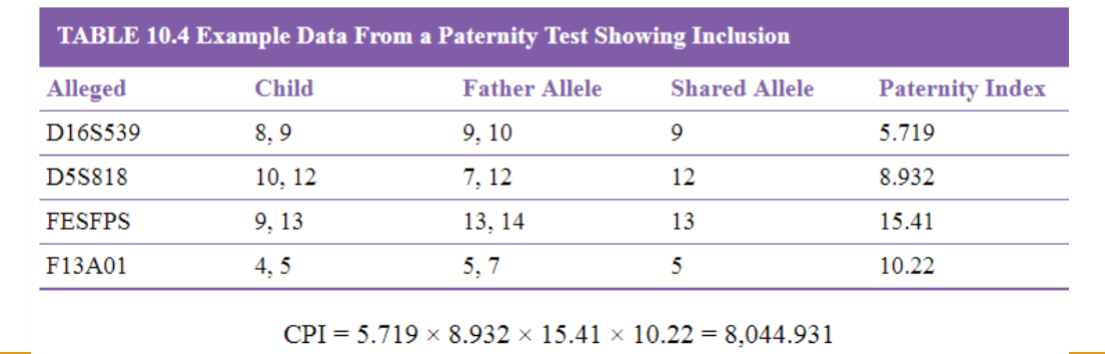
Probability of Paternity
combines CPI and prior odds of someone being the father

Linkage Analysis
used to map genes associated with disease
- if an allele of a particular locus is always present: disease
- linkage equilibrium: 2 or more alleles occur randomly
- linkage disequilibrium: whe they do not occur randomly
Marker for Disease (STR)
occurs if linkage is close to the gene