Clinical application of non-Type I hypersensitivity reactions
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Signs and symptoms of Myasthenia gravis
ptosis + diplopia
dysphagia
slurred speech
dyspnoea
weakness in arms/ legs that gets better with rest/ worse with use
What happens in myasthenia gravis?
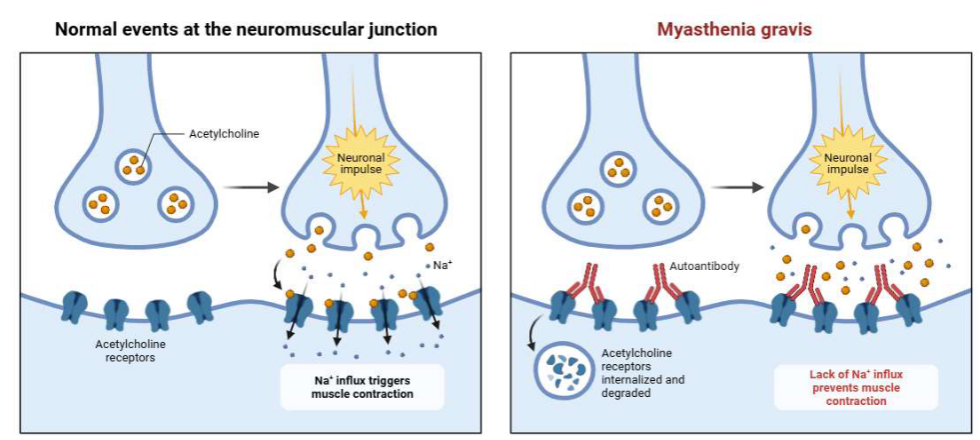
How do you treat myasthenia gravis?
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Pyridostigmine)
Inhibition increases local ACh conc in the synaptic cleft → prolonged action of released Ach → increased probability of successful conduction across the synapse
may use steroids and other immunosuppressants (CPT)
IVIG / Plasma exchange → helpful in a myasthenia crisis
What can happen if you over treat myasthenia gravis?
Cholinergic crisis
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Diarrhoea
GI distress (cramping)
Emesis
What can happen if you under treat myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenic crisis
Respiratory arrest
Ventilation and removal of autoantibodies
What would the blood work look like in graves disease?
Free T3/4: high
TSH: low
Treatment for graves disease
Carbimazole → TPO inhibitor
Radioactive iodine
Thyroidectomy
Signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Kussmaul breathing
Acetone breath
Polyuria, polydypsia, fatigue (common in diabetes mellitis)
Nausea, vomiting
Pathophysiology of Type 1 diabetes
Islet cell autoantibodies (ICA)
Autoantibodies to GAD (GAD65; glutamic acid decarboxylase)
Autoantibodies to insulin, the tyrosine phosphatases IA-2 and IA-2b, and zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8)
CD8+ & CD4+ cells damage islet cells → ER stress, oxidative stress, inflammation
** type IV hypersensitivity
Treatment for type 1 diabetes
Metformin: insulin sensitisers (decrease hepatic glucose production)
Sulphonylurea (stimulate insulin secretion)
GLP-1:glucagon peptide agonist (Stimulates insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon secretion + slows gastric emptying)
SGLT2: (increase excretion of glucose through kidneys (renal glucose elimination))
Pathophysiology of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Infection with nephritogenic strain of group A ß-hemolytic streptococ streptococci → different surface M protein → immune complexes
** type III hypersensitivity
Note rheumatogenic strains → can cause Rheumatic fever
** Streptokinase no longer used as a fibrinolysis →