UVA PSYC 2005 - Final Exam
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
A research group decides to put up flyers to get participants to join their study. What type of sampling would this be?
AD HOC SAMPLING
Research that is conducted to provide solutions to practical problems is called ____________
applied research
________ research is carried out to add to knowledge. Also known as pure research
Basic
Any research, particularly basic research, that is planned so as to lead to practical applications such as in medicine, education, and industry
translational research
What is the most common central tendency that we know?
Mean
________ variable represents some aspect of an organism's behavior (any observable response)
behavioral
What is a stimulus variable?
Any part of the environment to which an organism reacts.
Characteristics of the participants, such as age, gender, racial attitudes, and musical ability can be classified into what type of variable?
Organismic variable
- Any characteristic of the individual that can be used for classification
Unplanned and uncontrolled factors that can arise in a study and affect the outcome are known as ________ variables
Extraneous
Validity refers to:
the quality or precision of a study, a procedure, or a measure—to "how well" each does what it is supposed to do
The Belmont Report proposed that ethical research with human beings rested on the following three principles:
Beneficence
Autonomy
Justice
Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) consist of:
researchers' peers and members of the community at large
A Z score describes a score in terms of how much it is above or below the ________
Average
The mean of any distribution of Z scores is always:
0
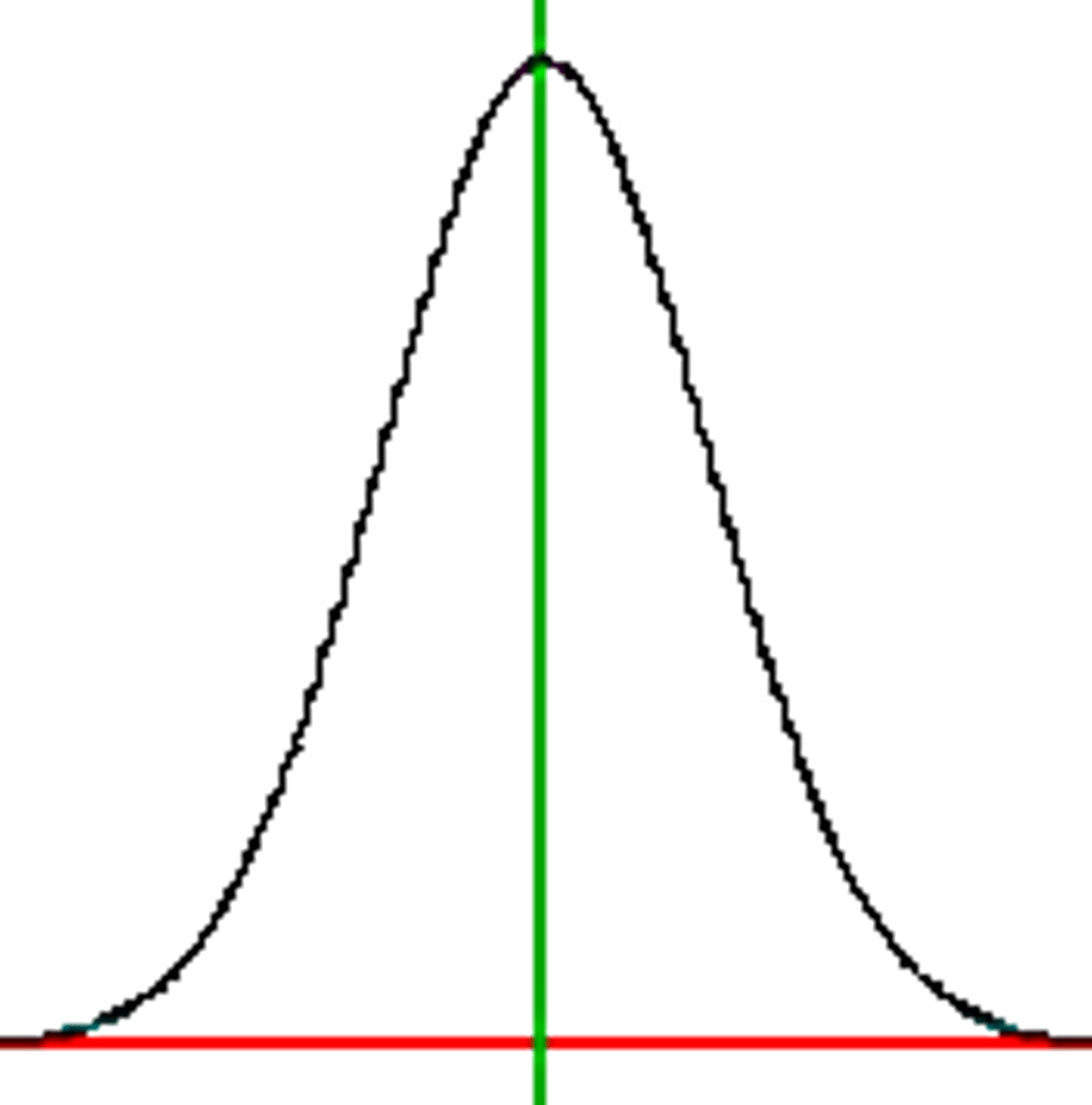
What does a normal curve look like?
bell-shape
True or False:
A population is the particular group of people studied.
FALSE:
- A population is the entire group of people to which a researcher intends the results of a study to apply
- A sample is the particular group of people studied.
Random selection is:
A method for selecting a sample that uses truly random procedures (usually meaning that each person in the population has an equal chance of being selected)
What is the formula for figuring the Z score for the sample's raw score based on the population mean and standard deviation of the comparison distribution?
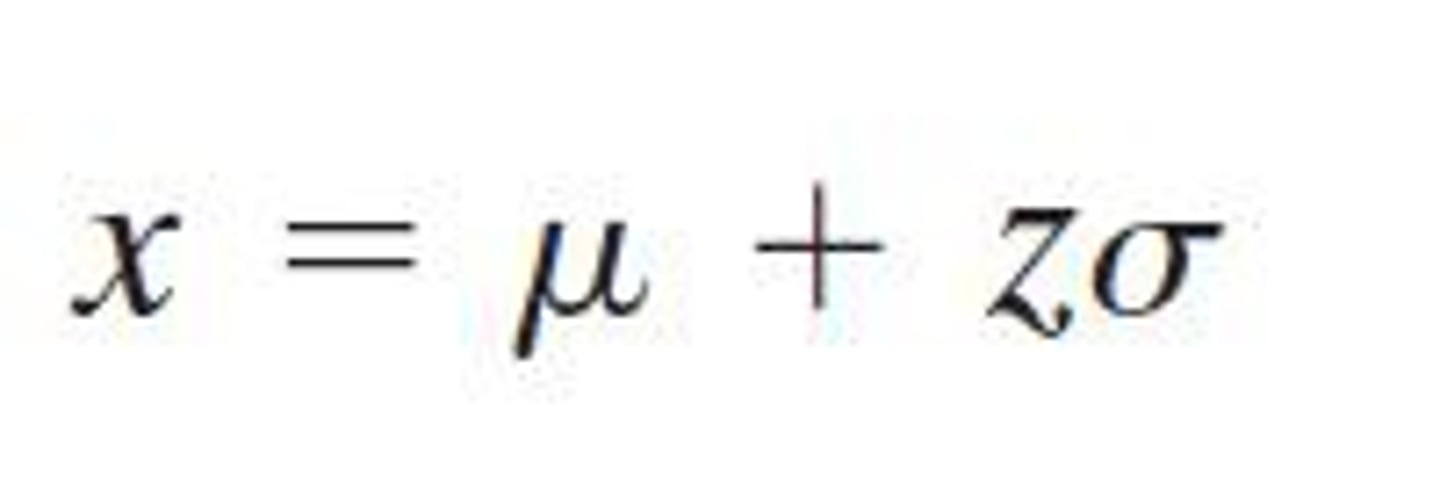
A research hypothesis that does not predict a particular direction of difference between the population like the sample studied and the population in general is called a _____________
Nondirectional hypothesis (two-tailed test)
What is an example of Nominal Scales and what property(s) does it have?
- Gender
- ONLY identity property
What is an example of Ordinal Scales and what property(s) does it have?
- Rankings
- magnitude as well as identity
Which property does Interval Scales NOT have?
TRUE ZERO
Which scale of measurement has every property?
Ratio Scales (identity, magnitude, equal intervals, and true zero)
Measurement errors:
distort the scores so that the observations do not accurately reflect reality
An Operational definition is:
a definition of a variable in terms of the procedures used to measure and/or manipulate it
Reliability = _____________
consistency
How many types of reliability did we learn?
3
- Interrater Reliability
- Test-Retest Reliability
- Internal Consistency Reliability
Interrater Reliability refers to...
the degree to which different observers agree on their observations
Test-Retest Reliability is...
a method for determining the reliability of a test by comparing a test taker's scores on the same test taken on separate occasions
Internal Consistency Reliability is used when...
several observations are made to obtain a score for each participant
A ___________ occurs when a high proportion of subjects in a study have maximum scores on the observed variable (left-skewed)
Ceiling effect
A ___________ occurs when a high proportion of subjects in a study have minimum scores on the observed variable (right-skewed)
Floor effect
When the measures gathered from one tool agree with the measures gathered from other assessment techniques it is __________ validity
concurrent
criterion-related validity is measured by a comparison of the test score and ___________ measures of what the test is designed to measure
independent
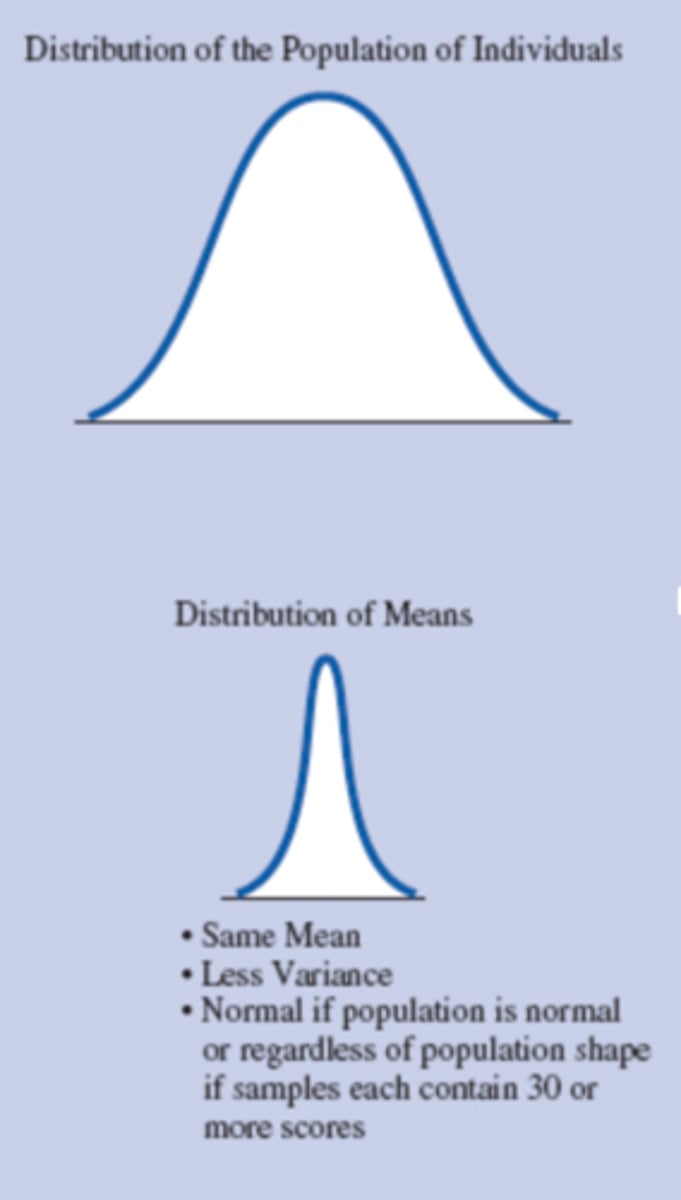
What are the three characteristics of the comparison distribution of a distribution of means?
1. Its mean
2. Its spread (which you measure using the variance and standard deviation).
3. Its shape.
True or False:
The mean of a distribution of means is the same as the mean of the population of individuals.
TRUE
The variance of a distribution of means is the variance of the population of individuals divided by....
the number of individuals in each sample
The standard deviation of a distribution of means is...
the square root of the variance of the distribution of means.
What is the Standard Error?
square root of the variance of a distribution of means
What is the difference between the distribution of the population of individuals and the distribution of means?
A Z-test is a hypothesis-testing procedure in which there is a single sample and the population variance is ________.
known
What does it mean to have a Type I Error in terms of null and research hypothesis?
- rejecting the null hypothesis when in fact it is true
- getting a statistically significant result when in fact the research hypothesis is not true
What does it mean to have a Type II Error in terms of null and research hypothesis?
- failing to reject the null hypothesis when in fact it is false
- failing to get a statistically significant result when in fact the research hypothesis is true.
What are the two types of decision errors?
Type I Error AND Type II Error
What type of error is a false positive?
TYPE I
What type of error is a false negative?
TYPE II
alpha (α) is the probability of making a ________ error; same as significance level.
TYPE I
- The lower the alpha, the smaller the chance of a Type I error
- Researchers who do not want to take a lot of risk set alpha lower than .05, such as p < .001
____________ is the probability of making a Type II error.
beta (β)
effect size is the standardized measure of ________(lack of overlap) between populations
difference
According to Cohen's conventions of effect size (d), what would an effect size of .15 be considered?
SMALL
.20 is a small effect size
.50 is a medium effect size
.80 is a large effect size
According to Cohen's conventions of effect size (d), what would an effect size of 1.00 be considered?
FRICKIN LARGE
.20 is a small effect size
.50 is a medium effect size
.80 is a large effect size
According to Cohen's conventions of effect size (d), what would an effect size of 0.62 be considered?
MEDIUM(sooooo mid...)
.20 is a small effect size
.50 is a medium effect size
.80 is a large effect size
What is the formula for figuring EFFECT SIZE?
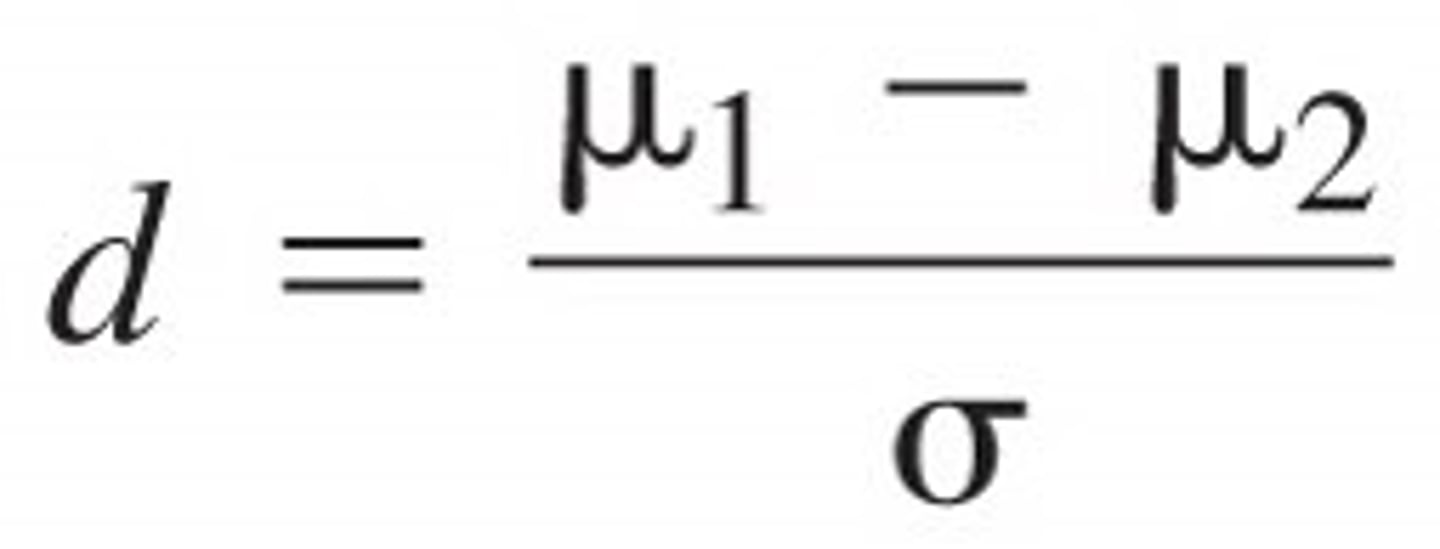
What is better, a larger confidence interval or a smaller confidence interval?
SMALLER
- narrows down the area in which we are confident holds the TRUE population mean
What is the formula for figuring the standard error?
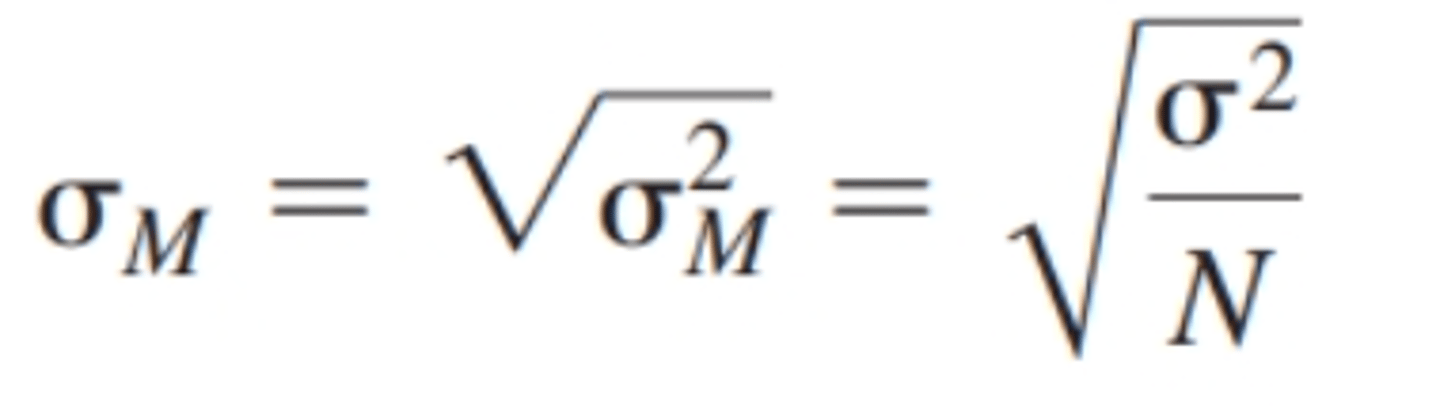
True or False:
If the confidence interval does not include the mean of the null hypothesis distribution, then the result is NOT statistically significant
FALSE
- If the confidence interval does not include the mean of the null hypothesis distribution, then the result is statistically significant
What are the types of field research we have learned? (HINT: there's six)
- Naturalistic observation
- archival research
- surveys
- case studies
- program evaluation
- field experiments
What is the Central Limit Theorem?
As sample size increases, the distribution of sample means of size approaches a normal distribution.
In order to counteract human tendency to see order when no order exists in reality, combine inductive and ________ reasoning, creating the ___________
deductive; critical thinking principle
True or False:
Inductive reasoning is specific to general.
TRUE
- used to generate theories based on observations (think Sherlock Holmes)
True or False:
Deductive reasoning is specific to general.
FALSE FALSE FLOSS
- Deductive reasoning is GENERAL to SPECIFIC
- uses constructs as the basis of making predictions about observations
What are Barnum statements?
Statements that could apply to anyone (e.g. an astrology column)
The similarity-uniqueness paradox is the tendency to _______ comparisons between objects as either similar to, or different from, one another
SIMPLIFY
The tendency to see statements as either true or false when, in fact, they are actually probabilistic is known as _____________ bias
all-or-none
Labeling an action as aggressive, then claiming the perpetrator of the action is aggressive is an example of which fallacy?
nominal fallacy
- confusing a label of a behavior as the explanation for the behavior
The two ways to gather data in naturalistic observation are as a(n)....
Unobtrusive observer
- Anyone who is able to observe the behavior of participants without the participants being aware that they are being observed.
Participant observer (becomes case study)
- Any researcher gathering data while being an active part of the setting.
Any effect on participant's behavior that results from the participant being aware that he or she is being observed is called...
Measurement reactivity
Coding data is the process by which _____ are assigned to _______
scores; behaviors
True or False:
Archival records are any data source for events that have already occurred.
TRUE
An ____________ fallacy is an error in reasoning in which we assume that the observed relationship between current and reported historical events represents a causal relationship.
Ex post facto
What is the difference between Experimenter reactivity and Experimenter bias?
Experimenter reactivity - Any action by the researcher, other than the independent variable manipulation, that tends to influence participants' responses.
VS
Experimenter bias - Biasing effects produced by the expectations of the researcher.
Correlational research assesses the ________ of relationships among variables
strength
True or False:
Correlation does establish causality
FRICKIN FALSE
**CORRELATION DOES NOT MEAN CAUSATION**
Can a correlational study prove a theory to be correct?
NO
- A correlational study cannot prove a theory correct, but it can negate a theory
Differential research compares two or more groups that differ on ______________ variables
pre-existing
An ________ is any apparent effect of an independent variable that is actually the result of some other variable that was not properly controlled
artifact
- Artifacts are the result of confounding
True or False:
Correlational research has no comparable control procedure.
TRUE
What is experimenter expectancy?
the tendency of investigators to see what they expect to see
In real research when do investigators calculate statistical power?
BEFORE THE STUDY
-helps identify how many participants are needed
________ is the probability that the study will give a significant result if the research hypothesis is true (your chances of finding what you're looking for if they're really there)
statistical power
The bigger the effect size is, the ______ the power is.
bigger, greater
The __________ the standard deviation is, the bigger the effect size is
smaller
Less extreme significance levels mean ________ power
more
What is the z score for one tailed p< 0.01?
2.33
What is the z score for one tailed p< 0.05?
1.64
What is the z score for two tailed p< 0.01?
2.58
What is the z score for two tailed p< 0.05?
1.96
When interpreting a boxplot, what does the top of the box tell you?
75th percentile score
Which validity uses a lot of operational definitions for one construct?
Convergent validity
Which of the following is necessary to establish causation?
- a time-order relationship
- covariation of the events
- alternative explanations have been ruled out
Two variables that vary at the same time are ________
confounded
What are the 2 main influences on power?
- Effect size
- Sample size
Order the research design from least to most constraint.
- naturalistic observation (LEAST)
- case study
- correlational
- differential
- experimental (MOST)
What the difference between a t distribution and a z distribution?
The t distribution has thicker tails, which means their are more scores in the tails
What is the unbiased estimate of the population variance formula?

What is the variance of the distribution of means formula?

What is the t score formula?
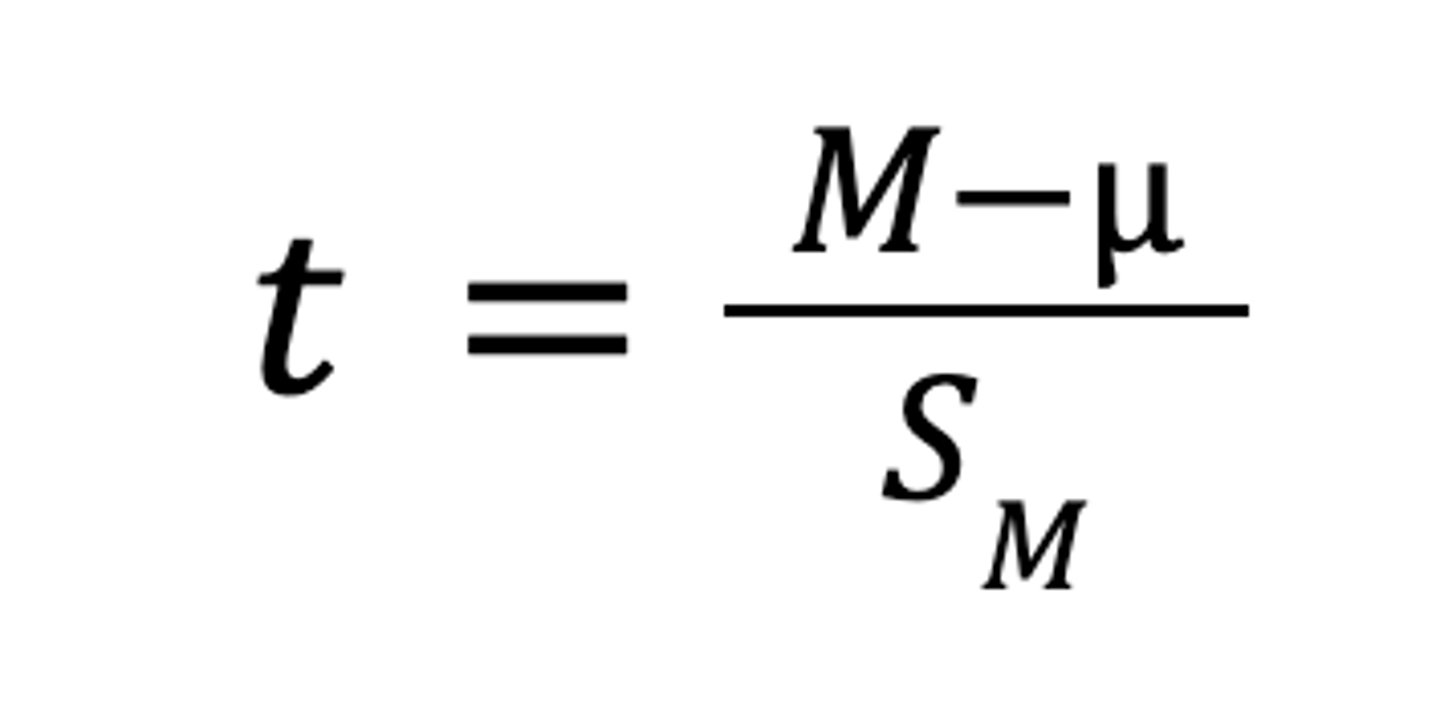
What do you call a research strategy in which each person is tested more than once (almost always twice)?
Repeated measures design
What kind of test do we use for repeated measures design?
t test for dependent means
What is a null hypothesis for dependent means t test?
There is no difference. DUH.