PA and Nutrition Exam 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions necessary to maintain life
Purpose of metabolism
Convert food to energy
What does metabolism contribute to
Regulate body temps, contract muscle, build tissue, and keep our heart beating
Energy
The capacity to perform work
Kilocalorie
A unit of energy (measured in calories)
What does kilocalories tell us
How much energy certain foods provide and how much energy we use during exercise
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Basic form of energy used by cells
Process of converting food to energy
Eat calories (digest or metabolize) - ATP production - Fuel/energy (for bodily functions)
Metobolic rate
Rate at which your body uses energy (in the form of calories)
What does metabolic rate determine
How quickly or slowly your body converts the calories you consume into ATP or useable energy
Resting metabolic rate
The number of calories your body needs at rest (to maintain basic functions)
Average RMR
1,400 kilocalories for women and 1,800 for men
Total daily energy expenditure (TDEE)
Number of calories an individual uses in a day
Thermic effect of food
Number of calories used for digestion, absorbtion, and processing of food
How to determine TDEE
RMR (60-75% of TDEE) + TEF (10% of TDEE) = Physical activity (remaining calories)
What characteristics impact our RMR?
How active a person is, biological sex, age, body composition
Macronutrients
Fuel substrates that provide calories/energy (ex. carbs, fats, protein)
Carbs to energy process
Carbohydrate - Digestion - Glucose - Enters bloodstream - can either 1. Travel to active tissue or 2. Glycogen (stored glucose) - energy in the form of ATP
What are the bodies preferred fuel source
Carbs
Fat to energy
Dietary fat can be stored in fat cells or used as energy
Is protein used for energy
No, used to build new tissue
3 energy systems
Immediate, Anaerobic, Aerobic
Fuel stores
Substrates - primarily carb + fat
Do cells store ATP
Not very much because it is heavy. Fuel stores are mobilized to increase ATP production
What are 3 energy systems used for
To create ATP
Immediate energy system
Rapid energy; strength - speed - power
Duration of immediate energy system
Less than 15 seconds
Fuel source of immediate energy system
Stored ATP ( glycogen) + creatine phosphate (high energy molecule produced by body and consumed from diet that is stored in muscles)
Anaerobic energy system
Longer bouts while maintaining high intensity
Duration of anaerobic energy system
15 seconds to 2 min
Fuel source of anaerobic energy system
Blood glucose, stored glycogen
Aerobic energy system
Slow to produce energy but last longer
Duration of aerobic energy system
More than 2 min
Fuel source of aerobic energy system
Blood glucose, stored glycogen, fats
Does our body use all 3 systems during exercise?
Yes, but they dominate depending on intensity and duration
Potential ergogenic benefits (creatine)
Enhanced glycogen synthesis, increased muscle mass + strength adaptations, increased single + repeated strength adaptations, increased single + repeated sprint performance, possible enhancement of aerobic capacity and enchanced recovery
Does consuming carb solution drink (gatorade) increase performance
Yes, during soccer drills it increased agility by 2%, dribbiling by 3.2% and kicking accuracy by 3.5% (due to carbs not electrolytes)
2 primary functions of cardiovasuclar system
Delivery of O2 (nutrients) and removal of Co2 (waste)
3 primary componets of cadiovasuclar system
The heart, blood vessels (veins, capillaries, arteries) and blood
How many chambers does the heart have
4
What are the 4 chambers of the heart
Left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle
What chambers of the heart are recieving
Left and right atrium
What chambers of the heart are pumping
Left and right ventricles
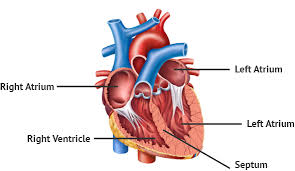
Atrium and Ventricles
Blood vessels
Veins, capillaries, arteries
What do veins do
Carry blood towards heart
What do capillaries do
Smallest vessels that serve as connection between arteries and veins
Arteries
Carry blood away from heart
How can we increase O2 delivery to muscle during exercise
Increase our HR
Red blood cells bind to ____ in the lungs and is returned to heart
O2
O2 rich blood is pumped by the ___ through the arteries
Heart
O2 rich blood reaches the ____ and drops ____ off to the muscle
Capillaries, O2
Skeletal muscle uses ____ to produce ATP
O2
Heart rate
Number of times heart beats per min
Stroke volume
Every time heart beats it ejects blood. SV is that amount of blood
Cardiac Output
Amount of blood pumped through CV system per min
Blood pressure
Pressure blood exerts on walls of arteries
Normal Blood pressure
Below 120/80
Normal resting HR
60-100 bpm
Maximal exercise HR
170-200 bpm
Resting SV
50-70 mL
Maximal exercise SV
80 -150 mL
How to measure CO
SV x HR = CO
Resting CO
4-5 L/min
Maximal exercise CO
20-40 L/min
Systolic BP
Pressure in arteries when heart contracts
Diastolic BP
Pressure in arteries when heart relaxes
What percent of adults have hypertension
47%
What does hypertension increase risk of
Cardiovascular diease, stroke, + dementia
Chronic effects of aerobic exercise in hypertensive people
Reduced systolic and diastolic BP
What happens to Hr, cardiac output, and stroke volume during exercise
All Increase
Maximal oxygen consumtion (VO2max)
Maximal ability to use oxygen during exercise
What does Vo2max indicate
Cardiorespitory fitness
How to measure vo2max
Analyzing inhaled and exhaled air during maximal exercise
What is the most important factor in increasing vo2max
Intensity
Fitt- vp principle in aerobic exercise
Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type, Volume, Progression
Frequency
Number of times per week
Aerobic frequency recommendations
3-5 days per week to acheive volume
Intensity
How hard the exercise is
3 categories for intensity
Low/light, moderate, vigourous
Methods for monitoring intensity
Hr, talk test, RPE
How to measure maximal HR
220-age or during a maximal exercise test
Rating of percieved exertion (RPE)
Subjectively rate level of exertion by asking how hard you feel like your working
What percent of people do a poor job assesing RPE
5-10%
What factors impact RPE
Sleep, hydration, nutrition, and enviromental factors
Talk test
Intensity is accompained by increased breath taking
Time
Amount of time per session
30 - 60 min a day (150 min a week)
Moderate
20-60 min a day (75 a week)
Vigourus
Type
Kind of exercise performed
Volume
Total exercise performed (FxIxT)
What do you do if a person wants extensive benefits
Double the recommendation
Progression
Increased challenge/ workload
How should we progress a client?
10% rule, only change one variable at a time (f,i or t)
Progression for inactive individuals
Increase session duration by 5-10 min every 1-2 weeks over first 4-6 weeks of training
MICT
Moderate intensity continuous training
HIIT
High intensity interval training
SIT
Sprint interval training
What is mict
Traditional form of cardio, consistant effort for long duration
Example of MICT
30-60 min at moderate intensity