17. Transcription factors
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
which GTF binds the TATA box
TBP (TATA bidning protein) within TFIID
6 RNAP II general transcription factors
TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH
what are the two main roles of TFIID
foundation for transcription complex assembly and nucleosome destabilization
which GTF has helicase and kinase activity
TFIIH
what happens to RNAP II’s CTD during promoter clearance
it is phosphorylated by TFIIH’s kinase activity
which factor recruits RNAP II to the promoter
TFIIB and TFIIF
what residues coordinate Zn in a C2H2 zinc finger
2 cysteines + 2 histidines
What DNA-binding motif is found in nuclear receptors
C4 zinc fingers
what is teh structure of a homeodomain
3 alpha-helices, 2 forma. helix-turn-helix, the 3rd inserts inot the major groove
what are the four possible domains in a TF
DN-binding, activation, dimerization, ligand binding
what does combinatorial control mean
different combinations of TF subunits regulate different genes
what is the role of coactivators
link activators to RNAP II complex and modify chromatin
what is the function of the mediator complex
bridge between activators and RNAP II: regulates initation rate
how far can enhancers act from the promoter
up to tens of kilobases; can be on different chromosomes
what does the yeast two-hybrid assay detect
interactions between a TF and DNA or between two proteins
How can promoter mapping be done
by creating a 5’ deletion series and measuring reporter gene expression
transcription initation complex
RNAP II + GTF bound: general transcription factors bound to promoter region
TFIID has two basic roles
foundation for the transcriptional complex
prevention of nucleosome stabilization
TBP is a component of the positioning factor
no matter which RNAP is transcribing → allows each type of polymerase to bind to its promoter
TAFs- TBP associated factors
determine whether or not TFIID stays at the promoter
TFIID complex
TATA binding proteins and 14 TBP associated factors (TAFs)
once TBP/TFIID bound
TFIIB can bin rate limiting step in transcription of many genes, proximal enhancers to TFIIB
monomeric protein
developmental regulation
TFIIB orients RNAP on DNA
TFIIB binds to bent DNA opposite and adjacent to TBP
RNAP II will come in contact with TFIIB near RNA exit site and active site
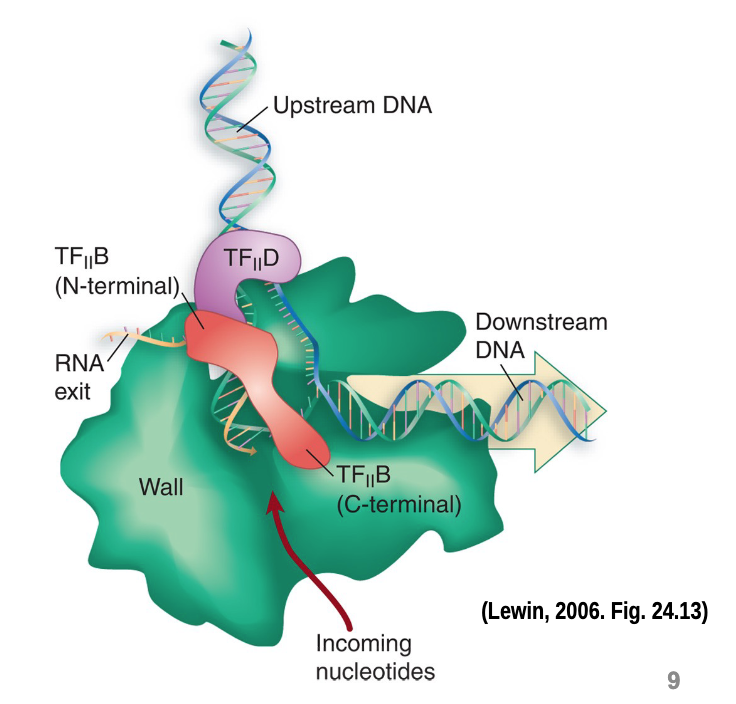
TFIIE is DNA-dependent ATPase
probably necessary for generating the energy involved in melting a promter
TFIIH contains nine subunits
it has helicase activity and protein kinase activity
for transcription to occur, RNAPII must
be released from the promoter
TFIIH helicase activity will unwind DNA (with energy from TFIIE) and kinase activity is responsible for
phosphorylation of CTD tail → ctd tail detaches from RNAPII from TFIID
transcription pause released by
additional phosphorylation of CTD and other factors by CDK9
promoter clearance
mediator and GTFs are released
eu transcript overview
TFIID + TBP binds at TATA box → TFIID complex (14 TBP associated factors)
TFIIB binds → orients RNAP on DNA
TFIIF binds to mediator RNAPII → gather general factors
two large subunits of RNAPII interact with TFIIB
CTD tail (unphosphor) of RNAPII direct contact with TFIID
TFIIE and TFIIH binds
RNAPII is at the promter
TFIIH helicase activity unwinds DNA phosphorylates CTD tail
CTD tail detaches RNAPII from TFII
in majority of TATA-less promoters
first TBP has to be placed at the right spot in respect to the existing core element and transcription start site
initator element
TBP alone cannot bind to Inr-only promoters - requires the entire TFIID complex via TAFII-250 and TAFII-150
alternatively: TAFII-250 and TAFII-150 tether TBP to the initiator, allowing the rest of TFIID to assemble
TBP alone cannot bind to GC-only promoters
requires whole TFIID via TAFII-110 and Sp1 transcription factor or,
Sp1 binds GC boxes and interacts with TAFII-110, TAFII-250 and TAFII-150, anchoring TBP so the rest of TFIID can bind
purpose fo the yeast two-hybrid TF activity assay
to measure the activity of a transcription factor by detecting reporter gene expression controlled by its binding site
why is the host cell used in the assay lacking functional TF c
to ensure that any reporter gene activation comes from the introduced TF X
how can the yeast two-hybrid system help identify important domains of a transcription factor
by introducing mutations in the TF gene or its binding site and observing effects on reporter gene expression
proteins that directly influence RNAP binding
GTFs
TF = activators and repressors bind to DNA at proximal elements, enhancers/silencers
other proteins/complexes that affect transcription
co-activators and mediators
chromatin remodelling enzymes and other regulators
in order for protein to be transcription activator OR repressor, it;
has to be able to bind to DNA
activate or repress transcription
transcription factors are modular proteins
different domains - different funcitons
DNA binding domain
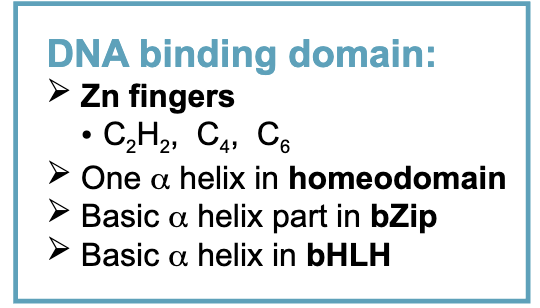
Dimerization domain
one of the Zn finger
alpha helix in Zn finger C6
leucine zipper part in bZip
second helix in bHLH
transcription activation domain
acidic
glutamin rich
proline rich
ligand binding domain
in zn finger - C4 factors (steroid hormone is ligand)
DBD usually
interaction between a helices from the DNA binding
domain & major DNA groove H-bonds, hydrophobicity and
Van der Waals (LDS) interaction
zinc fingers
protein structural motifs involving zinc ion coordination, often used for DNA binding, but also found in non-DNA-binding proteins
Three types of zinc fingers
C2H2 zinc finger (classical form found in >1000 transcription factors)
C4 zinc finger (nuclear receptors, often for dimerization)
C6 zinc finger (found in yeast transcription factors like GAL4)
homeodomain proteins
drosophila - group of homeotic genes, when altered lead to transformations of one body part for another (legs for antenna) = homeotic transformations (transitions)
the locations and developmental roles of homeotic genes are
strikingly similar across many species
the gene order in clusters corresponds to the order of
expression of genes and their function along the anterior-posterior body axis
homeotic genes mostly code for
transcription factors - involved in controlling development - establishment of spatial pattern
leucine-zipper proteins bZIP
hydrophobic aa leu in every 7th position fo the c-terminal region for dimerization
forms alpha-helix with leucine residues
second alpha helical regino is invovled in DNA binding
form homodimers and heterodimers through a coiled structure maintained by hydrophobic forces
helix-loop-helix
hydrophobic residues on one side
non-helical loop of polypetide chain separates teh two alpha helices from each monomeric protein, second alpha helix responsible for DNA binding (basic charge)
form heterodimers