Quiz 2: Ascomycetes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Ascomycete role
Agricultural pathogen
Abruscular mycorryhizal
Human pathogens
spoilage /toxins and preservatives in food
Secondary products in industrialand food enzymes and pharmaceuticals
Abruscular mycorryhizal
Human pathogens
spoilage /toxins and preservatives in food
Secondary products in industrialand food enzymes and pharmaceuticals
2
New cards
Ascomycota Characterisitcs
Chitin in cell walls, septate hyphae, conidia in asexual repro, sexual repro has various gametes that give rise to ascospores, usually haploid
3
New cards
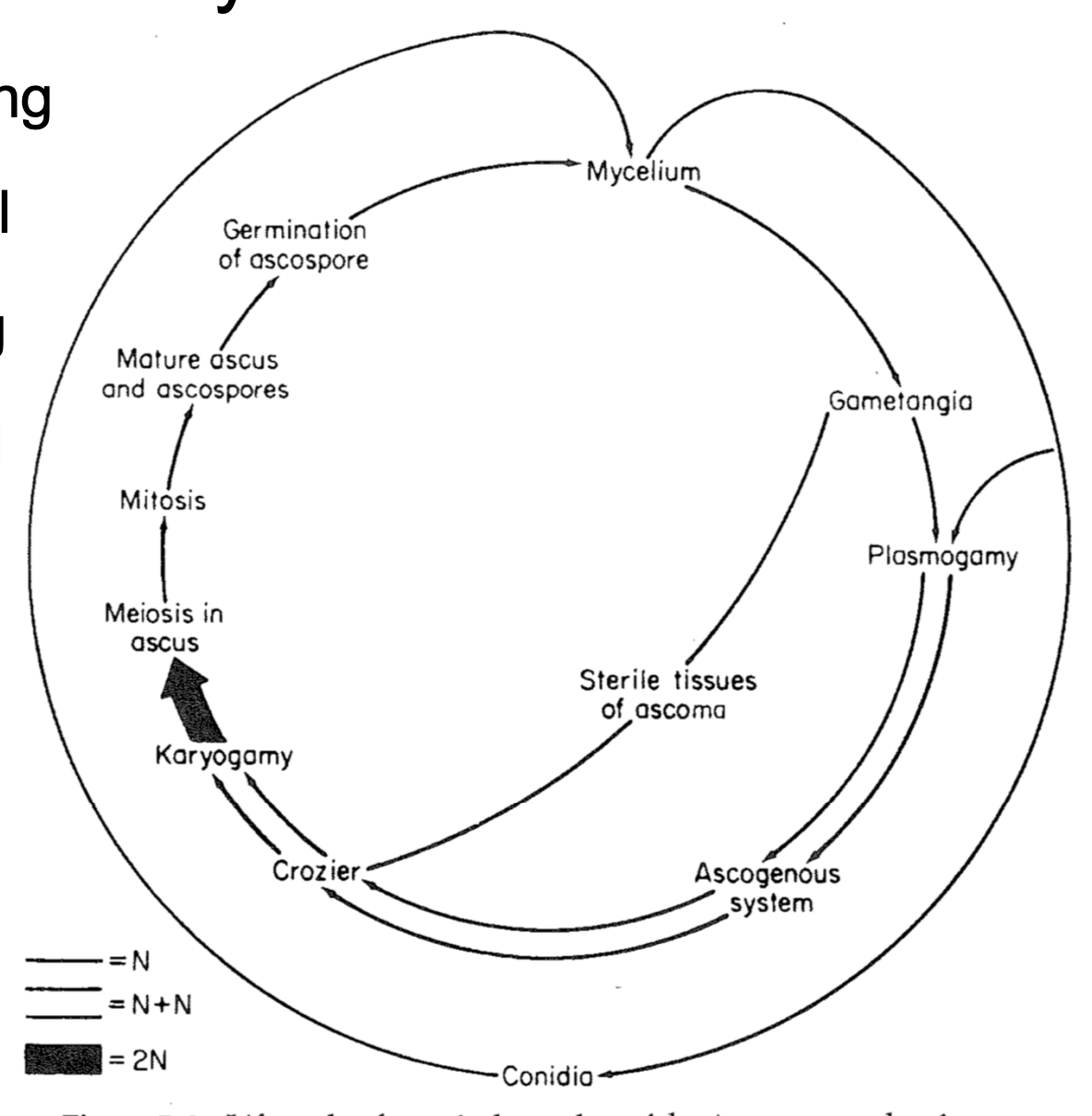
Sexual/Asexual Life Cycle
4
New cards
types of plasmogomy
gametangio-gametangiogamy, gameto-gametangiogamy, somatogamy
5
New cards
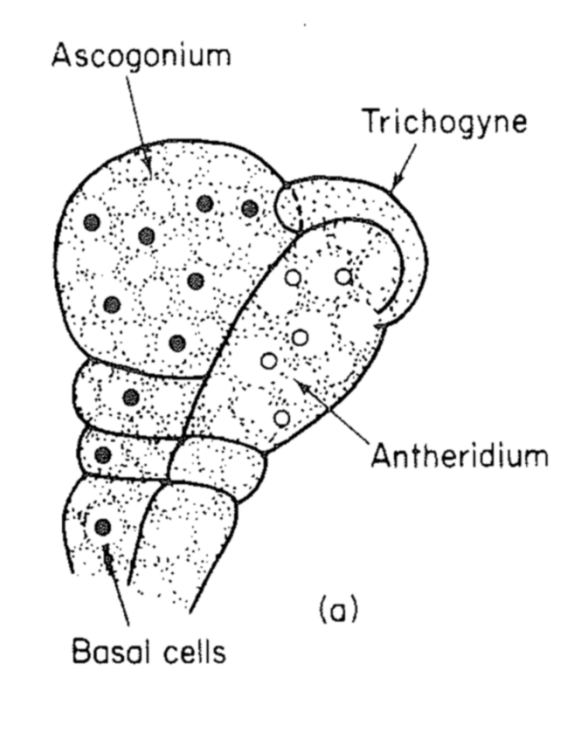
gametangio-gametangiogamy
Female looks different from male
Initially looks similar oomycetes
Initially looks similar oomycetes
6
New cards
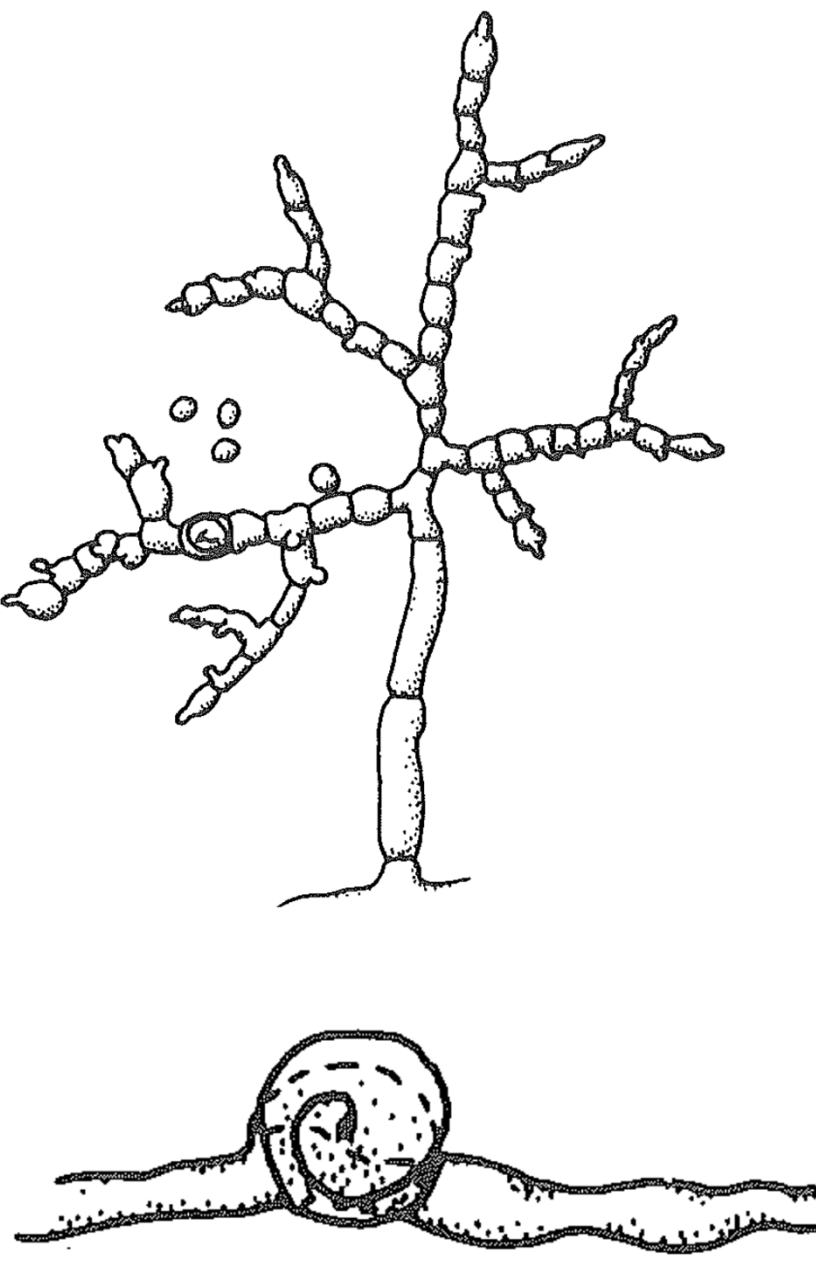
gameto-gametangiogamy
Has spermatium - small unicellular male that fuses with femal ascogonium
7
New cards
somatogamy
No recongizable sexual structures with undifferentiated hyphae
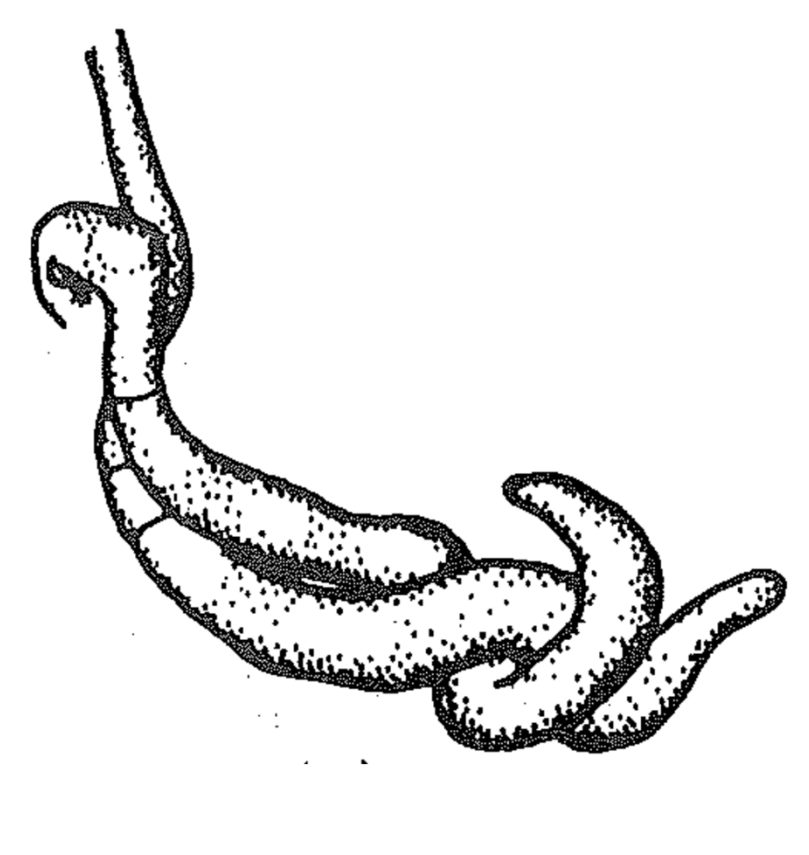

8
New cards
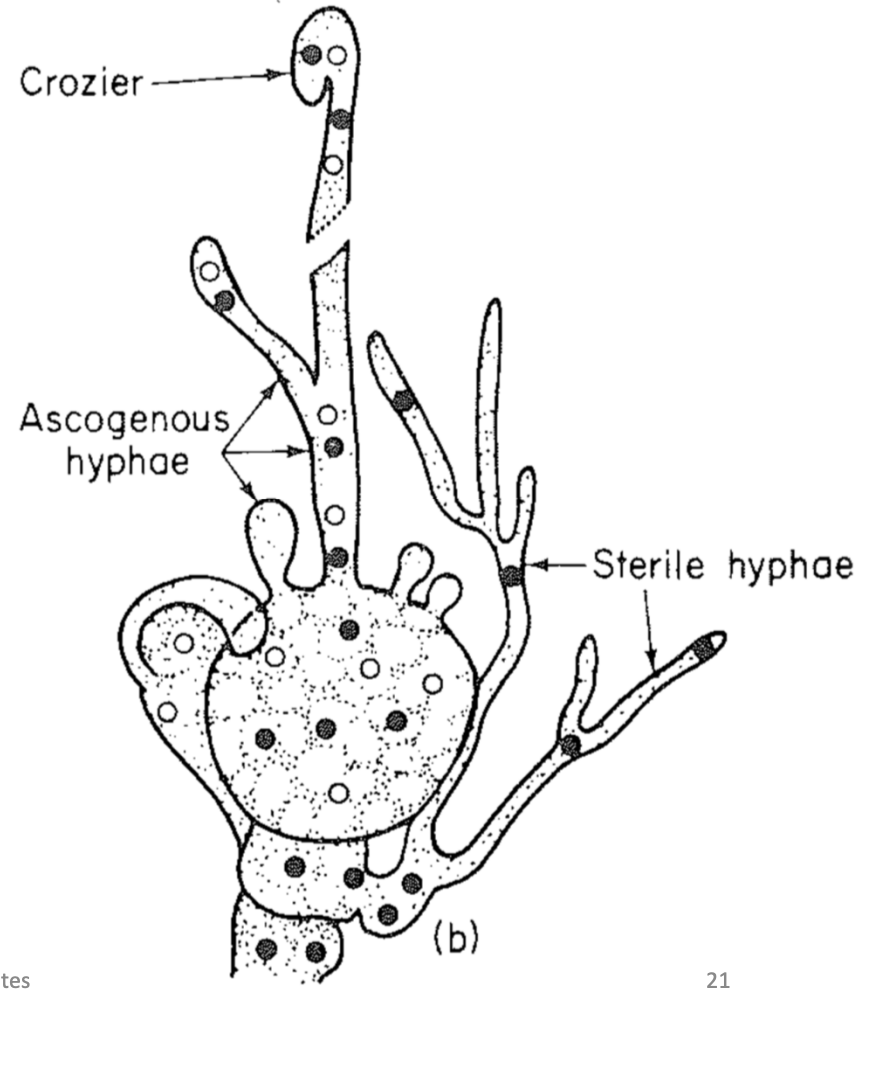
Ascogenous (secondary) hyphae
Formed from an ascogonium
Branch repeatedly
Each cell contains several nuclei
Results in production of crozier cell
Branch repeatedly
Each cell contains several nuclei
Results in production of crozier cell
9
New cards
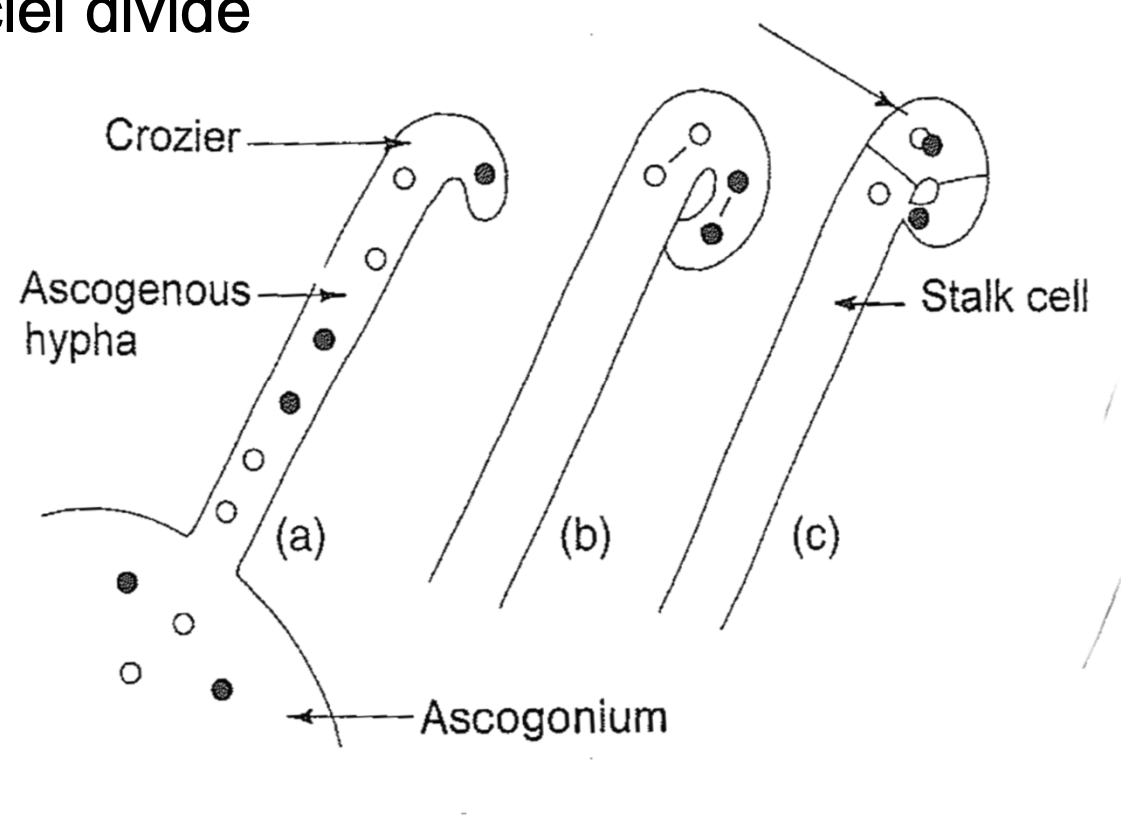
Ascus Formation
A: crozier cell forms from a hooj in the tup of the ascogenous hyphar
B: two dikaryotic nyckeu divide simultaneously
C: septa delimit the pentulitmte cell from the stalk
Karyogamy occurs
D: diploid nucelus in the ascus intial
Only diploid stage in life cycle and new crozier is developing alongside first
E: meiosis
F: mitosis in 4 haploid nuclei results in 8
G: ascospores are formed froma scus cytoplasm
B: two dikaryotic nyckeu divide simultaneously
C: septa delimit the pentulitmte cell from the stalk
Karyogamy occurs
D: diploid nucelus in the ascus intial
Only diploid stage in life cycle and new crozier is developing alongside first
E: meiosis
F: mitosis in 4 haploid nuclei results in 8
G: ascospores are formed froma scus cytoplasm
10
New cards
types of ascocarp
apothecium
cleistothecium
perithecium
loculate
cleistothecium
perithecium
loculate
11
New cards
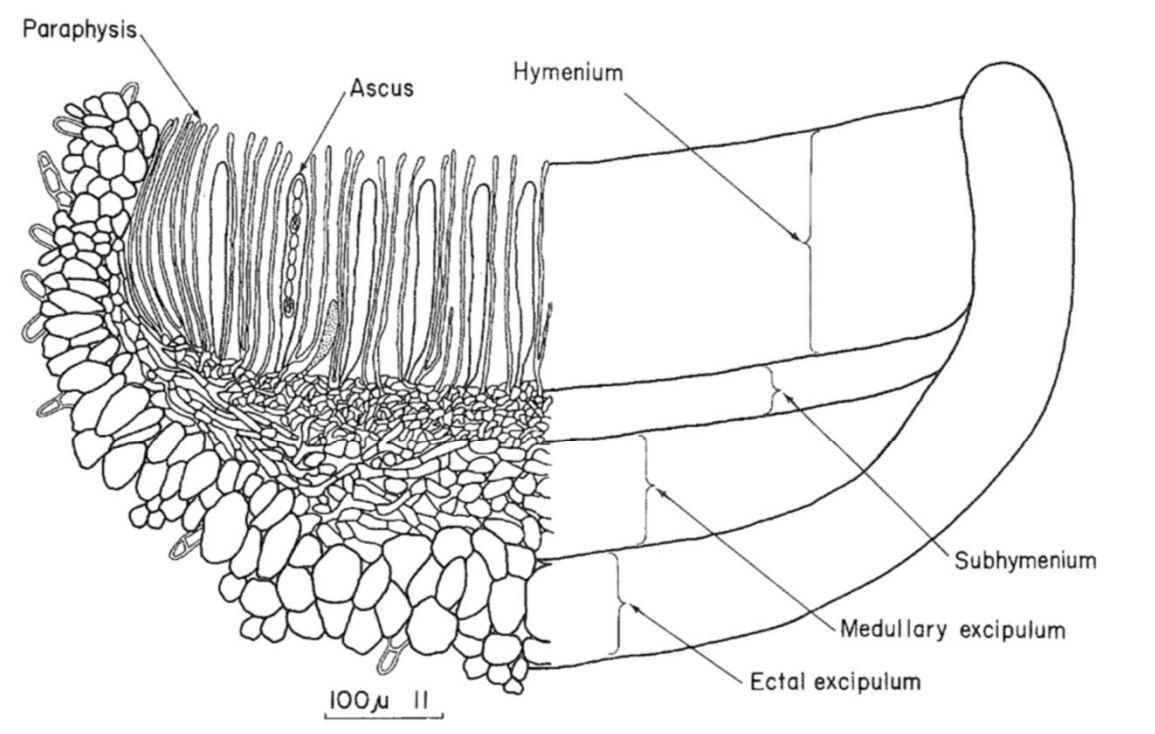
Apothecium
Shaped like cup or saucer
Asci discharge simultaneously
Distinct structural layers
-Hymenium
-Subhymeinum
-Excipulum
Development
-Sterile hyphae intertwined with ascogenous hyphae
-Paraphyses appear before asci
-Crozier cells form at base of paraphyses
-Hymenium may be celistohymenial (closed) or gymnohymenial (exposed)
Asci discharge simultaneously
Distinct structural layers
-Hymenium
-Subhymeinum
-Excipulum
Development
-Sterile hyphae intertwined with ascogenous hyphae
-Paraphyses appear before asci
-Crozier cells form at base of paraphyses
-Hymenium may be celistohymenial (closed) or gymnohymenial (exposed)
12
New cards
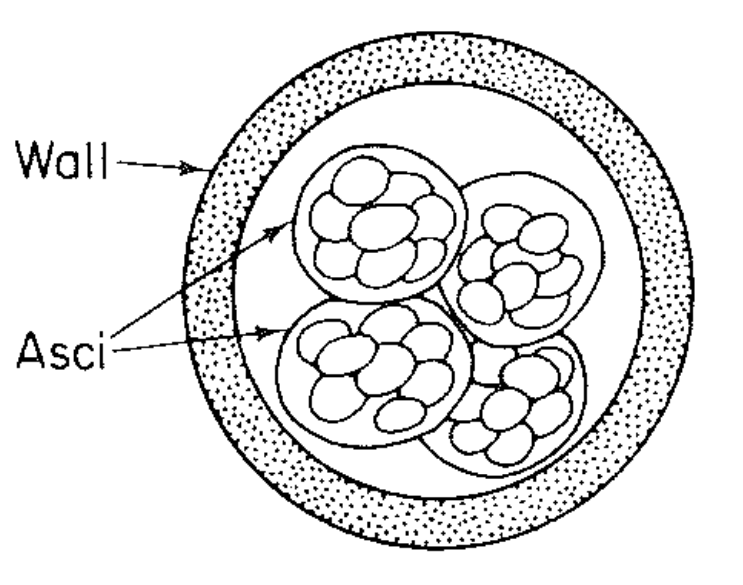
Cleistothecium
Totally encoled by wall of sterile hyphae (peridium)
Asci are released after the wall breaks down from weathering
Chemical attractants encourage dispersal by animals
Asci are released after the wall breaks down from weathering
Chemical attractants encourage dispersal by animals
13
New cards
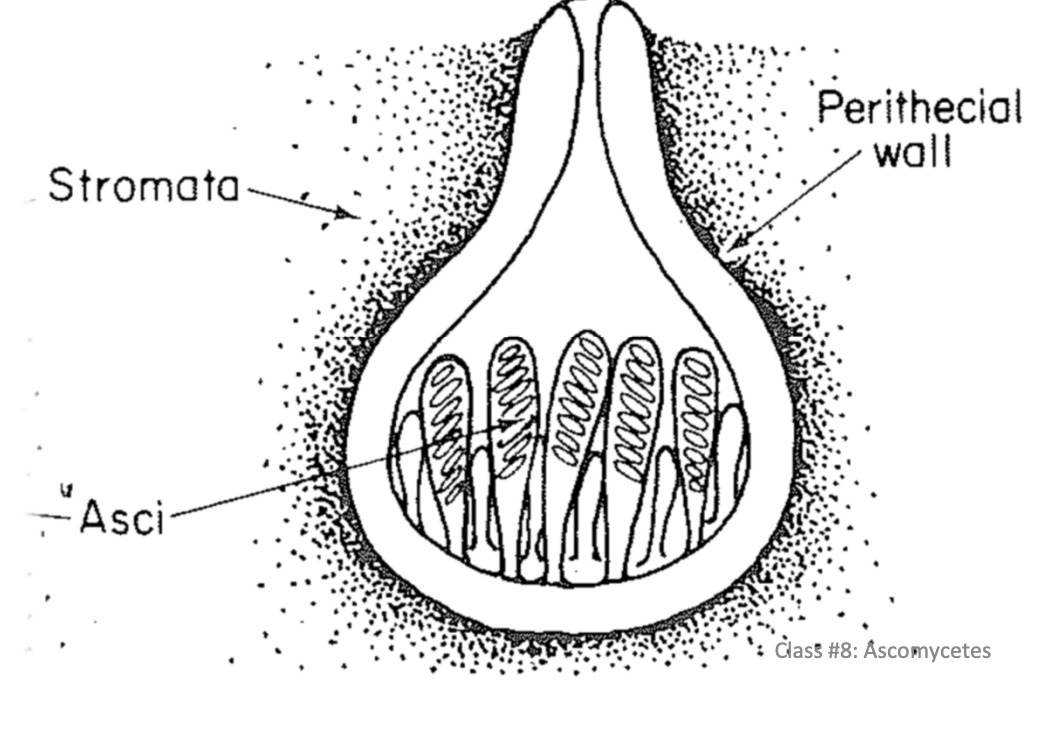
Perithecium
Flask shaped, can be globular
pore/slit for ascospore release
Ascospore discharge from nlyone or a few asci at a time
Neck length varies
Can be
-Embedded in host
-On surface of host
-Embedded ina s troma
Sterile filaments throughout
-Paraphyses - apical ends free
-Pseudoparaphyses - grow from the top down
-Periphyses - short hairs within the neck
pore/slit for ascospore release
Ascospore discharge from nlyone or a few asci at a time
Neck length varies
Can be
-Embedded in host
-On surface of host
-Embedded ina s troma
Sterile filaments throughout
-Paraphyses - apical ends free
-Pseudoparaphyses - grow from the top down
-Periphyses - short hairs within the neck
14
New cards
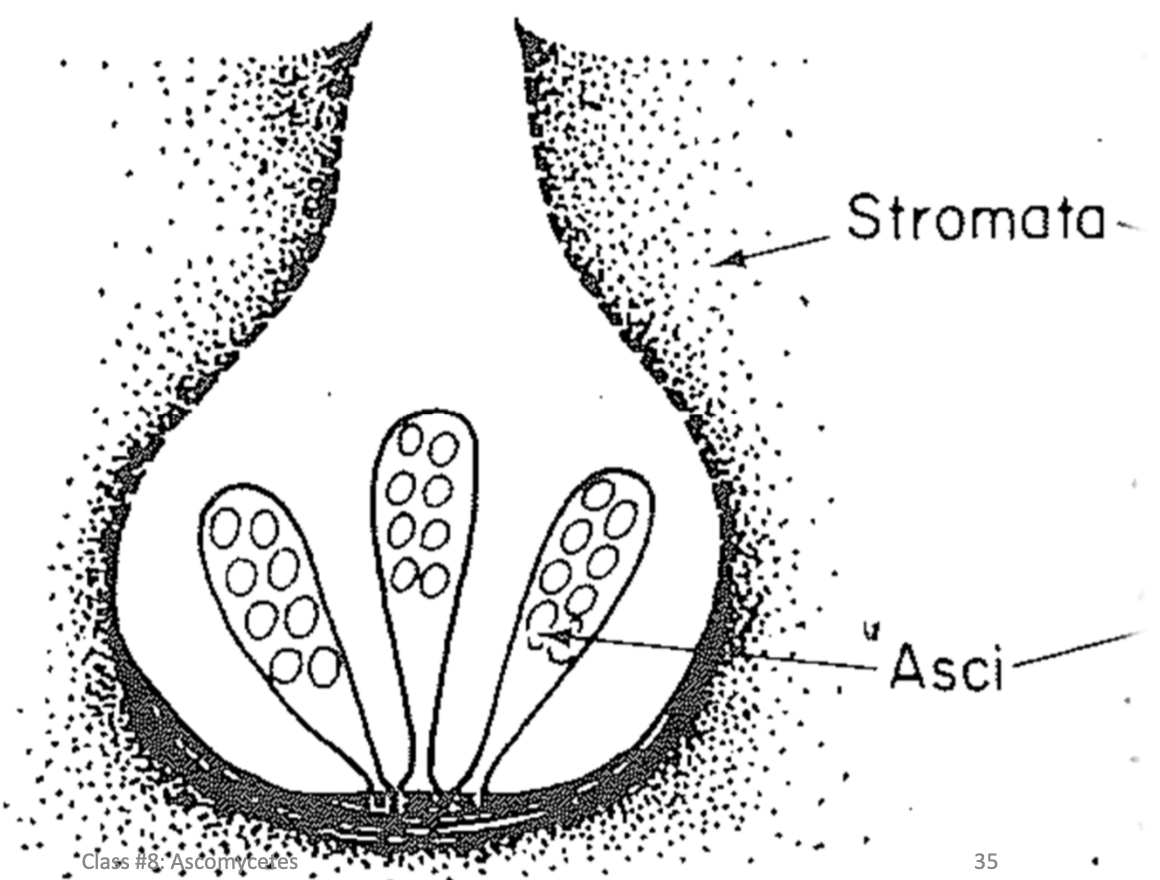
Loculate
Form asci in cavities (locules) within strom but DONT have a distinct wall
One or several within each strom
Hard to distunguis from perithecia
Ascospore discharge perithecia
One or several within each strom
Hard to distunguis from perithecia
Ascospore discharge perithecia
15
New cards
Ascus types
Unitunicate-operculate,Unitunicate-inoperculate, Protunicate, Bitunicate
16
New cards
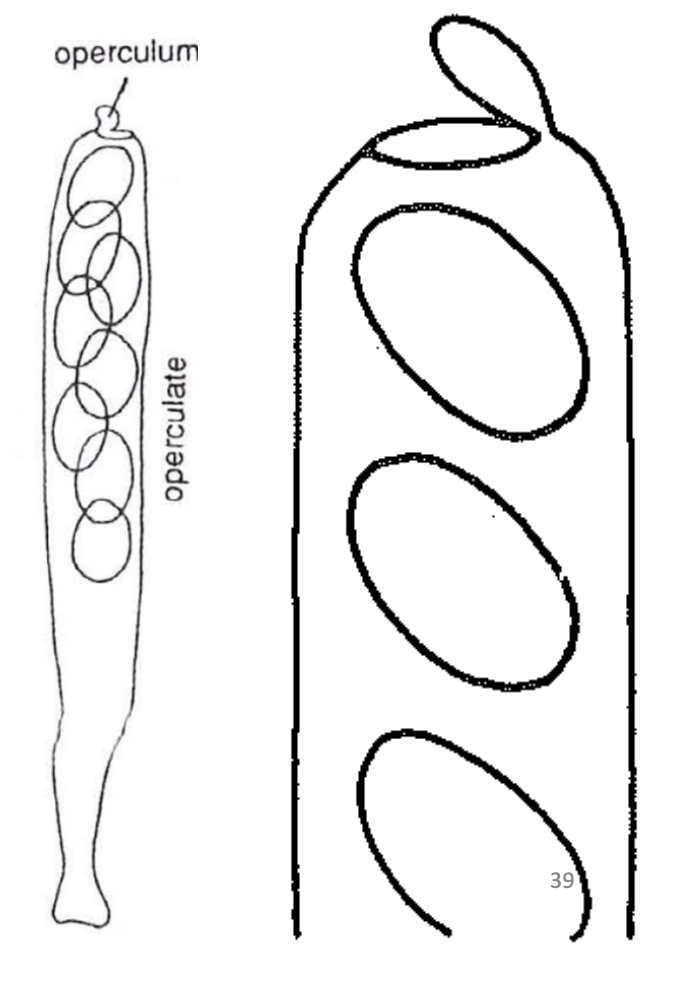
Unitunicate-operculate
Single functional wall
Wall doesnt separate during ascospore discharge
Built in lid (operculum) at the tip
Found only in apothecial ascomata
Wall doesnt separate during ascospore discharge
Built in lid (operculum) at the tip
Found only in apothecial ascomata
17
New cards
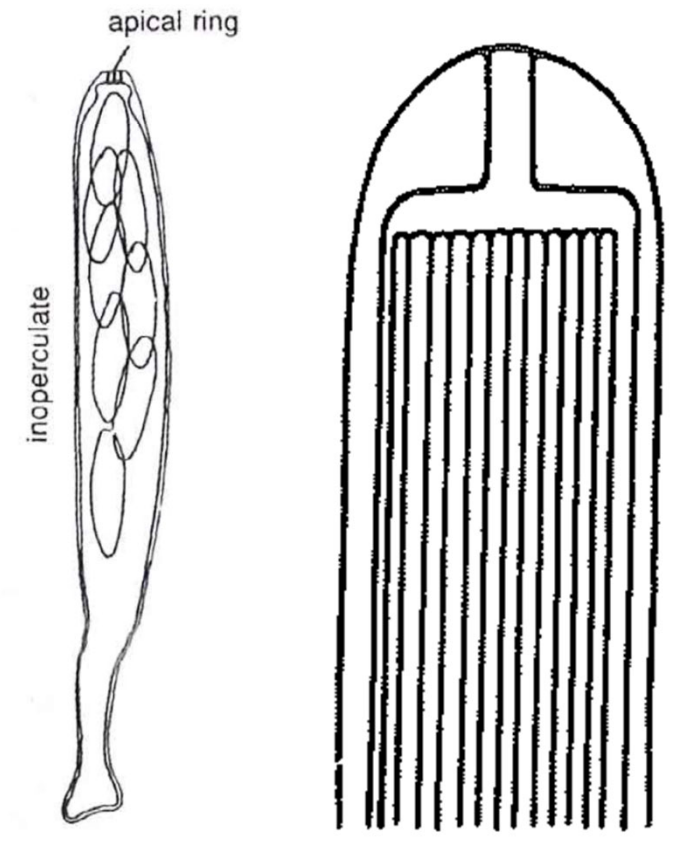
Unitunicate-inoperculate
No operculum (lid)
Elastic ring mechanism in the tip
Found in mostly perithecial ascomata and some apothecial
Elastic ring mechanism in the tip
Found in mostly perithecial ascomata and some apothecial
18
New cards
Protunicate
No active spore dispersal
Usually round
Wall dissolves/ruptured at maturity
Found in several ascomycete orders
Usually round
Wall dissolves/ruptured at maturity
Found in several ascomycete orders
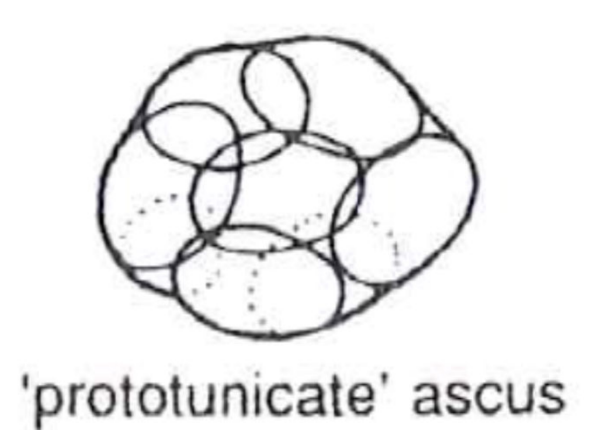
19
New cards
Bitunicate
Ascus wall separates during discharge
At maturity rigid outerwall splits
Elastic inner wall absorbs water and expands
Asci stretch to the ascoma necka nd shoots spores
Produced by pseudothecial ascocrps
At maturity rigid outerwall splits
Elastic inner wall absorbs water and expands
Asci stretch to the ascoma necka nd shoots spores
Produced by pseudothecial ascocrps
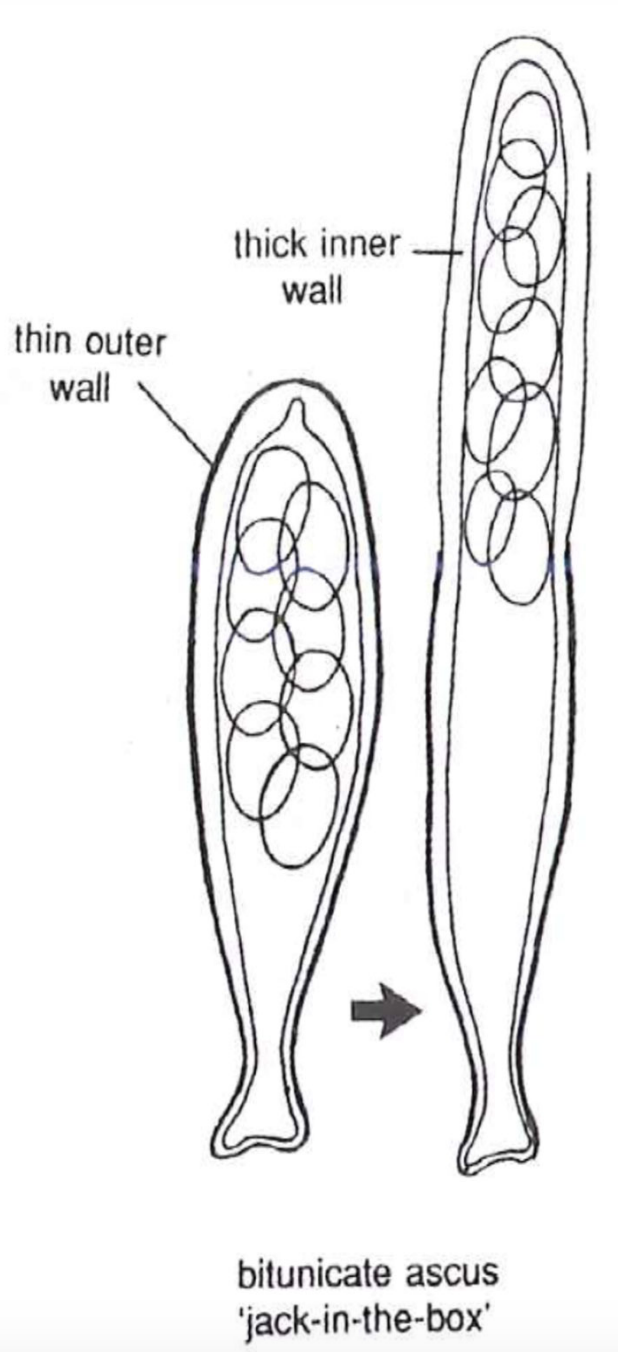
20
New cards
hyphomycetes
asexual fungi tht produce conidia freely or on a sporodochium or synnema
-Dematiaceous: Produce dark brown conidia, green-black or black colonies
-Hyaline: Colonies are hyaline or brightly colored, not dark pigmented
-Dematiaceous: Produce dark brown conidia, green-black or black colonies
-Hyaline: Colonies are hyaline or brightly colored, not dark pigmented
21
New cards
Coelomycetes
asexual fungi that produce pycnidia or acervuli
22
New cards
stages of conidial production
Conidial initiation
Maturation
Delimitation - secondary septa formation
Secession - separation from condidiogenous cells
Proliferation to form further conidia
Maturation
Delimitation - secondary septa formation
Secession - separation from condidiogenous cells
Proliferation to form further conidia
23
New cards
blastic conidia
Condiia are formed by blowing out the cell wall usually from hyphal tip
24
New cards
holoblastic conidia
All wall layers of the conidiogenous cell contribute to the wall of the conidium
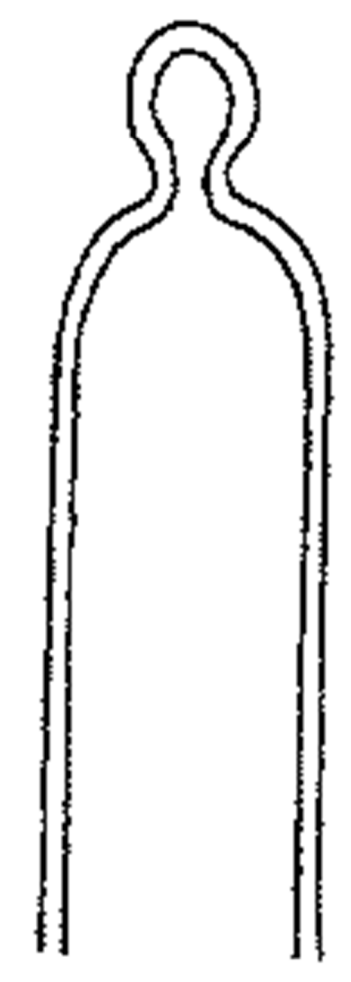
25
New cards
enteroblastic conidia
Wall of the conidiiogenous cell is rigid and breaks open
Conidium is pushed through the opening surrounded by a newly formed wall
Conidium is pushed through the opening surrounded by a newly formed wall
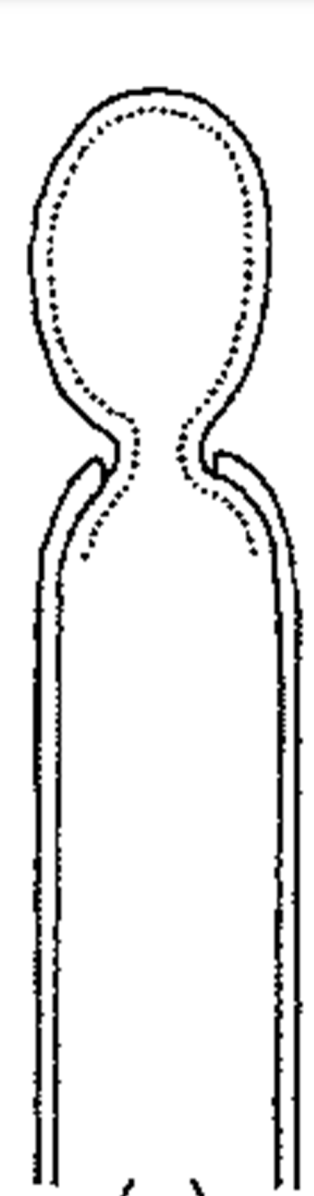
26
New cards
phialidic enteroblastic conidia
Initially holoblastic
Phialide wall breaks at the tip
First conidium cut off by a septum
Second adn third conidia develop beneath first
Lower part of the phialide wall persists as a collarette
Phialide wall breaks at the tip
First conidium cut off by a septum
Second adn third conidia develop beneath first
Lower part of the phialide wall persists as a collarette
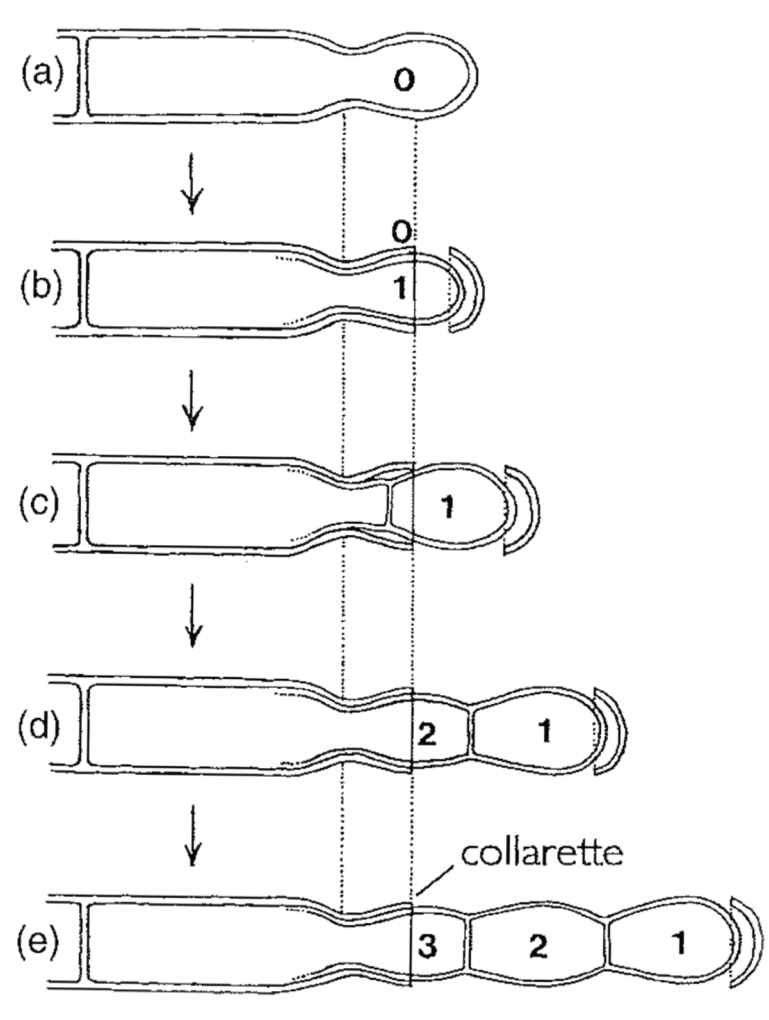
27
New cards
annellidic enteroblastic conidia
Initially holoblastic
First conidium cut off by a septum
Second conidium develops beneath first
Septum cuts off second cindiia beyond the point of the first
The development of more conidia results in further annellations
First conidium cut off by a septum
Second conidium develops beneath first
Septum cuts off second cindiia beyond the point of the first
The development of more conidia results in further annellations
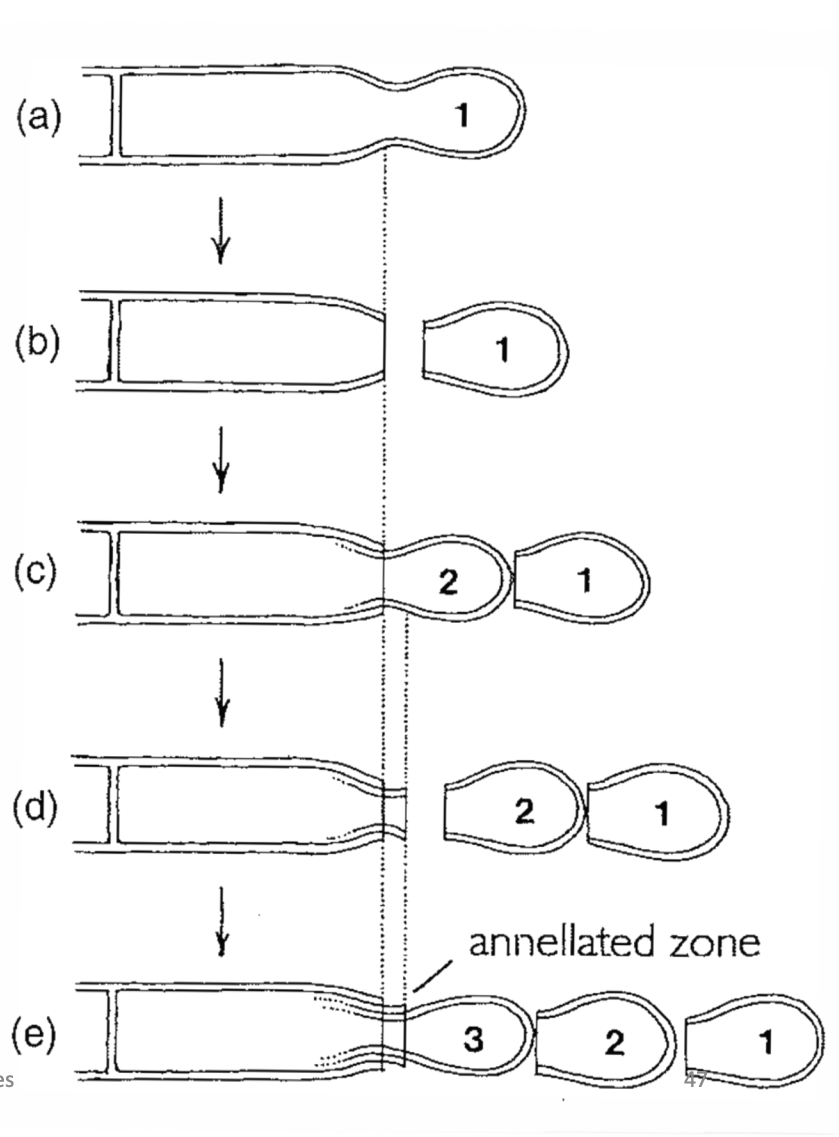
28
New cards
holothallic conidia
Terminal hyphal segment cut off by septum
A second septum is formed near the first cutting off the separating cell
The terminal cell enlarges
The separating cell collapses and the condiia release
A second septum is formed near the first cutting off the separating cell
The terminal cell enlarges
The separating cell collapses and the condiia release
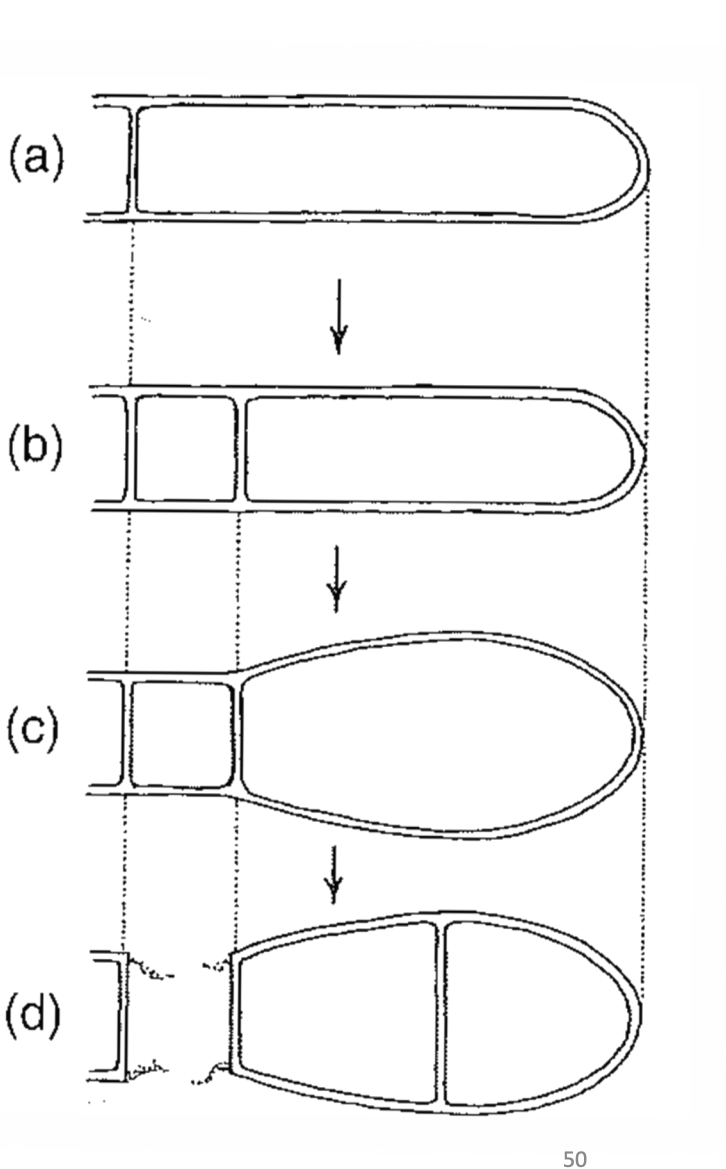
29
New cards
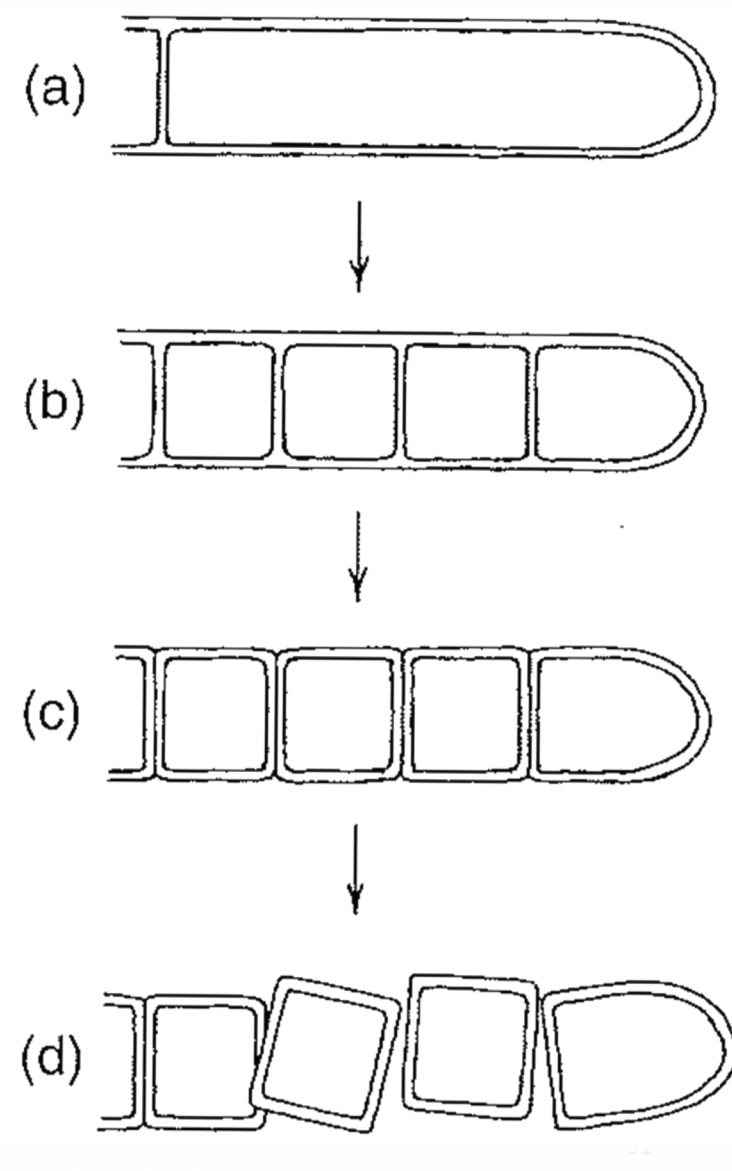
Thallic-arthic conidia
Terminal hyphal segment cut off by a septum
Septa divide the segment into several sections
The septa each divide into two layers
The daughter cells separate
Septa divide the segment into several sections
The septa each divide into two layers
The daughter cells separate