Lab Pratical 8 - PNS and special senses
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the three Sensory Cranial Nerves?
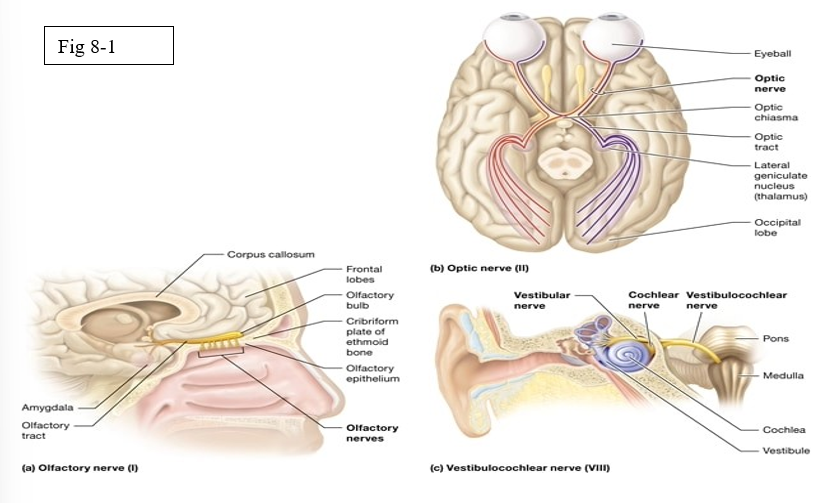
Olfactory (I)
Optic (II)
Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
What are the five Motor Cranial Nerves?
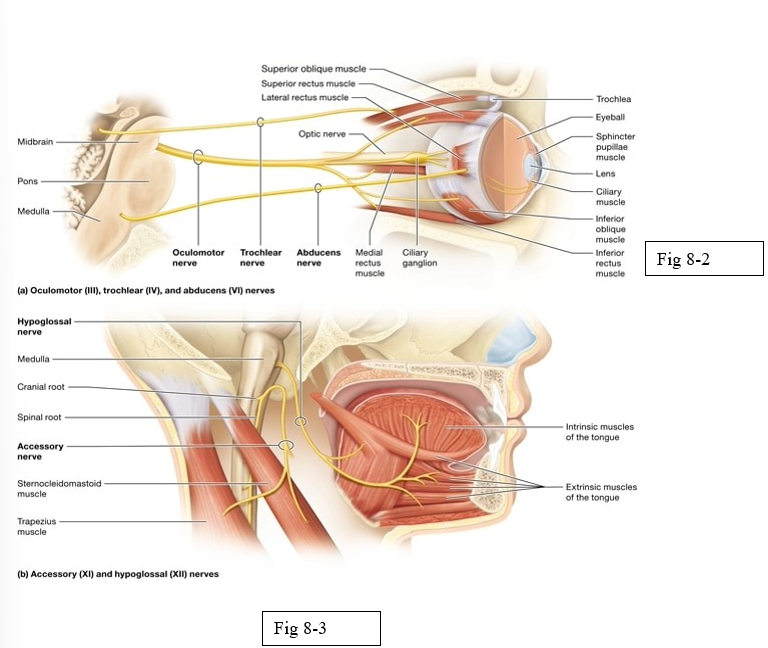
Oculomotor (III)
Trochlear (IV)
Abducens (VI)
Accessory (XI)
Hypoglossal (XII)
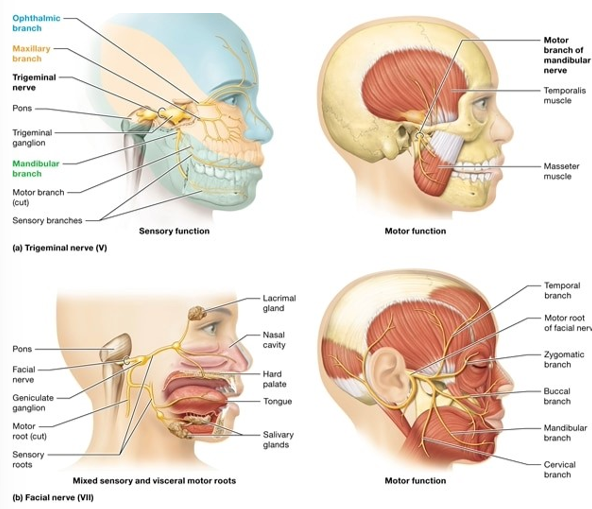
What are the four mixed cranial nerves
Trigeminal (V)
Facial (VII)
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Vagus (X)
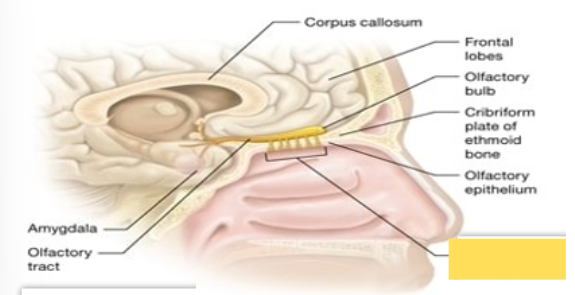
Olfactory (I)
Sensory cranial nerve; nerve for olfaction or the sense of smell
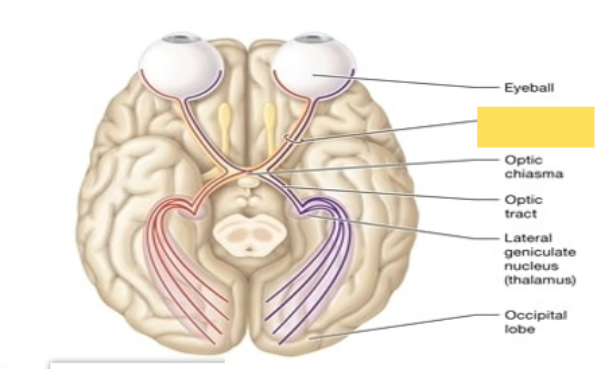
Optic (II)
Sensory Cranial Nerve; nerve for vision
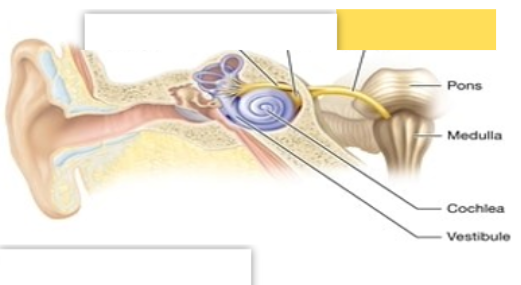
Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
Sensory Cranial Nerve; balance and equilibrium
Oculomotor (III)
moves the eyeball; opening the eye; constricts the pupil; changes the lens shape
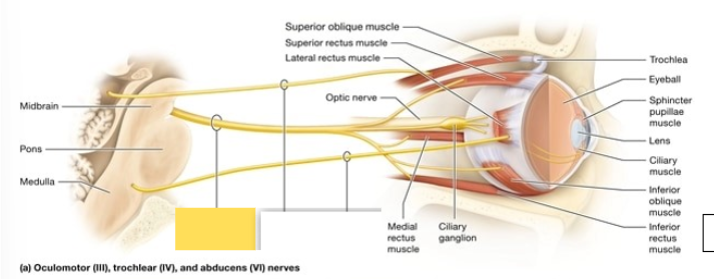
Trochlear (IV)
innervate superior oblique muscle which moves the eye medially and inferiorly (outward and downward)
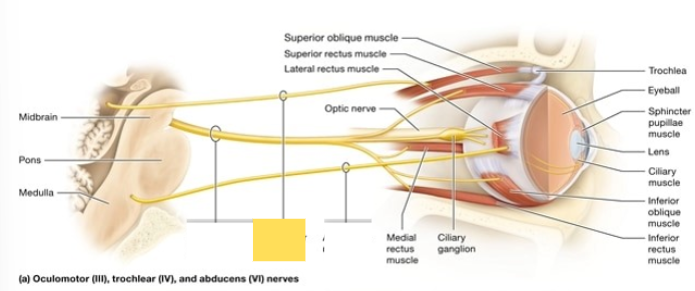
Abducens (VI)
innervate lateral rectus muscle; abducts the gaze when it turns the eye laterally (horizontally outward)
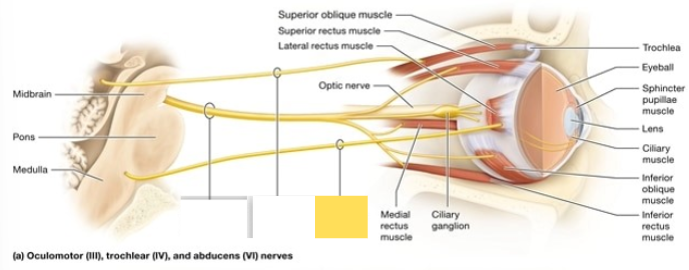
Accessory (XI)
innervates certain muscles of speech; spinal component innervates muscles that move the head and shoulder
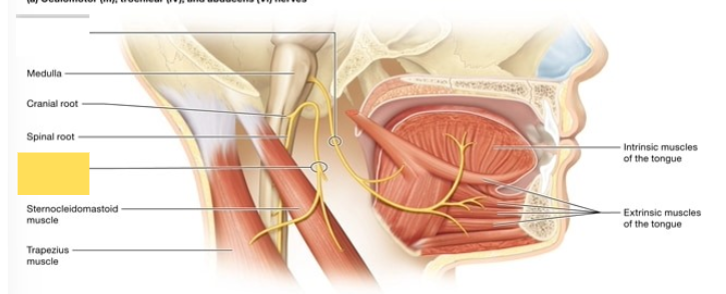
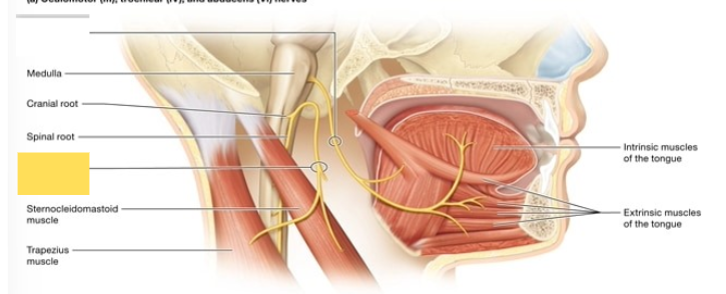
Hypoglossal (XII)
innervates the muscles of the tongue (no role in taste sensation)
Trigeminal (V)
Sensory detects facial sensation, including stimuli from the oral and nasal cavities; motor supply to the masseter and temporalis muscles, which elevate the mandible (close the jaw) during mastication (chewing) and swallowing
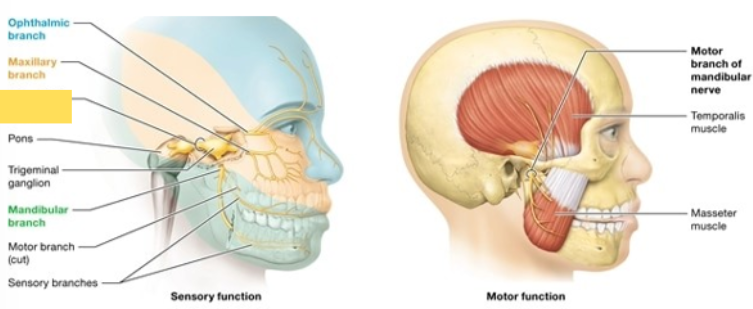
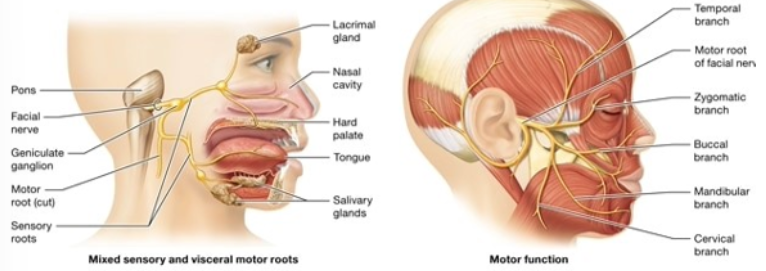
Facial (VII)
taste sensation from chemoreceptors ⅔ of tongue, somatic sensation from the external ear; motor root supplies the muscles of facial expression and other facial muscles; salivary glands, lacrimal (tear) glands, nasal mucous glands
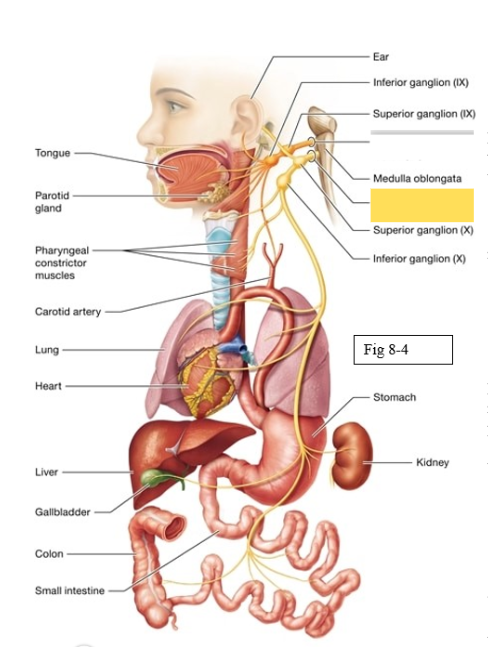
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Detects sensation on ⅓ of tongue, innervate external ear; responsible for swallowing, trigger salivation from parotid gland (salivation in cheeks from salty or acidic foods such as pickles or lemons
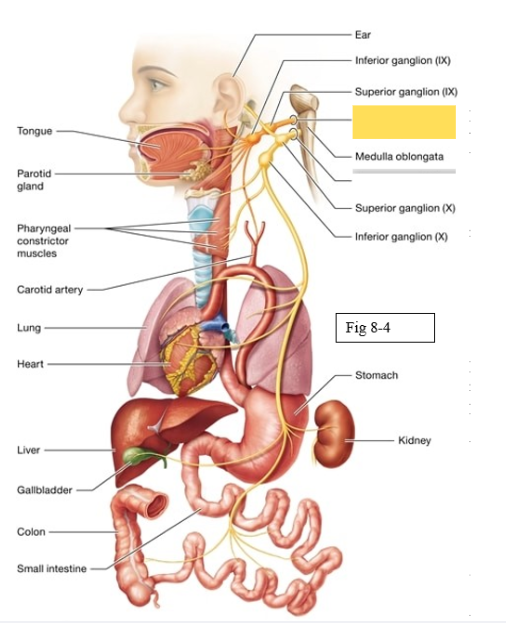
Vagus (X)
sensory around skin of ear, taste sensation from pharnyx; muscles surrounding the pharynx and larynx voice box during speaking and swallowing
Name all the nerve plexus
Cervical plexuses
Brachial plexuses
Lumbar plexuses
Sacral plexuses
What muscles does the Cervical Plexus (C1-C5) supply
skin and muscles of neck and shoulder
Phrenic- diaphragm
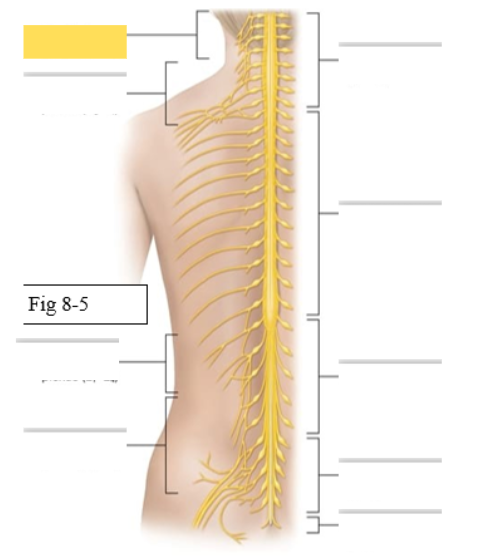
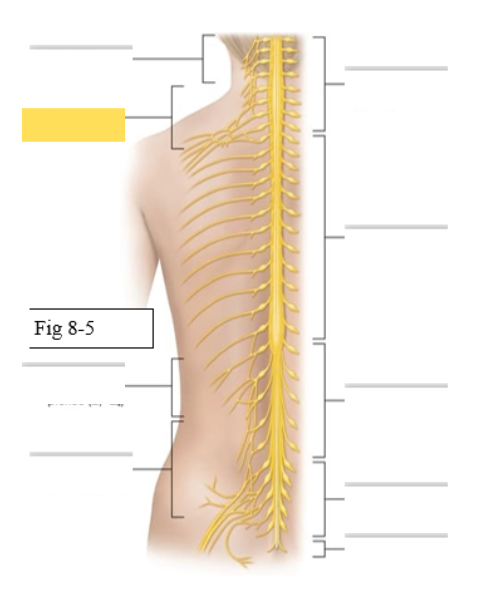
What muscles does the Brachial Plexus (C5-T1) supply
skin and muscles of upper limb
Axillary- deltoid, teres minor
Musculocutaneous- biceps brachii, brachialis
Radial- triceps brachii, brachioradialis
Median- palmaris longus
Ulnar- flexor carpi ulnaris
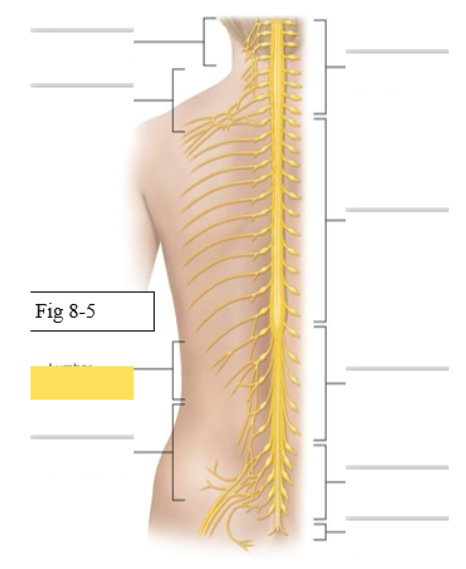
What muscles does the Lumbar Plexus (L1-L4) supply
skin and muscles of abdomen and anterior thigh
Genitofemoral
Femoral- rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, sartorius
Obturator- gracilis, adductor longus
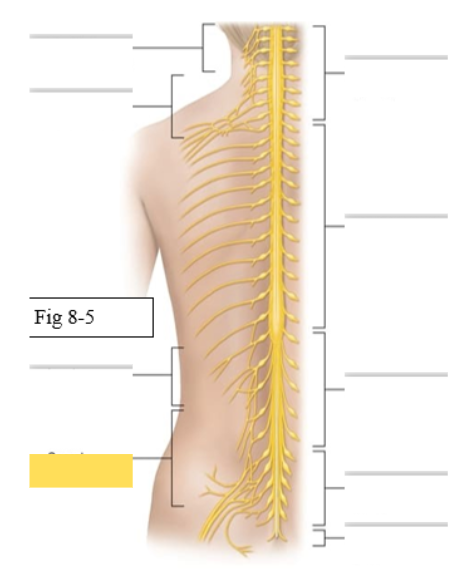
What muscles does the Sacral Plexus (L4-S4) supply
skin and muscles of posterior thigh, leg, and buttocks
Sciatic- made up of 2 nerves
Tibial- biceps femoris (long head), gastrocnemius, soleus
Common fibular- tibialis anterior, biceps femoris (short head) Pudendal
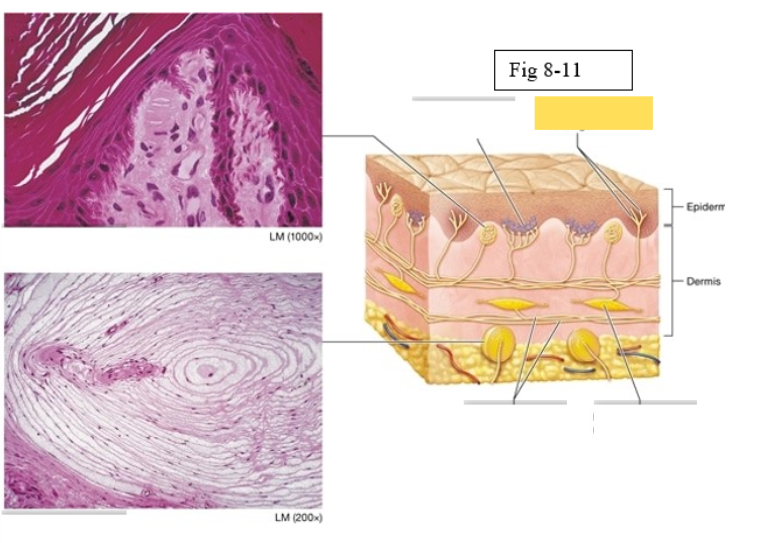
Tactile corpuscle
light pressure, discriminative touch
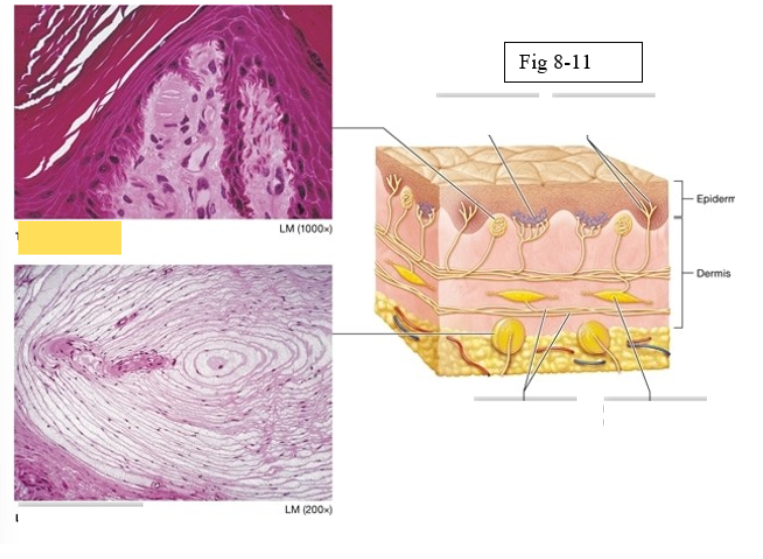
Lamellated corpuscle
deep pressure, vibration
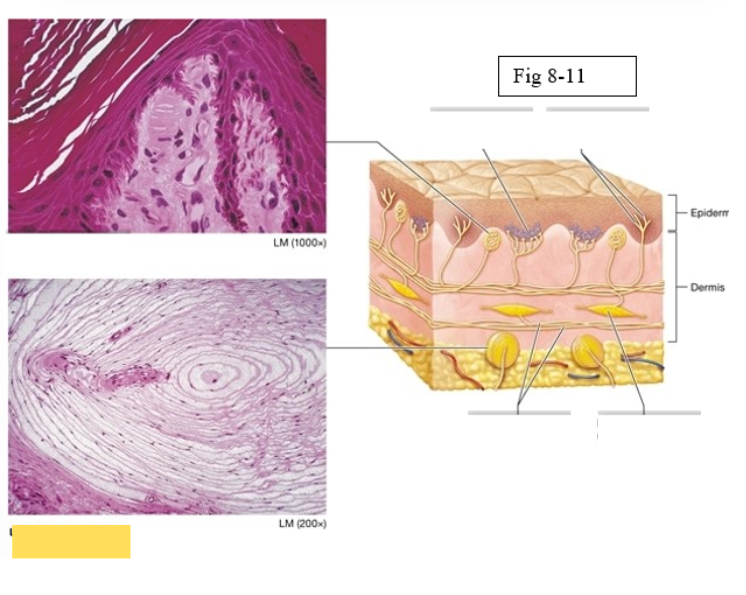
Axons of sensory neurons
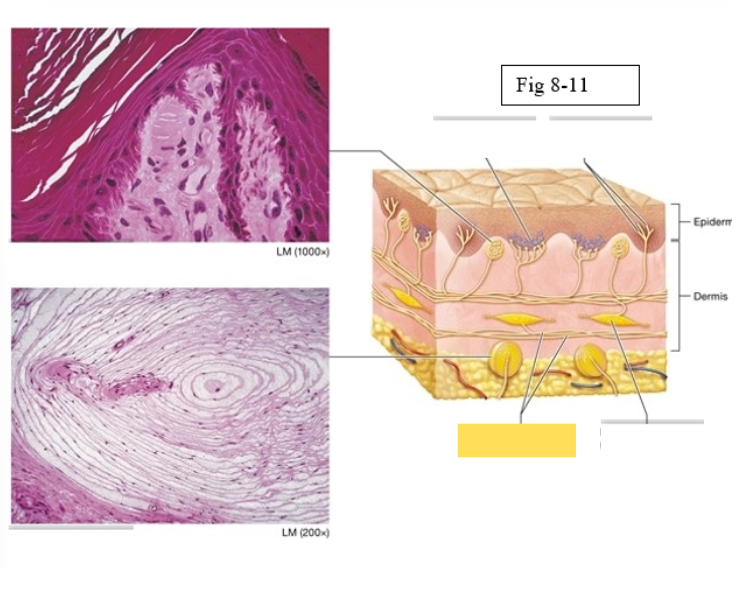
Ruffini ending
deep pressure, stretch
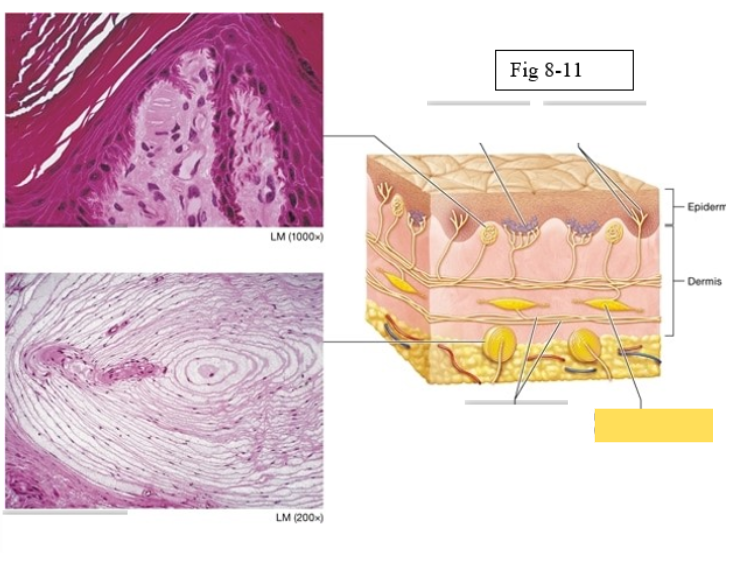
Merkel discs (cell fibers)
light touch
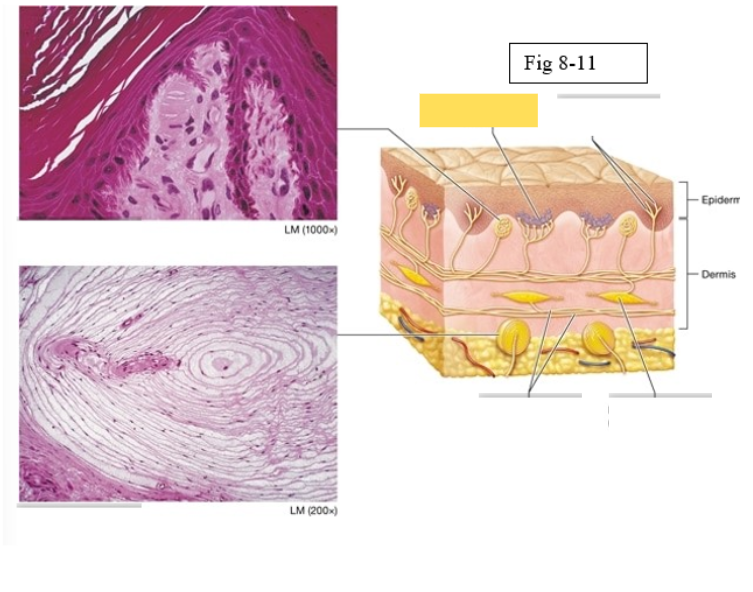
Free nerve endings
temperature and pain
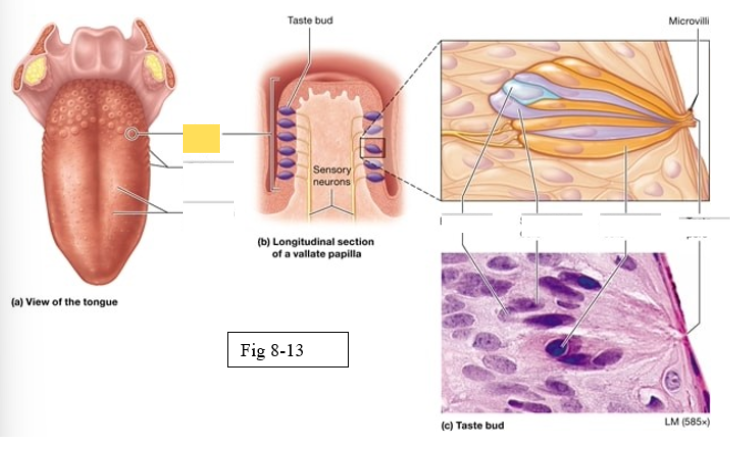
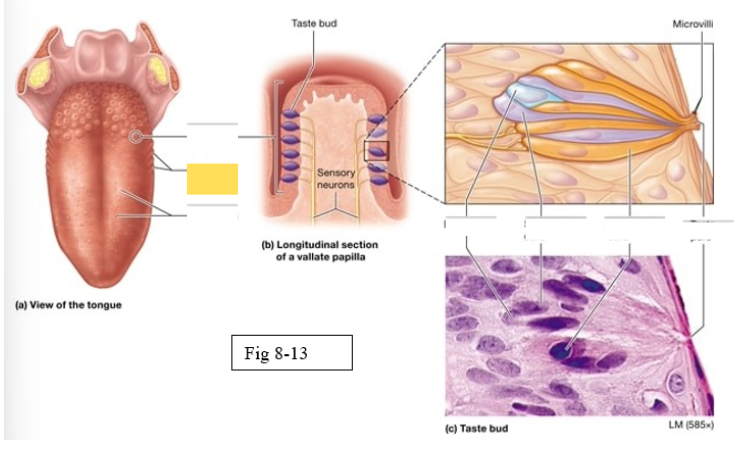
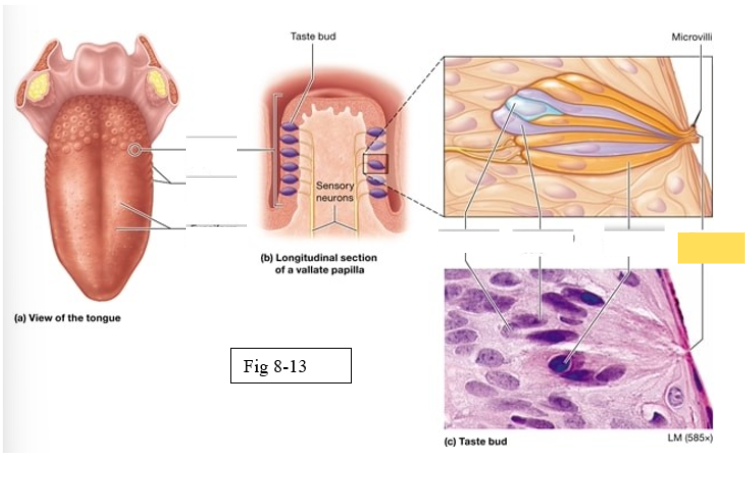
Papillae
Taste buds on the tongue are located within the surface projections
Four types of papillae
vallate
foliate
fungiform
filiform
Vallate
largest, arranged in an inverted V shape on the posterior surface of the tongue
Foliate
located on the lateral surfaces of he tongue, are present mostly in children
Fungiform
Scattered across the anterior two thirds of the tongue’s surface Muschroom shaped
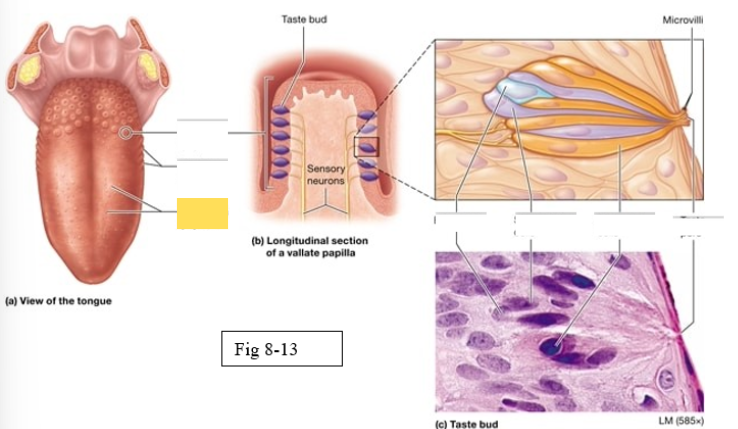
Filiform
Scattered across the anterior two thirds of the tongue’s surface; most abundant; contain tactile receptors instead of taste buds, provide a rigid, abrasive surface for food manipulation
Gustatory cells
receptors for gustation; located primarily on the superior surface of the tongue
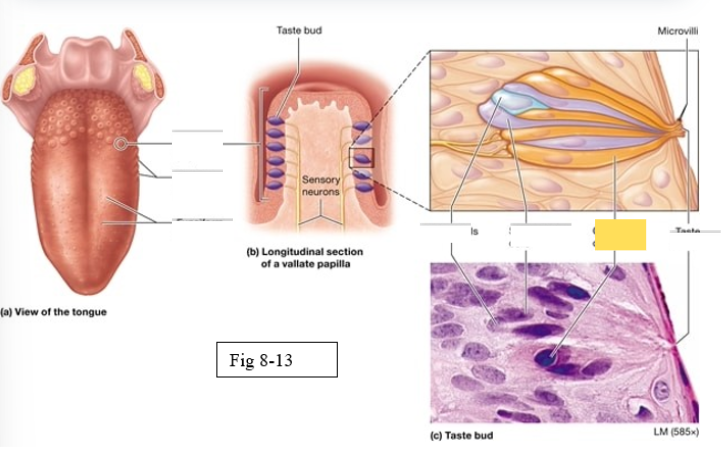
Basal cells
stem cells that divide to produce new gustatory cells
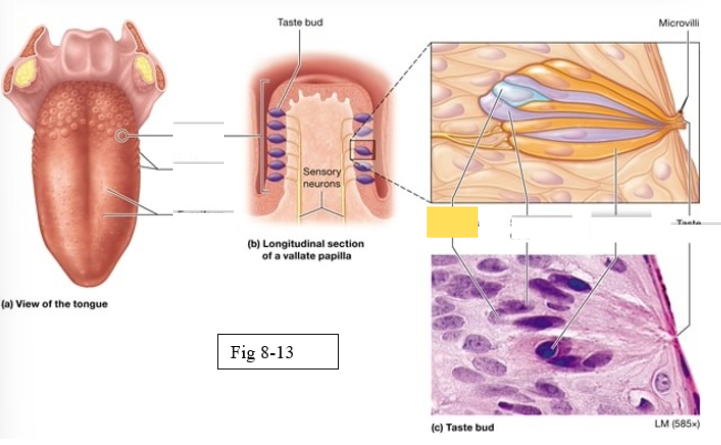
Supporting cells
support and nourish gustatory cells
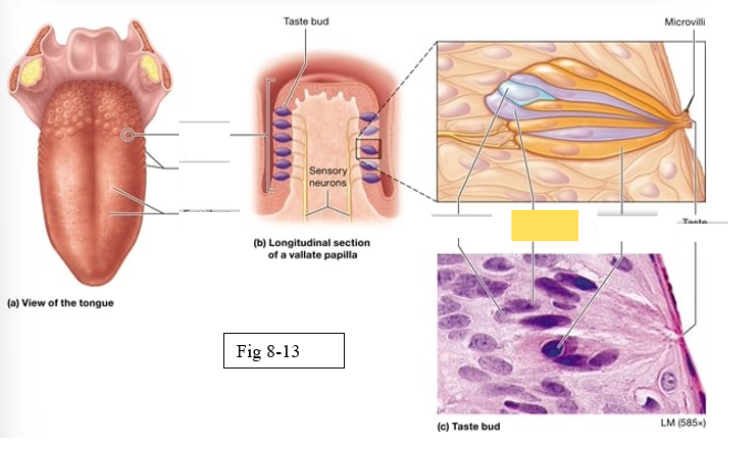
taste bud
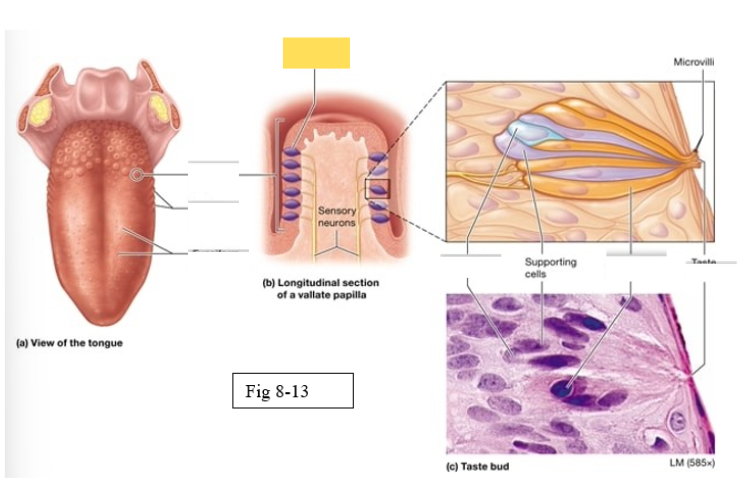
Microvilli
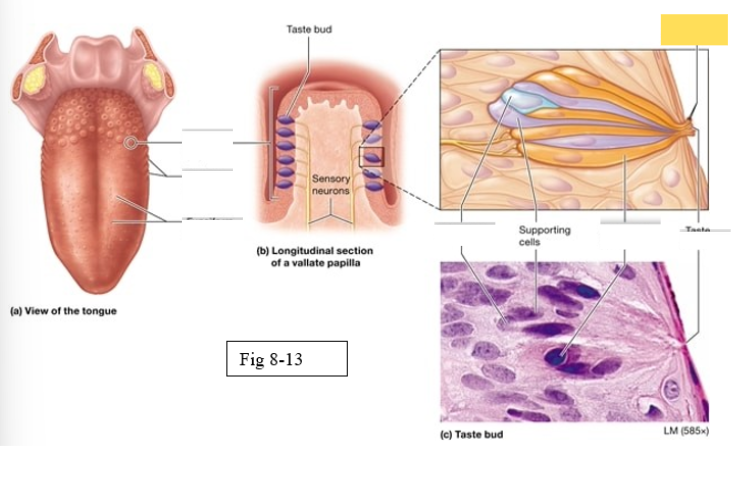
taste pore
Cranial Nerves involved in olfaction
Olfactory nerve (I)
Cranial Nerves involved in Gustation
Facial (VII)
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Vagus (X)
Cranial Nerves involved in vision
Optic Nerve
Cranial Nerves involved in hearing
Cochlear nerve
Cranial nerve involved in equilibrium
Vestibular nerve
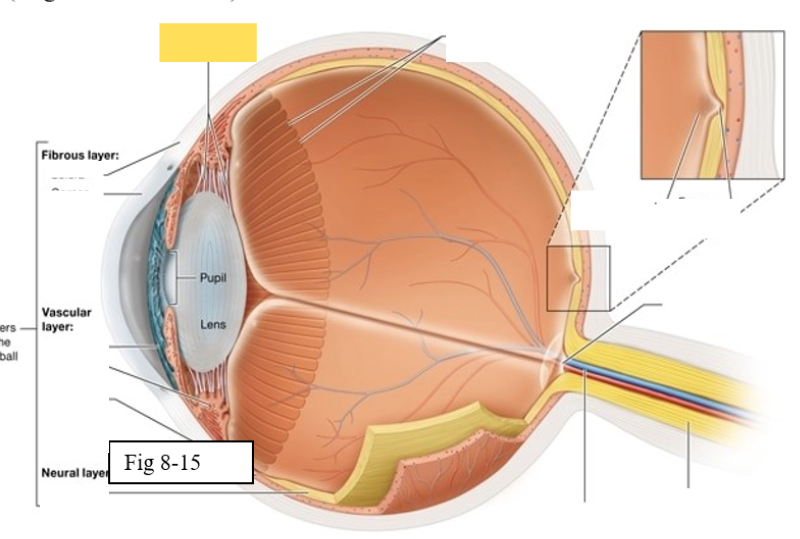
Three layers of the eye
Outer fibrous layer
Middle vascular layer
Inner neural layer
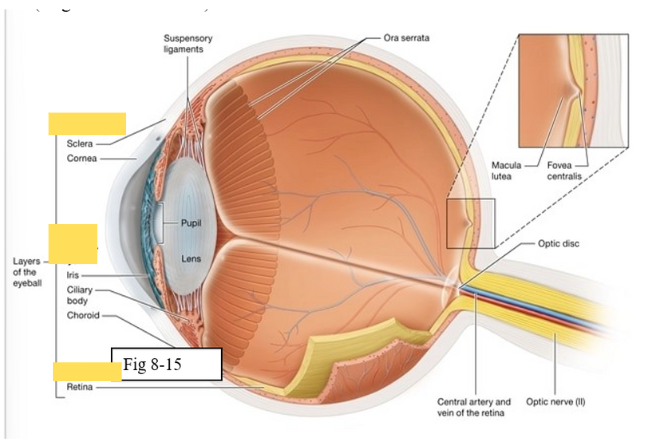
Cornea
bends light as it enters the eye
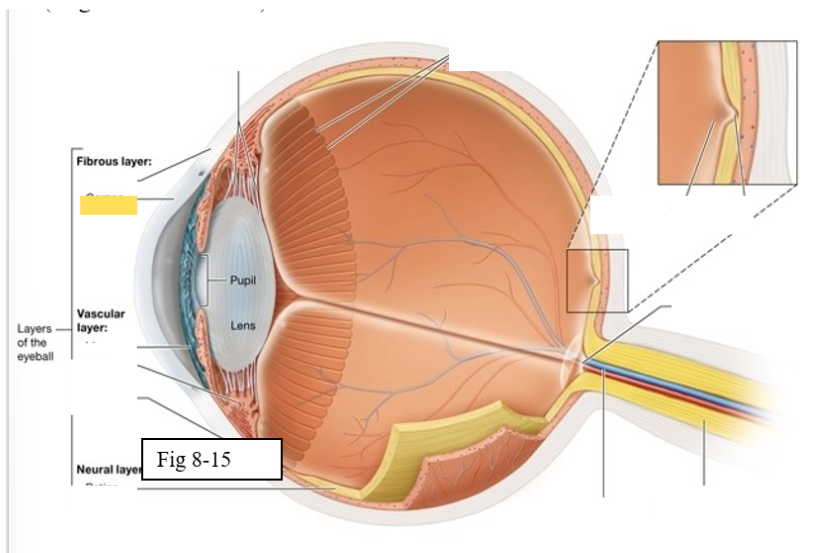
Sclera
protects the eye and serves as an attachment site for the extrinsic eye muscles
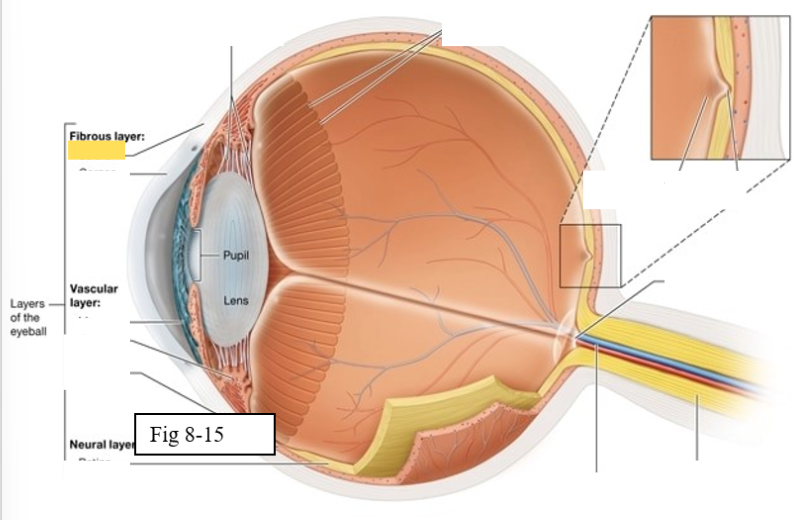
Choroid
supplies oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the eye
Contains melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin, and absorbs excess light
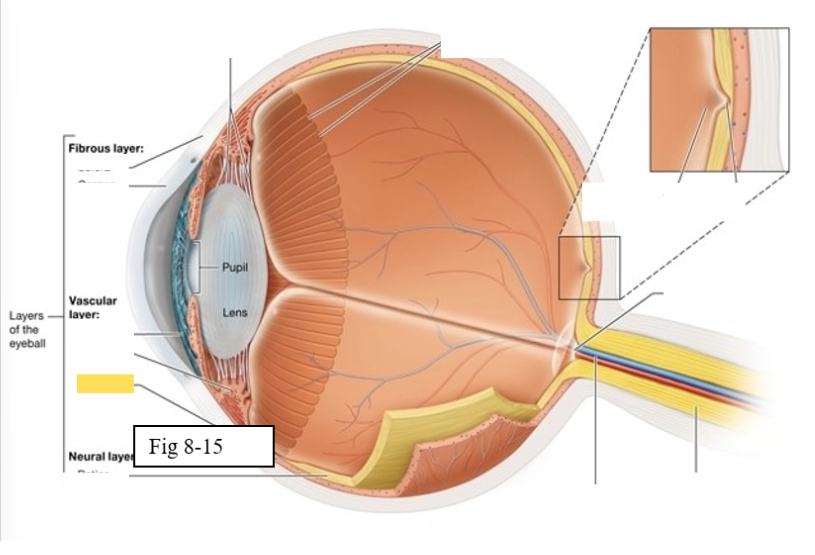
Ciliary body
regulates the shape of the lens to enable light to be focused on the retina; secretes aqueous humor (clear watery fluid)
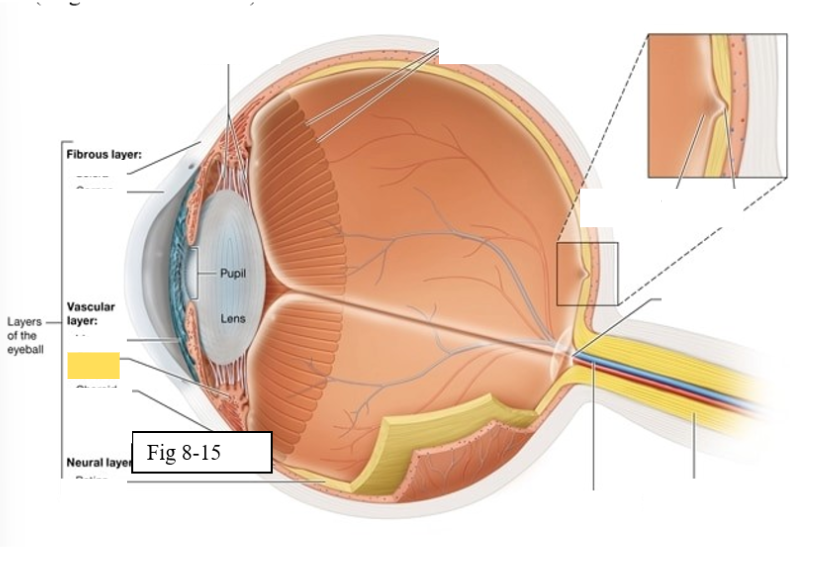
Iris
contains pigmented cells that are responsible for eye color and smooth muscle fibers that regulate the size of the pupil & the amount of light that enters the eye
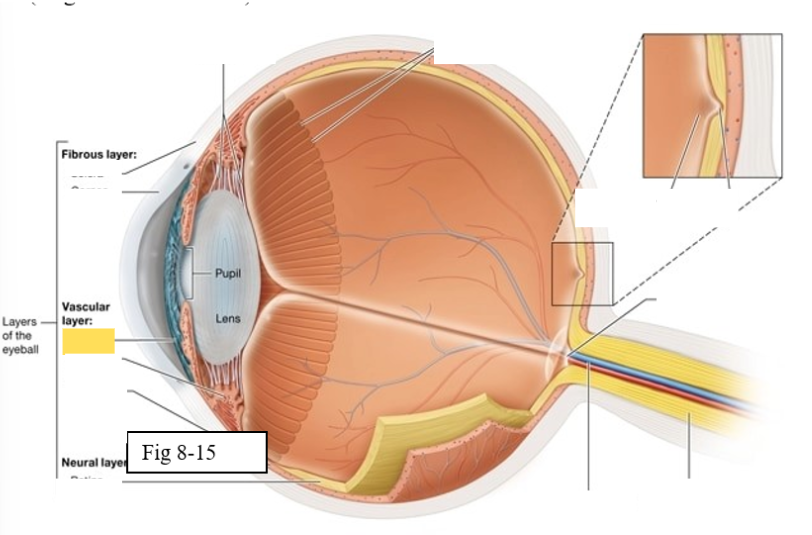
Retina
The retina is composed of two layers
Outer pigmented epithelium - absorbs light and prevents it from scattering
Inner neural layer - contains the photoreceptors (rods and cones)
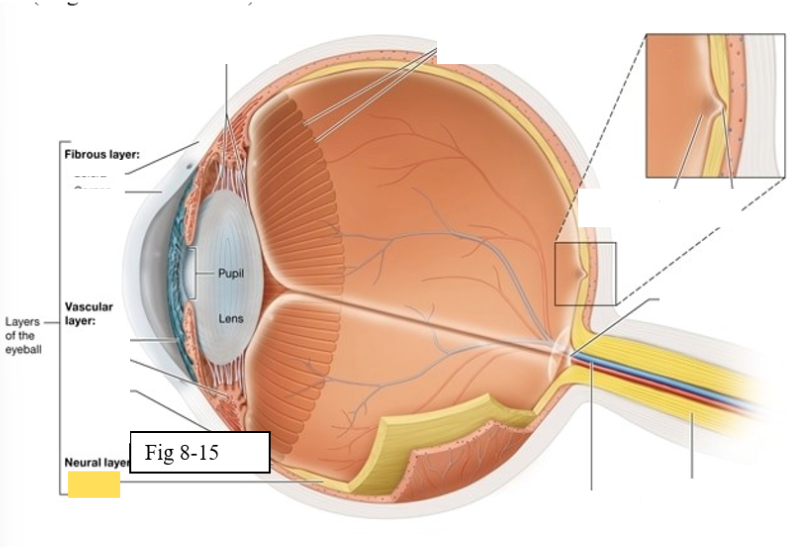
Ora Serrata
serrated boundary between the retina and the ciliary body
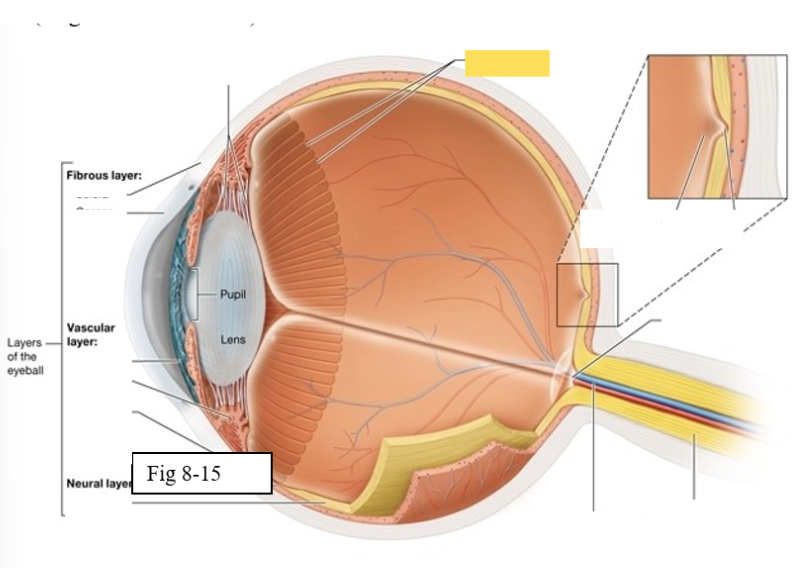
Optic disk
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eyeball
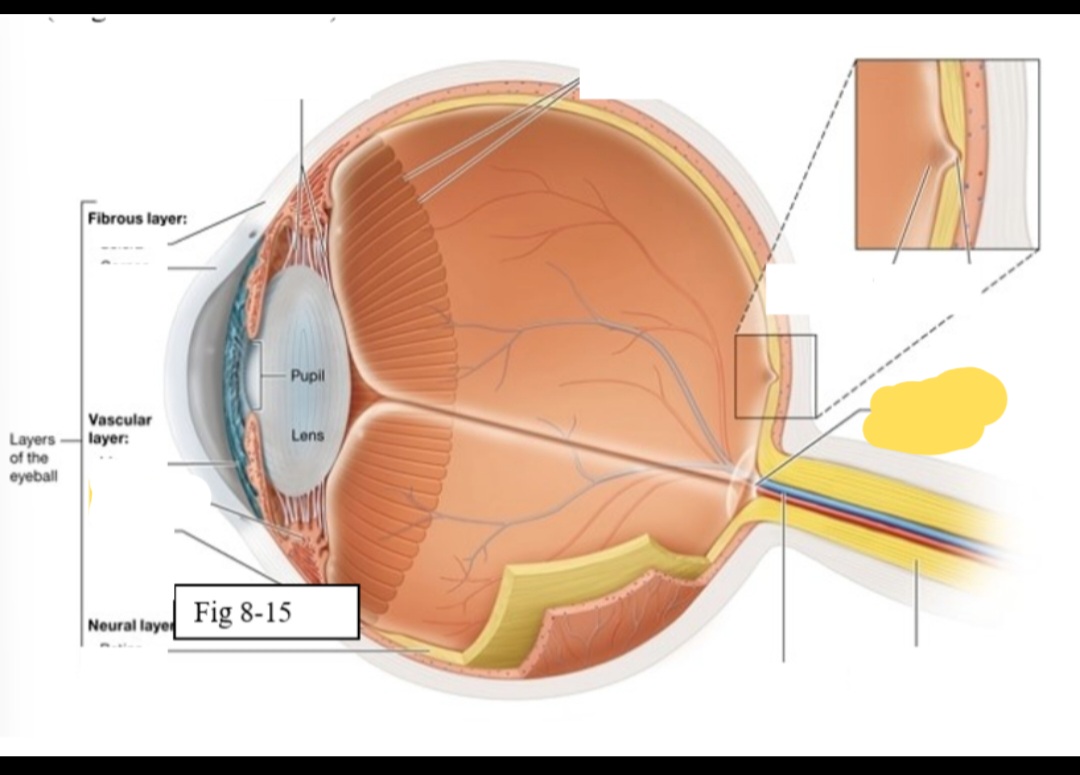
Macula lutea
yellow spot in retina; concentration of cones is high wich are responsible for color vision and sharp detail
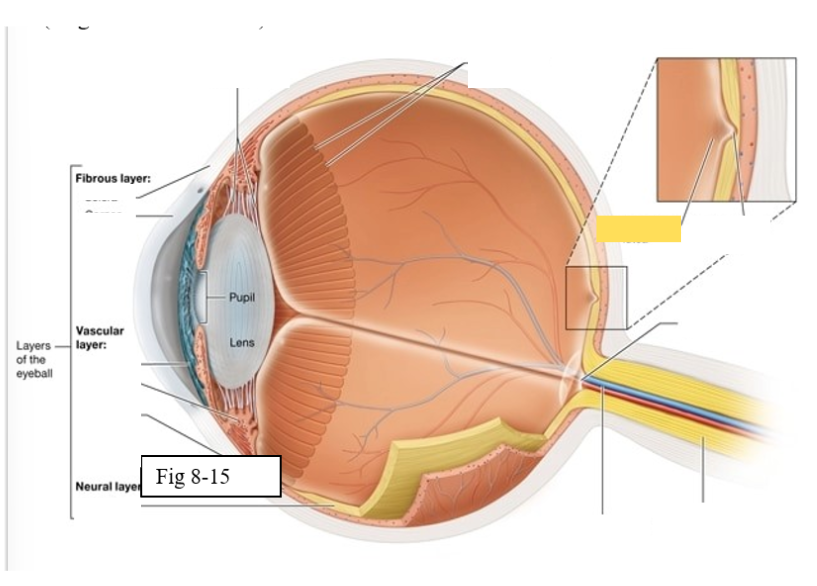
Fovea centralis
small pit within the macula lutea concentration of cones is greatest, vision is the sharpest
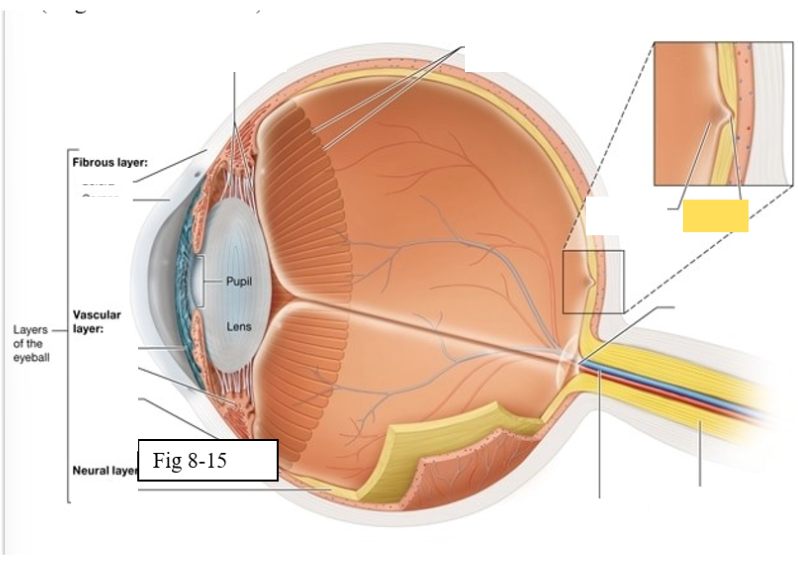
Optic Nerve (II) eye diagram
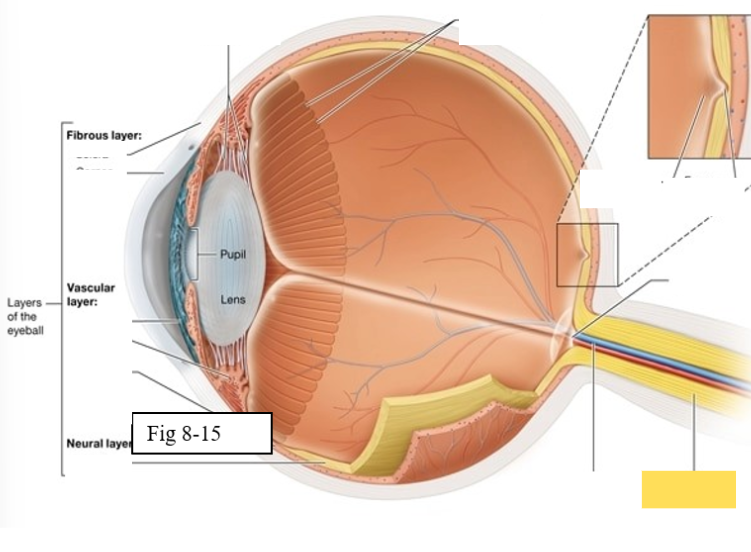
Central artery and vein of the retina
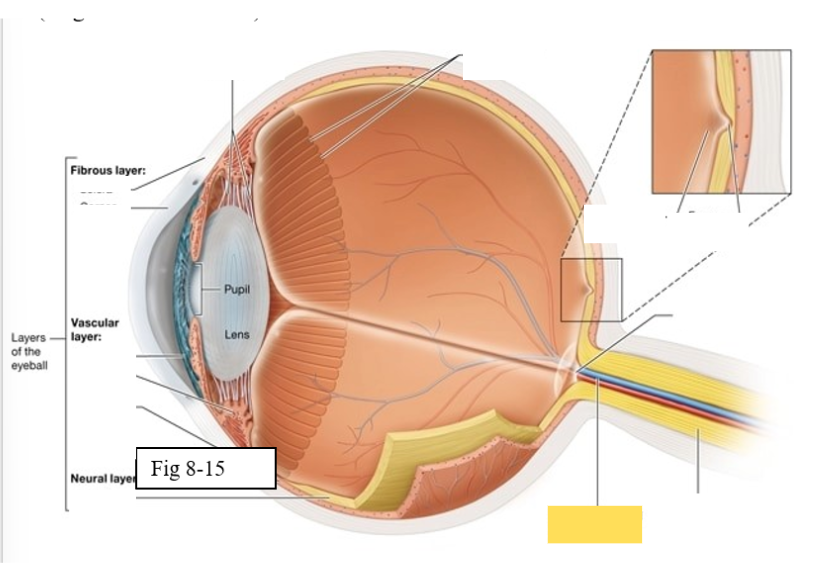
Suspensory ligament
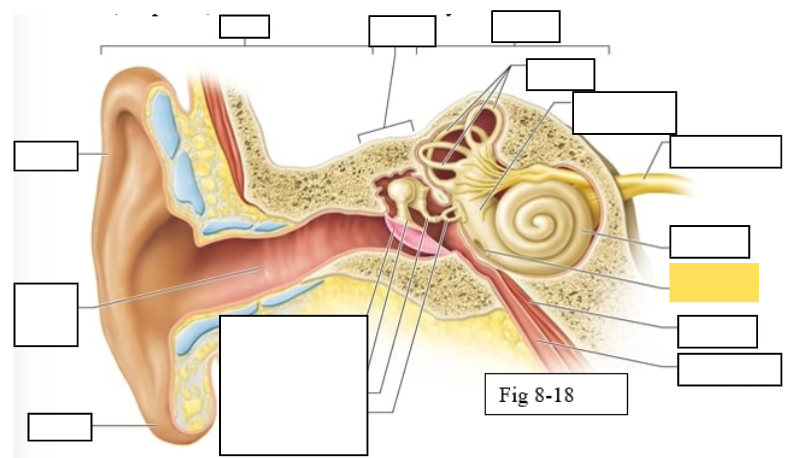
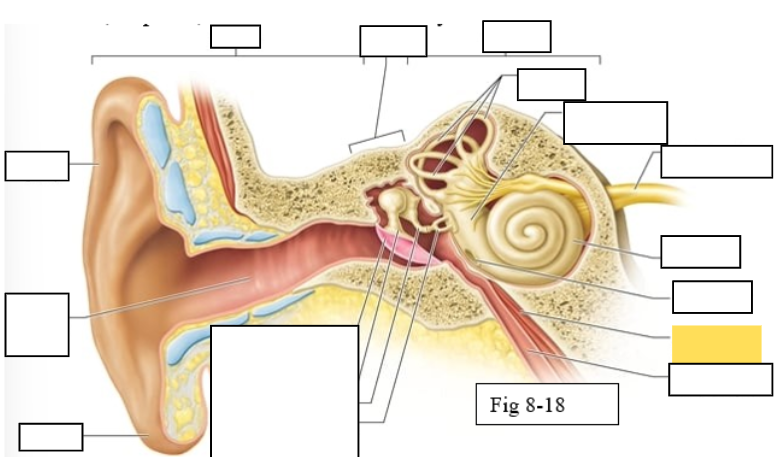
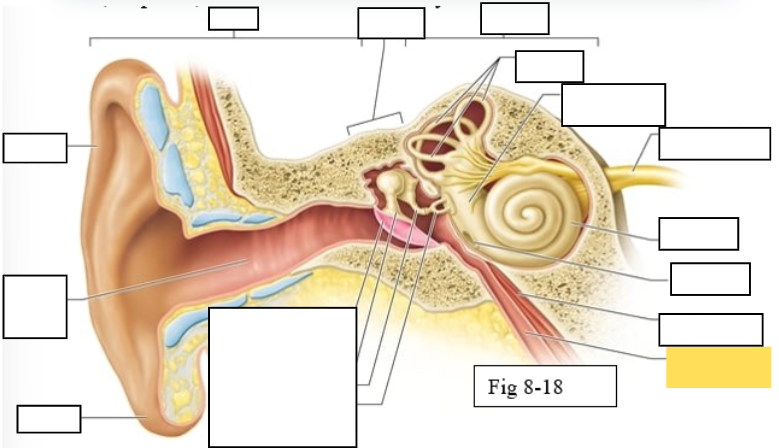
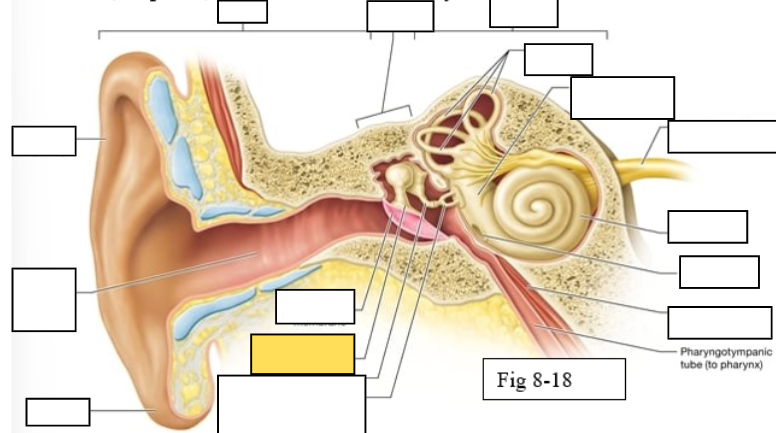
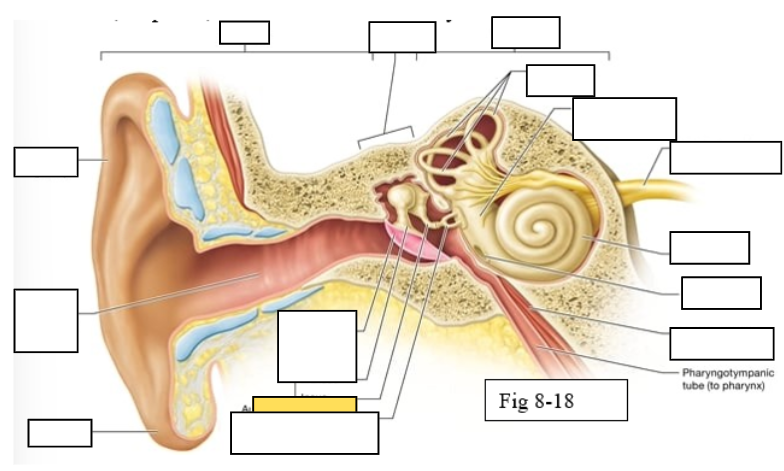
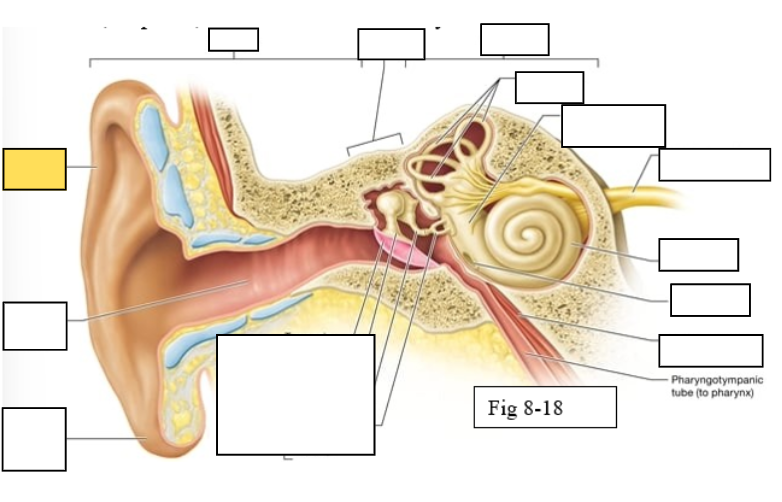
Outer ear
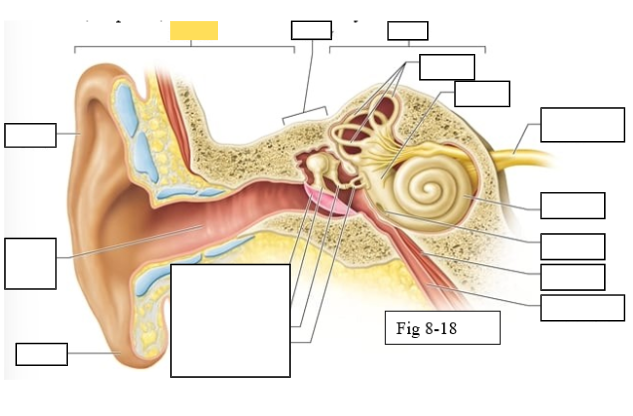
Middle ear
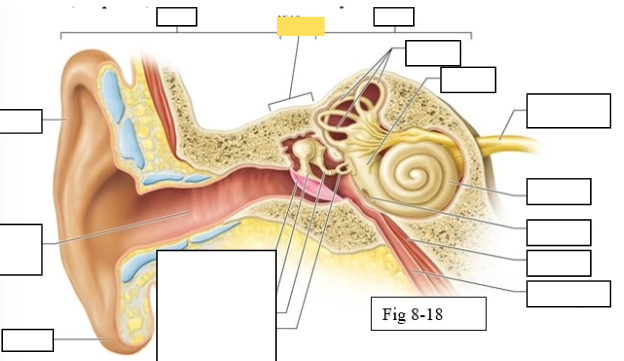
Inner ear
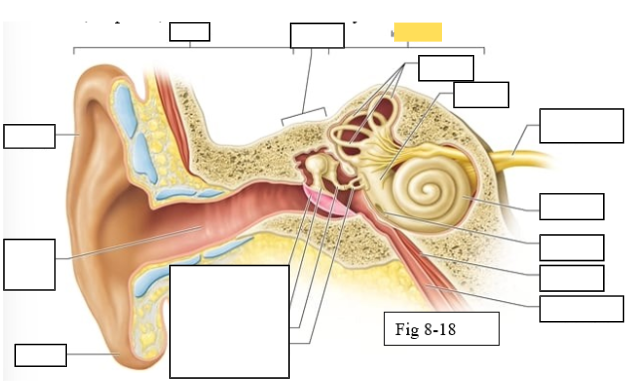
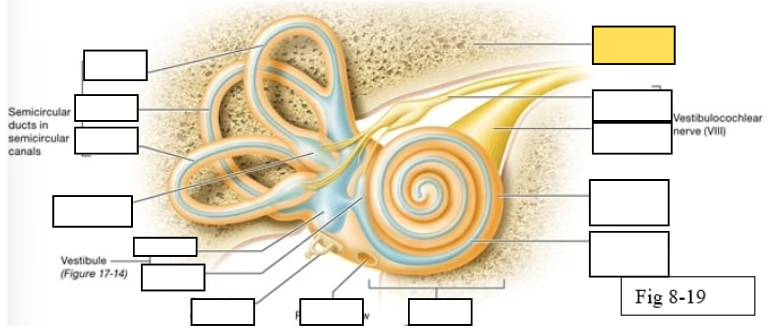
Semicircular canals
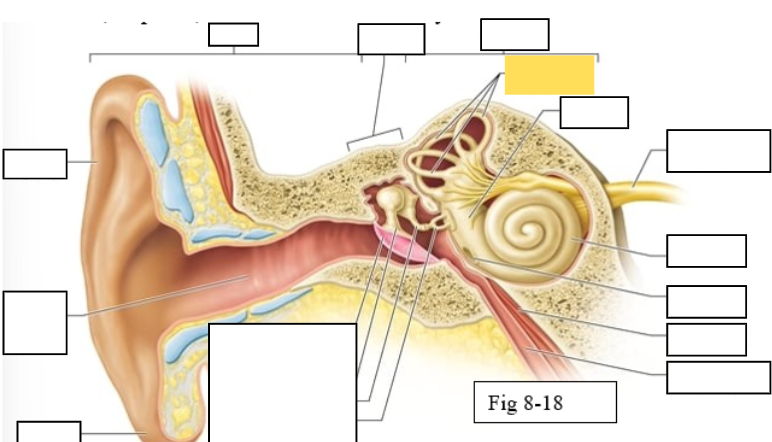
vestibule
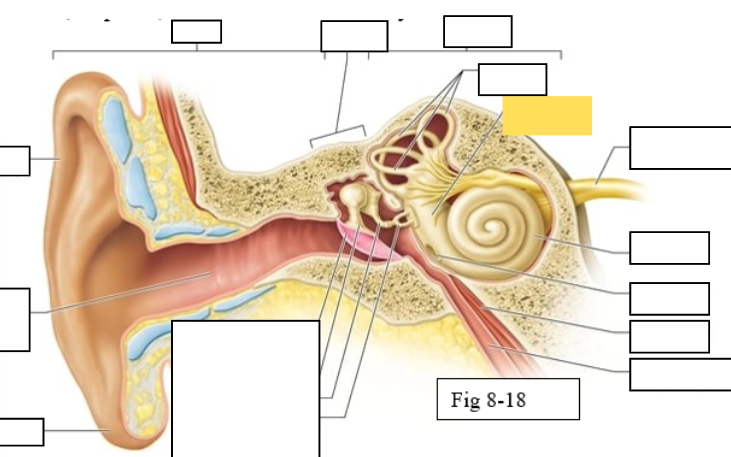
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) ear diagram
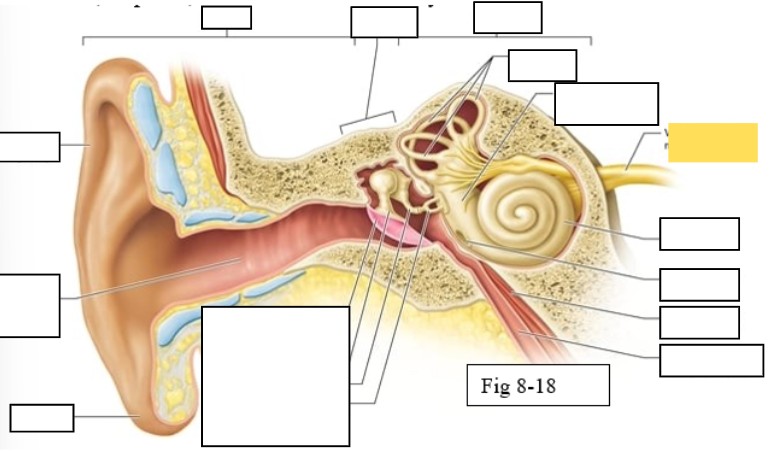
Cochlea
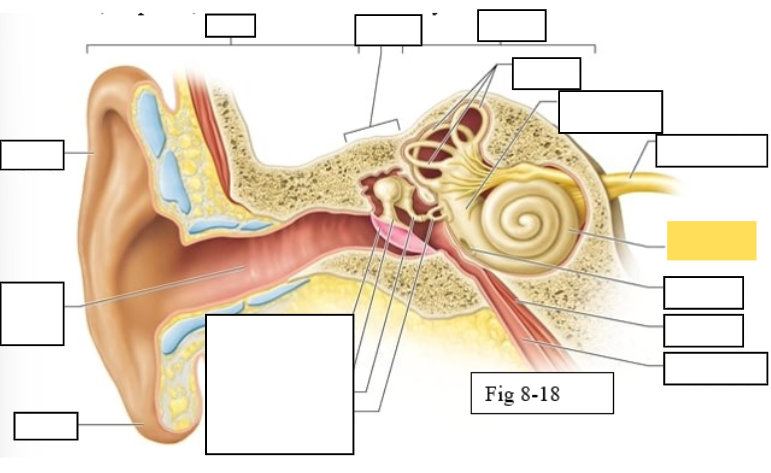
Round window
Tensor tympani muscle
Pharyngotympanic tube (to pharynx)
Tympanic Membrane
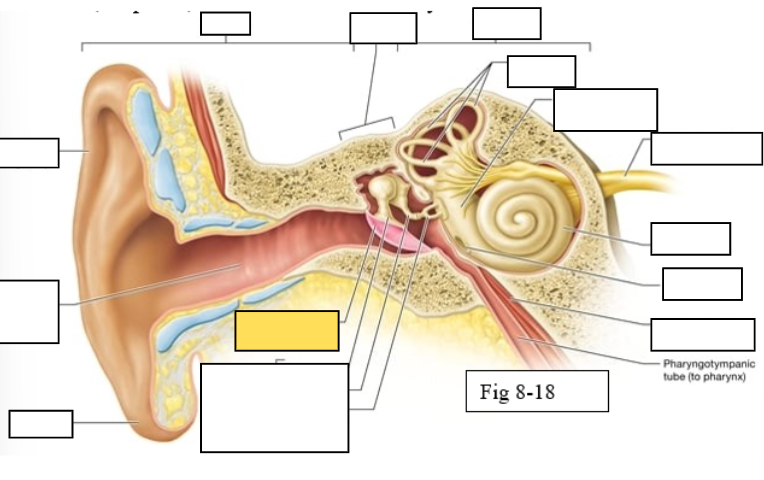
Auditory ossicles: Malleus
Auditory ossicles: Incus
Auditory ossicles: Stapes
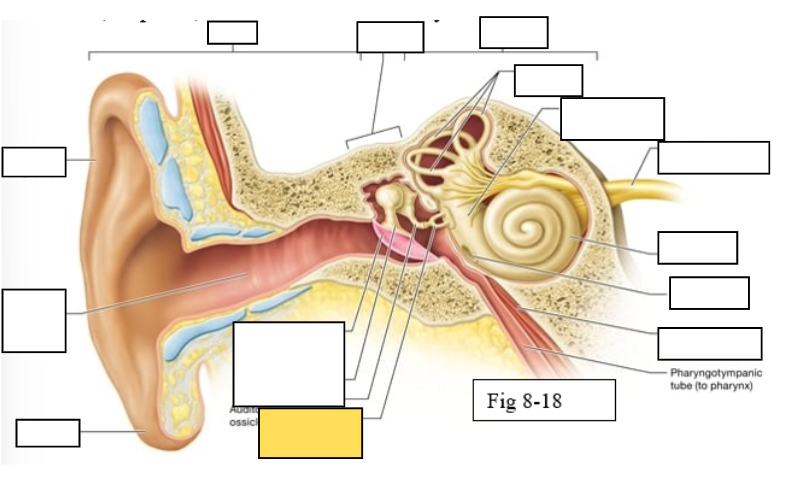
Lobule
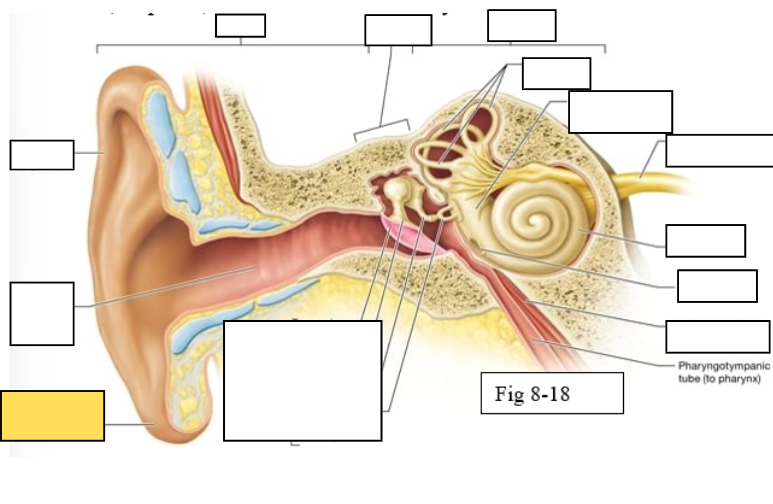
External auditory canal
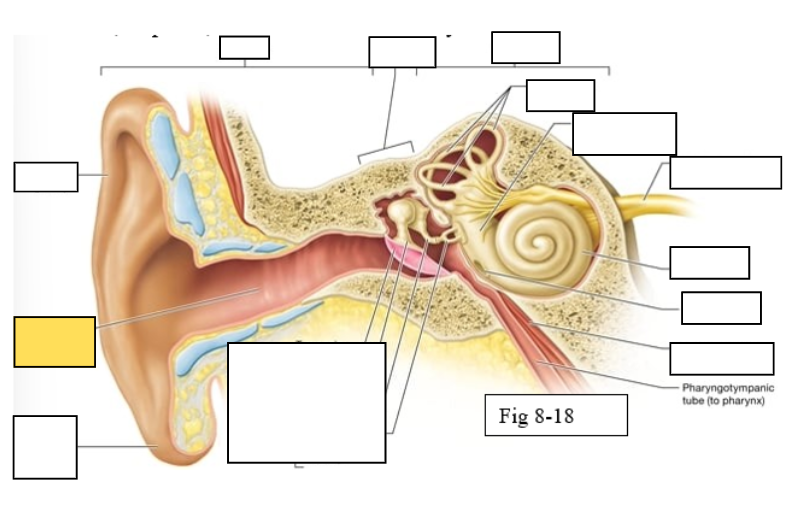
Auricle (pinna)
Semicircular ducts: Anterior
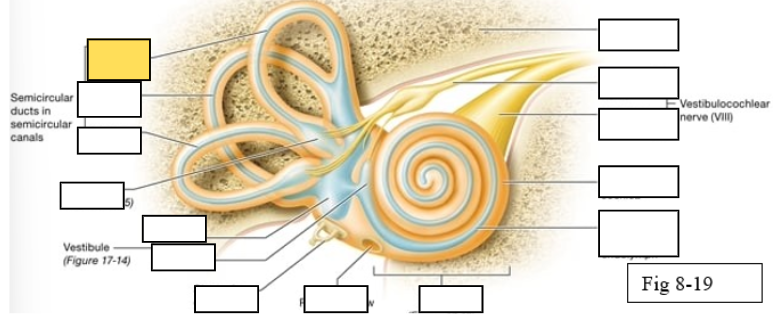
Semicircular ducts: Posterior
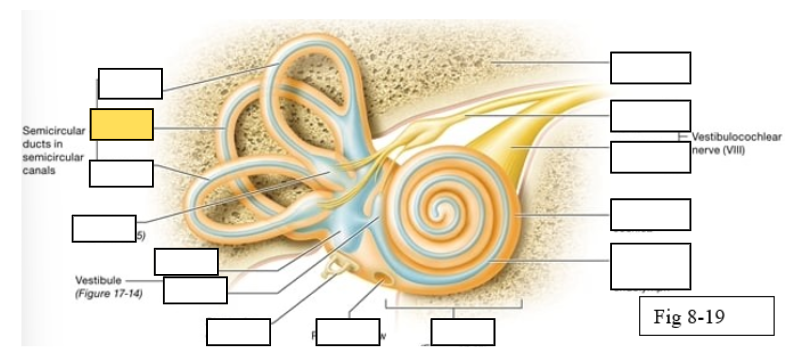
Semicircular ducts: Lateral
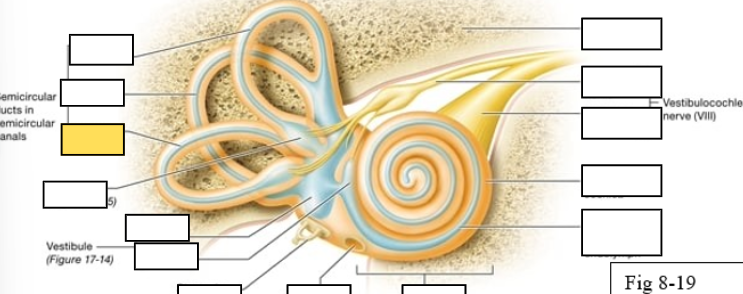
Vestibule: Utricle
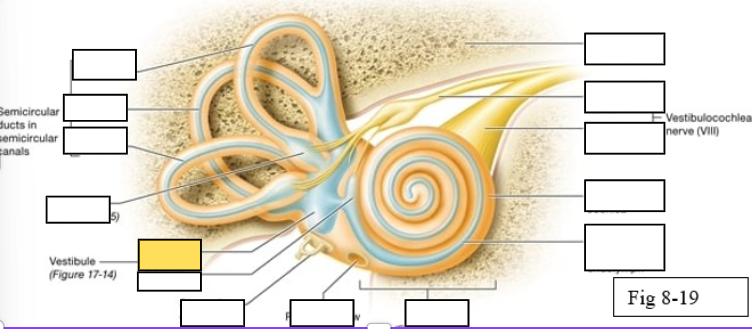
Vestibule: Saccule
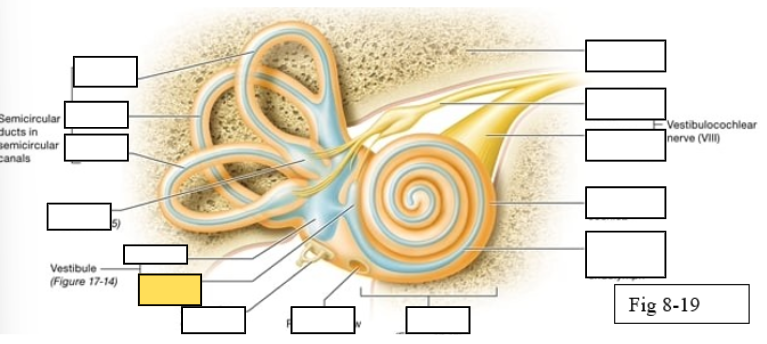
Ampulla
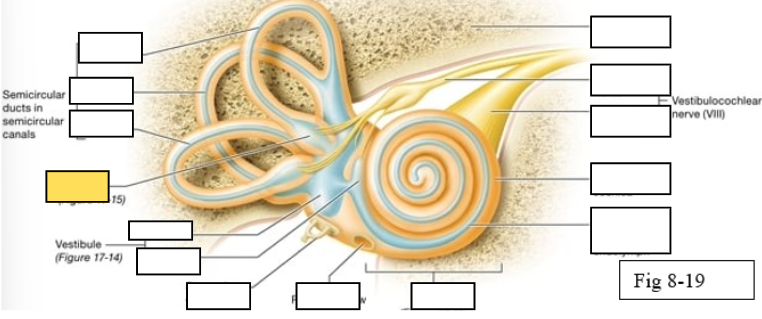
Perilymph
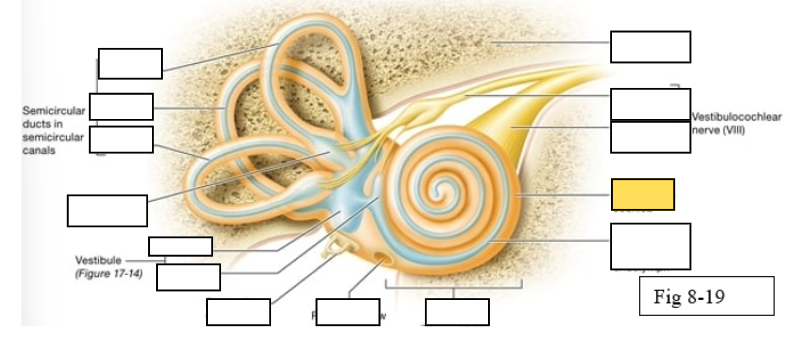
Cochlear duct filled with endolymph
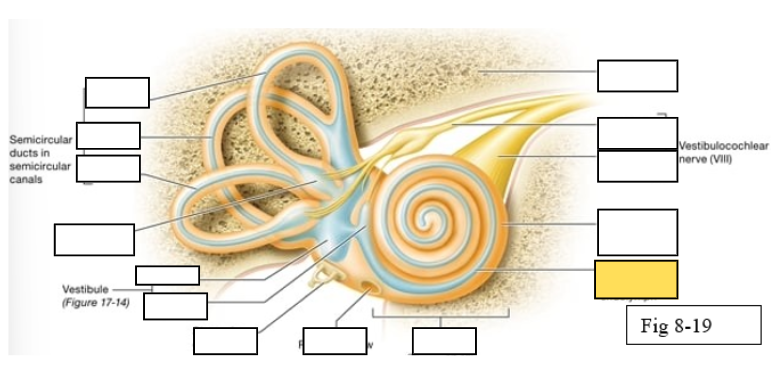
temporal bone