Biology: B1 - Cell Structure and Transport (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
Differences between the light and electron microscope
\-Electron microscope has higher resolution and better magnification
\-Light microscope relies on light but electron microscopes use electrons instead
\- Light mircroscopes are easy to use and cheaper than electron microscopes
\
\-Light microscope relies on light but electron microscopes use electrons instead
\- Light mircroscopes are easy to use and cheaper than electron microscopes
\
2
New cards
Resolution
The ability to distinguish between two separate points without them being blurred.
higher resolution = more detail
higher resolution = more detail
3
New cards
Why does increased resolution give more information about cells?
Cells can be looked at closer and scientists can further understand their structure
4
New cards
Uses of the light microscope
\-Studying living cells
5
New cards
Uses of the electron microscope
\-Studying details within non-living cells (nucleus ext)
6
New cards
Magnification equation
image size/actual size
7
New cards
Eukaryotic cells (animal + plant cells)
Cells which their genetic material is enclosed in a nucleus
8
New cards
Prokaryotic cells (bacterial cells)
Cells which their genetic material is not enclosed in a nucleus
9
New cards
What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell?
prokaryotic is smaller
in eukaryotic cell dna is enclosed in nucleus but not in prokaryotic cells
prokaryotic cell contains plasmids
prokaryotic cell doesn’t have a vacoule, chloroplasts or mitochondria
10
New cards
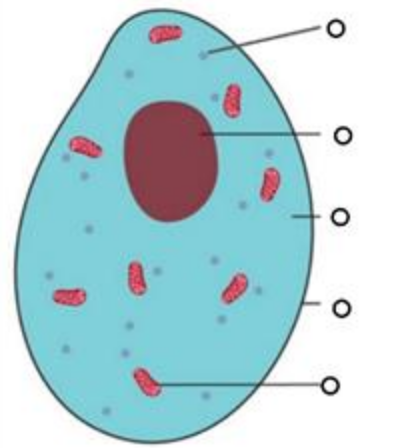
Label animal cell (top to bottom)
\-Ribosome
\-Nucleus
\-Cytoplasm
\-Cell membrane
\-Mitochondria
\-Nucleus
\-Cytoplasm
\-Cell membrane
\-Mitochondria
11
New cards
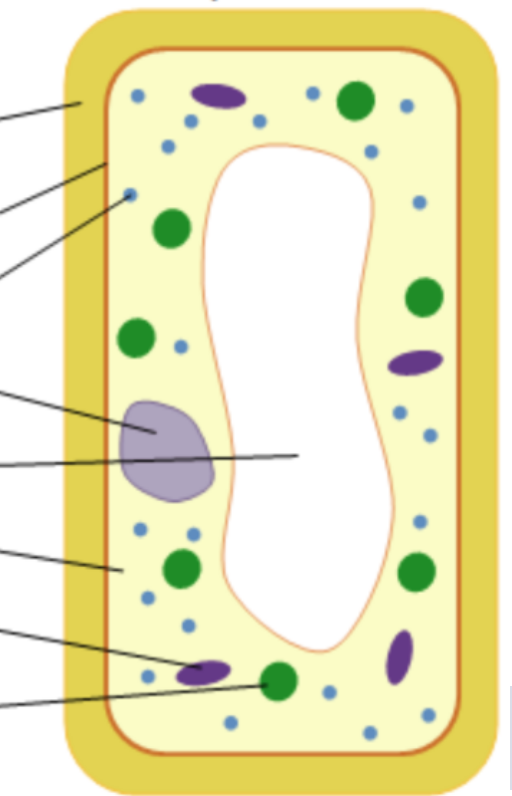
Label plant cell (top to bottom)
\-Cell wall
\-Cell membrane
\-Ribosomes
\-Nucleus
\-Vacuole
\-Cytoplasm
\-Mitochondria
\-Chloroplast
\-Cell membrane
\-Ribosomes
\-Nucleus
\-Vacuole
\-Cytoplasm
\-Mitochondria
\-Chloroplast
12
New cards
What are the main differences between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells contain cell wall, vacuole and chloroplasts
13
New cards
Organelle
A specialised unit within a cell which performs a specific function
14
New cards
What is the function of a cytoplasm?
Place where chemical reactions happen
15
New cards
What is the function of a nucleus?
Holds genetic material
16
New cards
What is the function of a cell membrane?
Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
17
New cards
What is the function of a mitochondria?
The place where aerobic respiration occurs
18
New cards
What is the function of a ribosome?
Protein synthesis occurs
19
New cards
What is the function of a cell wall?
Provides strength and support to the plant
20
New cards
What is the function of a chloroplast?
Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis
21
New cards
What is the function of a vacuole?
Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid
22
New cards
One order of magnitude is how many times bigger than the smaller object?
10
23
New cards
What is the rule of the order of magnitude
Each order of magnitude is 10 times bigger than the last
24
New cards
Specialised Cells
Cells which are adapted to help them carry out functions
25
New cards
Root hair cell adaptations
\-Hairs increase surface area of root so it can absorb water and minerals more effectively
\-No chloroplasts because they are underground
\-No chloroplasts because they are underground
26
New cards
Xylem cell adaptations
\-Thick walls which provide support
\-End walls between cells have been broken down, making a long tube so water and minerals can flow more easily
\-No internal structures
\-End walls between cells have been broken down, making a long tube so water and minerals can flow more easily
\-No internal structures
27
New cards
Phloem adaptations
\-End walls of vessel cells have pores so dissolved sugars can pass through
\-No nucleus
\-Mitochondria in companion cell to provide energy
\-No nucleus
\-Mitochondria in companion cell to provide energy
28
New cards
Sperm cell adaptations
\-Long tail and streamlined to they can swim to the egg
\-Only contain half the genetic information of the normal adult cell so it can bond with the egg
\-Only contain half the genetic information of the normal adult cell so it can bond with the egg
29
New cards
Muscle cell adaptations
\-Contain protein fibres which can change their length so they can contract
\-Packed with mitochondria to provide energy for contraction
\-Packed with mitochondria to provide energy for contraction
30
New cards
Nerve cell adaptations
\-Long fibre so they can carry messages up and down the body over long distances
\-Insulated by a fat which increases the speed of the nerve impulses along the neuron
\-Insulated by a fat which increases the speed of the nerve impulses along the neuron
31
New cards
What is the link between cell structure and function?
Cells adapt their structure in order for efficiently complete their function
32
New cards
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down the concentration gradient
33
New cards
How do differences in concentration and temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
The greater the difference in concentration, the quicker the rate of diffusion
34
New cards
How do Microvilli affect the rate of diffusion?
Microvilli increase the surface area available for diffusion even more so rate of diffusion is higher.
35
New cards
Examples of a substances that leaves cell by diffusion
\-Carbon dioxide
\-Water
\-Water
36
New cards
Example of a substance that enters cell by diffusion
Glucose
37
New cards
Osmosis
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
38
New cards
What is active transport?
The movement of dissolved molecules from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
39
New cards
Differences between diffusion and active transport
simple diffusion moves molecules down concentration gradient while active transport takes them against concentration gradient
40
New cards
Examples of active transport in animals
Amino acids moving along the intestine
41
New cards
Examples of active transport in plants
Uptake of mineral ions into root hair cells
42
New cards
Surface area to volume ratio formula
Surface area/volume
43
New cards
how do light microscopes work?
\-light hits the mirror and is reflected through the object
\-pass through objective lens-eyepiece lens and then into your eye
* lenses spread out light rays so image is much larger than object
\-pass through objective lens-eyepiece lens and then into your eye
* lenses spread out light rays so image is much larger than object