Business and Corporate Strategy Overview
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Blue Ocean/ Value Innovation
Increase value, decrease cost

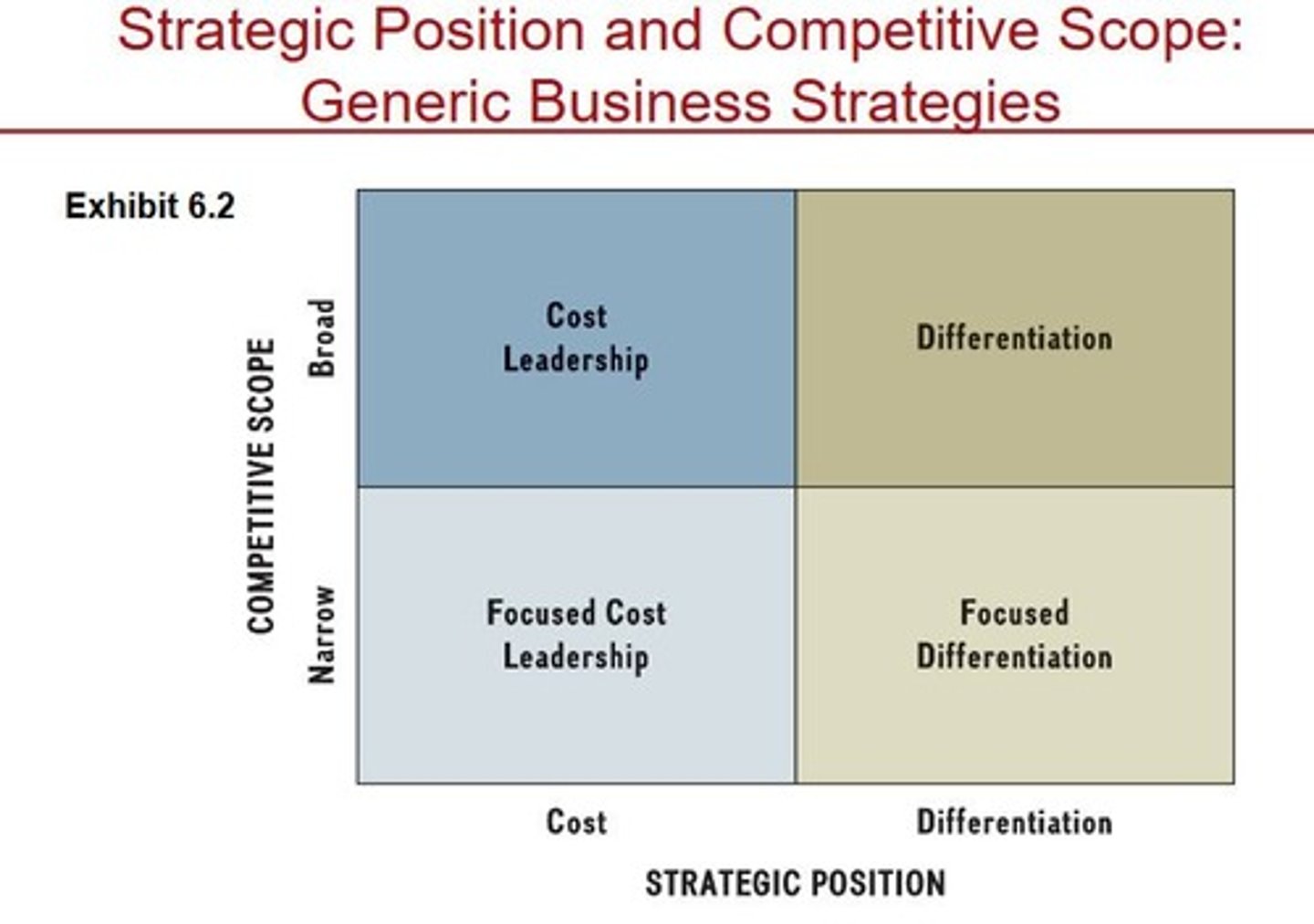
Differentiation
A strategy to offer unique products or services that stand out in the market.

Cost Leadership
A strategy to become the lowest-cost producer in the industry.

Focus
A strategy that targets a specific market segment, either through differentiation or cost leadership.
Business Level Strategy
A strategy that outlines how a company will compete in a particular market.
Goal-directed actions
To achieve competitive advantage in a single product market.
Strategic Position
The position a firm occupies in the market relative to its competitors.

Strategic Trade Offs
Choices between a cost or value proposition.
Economic value creation
The difference between the value created by a firm and the cost incurred to create that value.
Profit margin
The difference between revenue and costs, expressed as a percentage of revenue.
Differentiation
Seeks to create higher value vs competitors by offering unique features and charging higher prices.

Cost Leadership
Seeks to create similar value vs competitors while charging lower prices.
Focused Differentiation
A strategy that targets a narrow competitive scope with unique features, exemplified by Mont Blanc's exquisite pens.
Focused Cost Leadership
A strategy that targets a narrow competitive scope while offering lower prices, exemplified by BIC's disposable pens.
Economies of Scale
Decreases in cost per unit achieved as output increases.

Economies of Scope
Savings that come from producing two outputs at less cost by sharing the same resources or technology.
Drivers that increase perceived value
Factors such as product features, customer service, and complements that enhance the value of a product or service.
Cost Leadership Strategy Goals
Reduce cost below competitors, offer adequate value, and optimize the value chain for low cost.
Learning curve effects
The phenomenon where less time is required to produce output as experience increases.
Experience-curve effects
Improvements to technology and production processes that reduce costs.
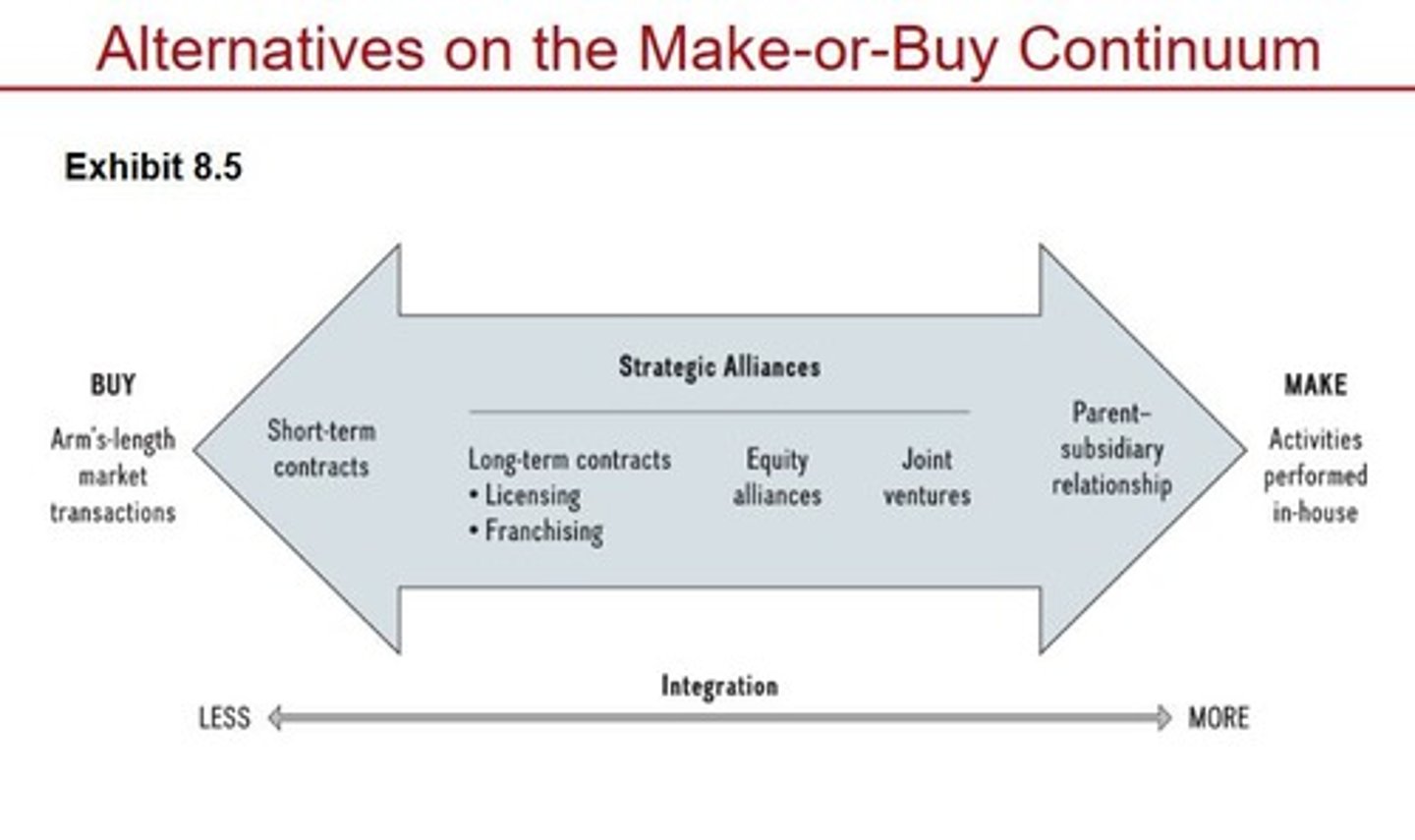
Vertical integration
The ownership of inputs or distribution channels within a firm.

Backward Vertical Integration
Owning inputs of the value chain.
Forward Vertical Integration
Owning activities closer to the customer.
Taper integration
A strategy that combines backward or forward integration with reliance on outside firms.
Strategic outsourcing
Moving internal value chain activities to other firms.
Product Diversification
Increasing the variety of products/services and being active in several product markets.

Geographic Diversification
Increasing the variety of markets/geographic regions, including regional, national, or international markets.
Unrelated Diversification
A strategy where no businesses share competencies.
Related Diversification
A strategy where businesses share competencies, either constrained or linked.
Restructuring
Reorganizing and divesting business units and activities to refocus a company.
Internal Capital Markets
A source of value creation in diversification strategy through efficient capital allocation.
Globalization
Closer integration and exchange between countries and people worldwide.
Foreign direct investment
Investments in value chain activities abroad.
Multinational enterprise
A firm that deploys resources and capabilities in two countries or more.
Corporate governance
The mechanisms to direct and control an enterprise, ensuring it pursues strategic goals successfully and legally.

The Board of Directors
The centerpiece of corporate governance tasked with providing oversight and representing the interests of shareholders.
Information asymmetry
A situation where one party has more or better information than the other in a transaction.

Adverse Selection
The increased likelihood of selecting inferior alternatives due to information asymmetry.
Moral Hazard
A situation where one party is incentivized to take undue risks or shirk responsibilities, incurring costs to another party.
Blue Ocean/Value Innovation
Increase value, decrease cost.

Focus
A strategy that can involve either differentiation or cost leadership within a narrower competitive scope.
Business Level Strategy
Goal-directed actions to achieve competitive advantage in a single product market.

Strategic Trade Offs
Choices between a cost or value proposition, highlighting the tension between value creation and cost control.
Economic Value Creation
The difference between the value a firm creates and the cost incurred to create that value.
Profit Margin
The difference between the revenue generated from sales and the costs associated with producing those sales.
Focused Differentiation
A strategy exemplified by Mont Blanc, offering exquisite pens at several hundred dollars.
Focused Cost Leadership
A strategy exemplified by BIC, providing disposable pens at low cost.
Cost Leadership Strategy Goals
Reduce cost below competitors, offer adequate value, reduce prices for customers, and optimize the value chain for low cost.
Drivers that Keep Cost Low
Include cost of input factors, economies of scale, learning curve effects, and experience-curve effects.
Vertical Integration
The ownership of inputs or distribution channels, affecting the percentage of a firm's sales generated within its boundaries.
Transaction Costs
Costs associated with an economic exchange.
Principal-Agent Problem
The challenge of ensuring that agents act in the best interests of principals.
Related Diversification
A strategy where constrained businesses share competencies, while linked businesses share some competencies.
Restructuring
Reorganizing and divesting business units and activities to help refocus a company.
Internal Capital Markets
A source of value creation in diversification strategy, allowing capital allocation at a lower cost.
Global Strategy
Part of a firm's corporate strategy to gain and sustain competitive advantage against foreign and domestic companies.
Board of Directors
The centerpiece of corporate governance, representing the interests of shareholders and providing oversight.
Information Asymmetry
A situation where one party has more or better information than the other, leading to adverse selection and moral hazard.
Moral Hazard
When one party is incentivized to take undue risks or shirk responsibilities, incurring costs to the other party.
Build, Borrow, Buy Framework
Helps strategic leaders determine how to access resource bundles for addressing strategic gaps.
Relevancy
How relevant are our internal resources in addressing the gap? If high, stop and build; if low, go to the next question.
Tradeability
Are resources tradable? If highly tradeable, stop and borrow; if low, go to the next question.
Closeness
How close do you need to be to your resource partner? If high, go to the next question; if low, stop and borrow through strategic equity alliances or joint ventures.
Integration
How likely is it that the companies integrate? If high, do it; if not, start over.
CAGE Distance Framework
Helps determine the distance between the host country and the domestic country when looking for globalization, assessing costs and risks.

Cultural Distance
One of the dimensions of the CAGE distance framework, referring to differences in language, ethnicity, and social norms.
Administrative and Political Distance
One of the dimensions of the CAGE distance framework, referring to differences in governance, legal systems, and political stability.
Geographic Distance
One of the dimensions of the CAGE distance framework, referring to physical distance and transportation costs.
Economic Distance
One of the dimensions of the CAGE distance framework, referring to differences in consumer incomes and economic conditions.
Information Asymmetry
Imbalance of information resulting in the party with more information having privileged knowledge.
Adverse Selection
Selecting an inferior alternative by not having all the information; for example, either interviewer or interviewee misrepresenting.
Moral Hazard
When one party is incentivized to take on undue risk or shirk responsibilities because the cost is borne by the other party.
Tapered Integration
A strategic approach that combines elements of both vertical integration and outsourcing.