Pelvic Viscera II
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
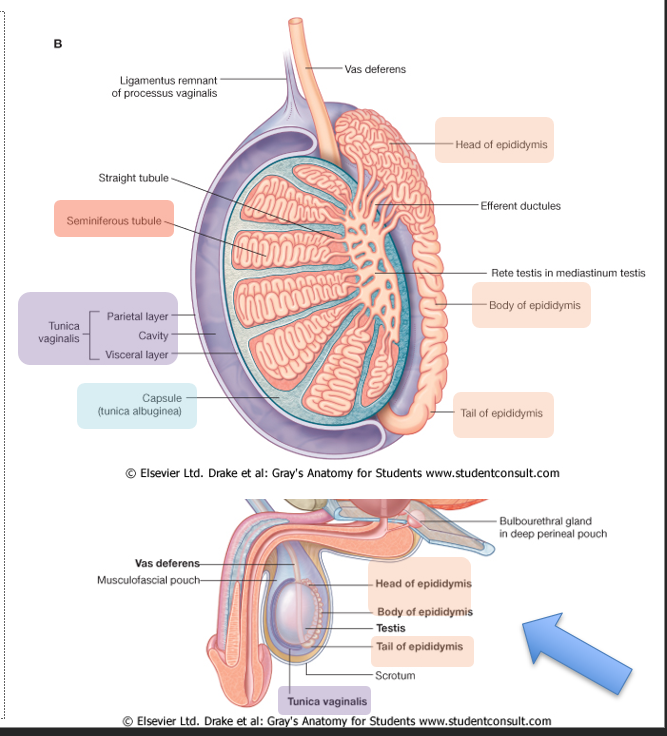
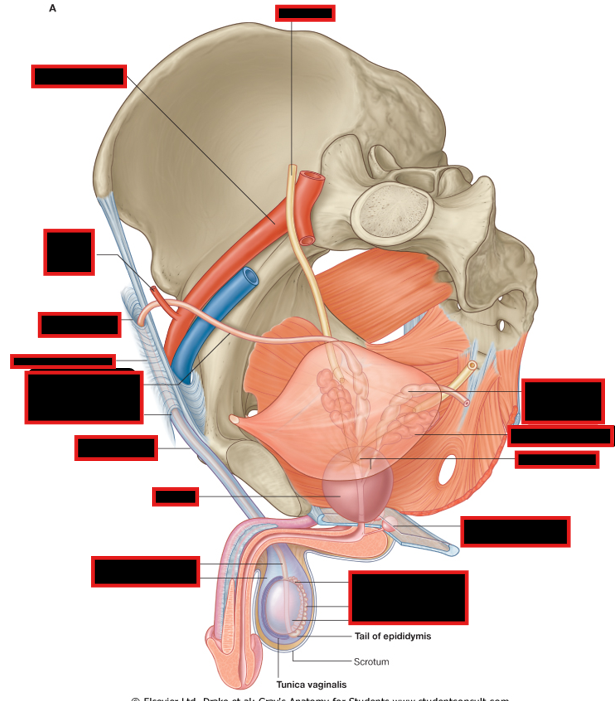
Where are the testes and epididymis located?
Describe sperm production and storage
Differentiate between the Tunica Albuginea and Vaginalis
Location:
scrotum of perineum (homologous to labia majora in female)
Sperm production & storage
produced in the seminiferous tubules
stored in the body of the epididymis
Transported via vas deferens, a continuation of tail of the epididymis
Tunica albuginea vs Tunica Vaginalis:
Albuginea: Tough outer surface of testes
Vaginalis: Peritoneal sac
Visceral layer covering testes & epididymis
Parietal layer adjacent to internal spermatic fascia
cavity w/ small amount of liquid between 2 layers
Describe the Embryonic descent of testes
Testes descent
posterior abdominal wall → inguinal canal → scrotum
Carry vessels, nerves, vas deferent found in spermatic cord
Testes and spermatic cord acquire coverings from inguinal canal
Processus vaginalis (peritoneum) close off to become the tunica vaginalis
what are the three layers of the sperm cord and which muscles/fascia covers each layer
What are the contents of the spermatic cord?
Layer/Covering of Sperm Cord:
Internal spermatic fascia: transversalis fascia
Cremaster muscles & fascia: internal oblique
External spermatic fascia: external oblique aponeurosis
Contents:
ductus (vas) deferens
artery to ductus deferens (inf. or sup. vesical artery)
testicular artery
pampiniform plexus of vv.
lymphatic vessels
autonomic nerves
remnants of processus vaginalis
cremasteric artery (br inf. epigastric a.)
genital branch of genitofemoral nerve- motor component of “cremaster reflex
Describe the Cremasteric reflex
lightly stroking superior and medial thigh → GSA of femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve & ilioinguinal nerve → GSE of genital branch of genitofemoral nerve →
cremasteric muscle contraction → pulls up ipsilateral testes
Describe the NVL (neurovascular Lymphatics) of the testes & spermatic cord
Arterial supply:
testicular artery
artery to ductus deferens
Venous drainage:
pampiniform plexus of veins → testicular vein @ deep inguinal ring
Lymph Drainage
lateral aortic nodes in abdominal cavity >
testicular cancer metastases to abdomen
Nerve Supply
sympathetic fibers (GVE, T10-11) for sperm transport & vasoconstriction
accompanied by afferent sensory fibers (GVA)
genital branch of genitofemoral nerve (GSE) to cremaster muscles of cord


Describe these diseases of the testes:
Hydrocele and hematocele of testis
Spermatocoele*
Varicocoele (of the spermatic cord):
Testicular cancer:
Vasectomy
Hydrocele and hematocele of testis
Accumulation of serous fluid1 or blood2 within cavity of tunica vaginalis
Spermatocoele*
sperm-filled cyst near the head of the epididymis; is usually asymptomatic.
Varicocoele (of the spermatic cord):
elongation and dilatation of the pampiniform plexus of veins (bag of worms);
common in teens;
majority occur on the left side;
due to bad valves
Testicular cancer:
Most common & most curable form of cancer in males between 18-35 years of age
Many different stages – once past tunica albuginea, spread is more extensive
Vasectomy:
Ductus deferens between testis & superficial inguinal ring can be dissected & divided bilaterally because of easy access through skin & superficial fascia of scrotum;
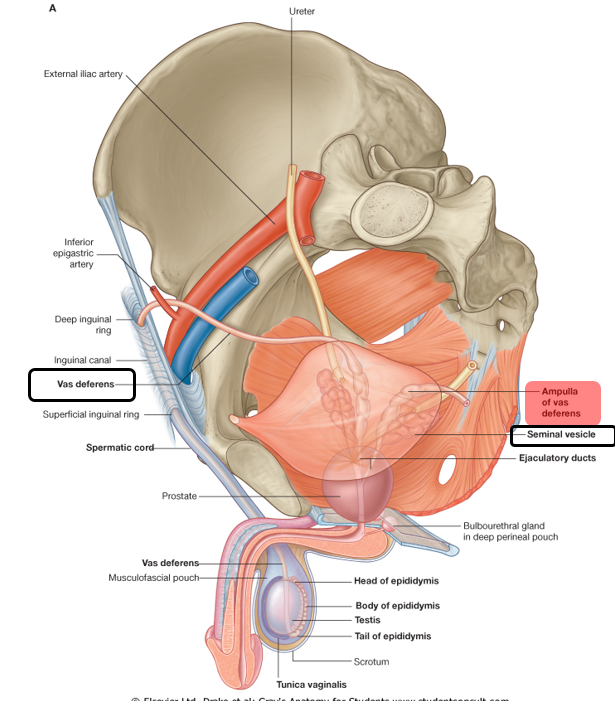
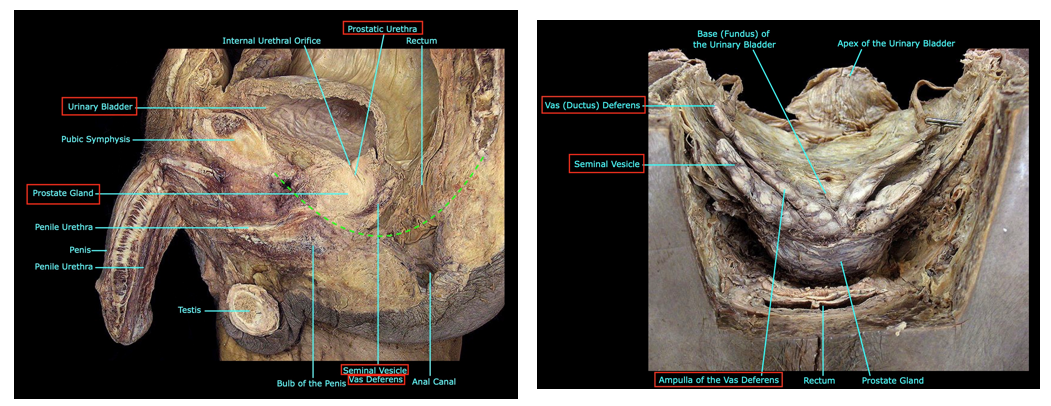
Describe the vas deferens:
Pathway
Function
Describe the seminal vesicles and its function
Vas Deferens:
Pathway:
Passes through the inguinal canal → abdominal cavity → courses posterior to urinary bladder
@ distal end → ampulla of the ductus deferens
Function: Transmits sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
Seminal vesicles
tortuous, coiled tube
Function: contributes thick, alkaline fluid containing fructose to seminal fluid
(essential for nutrition of spermatozoa)
does not store sperm
Describe the ejaculatory ducts:
Union of
Pathway
opens into
Each ejaculatory duct:
union: seminal vesicle + ductus deferens
Pathway: Traverses posterior part of prostate
Seperates middle lobe (superomedial lobule) and posterior lobe (inferoposterior lobule)
Opens into the prostatic urethra on the seminal colliculus
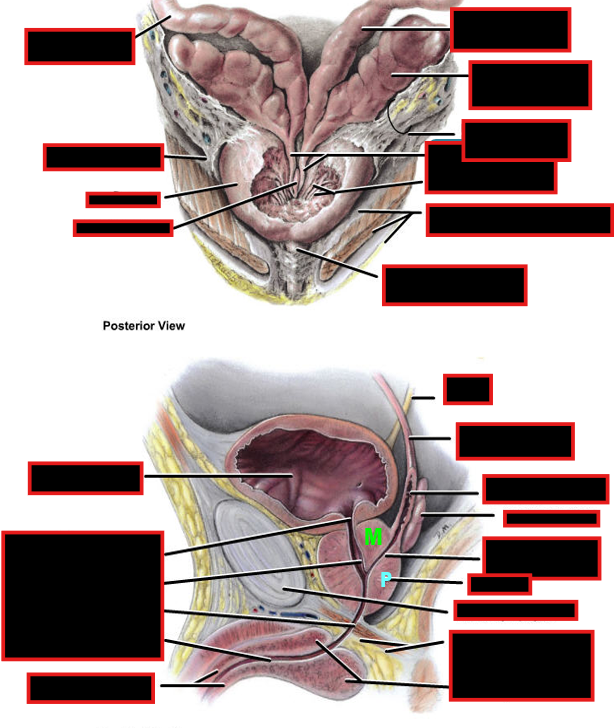
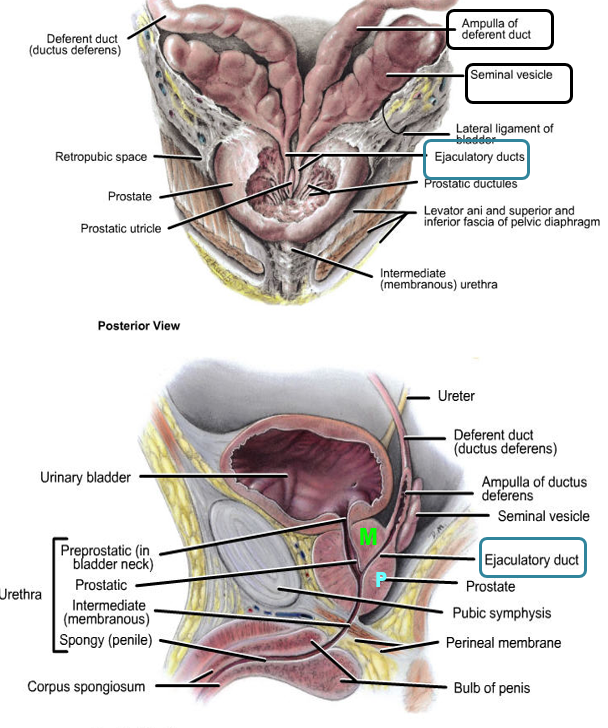
Describe the Prostatic Urethra
Function of prostate
Prostatic urethra:
Fibrous capsule with neurovascular plexuses
Urethral crest
Prostatic colliculus: utricle & opening of ejaculatory ducts
Urethral sinuses: opening of prostatic ducts
Prostate Function:
Produces alkaline fluid containing nutrients for spermatozoids & enzymes that is added to seminal fluid.
helps liquify semen & neutralize vaginal acidity
Prostatic fluids empty into the prostatic urethra through individual duct openings
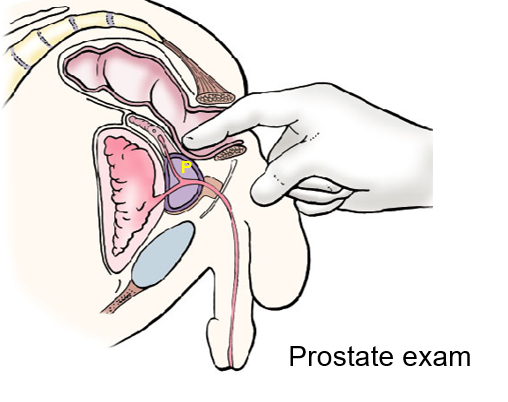
Describe the various problems with the prostate
BPH
Cancer
benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH
enlargement in middle aged and older males @ transition zone (surrounds urethra)
Symptoms: nocturia, urgency, and dysuria
Prostate Cancer:
Elderly males in peripheral Zone
The area posterior (P) to urethra & inferior to ejaculatory duct is palpable by digital rectal examination.
can spread to spine & CNS via vertebral venous plexuses.
Describe the NVL of the prostate, ampula* of vas deferent & seminal vesicles
Blood Supply:
inferior vesical A/V
artery to ductus deferens*
prostatic plexus of veins* that drains via vesical plexus in internal iliac vein or vertebral venous plexus
Lymphatic:
internal iliac nodes
Prostatic Plexus; Contains:
Sympathetic fibers (preganglionic fibers T11-L2)
Rich innervation of internal genital organs
Semen transport in vas deferens
Parasympathetic fibers (S2-4)
Gland secretion
formthe cavernous nerves → erectile tissues of penis in perineum
GVA fibers
Above pain line, travel with sympathetic fibers: vas deferent, upper part of seminal vesicles
Below pain line, travel with parasympathetics fibers: prostate, lower part of seminal vesicles & ampulla of vas deferent
Other visceral sensations travel with parasympathetic fibers
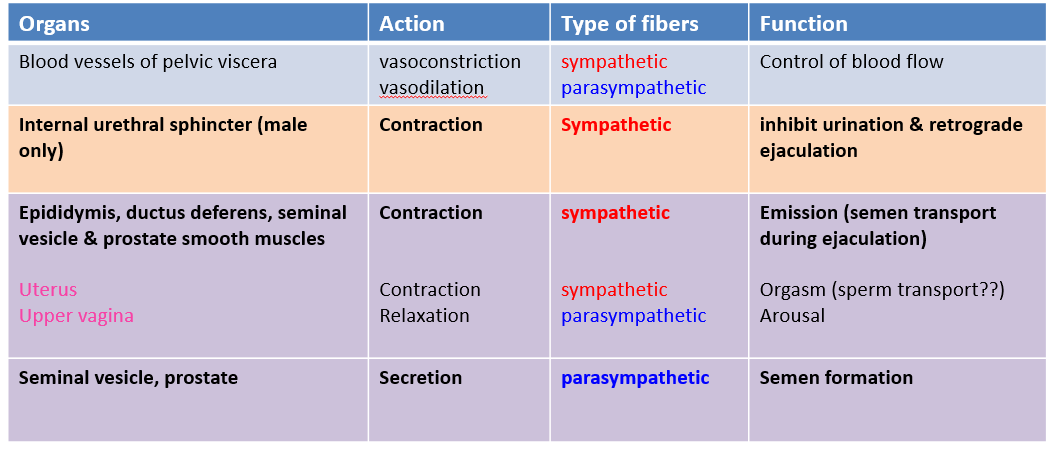
Describe the formation and transport of semen
Emission
Gland secretion
Emission:
Delivery of semen to urethra
via peristalsis of vas deferens and ducts of accessory glands (sympathetic, GVE)
Gland secretion (parasympathetic, GVE )
Seminal fluids
seminal vesicles
Prostate
Ejaculatory fluid
bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands in perineum
What is prostatectomy and its potential consequences
Prostatectomy: Radical surgery to cure prostate cancer that involves removing prostate & seminal vesicles
Possible Complication:
damage parasympathetic fibers of prostatic plexus & cavernous nerves
innervate erectile tissues
cause impotence (erectile dysfunction)
also damage sympathetic fibers of vesical plexus
controls internal urethral sphincter → retrograde ejaculation → decreased fertility
emission → low volume ejaculate → decreased fertility
Can also cause urinary incontinence (damage to nerves & muscles of bladder, urethra and external urinary sphincter)
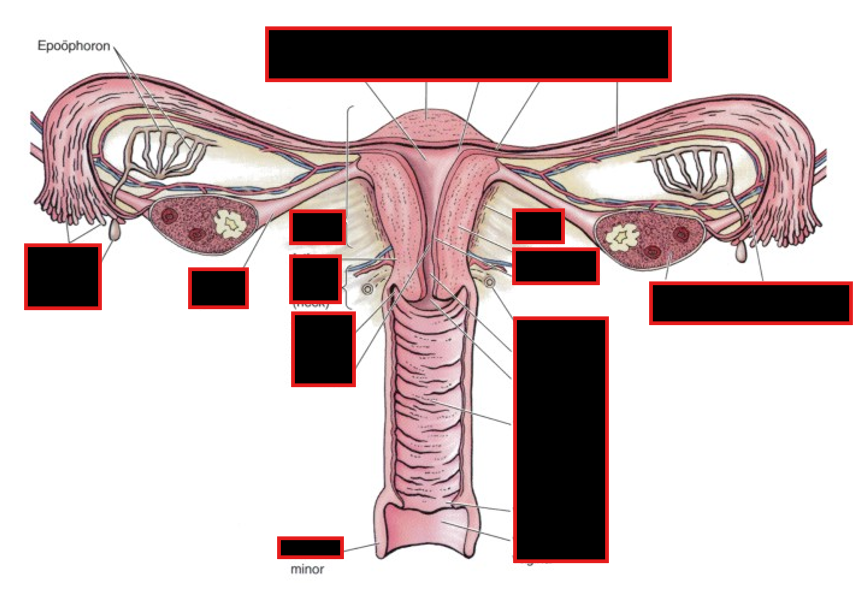
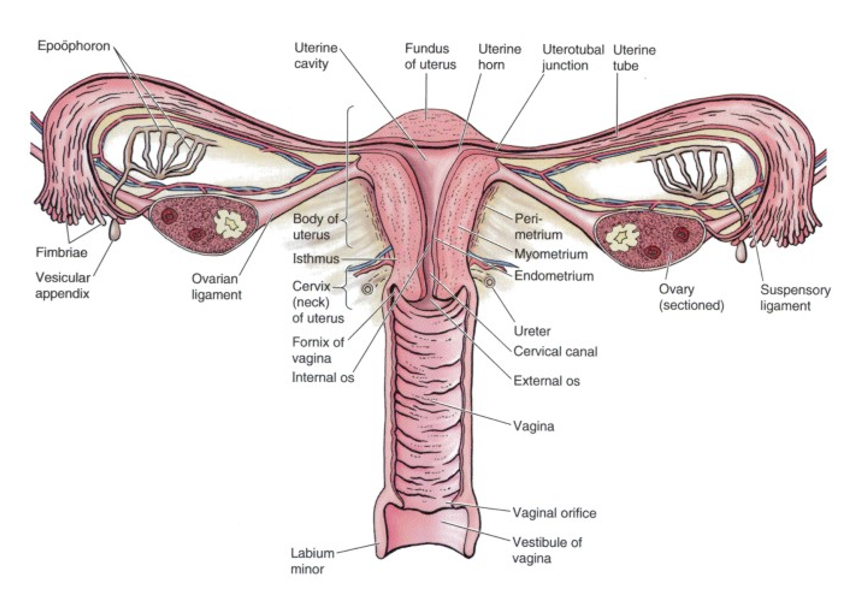
What is the round ligament of the uterus
What are the 3 broad ligaments
Round ligament of uterus
passes into inguinal canal to labium majorum (embryological remnant, called gubernaculum, used for ovaries descent from abdomen to pelvis) & assists in keeping uterus in position
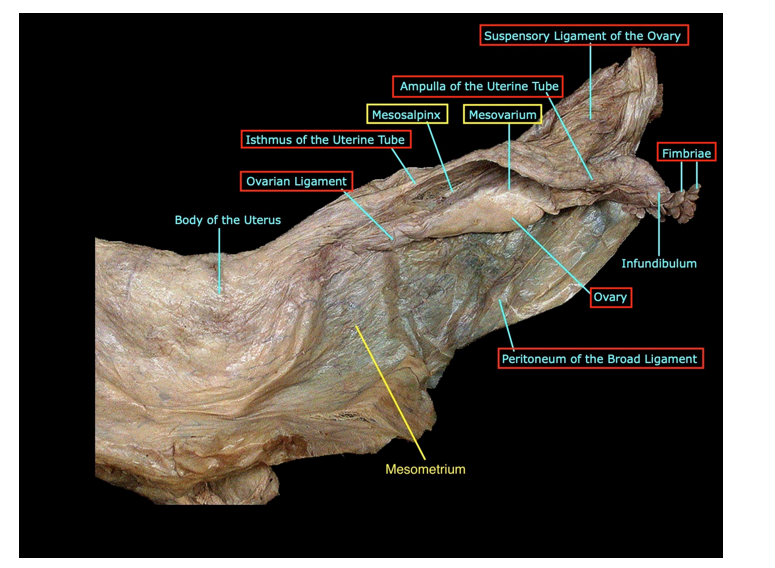
Broad ligament of the uterus is peritoneum divided in
Mesosalpinx around & below the uterine tube
Mesovarium, suspends the ovary
Mesometrium over & lateral to the body of the uterus
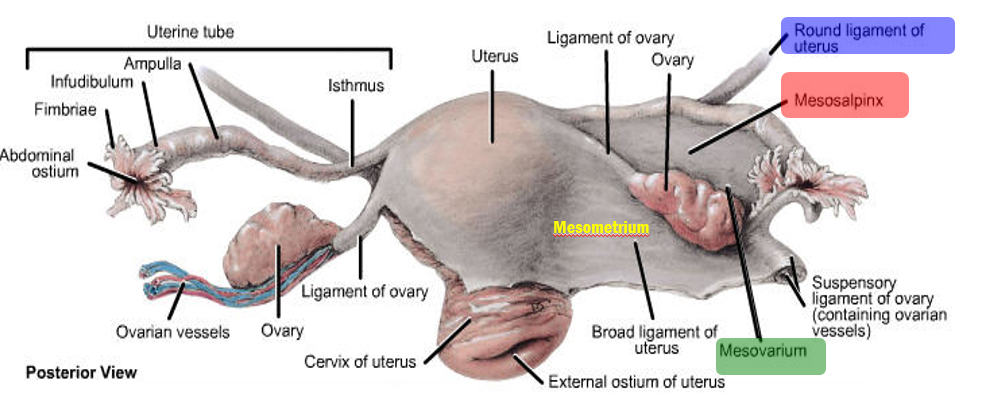
Describe the uterus
What are its parts
What is the vagina
Vaginal Fornix?
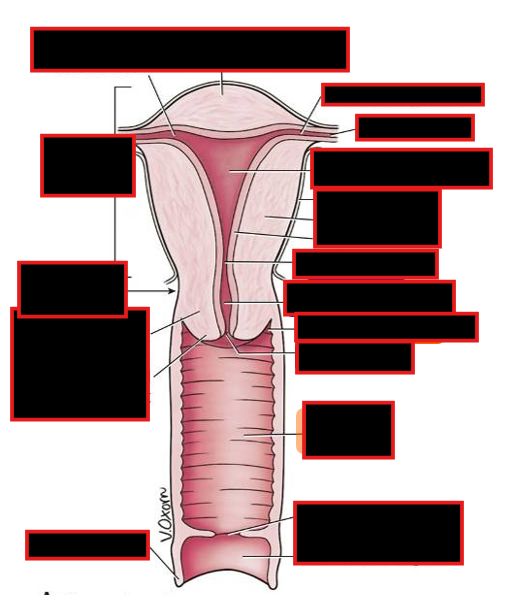
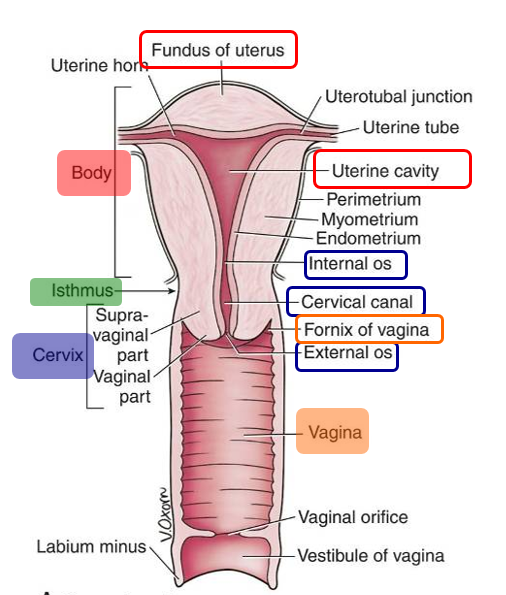
Uterus:
thick-walled, hollow, muscular organ; consists of:
Body with rounded fundus superiorly & containing the uterine cavity & ostia of uterine tubes
Isthmus is the junction between the body and the cervix
Cervix containing the cervical canal that connects internal and external ostia
Vagina:
distensible tube that connects cervix of uterus to vestibule in perineum.
Mostly a pelvic structure except for inferiormost part in perineum
cervix forms a continuous recess around the vagina, the vaginal fornix, which is divided into anterior, posterior, and lateral fornices.
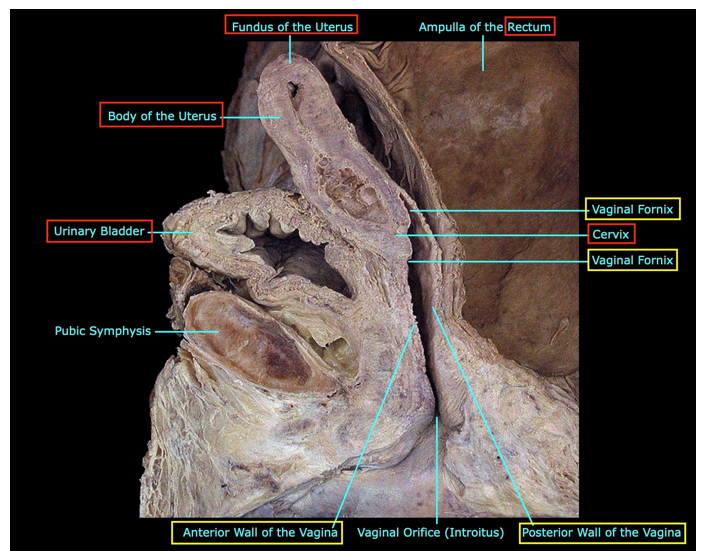
How can you describe the position of the uterus
Position of the uterus:
Angle of anteversion: between the axis of the uterine cervix and the axis of the vagina
Angle of anteflexion: between the axis of the uterine body and the axis of the cervix
Normal position is: anteverted and anteflexed
Can be described as…:
Anteverted (A)
Anteflexed (B)
Retroverted (C)
Retroflexed (D)
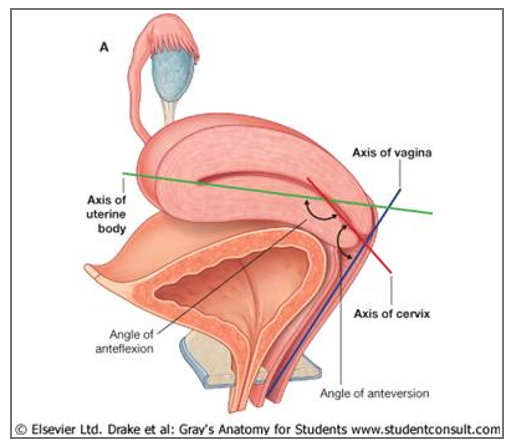
Describe what may happens if there is Obstetrical trauma to vagina
What happens if there is a weakening of walls?
Tumor?
Obstetrical trauma
open communications → Fistulas:
vagina and urethra (urethrovaginal fistula),
bladder (vesicovaginal fistula)
rectum (rectovaginal fistula).
Weakening of walls of vagina w/o open communication → prolapse into vagina
bladder (cystocele),
urethra (urethocele)
rectum (rectocele) into vagina.
Tumor: Tumor on the posterior part of the bladder may bulge into the vaginal vault
Describe pelvic organ prolapses:
Due to?
Support?
Incidence increases w/?
Pelvic Organ Prolapses:
Protrusion or herniation of pelvic viscera into the vagina.
Due to: weakness of supporting musculature, ligaments, and fascia
Active support: levator ani m.
Passive support: uterosacral, transverse cervical, and pubocervical ligaments
Incidence increases: w/ age and parity
Describe the ligaments supporting the uterus
Supporting Ligaments:
from cervix to the anterior (pubocervical),
lateral (transverse cervical or cardinal ligament or Mackenrodt ligament )
provides the main passive support of the uterus.
posterior (uterosacral ligament) pelvic walls.
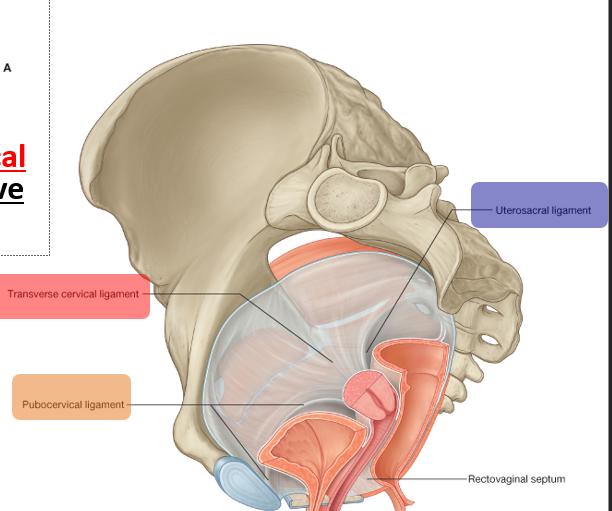
Describe pap smears:
Official Name
Purpose
samples taken
Papanicolaou Exam
Purpose: Evaluates condition of the cervical cells;
important for early detection of premalignant lesions and cervical cancer
Minimum of two samples taken:
Ectocervical specimen
Endocervical specimen
Describe Carcinoma of the cervix and body of uterus
Diagnoses
Spread
What is Hysterectomy and when is it used?
Carcinoma of the cervix and body of uterus
diagnosed by
inspection,
PAP smear,
imaging,
dilatation
curettage of uterus
Spread to internal & common iliac nodes
Hysterectomy:
surgical removal of the uterus.
Indicated in patient with uterine, cervical & ovarian cancers; endometriosis & excessive bleeding; excessive postpartum bleeding.
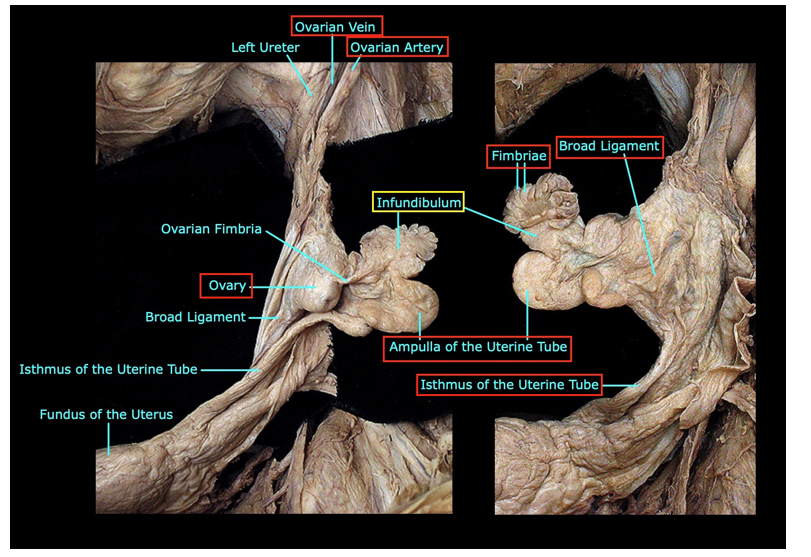
Describe the uterine tubes:
location and clinical consequence of that
Parts
Fallopian tubes:
Location:
Extend laterally from the uterus in the mesosalpinx;
open to the peritoneal cavity (risk of peritonitis if infection of genital tract)
Parts:
Funnel-shaped infundibulum laterally, end with fimbriae & abdominal ostium
Ampulla, the widest part; usual site of fertilization
Narrow isthmus
Uterine part, intramural part, pierces uterine wall
Explain what ectopic pregnancy is
Stats?
Placenta Previa?
Ectopic pregnancy:
Development of a fertilized ovum outside of the uterine cavity
Most (95%) develop in the uterine tube - aka tubal pregnancy
Placenta previa:
implantation close to the internal os
growing placenta may later bridge the opening
results in hemorrhaging late in pregnancy
Describe the Ovary:
Ligaments
Ovaries:
gonad and endocrine gland
Ligaments:
Mesovarium:
from the posterior lamina
ovarian cancer can metastasize directly into peritoneal cavity
Ligament of the ovary
attached to uterus
Suspensory ligament
Connects to posterior abdominal wall
Contains NVL
Describe:
Salpingitis
tubal ligation
Salpingectomy & oophorectomy
Ovarian cancer
Salpingitis:
Inflammation of fallopian tubes
May be come obstructed
increases risk of infertily or ectopic pregnancy
Secondary to:
STDs/ abdominal infections
Tubal Ligation:
surgical ligation of uterine tubes to prevent spermatozoa to reach ampula
Salpingectomy & oophorectomy
surgical removal of uterine tubes & ovaries, respectively
Ovarian Cancer:
can spread via blood & lymphatics and can metastazise directly into peritoneal cavity
Describe the NVL of femal internal organs
Blood supply:
Ovaries: ovarian a. & v.
right ovarian vein drains to the IVC, but the left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein
Uterus: uterine a. & v.
anastomoses with ovarian and vaginal arteries;
vaginal artery often branches from the uterine artery
Tubes: tubal br of ovarian a. & v. & ascending br of uterine a & v.
Upper vagina: vaginal a. & v.
Lower vagina in perineum: internal pudendal a. & v.
Lymphatics:
Ovaries: lateral aortic nodes
Uterus, tubes & upper vagina: internal iliac nodes
Lower vagina in perineum: superficial inguinal nodes
Some lymph vessels follow the round ligament of the uterus from the uterus to the labium majus, which then drains to superficial inguinal nodes.
Nerves:
Plexuses
Ovarian plexus associated with ovaries (periarterial plexus follows ovarian vessels )
uterovaginal plexus associated with uterus, tubes & vagina
contains
Sympathetic fibers (T11-L2)
Parasympathetic fibers (S2-4)
GVA fibers
Above pain line, travel with sympathetic fibers: ovaries, uterine tubes, body of uterus
Below pain line, travel with parasympathetics fibers: cervix, upper vagina
Other visceral sensations with parasympathetic fibers
Describe the three methods of Anesthesia during delivery
Spinal block via lumbar puncture in subarachnoid space (L3-4)
From waist down
Sensory block // visceral (GVA at both lumbar L1,2 and sacral S2-4 levels) & somatic (GSA) from L1 to Co levels
Perineum, pelvic floor, upper vagina, uterine cervix, body of uterus / no sensation of uterine contraction
Also motor & sensory functions of lower limbs
Epidural block via catheter into epidural space (L3-4)
has replaced caudal epidural block via sacral hiatus (arrow) that had similar action
Sensory block / / visceral (GVA S2-4) & somatic (GSA L4-Co)
Perineum, pelvic floor, upper vagina, uterine cervix
Pudendal nerve block via local injection in tissues surrounding nerve (more in perineum lecture)
Sensory block, somatic (GSA S2-4 level)
Perineum including lower vagina
Describe the Sympathetic & parasympathetic innervation of female internal genital organs
Gestation & delivery: under hormonal control
Female sex response
Parasympathetic
Arousal
Dilation of upper vagina
Vaginal “sweating” (transudate from blood vessels)
Sympathetic
orgasm: increase uterus contraction (induced by oxytocin) that may have a role in sperm transport to uterine tubes
Resolution: tissues return to pre-arousal state