IP Addressing | Intro to Networks Chapter 6 Quiz | ITEC 3100
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ape together strong
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is the primary function of a subnet mask?
to enable network segmentation, aka subnetting
What is an IP address?
an identifier for a computer/device on a network.
True or False: Devices don’t need an IP address to communicate
False. Devices cannot communicate with one another without an IP address.
What two parts does an private network consist of?
A network ID and a host ID
What is a subnet mask?
a number that resembles reveals how many bits in the IP address are used for the network by masking the network portion of the IP address
Computers can only understand numbers in ______ format.
Binary
Why does an IP address have a host and network portion?
Manageability. Breaking down a network into smaller networks (or subnetworks) is easier to manage than one huge network with lots of traffic.

Once a network is segmented, how would information travel from a computer in one network to a computer in a different network?
data packets would first go to the default gateway, which would then find the smartest route for them to reach their destination.
How many bits make up IPv6?
128 bits, 8 × 16 bit groups
What is the APIPA address used for IPv4?
From 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255
What is the APIPA address used for IPv6?
From fe90::/10
Why is the default gateway so important in all networks?
It acts as a front door/exit to the rest of the connected networks to let traffic in and out.
What does Netstat allow you to see?
It lets you see which servers are running on your computer and which ports are open.
What does netstat –n do and why is it faster then running just Netstat?
it doesn’t use DNS to resolve numbers to names. It only shows numbers.
What does netstat -r do?
displays the IP routing table, showing the routes the host knows about
What does tracert/traceroute allow you to see and its purpose?
It allows you to see how long it took your packet to reach its destination and pings every router used, so you can track its path.
What does it mean when you see asterisks in the tracert/traceroute command?
It either means that there was an issue connecting to that router or that the router isn’t configured to give information to traceroute
What is the maximum number of router hops?
30 hops
What is the purpose of the TTL (Time To Live)?
TTL kills the packets after a certain amount of hops.
Data packets could endlessly travel around the internet without returning if there wasn’t a limit.
What is the Teredo tunneling protocol and what does it do?
It’s a protocol that allows IPv6 devices to communicate over IPv4 networks.
TIP: If you see ‘tunneling’, assume Teredo
What are the 2 types of IPv4 addresses?
Public and Private
Which type of IP address is used on the internet? Public or Private?
Public, and they are 100% unique.
Base2
0 or 1
Decimal / Base10
0 - 9
Hexadecimal / Base16
0 - 9 and A - F
Is the following IP address IPv4 or IPv6?
FE80:0:0:0:18FF:0024:8E5A:60
IPv6
Class A Public
(1 – 126) Reserved for large corporations
ex: AT&T owns 12.0.0.0 address range
Class B Public
(128 - 191) Reserved for medium to large network
ex: PeachNet 168.2.98.2
Class C Public
(192 - 223) Reserved for small network such as home networks
ex: 192.168.1.1
Class D Public
(224+) Reserved for mutlicasting
NOT USED
True or False: Private IP Addresses cannot be used on the Internet
True. Private IPs are not publicly registered, meaning they can’t be used to connect directly to the internet.
Default Subnet Mask for Class A
255.0.0.0
Default Subnet Mask for Class B
255.255.0.0
Default Subnet Mask for Class C
255.255.255.0
Default Subnet Mask for Class D
255.255.255.255
LOOPBACK ADDRESS FOR TESTING
When does a device use APIPA?
When DHCP isn’t working
Default Gateway
Always used in IP configurations and usually the address of a router interface (EXIT)
this is ALWAYS a router address
What is traceroute/tracert?
a tool that can be used to find out the exact path a data packet is taking from the sender to the destination.
What is the difference between ping and traceroute?
Traceroute tells us more information. Like pinging, traceroute tells you how long the trip took and if your packets got returned, but it also pings each router it used on the way to its destination.
What do asterisks coming from a router indicate?
It could indicate that there’s a problem with the router, or that the router is fine and just not configured to return traceroute replies (it’ll still pass the packets on to the next router).
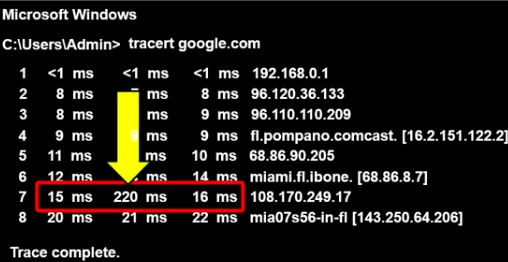
What do strange hop times usually indicate?
They’re usually not a big deal and just mean something strange has happened. If all 3 timings were high, it would indicate an issue (which is why 3 packets are sent)
What is TTL?
a given value to the data packets on how long they can live before they're discarded.
It prevents data packets from traveling endlessly around the internet.
What are the differences between private and public IP
addresses?
A public IP is used for to communicate with the globe over the internet, and a private IP is used within a local network or intranet
What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6
addresses?
IPv4 uses 32-bits to assign IPs with public and private IP addresses
IPv6 uses 128-bits and only has public addresses no private.
Why does the US still use IPv4 addressing?
Backwards compatibility. There is still a LOT of network infrastructure that was built before IPv6 was mainstream so either the hardware doesn't support it, or it was never configured to work with IPv6
Class A Private IP
10.x.x.x
Class B Private IP
172.16.x.x
Class C Private IP
192.168.x.x
Class D Private IP
127.0.0.1
What are the public IP address ranges for Class A?
1 - 126
What are the public IP address ranges for Class B?
128 - 191
What are the public IP address ranges for Class C?
192 - 223
What are the Default Subnet Masks for Class A?
255.0.0.0
What are the Default Subnet Masks for Class B?
255.255.0.0
What are the Default Subnet Masks for Class C?
255.255.255.0
What are the Private Address Ranges for Class A?
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
What are the Private Address Ranges for Class B?
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
What are the Private Address Ranges for Class C?
192.168.0.0 - 198.168.255.255
What is the purpose of private addresses?
They’re used for devices to communicate in internal networks. Devices, even without internet, cannot communicate with one another without some kind of IP address.
What is the APIPA address?
A self-assigned IP address that is a device uses when they can't get an IP from a DHCP server.
Computers using this can communicate with other devices on the same LAN/subnet but those devices would also need to have a self-assigned IP address.
What is the NAT (Network Address Translator)?
a service used to translate a set of IP addresses to another set of IP addresses to help preserve the limited amount of IPv4 addresses.
What is the PAT (Port Address Translator)?
PAT is a form of NAT maps multiple private IP addresses to one port number.
Why are NAT/PAT so important?
there is a limited number of IPv4 addresses and since you can split the IP addresses into public and private, that allows IPv4 addresses to be conserved.
Adds security since private IP is hiding when browsing on the internet.
The most cost effective for infrastructures still using IPv4.
What is special about the 127.x.x.x address range and what is 127.0.0.1 used for?
It is known as the loop-back range and used for testing and diagnostics.
If you get a 169.254.x.x address what is most likely the issue?
There is a communication error between the device and the DHCP server, could be a network issues, or hardware.
What is the purpose of the default gateway and what device does it usually represent?
It allows devices to enter and exit the network usually the default gateway is the router itself.
How are those port numbers represented and selected when you run the netstat command?
Selected randomly and represent public and private IPs
Private IPs always begin with ___ . ___
169.254
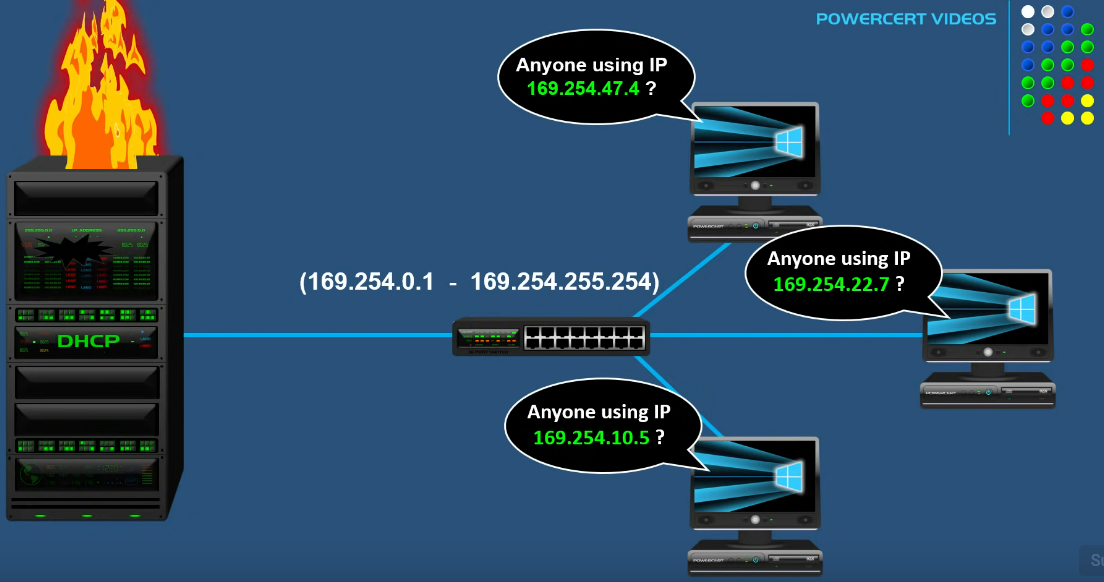
How do computers ensure that they don’t get the same APIPA?
Computers broadcast an ARP message on the network to make sure no other computers picks the same one.
How many IPv4 addresses were originally available?
Approx. 4 billion
True or False: You can directly access the internet with a private IP
False.
True or False: NAT can translate private to public AND public to private.
True.
How many IP addresses is IPv6 capable of producing?
340 undecillion
What is a 32-bit numeric address that is written as four numbers separated by periods?
An IPv4 address