Eukaryotic Infections
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what are the 3 monophyletic “kingdoms”
plants (kingdom plantae)
multicellular, chloroplast, cellulose
fungi (kingdom fungi)
uni/multicellular, heterotrophic, chitin
animals (kingdom animalia)
multicellular heterotrophic
what is the 1 polyphyletic “kingdom”
protists (kingdom Protista)
everything not categorized
algae
protozoa
smile molds
what eukaryotic microbes are in the animal & fungi kingdom
animal:
round worms
flat worms
fungi:
yeasts
molds
what are 2 categories of parasite
ectoparasite:
arthropods (mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, lice)
many are vectors for disease
endoparasites:
protozoa & helminths (tapeworms)
can reside extra/intracellularly in host
what is the difference between a definitive host & intermediate host
definitive - the host in which sexual reproduction occurs
intermediate - other hosts which the parasite may occupy
what are the 3 eukaryotic supergroups of protozoal parasites
SAR clade
excavates
amoebozoa
what are some qualities of SAR clade protozoal parasites
apicomplexans (apicoplast - fatty acid synthesis)
ciliates (ciliated - movement
what are some qualities of excavates protozoal parasites
kinetoplastids (kinetoplast - modified mitochondria, kDNA)
diplomonads (mitosomes - reduced mitochondria)
parabasalids (no mitochondria)
what are some qualities of amoebozoa protozoal parasites
entamoebae (form cysts)
what are some general qualities of protozoal parasites
complex lifecycles
most are motile
various forms of transmission (e.g. vectors, cysts)
what are the 3 categories of helminths
nematodes (round worms)
platyhelminthes (flat worms)
trematodes (flukes)
cestodes (tapeworms)
what are some qualities of nematodes (round worms)
pseudocoelomate (fluid-filled cavity meso/endoderm)
round bodies
non-segmented
what are some qualities of Platyhelminthes (flat worms)
acoelomate (no fluid-filled body cavity)
flattened bodies
what are some qualities of trematodes (flukes)
non-segmented
suckers for attachment
what are some qualitied for cestodes (tapeworms)
segmented
scolex
what are some general qualities of helminths
complex life cycles
various forms of transmissions (e.g. vectors, eggs, cysts)
can migrate through the body (e.g. GIT, tissues)
what are 2 possible forms of fungal pathogens
endogenous - overgrowth of host microbiota → disease
exogenous - inhalation/inoculation of fungal spores from soil
what is some general information about fugal pathogens
commonly superficial infections
almost always opportunistic
what does dikaryotic mean for fungi
only found in fungi classified as:
basidiomycetes
ascomycetes
refers to organisms that alternate between haploid & diploid
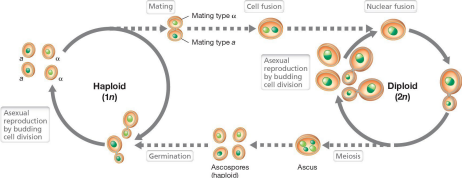
what does dimorphic mean for fungi
switching between unicellular yeast & multicellular mold growth morphologies
usually in response to temperature
what is the most common infectious agent for fungi
spores, can arise through 2 methods:
asexual
sexual